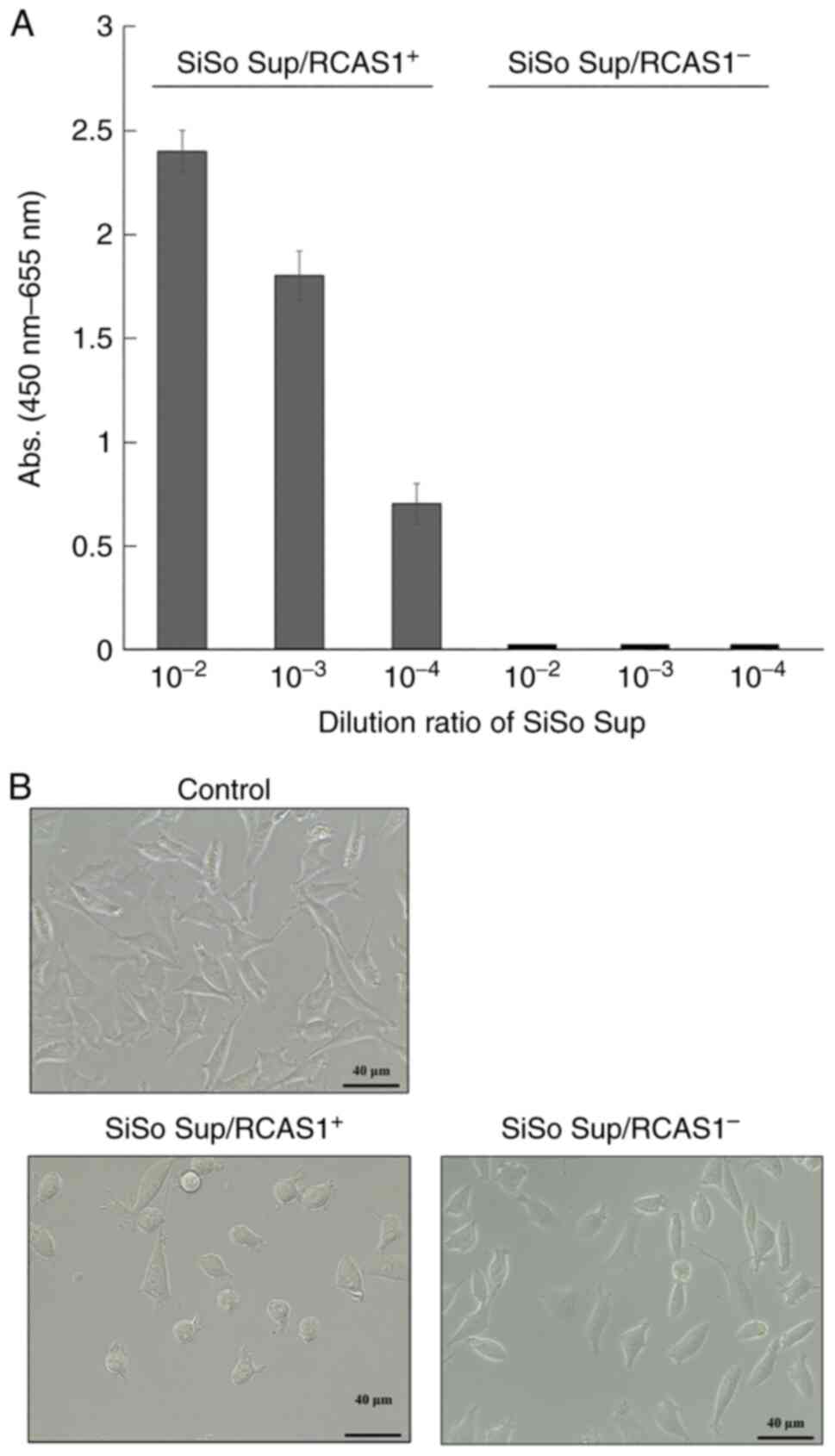
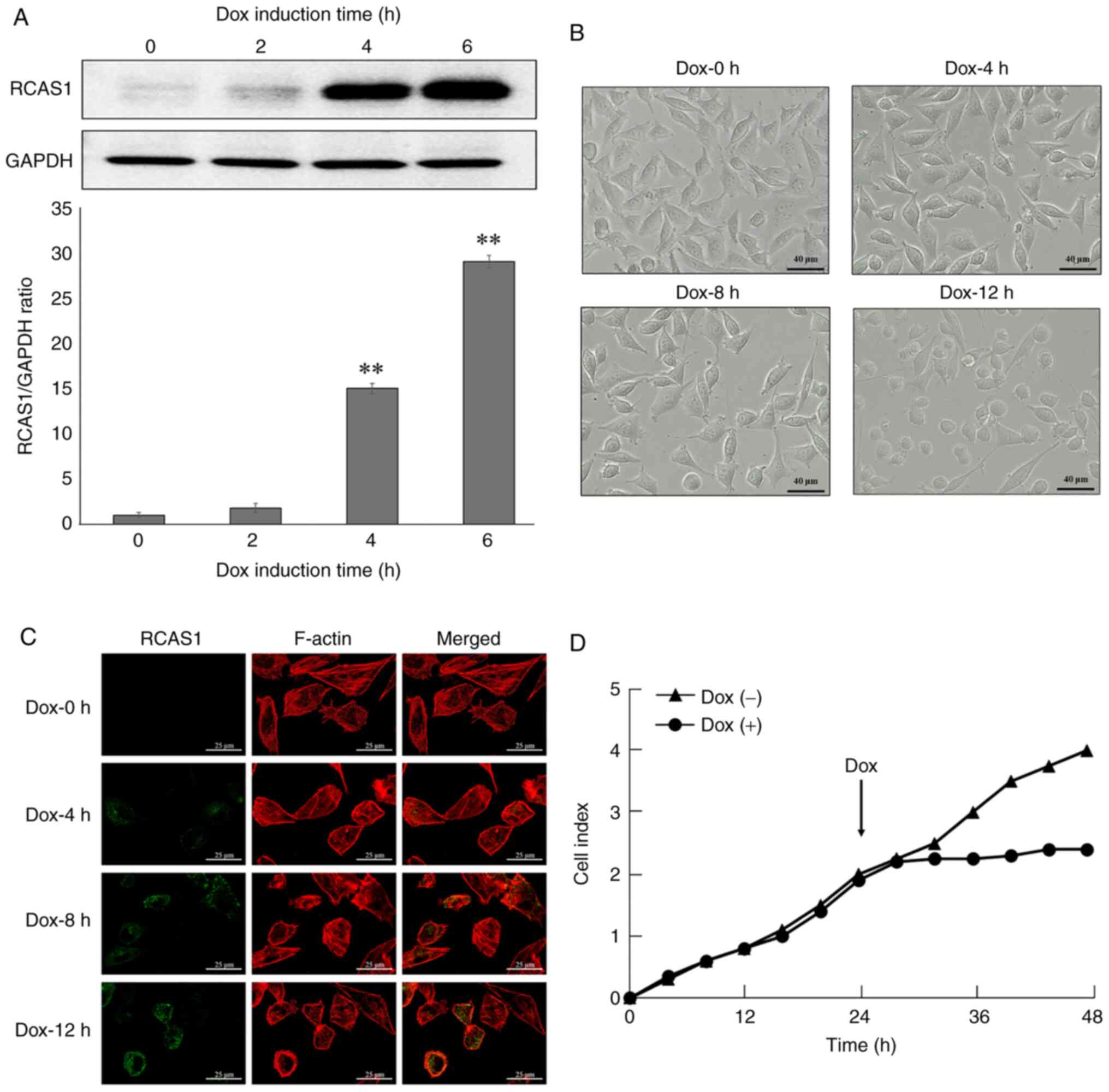
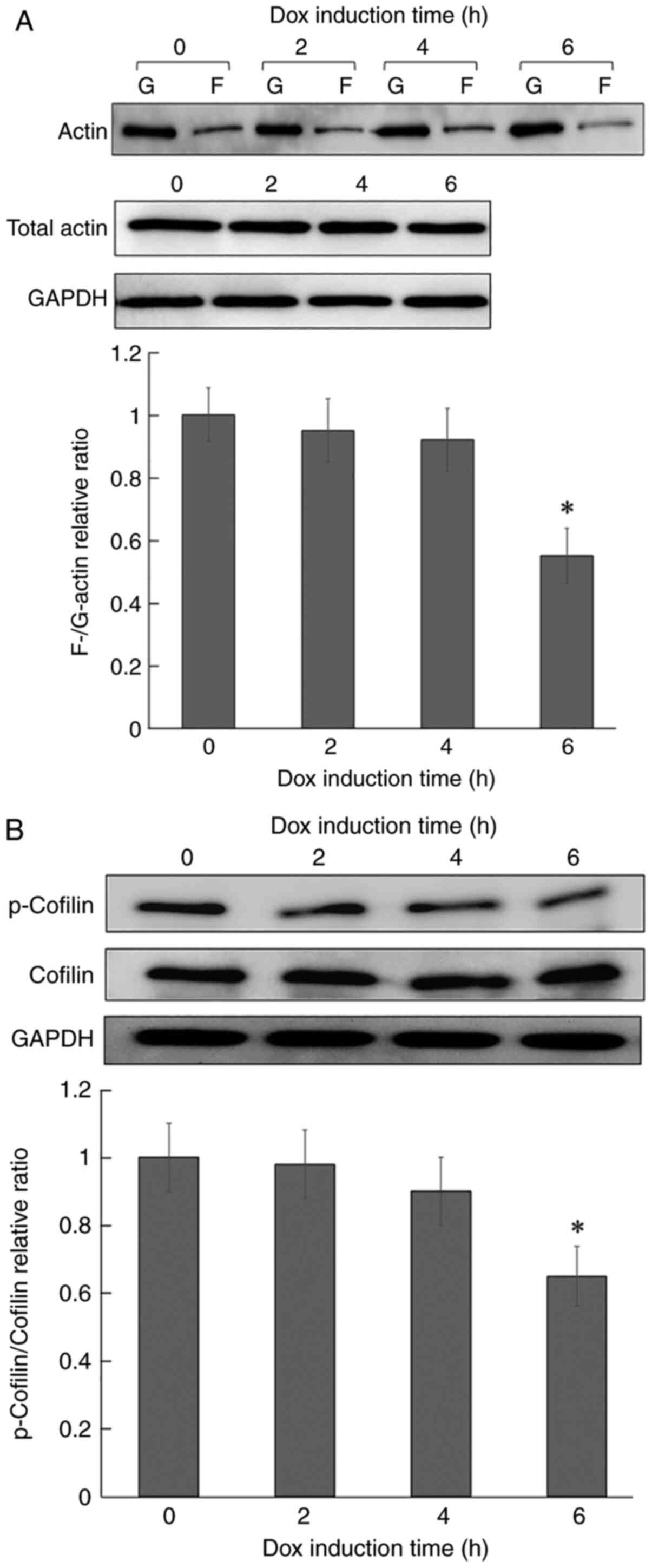
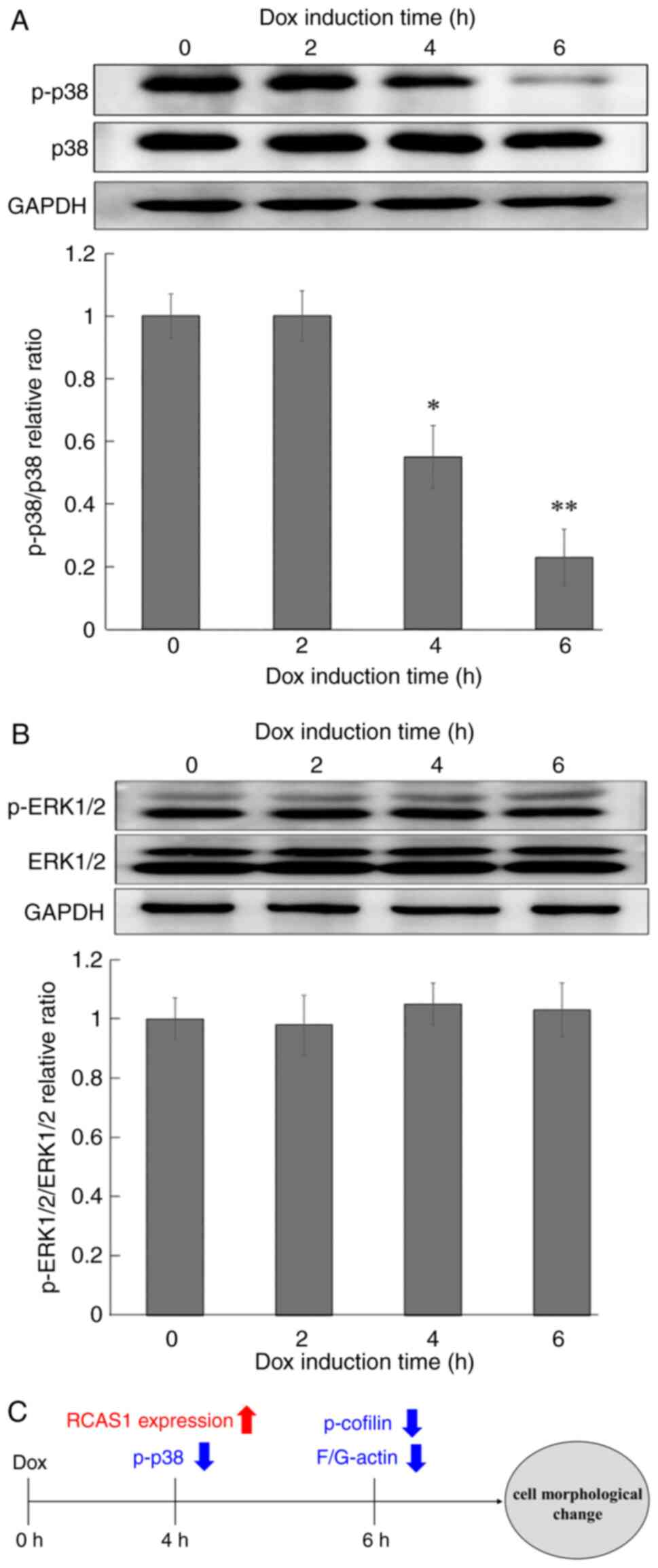
|
1
|
Fontana A, Frei K, Bodmer S, Hofer E,
Schreier MH, Palladino MA Jr and Zinkernagel RM: Transforming
growth factor-beta inhibits the generation of cytotoxic T cells in
virus-infected mice. J Immunol. 143:3230–3234. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li MO, Wan YY, Sanjabi S, Robertson AK and
Flavell RA: Transforming growth factor-beta regulation of immune
responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 24:99–146. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kriegel MA, Li MO, Sanjabi S, Wan YY and
Flavell RA: Transforming growth factor-beta: Recent advances on its
role in immune tolerance. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 8:138–144. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pisa P, Halapi E, Pisa EK, Gerdin E,
Hising C, Bucht A, Gerdin B and Kiessling R: Selective expression
of interleukin 10, interferon gamma, and granulocyte-macrophage
colony-stimulating factor in ovarian cancer biopsies. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 89:7708–7712. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
De Smedt T, Van Mechelen M, De Becker G,
Urbain J, Leo O and Moser M: Effect of interleukin-10 on dendritic
cell maturation and function. Eur J Immunol. 27:1229–1235. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Reed JC: Apoptosis-targeted therapies for
cancer. Cancer Cell. 3:17–22. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Andreola G, Rivoltini L, Castelli C, Huber
V, Perego P, Deho P, Squarcina P, Accomero P, Lozupone P, Lugini L,
et al: Induction of lymphocyte apoptosis by tumor cell secretion of
FasL-bearing microvesicles. J Exp Med. 195:1303–1316. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Okada K, Komuta K, Hashimoto S, Matsuzaki
S, Kanematsu T and Koji T: Frequency of apoptosis of
tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes induced by fas counterattack in
human colorectal carcinoma and its correlation with prognosis. Clin
Cancer Res. 6:3560–3564. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Reimer T, Herrnring C, Koczan D, Richter
D, Gerber B, Kabelitz D, Friese K and Thiesen HJ: FasL:Fas ratio-a
prognostic factor in breast carcinomas. Cancer Res. 60:822–828.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bennett MW, O'Connell J, O'Sullivan GC,
Brady C, Roche D, Collins JK and Shanahan F: The Fas counterattack
in vivo: Apoptotic depletion of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes
associated with Fas ligand expression by human esophageal
carcinoma. J Immunol. 160:5669–5675. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
O'Connell J, Bennett MW, O'Sullivan GC,
Collins JK and Shanahan F: The Fas counterattack: Cancer as a site
of immune privilege. Immunol Today. 120:46–52. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Rivoltini L, Carrabba M, Huber V, Castelli
C, Novellino L, Dalerba P, Mortarini R, Arancia G, Anichini A, Fais
S and Parmiani G: Immunity to cancer: Attack and escape in T
lymphocyte-tumor cell interaction. Immunol Rev. 188:97–113. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huber V, Fais S, Iero M, Lugini L, Canese
P, Squarcina P, Zaccheddu A, Colone M, Arancia G, Gentile M, et al:
Human colorectal cancer cells induce T-cell death through release
of proapoptotic microvesicles: Role in immune escape.
Gastroenterology. 128:1796–1804. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Giovarelli M, Musiani P, Garotta G, Ebner
R, Di Carlo E, Kim Y, Cappello P, Rigamonti L, Bernabei P, Novelli
F, et al: A ‘stealth effect’: Adenocarcinoma cells engineered to
express TRAIL elude tumor-specific and allogeneic T cell reactions.
J Immunol. 163:4886–4893. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Koyama S, Koike N and Adachi S: Expression
of TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) and its receptors
in gastric carcinoma and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes: A possible
mechanism of immune evasion of the tumor. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
128:73–79. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kassouf N and Thornhill MH: Oral cancer
cell lines can use multiple ligands, including Fas-L, TRAIL and
TNF-alpha, to induce apoptosis in Jurkat T cells: Possible
mechanisms for immune escape by head and neck cancers. Oral Oncol.
44:672–682. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sonoda K, Nakashima M, Saito T, Amada S,
Kamura T, Nakano H and Watanabe T: Establishment of a new human
uterine cervical adenocarcinoma cell-line, siso, and its reactivity
to anticancer reagents. Int J Oncol. 6:1099–1104. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sonoda K, Nakashima M, Kaku T, Kamura T,
Nakano H and Watanabe T: A novel tumor-associated antigen expressed
in human uterine and ovarian carcinomas. Cancer. 77:1501–1509.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nakashima M, Sonoda K and Watanabe T:
Inhibition of cell growth and induction of apoptotic cell death by
the human tumor-associated antigen RCAS1. Nat Med. 5:938–942. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Enjoji M, Nakamuta M, Noguchi K, Sugimoto
R, Kotoh K, Nawata H, Nakashima M and Watanabe T: RCAS1 expression
in immune-mediated liver diseases. J Clin Gastroenterol.
34:286–287. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Enjoji M, Nakashima M, Yamaguchi K, Kotoh
K and Nakamuta M: Significance of RCAS1 antigen in hepatocellular,
cholangiocellular and pancreatic carcinomas. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 20:1143–1148. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Giaginis C, Giagini A and Theocharis S:
Receptor-binding cancer antigen expressed on SiSo cells (RCAS1): A
novel biomarker in the diagnosis and prognosis of human neoplasia.
Histol Histopathol. 24:761–776. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dutsch-Wicherek M: RCAS1, MT, and vimentin
as potential markers of tumor microenvironment remodeling. Am J
Reprod Immunol. 63:181–188. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sonoda K: Novel therapeutic strategies to
target RCAS1, which induces apoptosis via ectodomain shedding.
Histol Histopathol. 26:1475–1486. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Szubert S, Dziobek K and Wicherek L: High
post-treatment serum soluble receptor-binding cancer antigen
expressed on SiSo cells (sRCAS1) levels is associated with poor
survival of patients with cervical cancer. J Obset Gynaecol Res.
46:499–506. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sonoda K, Miyamoto S, Nakashima M and Wake
N: Receptor-binding cancer antigen expressed on SiSo cells induces
apoptosis via ectodomain shedding. Exp Cell Res. 316:1795–1803.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nishinakagawa T, Fujii S, Nozaki T, Maeda
T, Machida K, Enjoji M and Nakashima M: Analysis of cell cycle
arrest and apoptosis induced by RCAS1. Int J Mol Med. 25:717–722.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yamaguchi H and Condeelis J: Regulation of
the actin cytoskeleton in cancer cell migration and invasion.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1773:642–652. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Condeelis J, Singer R and Segall JE: The
great escape: When cancer cells hijack the genes for chemotaxis and
motility. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 21:695–718. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sahai E: Mechanisms of cancer cell
invasion. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 15:87–96. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yamaguchi H, Wyckoff J and Condeelis J:
Cell migration in tumors. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 17:559–564. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim B, van Golen CM and Feldman EL:
Insulin-like growth factor I induces preferential degradation of
insulin receptor substrate-2 through the phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase pathway in human neuroblastoma cells. Endocrinology.
146:5350–5357. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lavastre V, Chiasson S, Cavalli H and
Girard D: Viscum album agglutinin-I induces apoptosis and
degradation of cytoskeletal proteins via caspases in human
leukaemia eosinophil AML14.3D10 cells: Differences with purified
human eosinophils. Br J Haematol. 130:527–535. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lavastre V, Pelletier M, Saller R,
Hostanska K and Girard D: Mechanisms involved in spontaneous and
Viscum album agglutinin-I-induced human neutrophil apoptosis:
Viscum album agglutinin-I accelerates the loss of antiapoptotic
Mcl-1 expression and the degradation of cytoskeletal paxillin and
vimentin proteins via caspases. J Immunol. 168:1419–1427. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Levkau B, Herren B, Koyama H, Ross R and
Raines EW: Caspase-mediated cleavage of focal adhesion kinase
pp125FAK and disassembly of focal adhesions in human endothelial
cell apoptosis. J Exp Med. 187:579–586. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Frisch SM and Francis H: Disruption of
epithelial cell-matrix interactions induces apoptosis. J Cell Biol.
124:619–626. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Frisch SM, Vuori K, Ruoslahti E and
Chan-Hui PY: Control of adhesion-dependent cell survival by focal
adhesion kinase. J Cell Biol. 134:793–799. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wu WB, Peng HC and Huang TF: Disintegrin
causes proteolysis of beta-catenin and apoptosis of endothelial
cells. Involvement of cell-cell and cell-ECM interactions in
regulating cell viability. Exp Cell Res. 286:115–127. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhao JH, Reiske H and Guan JL: Regulation
of the cell cycle by focal adhesion kinase. J Cell Biol.
143:1997–2008. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Milligan RA, Whittaker D and Safer D:
Molecular structure of F-actin and location of surface binding
sites. Nature. 348:217–221. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Dos Remedios CG, Chhabra D, Kekic M,
Dedova IV, Tsubakihara M, Berry DA and Nosworthy NJ: Actin binding
proteins: Regulation of cytoskeletal microfilaments. Physiol Rev.
83:433–473. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Moon A and Drubin DG: The ADF/cofilin
proteins: Stimulus-responsive modulators of actin dynamics. Mol
Biol Cell. 6:1423–1431. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Qi M and Elion EA: MAP kinase pathways. J
Cell Sci. 118:3569–3572. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Johnson GL and Lapadat R:
Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and
p38 protein kinases. Science. 298:1911–1912. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kobayashi M, Nishita M, Mishima T, Ohashi
K and Mizuno K: MAPKAPK-2-mediated LIM-kinase activation is
critical for VEGF-induced actin remodeling and cell migration. EMBO
J. 25:713–726. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bian H, Li F, Wang W, Zhao Q, Gao S, Ma J,
Li X, Ren W, Qin C and Qi J: MAPK/p38 regulation of cytoskeleton
rearrangement accelerates induction of macrophage activation by
TLR4, but not TLR3. Int J Mol Med. 40:1495–1503. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Koul HK, Pal M and Koul S: Role of p38 MAP
kinase signal transduction in solid tumors. Genes Cancer.
4:342–359. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Pereira L, Igea A, Canovas B, Dolado I and
Nebreda AR: Inhibition of p38 MAPK sensitizes tumour cells to
cisplatin-induced apoptosis mediated by reactive oxygen species and
JNK. EMBO Mol Med. 5:1759–1774. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bakour N, Moriarty F, Moore G, Robson T
and Annett SL: Prognostic significance of glucocorticoid receptor
expression in cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Cancers (Basel). 13:16492021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|