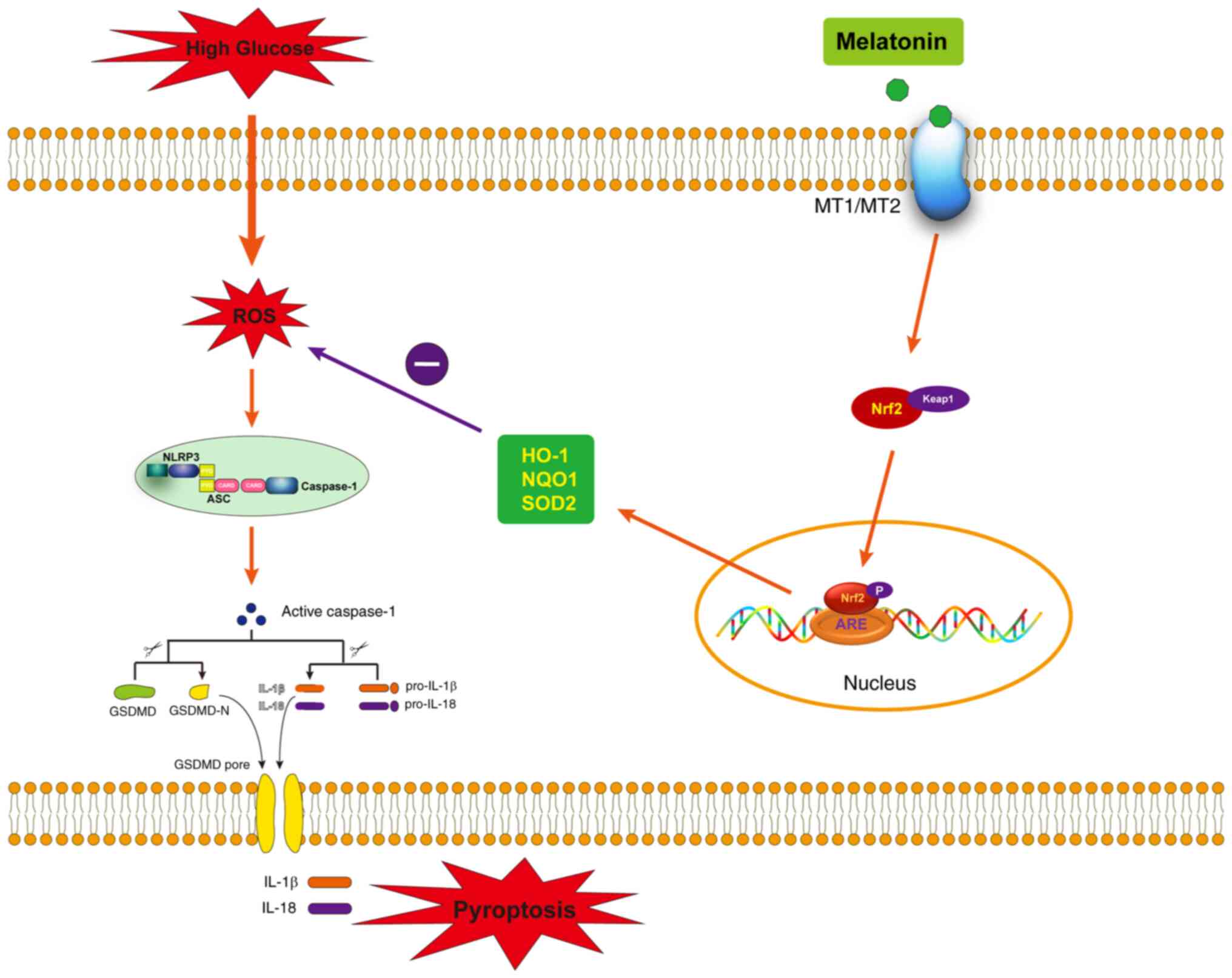
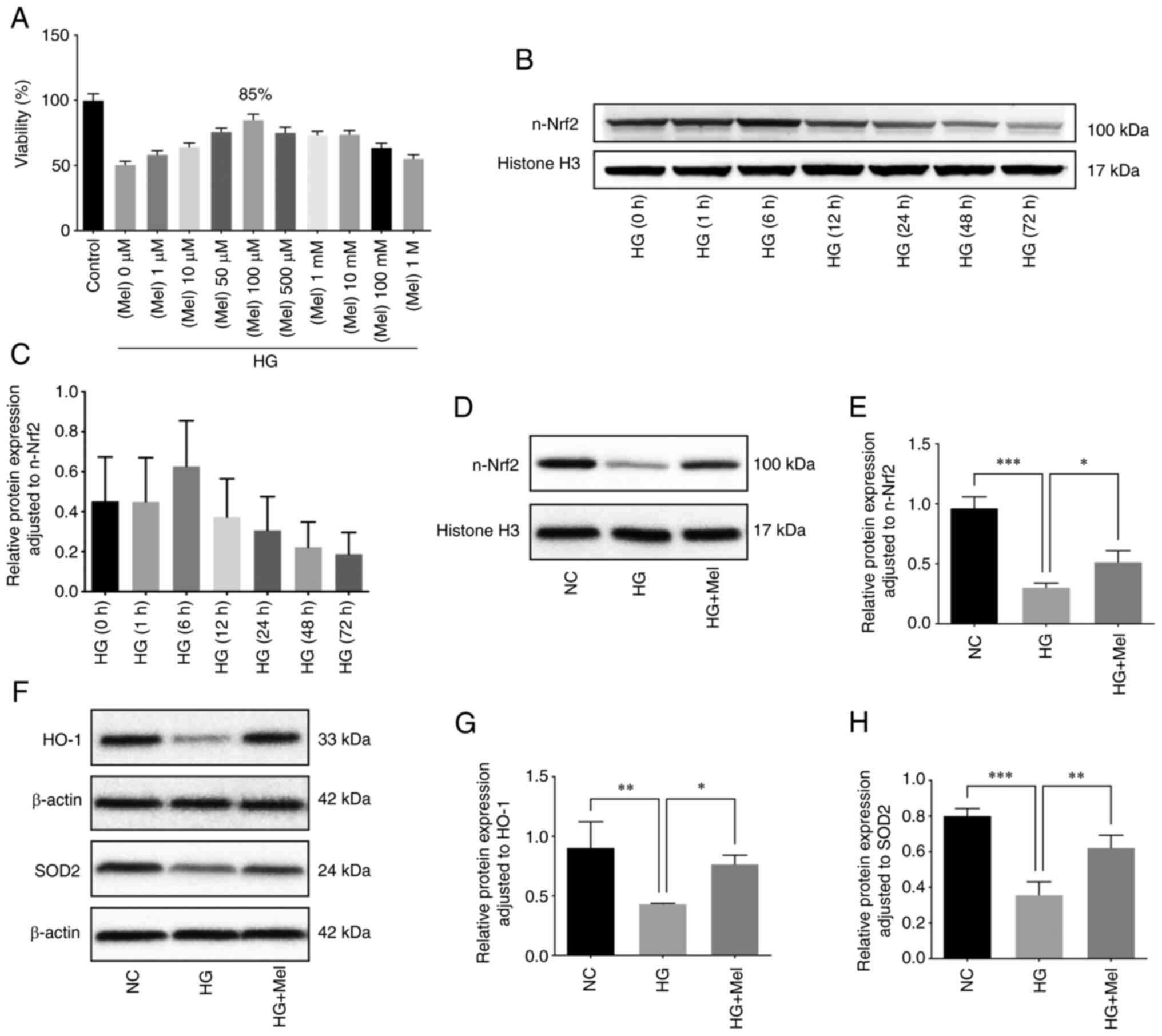
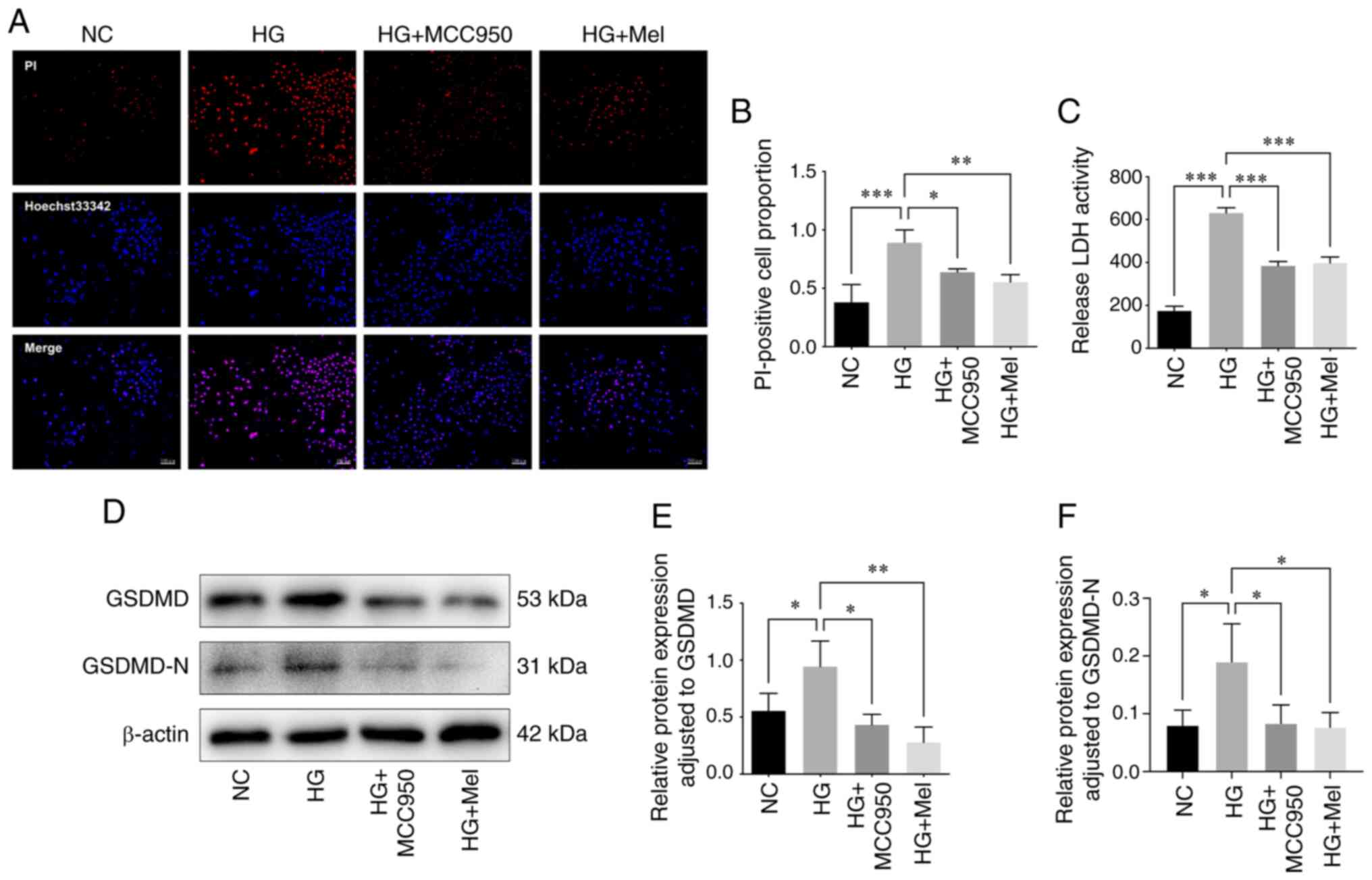
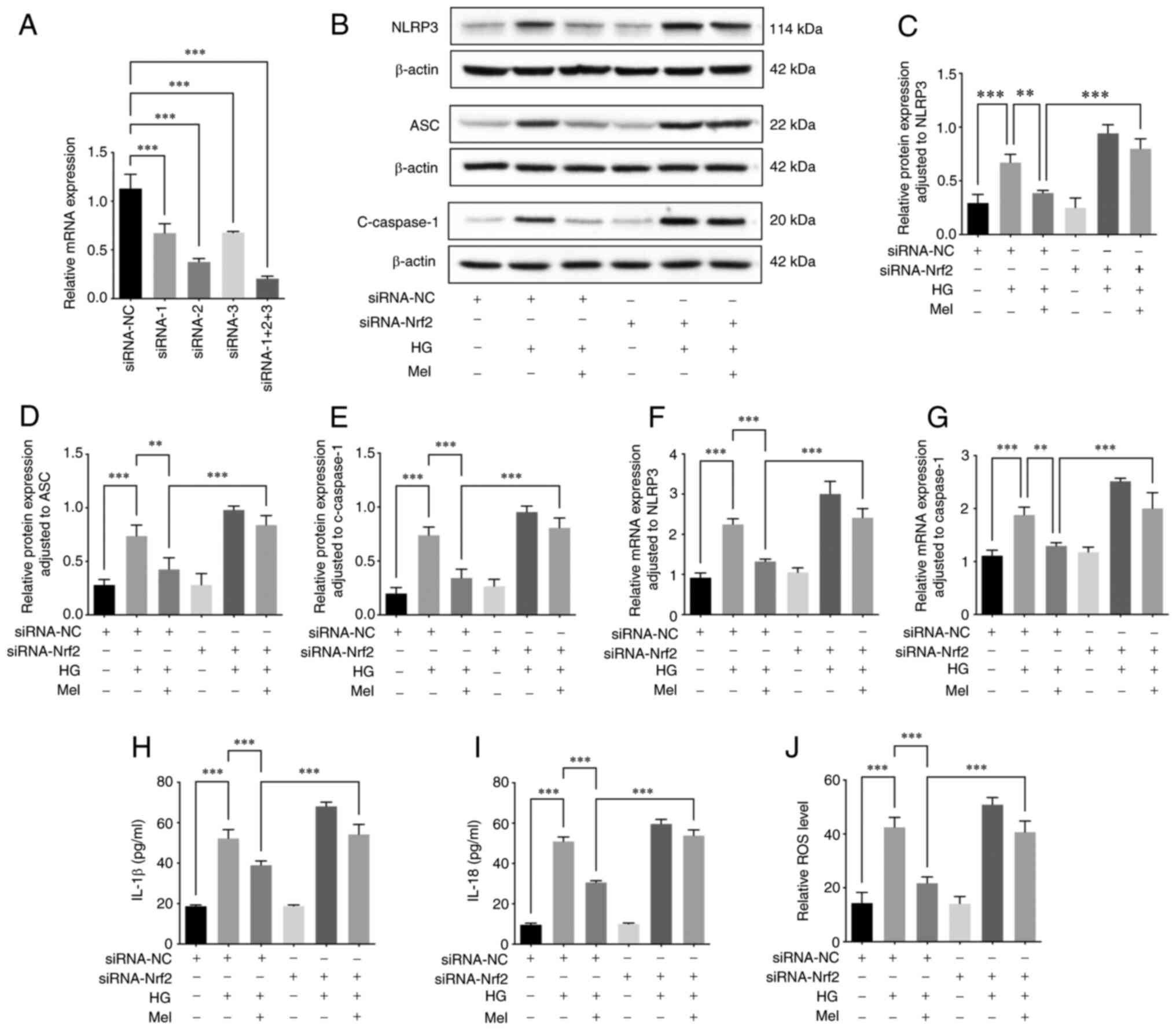
|
1
|
Vijan S: Type 2 diabetes: Ann Intern Med.
171:ITC65-ITC80. 2019.
|
|
2
|
Kaur R, Kaur M and Singh J: Endothelial
dysfunction and platelet hyperactivity in type 2 diabetes mellitus:
Molecular insights and therapeutic strategies. Cardiovasc Diabetol.
17:1212018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gimbrone MA Jr and Garcia-Cardeña G:
Endothelial cell dysfunction and the pathobiology of
atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 118:620–636. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ma B, Wang X, Zhang R, Niu S, Rong Z, Ni
L, Di X, Han Q and Liu C: Cigarette smoke extract stimulates PCSK9
production in HepG2 cells via ROS/NF-κB signaling. Mol Med Rep.
23:3312021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Salmanoglu DS, Gurpinar T, Vural K,
Ekerbicer N, Dariverenli E and Var A: Melatonin and L-carnitin
improves endothelial disfunction and oxidative stress in type 2
diabetic rats. Redox Biol. 8:199–204. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tiong YL, Ng KY, Koh RY, Ponnudurai G and
Chye SM: Melatonin inhibits high glucose-induced ox-LDL/LDL
expression and apoptosis in human umbilical endothelial cells. Horm
Mol Biol Clin Investig. 41:2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhaolin Z, Guohua L, Shiyuan W and Zuo W:
Role of pyroptosis in cardiovascular disease. Cell Prolif.
52:e125632019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Komada T and Muruve DA: The role of
inflammasomes in kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 15:501–520. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
He Y, Hara H and Núñez G: Mechanism and
regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Trends Biochem Sci.
41:1012–1021. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu Z, Gan L, Xu Y, Luo D, Ren Q, Wu S and
Sun C: Melatonin alleviates inflammasome-induced pyroptosis through
inhibiting NF-κB/GSDMD signal in mice adipose tissue. J Pineal Res.
63:2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wang X, Bian Y, Zhang R, Liu X, Ni L, Ma
B, Zeng R, Zhao Z, Song X and Liu C: Melatonin alleviates cigarette
smoke-induced endothelial cell pyroptosis through inhibiting
ROS/NLRP3 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 519:402–408. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li C, Cheng L, Wu H, He P, Zhang Y, Yang
Y, Chen J and Chen M: Activation of the KEAP1-NRF2-ARE signaling
pathway reduces oxidative stress in Hep2 cells. Mol Med Rep.
18:2541–2550. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yamamoto M, Kensler TW and Motohashi H:
The KEAP1-NRF2 system: A thiol-based sensor-effector apparatus for
maintaining redox homeostasis. Physiol Rev. 98:1169–1203. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang Y, Qiao B, Gao F, Wang H, Miao S and
Zhao H: Melatonin protects H9c2 cells against
ischemia/reperfusion-induced apoptosis and oxidative stress via
activation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep.
18:3497–3505. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li Y, Yu H, Xu Z, Shi S, Wang D, Shi X,
Wang Y, Zeng B, Deng H, Deng X, et al: Melatonin ameliorates
ANIT-induced cholestasis by activating Nrf2 through a
PI3K/Akt-dependent pathway in rats. Mol Med Rep. 19:1185–1193.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kelley N, Jeltema D, Duan Y and He Y: The
NLRP3 inflammasome: An overview of mechanisms of activation and
regulation. Int J Mol Sci. 20:33282019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cecon E, Oishi A and Jockers R: Melatonin
receptors: Molecular pharmacology and signalling in the context of
system bias. Br J Pharmacol. 175:3263–3280. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu X, Zhang H, Qi W, Zhang Y, Li J, Li Z,
Lin Y, Bai X, Liu X, Chen X, et al: Nicotine promotes
atherosclerosis via ROS-NLRP3-mediated endothelial cell pyroptosis.
Cell Death Dis. 9:1712018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang Y, Liu X, Bai X, Lin Y, Li Z, Fu J,
Li M, Zhao T, Yang H, Xu R, et al: Melatonin prevents endothelial
cell pyroptosis via regulation of long noncoding RNA
MEG3/miR-223/NLRP3 axis. J Pineal Res. 64:2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Xu J, Tian F, Hu S, Chen
Y and Fu Z: Melatonin attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion
injury via improving mitochondrial fusion/mitophagy and activating
the AMPK-OPA1 signaling pathways. J Pineal Res. 66:e125422019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Scheer FAJL, Van Montfrans GA, van Someren
EJ, Mairuhu G and Buijs RM: Daily nighttime melatonin reduces blood
pressure in male patients with essential hypertension.
Hypertension. 43:192–197. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cheng X, Wan Y, Xu Y, Zhou Q, Wang Y and
Zhu H: Melatonin alleviates myosin light chain kinase expression
and activity via the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway
during atherosclerosis in rabbits. Mol Med Rep. 11:99–104. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sadeghi M, Khosrawi S,
Heshmat-Ghahdarijani K, Gheisari Y, Roohafza H, Mansoorian M and
Hoseini SG: Effect of melatonin on heart failure: Design for a
double-blinded randomized clinical trial. ESC Heart Fail.
7:3142–3150. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ghaeli P, Solduzian M, Vejdani S and
Talasaz AH: Comparison of the effects of melatonin and oxazepam on
anxiety levels and sleep quality in patients with
ST-segment-elevation myocardial Infarction following primary
percutaneous coronary intervention: A randomized clinical trial.
Ann Pharmacother. 52:949–955. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nasseh N, Khezri MB, Farzam S, Shiravandi
S and Shafikhani AA: The effect of melatonin on cardiac biomarkers
after coronary artery bypass graft surgery: A double-blind,
randomized pilot study. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 36:3800–3805.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dominguez-Rodriguez A, Abreu-Gonzalez P,
de la Torre-Hernandez JM, Consuegra-Sanchez L, Piccolo R,
Gonzalez-Gonzalez J, Garcia-Camarero T, Del Mar Garcia-Saiz M,
Aldea-Perona A, Reiter RJ, et al: Usefulness of early treatment
with melatonin to reduce infarct size in patients with ST-segment
elevation myocardial infarction receiving percutaneous coronary
intervention (from the melatonin adjunct in the acute myocardial
infarction treated with angioplasty trial). Am J Cardiol.
120:522–526. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ekeloef S, Halladin N, Fonnes S, Jensen
SE, Zaremba T, Rosenberg J, Jonsson G, Aarøe J, Gasbjerg LS,
Rosenkilde MM and Gögenur I: Effect of intracoronary and
intravenous melatonin on myocardial salvage index in patients with
ST-elevation myocardial infarction: A randomized placebo controlled
trial. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 10:470–479. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zahid JA, Isbrand A, Kleif J,
Schou-Pedersen AV, Lykkesfeldt J, Madsen MT and Gögenur I: The
effect of melatonin on endothelial dysfunction in patients after
acute coronary syndrome: The MEFACS randomized clinical trial. J
Pineal Res. 67:e126002019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kücükakin B, Wilhelmsen M, Lykkesfeldt J,
Reiter RJ, Rosenberg J and Gögenur I: No effect of melatonin to
modify surgical-stress response after major vascular surgery: A
randomised placebo-controlled trial. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg.
40:461–467. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhao S, Wang Y, Zhang X, Zheng L, Zhu B,
Yao S, Yang L and Du J: Melatonin protects against
hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced dysfunction of human umbilical vein
endothelial cells through inhibiting reactive oxygen species
generation. Acta Cardiol Sin. 34:424–431. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dayoub JC, Ortiz F, López LC, Venegas C,
Del Pino-Zumaquero A, Roda O, Sanchez-Montesinos I,
Acuña-Castroviejo D and Escames G: Synergism between melatonin and
atorvastatin against endothelial cell damage induced by
lipopolysaccharide. J Pineal Res. 51:324–330. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Qian Z, Zhao Y, Wan C, Deng Y, Zhuang Y,
Xu Y, Zhu Y, Lu S and Bao Z: Pyroptosis in the initiation and
progression of atherosclerosis. Front Pharmacol. 12:6529632021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zeng J, Tao J, Xia L, Zeng Z, Chen J, Wang
Z, Meng J and Liu L: Melatonin inhibits vascular endothelial cell
pyroptosis by improving mitochondrial function via up-regulation
and demethylation of UQCRC1. Biochem Cell Biol. 99:339–347. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Afzal-Ahmed I, Mann GE, Shennan AH, Poston
L and Naftalin RJ: Preeclampsia inactivates glucose-6-phosphate
dehydrogenase and impairs the redox status of erythrocytes and
fetal endothelial cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 42:1781–1790. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Paravicini TM and Touyz RM: NADPH
oxidases, reactive oxygen species, and hypertension: Clinical
implications and therapeutic possibilities. Diabetes Care. 31
(Suppl 2):S170–S180. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Minutoli L, Puzzolo D, Rinaldi M, Irrera
N, Marini H, Arcoraci V, Bitto A, Crea G, Pisani A, Squadrito F, et
al: ROS-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation in brain, heart,
kidney, and testis ischemia/reperfusion injury. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2016:21830262016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fan Y, Zhang X, Yang L, Wang J, Hu Y, Bian
A, Liu J and Ma J: Zinc inhibits high glucose-induced NLRP3
inflammasome activation in human peritoneal mesothelial cells. Mol
Med Rep. 16:5195–5202. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Su Y, Wang Y, Liu M and Chen H: Hydrogen
sulfide attenuates renal I/R-induced activation of the inflammatory
response and apoptosis via regulating Nrf2-mediated NLRP3 signaling
pathway inhibition. Mol Med Rep. 24:5182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hou Y, Wang Y, He Q, Li L, Xie H, Zhao Y
and Zhao J: Nrf2 inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation through
regulating Trx1/TXNIP complex in cerebral ischemia reperfusion
injury. Behav Brain Res. 336:32–39. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shi S, Lei S, Tang C, Wang K and Xia Z:
Melatonin attenuates acute kidney ischemia/reperfusion injury in
diabetic rats by activation of the SIRT1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling
pathway. Biosci Rep. 39:BSR201816142019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Shah SA, Khan M, Jo MH, Jo MG, Amin FU and
Kim MO: Melatonin stimulates the SIRT1/Nrf2 signaling pathway
counteracting lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced oxidative stress to
rescue postnatal rat brain. CNS Neurosci Ther. 23:33–44. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sadek KM, Lebda MA and Abouzed TK: The
possible neuroprotective effects of melatonin in aluminum
chloride-induced neurotoxicity via antioxidant pathway and Nrf2
signaling apart from metal chelation. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int.
26:9174–9183. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Arioz BI, Tastan B, Tarakcioglu E, Tufekci
KU, Olcum M, Ersoy N, Bagriyanik A, Genc K and Genc S: Melatonin
attenuates LPS-induced acute depressive-like behaviors and
microglial NLRP3 inflammasome activation through the SIRT1/Nrf2
pathway. Front Immunol. 10:15112019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Rahim I, Sayed RK, Fernández-Ortiz M,
Aranda-Martínez P, Guerra-Librero A, Fernández-Martínez J, Rusanova
I, Escames G, Djerdjouri B and Acuña-Castroviejo D: Melatonin
alleviates sepsis-induced heart injury through activating the Nrf2
pathway and inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome. Naunyn Schmiedebergs
Arch Pharmacol. 394:261–277. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhao Z, Wang X, Zhang R, Ma B, Niu S, Di
X, Ni L and Liu C: Melatonin attenuates smoking-induced
atherosclerosis by activating the Nrf2 pathway via NLRP3
inflammasomes in endothelial cells. Aging (Albany NY).
13:11363–11380. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chen X, Xi Z, Liang H, Sun Y, Zhong Z,
Wang B, Bian L and Sun Q: Melatonin prevents mice cortical
astrocytes from hemin-induced toxicity through activating
PKCα/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling in vitro. Front Neurosci. 13:7602019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jumnongprakhon P, Govitrapong P, Tocharus
C and Tocharus J: Melatonin promotes blood-brain barrier integrity
in methamphetamine-induced inflammation in primary rat brain
microvascular endothelial cells. Brain Res. 1646:182–192. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Pandi-Perumal SR, Trakht I, Srinivasan V,
Spence DW, Maestroni GJ, Zisapel N and Cardinali DP: Physiological
effects of melatonin: Role of melatonin receptors and signal
transduction pathways. Prog Neurobiol. 85:335–353. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Gobbi G and Comai S: Sleep well.
Untangling the role of melatonin MT1 and MT2 receptors in sleep. J
Pineal Res. 66:e125442019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Cui P, Yu M, Luo Z, Dai M, Han J, Xiu R
and Yang Z: Intracellular signaling pathways involved in cell
growth inhibition of human umbilical vein endothelial cells by
melatonin. J Pineal Res. 44:107–114. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Duan MX, Zhou H, Wu QQ, Liu C, Xiao Y,
Deng W and Tang QZ: Andrographolide protects against HG-induced
inflammation, apoptosis, migration, and impairment of angiogenesis
via PI3K/AKT-eNOS SIgnalling in HUVECs. Mediators Inflamm.
2019:61683402019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Leng B, Zhang Y, Liu X, Zhang Z, Liu Y,
Wang H and Lu M: Astragaloside IV suppresses high glucose-induced
NLRP3 inflammasome activation by inhibiting TLR4/NF-κ B and CaSR.
Mediators Inflamm. 2019:10824972019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wang J, Shen X, Liu J, Chen W, Wu F, Wu W,
Meng Z, Zhu M and Miao C: High glucose mediates NLRP3 inflammasome
activation via upregulation of ELF3 expression. Cell Death Dis.
11:3832020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Nie J: UNC0321 inhibits high glucose
induced apoptosis in HUVEC by targeting Rab4. Biomed Pharmacother.
131:1106622020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|