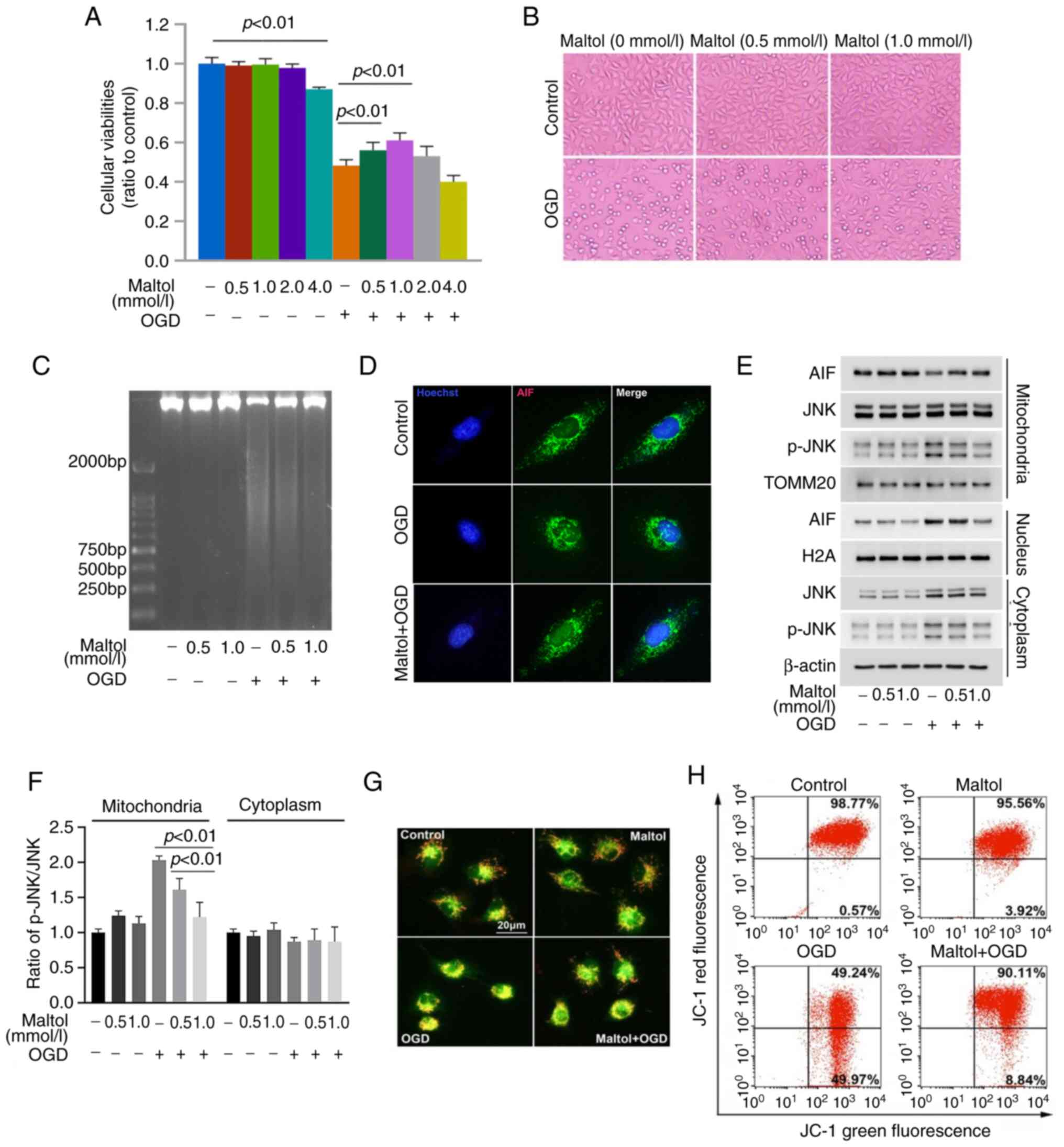
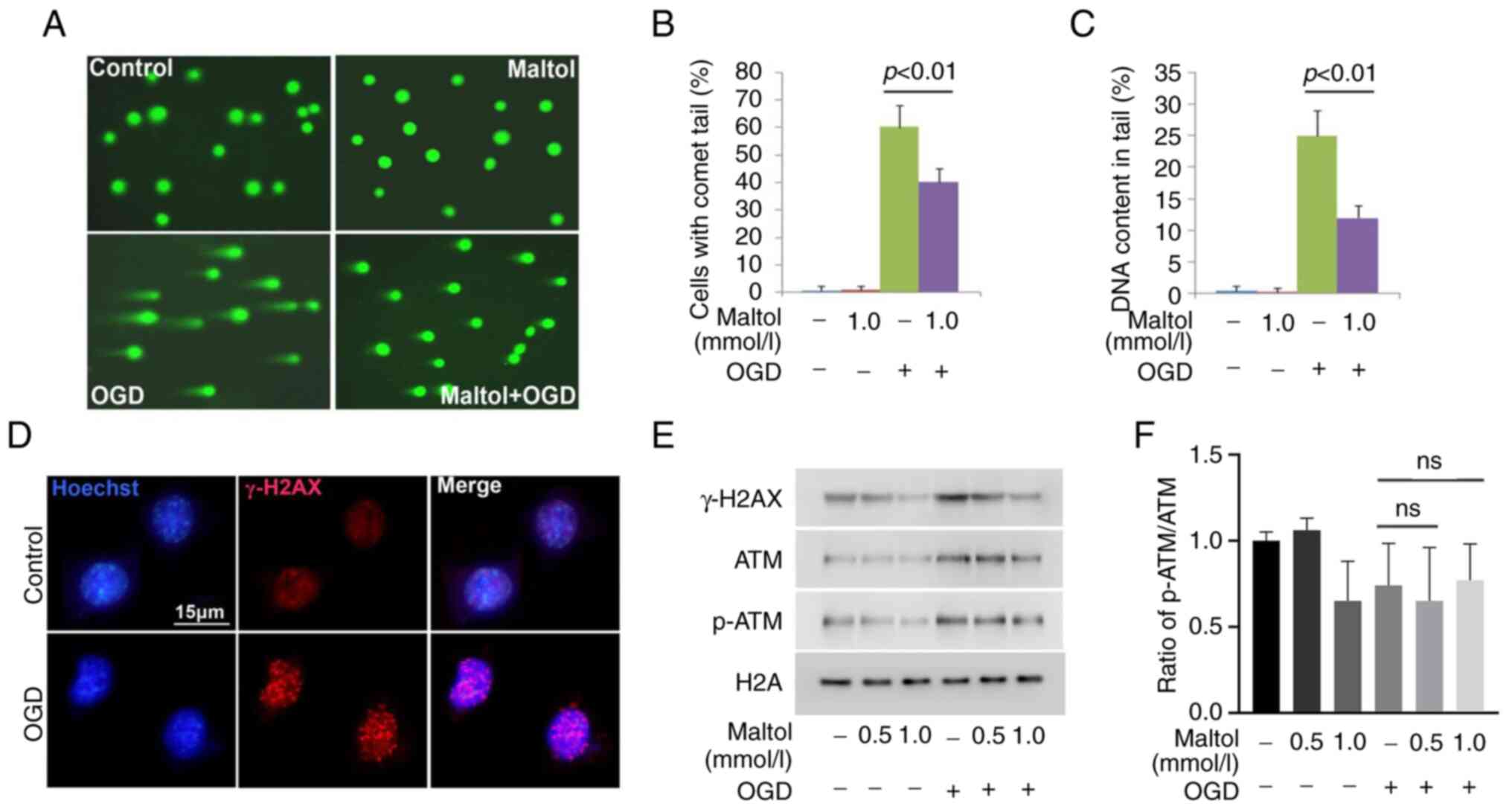
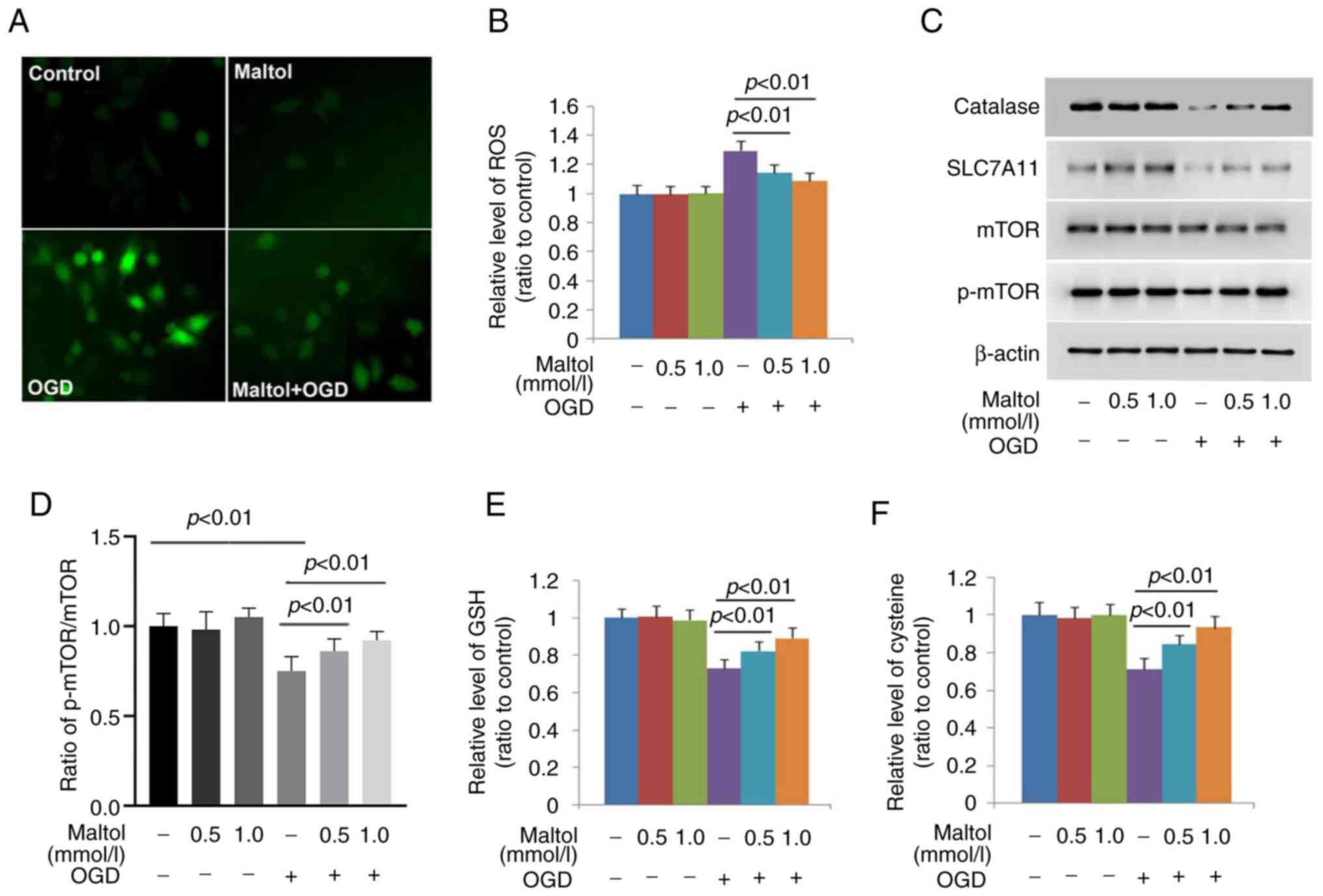
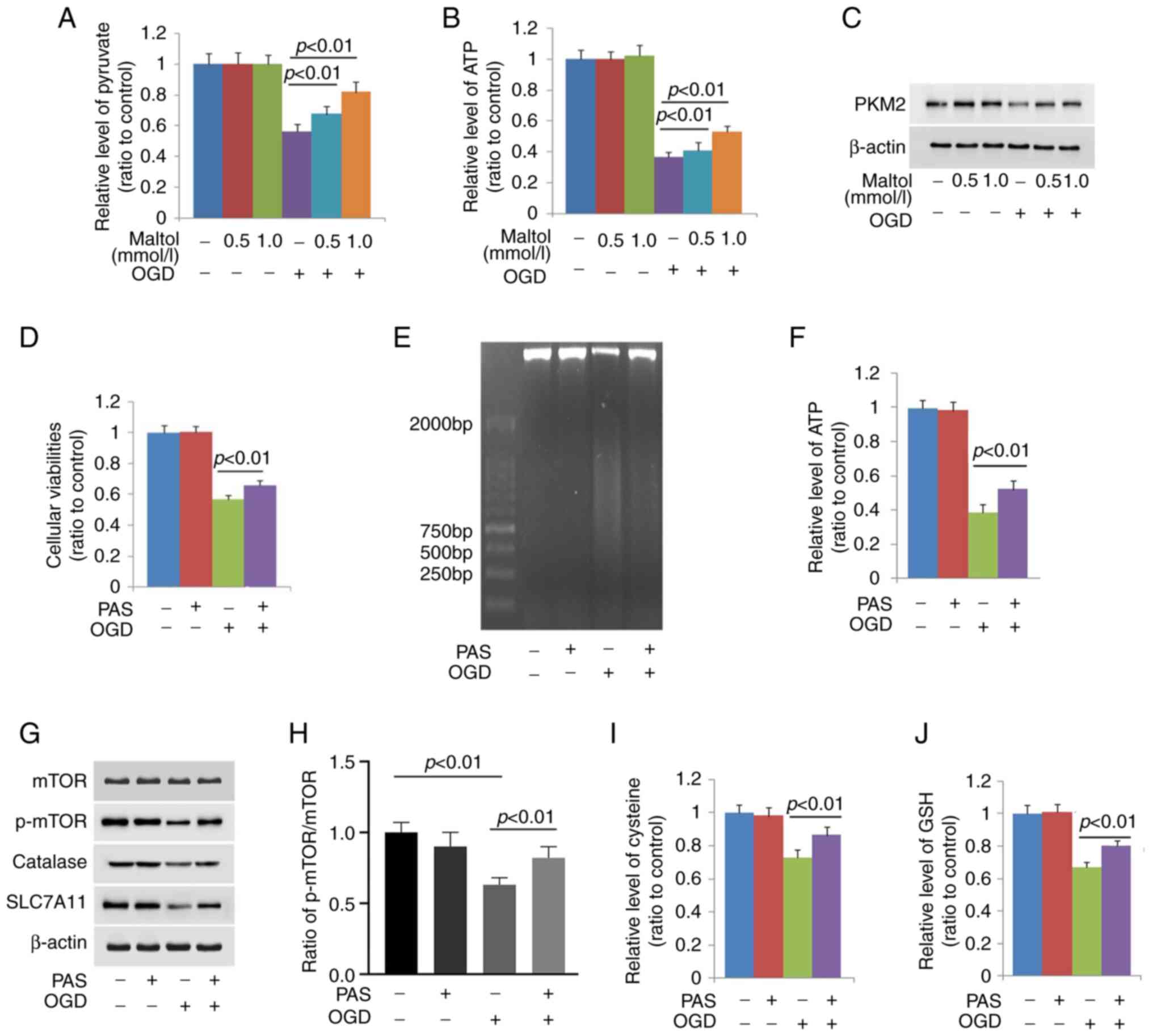
|
1
|
Kawane K, Motani K and Nagata S: DNA
degradation and its defects. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
6:a0163942014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Artus C, Boujrad H, Bouharrour A, Brunelle
MN, Hoos S, Yuste VJ, Lenormand P, Rousselle JC, Namane A, England
P, et al: AIF promotes chromatinolysis and caspase-independent
programmed necrosis by interacting with histone H2AX. Embo J.
29:1585–1599. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Baritaud M, Cabon L, Delavallée L,
Galán-Malo P, Gilles ME, Brunelle-Navas MN and Susin SA:
AIF-mediated caspase-independent necroptosis requires ATM and
DNA-PK-induced histone H2AX Ser139 phosphorylation. Cell Death Dis.
3:e3902012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pilch DR, Sedelnikova OA, Redon C, Celeste
A, Nussenzweig A and Bonner WM: Characteristics of gamma-H2AX foci
at DNA double-strand breaks sites. Biochem Cell Biol. 81:123–129.
2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ding Y, He C, Lu S, Wang X, Wang C, Wang
L, Zhang J, Piao M, Chi G, Luo Y, et al: MLKL contributes to
shikonin-induced glioma cell necroptosis via promotion of
chromatinolysis. Cancer Lett. 467:58–71. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
He C, Lu S, Wang XZ, Wang CC, Wang L,
Liang SP, Luo TF, Wang ZC, Piao MH, Chi GF and Ge PF: FOXO3a
protects glioma cells against temozolomide-induced DNA double
strand breaks via promotion of BNIP3-mediated mitophagy. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 42:1324–1337. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Berdelle N, Nikolova T, Quiros S, Efferth
T and Kaina B: Artesunate induces oxidative DNA damage, sustained
DNA double-strand breaks, and the ATM/ATR damage response in cancer
cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 10:2224–2233. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Han Y, Xu Q, Hu JN, Han XY, Li W and Zhao
LC: Maltol, a food flavoring agent, attenuates acute
alcohol-induced oxidative damage in mice. Nutrients. 7:682–696.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Murakami K, Ishida K, Watakabe K,
Tsubouchi R, Haneda M and Yoshino M: Prooxidant action of maltol:
Role of transition metals in the generation of reactive oxygen
species and enhanced formation of 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine
formation in DNA. Biometals. 19:253–257. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu W, Wang Z, Hou JG, Zhou YD, He YF,
Jiang S, Wang YP, Ren S and Li W: The liver protection effects of
maltol, a flavoring agent, on carbon tetrachloride-induced acute
liver injury in mice via inhibiting apoptosis and inflammatory
response. Molecules. 23:21202018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Z, Hao W, Hu J, Mi X, Han Y, Ren S,
Jiang S, Wang Y, Li X and Li W: Maltol Improves APAP-Induced
hepatotoxicity by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation
response via NF-κB and PI3K/Akt signal pathways. Antioxidants
(Basel). 8:3952019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhu DC, Wang YH, Lin JH, Miao ZM, Xu JJ
and Wu YS: Maltol inhibits the progression of osteoarthritis via
the nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor-2/heme oxygenase-1
signal pathway in vitro and in vivo. Food Funct. 12:1327–1337.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Guo N, Li C, Liu Q, Liu S, Huan Y, Wang X,
Bai G, Yang M, Sun S, Xu C and Shen Z: Maltol, a food flavor
enhancer, attenuates diabetic peripheral neuropathy in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Food Funct. 9:6287–6297.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mi XJ, Hou JG, Jiang S, Liu Z, Tang S, Liu
XX, Wang YP, Chen C, Wang Z and Li W: Maltol mitigates
thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis through TGF-β1-mediated
activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. J Agric Food Chem.
67:1392–1401. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hong S, Iizuka Y, Lee T, Kim CY and Seong
GJ: Neuroprotective and neurite outgrowth effects of maltol on
retinal ganglion cells under oxidative stress. Mol Vis.
20:1456–1462. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim YB, Oh SH, Sok DE and Kim MR:
Neuroprotective effect of maltol against oxidative stress in brain
of mice challenged with kainic acid. Nutr Neurosci. 7:33–39. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mao Y, Du J, Chen X, Al Mamun A, Cao L,
Yang Y, Mubwandarikwa J, Zaeem M, Zhang W, Chen Y, et al: Maltol
promotes mitophagy and inhibits oxidative stress via the
Nrf2/PINK1/Parkin pathway after spinal cord injury. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2022:13376302022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Badiola N, Penas C, Miñano-Molina A,
Barneda-Zahonero B, Fadó R, Sánchez-Opazo G, Comella JX, Sabriá J,
Zhu C, Blomgren K, et al: Induction of ER stress in response to
oxygen-glucose deprivation of cortical cultures involves the
activation of the PERK and IRE-1 pathways and of caspase-12. Cell
Death Dis. 2:e1492011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee HJ, Lyu da H, Koo U, Lee SJ, Hong SS,
Kim K, Kim KH, Lee D and Mar W: Inhibitory effect of
2-arylbenzofurans from the Mori Cortex Radicis (Moraceae) on oxygen
glucose deprivation (OGD)-induced cell death of SH-SY5Y cells. Arch
Pharm Res. 34:1373–1380. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou Z, Lu B, Wang C, Wang Z, Luo T, Piao
M, Meng F, Chi G, Luo Y and Ge P: RIP1 and RIP3 contribute to
shikonin-induced DNA double-strand breaks in glioma cells via
increase of intracellular reactive oxygen species. Cancer Lett.
390:77–90. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang C, He C, Lu S, Wang X, Wang L, Liang
S, Wang X, Piao M, Cui J, Chi G and Ge P: Autophagy activated by
silibinin contributes to glioma cell death via induction of
oxidative stress-mediated BNIP3-dependent nuclear translocation of
AIF. Cell Death Dis. 11:6302020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Begum H, Murugesan P and Tangutur AD:
Western blotting: A powerful staple in scientific and biomedical
research. Biotechniques. 73:58–69. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huang Y, Wen Q, Huang J, Luo M, Xiao Y, Mo
R and Wang J: Manganese (II) chloride leads to dopaminergic
neurotoxicity by promoting mitophagy through BNIP3-mediated
oxidative stress in SH-SY5Y cells. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 26:232021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang HF, Wang ZQ, Ding Y, Piao MH, Feng
CS, Chi GF, Luo YN and Ge PF: Endoplasmic reticulum stress
regulates oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced parthanatos in human
SH-SY5Y cells via improvement of intracellular ROS. CNS Neurosci
Ther. 24:29–38. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Andrabi SA, Dawson TM and Dawson VL:
Mitochondrial and nuclear cross talk in cell death: Parthanatos.
Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1147:233–241. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xia P, Zhang F, Yuan Y, Chen C, Huang Y,
Li L, Wang E, Guo Q and Ye Z: ALDH 2 conferred neuroprotection on
cerebral ischemic injury by alleviating mitochondria-related
apoptosis through JNK/caspase-3 signing pathway. Int J Biol Sci.
16:1303–1323. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ali SS, Ahsan H, Zia MK, Siddiqui T and
Khan FH: Understanding oxidants and antioxidants: Classical team
with new players. J Food Biochem. 44:e131452020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li C, Chen H, Lan Z, He S, Chen R, Wang F,
Liu Z, Li K, Cheng L, Liu Y, et al: mTOR-dependent upregulation of
xCT blocks melanin synthesis and promotes tumorigenesis. Cell Death
Differ. 26:2015–2028. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dey P, Kundu A, Sachan R, Park JH, Ahn MY,
Yoon K, Lee J, Kim ND, Kim IS, Lee BM, et al: PKM2 knockdown
induces autophagic cell death via AKT/mTOR pathway in human
prostate cancer cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 52:1535–1552.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li XB, Gu JD and Zhou QH: Review of
aerobic glycolysis and its key enzymes-new targets for lung cancer
therapy. Thorac Cancer. 6:17–24. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Candé C, Vahsen N, Kouranti I, Schmitt E,
Daugas E, Spahr C, Luban J, Kroemer RT, Giordanetto F, Garrido C,
et al: AIF and cyclophilin A cooperate in apoptosis-associated
chromatinolysis. Oncogene. 23:1514–1521. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li J, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Song Y,
Wei S, He M, You S, Jia J and Cheng J: TRAF2 protects against
cerebral ischemia-induced brain injury by suppressing necroptosis.
Cell Death Dis. 10:3282019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tang MB, Li YS, Li SH, Cheng Y, Zhang S,
Luo HY, Mao CY, Hu ZW, Schisler JC, Shi CH, et al: Anisomycin
prevents OGD-induced necroptosis by regulating the E3 ligase CHIP.
Sci Rep. 8:63792018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Park YH, Broyles HV, He S, McGrady NR, Li
L and Yorio T: Involvement of AMPA receptor and its flip and flop
isoforms in retinal ganglion cell death following oxygen/glucose
deprivation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 57:508–526. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li HQ, Xia SN, Xu SY, Liu PY, Gu Y, Bao
XY, Xu Y and Cao X: γ-Glutamylcysteine alleviates ischemic
stroke-induced neuronal apoptosis by inhibiting ROS-Mediated
endoplasmic reticulum stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2021:29610792021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Qu Y, Tang J, Wang H, Li S, Zhao F, Zhang
L, Richard Lu Q and Mu D: RIPK3 interactions with MLKL and CaMKII
mediate oligodendrocytes death in the developing brain. Cell Death
Dis. 8:e26292017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang Y, An R, Umanah GK, Park H, Nambiar
K, Eacker SM, Kim B, Bao L, Harraz MM, Chang C, et al: A nuclease
that mediates cell death induced by DNA damage and poly(ADP-ribose)
polymerase-1. Science. 354:aad68722016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li WH, Yang YL, Cheng X, Liu M, Zhang SS,
Wang YH and Du GH: Baicalein attenuates caspase-independent cells
death via inhibiting PARP-1 activation and AIF nuclear
translocation in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion rats. Apoptosis.
25:354–369. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liang J, Yu Y, Wang B, Lu B, Zhang J,
Zhang H and Ge P: Ginsenoside Rb1 attenuates oxygen-glucose
deprivation-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells via protection of
mitochondria and inhibition of AIF and cytochrome c release.
Molecules. 18:12777–12792. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lee JH and Paull TT: Cellular functions of
the protein kinase ATM and their relevance to human disease. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 22:796–814. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sánchez-Morán I, Rodríguez C, Lapresa R,
Agulla J, Sobrino T, Castillo J, Bolaños JP and Almeida A: Nuclear
WRAP53 promotes neuronal survival and functional recovery after
stroke. Sci Adv. 6:eabc57022020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cheng J, Fan YQ, Jiang HX, Chen SF, Chen
J, Liao XY, Zou YY, Lan HY, Cui Y, Chen ZB, et al: Transcranial
direct-current stimulation protects against cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion injury through regulating Cezanne-dependent
signaling. Exp Neurol. 345:1138182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kihara S, Shiraishi T, Nakagawa S, Toda K
and Tabuchi K: Visualization of DNA double strand breaks in the
gerbil hippocampal CA1 following transient ischemia. Neurosci Lett.
175:133–136. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Floyd RA and Carney JM: Free radical
damage to protein and DNA: Mechanisms involved and relevant
observations on brain undergoing oxidative stress. Ann Neurol. 32
(Suppl 1):S22–S27. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yang Y, Wang J, Xu C, Pan H and Zhang Z:
Maltol inhibits apoptosis of human neuroblastoma cells induced by
hydrogen peroxide. J Biochem Mol Biol. 39:145–149. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Song Y, Hong S, Iizuka Y, Kim CY and Seong
GJ: The neuroprotective effect of maltol against oxidative stress
on rat retinal neuronal cells. Korean J Ophthalmol. 29:58–65. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang H, Davies KJA and Forman HJ:
Oxidative stress response and Nrf2 signaling in aging. Free Radic
Biol Med. 88:314–336. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Dai Y, Zhang H, Zhang J and Yan M:
Isoquercetin attenuates oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis
after ischemia/reperfusion injury via Nrf2-mediated inhibition of
the NOX4/ROS/NF-κB pathway. Chem Biol Interact. 284:32–40. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Liu A, Zhang W, Wang S, Wang Y and Hong J:
HMGB-1/RAGE signaling inhibition by dioscin attenuates hippocampal
neuron damage induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion.
Exp Ther Med. 20:2312020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Armogida M, Spalloni A, Amantea D, Nutini
M, Petrelli F, Longone P, Bagetta G, Nisticò R and Mercuri NB: The
protective role of catalase against cerebral ischemia in vitro and
in vivo. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 24:735–747. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Rhee SG and Kil IS: Mitochondrial
H2O2 signaling is controlled by the concerted
action of peroxiredoxin III and sulfiredoxin: Linking mitochondrial
function to circadian rhythm. Free Radic Biol Med. 99:120–127.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Fu C, Wu Y, Liu S, Luo C, Lu Y, Liu M,
Wang L, Zhang Y and Liu X: Rehmannioside A improves cognitive
impairment and alleviates ferroptosis via activating PI3K/AKT/Nrf2
and SLC7A11/GPX4 signaling pathway after ischemia. J
Ethnopharmacol. 289:1150212022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wei N, Lu T, Yang L, Dong Y and Liu X:
Lipoxin A4 protects primary spinal cord neurons from
Erastin-induced ferroptosis by activating the Akt/Nrf2/HO-1
signaling pathway. FEBS Open Bio. 11:2118–2126. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Woo Y, Lee HJ, Kim J, Kang SG, Moon S, Han
JA, Jung YM and Jung YJ: Rapamycin Promotes ROS-Mediated cell death
via functional inhibition of xCT Expression in Melanoma Under
γ-Irradiation. Front Oncol. 11:6654202021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Horikawa I, Fujita K, Jenkins LM, Hiyoshi
Y, Mondal AM, Vojtesek B, Lane DP, Appella E and Harris CC:
Autophagic degradation of the inhibitory p53 isoform Δ133p53α as a
regulatory mechanism for p53-mediated senescence. Nat Commun.
5:47062014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Mi XJ, Hou JG, Wang Z, Han Y, Ren S, Hu
JN, Chen C and Li W: The protective effects of maltol on
cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity through the AMPK-mediated PI3K/Akt
and p53 signaling pathways. Sci Rep. 8:159222018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wang X, Perez E, Liu R, Yan LJ, Mallet RT
and Yang SH: Pyruvate protects mitochondria from oxidative stress
in human neuroblastoma SK-N-SH cells. Brain Res. 1132:1–9. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zeng J, Yang GY, Ying W, Kelly M, Hirai K,
James TL, Swanson RA and Litt L: Pyruvate improves recovery after
PARP-1-associated energy failure induced by oxidative stress in
neonatal rat cerebrocortical slices. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
27:304–315. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Wu H, Zhao H and Chen L: Deoxyshikonin
inhibits viability and glycolysis by suppressing the Akt/mTOR
pathway in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Front Oncol. 10:12532020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|