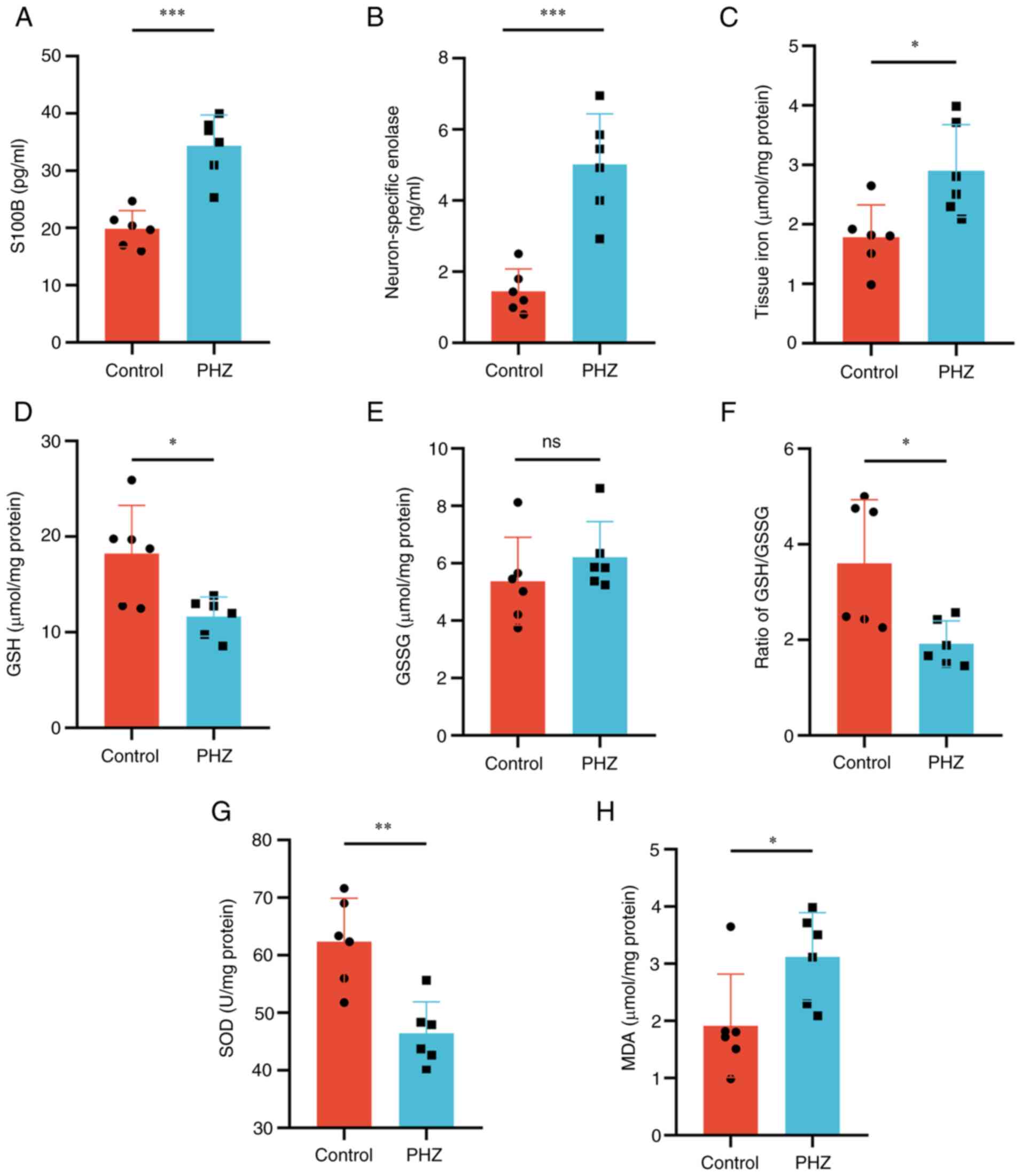
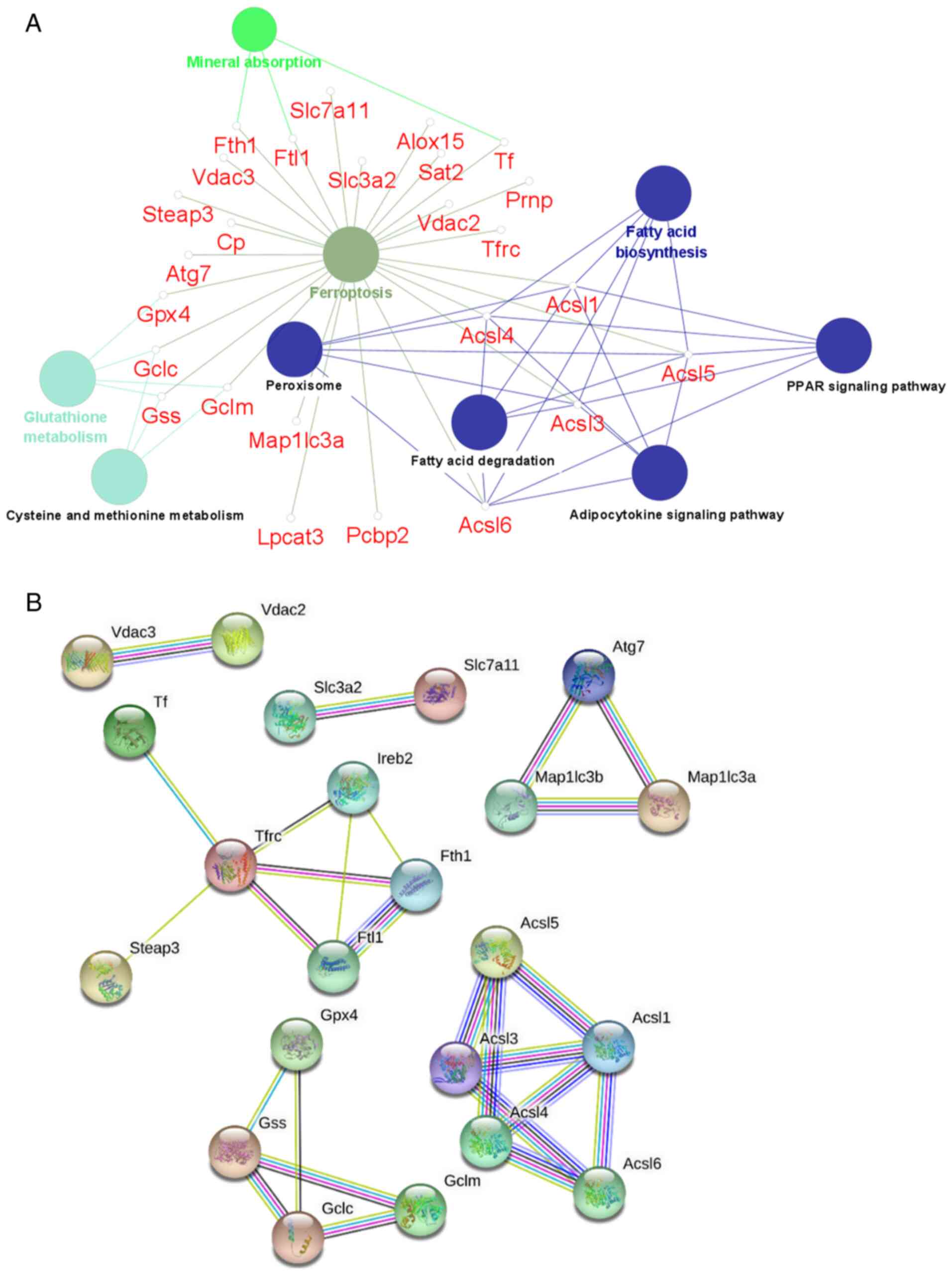
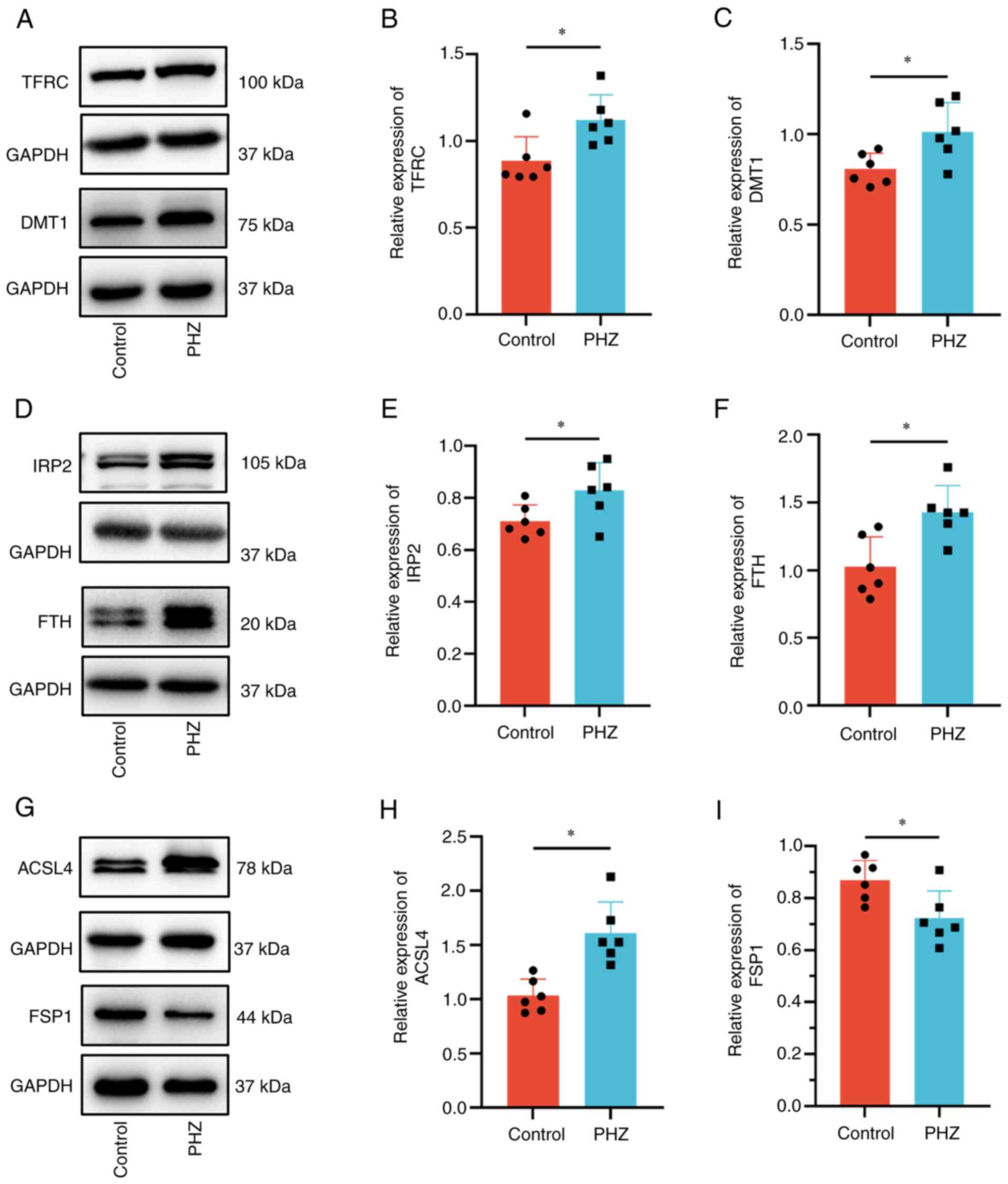
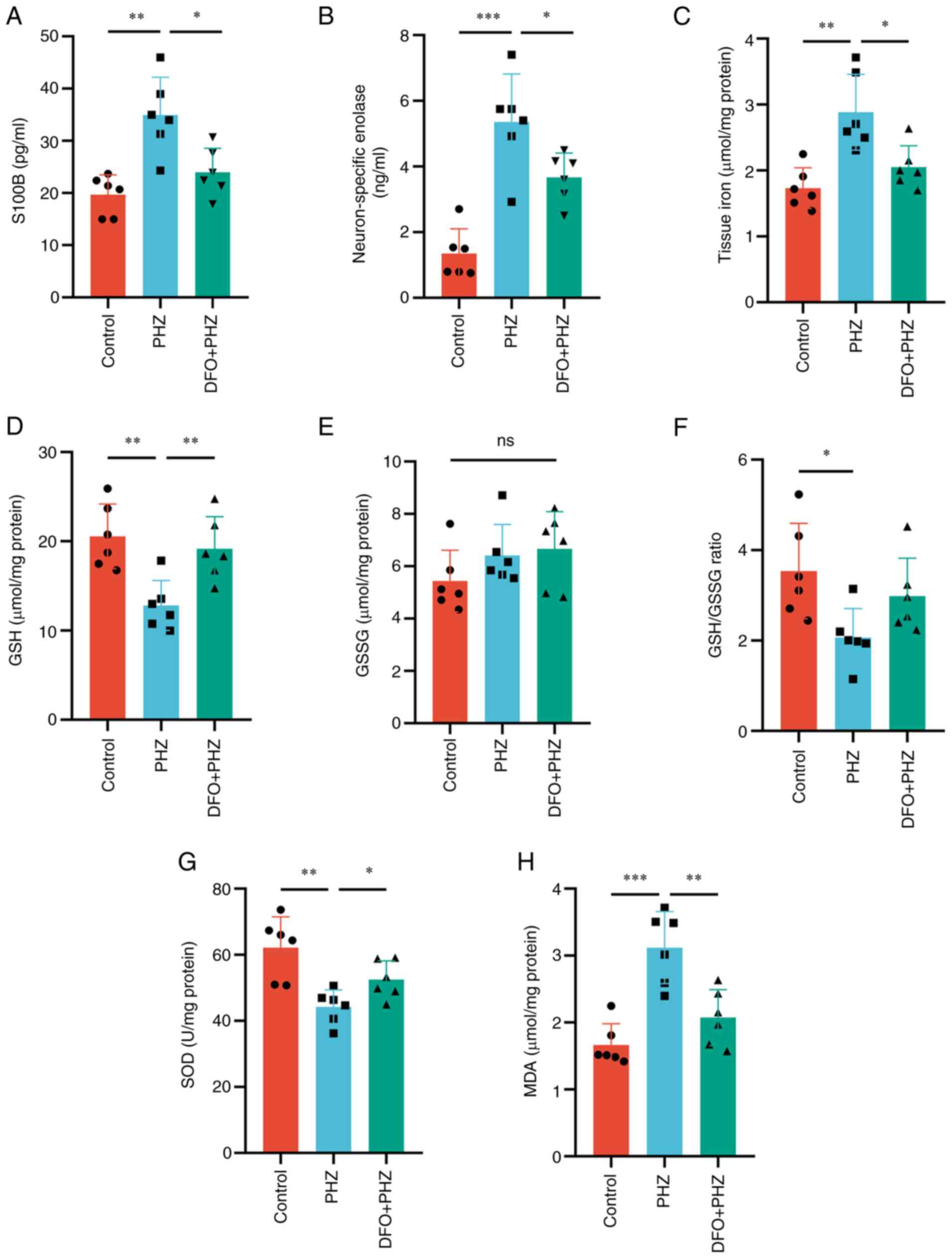
|
1
|
Lauer BJ and Spector ND:
Hyperbilirubinemia in the Newborn. Pediatr Rev. 32:341–349. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Soto Conti CP: Bilirubin: The toxic
mechanisms of an antioxidant molecule. Arch Argent Pediatr.
119:e18–e25. 2021.(In English, Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Christensen RD, Agarwal AM, George TI,
Bhutani VK and Yaish HM: Acute neonatal bilirubin encephalopathy in
the State of Utah 2009–2018. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 72:10–13. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wong RJ and Stevenson DK: Neonatal
hemolysis and risk of bilirubin-induced neurologic dysfunction.
Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 20:26–30. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kumar V, Kumar P, Sundaram V, Munjal SK,
Malhi P and Panda NK: Childhood neurodevelopmental outcomes of
survivors of acute bilirubin encephalopathy: A retrospective cohort
study. Early Hum Dev. 158:1053802021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Subspecialty Group of Neonatology, Society
of Pediatrics, Chinese Medical Association and Chinese Multicenter
Study Coordination Group for Neonatal Bilirubin Encephalopathy, .
Clinical characteristics of bilirubin encephalopathy in Chinese
newborn infants-a national multicenter survey. Zhonghua Er Ke Za
Zhi. 50:331–335. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Par EJ, Hughes CA and DeRico P: Neonatal
Hyperbilirubinemia: Evaluation and treatment. Am Fam Physician.
107:525–534. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Viktorinova A: Iron-mediated oxidative
cell death is a potential contributor to neuronal dysfunction
induced by neonatal hemolytic hyperbilirubinemia. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 654:185–193. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Khdair-Ahmad F, Aladily T, Khdair-Ahmad O
and Badran EF: Chelation therapy for secondary neonatal iron over
load: Lessons learned from rhesus hemolytic disease. Turk J
Pediatr. 60:335–339. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Aygun C, Tekinalp G and Gurgey A:
Increased Fetal iron load in rhesus hemolytic disease. Pediatr
Hematol Oncol. 21:329–333. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kaplan M, Bromiker R and Hammerman C:
Hyperbilirubinemia, hemolysis, and increased bilirubin
neurotoxicity. Semin Perinatol. 38:429–437. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nishiie-Yano R, Hirayama S, Tamura M,
Kanemochi T, Ueno T, Hirayama A, Hori A, Ai T, Hirose N and Miida
T: Hemolysis is responsible for elevation of serum iron
concentration after Regular exercises in judo athletes. Biol Trace
Elem Res. 197:63–69. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Comporti M, Signorini C, Buonocore G and
Ciccoli L: Iron release, oxidative stress and erythrocyte ageing.
Free Radic Biol Med. 32:568–576. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sun S, Shen J, Jiang J, Wang F and Min J:
Targeting ferroptosis opens new avenues for the development of
novel therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 8:3722023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jiang X, Stockwell BR and Conrad M:
Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 22:266–282. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ashraf A, Jeandriens J, Parkes HG and So
PW: Iron dyshomeostasis, lipid peroxidation and perturbed
expression of cystine/glutamate antiporter in Alzheimer's disease:
Evidence of ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 32:1014942020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rui T, Wang H, Li Q, Cheng Y, Gao Y, Fang
X, Ma X, Chen G, Gao C, Gu Z, et al: Deletion of ferritin H in
neurons counteracts the protective effect of melatonin against
traumatic brain injury-induced ferroptosis. J Pineal Res.
70:e127042021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vitalakumar D, Sharma A and Flora SJS:
Ferroptosis: A potential therapeutic target for neurodegenerative
diseases. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 35:e228302021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ding X, Gao L, Han Z, Eleuteri S, Shi W,
Shen Y, Song ZY, Su M, Yang Q, Qu Y, et al: Ferroptosis in
Parkinson's disease: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic
potential. Ageing Res Rev. 91:1020772023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bu ZQ, Yu HY, Wang J, He X, Cui YR, Feng
JC and Feng J: Emerging Role of Ferroptosis in the Pathogenesis of
Ischemic Stroke: A new therapeutic target? ASN Neuro.
13:1759091421103752021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lu C, Tan C, Ouyang H, Chen Z, Yan Z and
Zhang M: Ferroptosis in Intracerebral hemorrhage: A panoramic
perspective of the metabolism, mechanism and theranostics. Aging
Dis. 13:13482022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li QS and Jia YJ: Ferroptosis: A critical
player and potential therapeutic target in traumatic brain injury
and spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 18:5062023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ren S, Chen Y, Wang L and Wu G: Neuronal
ferroptosis after intracerebral hemorrhage. Front Mol Biosci.
9:9664782022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Luykx LM, Berger HM, Geerdink J, Kanhai
HHH and Egberts J: Non-protein-bound iron and free radical damage
in fetuses with rhesus haemolytic disease: Influence of
intrauterine transfusions. BJOG. 111:303–310. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mejia GB, Sanz CR, Avila MM, Peraza AV,
Guzmán DC, Olguín HJ, Ramírez AM and Cruz EG: Experimental
hemolysis model to study bilirubin encephalopathy in rat brain. J
Neurosci Methods. 168:35–41. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pazar A, Kolgazi M, Memisoglu A, Bahadir
E, Sirvanci S, Yaman A, Yeğen BÇ and Ozek E: The neuroprotective
and anti-apoptotic effects of melatonin on hemolytic
hyperbilirubinemia-induced oxidative brain damage. J Pineal Res.
60:74–83. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Luo Y, Peng M and Wei H: Melatonin
promotes brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression and
anti-apoptotic effects in neonatal hemolytic hyperbilirubinemia via
a phospholipase (PLC)-mediated mechanism. Med Sci Monit.
23:5951–5959. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yao X, Zhang Y, Hao J, Duan HQ, Zhao CX,
Sun C, Li B, Fan BY, Wang X, Li WX, et al: Deferoxamine promotes
recovery of traumatic spinal cord injury by inhibiting ferroptosis.
Neural Regen Res. 14:532–541. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jin T, He Q, Cheng C, Li H, Liang L, Zhang
G, Su C, Xiao Y, Bradley J, Peberdy MA, et al: UAMC-3203 or/and
Deferoxamine improve Post-Resuscitation myocardial dysfunction
through suppressing ferroptosis in a rat model of cardiac arrest.
Shock. 57:344–350. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chian S, Jiang ZC, Jiang LX, Wang KT, Fan
YX, Liao T, Chen WS and Yao WX: Caffeine-induced neurotoxicity
mediated by Nrf2 pathway in PC12 cells and zebrafish larvae. J Appl
Toxicol. 42:629–637. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wiatrak B, Kubis-Kubiak A, Piwowar A and
Barg E: PC12 cell line: Cell types, coating of culture vessels,
differentiation and other culture conditions. Cells. 9:9582020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rand RN and Di Pasqua A: A new diazo
method for the determination of bilirubin. Clin Chem. 8:570–578.
1962. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zecha J, Satpathy S, Kanashova T,
Avanessian SC, Kane MH, Clauser KR, Mertins P, Carr SA and Kuster
B: TMT Labeling for the Masses: A Robust and Cost-efficient,
In-solution Labeling Approach. Mol Cell Proteomics. 18:1468–1478.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Grebe SK and Singh RJ: LC-MS/MS in the
Clinical Laboratory-Where to from here? Clin Biochem Rev. 32:5–31.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Men L, Li Y, Wang X, Li R, Zhang T, Meng
X, Liu S, Gong X and Gou M: Protein biomarkers associated with
frozen Japanese puffer fish (Takifugu rubripes) quality traits.
Food Chem. 327:1270022020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jiang Y, Zhao J, Li R, Liu Y, Zhou L, Wang
C, Lv C, Gao L and Cui D: CircLRFN5 inhibits the progression of
glioblastoma via PRRX2/GCH1 mediated ferroptosis. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 41:3072022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhou Y, Li L, Mao C and Zhou D:
Astragaloside IV ameliorates spinal cord injury through controlling
ferroptosis in H2O2-damaged PC12 cells in vitro. Ann Transl Med.
10:11762022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zuo X, Zeng H, Wang B, Yang X, He D, Wang
L, Ouyang H and Yuan J: AKR1C1 Protects corneal epithelial cells
against oxidative stress-mediated ferroptosis in dry eye. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 63:32022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Huang S, Cao B, Zhang J, Feng Y, Wang L,
Chen X, Su H, Liao S, Liu J, Yan J and Liang B: Induction of
ferroptosis in human nasopharyngeal cancer cells by cucurbitacin B:
Molecular mechanism and therapeutic potential. Cell Death Dis.
12:2372021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lorimier P, Lamarcq L, Labat-Moleur F,
Guillermet C, Bethier R and Stoebner P: Enhanced chemiluminescence:
A high-sensitivity detection system for in situ hybridization and
immunohistochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 41:1591–1597. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Jia B, Li J, Song Y and Luo C:
ACSL4-Mediated ferroptosis and its potential role in central
nervous system diseases and injuries. Int J Mol Sci. 24:100212023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bersuker K, Hendricks JM, Li Z, Magtanong
L, Ford B, Tang PH, Roberts MA, Tong B, Maimone TJ, Zoncu R, et al:
The CoQ oxidoreductase FSP1 acts parallel to GPX4 to inhibit
ferroptosis. Nature. 575:688–692. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hankø E, Hansen TWR, Almaas R, Lindstad J
and Rootwelt T: Bilirubin induces apoptosis and necrosis in human
NT2-N Neurons. Pediatr Res. 57:179–184. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Shapiro SM: Somatosensory and brainstem
auditory evoked potentials in the gunn rat model of acute bilirubin
neurotoxicity. Pediatr Res. 52:844–849. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Roger C, Koziel V, Vert P and Nehlig A:
Autoradiographic mapping of local cerebral permeability to
bilirubin in immature rats: Effects of hyperbilirubinemia. Pediatr
Res. 39:64–71. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Qaisiya M, Coda Zabetta CD, Bellarosa C
and Tiribelli C: Bilirubin mediated oxidative stress involves
antioxidant response activation via Nrf2 pathway. Cell Signal.
26:512–520. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Qaisiya M, Brischetto C, Jašprová J, Vitek
L, Tiribelli C and Bellarosa C: Bilirubin-induced ER stress
contributes to the inflammatory response and apoptosis in neuronal
cells. Arch Toxicol. 91:1847–1858. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Schiavon E, Smalley JL, Newton S, Greig NH
and Forsythe ID: Neuroinflammation and ER-stress are key mechanisms
of acute bilirubin toxicity and hearing loss in a mouse model. PLoS
One. 13:e02010222018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Vodret S, Bortolussi G, Iaconcig A,
Martinelli E, Tiribelli C and Muro AF: Attenuation of
neuro-inflammation improves survival and neurodegeneration in a
mouse model of severe neonatal hyperbilirubinemia. Brain Behav
Immun. 70:166–178. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Qaisiya M, Mardešić P, Pastore B,
Tiribelli C and Bellarosa C: The activation of autophagy protects
neurons and astrocytes against bilirubin-induced cytotoxicity.
Neurosci Lett. 661:96–103. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Shi HS, Lai K, Yin XL, Liang M, Ye HB, Shi
HB, Wang LY and Yin SK: Ca2+-dependent recruitment of voltage-gated
sodium channels underlies bilirubin-induced overexcitation and
neurotoxicity. Cell Death Dis. 10:7742019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ye H, Xing Y, Zhang L, Zhang J, Jiang H,
Ding D, Shi H and Yin S: Bilirubin-induced neurotoxic and ototoxic
effects in rat cochlear and vestibular organotypic cultures.
Neurotoxicology. 71:75–86. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Rawat V, Bortolussi G, Gazzin S, Tiribelli
C and Muro AF: Bilirubin-induced oxidative stress leads to DNA
damage in the cerebellum of hyperbilirubinemic neonatal mice and
activates DNA Double-Strand break repair pathways in human cells.
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018:18012432018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Youdim MB, Ben-Shachar D, Yehuda S and
Riederer P: The role of iron in the basal ganglion. Adv Neurol.
53:155–162. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yang WS and Stockwell BR: Ferroptosis:
Death by lipid peroxidation. Trends Cell Biol. 26:165–176. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Al-Abdi S: Decreased glutathione
S-transferase level and neonatal hyperbilirubinemia associated with
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency: A perspective review.
Am J Perinatol. 34:305–314. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Chen GH, Song CC, Pantopoulos K, Wei XL,
Zheng H and Luo Z: Mitochondrial oxidative stress mediated
Fe-induced ferroptosis via the NRF2-ARE pathway. Free Radic Biol
Med. 180:95–107. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Cheng J, Fan Y, Liu B, Zhou H, Wang J and
Chen Q: ACSL4 suppresses glioma cells proliferation via activating
ferroptosis. Oncol Rep. 43:147–158. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Chen J, Yang L, Geng L, He J, Chen L, Sun
Q, Zhao J and Wang X: Inhibition of Acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain
family member 4 facilitates neurological recovery after stroke by
regulation ferroptosis. Front Cell Neurosci. 15:6323542021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Cui Y, Zhang Y, Zhao X, Shao L, Liu G, Sun
C, Xu R and Zhang Z: ACSL4 exacerbates ischemic stroke by promoting
ferroptosis-induced brain injury and neuroinflammation. Brain Behav
Immun. 93:312–321. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Doll S, Freitas FP, Shah R, Aldrovandi M,
da Silva MC, Ingold I, Goya Grocin A, Xavier da Silva TN, Panzilius
E, Scheel CH, et al: FSP1 is a glutathione-independent ferroptosis
suppressor. Nature. 575:693–698. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Doll S and Conrad M: Iron and ferroptosis:
A still ill-defined liaison. IUBMB Life. 69:423–434. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Rath MEA, Smits-Wintjens VEHJ, Oepkes D,
Walther FJ and Lopriore E: Iron status in infants with alloimmune
haemolytic disease in the first three months of life. Vox Sang.
105:328–333. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Mleczko-Sanecka K and Silvestri L:
Cell-type-specific insights into iron regulatory processes. Am J
Hematol. 96:110–127. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Ganz T: New regulators of systemic iron
homeostasis. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 6:2802021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Gao G, Li J, Zhang Y and Chang YZ:
Cellular iron metabolism and regulation. Adv Exp Med Biol.
1173:21–32. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Sfera A, Bullock K, Price A, Inderias L
and Osorio C: Ferrosenescence: The iron age of neurodegeneration?
Mech Ageing Dev. 174:63–75. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Lu Y, Yang Q, Su Y, Ji Y, Li G, Yang X, Xu
L, Lu Z, Dong J, Wu Y, et al: MYCN mediates TFRC-dependent
ferroptosis and reveals vulnerabilities in neuroblastoma. Cell
Death Dis. 12:5112021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Xiong Q, Li X, Li W, Chen G, Xiao H, Li P
and Wu C: WDR45 Mutation impairs the autophagic degradation of
transferrin receptor and promotes ferroptosis. Front Mol Biosci.
8:6458312021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Zhang J, Chen X, Hong J, Tang A, Liu Y,
Xie N, Nie G, Yan X and Liang M: Biochemistry of mammalian
ferritins in the regulation of cellular iron homeostasis and
oxidative responses. Sci China Life Sci. 64:352–362. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Wang P, Cui Y, Ren Q, Yan B, Zhao Y, Yu P,
Gao G, Shi H, Chang S and Chang YZ: Mitochondrial ferritin
attenuates cerebral ischaemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting
ferroptosis. Cell Death Dis. 12:4472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Liu Y, Bell BA, Song Y, Kim HJ, Sterling
JK, Kim BJ, Poli M, Guo M, Zhang K, Rao A, et al: Intraocular iron
injection induces oxidative stress followed by elements of
geographic atrophy and sympathetic ophthalmia. Aging Cell.
20:e134902021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Yang J, Zhou Y, Xie S, Wang J, Li Z, Chen
L, Mao M, Chen C, Huang A, Chen Y, et al: Metformin induces
ferroptosis by inhibiting UFMylation of SLC7A11 in breast cancer. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 40:2062021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Yu H, Yang C, Jian L, Guo S, Chen R, Li K,
Qu F, Tao K, Fu Y, Luo F and v Liu S: Sulfasalazine-induced
ferroptosis in breast cancer cells is reduced by the inhibitory
effect of estrogen receptor on the transferrin receptor. Oncol Rep.
42:826–838. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Chen Y, Fang Z-M, Yi X, Wei X and Jiang
DS: The interaction between ferroptosis and inflammatory signaling
pathways. Cell Death Dis. 14:2052023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Dou J, Liu X, Yang L, Huang D and Tan X:
Ferroptosis interaction with inflammatory microenvironments:
Mechanism, biology, and treatment. Biomed Pharmacother.
155:1137112022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|