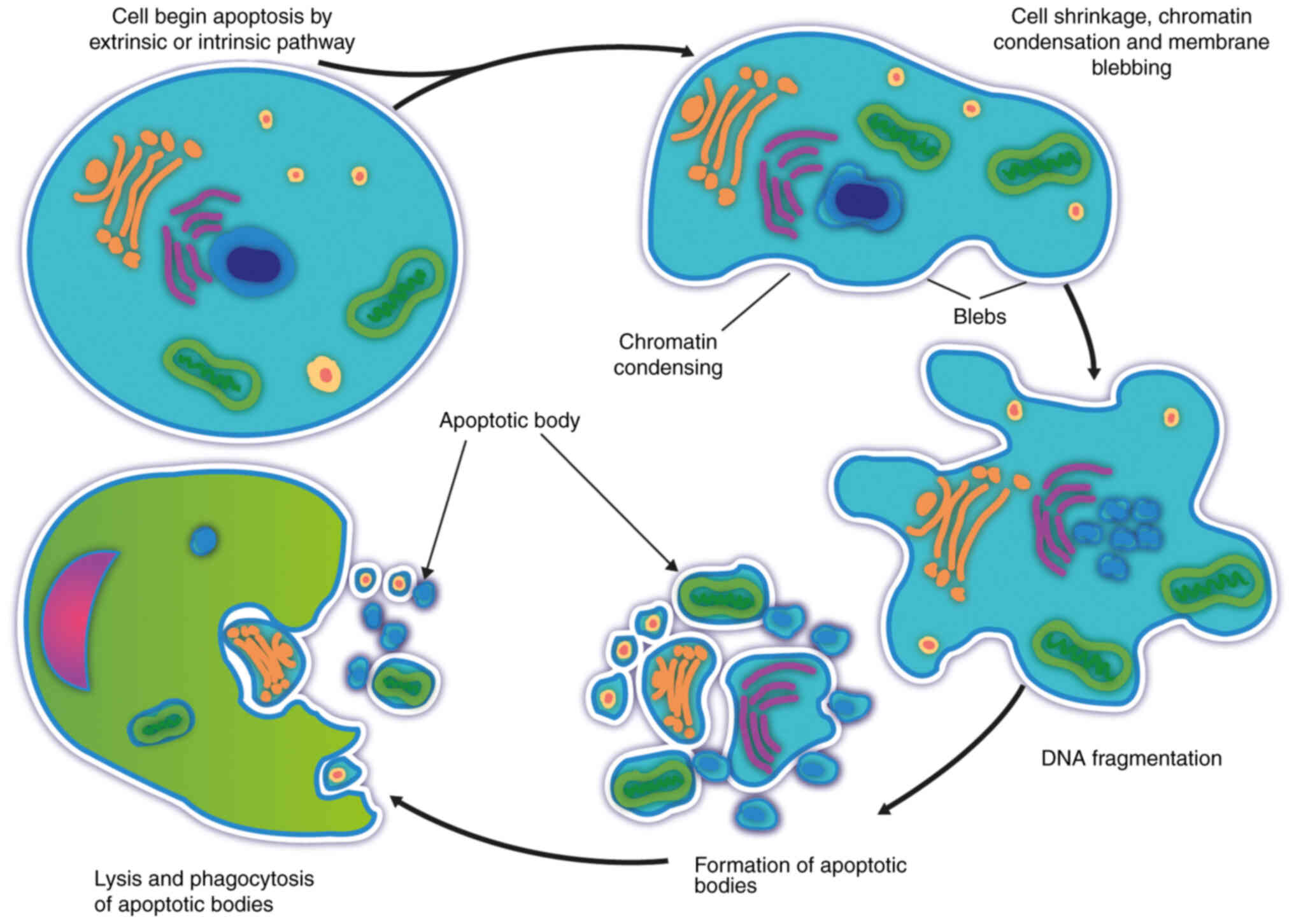
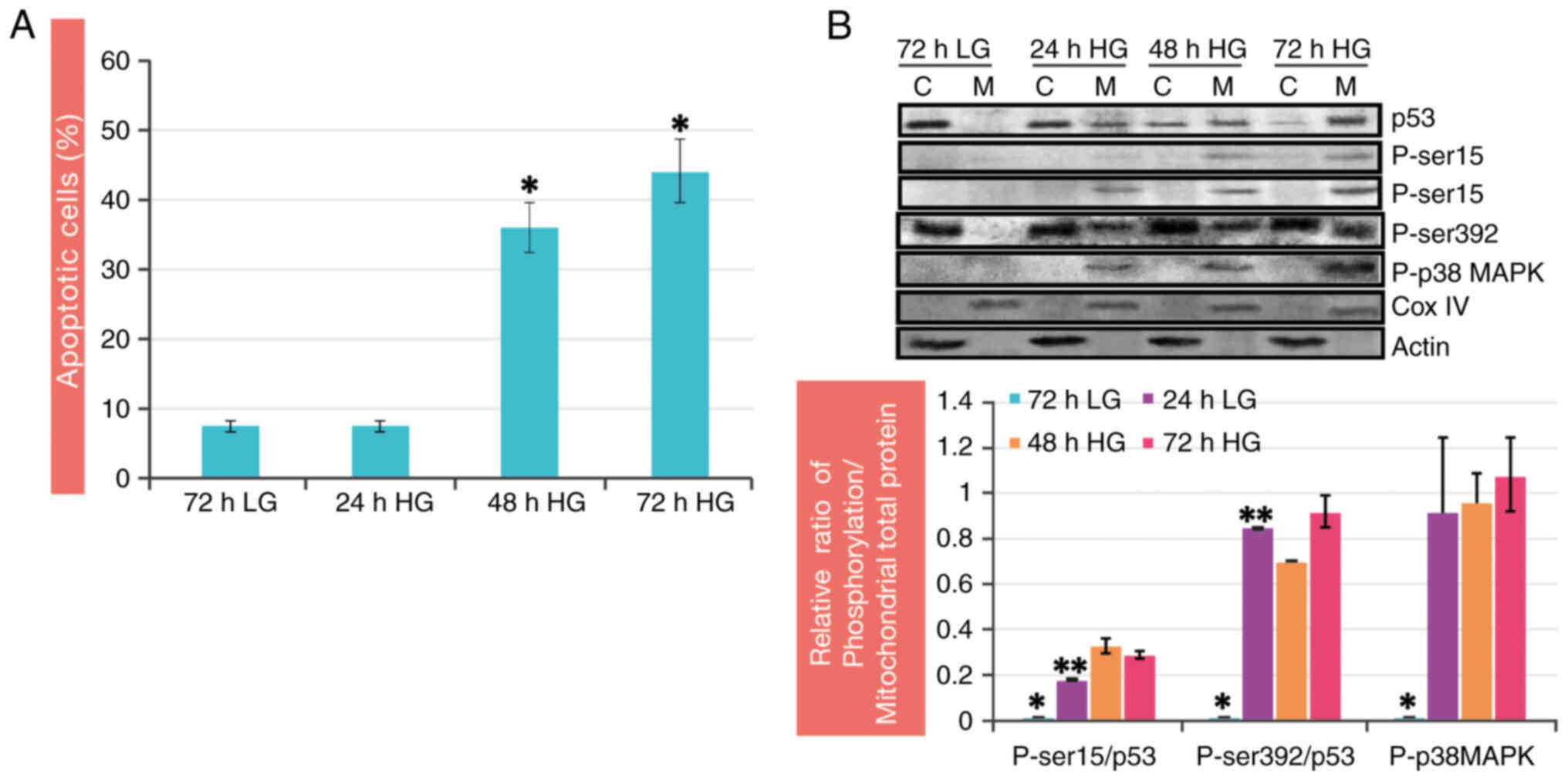
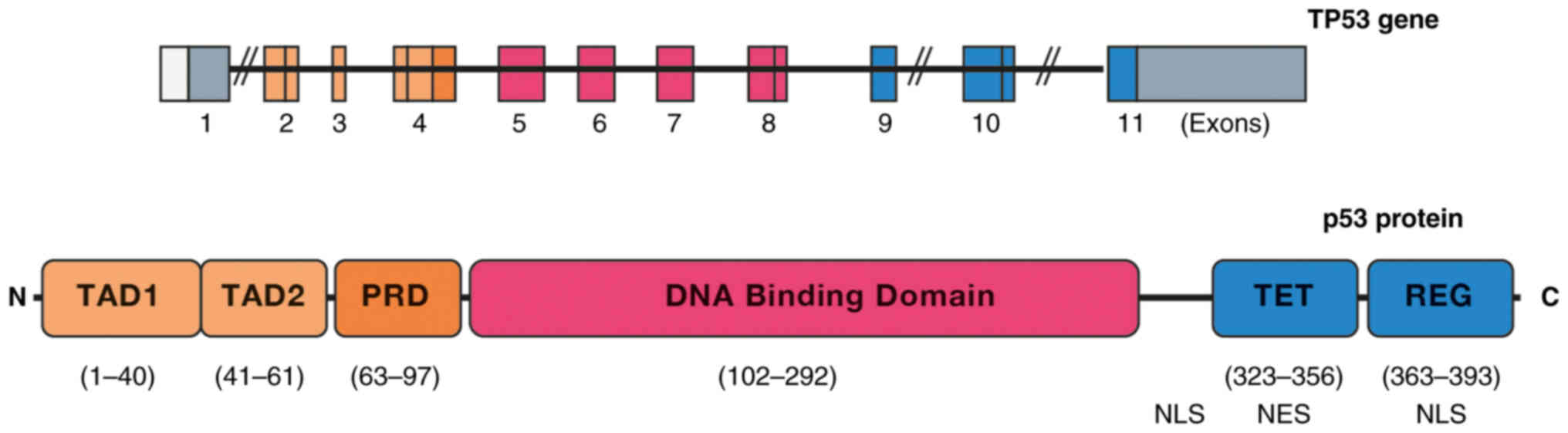
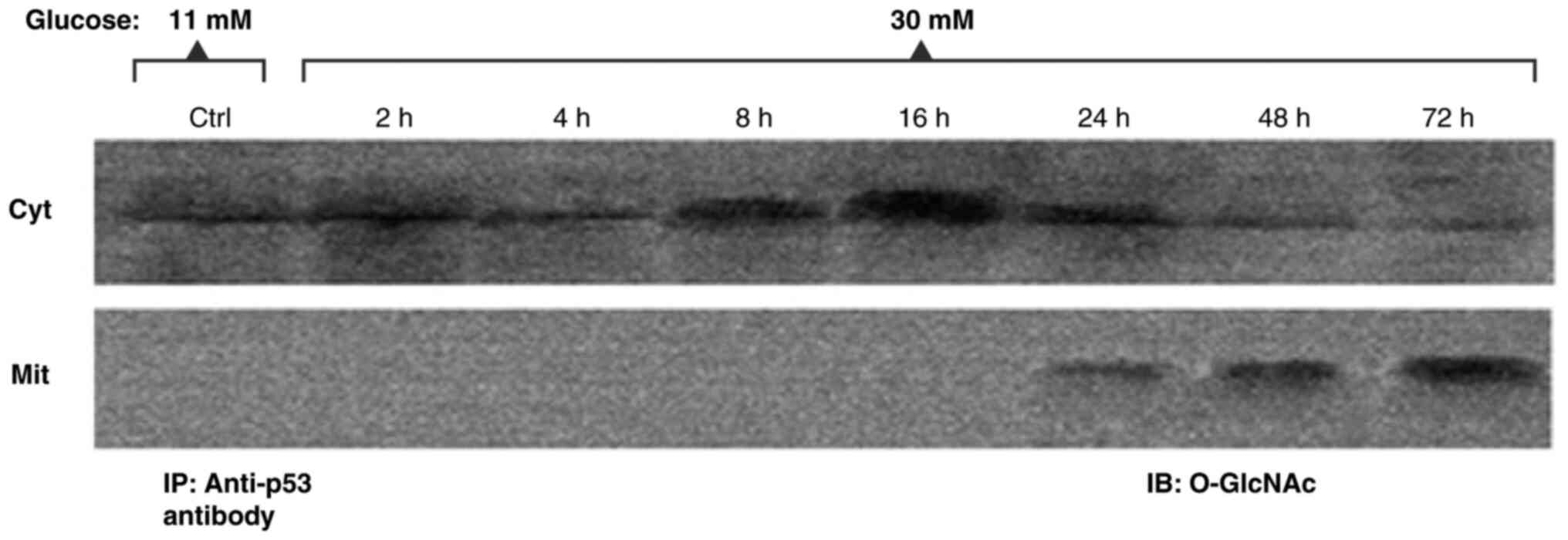
|
1
|
Marchetti P, Bugliani M, De Tata V,
Suleiman M and Marselli L: Pancreatic beta cell identity in humans
and the role of type 2 diabetes. Front Cell Dev Biol. 5:552017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang P, Fiaschi-Taesch NM, Vasavada RC,
Scott DK, García-Ocaña A and Stewart AF: Diabetes mellitus-advances
and challenges in human β-cell proliferation. Nat Rev Endocrinol.
11:201–212. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Abdul-Ghani MA, Tripathy D and DeFronzo
RA: Contributions of beta-cell dysfunction and insulin resistance
to the pathogenesis of impaired glucose tolerance and impaired
fasting glucose. Diabetes Care. 29:1130–1139. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, Pinkepank M,
Ogurtsova K, Duncan BB, Stein C, Basit A, Chan JCN, Mbanya JC, et
al: IDF diabetes atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes
prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes
Res Clin Pract. 183:1091192022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lin X, Xu Y, Pan X, Xu J, Ding Y, Sun X,
Song X, Ren Y and Shan PF: Global, regional, and national burden
and trend of diabetes in 195 countries and territories: An analysis
from 1990 to 2025. Sci Rep. 10:147902020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
International Diabetes Federation, .
Diabetes Atlas. (10th Edition). https://fmdiabetes.org/atlas-idf-10o-edicion-2021/September
13–2023
|
|
7
|
Harreiter J and Roden M: Diabetes
mellitus: Definition, classification, diagnosis, screening and
prevention (update 2023). Wien Klin Wochenschr. 135 (Suppl
1):S7–S17. 2023.(In German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rojas J, Bermudez V, Palmar J, Martínez
MS, Olivar LC, Nava M, Tomey D, Rojas M, Salazar J, Garicano C and
Velasco M: Pancreatic beta cell death: Novel potential mechanisms
in diabetes therapy. J Diabetes Res. 2018:96018012018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Barzalobre-Geronimo R, Contreras-Ramos A,
Cervantes-Cruz AI, Cruz M, Suárez-Sánchez F, Goméz-Zamudio J,
Diaz-Rosas G, Ávalos-Rodríguez A, Díaz-Flores M and
Ortega-Camarillo C: Pancreatic β-cell apoptosis in normoglycemic
rats is due to mitochondrial translocation of p53-induced by the
consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages. Cell Biochem Biophys.
81:503–514. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Barzalobre-Gerónimo R, Flores-López LA,
Baiza-Gutman LA, Cruz M, García-Macedo R, Ávalos-Rodríguez A,
Contreras-Ramos A, Díaz-Flores M and Ortega-Camarillo C: Erratum
to: Hyperglycemia promotes p53-Mdm2 interaction but reduces p53
ubiquitination in RINm5F cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 406:3012015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Flores-López LA, Díaz-Flores M,
García-Macedo R, Ávalos-Rodríguez A, Vergara-Onofre M, Cruz M,
Contreras-Ramos A, Konigsberg M and Ortega-Camarillo C: High
glucose induces mitochondrial p53 phosphorylation by p38 MAPK in
pancreatic RINm5F cells. Mol Biol Rep. 40:4947–4958. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Butler AE, Janson J, Bonner-Weir S, Ritzel
R, Rizza RA and Butler PC: Beta-cell deficit and increased
beta-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes.
52:102–110. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
McFarland KF, Catalano EW, Day JF, Thorpe
SR and Baynes JW: Nonenzymatic glucosylation of serum proteins in
diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 28:1011–1014. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tomita T: Apoptosis in pancreatic β-islet
cells in type 2 diabetes. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 16:162–179. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chandra J, Zhivotovsky B, Zaitsev S,
Juntti-Berggren L, Berggren PO and Orrenius S: Role of apoptosis in
pancreatic beta-cell death in diabetes. Diabetes. 50 (Suppl
1):S44–S47. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gottlieb TM and Oren M: p53 and apoptosis.
Semin Cancer Biol. 8:359–368. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ortega-Camarillo C, Guzmán-Grenfell AM,
García-Macedo R, Rosales-Torres AM, Avalos-Rodríguez A, Durán-Reyes
G, Medina-Navarro R, Cruz M, Díaz-Flores M and Kumate J:
Hyperglycemia induces apoptosis and p53 mobilization to
mitochondria in RINm5F cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 281:163–171. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Flores-López LA, Cruz-López M,
García-Macedo R, Gómez-Olivares JL, Díaz-Flores M,
Konigsberg-Fainstein M and Ortega-Camarillo C: Phosphorylation,
O-N-acetylglucosaminylation and poly-ADP-ribosylation of P53 in
RINm5F cells cultured in high glucose. Free Radic Biol Med. 53
(Suppl 2):S952012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
DeLong MJ: Apoptosis: A modulator of
cellular homeostasis and disease states. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
842:82–90. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nicholson DW and Thornberry NA: Caspases:
Killer proteases. Trends Biochem Sci. 22:299–306. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Peter ME and Krammer PH: Mechanisms of
CD95 (APO-1/Fas)-mediated apoptosis. Curr Opin Immunol. 10:545–551.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ichim G and Tait SWG: A fate worse than
death: Apoptosis as an oncogenic process. Nat Rev Cancer.
16:539–548. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: A review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Johnson N, Khan A, Virji S, Ward JM and
Crompton M: Import and processing of heart mitochondrial
cyclophilin D. Eur J Biochem. 263:353–359. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Crompton M: Mitochondrial intermembrane
junctional complexes and their role in cell death. J Physiol.
529:11–21. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Andreeva L, Heads R and Green CJ:
Cyclophilins and their possible role in the stress response. Int J
Exp Pathol. 80:305–315. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Marchenko ND, Zaika A and Moll UM: Death
signal-induced localization of p53 protein to mitochondria. A
potential role in apoptotic signaling. J Biol Chem.
275:16202–16212. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lemasters JJ, Qian T, He L, Kim JS, Elmore
SP, Cascio WE and Brenner DA: Role of mitochondrial inner membrane
permeabilization in necrotic cell death, apoptosis, and autophagy.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 4:769–781. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Susin SA, Lorenzo HK, Zamzami N, Marzo I,
Snow BE, Brothers GM, Mangion J, Jacotot E, Costantini P, Loeffler
M, et al: Molecular characterization of mitochondrial
apoptosis-inducing factor. Nature. 397:441–446. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Singh R, Letai A and Sarosiek K:
Regulation of apoptosis in health and disease: The balancing act of
BCL-2 family proteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 20:175–193. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tsujimoto Y and Shimizu S: VDAC regulation
by the Bcl-2 family of proteins. Cell Death Differ. 7:1174–1181.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Garrido C, Galluzzi L, Brunet M, Puig PE,
Didelot C and Kroemer G: Mechanisms of cytochrome c release from
mitochondria. Cell Death Differ. 13:1423–1433. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Roche E: Diabetes tipo 2:
Gluco-lipo-toxicidad y disfunción de la célula β pancreática. Ars
Pharm. 44:313–332. 2003.
|
|
34
|
Chen SS, Jiang T, Wang Y, Gu LZ, Wu HW,
Tan L and Guo J: Activation of double-stranded RNA-dependent
protein kinase inhibits proliferation of pancreatic β-cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 443:814–820. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yuan H, Zhang X, Huang X, Lu Y, Tang W,
Man Y, Wang S, Xi J and Li J: NADPH oxidase 2-derived reactive
oxygen species mediate FFAs-induced dysfunction and apoptosis of
β-cells via JNK, p38 MAPK and p53 pathways. PLoS One. 5:e157262010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lu H, Hao L, Li S, Lin S, Lv L, Chen Y,
Cui H, Zi T, Chu X, Na L and Sun C: Elevated circulating stearic
acid leads to a major lipotoxic effect on mouse pancreatic beta
cells in hyperlipidaemia via a miR-34a-5p-mediated
PERK/p53-dependent pathway. Diabetologia. 59:1247–1257. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mayo LD and Donner DB: A
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway promotes translocation of
Mdm2 from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:11598–11603. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lytrivi M, Castell AL, Poitout V and Cnop
M: Recent insights into mechanisms of β-Cell Lipo- and
glucolipotoxicity in type 2 diabetes. J Mol Biol. 432:1514–1534.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cunha DA, Igoillo-Esteve M, Gurzov EN,
Germano CM, Naamane N, Marhfour I, Fukaya M, Vanderwinden JM,
Gysemans C, Mathieu C, et al: Death protein 5 and p53-upregulated
modulator of apoptosis mediate the endoplasmic reticulum
stress-mitochondrial dialog triggering lipotoxic rodent and human
β-cell apoptosis. Diabetes. 61:2763–2775. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Saltevo J, Vanhala M, Kautiainen H,
Kumpusalo E and Laakso M: Association of C-reactive protein,
interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and adiponectin with the
metabolic syndrome. Mediators Inflamm. 2007:935732007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hotamisligil GS: Inflammation and
metabolic disorders. Nature. 444:860–867. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tilg H and Moschen AR: Inflammatory
mechanisms in the regulation of insulin resistance. Mol Med.
14:222–231. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhao YF and Chen C: Regulation of
pancreatic beta-cell function by adipocytes. Sheng Li Xue Bao.
59:247–252. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Donath MY, Schumann DM, Faulenbach M,
Ellingsgaard H, Perren A and Ehses JA: Islet inflammation in type 2
diabetes: From metabolic stress to therapy. Diabetes Care. 31
(Suppl 2):S161–S164. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Eldor R, Yeffet A, Baum K, Doviner V, Amar
D, Ben-Neriah Y, Christofori G, Peled A, Carel JC, Boitard C, et
al: Conditional and specific NF-kappaB blockade protects pancreatic
beta cells from diabetogenic agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:5072–5077. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Nolan CJ, Madiraju MSR,
Delghingaro-Augusto V, Peyot ML and Prentki M: Fatty acid signaling
in the beta-cell and insulin secretion. Diabetes. 55 (Suppl
2):S16–S23. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kadowaki T, Yamauchi T, Kubota N, Hara K,
Ueki K and Tobe K: Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in insulin
resistance, diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest.
116:1784–1792. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Bensellam M, Laybutt DR and Jonas JC: The
molecular mechanisms of pancreatic β-cell glucotoxicity: Recent
findings and future research directions. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
364:1–27. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Brownlee M: The pathobiology of diabetic
complications: A unifying mechanism. Diabetes. 54:1615–1625. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Du X, Matsumura T, Edelstein D, Rossetti
L, Zsengellér Z, Szabó C and Brownlee M: Inhibition of GAPDH
activity by poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activates three major
pathways of hyperglycemic damage in endothelial cells. J Clin
Invest. 112:1049–1057. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Grankvist K, Marklund SL and Täljedal IB:
CuZn-superoxide dismutase, Mn-superoxide dismutase, catalase and
glutathione peroxidase in pancreatic islets and other tissues in
the mouse. Biochem J. 199:393–398. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Gottlieb RA: Mitochondria: Execution
central. FEBS Lett. 482:6–12. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Schellenberg B, Wang P, Keeble JA,
Rodriguez-Enriquez R, Walker S, Owens TW, Foster F, Tanianis-Hughes
J, Brennan K, Streuli CH and Gilmore AP: Bax exists in a dynamic
equilibrium between the cytosol and mitochondria to control
apoptotic priming. Mol Cell. 49:959–971. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 protein
family: Arbiters of cell survival. Science. 281:1322–1326. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Huang Q, Bu S, Yu Y, Guo Z, Ghatnekar G,
Bu M, Yang L, Lu B, Feng Z, Liu S and Wang F: Diazoxide prevents
diabetes through inhibiting pancreatic beta-cells from apoptosis
via Bcl-2/Bax rate and p38-beta mitogen-activated protein kinase.
Endocrinology. 148:81–91. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Lawrence M, Shao C, Duan L, McGlynn K and
Cobb MH: The protein kinases ERK1/2 and their roles in pancreatic
beta cells. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 192:11–17. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ito K, Nakazato T, Yamato K, Miyakawa Y,
Yamada T, Hozumi N, Segawa K, Ikeda Y and Kizaki M: Induction of
apoptosis in leukemic cells by homovanillic acid derivative,
capsaicin, through oxidative stress: Implication of phosphorylation
of p53 at Ser-15 residue by reactive oxygen species. Cancer Res.
64:1071–1078. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Shen Y and White E: p53-dependent
apoptosis pathways. Adv Cancer Res. 82:55–84. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Green DR and Kroemer G: Cytoplasmic
functions of the tumor suppressor p53. Nature. 458:1127–1130. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Riley T, Sontag E, Chen P and Levine A:
Transcriptional control of human p53-regulated genes. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:402–412. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Jenkins LM, Durell SR, Mazur SJ and
Appella E: p53 N-terminal phosphorylation: A defining layer of
complex regulation. Carcinogenesis. 33:1441–1449. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
el-Deiry WS, Kern SE, Pietenpol JA,
Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B: Definition of a consensus binding site
for p53. Nat Genet. 1:45–49. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ahn J and Prives C: The C-terminus of p53:
The more you learn the less you know. Nat Struct Biol. 8:730–732.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Aubrey BJ, Kelly GL, Janic A, Herold MJ
and Strasser A: How does p53 induce apoptosis and how does this
relate to p53-mediated tumour suppression? Cell Death Differ.
25:104–113. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Yang J, Liu X, Bhalla K, Kim CN, Ibrado
AM, Cai J, Peng TI, Jones DP and Wang X: Prevention of apoptosis by
Bcl-2: Release of cytochrome c from mitochondria blocked. Science.
275:1129–1132. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Müller M, Wilder S, Bannasch D, Israeli D,
Lehlbach K, Li-Weber M, Friedman SL, Galle PR, Stremmel W, Oren M
and Krammer PH: p53 activates the CD95 (APO-1/Fas) gene in response
to DNA damage by anticancer drugs. J Exp Med. 188:2033–2045. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Caelles C, Helmberg A and Karin M:
p53-dependent apoptosis in the absence of transcriptional
activation of p53-target genes. Nature. 370:220–223. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Sansome C, Zaika A, Marchenko ND and Moll
UM: Hypoxia death stimulus induces translocation of p53 protein to
mitochondria. Detection by immunofluorescence on whole cells. FEBS
Lett. 488:110–115. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Schuler M, Bossy-Wetzel E, Goldstein JC,
Fitzgerald P and Green DR: p53 induces apoptosis by caspase
activation through mitochondrial cytochrome c release. J Biol Chem.
275:7337–7342. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Donahue RJ, Razmara M, Hoek JB and Knudsen
TB: Direct influence of the p53 tumor suppressor on mitochondrial
biogenesis and function. FASEB J. 15:635–644. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Mihara M, Erster S, Zaika A, Petrenko O,
Chittenden T, Pancoska P and Moll UM: p53 has a direct apoptogenic
role at the mitochondria. Mol Cell. 11:577–590. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Wei H, Wang H, Wang G, Qu L, Jiang L, Dai
S, Chen X, Zhang Y, Chen Z, Li Y, et al: Structures of p53/BCL-2
complex suggest a mechanism for p53 to antagonize BCL-2 activity.
Nat Commun. 14:43002023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Hinault C, Kawamori D, Liew CW, Maier B,
Hu J, Keller SR, Mirmira RG, Scrable H and Kulkarni RN: Δ40 Isoform
of p53 controls β-cell proliferation and glucose homeostasis in
mice. Diabetes. 60:1210–1222. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Kon N, Zhong J, Qiang L, Accili D and Gu
W: Inactivation of arf-bp1 induces p53 activation and diabetic
phenotypes in mice. J Biol Chem. 287:5102–5111. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Uhlemeyer C, Müller N, Rieck M, Kuboth J,
Schlegel C, Grieß K, Dorweiler TF, Heiduschka S, Eckel J, Roden M,
et al: Selective ablation of P53 in pancreatic beta cells fails to
ameliorate glucose metabolism in genetic, dietary and
pharmacological models of diabetes mellitus. Mol Metab.
67:1016502023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Douc-Rasy S and Bénard J: A new view on
p53 protein cytoplasmic sequestration. Bull Cancer. 90:380–382.
2003.(In French). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Giaccia AJ and Kastan MB: The complexity
of p53 modulation: Emerging patterns from divergent signals. Genes
Dev. 12:2973–2983. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Harris SL and Levine AJ: The p53 pathway:
Positive and negative feedback loops. Oncogene. 24:2899–2908. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Gonzalez-Rellan MJ, Fondevila MF,
Fernandez U, Rodríguez A, Varela-Rey M, Veyrat-Durebex C, Seoane S,
Bernardo G, Lopitz-Otsoa F, Fernández-Ramos D, et al:
O-GlcNAcylated p53 in the liver modulates hepatic glucose
production. Nat Commun. 12:50682021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Labuschagne CF, Zani F and Vousden KH:
Control of metabolism by p53-cancer and beyond. Biochim Biophys
Acta Rev Cancer. 1870:32–42. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Yang WH, Kim JE, Nam HW, Ju JW, Kim HS,
Kim YS and Cho JW: Modification of p53 with O-linked
N-acetylglucosamine regulates p53 activity and stability. Nat Cell
Biol. 8:1074–1083. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Wen J and Wang D: Deciphering the PTM
codes of the tumor suppressor p53. J Mol Cell Biol. 13:774–785.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Liu Y, Tavana O and Gu W: p53
modifications: Exquisite decorations of the powerful guardian. J
Mol Cell Biol. 11:564–577. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Lavin MF and Gueven N: The complexity of
p53 stabilization and activation. Cell Death Differ. 13:941–950.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Thompson T, Tovar C, Yang H, Carvajal D,
Vu BT, Xu Q, Wahl GM, Heimbrook DC and Vassilev LT: Phosphorylation
of p53 on key serines is dispensable for transcriptional activation
and apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 279:53015–53022. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Steegenga WT, van der Eb AJ and Jochemsen
AG: How phosphorylation regulates the activity of p53. J Mol Biol.
263:103–113. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Hoogervorst EM, Bruins W, Zwart E, van
Oostrom CTM, van den Aardweg GJ, Beems RB, van den Berg J, Jacks T,
van Steeg H and de Vries A: Lack of p53 Ser389 phosphorylation
predisposes mice to develop 2-acetylaminofluorene-induced bladder
tumors but not ionizing radiation-induced lymphomas. Cancer Res.
65:3610–3616. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Park BS, Song YS, Yee SB, Lee BG, Seo SY,
Park YC, Kim JM, Kim HM and Yoo YH: Phospho-ser 15-p53 translocates
into mitochondria and interacts with Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL in
eugenol-induced apoptosis. Apoptosis. 10:193–200. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Fiordaliso F, Leri A, Cesselli D, Limana
F, Safai B, Nadal-Ginard B, Anversa P and Kajstura J: Hyperglycemia
activates p53 and p53-regulated genes leading to myocyte cell
death. Diabetes. 50:2363–2375. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Malhotra A, Vashistha H, Yadav VS, Dube
MG, Kalra SP, Abdellatif M and Meggs LG: Inhibition of p66ShcA
redox activity in cardiac muscle cells attenuates
hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis. Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol. 296:H380–H388. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Sumara G, Formentini I, Collins S, Sumara
I, Windak R, Bodenmiller B, Ramracheya R, Caille D, Jiang H, Platt
KA, et al: Regulation of PKD by the MAPK p38delta in insulin
secretion and glucose homeostasis. Cell. 136:235–248. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Evans JL, Goldfine ID, Maddux BA and
Grodsky GM: Oxidative stress and stress-activated signaling
pathways: A unifying hypothesis of type 2 diabetes. Endocr Rev.
23:599–622. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Chen K, Albano A, Ho A and Keaney JF Jr:
Activation of p53 by oxidative stress involves platelet-derived
growth factor-beta receptor-mediated ataxia telangiectasia mutated
(ATM) kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 278:39527–39533. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Thornton TM and Rincon M: Non-classical
p38 map kinase functions: Cell cycle checkpoints and survival. Int
J Biol Sci. 5:44–51. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Nakagami H, Morishita R, Yamamoto K,
Yoshimura SI, Taniyama Y, Aoki M, Matsubara H, Kim S, Kaneda Y and
Ogihara T: Phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
downstream of bax-caspase-3 pathway leads to cell death induced by
high D-glucose in human endothelial cells. Diabetes. 50:1472–1481.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
She QB, Chen N and Dong Z: ERKs and p38
kinase phosphorylate p53 protein at serine 15 in response to UV
radiation. J Biol Chem. 275:20444–20449. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Fu X, Wan S, Lyu YL, Liu LF and Qi H:
Etoposide induces ATM-dependent mitochondrial biogenesis through
AMPK activation. PLoS One. 3:e20092008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Barzilai A, Rotman G and Shiloh Y: ATM
deficiency and oxidative stress: A new dimension of defective
response to DNA damage. DNA Repair (Amst). 1:3–25. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Reliene R, Fischer E and Schiestl RH:
Effect of N-acetyl cysteine on oxidative DNA damage and the
frequency of DNA deletions in atm-deficient mice. Cancer Res.
64:5148–5153. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Uhlemeyer C, Müller N, Grieß K, Wessel C,
Schlegel C, Kuboth J and Belgardt BF: ATM and P53 differentially
regulate pancreatic beta cell survival in Ins1E cells. PLoS One.
15:e02376692020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Borges HL, Linden R and Wang JYJ: DNA
damage-induced cell death: Lessons from the central nervous system.
Cell Res. 18:17–26. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Halaby MJ, Hibma JC, He J and Yang DQ: ATM
protein kinase mediates full activation of Akt and regulates
glucose transporter 4 translocation by insulin in muscle cells.
Cell Signal. 20:1555–1563. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Xu Y: Regulation of p53 responses by
post-translational modifications. Cell Death Differ. 10:400–403.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Hart GW, Slawson C, Ramirez-Correa G and
Lagerlof O: Cross talk between O-GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation:
Roles in signaling, transcription, and chronic disease. Annu Rev
Biochem. 80:825–858. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Jahangir Z, Ahmad W and Shabbiri K:
Alternate phosphorylation/O-GlcNAc modification on human insulin
IRSs: A road towards impaired insulin signaling in Alzheimer and
diabetes. Adv Bioinformatics. 2014:3247532014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Bond MR and Hanover JA: O-GlcNAc cycling:
A link between metabolism and chronic disease. Annu Rev Nutr.
33:205–229. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Akimoto Y, Hart GW, Wells L, Vosseller K,
Yamamoto K, Munetomo E, Ohara-Imaizumi M, Nishiwaki C, Nagamatsu S,
Hirano H and Kawakami H: Elevation of the post-translational
modification of proteins by O-linked N-acetylglucosamine leads to
deterioration of the glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in the
pancreas of diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. Glycobiology. 17:127–140.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Schraufstatter IU, Hyslop PA, Hinshaw DB,
Spragg RG, Sklar LA and Cochrane CG: Hydrogen peroxide-induced
injury of cells and its prevention by inhibitors of
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 83:4908–4912.
1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
D'Amours D, Desnoyers S, D'Silva I and
Poirier GG: Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation reactions in the regulation of
nuclear functions. Biochem J. 342:249–268. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Oliver FJ, Menissier-de Murcia J and de
Murcia G: Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in the cellular response to
DNA damage, apoptosis, and disease. Am J Hum Genet. 64:1282–1288.
1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Elkholi R and Chipuk JE: How do I kill
thee? Let me count the ways: p53 regulates PARP-1 dependent
necrosis. Bioessays. 36:46–51. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Ba X and Garg NJ: Signaling mechanism of
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) in inflammatory diseases. Am
J Pathol. 178:946–955. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Chaitanya GV, Steven AJ and Babu PP:
PARP-1 cleavage fragments: Signatures of cell-death proteases in
neurodegeneration. Cell Commun Signal. 8:312010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Li M, Brooks CL, Wu-Baer F, Chen D, Baer R
and Gu W: Mono- versus polyubiquitination: Differential control of
p53 fate by Mdm2. Science. 302:1972–1975. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Feng J, Tamaskovic R, Yang Z, Brazil DP,
Merlo A, Hess D and Hemmings BA: Stabilization of Mdm2 via
decreased ubiquitination is mediated by protein kinase
B/Akt-dependent phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 279:35510–35517.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Ogawara Y, Kishishita S, Obata T, Isazawa
Y, Suzuki T, Tanaka K, Masuyama N and Gotoh Y: Akt enhances
Mdm2-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of p53. J Biol Chem.
277:21843–21850. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Fang S, Jensen JP, Ludwig RL, Vousden KH
and Weissman AM: Mdm2 is a RING finger-dependent ubiquitin protein
ligase for itself and p53. J Biol Chem. 275:8945–8951. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|