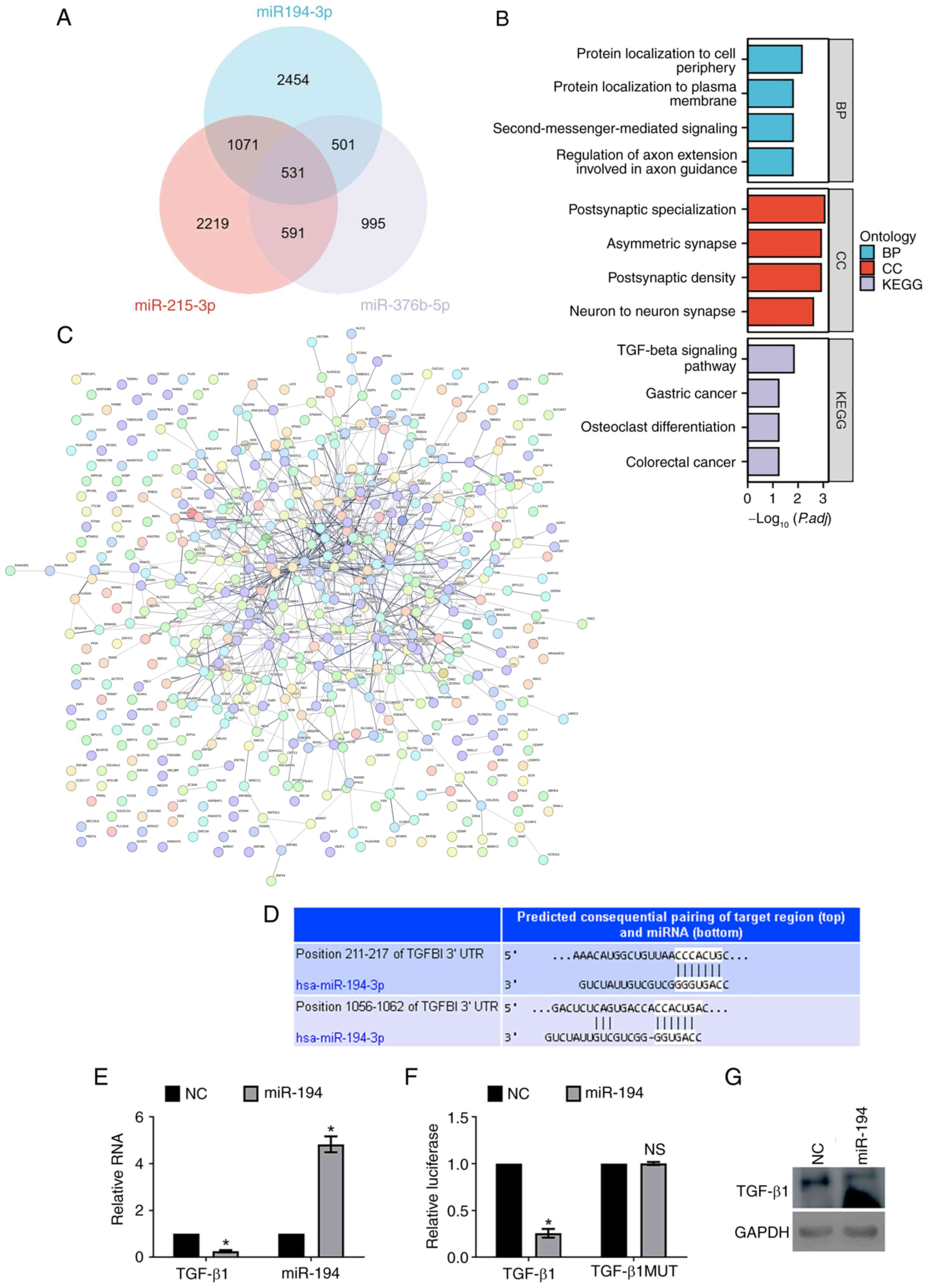
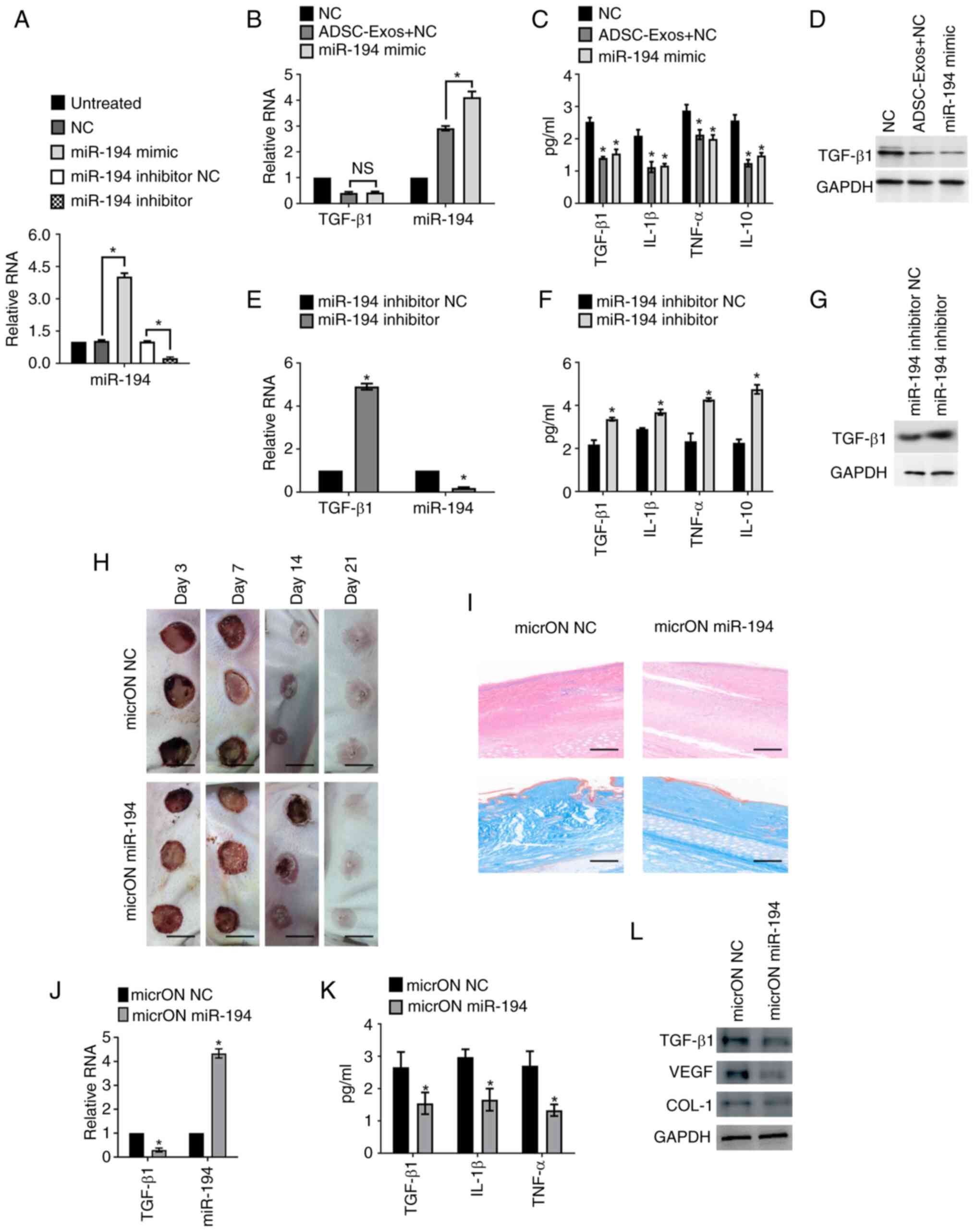
|
1
|
Barone N, Safran T, Vorstenbosch J,
Davison PG, Cugno S and Murphy AM: Current advances in hypertrophic
scar and keloid management. Semin Plast Surg. 35:145–152. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Finnerty CC, Jeschke MG, Branski LK,
Barret JP, Dziewulski P and Herndon DN: Hypertrophic scarring: The
greatest unmet challenge after burn injury. Lancet. 388:1427–1436.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Edwards J: Hypertrophic scar management.
Br J Nurs. 31:S24–S31. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Frech FS, Hernandez L, Urbonas R, Zaken
GA, Dreyfuss I and Nouri K: Hypertrophic scars and keloids:
Advances in treatment and review of established therapies. Am J
Clin Dermatol. 24:225–245. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gauglitz GG, Korting HC, Pavicic T,
Ruzicka T and Jeschke MG: Hypertrophic scarring and keloids:
Pathomechanisms and current and emerging treatment strategies. Mol
Med. 17:113–125. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Schmieder SJ and Ferrer-Bruker SJ:
Hypertrophic scarring. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls
Publishing; Treasure Island, FL: 2024
|
|
7
|
Su L and Han J: Non-coding RNAs in
hypertrophic scars and keloids: Current research and clinical
relevance: A review. Int J Biol Macromol. 256:1283342024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jia Q, Zhao H, Wang Y, Cen Y and Zhang Z:
Mechanisms and applications of adipose-derived stem
cell-extracellular vesicles in the inflammation of wound healing.
Front Immunol. 1:1214757 4. 2023.
|
|
9
|
Romano IR, D'Angeli F, Vicario N, Russo C,
Genovese C, Lo Furno D, Mannino G, Tamburino S, Parenti R and
Giuffrida R: Adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells: A tool for
bone and cartilage repair. Biomedicines. 11:17812023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lopez-Yus M, García-Sobreviela MP, Del
Moral-Bergos R and Arbones-Mainar JM: Gene therapy based on
mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue for the
treatment of obesity and its metabolic complications. Int J Mol
Sci. 24:74682023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee JH, Won YJ, Kim H, Choi M, Lee E,
Ryoou B, Lee SG and Cho BS: Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem
cell-derived exosomes promote wound healing and tissue
regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 24:104342023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen Y, Younis MR, He G, Zheng Z, Wang Y,
Xue K, Sun J, Liu K, Huang P and Wang X: Oxidative
stimuli-responsive ‘pollen-like’ exosomes from silver nanoflowers
remodeling diabetic wound microenvironment for accelerating wound
healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 12:e23004562023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jing S, Li H and Xu H: Mesenchymal stem
cell derived exosomes therapy in diabetic wound repair. Int J
Nanomedicine. 18:2707–2720. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Edis A, Lumbis RH and Hedley J: Nursing
management of a rabbit undergoing a rhinostomy. Vet Nurse. 7:18–24.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Feldman ER, Singh B, Mishkin NG,
Lachenauer ER, Martin-Flores M and Daugherity EK: Effects of
cisapride, buprenorphine, and their combination on gastrointestinal
transit in New Zealand white rabbits. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci.
60:221–228. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Askar R, Fredriksson E, Manell E, Hedeland
M, Bondesson U, Bate S, Olsén L and Hedenqvist P: Bioavailability
of subcutaneous and intramuscular administrated buprenorphine in
New Zealand white rabbits. BMC Vet Res. 16:4362020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Leary S and Johnson C: AVMA guidelines for
the euthanasia of animals: 2020 edition*. Members of the Panel on
Euthanasia AVMA Staff Consultants; 2020
|
|
18
|
Suvik A and Effendy A: The use of modified
Masson's trichrome staining in collagen evaluation in wound healing
study. Mal J Vet Res. 3:39–47. 2012.
|
|
19
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
eLife. 4:e050052015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen Y and Wang X: miRDB: An online
database for prediction of functional microRNA targets. Nucleic
Acids Res. 48(D1): D127–D131. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang JH, Li JH, Shao P, Zhou H, Chen YQ
and Qu LH: starBase: A database for exploring microRNA-mRNA
interaction maps from Argonaute CLIP-Seq and Degradome-Seq data.
Nucleic Acids Res. 39((Database Issue)): D202–D209. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xie S, Zhu Q, Qu W, Xu Z, Liu X, Li X, Li
S, Ma W, Miao Y, Zhang L, et al: sRNAPrimerDB: Comprehensive primer
design and search web service for small non-coding RNAs.
Bioinformatics. 35:1566–1572. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhu Z, Hou Q, Li M and Fu X: Molecular
mechanism of myofibroblast formation and strategies for clinical
drugs treatments in hypertrophic scars. J Cell Physiol.
235:4109–4119. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu B, Lin L, Yu S, Xia R and Zheng L:
Long non-coding RNA H19 acts as a microRNA-194 sponge to inhibit
the apoptosis and promote the proliferation of hypertrophic scar
fibroblasts. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 99:1288–1297. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen SH, Chen ZY, Lin YH, Chen SH, Chou
PY, Kao HK and Lin FH: Extracellular vesicles of adipose-derived
stem cells promote the healing of traumatized achilles tendons. Int
J Mol Sci. 22:123732021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu Y and Holmes C: Tissue regeneration
capacity of extracellular vesicles isolated from bone
marrow-derived and adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal/stem cells.
Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:6480982021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu Y, Li Y, Li N, Teng W, Wang M, Zhang Y
and Xiao Z: TGF-β1 promotes scar fibroblasts proliferation and
transdifferentiation via up-regulating MicroRNA-21. Sci Rep.
6:322312016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu SC, Bamodu OA, Kuo KT, Fong IH, Lin
CC, Yeh CT and Chen SG: Adipose-derived stem cell induced-tissue
repair or wound healing is mediated by the concomitant upregulation
of miR-21 and miR-29b expression and activation of the AKT
signaling pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys. 705:1088952021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang S and Pan S: miR-124-3p targeting of
TGF-β1 inhibits the proliferation of hypertrophic scar fibroblasts.
Adv Clin Exp Med. 30:263–271. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yao W, Li Y, Han L, Ji X, Pan H, Liu Y,
Yuan J, Yan W and Ni C: The CDR1as/miR-7/TGFBR2 axis modulates EMT
in silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Toxicol Sci. 166:465–478.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Firmansyah Y, Sidharta VM, Wijaya L and
Tan ST: Unraveling the significance of growth factors (TGF-β, PDGF,
KGF, FGF, Pro Collagen, VEGF) in the dynamic of wound healing.
Asian J Med Health. 22:49–61. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Qi J, Wu Y, Zhang H and Liu Y: LncRNA
NORAD regulates scar hypertrophy via miRNA-26a mediating the
regulation of TGFβR1/2. Adv Clin Exp Med. 30:395–403. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yu J, Zhang L, Zhang S, Xian G, Zhao Y and
Bu X: MiR-29b inhibits hypertrophic scar tissue inflammation after
burn through regulating TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway. Ital J
Dermatol Venerol. 156:251–252. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Qi X, Liu Y and Yang M: Circ_0057452
functions as a ceRNA in hypertrophic scar fibroblast proliferation
and VEGF expression by regulating TGF-β2 expression and adsorbing
miR-145-5p. Am J Transl Res. 13:6200–6210. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xu S, Dong W and Shi Y: LncRNA PICSAR
binds to miR-485-5p and activates TGF-β1/Smad to promote abnormal
proliferation of hypertrophic scar fibroblasts (HSFs) and excessive
deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM). Med Mol Morphol.
54:337–345. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pang J, Zhu L, Lv Y, Xu L, Li N, Guo P and
Feng Q: miR-15a-5p up-regulates TLR4 and induces the formation of
hypertrophic scars and keloids. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand).
69:158–163. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lian N and Li T: Growth factor pathways in
hypertrophic scars: Molecular pathogenesis and therapeutic
implications. Biomed Pharmacother. 84:42–50. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhou X, Lu J, Wu B and Guo Z: HOXA11-AS
facilitates the proliferation, cell cycle process and migration of
keloid fibroblasts through sponging miR-188-5p to regulate VEGFA. J
Dermatol Sci. 106:111–118. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen L, Zheng Q, Liu Y, Li L, Chen X and
Wang L and Wang L: Adipose-derived stem cells promote diabetic
wound healing via the recruitment and differentiation of
endothelial progenitor cells into endothelial cells mediated by the
VEGF-PLCγ-ERK pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys. 692:1085312020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang YF, Li HZ, Wang XY, Ma HC, Wu Y,
Yuan XH and Chu YH: Morphology of hypertrophic scar tissues and
expressions of vascular endothelial growth factor and transforming
growth factor beta activated kinase 1 in these tissues. Zhongguo Yi
Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 37:446–450. 2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kinashi H, Ito Y, Mizuno M, Suzuki Y,
Terabayashi T, Nagura F, Hattori R, Matsukawa Y, Mizuno T, Noda Y,
et al: TGF-β1 promotes lymphangiogenesis during peritoneal
fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 24:1627–1642. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Komi DEA, Khomtchouk K and Santa Maria PL:
A review of the contribution of mast cells in wound healing:
Involved molecular and cellular mechanisms. Clin Rev Allergy
Immunol. 58:298–312. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ohnuma K, Kasagi S, Uto K, Noguchi Y,
Nakamachi Y, Saegusa J and Kawano S: MicroRNA-124 inhibits TNF-α-
and IL-6-induced osteoclastogenesis. Rheumatol Int. 39:689–695.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ma Y, Liu Z, Miao L, Jiang X, Ruan H, Xuan
R and Xu S: Mechanisms underlying pathological scarring by
fibroblasts during wound healing. Int Wound J. 20:2190–2206. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Eremenko EE, Kwan PO, Ding J, Ghosh S and
Tredget EE: The effects of TGF-β1 and IFN-α2b on decorin, decorin
isoforms and type I collagen in hypertrophic scar dermal
fibroblasts. Wound Repair Regen. 32:135–145. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|