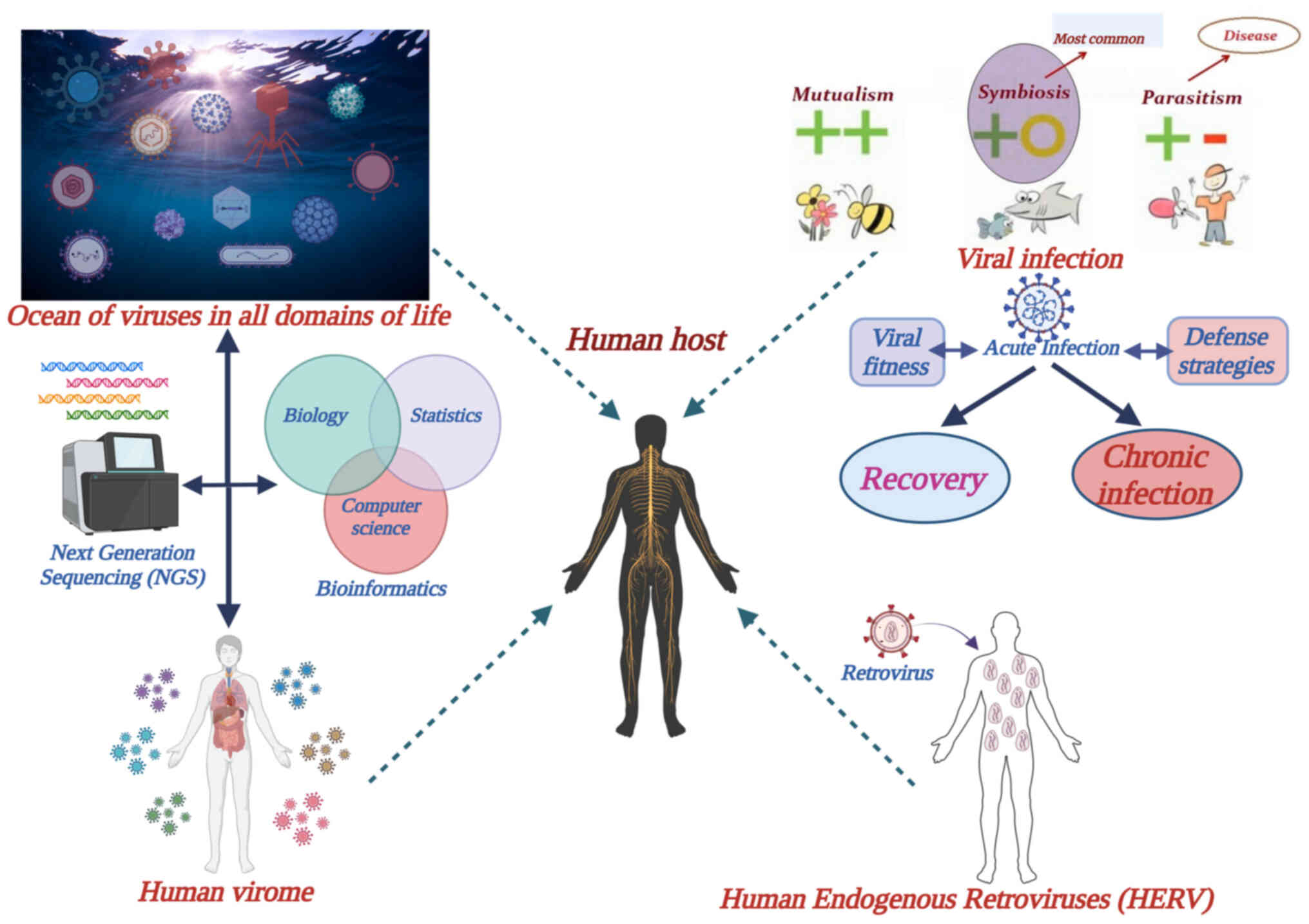
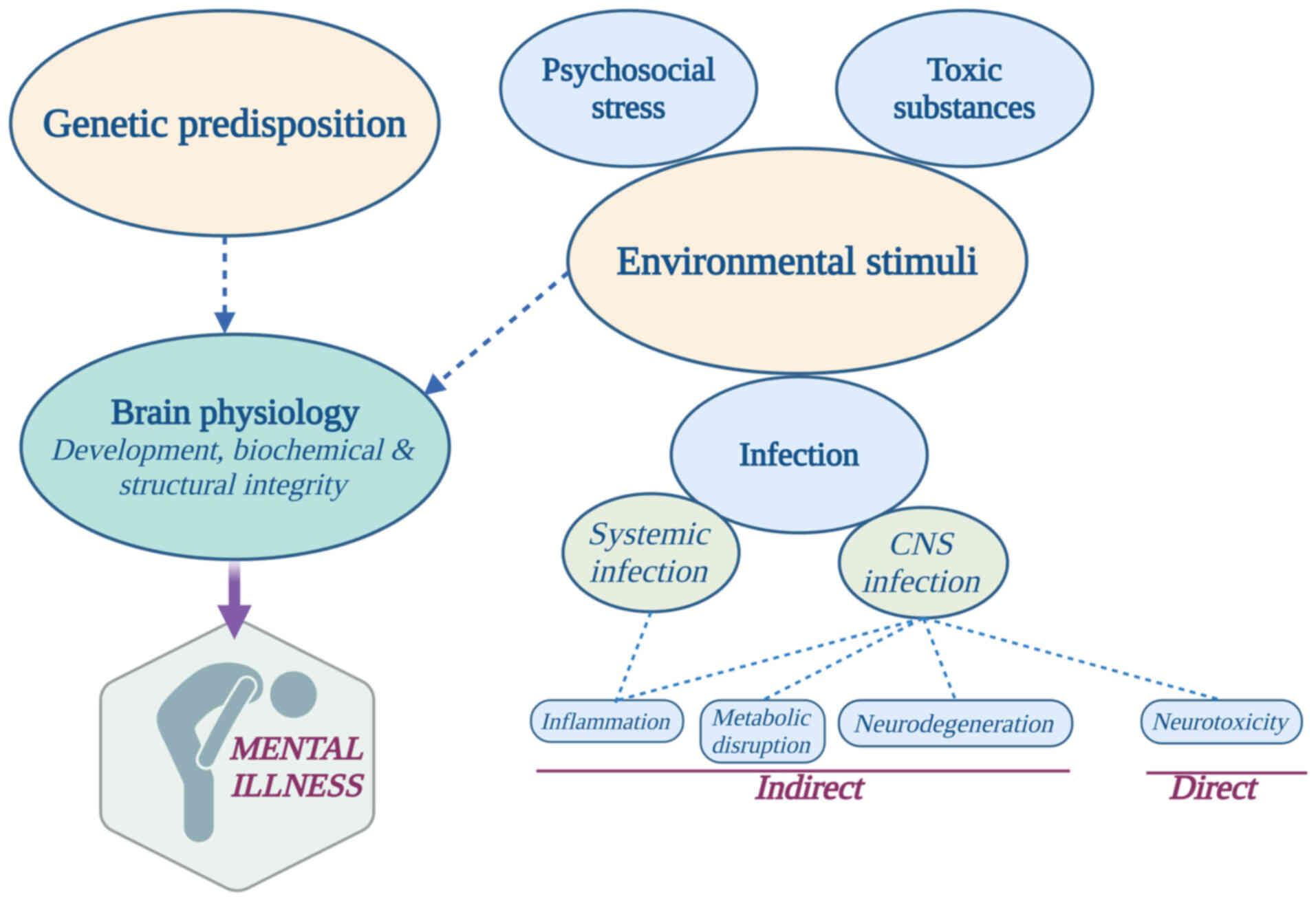
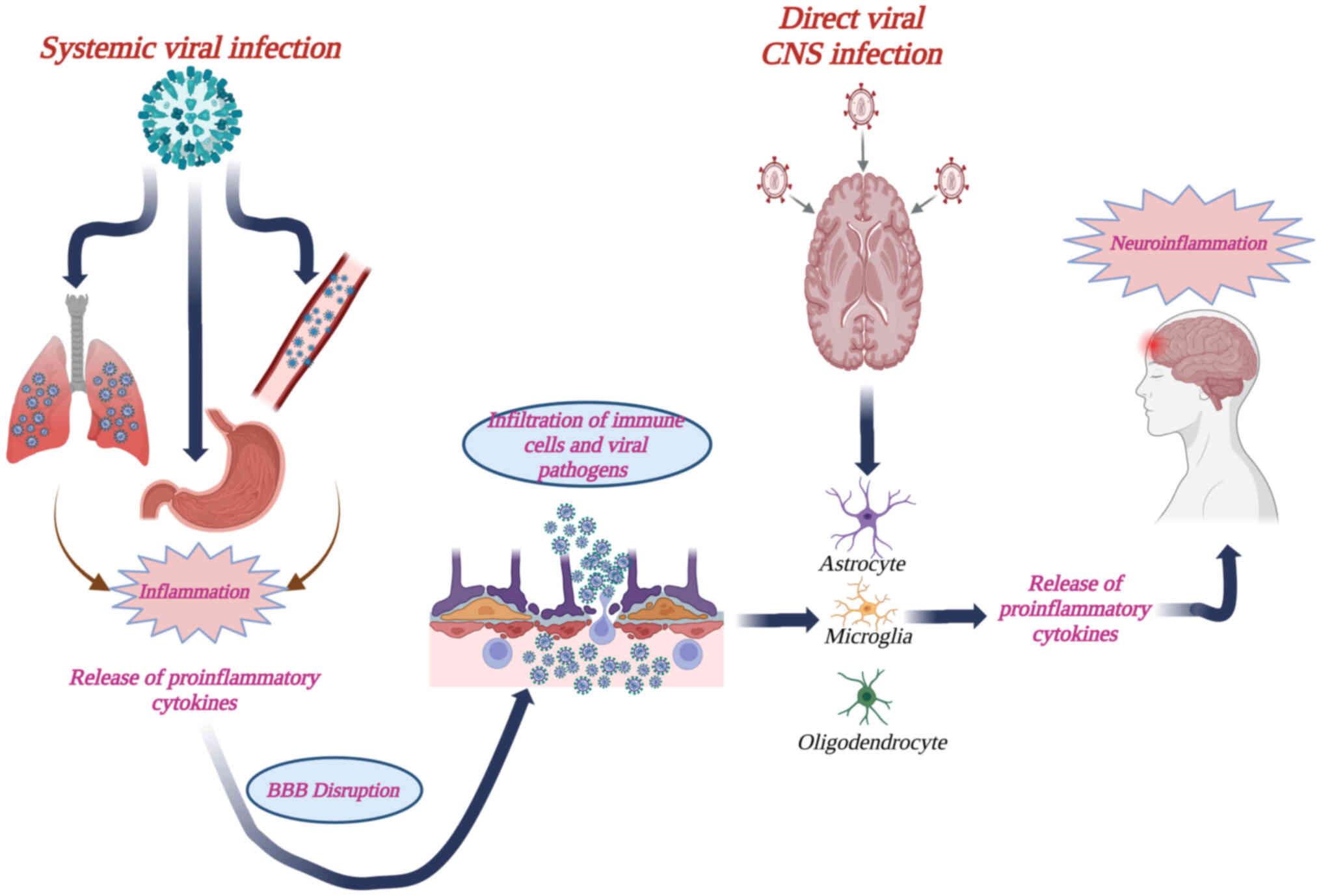
|
1
|
Nasir A, Forterre P, Kim KM and
Caetano-Anollés G: The distribution and impact of viral lineages in
domains of life. Front Microbiol. 5:1942014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Call L, Nayfach S and Kyrpides NC:
Illuminating the virosphere through global metagenomics. Annu Rev
Biomed Data Sci. 4:369–391. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gregory AC, Zayed AA, Conceição-Neto N,
Temperton B, Bolduc B, Alberti A, Ardyna M, Arkhipova K, Carmichael
M, Cruaud C, et al: Marine DNA viral macro- and microdiversity from
pole to pole. Cell. 177:1109–1123.e14. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Neri U, Wolf YI, Roux S, Camargo AP, Lee
B, Kazlauskas D, Chen IM, Ivanova N, Zeigler Allen L, Paez-Espino
D, et al: Expansion of the global RNA virome reveals diverse clades
of bacteriophages. Cell. 185:4023–4037.e18. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mohapatra S and Menon NG: Factors
responsible for the emergence of novel viruses: An emphasis on
SARS-CoV-2. Curr Opin Environ Sci Health. 27:1003582022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Marie V and Gordon ML: The (Re-)emergence
and spread of viral zoonotic disease: A perfect storm of human
ingenuity and stupidity. Viruses. 15:16382023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Piret J and Boivin G: Pandemics throughout
history. Front Microbiol. 11:6317362021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Davis HE, McCorkell L, Vogel JM and Topol
EJ: Long COVID: Major findings, mechanisms and recommendations. Nat
Rev Microbiol. 21:133–146. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Boufidou F, Medić S, Lampropoulou V,
Siafakas N, Tsakris A and Anastassopoulou C: SARS-CoV-2
reinfections and long COVID in the post-omicron phase of the
pandemic. Int J Mol Sci. 24:129622023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Castanares-Zapatero D, Chalon P, Kohn L,
Dauvrin M, Detollenaere J, Maertens de Noordhout C, Primus-de Jong
C, Cleemput I and Van den Heede K: Pathophysiology and mechanism of
long COVID: A comprehensive review. Ann Med. 54:1473–1487. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Virgin HW, Wherry EJ and Ahmed R:
Redefining chronic viral infection. Cell. 138:30–50. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Grandi N and Tramontano E: HERV envelope
proteins: Physiological role and pathogenic potential in cancer and
autoimmunity. Front Microbiol. 9:4622018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang M, Liang JQ and Zheng S:
Expressional activation and functional roles of human endogenous
retroviruses in cancers. Rev Med Virol. 29:e20252019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Luganini A and Gribaudo G: Retroviruses of
the human virobiota: The recycling of viral genes and the resulting
advantages for human hosts during evolution. Front Microbiol.
11:11402020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liang G and Bushman FD: The human virome:
Assembly, composition and host interactions. Nat Rev Microbiol.
19:514–527. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Seo SU and Kweon MN: Virome-host
interactions in intestinal health and disease. Curr Opin Virol.
37:63–71. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
van Os J, Rutten BP and Poulton R:
Gene-environment interactions in schizophrenia: Review of
epidemiological findings and future directions. Schizophr Bull.
34:1066–1082. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pearce BD: Viruses and psychiatric
disorders. Siegel A and Zalcman SS: The Neuroimmunological Basis of
Behavior and Mental Disorders. Springer; Boston, MA: pp. 383–410.
2009, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Hobbs JA: The virus connection: How
viruses affect psychiatric pathologies. Psychiatr Times.
33:2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Müller N and Schwarz MJ: Immune system and
schizophrenia. Curr Immunol Rev. 6:213–220. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fatemi SH and Folsom TD: The
neurodevelopmental hypothesis of schizophrenia, revisited.
Schizophr Bull. 35:528–548. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Blomström Å, Karlsson H, Svensson A,
Frisell T, Lee BK, Dal H, Magnusson C and Dalman C: Hospital
admission with infection during childhood and risk for psychotic
illness-a population-based cohort study. Schizophr Bull.
40:1518–1525. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hickie IB, Banati R, Stewart CH, Stewart
CH and Lloyd AR: Are common childhood or adolescent infections risk
factors for schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders? Med J
Aust. 190 (S4):S17–S21. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liang W and Chikritzhs T: Early childhood
infections and risk of schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 200:214–217.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Maynard TM, Sikich L, Lieberman JA and
LaMantia AS: Neural development, cell-cell signaling, and the
‘two-hit’ hypothesis of schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 27:457–476.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Debost JCPG, Larsen JT, Munk-Olsen T,
Mortensen PB, Meyer U and Petersen L: Joint effects of exposure to
prenatal infection and peripubertal psychological trauma in
schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 43:171–179. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Raison CL, Borisov AS, Majer M, Drake DF,
Pagnoni G, Woolwine BJ, Vogt GJ, Massung B and Miller AH:
Activation of central nervous system inflammatory pathways by
interferon-alpha: Relationship to monoamines and depression. Biol
Psychiatry. 65:296–303. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rocamonde B, Hasan U, Mathieu C and
Dutartre H: Viral-induced neuroinflammation: Different mechanisms
converging to similar exacerbated glial responses. Front Neurosci.
17:11082122023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Niranjan R, Muthukumaravel S and
Jambulingam P: The involvement of neuroinfammation in dengue viral
disease: Importance of innate and adaptive immunity.
Neuroimmunomodulation. 26:111–118. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bogovic P and Strle F: Tick-borne
encephalitis: A review of epidemiology, clinical characteristics,
and management. World J Clin Cases. 3:430–441. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lannes N, Neuhaus V, Scolari B,
Kharoubi-Hess S, Walch M, Summerfield A and Filgueira L:
Interactions of human microglia cells with Japanese encephalitis
virus. Virol J. 14:82017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shao Q, Herrlinger S, Yang SL, Lai F,
Moore JM, Brindley MA and Chen JF: Zika virus infection disrupts
neurovascular development and results in postnatal microcephaly
with brain damage. Development. 143:4127–4136. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
de Sousa JR, Azevedo RSS, Martins Filho
AJ, Araujo MTF, Moutinho ERC, Baldez Vasconcelos BC, Cruz ACR,
Oliveira CS, Martins LC, Baldez Vasconcelos BH, et al: Correlation
between apoptosis and in situ immune response in fatal cases of
microcephaly caused by Zika virus. Am J Pathol. 188:2644–2652.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li Y, Zhao L, Luo Z, Zhang Y, Lv L, Zhao
J, Sui B, Huang F, Cui M, Fu ZF and Zhou M: Interferon-λ attenuates
rabies virus infection by inducing interferon-stimulated genes and
alleviating neurological inflammation. Viruses. 12:4052020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Marsland AL, Petersen KL, Sathanoori R,
Muldoon MF, Neumann SA, Ryan C, Flory JD and Manuck SB:
Interleukin-6 covaries inversely with cognitive performance among
middle-aged community volunteers. Psychosom Med. 68:895–903. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dickerson SS, Gable SL, Irwin MR, Aziz N
and Kemeny ME: Social-evaluative threat and proinflammatory
cytokine regulation: An experimental laboratory investigation.
Psychol Sci. 20:1237–1244. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Metcalf SA, Jones PB, Nordstrom T, Timonen
M, Mäki P, Miettunen J, Jääskeläinen E, Järvelin MR, Stochl J,
Murray GK, et al: Serum C-reactive protein in adolescence and risk
of schizophrenia in adulthood: A prospective birth cohort study.
Brain BehavImmun. 59:253–259. 2017.
|
|
38
|
Müller N: Inflammation in schizophrenia:
Pathogenetic aspects and therapeutic considerations. Schizophr
Bull. 44:973–982. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Khandaker GM, Pearson RM, Zammit S, Lewis
G and Jones PB: Association of serum interleukin 6 and C-reactive
protein in childhood with depression and psychosis in young adult
life: A population-based longitudinal study. JAMA Psychiatry.
71:1121–1128. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Maxeiner HG, Marion Schneider E, Kurfiss
ST, Brettschneider J, Tumani H and Bechter K: Cerebrospinal fluid
and serum cytokine profiling to detect immune control of infectious
and inflammatory neurological and psychiatric diseases. Cytokine.
69:62–67. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sarma JV and Ward PA: The complement
system. Cell Tissue Res. 343:227–235. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Keshavan M, Lizano P and Prasad K: The
synaptic pruning hypothesis of schizophrenia: Promises and
challenges. World Psychiatry. 19:110–111. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Druart M and Le Magueresse C: Emerging
roles of complement in psychiatric disorders. Front Psychiatry.
10:5732019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mondelli V, Di Forti M, Morgan BP, Murray
RM, Pariante CM and Dazzan P: Baseline high levels of complement
component 4 predict worse clinical outcome at 1-year follow-up in
first-episode psychosis. Brain BehavImmun. 88:913–915.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tomonaga K: Virus-induced neurobehavioral
disorders: Mechanisms and implications. Trends Mol Med. 10:71–77.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kotsiri I, Resta P, Spyrantis A,
Panotopoulos C, Chaniotis D, Beloukas A and Magiorkinis E: Viral
infections and schizophrenia: A comprehensive review. Viruses.
15:13452023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sayeh A, Cheikh CB, Mrad M, Lakhal N,
Gritli N, Galelli S, Oumaya A and Fekih-Mrissa N: Association of
HLA-DR/DQ polymorphisms with schizophrenia in Tunisian patients.
Ann Saudi Med. 34:503–507. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Prasard S, Semwal P, Deshpande S, Bhatia
T, Nimgaonkar VL and Thelma BK: Molecular genetics of
schizophrenia: Past, present and future. J Biosci. 27 (Suppl
1):S35–S52. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Wright P, Donaldson PT, Underhill JA,
Choudhuri K, Doherty DG and Murray RM: Genetic association of the
HLA DRB1 gene locus on chromosome 6p21.3 with schizophrenia. Am J
Psychiatry. 153:1530–1533. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Nimgaonkar VL, Rudert WA, Zhang X, Trucco
M and Ganguli R: Negative association of schizophrenia with HLA
DQB1*0602: Evidence from a second African-American cohort.
Schizophr Res. 23:81–86. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
James LM, Charonis SA and Georgopoulos AP:
Schizophrenia, human leukocyte antigen (HLA), and herpes viruses:
Immunogenetic associations at the population level. Neurosci
Insights. 18:263310552311664112023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wongchitrat P, Chanmee T and Govitrapong
P: Molecular mechanisms associated with neurodegeneration of
neurotropic viral infection. Mol Neurobiol. 61:2881–2903. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Li C, Xu D, Ye Q, Hong S, Jiang Y, Liu X,
Zhang N, Shi L, Qin CF and Xu Z: Zika virus disrupts neural
progenitor development and leads to microcephaly in mice. Cell Stem
Cell. 19:120–126. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Tiwari SK, Dang JW, Lin N, Qin Y, Wang S
and Rana TM: Zika virus depletes neural stem cells and evades
selective autophagy by suppressing the Fanconi anemia protein
FANCC. EMBO Rep. 21:e491832020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Gabriel E, Ramani A, Karow U, Gottardo M,
Natarajan K, Gooi LM, Goranci-Buzhala G, Krut O, Peters F, Nikolic
M, et al: Recent Zika virus isolates induce premature
differentiation of neural progenitors in human brain organoids.
Cell Stem Cell. 20:397–406.e5. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Crunfi F, Carregari VC, Veras FP, Silva
LS, Nogueira MH, Antunes ASLM, Vendramini PH, Valença AGF,
Brandão-Teles C, Zuccoli GDS, et al: Morphological, cellular, and
molecular basis of brain infection in COVID-19 patients. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 119:e22009601192022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
de Oliveira LG, de Souza Angelo Y,
Yamamoto P, Carregari VC, Crunfli F, Reis-de-Oliveira G, Costa L,
Vendramini PH, Duque ÉA, Dos Santos NB, et al: SARS-CoV-2 infection
impacts carbon metabolism and depends on glutamine for replication
in Syrian hamster astrocytes. J Neurochem. 163:113–132. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Fan Y and He JJ: HIV-1 Tat induces
unfolded protein response and endoplasmic reticulum stress in
astrocytes and causes neurotoxicity through glial fbrillary acidic
protein (GFAP) activation and aggregation. J Biol Chem.
291:22819–22829. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zhou BY, Liu Y, Kim BO, Xiao Y and He JJ:
Astrocyte activation and dysfunction and neuron death by HIV-1 Tat
expression in astrocytes. Mol Cell Neurosci. 27:296–305. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Teodorof-Diedrich C and Spector SA: Human
immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 and Tat induce mitochondrial
fragmentation and incomplete mitophagy in human neurons. J Virol.
92:e00993–18. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
McGavern DB and Kang SS: Illuminating
viral infections in the nervous system. Nat Rev Immunol.
11:318–329. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Bhatia MS, Gautam P and Jhanjee A:
Psychiatric morbidity in patients with chikungunya Fever: First
report from India. J Clin Diagn Res. 9:VC01–VC03. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Figueiredo T, Dias da Costa M and
Segenreich D: Manic episode after a chikungunya virus infection in
a bipolar patient previously stabilized with valproic acid. J Clin
Psychopharmacol. 38:395–397. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Samaan Z, McDermid Vaz S, Bawor M, Potter
TH, Eskandarian S and Loeb M: Neuropsychological impact of west
nile virus infection: An extensive neuropsychiatric assessment of
49 cases in Canada. PLoS One. 11:e01583642016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Srivastava R, Kalita J, Khan MY and Misra
UK: Free radical generation by neurons in rat model of Japanese
encephalitis. Neurochem Res. 34:2141–2146. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
James HJ, Sharer LR, Zhang Q, Wang HG,
Epstein LG, Reed JC and Gelbard HA: Expression of caspase-3 in
brains from paediatric patients with HIV-1 encephalitis.
Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 25:380–386. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Du X, Wang H, Xu F, Huang Y, Liu Z and Liu
T: Enterovirus 71 induces apoptosis of SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma
cells through stimulation of endogenous microRNA let-7b expression.
Mol Med Rep. 12:953–959. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Jackson AC and Rossiter JP: Apoptosis
plays an important role in experimental rabies virus infection. J
Virol. 71:5603–5607. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Rutherford M and Jackson AC: Neuronal
apoptosis in immunodeficient mice infected with the challenge virus
standard strain of rabies virus by intracerebral inoculation. J
Neurovirol. 10:409–413. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Jackson AC: Apoptosis in experimental
rabies in bax-deficient mice. Acta Neuropathol. 98:288–294. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Fu ZF and Jackson AC: Neuronal dysfunction
and death in rabies virus infection. J Neurovirol. 11:101–106.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Kojima D, Park CH, Tsujikawa S, Kohara K,
Hatai H, Oyamad T, Noguchi A and Inoue S: Lesions of the central
nervous system induced by intracerebral inoculation of BALB/c mice
with rabies virus (CVS-11). J Vet Med Sci. 72:1011–1016. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Parquet MC, Kumatori A, Hasebe F, Morita K
and Igarashi A: West Nile virus-induced bax-dependent apoptosis.
FEBS Lett. 500:17–24. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Kleinschmidt MC, Michaelis M, Ogbomo H,
Doerr HW and Cinatl J Jr: Inhibition of apoptosis prevents West
Nile virus induced cell death. BMC Microbiol. 7:492007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
van Marle G, Antony J, Ostermann H, Dunham
C, Hunt T, Halliday W, Maingat F, Urbanowski MD, Hobman T, Peeling
J and Power C: West Nile virus-induced neuroinflammation: Glial
infection and capsid protein-mediated neurovirulence. J Virol.
81:10933–10949. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Yang JS, Ramanathan MP, Muthumani K, Choo
AY, Jin SH, Yu QC, Hwang DS, Choo DK, Lee MD, Dang K, et al:
Induction of inflammation by West Nile virus capsid through the
caspase-9 apoptotic pathway. Emerg Infect Dis. 8:1379–1384. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Ramanathan MP, Chambers JA, Pankhong P,
Chattergoon M, Attatippaholkun W, Dang K, Shah N and Weiner DB:
Host cell killing by the West Nile virus NS2B-NS3 proteolytic
complex: NS3 alone is sufficient to recruit caspase-8-based
apoptotic pathway. Virology. 345:56–72. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Swarup V, Das S, Ghosh S and Basu A: Tumor
necrosis factor receptor-1-induced neuronal death by TRADD
contributes to the pathogenesis of Japanese encephalitis. J
Neurochem. 103:771–783. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Mishra MK and Basu A: Minocycline
neuroprotects, reduces microglial activation, inhibits caspase 3
induction, and viral replication following Japanese encephalitis. J
Neurochem. 105:1582–1595. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Chen T, Tu S, Ding L, Jin M, Chen H and
Zhou H: The role of autophagy in viral infections. J Biomed Sci.
30:52023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Huang SC, Chang CL, Wang PS, Tsai Y and
Liu HS: Enterovirus 71-induced autophagy detected in vitro and in
vivo promotes viral replication. J Med Virol. 81:1241–1252. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Liu ZW, Zhuang ZC, Chen R, Wang XR, Zhang
HL, Li SH, Wang ZY and Wen HL: Enterovirus 71 VP1 protein regulates
viral replication in SH-SY5Y cells via the mTOR autophagy signaling
pathway. Viruses. 12:112019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Too IH, Yeo H, Sessions OM, Yan B, Libau
EA, Howe JLC, Lim ZQ, Suku-Maran S, Ong WY, Chua KB, et al:
Enterovirus 71 infection of motor neuron-like NSC-34 cells
undergoes a non-lytic exit pathway. Sci Rep. 6:369832016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Fields JA, Metcalf J, Overk C, Adame A,
Spencer B, Wrasidlo W, Florio J, Rockenstein E, He JJ and Masliah
E: The anticancer drug sunitinib promotes autophagyand protects
from neurotoxicity in an HIV-1 Tat model of neurodegeneration. J
Neurovirol. 23:290–303. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Cheney L, Guzik H, Macaluso FP, Macian F,
Cuervo AM and Berman JW: HIV Nef and antiretroviral therapy have an
inhibitory effect on autophagy in human astrocytes that may
contribute to HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. Cells.
9:14262020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Fields J, Dumaop W, Elueteri S, Campos S,
Serger E, Trejo M, Kosberg K, Adame A, Spencer B, Rockenstein E, et
al: HIV-1 Tat alters neuronal autophagy by modulating autophagosome
fusion to the lysosome: Implications for HIV-associated
neurocognitive disorders. J Neurosci. 35:1921–1938. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Fischer M, Lindsey N, Staples JE and Hills
S; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), : Japanese
encephalitis vaccines: Recommendations of the advisory committee on
immunization practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 59:1–27. 2010.
|
|
88
|
Unni SK, Růžek D, Chhatbar C, Mishra R,
Johri MK and Singh SK: Japanese encephalitis virus: From genome to
infectome. Microbes Infect. 13:312–321. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Hu S, Sheng WS, Schachtele SJ and
Lokensgard JR: Reactive oxygen species drive herpes simplex virus
(HSV)-1-induced proinflammatory cytokine production by murine
microglia. J Neuroinflammation. 8:1232011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Kavouras JH, Prandovszky E, Valyi-Nagy K,
Kovacs SK, Tiwari V, Kovacs M, Shukla D and Valyi-Nagy T: Herpes
simplex virus type 1 infection induces oxidative stress and the
release of bioactive lipid peroxidation by-products in mouse P19N
neural cell cultures. J Neurovirol. 13:416–425. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Gorska AM and Eugenin EA: The glutamate
system as a crucial regulator of CNS toxicity and survival of HIV
reservoirs. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 10:2612020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Alandijany T, Kammouni W, Roy Chowdhury
SK, Fernyhough P and Jackson AC: Mitochondrial dysfunction in
rabies virus infection of neurons. J Neurovirol. 19:537–549. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Ghosh Roy S, Sadigh B, Datan E, Lockshin
RA and Zakeri Z: Regulation of cell survival and death during
flavivirus infections. World J Biol Chem. 5:93–105. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Mukherjee S, Singh N, Sengupta N, Fatima
M, Seth P, Mahadevan A, Shankar SK, Bhattacharyya A and Basu A:
Japanese encephalitis virus induces human neural stem/progenitor
cell death by elevating GRP78, PHB and hnRNPC through ER stress.
Cell Death Dis. 8:e25562017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Tan Z, Zhang W, Sun J, Fu Z, Ke X, Zheng
C, Zhang Y, Li P, Liu Y, Hu Q, et al: ZIKV infection activates the
IRE1-XBP1 and ATF6 pathways of unfolded protein response in neural
cells. J Neuroinflammation. 15:2752018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Hu DD, Mai JN, He LY, Li PQ, Chen WX, Yan
JJ, Zhu WD, Deng L, Wei D, Liu DH, et al: Glucocorticoids prevent
enterovirus 71 capsid protein VP1 induced calreticulin surface
exposure by alleviating neuronal ER stress. Neurotox Res.
31:204–217. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Cheng ML, Weng SF, Kuo CH and Ho HY:
Enterovirus 71 induces mitochondrial reactive oxygen species
generation that is required for efficient replication. PLoS One.
9:e1132342014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Guo L, Xing Y, Pan R, Jiang M, Gong Z, Lin
L, Wang J, Xiong G and Dong J: Curcumin protects microglia and
primary rat cortical neurons against HIV-1 gp120-mediated
inflammation and apoptosis. PLoS One. 8:e705652013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Shah A, Kumar S, Simon SD, Singh DP and
Kumar A: HIV gp120- and methamphetamine-mediated oxidative stress
induces astrocyte apoptosis via cytochrome P450 2E1. Cell Death
Dis. 4:e8502013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Ivanov AV, Valuev-Elliston VT, Ivanova ON,
Kochetkov SN, Starodubova ES, Bartosch B and Isaguliants MG:
Oxidative stress during HIV infection: Mechanisms and consequences.
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016:89103962016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Simanjuntak Y, Liang JJ, Lee YL and Lin
YL: Japanese encephalitis virus exploits dopamine D2
receptor-phospholipase C to target dopaminergic human neuronal
cells. Front Microbiol. 8:6512017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Damsgaard J, Hjerrild S, Andersen H and
Leutscher PDC: Long-term neuropsychiatric consequences of aseptic
meningitis in adult patients. Infect Dis (Lond). 47:357–363. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Omland LH, Vestergaard BF and Wandall JH:
Herpes simplex virus type 2 infections of the central nervous
system: A retrospective study of 49 patients. Scand J Infect Dis.
40:59–62. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Persson A, Bergström T, Lindh M, Namvar L
and Studahl M: Varicella-zoster virus CNS disease-viral load,
clinical manifestations and sequels. J Clin Virol. 46:249–253.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Sittinger H, Müller M, Schweizer I and
Merkelbach S: Mild cognitive impairment after viral meningitis in
adults. J Neurol. 249:554–560. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Du C, Li G and Han G: Biosafety and mental
health: Virus induced cognitive decline. Biosaf Health. 5:159–167.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Hare EH, Price JS and Slater E:
Schizophrenia and season of birth. Br J Psychiatry. 120:124–125.
1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Machón RA, Mednick SA and Schulsinger F:
The interaction of seasonality, place of birth, genetic risk and
subsequent schizophrenia in a high risk sample. Br J Psychiatry.
143:383–388. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Pallast EG, Jongbloet PH, Straatman HM and
Zielhuis GA: Excess seasonality of births among patients with
schizophrenia and seasonal ovopathy. Schizophr Bull. 20:269–276.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Susser ES, Brown AS and Gorman JM:
Prenatal exposures in schizophrenia. American Psychiatric
Association; 1999
|
|
111
|
Mednick SA, Machon RA, Huttunen MO and
Bonett D: Adult schizophrenia following prenatal exposure to an
influenza epidemic. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 45:189–192. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Brown AS, Begg MD, Gravenstein S, Schaefer
CA, Wyatt RJ, Bresnahan M, Babulas VP and Susser ES: Serologic
evidence of prenatal influenza in the etiology of schizophrenia.
Arch Gen Psychiatry. 61:774–780. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Bonkovsky HL, Snow KK, Malet PF,
Back-Madruga C, Fontana RJ, Sterling RK, Kulig CC, Di Bisceglie AM,
Morgan TR, Dienstag JL, et al: Health-related quality of life in
patients with chronic hepatitis C and advanced fibrosis. J Hepatol.
46:420–431. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Gragnani L, Cerretelli G, Lorini S, Steidi
C, Giovannelli A, Monti M, Petraccia L, Sadalla S, Urraro T, Caini
P, et al: Interferon-free therapy in hepatitis C virus mixed
cryoglobulinaemia: A prospective, controlled, clinical and quality
of live analysis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 48:440–450. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Torrey EF, Bowler AE and Rawlings R: An
influenza epidemic and the seasonality of schizophrenic births.
Kurstak: Psychiatry and Biological Factors. Springer; Boston, MA:
pp. 109–116. 1991, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Nicoll MP, Proença JT and Efstathiou S:
The molecular basis of herpes simplex virus latency. FEMS Microbiol
Rev. 36:684–705. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Torrey EF, Leweke MF, Schwarz MJ, Mueller
N, Bachmann S, Schroeder J, Dickerson F and Yolken RH:
Cytomegalovirus and schizophrenia. CNS Drugs. 20:879–885. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Prasad KMR, Shirts BH, Yolken RH, Keshavan
MS and Nimgaonkar VL: Brain morphological changes associated with
exposure to HSV1 in first-episode schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry.
12:105–113. 12007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Burgdorf KS, Trabjerg BB, Pedersen MG,
Nissen J, Banasik K, Pedersen OB, Sørensen E, Nielsen KR, Larsen
MH, Erikstrup C, et al: Large-scale study of toxoplasma and
cytomegalovirus shows an association between infection and serious
psychiatric disorders. Brain BehavImmun. 79:152–158. 2019.
|
|
120
|
Dickerson F, Jones-Brando L, Ford G,
Genovese G, Stallings C, Origoni A, O'Dushlaine C, Katsafanas E,
Sweeney K, Khushalani S and Yolken R: Schizophrenia is associated
with an aberrant immune response to epstein-barr virus. Schizophr
Bull. 45:1112–1119. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Dickerson FB, Boronow JJ, Stallings C,
Origoni AE, Ruslanova I and Yolken RH: Association of serum
antibodies to herpes simplex virus 1 with cognitive deficits in
individuals with schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 60:466–472.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Thomas P, Bhatia T, Gauba D, Wood J, Long
C, Prasad K, Dickerson FB, Gur RE, Gur RC, Yolken RH, et al:
Exposure to herpes simplex virus, type 1 and reduced cognitive
function. J Psychiatr Res. 47:1680–1685. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Yolken RH, Torrey EF, Lieberman JA, Yang S
and Dickerson FB: Serological evidence of exposure to herpes
simplex virus type 1 is associated with cognitive deficits in the
CATIE schizophrenia sample. Schizophr Res. 128:61–65. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Krause D, Matz J, Weidinger E, Wagner J,
Wildenauer A, Obermeier M, Riedel M and Müller N: The association
of infectious agents and schizophrenia. World J Biol Psychiatry.
11:739–743. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Waechter R, Ingraham E, Evans R, Cudjoe N,
Krystosik A, Isaac R, Watts A, Noël T, Landon B, Fernandes M, et
al: Pre and postnatal exposure to chikungunya virus does not affect
child neurodevelopmental outcomes at two years of age. PLoS Negl
Trop Dis. 14:e00085462020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Mazzaro C, Quartuccio L, Adinolfi LE,
Roccatello D, Pozzato G, Nevola R, Tonizzo M, Gitto S, Andreone P
and Gattei V: A review on extrahepatic manifestations of chronic
hepatitis C virus infection and the impact of direct-acting
antiviral therapy. Viruses. 13:22492021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Fishman SL, Murray JM, Eng FJ, Walewski
JL, Morgello S and Branch AD: Molecular and bioinformatic evidence
of hepatitis C virus evolution in brain. J Infect Dis. 197:597–607.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Wilkinson J, Radkowski M and Laskus T:
Hepatitis C virus neuroinvasion: Identification of infected cells.
J Virol. 83:1312–1319. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Laskus T, Radkowski M, Bednarska A,
Wilkinson J, Adair D, Nowicki M, Nikolopoulou GB, Vargas HE and
Rakela J: Detection and analysis of hepatitis C virus sequences in
cerebrospinal fluid. J Virol. 76:10064–10068. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Min S, Gandal MJ, Kopp RF, Liu C and Chen
C: No increased detection of nucleic acids of CNS-related viruses
in the brains of patients with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and
autism spectrum disorder. Schizophr Bull. 49:551–558. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Yolken RH, Kinnunen PM, Vapalahti O,
Dickerson F, Suvisaari J, Chen O and Sabunciyan S: Studying the
virome in psychiatric disease. Schizophr Res. 234:78–86. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Kneeland RE and Fatemi SH: Viral
infection, inflammation and schizophrenia. Prog
Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 42:35–48. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Gu CJ, Borjabad A, Hadas E, Kelschenbach
J, Kim BH, Chao W, Arancio O, Suh J, Polsky B, McMillan J, et al:
EcoHIV infection of mice establishes latent viral reservoirs in T
cells and active viral reservoirs in macrophages that are
sufficient for induction of neurocognitive impairment. PLoS Pathog.
14:e10070612018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Gruchot J, Herrero F, Weber-Stadlbauer U,
Meyer U and Küry P: Interplay between activation of endogenous
retroviruses and inflammation as common pathogenic mechanism in
neurological and psychiatric disorders. Brain BehavImmun.
107:242–252. 2023.
|
|
135
|
Kamitani W, Ono E, Yoshino S, Kobayashi T,
Taharaguchi S, Lee BJ, Yamashita M, Kobayashi T, Okamoto M,
Taniyama H, et al: Glial expression of Borna disease virus
phosphoprotein induces behavioral and neurological abnormalities in
transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:8969–8974. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Li F, Sabunciyan S, Yolken RH, Lee D, Kim
S and Karlsson H: Transcription of human endogenous retroviruses in
human brain by RNA-seq analysis. PLoS One. 14:e02073532019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Karlsson H, Bachmann S, Schröder J,
McArthur J, Torrey EF and Yolken RH: Retroviral RNA identified in
the cerebrospinal fluids and brains of individuals with
schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:4634–4639. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Perron H, Hamdani N, Faucard R, Lajnef M,
Jamain S, Daban-Huard C, Sarrazin S, LeGuen E, Houenou J, Delavest
M, et al: Molecular characteristics of human endogenous retrovirus
type-W in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Transl Psychiatry.
2:e2012012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Tamouza R, Meyer U, Foiselle M, Richard
JR, Wu CL, Boukouaci W, Le Corvoisier P, Barrau C, Lucas A, Perron
H and Leboyer M: Identification of inflammatory subgroups of
schizophrenia and bipolar disorder patients with HERV-W ENV
antigenemia by unsupervised cluster analysis. Transl Psychiatry.
11:3772021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Slokar G and Hasler G: Human endogenous
retroviruses as pathogenic factors in the development of
schizophrenia. Front Psychiatry. 6:1832016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Jesuthasan A, Massey F, Manji H, Zandi MS
and Wiethoff S: Emerging potential mechanisms and predispositions
to the neurological manifestations of COVID-19. J Neurol Sci.
428:1176082021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Guedj E, Campion JY, Dudouet P, Kaphan E,
Bregeon F, Tissot-Dupont H, Guis S, Barthelemy F, Habert P,
Ceccaldi M, et al: 18F-FDG brain PET hypometabolism in
patients with long COVID. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 48:2823–2833.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Tromans S, Kinney M, Chester V, Alexander
R, Roy A, Sander JW, Dudson H and Shankar R: Priority concerns for
people with intellectual and developmental disabilities during the
COVID-19 pandemic. BJPsych Open. 6:e1282020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Holmes EA, O'Connor RC, Perry VH, Tracey
I, Wessely S, Arsenault L, Ballard C, Christensen H, Cohen Silver
R, Everall I, et al: Multidisciplinary research priorities for the
COVID-19 pandemic: A call for action for mental health science.
Lancet Psychiatry. 7:547–560. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Ho CS, Chee CY and Ho RC: Mental health
strategies to combat the psychological impact of coronavirus
disease 2019 (COVID-19) beyond paranoia and panic. Ann Acad Med
Singap. 49:155–160. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Tsamakis K, Tsiptsios D, Ouranidis A,
Mueller C, Schizas D, Terniotis C, Nikolakakis N, Tyros G,
Kympouropoulos S, Lazaris A, et al: COVID-19 and its consequences
on mental health (Review). Exp Ther Med. 21:2442021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Efstathiou V, Stefanou MI, Demetriou M,
Siafakas N, Makris M, Tsivgoulis G, Zoumpourlis V, Kympouropoulos
SP, Tsoporis JN, Spandidos DA, et al: Long COVID and
neuropsychiatric manifestations (Review). Exp Ther Med. 23:3632022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Efstathiou V, Stefanou MI, Demetriou M,
Siafakas N, Katsantoni E, Makris M, Tsivgoulis G, Zoumpourlis V,
Kympouropoulos SP, Tsoporis JN, et al: New-onset neuropsychiatric
sequelae and ‘long-COVID’ syndrome (Review). Exp Ther Med.
24:7052022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Yuan K, Gong YM, Liu L, Sun YK, Tian SS,
Wang YJ, Zhong Y, Zhang AY, Su SZ, Liu XX, et al: Prevalence of
posttraumatic stress disorder after infectious disease pandemics in
the twenty-first century, including COVID-19: A meta-analysis and
systematic review. Mol Psychiatry. 26:4982–4998. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Antonelli G and Cutler S: Evolution of the
Koch postulates: Towards a 21st-century understanding of microbial
infection. Clin Microbiol Infect. 22:583–584. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Taquet M, Geddes JR, Husain M, Luciano S
and Harrison PJ: 6-Month neurological and psychiatric outcomes in
236 379 survivors of COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study using
electronic health records. Lancet Psychiatry. 8:416–427. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Schou TM, Joca S, Wegener G and
Bay-Richter C: Psychiatric and neuropsychiatric sequelae of
COVID-19-A systematic review. Brain Behav Immun. 97:328–348. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Shanbehzadeh S, Tavahomi M, Zanjari N,
Ebrahimi-Takamjani I and Amiri-Arimi S: Physical and mental health
complications post-COVID-19: Scoping review. J Psychosom Res.
147:1105252021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Chen C, Wang J, Pan D, Wang X, Xu Y, Yan
J, Wang L, Yang X, Yang M and Liu GP: Applications of multi-omics
analysis in human diseases. MedComm (2020). 4:e3152023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Ong K, Ng K, Ng C, Tan S, Teo W, Karim N,
Kumar S and Wong KT: Neuronal infection is a major pathogenetic
mechanism and cause of fatalities in human acute nipah virus
encephalitis. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 48:e128282022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Mathieu C, Bovier FT, Ferren M, Lieberman
NAP, Predella C, Lalande A, Peddu V, Lin MJ, Addetia A, Patel A, et
al: Molecular features of the measles virus viral fusion complex
that favor infection and spread in the brain. mBio.
12:e00799212021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|