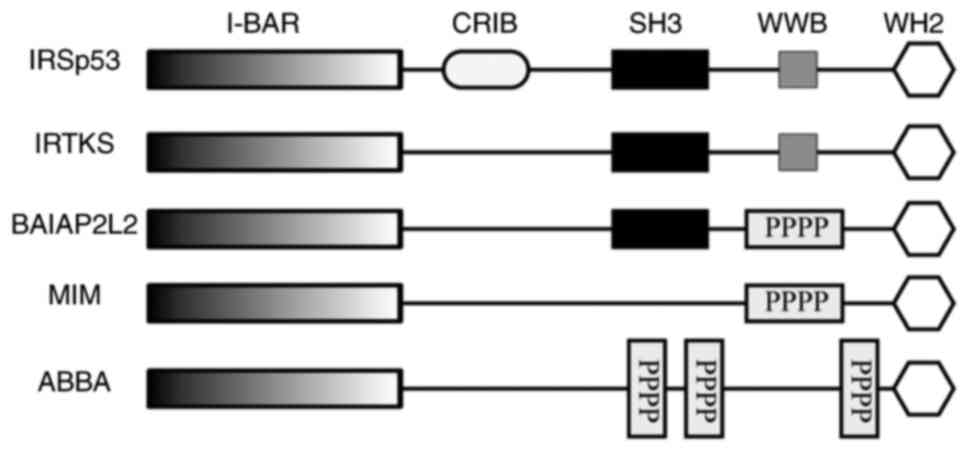
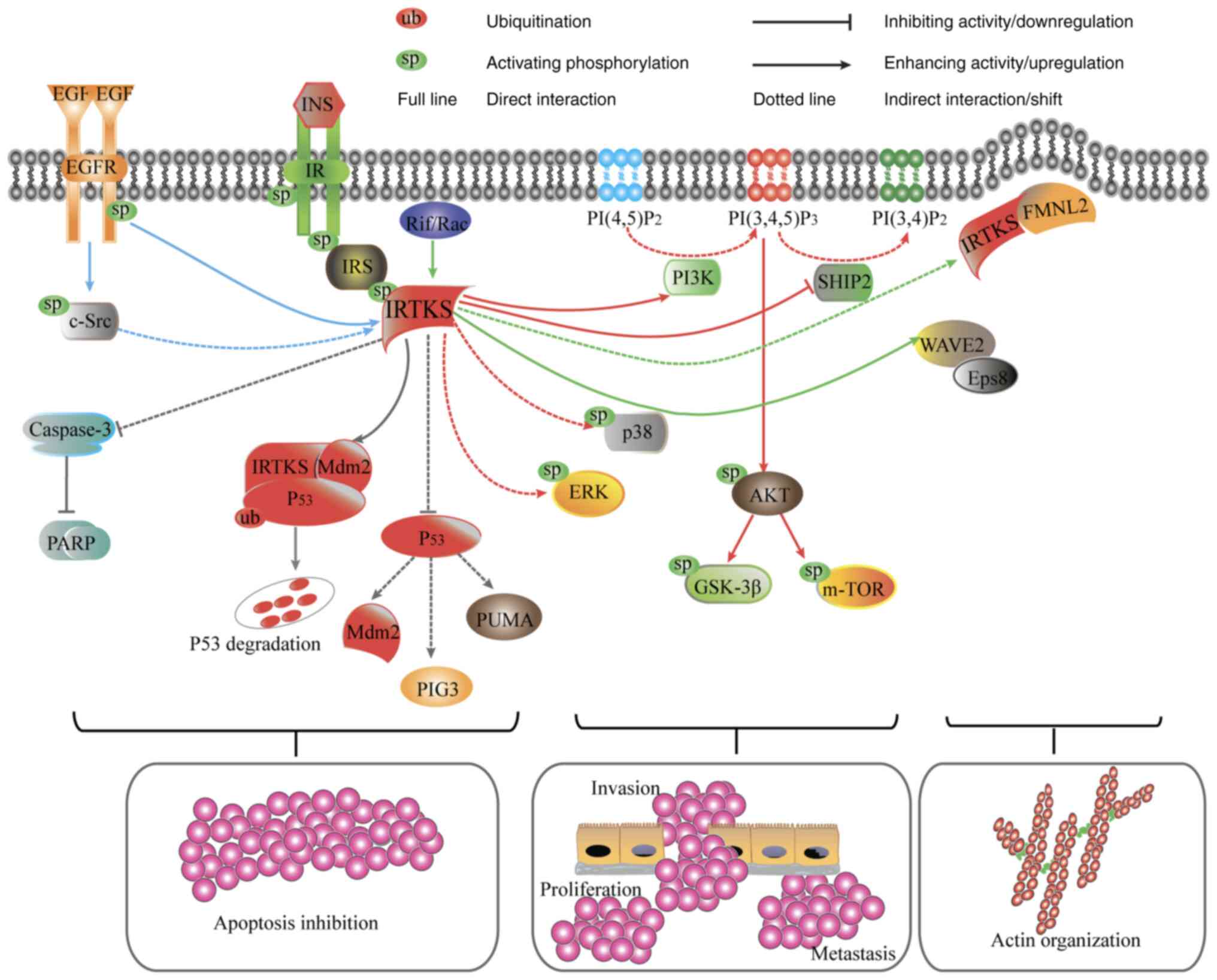
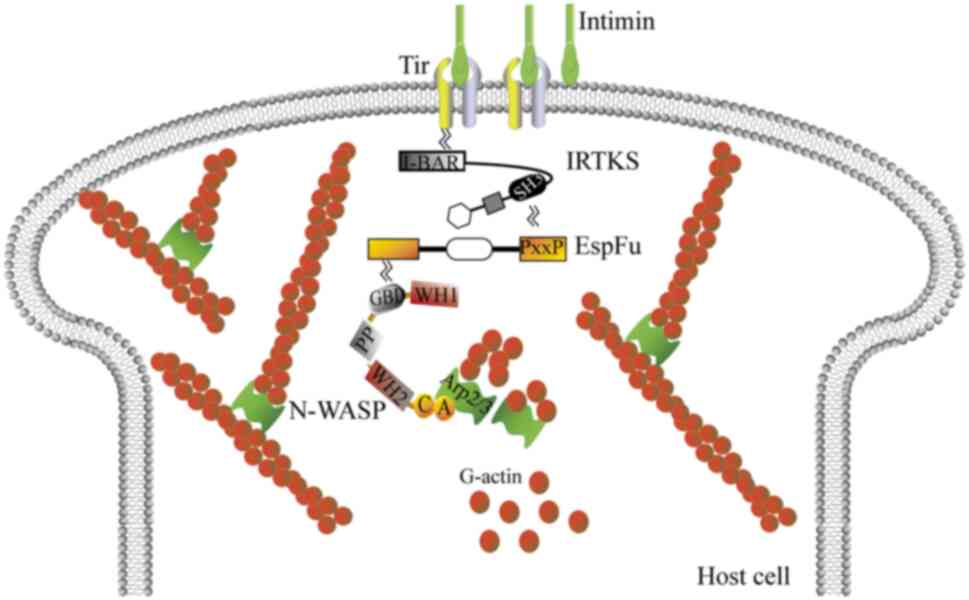
|
1
|
Millard TH, Dawson J and Machesky LM:
Characterisation of IRTKS, a novel IRSp53/MIM family actin
regulator with distinct filament bundling properties. J Cell Sci.
120:1663–1672. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Saarikangas J, Zhao HX, Pykäläinen A,
Laurinmäki P, Mattila PK, Kinnunen PK, Butcher SJ and Lappalainen
P: Molecular mechanisms of membrane deformation by I-BAR domain
proteins. Curr Biol. 19:95–107. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yamagishi A, Masuda M, Ohki T, Onishi H
and Mochizuki N: A novel actin bundling/filopodium-forming domain
conserved in insulin receptor tyrosine kinase substrate p53 and
missing in metastasis protein. J Biol Chem. 279:14929–14936. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fagerberg L, Hallstrom BM, Oksvold P,
Kampf C, Djureinovic D, Odeberg J, Habuka M, Tahmasebpoor S,
Danielsson A, Edlund K, et al: Analysis of the human
tissue-specific expression by genome-wide integration of
transcriptomics and antibody-based proteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics.
13:397–406. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hu RM, Han ZG, Song HD, Peng YD, Huang QH,
Ren SX, Gu YJ, Huang CH, Li YB, Jiang CL, et al: Gene expression
profiling in the human hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis and
full-length cDNA cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:9543–9548.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Peter BJ, Kent HM, Mills IG, Vallis Y,
Butler PJ, Evans PR and McMahon HT: BAR domains as sensors of
membrane curvature: The amphiphysin BAR structure. Science.
303:495–499. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhao HX, Pykäläinen A and Lappalainen P:
I-BAR domain proteins: Linking actin and plasma membrane dynamics.
Curr Opin Cell Biol. 23:14–21. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Frost A, Unger VM and De Camilli P: The
BAR domain superfamily: Membrane-molding macromolecules. Cell.
137:191–196. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Qualmann B, Koch D and Kessels MM: Let's
go bananas: Revisiting the endocytic BAR code. EMBO J.
30:3501–3515. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Suetsugu S, Toyooka K and Senju Y:
Subcellular membrane curvature mediated by the BAR domain
superfamily proteins. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 21:340–349. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mullins RD, Heuser JA and Pollard TD: The
interaction of Arp2/3 complex with actin: Nucleation, high affinity
pointed end capping, and formation of branching networks of
filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:6181–6186. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bompard G and Caron E: Regulation of
WASP/WAVE proteins: Making a long story short. J Cell Biol.
166:957–962. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Machesky LM and Insall RH: Scar1 and the
related Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein, WASP, regulate the actin
cytoskeleton through the Arp2/3 complex. Curr Biol. 8:1347–1356.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pollard TD and Borisy GG: Cellular
motility driven by assembly and disassembly of actin filaments.
Cell. 112:453–465. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bear JE, Svitkina TM, Krause M, Schafer
DA, Loureiro JJ, Strasser GA, Maly IV, Chaga OY, Cooper JA, Borisy
GG and Gertler FB: Antagonism between Ena/VASP proteins and actin
filament capping regulates fibroblast motility. Cell. 109:509–521.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lebrand C, Dent EW, Strasser GA, Lanier
LM, Krause M, Svitkina TM, Borisy GG and Gertler FB: Critical role
of Ena/VASP proteins for filopodia formation in neurons and in
function downstream of netrin-1. Neuron. 42:37–49. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pellegrin S and Mellor H: The Rho family
GTPase Rif induces filopodia through mDia2. Curr Biol. 15:129–133.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Revenu C, Athman R, Robine S and Louvard
D: The co-workers of actin filaments: From cell structures to
signals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 5:635–646. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Vignjevic D, Kojima S, Aratyn Y, Danciu O,
Svitkina T and Borisy GG: Role of fascin in filopodial protrusion.
J Cell Biol. 174:863–875. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Krugmann S, Jordens I, Gevaert K,
Driessens M, Vandekerckhove J and Hall A: Cdc42 induces filopodia
by promoting the formation of an IRSp53:Mena complex. Curr Biol.
11:1645–1655. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Disanza A, Mantoani S, Hertzog M, Gerboth
S, Frittoli E, Steffen A, Berhoerster K, Kreienkamp HJ, Milanesi F,
Di Fiore PP, et al: Regulation of cell shape by Cdc42 is mediated
by the synergic actin-bundling activity of the Eps8-IRSp53 complex.
Nat Cell Biol. 8:1337–1347. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Suetsugu S, Kurisu S, Oikawa T, Yamazaki
D, Oda A and Takenawa T: Optimization of WAVE2 complex-induced
actin polymerization by membrane-bound IRSp53, PIP(3), and Rac. J
Cell Biol. 173:571–585. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Goh WI, Lim KB, Sudhaharan T, Sem KP, Bu
W, Chou AM and Ahmed S: mDia1 and WAVE2 proteins interact directly
with IRSp53 in filopodia and are involved in filopodium formation.
J Biol Chem. 287:4702–4714. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Miki H, Yamaguchi H, Suetsugu S and
Takenawa T: IRSp53 is an essential intermediate between Rac and
WAVE in the regulation of membrane ruffling. Nature. 408:732–735.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fujiwara T, Mammoto A, Kim Y and Takai Y:
Rho small G-protein-dependent binding of mDia to an Src homology 3
domain-containing IRSp53/BAIAP2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
271:626–629. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chou AM, Sem KP, Wright GD, Sudhaharan T
and Ahmed S: Dynamin1 is a novel target for IRSp53 protein and
works with mammalian enabled (Mena) protein and Eps8 to regulate
filopodial dynamics. J Biol Chem. 289:24383–24396. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sudhaharan T, Sem KP, Liew HF, Yu YH, Goh
WI, Chou AM and Ahmed S: The Rho GTPase Rif signals through IRTKS,
Eps8 and WAVE2 to generate dorsal membrane ruffles and filopodia. J
Cell Sci. 129:2829–2840. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Crepin VF, Girard F, Schüller S, Phillips
AD, Mousnier A and Frankel G: Dissecting the role of the Tir:Nck
and Tir:IRTKS/IRSp53 signalling pathways in vivo. Mol Microbiol.
75:308–323. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li T, Cheng Z, Wang K, Chen F, Han Z and
Zhang X: Cloning and expressing of IRTKS and its effect on cell
morphology. J Med Mol Biol. 6:214–218. 2009.
|
|
30
|
Fox S, Tran A, Trinkle-Mulcahy L and
Copeland JW: Cooperative assembly of filopodia by the formin FMNL2
and I-BAR domain protein IRTKS. J Biol Chem. 298:1025122022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tapon N and Hall A: Rho, Rac and Cdc42
GTPases regulate the organization of the actin cytoskeleton. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 9:86–92. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hall A: Ras-related GTPases and the
cytoskeleton. Mol Biol Cell. 3:475–479. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Campellone KG, Brady MJ, Alamares JG, Rowe
DC, Skehan BM, Tipper DJ and Leong JM: Enterohaemorrhagic
Escherichia coli Tir requires a C-terminal 12-residue
peptide to initiate EspF-mediated actin assembly and harbours
N-terminal sequences that influence pedestal length. Cell
Microbiol. 8:1488–1503. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kühn S, Erdmann C, Kage F, Block J,
Schwenkmezger L, Steffen A, Rottner K and Geyer M: The structure of
FMNL2-Cdc42 yields insights into the mechanism of lamellipodia and
filopodia formation. Nat Commun. 6:70882015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Young LE, Heimsath EG and Higgs HN: Cell
type-dependent mechanisms for formin-mediated assembly of
filopodia. Mol Biol Cell. 26:4646–4659. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Veltman DM, Auciello G, Spence HJ,
Machesky LM, Rappoport JZ and Insall RH: Functional analysis of
Dictyostelium IBARa reveals a conserved role of the I-BAR domain in
endocytosis. Biochem J. 436:45–52. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li LS, Baxter SS, Zhao P, Gu N and Zhan X:
Differential interactions of missing in metastasis and insulin
receptor tyrosine kinase substrate with RAB proteins in the
endocytosis of CXCR4. J Biol Chem. 294:6494–6505. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Postema MM, Grega-Larson NE, Neininger AC
and Tyska MJ: IRTKS (BAIAP2L1) elongates epithelial microvilli
using EPS8-dependent and independent mechanisms. Curr Biol.
28:2876–2888.e4. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Meenderink LM, Gaeta IM, Postema MM,
Cencer CS, Chinowsky CR, Krystofiak ES, Millis BA and Tyska MJ:
Actin dynamics drive microvillar motility and clustering during
brush border assembly. Dev Cell. 50:545–556.e4. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gaeta IM, Meenderink LM, Postema MM,
Cencer CS and Tyska MJ: Direct visualization of epithelial
microvilli biogenesis. Curr Biol. 31:2561–2575.e6. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shifrin DA Jr, McConnell RE, Nambiar R,
Higginbotham JN, Coffey RJ and Tyska MJ: Enterocyte
microvillus-derived vesicles detoxify bacterial products and
regulate epithelial-microbial interactions. Curr Biol. 22:627–631.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Vallance BA, Chan C, Robertson ML and
Finlay BB: Enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia
coli infections: Emerging themes in pathogenesis and
prevention. Can J Gastroenterol. 16:771–778. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kaper JB, Nataro JP and Mobley HL:
Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2:123–140.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Campellone KG and Leong JM: Tails of two
Tirs: Actin pedestal formation by enteropathogenic E. coli
and enterohemorrhagic E. coli O157:H7. Curr Opin Microbiol.
6:82–90. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Allen-Vercoe E, Waddell B, Toh MC and
DeVinney R: Amino acid residues within enterohemorrhagic
Escherichia coli O157:H7 Tir involved in phosphorylation,
alpha-actinin recruitment, and Nck-independent pedestal formation.
Infect Immun. 74:6196–6205. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Brady MJ, Campellone KG, Ghildiyal M and
Leong JM: Enterohaemorrhagic and enteropathogenic Escherichia
coli Tir proteins trigger a common Nck-independent actin
assembly pathway. Cell Microbiol. 9:2242–2253. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Coburn B, Sekirov I and Finlay BB: Type
III secretion systems and disease. Clin Microbiol Rev. 20:535–549.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Loquet A, Sgourakis NG, Gupta R, Giller K,
Riedel D, Goosmann C, Griesinger C, Kolbe M, Baker D, Becker S and
Lange A: Atomic model of the type III secretion system needle.
Nature. 486:276–279. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Campellone KG: Cytoskeleton-modulating
effectors of enteropathogenic and enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia
coli: Tir, EspFU and actin pedestal assembly. FEBS J.
277:2390–2402. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Vingadassalom D, Kazlauskas A, Skehan B,
Cheng HC, Magoun L, Robbins D, Rosen MK, Saksela K and Leong JM:
Insulin receptor tyrosine kinase substrate links the E. coli
O157:H7 actin assembly effectors Tir and EspF(U) during pedestal
formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:6754–6759. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Aitio O, Hellman M, Kazlauskas A,
Vingadassalom DF, Leong JM, Saksela K and Permi P: Recognition of
tandem PxxP motifs as a unique Src homology 3-binding mode triggers
pathogen-driven actin assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:21743–21748. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Aitio O, Hellman M, Skehan B, Kesti T,
Leong JM, Saksela K and Permi P: Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia
coli exploits a tryptophan switch to hijack host f-actin
assembly. Structure. 20:1692–1703. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Huang LY, Wang YP, Wei BF, Yang J, Wang
JQ, Wu BH, Zhang ZZ, Hou YY, Sun WM, Hu RM, et al: Deficiency of
IRTKS as an adaptor of insulin receptor leads to insulin
resistance. Cell Res. 23:1310–1321. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wu CC, Cui XF, Huang LY, Shang X, Wu B,
Wang N, He K and Han Z: IRTKS promotes insulin signaling
transduction through inhibiting SHIP2 phosphatase activity. Int J
Mol Sci. 20:28342019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wang S, Liu Z, Ma YM, Guan X, Jiang Z, Sun
P, Liu ER, Zhang YK, Wang HY and Wang XS: Upregulated insulin
receptor tyrosine kinase substrate promotes the proliferation of
colorectal cancer cells via the bFGF/AKT signaling pathway.
Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 9:166–175. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Chao A, Tsai CL, Jung SM, Chuang WC, Kao
C, Hsu A, Chen SH, Lin CY, Lee YC, Lee YS, et al: BAI1-associated
protein 2-like 1 (BAIAP2L1) is a potential biomarker in ovarian
cancer. PLoS One. 10:e01330812015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Huang LY, Wang XF, Cui XF, Li H, Zhao J,
Wu CC, Min L, Zhou Z, Wan L, Wang YP, et al: IRTKS is correlated
with progression and survival time of patients with gastric cancer.
Gut. 67:1400–1409. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wang YP, Huang LY, Sun WM, Zhang ZZ, Fang
JZ, Wei BF, Wu BH and Han ZG: Insulin receptor tyrosine kinase
substrate activates EGFR/ERK signalling pathway and promotes cell
proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 337:96–106.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Lu Y, Zhou XY, Zhou CL, Liu J, Yong T, Fan
Y and Wang C: Insulin receptor tyrosine kinase substrate (IRTKS)
promotes the tumorigenesis of pancreatic cancer via PI3K/AKT
signaling. Hum Cell. 35:1885–1899. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Zhang H, Ma H, Yang X, Fan L, Tian S, Niu
R, Yan M, Zheng M and Zhang S: Cell fusion-related proteins and
signaling pathways, and their roles in the development and
progression of cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:8096682022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Oikawa T and Matsuo K: Possible role of
IRTKS in Tks5-driven osteoclast fusion. Commun Integr Biol.
5:511–515. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Li M, Brooks CL, Wu-Baer F, Chen D, Baer R
and Gu W: Mono-versus polyubiquitination: Differential control of
p53 fate by Mdm2. Science. 302:1972–1975. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Li LS, Liu HY, Baxter SS, Gu N, Ji M and
Zhan X: The SH3 domain distinguishes the role of I-BAR proteins
IRTKS and MIM in chemotactic response to serum. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 479:787–792. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Bromann PA, Korkaya H and Courtneidge SA:
The interplay between Src family kinases and receptor tyrosine
kinases. Oncogene. 23:7957–7968. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Chen G, Li T, Zhang L, Yi M, Chen F, Wang
Z and Zhang X: Src-stimulated IRTKS phosphorylation enhances cell
migration. FEBS Lett. 585:2972–2978. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Ebadi Zavieh S and Safari F: The antitumor
activity of hAMSCs secretome in HT-29 colon cancer cells through
downregulation of EGFR/c-Src/IRTKS expression and p38/ERK1/2
phosphorylation. Cell Biochem Biophys. 80:395–402. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Wang KS, Chen G, Shen HL, Li TT, Chen F,
Wang QW, Wang ZQ, Han ZG and Zhang X: Insulin receptor tyrosine
kinase substrate enhances low levels of MDM2-mediated p53
ubiquitination. PLoS One. 6:e235712011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
D'Amours D, Sallmann FR, Dixit VM and
Poirier GG: Gain-of-function of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 upon
cleavage by apoptotic proteases: Implications for apoptosis. J Cell
Sci. 114:3771–3778. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Hickman ES, Moroni MC and Helin K: The
role of p53 and pRB in apoptosis and cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev.
12:60–66. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Nakanishi Y, Akiyama N, Tsukaguchi T,
Fujii T, Satoh Y, Ishii N and Aoki M: Mechanism of oncogenic signal
activation by the novel fusion kinase FGFR3-BAIAP2L1. Mol Cancer
Ther. 14:704–712. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Williams SV, Hurst CD and Knowles MA:
Oncogenic FGFR3 gene fusions in bladder cancer. Hum Mol Genet.
22:795–803. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Wu YM, Su F, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Khazanov
N, Ateeq B, Cao X, Lonigro RJ, Vats P, Wang R, Lin SF, et al:
Identification of targetable FGFR gene fusions in diverse cancers.
Cancer Discov. 3:636–647. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Wu G, Barnhill RL, Lee S, Li Y, Shao Y,
Easton J, Dalton J, Zhang J, Pappo A and Bahrami A: The landscape
of fusion transcripts in spitzoid melanoma and biologically
indeterminate spitzoid tumors by RNA sequencing. Mod Pathol.
29:359–369. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Guo R, Luo J, Chang J, Rekhtman N, Arcila
M and Drilon A: MET-dependent solid tumours-molecular diagnosis and
targeted therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 17:569–587. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Stransky N, Cerami E, Schalm S, Kim JL and
Lengauer C: The landscape of kinase fusions in cancer. Nat Commun.
5:48462014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Cui XF, Shang XY, Xie J, Xie C, Tang Z,
Luo Q, Wu C, Wang G, Wang N, He K, et al: Cooperation between IRTKS
and deubiquitinase OTUD4 enhances the SETDB1-mediated H3K9
trimethylation that promotes tumor metastasis via suppressing
E-cadherin expression. Cancer Lett. 575:2164042023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Xie J, Lu ZN, Bai SH, Cui XF, Lian HY, Xie
CY, Wang N, Wang L and Han ZG: Heterochromatin formation and
remodeling by IRTKS condensates counteract cellular senescence.
EMBO J. 43:4542–4577. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Yuan GF, Ding WW, Sun BJ, Zhu L, Gao YW
and Chen LL: Upregulated circRNA_102231 promotes gastric cancer
progression and its clinical significance. Bioengineered.
12:4936–4945. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Chou AM, Sem KP, Lam WJ, Ahmed S and Lim
CY: Redundant functions of I-BAR family members, IRSp53 and IRTKS,
are essential for embryonic development. Sci Rep. 7:404852017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Galligan CL, Baig E, Bykerk V, Keystone EC
and Fish EN: Distinctive gene expression signatures in rheumatoid
arthritis synovial tissue fibroblast cells: Correlates with disease
activity. Genes Immun. 8:480–491. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Xia P, Wang S, Xiong Z, Ye B, Huang LY,
Han ZG and Fan Z: IRTKS negatively regulates antiviral immunity
through PCBP2 sumoylation-mediated MAVS degradation. Nat Commun.
6:81322015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Rehwinkel J and Gack MU: RIG-I-like
receptors: Their regulation and roles in RNA sensing. Nat Rev
Immunol. 20:537–551. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Naesens L, Haerynck F and Gack MU: The RNA
polymerase III-RIG-I axis in antiviral immunity and inflammation.
Trends Immunol. 44:435–449. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Makeyev AV and Liebhaber SA: The
poly(C)-binding proteins: a multiplicity of functions and a search
for mechanisms. RNA. 8:265–278. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Rousseau G, Reynier P, Jousset N,
Rougé-Maillart C and Palmiere C: Updated review of postmortem
biochemical exploration of hypothermia with a presentation of
standard strategy of sampling and analyses. Clin Chem Lab Med.
56:1819–1827. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Elmsjö A, Ward LJ, Horioka K, Watanabe S,
Kugelberg FC, Druid H and Green H: Biomarker patterns and
mechanistic insights into hypothermia from a postmortem
metabolomics investigation. Sci Rep. 14:189722024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Bańka K, Teresiński G and Buszewicz G:
Free fatty acids as markers of death from hypothermia. Forensic Sci
Int. 234:79–85. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Takamiya M, Saigusa K and Dewa K: DNA
microarray analysis of hypothermia-exposed murine lungs for
identification of forensic biomarkers. Leg Med (Tokyo).
48:1017892021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Peng Y, Wang Y, Zhou C, Mei W and Zeng C:
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and its role in cancer therapeutics: Are we
making headway? Front Oncol. 12:8191282022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Ramasubbu K and Devi Rajeswari V:
Impairment of insulin signaling pathway PI3K/Akt/mTOR and insulin
resistance induced AGEs on diabetes mellitus and neurodegenerative
diseases: A perspective review. Mol Cell Biochem. 478:1307–1324.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Ebrahimi N, Fardi E, Ghaderi H, Palizdar
S, Khorram R, Vafadar R, Ghanaatian M, Rezaei-Tazangi F, Baziyar P,
Ahmadi A, et al: Receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 80:1042023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Fares A, Carracedo Uribe C, Martinez D,
Rehman T, Silva Rondon C and Sandoval-Sus J: Bruton's tyrosine
kinase inhibitors: Recent updates. Int J Mol Sci. 25:22082024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Roskoski R Jr: Properties of FDA-approved
small molecule protein kinase inhibitors: A 2024 update. Pharmacol
Res. 200:1070592024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Nammour HM, Madrigal K, Starling CT and
Doan HQ: Advancing treatment options for merkel cell carcinoma: A
review of tumor-targeted therapies. Int J Mol Sci. 25:110552024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Bae WH, Maraka S and Daher A: Challenges
and advances in glioblastoma targeted therapy: The promise of drug
repurposing and biomarker exploration. Front Oncol. 14:14414602024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Myers SH, Brunton VG and Unciti-Broceta A:
AXL inhibitors in cancer: A medicinal chemistry perspective. J Med
Chem. 59:3593–3608. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Shyam Sunder S, Sharma UC and Pokharel S:
Adverse effects of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer therapy:
Pathophysiology, mechanisms and clinical management. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 8:2622023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|