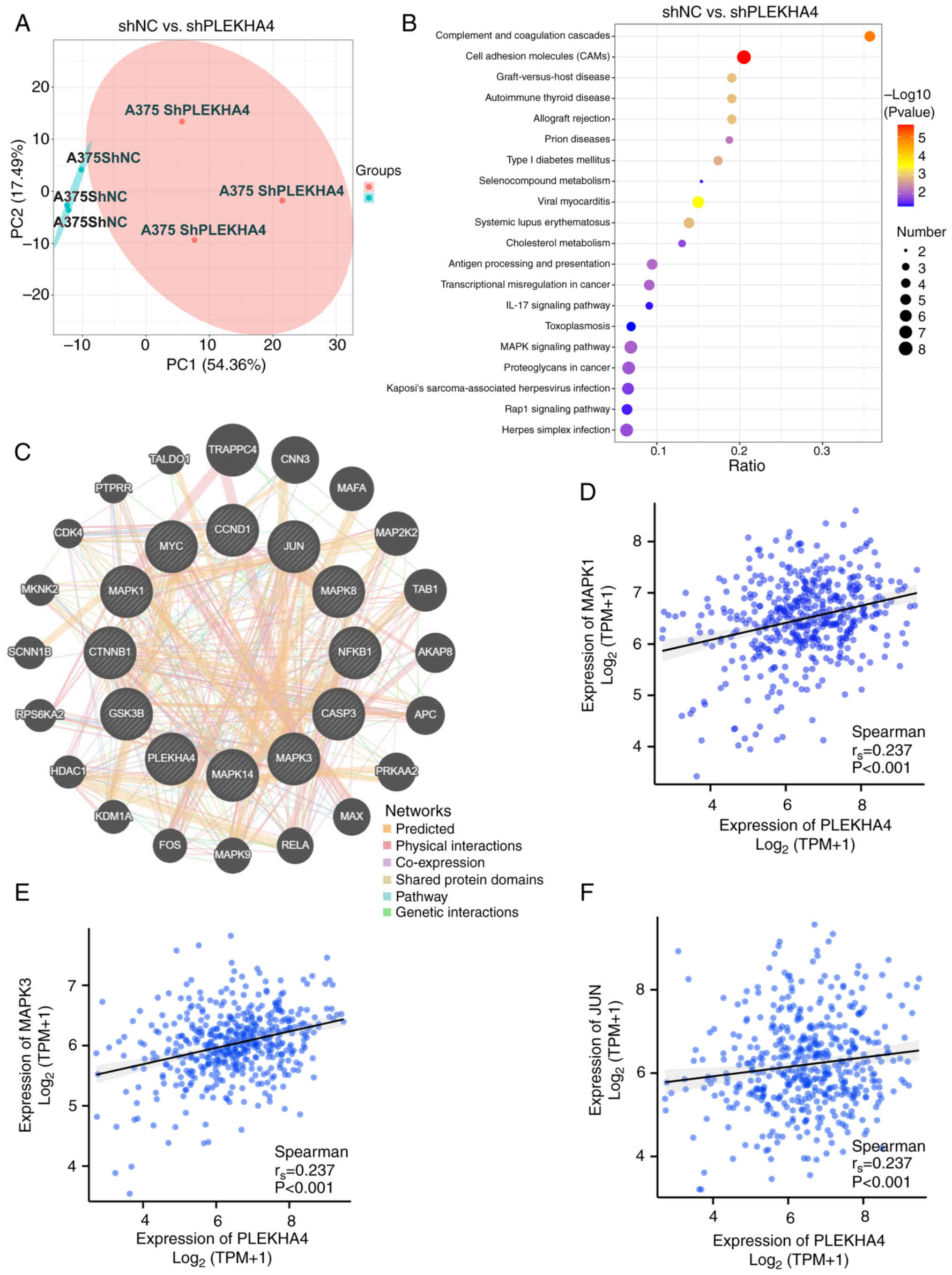
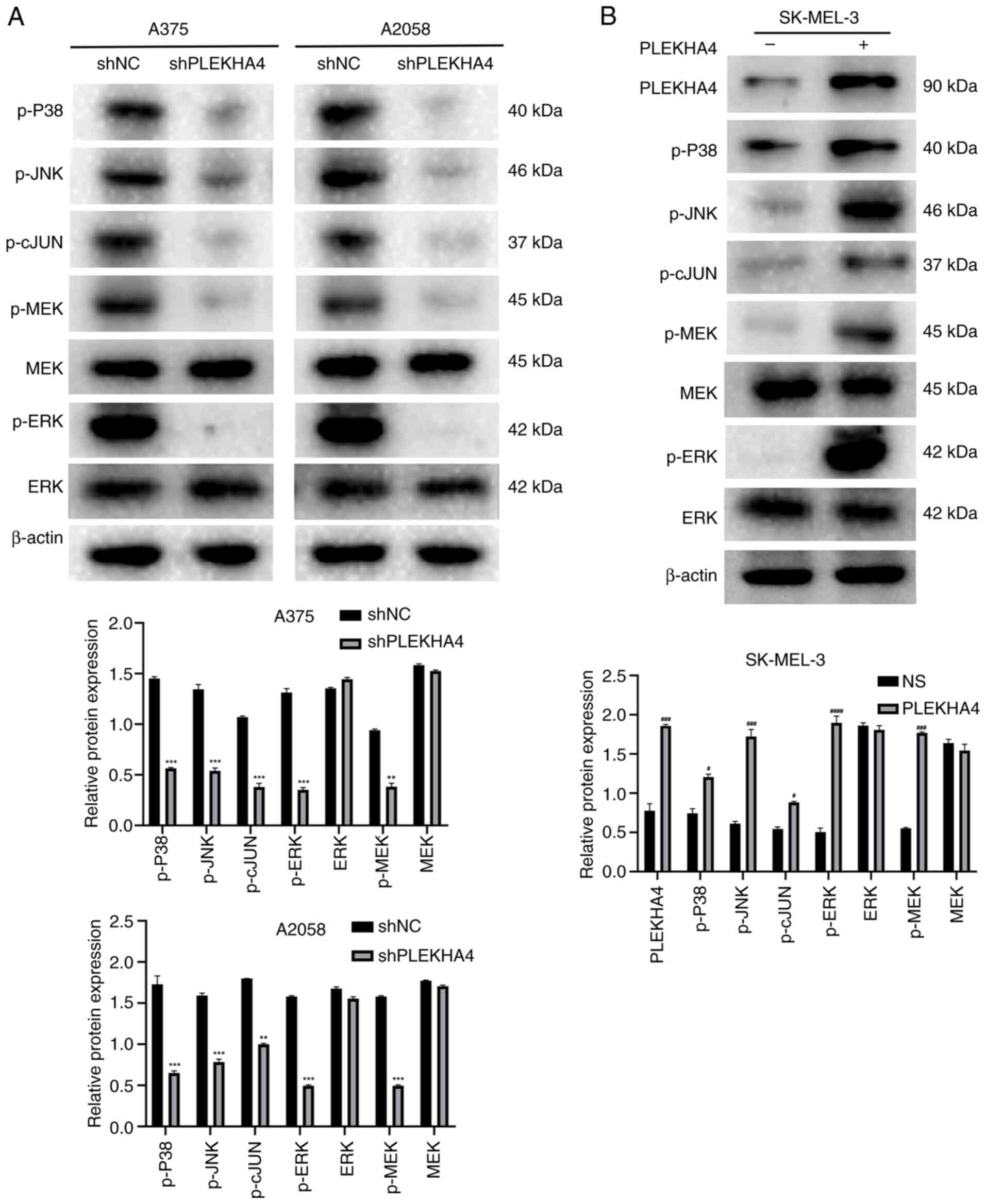
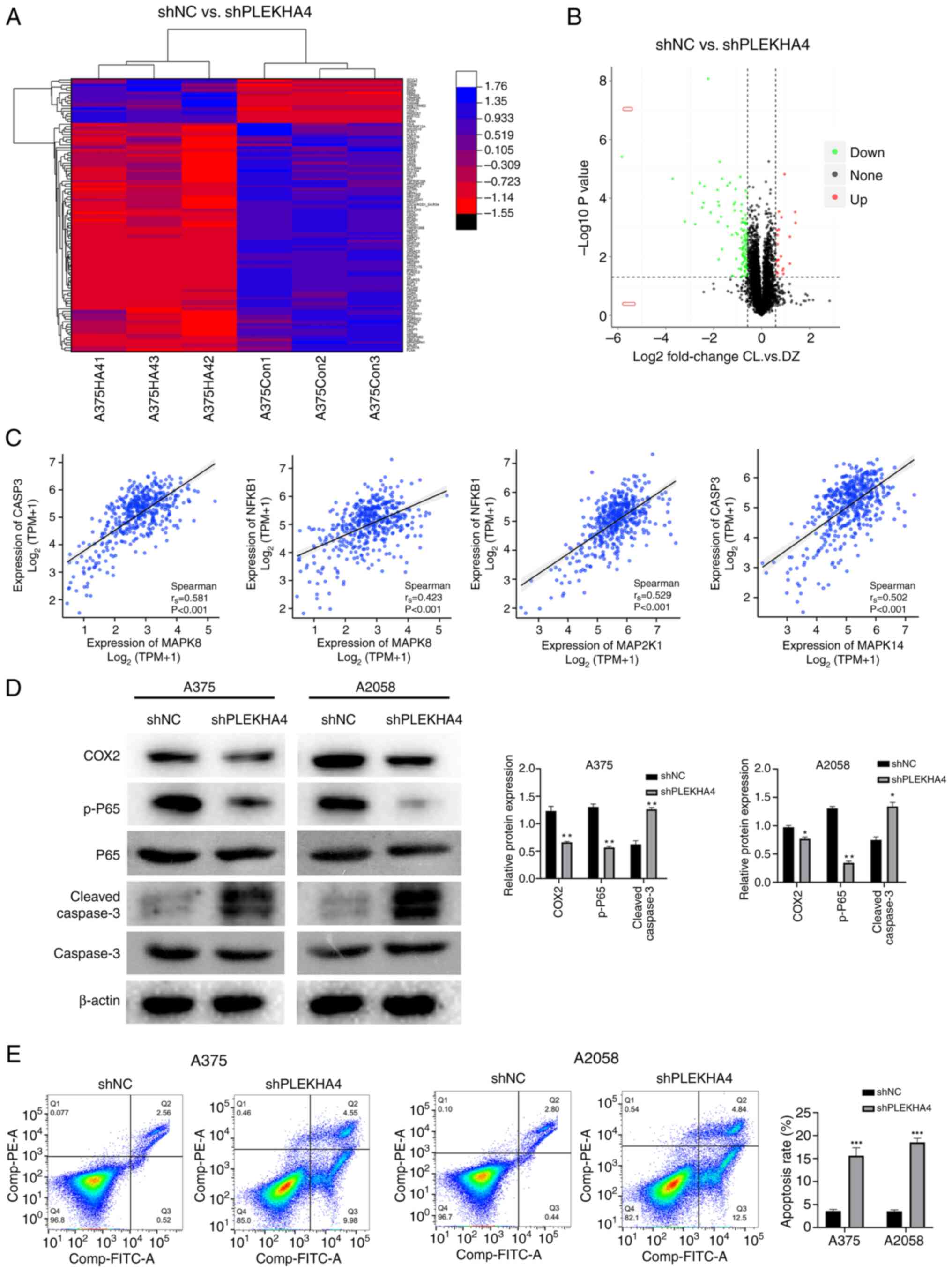
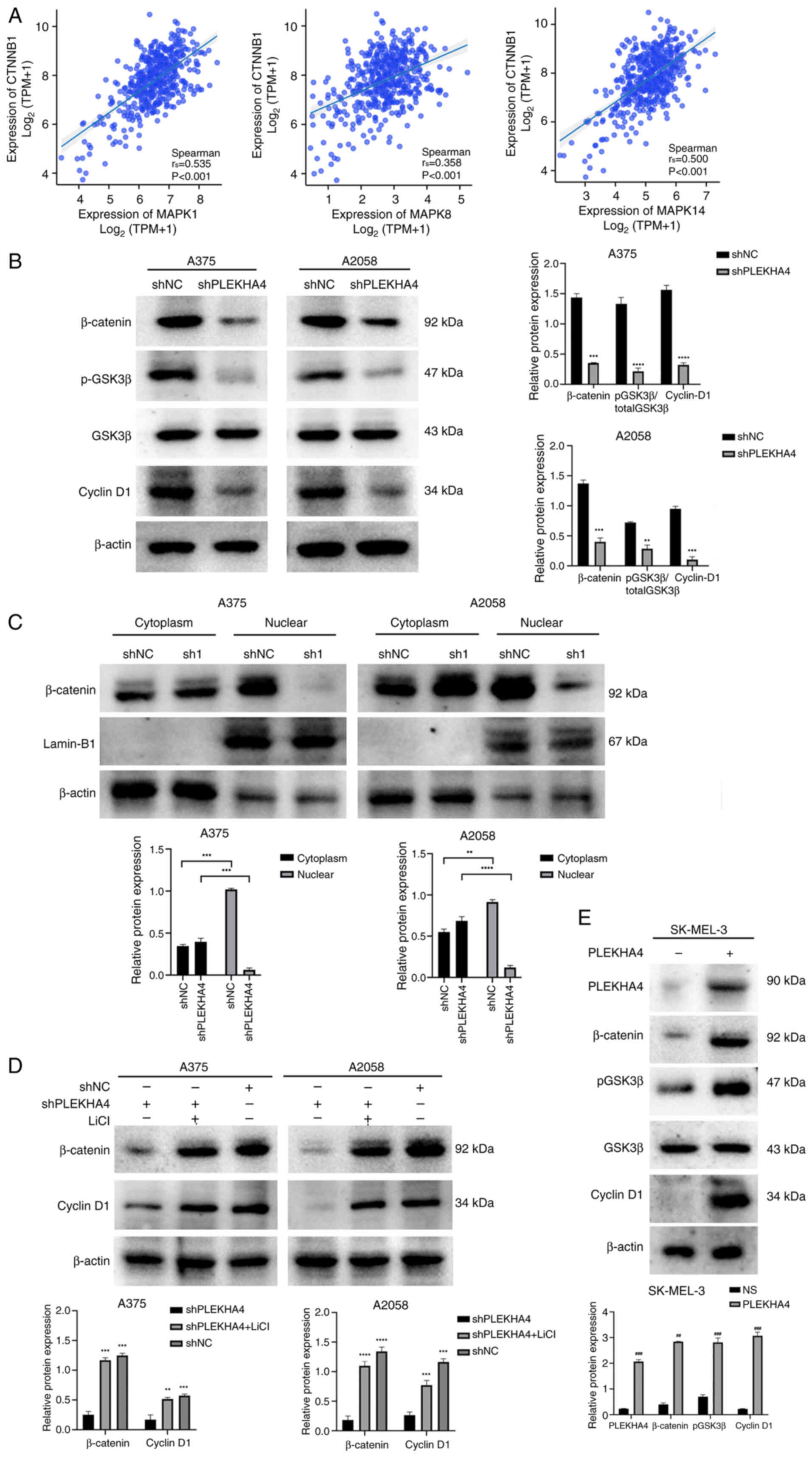
|
1
|
Sood S, Jayachandiran R and Pandey S:
Current advancements and novel strategies in the treatment of
metastatic melanoma. Integr Cancer Ther. 20:15347354219900782021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lee CS, Thomas CM and Ng KE: An overview
of the changing landscape of treatment for advanced melanoma.
Pharmacotherapy. 37:319–333. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
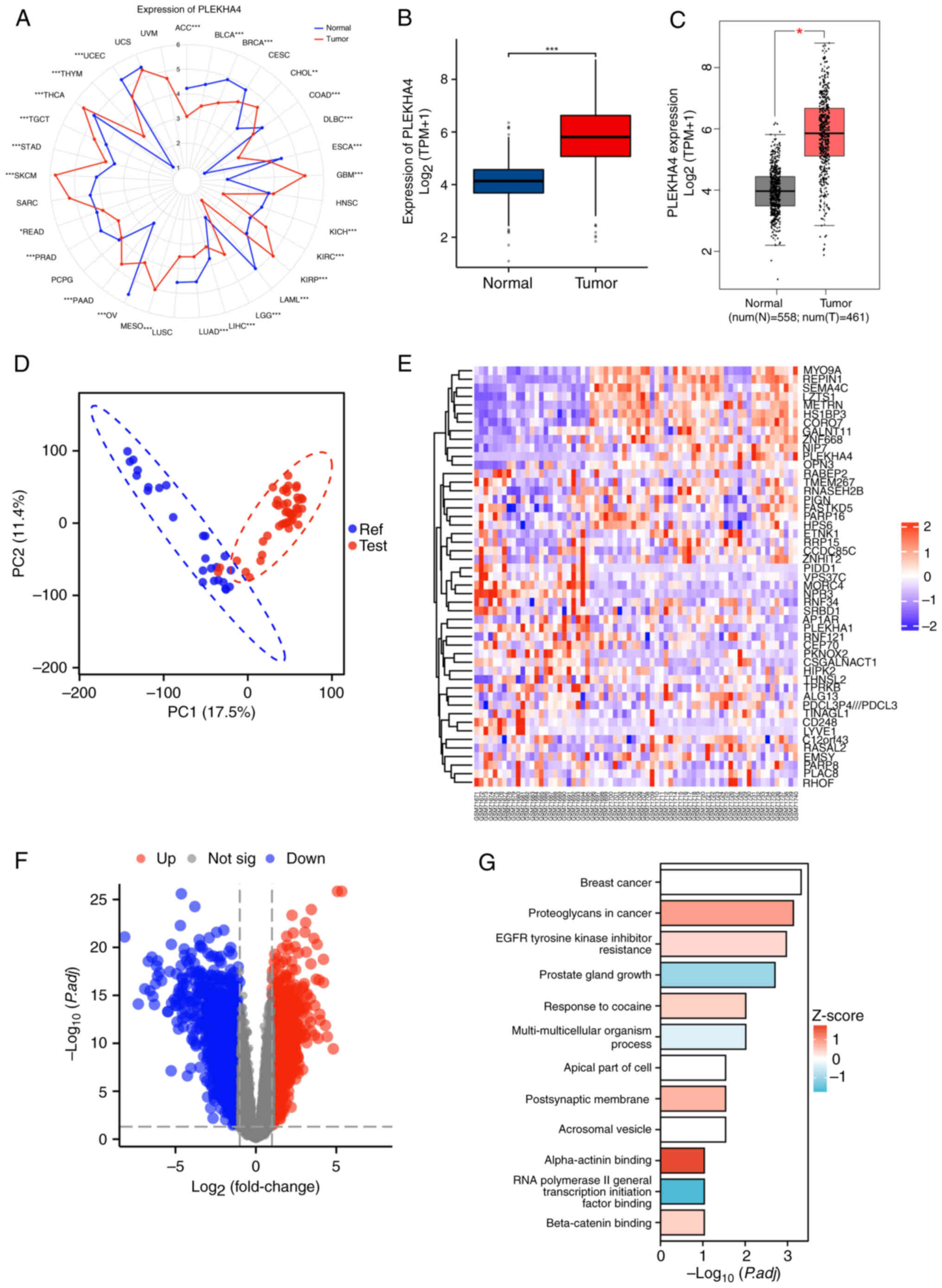
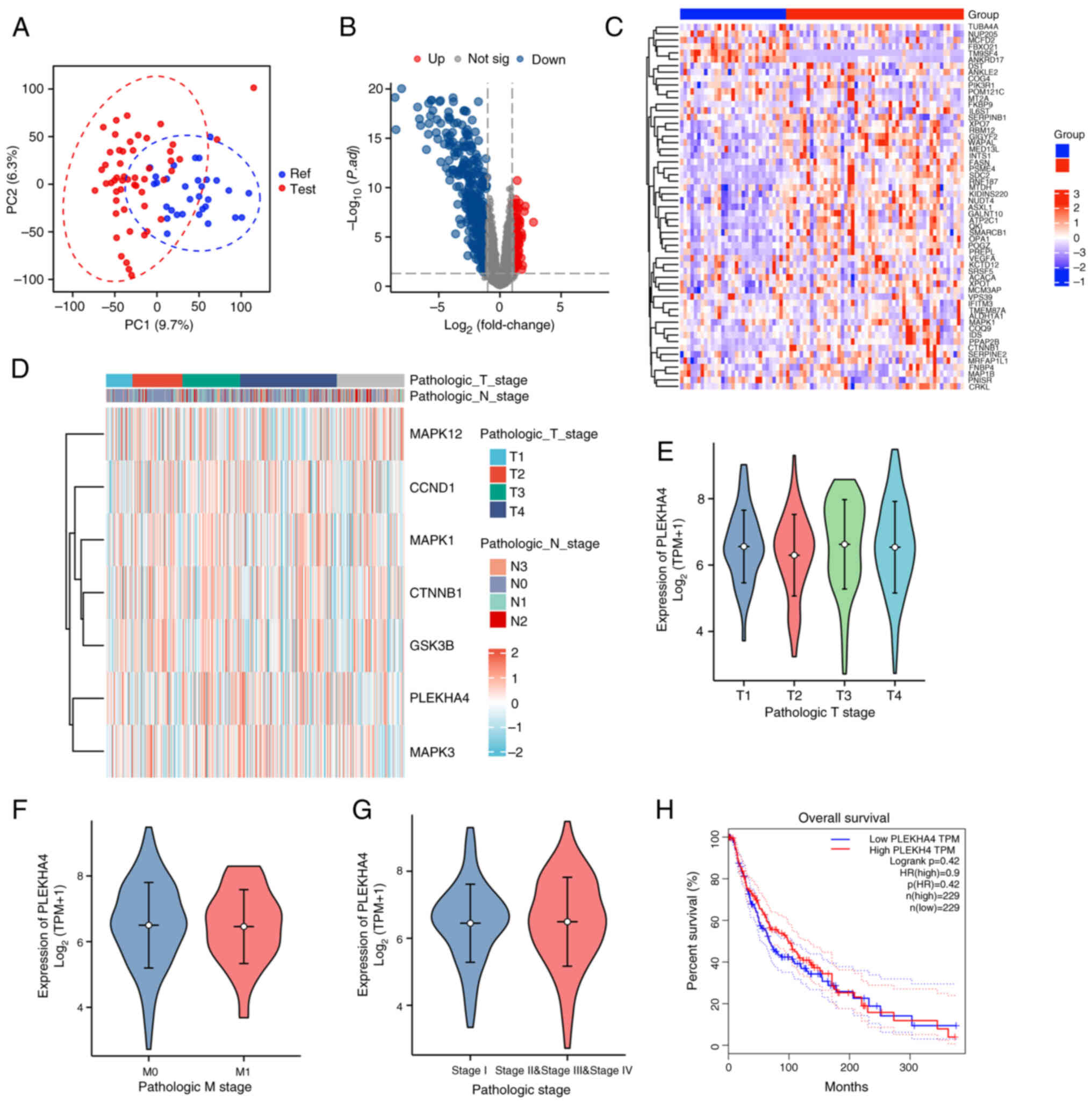
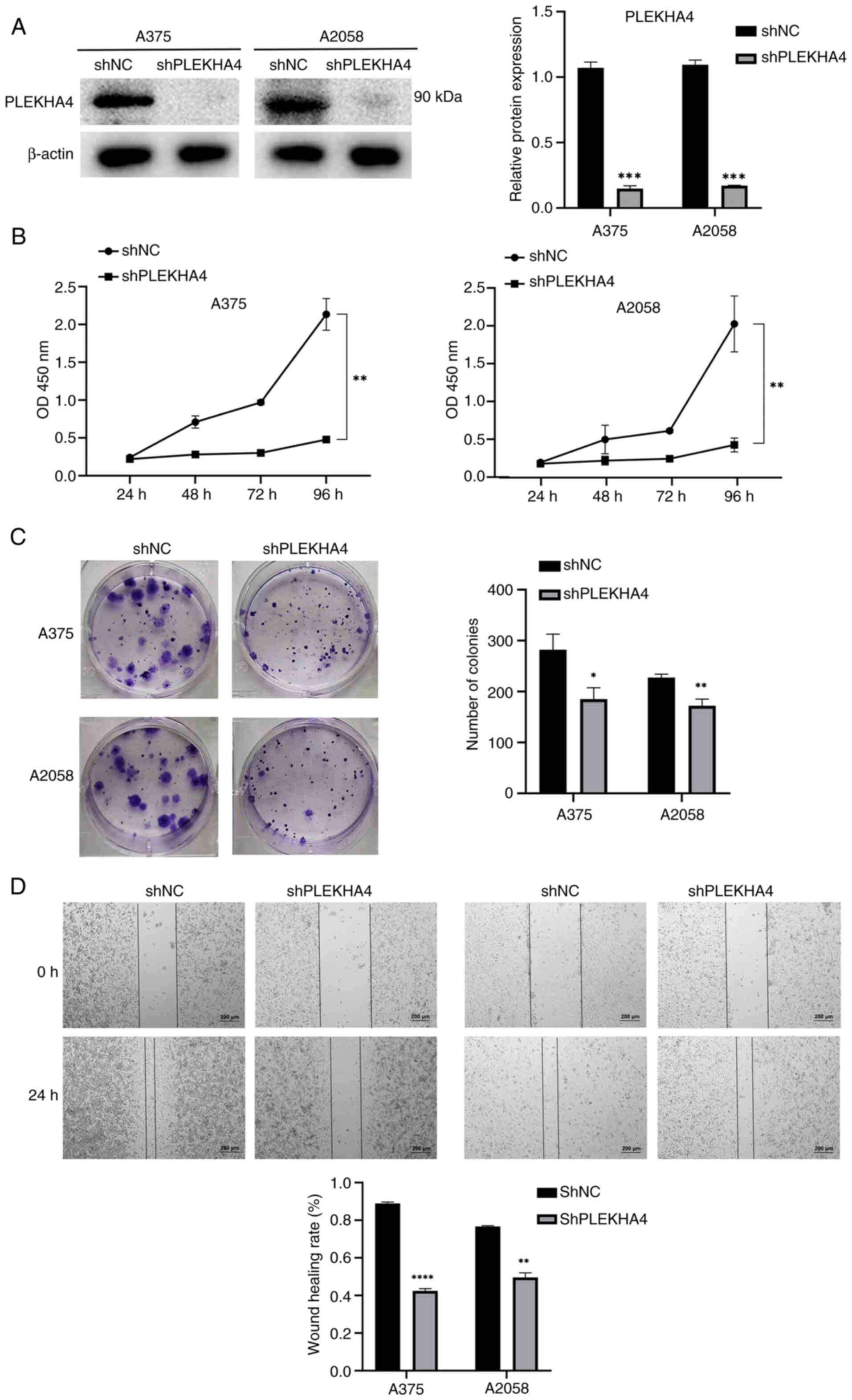
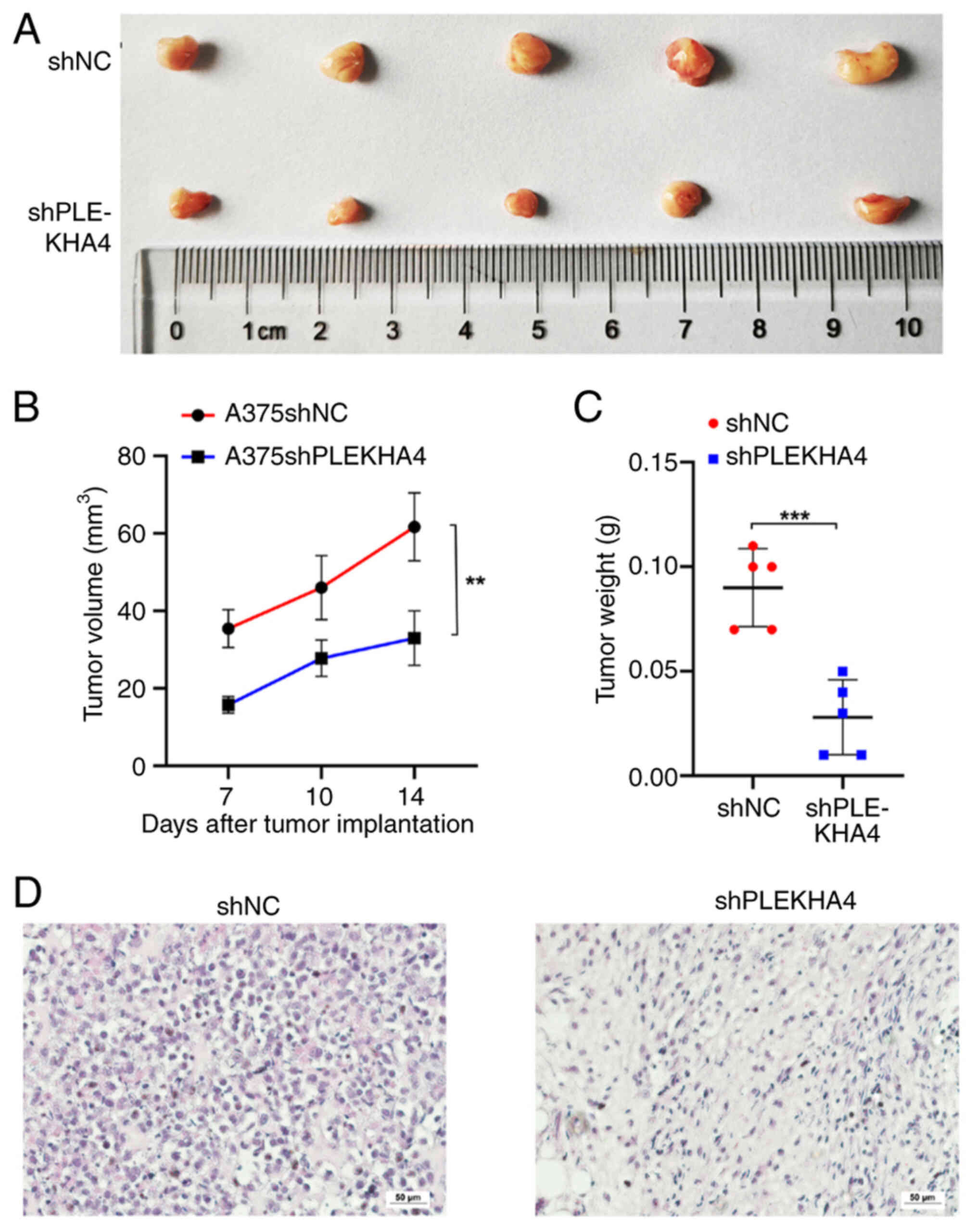
|
3
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Network, . Genomic
classification of cutaneous melanoma. Cell. 161:1681–1696. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Inamdar GS, Madhunapantula SV and
Robertson GP: Targeting the MAPK pathway in melanoma: Why some
approaches succeed and other fail. Biochem Pharmacol. 80:624–637.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Samatar AA and Poulikakos PI: Targeting
RAS-ERK signalling in cancer: Promises and challenges. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 13:928–942. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Braicu C, Buse M, Busuioc C, Drula R,
Gulei D, Raduly L, Rusu A, Irimie A, Atanasov AG, Slaby O, et al: A
comprehensive review on MAPK: A promising therapeutic target in
cancer. Cancers (Basel). 11:16182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhan T, Rindtorff N and Boutros M: Wnt
signaling in cancer. Oncogene. 36:1461–1473. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang Y and Wang X: Targeting the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in cancer. J Hematol Oncol.
13:1652020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gajos-Michniewicz A and Czyz M: WNT
signaling in melanoma. Int J Mol Sci. 21:48522020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pawlikowski JS, McBryan T, van Tuyn J,
Drotar ME, Hewitt RN, Maier AB, King A, Blyth K, Wu H and Adams PD:
Wnt signaling potentiates nevogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:16009–16014. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Juan J, Muraguchi T, Iezza G, Sears RC and
McMahon M: Diminished WNT -> β-catenin -> c-MYC signaling is
a barrier for malignant progression of BRAFV600E-induced lung
tumors. Genes Dev. 28:561–575. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Damsky WE, Curley DP, Santhanakrishnan M,
Rosenbaum LE, Platt JT, Gould Rothberg BE, Taketo MM, Dankort D,
Rimm DL, McMahon M and Bosenberg M: β-catenin signaling controls
metastasis in Braf-activated Pten-deficient melanomas. Cancer Cell.
20:741–754. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sun Q, Lee W, Mohri Y, Takeo M, Lim CH, Xu
X, Myung P, Atit RP, Taketo MM, Moubarak RS, et al: A novel mouse
model demonstrates that oncogenic melanocyte stem cells engender
melanoma resembling human disease. Nat Commun. 10:50232019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chien AJ, Haydu LE, Biechele TL,
Kulikauskas RM, Rizos H, Kefford RF, Scolyer RA, Moon RT and Long
GV: Targeted BRAF inhibition impacts survival in melanoma patients
with high levels of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. PLoS One.
9:e947482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhi W, Wang Y, Jiang C, Gong Y, Chen Q,
Mao X, Deng W and Zhao S: PLEKHA4 is a novel prognostic biomarker
that reshapes the tumor microenvironment in lower-grade glioma.
Front Immunol. 14:11282442023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gao X, Liu Y, Hong S, Yang H, Guan B and
Ma X: PLEKHA4 is associated with tumour microenvironment, stemness,
proliferation and poor prognosis of gliomas. J Integr Neurosci.
22:1352023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
He Y, Zheng W, Huo Y, Sa L, Zhang H, He G
and Shang P: PLEKHA4 promotes glioblastoma progression through
apoptosis inhibition, tumor cell migration, and macrophage
infiltration. Immunobiology. 228:1527462023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shami Shah A, Batrouni AG, Kim D, Punyala
A, Cao W, Han C, Goldberg ML, Smolka MB and Baskin JM:
PLEKHA4/kramer attenuates dishevelled ubiquitination to modulate
Wnt and planar cell polarity signaling. Cell Rep. 27:2157–2170.e8.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Koelblinger P, Thuerigen O and Dummer R:
Development of encorafenib for BRAF-mutated advanced melanoma. Curr
Opin Oncol. 30:125–133. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Talantov D, Mazumder A, Yu JX, Briggs T,
Jiang Y, Backus J, Atkins D and Wang Y: Novel genes associated with
malignant melanoma but not benign melanocytic lesions. Clin Cancer
Res. 11:7234–7242. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jalili A, Mertz KD, Romanov J, Wagner C,
Kalthoff F, Stuetz A, Pathria G, Gschaider M, Stingl G and Wagner
SN: NVP-LDE225, a potent and selective SMOOTHENED antagonist
reduces melanoma growth in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One.
8:e690642013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Llombart V and Mansour MR: Therapeutic
targeting of ‘undruggable’ MYC. EBioMedicine. 75:1037562022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sun XX, Sears RC and Dai MS:
Deubiquitinating c-Myc: USP36 steps up in the nucleolus. Cell
Cycle. 14:3786–3793. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang YF, Jiang CC, Kiejda KA, Gillespie S,
Zhang XD and Hersey P: Apoptosis induction in human melanoma cells
by inhibition of MEK is caspase-independent and mediated by the
Bcl-2 family members PUMA, Bim, and Mcl-1. Clin Cancer Res.
13:4934–4942. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang J and Tai G: Role of C-Jun N-terminal
kinase in hepatocellular carcinoma development. Target Oncol.
11:723–738. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Feng C, He K, Zhang C, Su S, Li B, Li Y,
Duan CY, Chen S, Chen R, Liu Y, et al: JNK contributes to the
tumorigenic potential of human cholangiocarcinoma cells through the
mTOR pathway regulated GRP78 induction. PLoS One. 9:e903882014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lu Z and Xu S: ERK1/2 MAP kinases in cell
survival and apoptosis. IUBMB Life. 58:621–631. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sugiura R, Satoh R and Takasaki T: ERK: A
double-edged sword in cancer. ERK-dependent apoptosis as a
potential therapeutic strategy for cancer. Cells. 10:25092021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Thamkachy R, Kumar R, Rajasekharan KN and
Sengupta S: ERK mediated upregulation of death receptor 5 overcomes
the lack of p53 functionality in the diaminothiazole DAT1 induced
apoptosis in colon cancer models: Efficiency of DAT1 in Ras-Raf
mutated cells. Mol Cancer. 15:222016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pan R, Ruvolo V, Mu H, Leverson JD,
Nichols G, Reed JC, Konopleva M and Andreeff M: Synthetic lethality
of combined Bcl-2 inhibition and p53 activation in AML: Mechanisms
and superior antileukemic efficacy. Cancer Cell. 32:748–760.e6.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Park BG, Yoo CI, Kim HT, Kwon CH and Kim
YK: Role of mitogen-activated protein kinases in hydrogen
peroxide-induced cell death in osteoblastic cells. Toxicology.
215:115–125. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Boutahar N, Reynaud E, Lassabliere F and
Borg J: Timing differences of signaling response in neuron cultures
activated by glutamate analogue or free radicals. Brain Res.
1191:20–29. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gungor H, Ilhan N and Eroksuz H: The
effectiveness of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors and evaluation of
angiogenesis in the model of experimental colorectal cancer. Biomed
Pharmacother. 102:221–229. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Spano D and Catara G: Targeting the
ubiquitin-proteasome system and recent advances in cancer therapy.
Cells. 13:292023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jiang M, Qi L, Li L and Li Y: The
caspase-3/GSDME signal pathway as a switch between apoptosis and
pyroptosis in cancer. Cell Death Discov. 6:1122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sun SC: The non-canonical NF-κB pathway in
immunity and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 17:545–558. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nagendraprabhu P and Sudhandiran G:
Astaxanthin inhibits tumor invasion by decreasing extracellular
matrix production and induces apoptosis in experimental rat colon
carcinogenesis by modulating the expressions of ERK-2, NFkB and
COX-2. Invest New Drugs. 29:207–224. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang Q, Zhou Y, Rychahou P, Harris JW,
Zaytseva YY, Liu J, Wang C, Weiss HL, Liu C, Lee EY and Evers BM:
Deptor is a novel target of Wnt/β-Catenin/c-Myc and contributes to
colorectal cancer cell growth. Cancer Res. 78:3163–3175. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dang CV: MYC on the path to cancer. Cell.
149:22–35. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tsai WB, Aiba I, Long Y, Lin HK, Feun L,
Savaraj N and Kuo MT: Activation of Ras/PI3K/ERK pathway induces
c-Myc stabilization to upregulate argininosuccinate synthetase,
leading to arginine deiminase resistance in melanoma cells. Cancer
Res. 72:2622–2633. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen H, Liu H and Qing G: Targeting
oncogenic Myc as a strategy for cancer treatment. Signal Transduct
Target Ther. 3:52018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hann SR: Role of post-translational
modifications in regulating c-Myc proteolysis, transcriptional
activity and biological function. Semin Cancer Biol. 16:288–302.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Akutsu M, Dikic I and Bremm A: Ubiquitin
chain diversity at a glance. J Cell Sci. 129:875–880. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Swatek KN and Komander D: Ubiquitin
modifications. Cell Res. 26:399–422. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Haglund K and Dikic I: Ubiquitylation and
cell signaling. EMBO J. 24:3353–3359. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Trulsson F, Akimov V, Robu M, van Overbeek
N, Berrocal DAP, Shah RG, Cox J, Shah GM, Blagoev B and Vertegaal
ACO: Deubiquitinating enzymes and the proteasome regulate
preferential sets of ubiquitin substrates. Nat Commun. 13:27362022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang J, Zhou Q, Ding J, Yin T, Ye P and
Zhang Y: The conceivable functions of protein ubiquitination and
deubiquitination in reproduction. Front Physiol. 13:8862612022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Mevissen TET and Komander D: Mechanisms of
deubiquitinase specificity and regulation. Annu Rev Biochem.
86:159–192. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sun T, Liu Z and Yang Q: The role of
ubiquitination and deubiquitination in cancer metabolism. Mol
Cancer. 19:1462020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Komander D and Rape M: The ubiquitin code.
Annu Rev Biochem. 81:203–229. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|