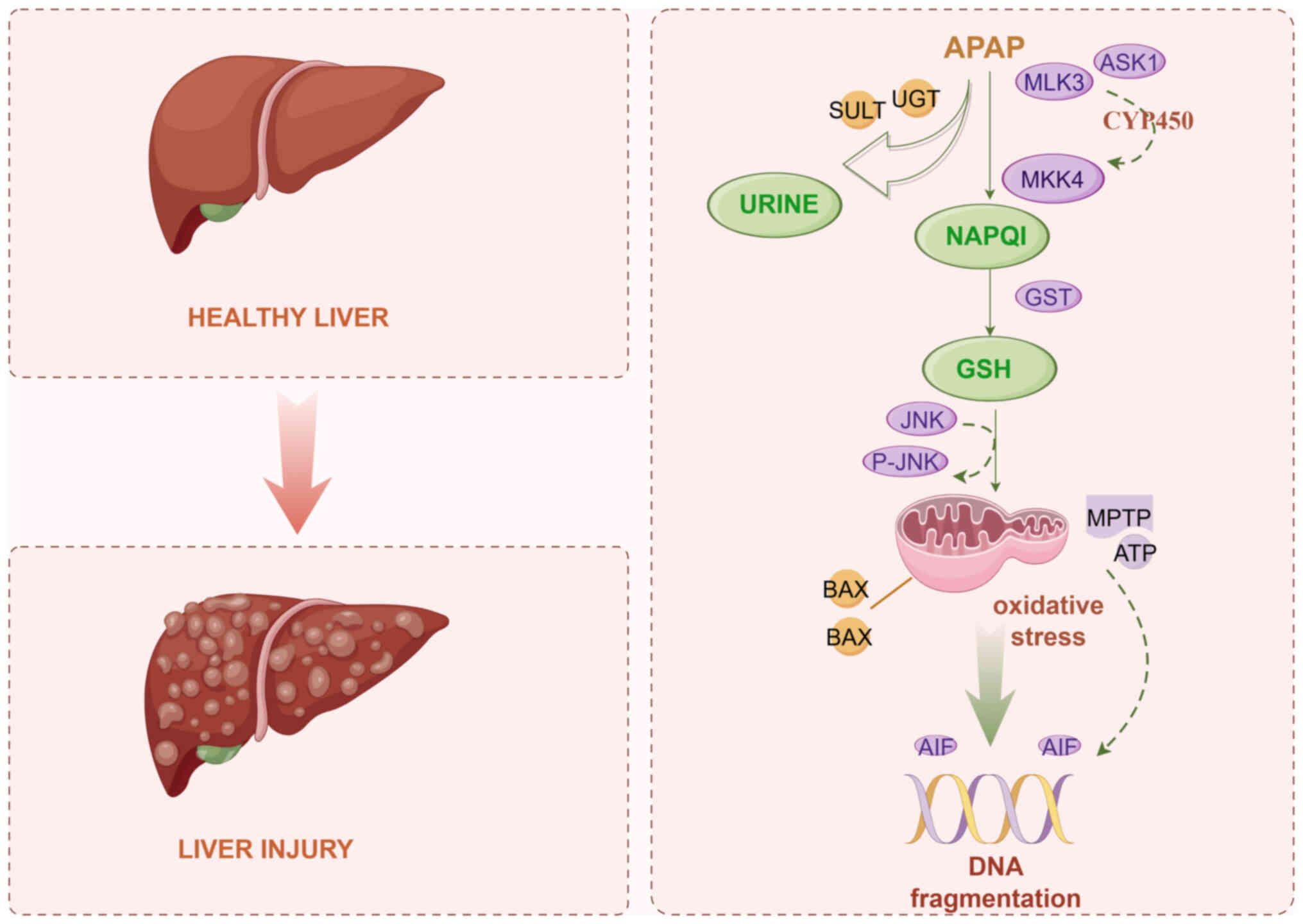
|
1
|
Hoofnagle JH and Björnsson ES:
Drug-induced liver injury-types and phenotypes. N Engl J Med.
381:264–273. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shen T, Liu Y, Shang J, Xie Q, Li J, Yan
M, Xu J, Niu J, Liu J, Watkins PB, et al: Incidence and etiology of
drug-induced liver injury in mainland China. Gastroenterology.
156:2230–2241.e11. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Es B: The epidemiology of newly recognized
causes of drug-induced liver injury: An update. Pharmaceuticals
(Basel). 17:5202024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Warnet JM, Bakar-Wesseling I, Thevenin M,
Serrano JJ, Jacqueson A, Boucard M and Claude JR: Effects of
subchronic low-protein diet on some tissue glutathione-related
enzyme activities in the rat. Arch Toxicol Suppl. 11:45–49.
1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Andrade RJ, Chalasani N, Björnsson ES,
Suzuki A, Kullak-Ublick GA, Watkins PB, Devarbhavi H, Merz M,
Lucena MI, Kaplowitz N and Aithal GP: Drug-induced liver injury.
Nat Rev Dis Primers. 5:582019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kjartansdottir I, Bergmann OM and
Arnadottir RS: Paracetamol intoxications: A retrospective
population-based study in iceland. Scand J Gastroenterol.
47:1344–1352. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tan ST, Lo CH, Liao CH and Su YJ:
Sex-based differences in the predisposing factors of overdose: A
retrospective study. Biomed Rep. 16:492022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Paulose-Ram R, Hirsch R, Dillon C,
Losonczy K, Cooper M and Ostchega Y: Prescription and
non-prescription analgesic use among the US adult population:
Results from the third national health and nutrition examination
survey (NHANES III). Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 12:315–326. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rubin JB, Hameed B, Gottfried M, Lee WM
and Sarkar M; Acute Liver Failure Study Group, :
Acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure is more common and more
severe in women. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 16:936–946. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang X, Wu Q, Liu A, Anadón A, Rodríguez
JL, Martínez-Larrañaga MR, Yuan Z and Martínez MA: Paracetamol:
Overdose-induced oxidative stress toxicity, metabolism, and
protective effects of various compounds in vivo and in vitro. Drug
Metab Rev. 49:395–437. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Brune K, Renner B and Tiegs G:
Acetaminophen/paracetamol: A history of errors, failures and false
decisions. Eur J Pain. 19:953–965. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chidiac AS, Buckley NA, Noghrehchi F and
Cairns R: Paracetamol (acetaminophen) overdose and hepatotoxicity:
Mechanism, treatment, prevention measures, and estimates of burden
of disease. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 19:297–317. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Davidson DG and Eastham WN: Acute liver
necrosis following overdose of paracetamol. Br Med J. 2:497–499.
1966. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
McGill MR and Hinson JA: The development
and hepatotoxicity of acetaminophen: Reviewing over a century of
progress. Drug Metab Rev. 52:472–500. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dart RC, Erdman AR, Olson KR, Christianson
G, Manoguerra AS, Chyka PA, Caravati EM, Wax PM, Keyes DC, Woolf
AD, et al: Acetaminophen poisoning: An evidence-based consensus
guideline for out-of-hospital management. Clin Toxicol (Phila).
44:1–18. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chiew AL, Isbister GK, Stathakis P,
Isoardi KZ, Page C, Ress K, Chan BSH and Buckley NA: Acetaminophen
metabolites on presentation following an acute acetaminophen
overdose (ATOM-7). Clin Pharmacol Ther. 113:1304–1314. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rumack BH, Peterson RC, Koch GG and Amara
IA: Acetaminophen overdose. 662 cases with evaluation of oral
acetylcysteine treatment. Arch Intern Med. 141:380–385. 1981.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Singer AJ, Carracio TR and Mofenson HC:
The temporal profile of increased transaminase levels in patients
with acetaminophen-induced liver dysfunction. Ann Emerg Med.
26:49–53. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Larson AM: Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity.
Clin Liver Dis. 11:525–548. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ramachandran A and Jaeschke H:
Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Semin Liver Dis. 39:221–234. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ma J, Li M, Li N, Chan WY and Lin G:
Pyrrolizidine alkaloid-induced hepatotoxicity associated with the
formation of reactive metabolite-derived pyrrole-protein adducts.
Toxins. 13:7232021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
McGill MR and Jaeschke H: Mechanistic
biomarkers in acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity and acute liver
failure: From preclinical models to patients. Expert Opin Drug
Metab Toxicol. 10:1005–1017. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nelson SD: Molecular mechanisms of the
hepatotoxicity caused by acetaminophen. Semin Liver Dis.
10:267–278. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee WM: Acetaminophen (APAP)
hepatotoxicity-isn't it time for APAP to go away? J Hepatology.
67:1324–1331. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang XP, Thiessen JJ, Spino M and
Templeton DM: Transport of iron chelators and chelates across MDCK
cell monolayers: Implications for iron excretion during chelation
therapy. Int J Hematol. 91:401–412. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Letelier ME, López-Valladares M,
Peredo-Silva L, Rojas-Sepúlveda D and Aracena P: Microsomal
oxidative damage promoted by acetaminophen metabolism. Toxicol In
Vitro. 25:1310–1313. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hinson JA, Pumford NR and Roberts DW:
Mechanisms of acetaminophen toxicity: Immunochemical detection of
drug-protein adducts. Drug Metab Rev. 27:73–92. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ramachandran A and Jaeschke H: A
mitochondrial journey through acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Food
Chem Toxicol. 140:1112822020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
McGill MR, Sharpe MR, Williams CD, Taha M,
Curry SC and Jaeschke H: The mechanism underlying
acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in humans and mice involves
mitochondrial damage and nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Clin Invest.
122:1574–1583. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nguyen NU and Stamper BD: Polyphenols
reported to shift APAP-induced changes in MAPK signaling and
toxicity outcomes. Chem Biol Interact. 277:129–136. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nakagawa H, Maeda S, Hikiba Y, Ohmae T,
Shibata W, Yanai A, Sakamoto K, Ogura K, Noguchi T, Karin M, et al:
Deletion of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 attenuates
acetaminophen-induced liver injury by inhibiting c-jun N-terminal
kinase activation. Gastroenterology. 135:1311–1321. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Thévenin AF, Zony CL, Bahnson BJ and
Colman RF: GST pi modulates JNK activity through a direct
interaction with JNK substrate, ATF2. Protein Sci. 20:834–848.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Akakpo JY, Ramachandran A, Curry SC, Rumac
BH and Jaeschke H: Comparing N-acetylcysteine and 4-methylpyrazole
as antidotes for acetaminophen overdose. Arch Toxicol. 96:453–465.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Moles A, Torres S, Baulies A, Garcia-Ruiz
C and Fernandez-Checa JC: Mitochondrial-lysosomal axis in
acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Front Pharmacol. 9:4532018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xu Y, Xia Y, Liu Q, Jing X, Tang Q, Zhang
J, Jia Q, Zhang Z, Li J, Chen J, et al: Glutaredoxin-1 alleviates
acetaminophen-induced liver injury by decreasing its toxic
metabolites. J Pharm Anal. 13:1548–1561. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chowdhury A, Lu J, Zhang R, Nabila J, Gao
H, Wan Z, Adelusi Temitope I, Yin X and Sun Y: Mangiferin
ameliorates acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity through APAP-cys
and JNK modulation. Biomed Pharmacother. 117:1090972019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jaeschke H, Adelusi OB, Akakpo JY, Nguyen
NT, Sanchez-Guerrero G, Umbaugh DS, Ding WX and Ramachandran A:
Recommendations for the use of the acetaminophen hepatotoxicity
model for mechanistic studies and how to avoid common pitfalls.
Acta Pharm Sin B. 11:3740–3755. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Radi R, Peluffo G, Alvarez MN, Naviliat M
and Cayota A: Unraveling peroxynitrite formation in biological
systems. Free Radic Biol Med. 30:463–488. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cover C, Mansouri A, Knight TR, Bajt ML,
Lemasters JJ, Pessayre D and Jaeschke H: Peroxynitrite-induced
mitochondrial and endonuclease-mediated nuclear DNA damage in
acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 315:879–887.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Saito C, Lemasters JJ and Jaeschke H:
c-jun N-terminal kinase modulates oxidant stress and peroxynitrite
formation independent of inducible nitric oxide synthase in
acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 246:8–17.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kon K, Kim JS, Uchiyama A, Jaeschke H and
Lemasters JJ: Lysosomal iron mobilization and induction of the
mitochondrial permeability transition in acetaminophen-induced
toxicity to mouse hepatocytes. Toxicol Sci. 117:101–108. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jaeschke H, Ramachandran A, Chao X and
Ding WX: Emerging and established modes of cell death during
acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Arch Toxicol. 93:3491–3502.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Bajt ML, Farhood A, Lemasters JJ and
Jaeschke H: Mitochondrial bax translocation accelerates DNA
fragmentation and cell necrosis in a murine model of acetaminophen
hepatotoxicity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 324:8–14. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li GW, Liu J and Chen L: Continuous
ambulatory peritoneal dialysis treatment and blood glucose control
in diabetics with end-stage diabetic nephropathy. Zhonghua Nei Ke
Za Zhi. 28:360–363. 3821989.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yoon E, Babar A, Choudhary M, Kutner M and
Pyrsopoulos N: Acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity: A
comprehensive update. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 4:131–142.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Knight TR, Ho YS, Farhood A and Jaeschke
H: Peroxynitrite is a critical mediator of acetaminophen
hepatotoxicity in murine livers: Protection by glutathione. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 303:468–475. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Gracia-Sancho J, Marrone G and
Fernández-Iglesias A: Hepatic microcirculation and mechanisms of
portal hypertension. Nat Rev Gastroenterol. 16:221–234. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Gracia-Sancho J, Caparrós E,
Fernández-Iglesias A and Francés R: Role of liver sinusoidal
endothelial cells in liver diseases. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
18:411–431. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
McCuskey RS, Bethea NW, Wong J, McCuskey
MK, Abril ER, Wang X, Ito Y and DeLeve LD: Ethanol binging
exacerbates sinusoidal endothelial and parenchymal injury elicited
by acetaminophen. J Hepatol. 42:371–377. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ito Y, Bethea NW, Abril ER and McCuskey
RS: Early hepatic microvascular injury in response to acetaminophen
toxicity. Microcirculation. 10:391–400. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
McCuskey RS: Sinusoidal endothelial cells
as an early target for hepatic toxicants. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc.
34:5–10. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Walker RM, Racz WJ and McElligott TF:
Acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxic congestion in mice. Hepatology.
5:233–240. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Damen L, Bruijn JKJ, Verhagen AP, Berger
MY, Passchier J and Koes BW: Symptomatic treatment of migraine in
children: A systematic review of medication trials. Pediatrics.
116:e295–e302. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Williams AM, Langley PG, Osei-Hwediah J,
Wendon JA and Hughes RD: Hyaluronic acid and endothelial damage due
to paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity. Liver Int. 23:110–115. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
DeLeve LD, Wang X, Kaplowitz N, Shulman
HM, Bart JA and van der Hoek A: Sinusoidal endothelial cells as a
target for acetaminophen toxicity. Direct action versus requirement
for hepatocyte activation in different mouse strains. Biochem
Pharmacol. 53:1339–1345. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Walter P and Ron D: The unfolded protein
response: From stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science.
334:1081–1086. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Maytin EV, Ubeda M, Lin JC and Habener JF:
Stress-inducible transcription factor CHOP/gadd153 induces
apoptosis in mammalian cells via p38 kinase-dependent and
-independent mechanisms. Exp Cell Res. 267:193–204. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Lee DH, Lee B, Park JS, Lee YS, Kim JH,
Cho Y, Jo Y, Kim HS, Lee YH, Nam KT and Bae SH: Inactivation of
Sirtuin2 protects mice from acetaminophen-induced liver injury:
Possible involvement of ER stress and S6K1 activation. BMB Rep.
52:190–195. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kalinec GM, Thein P, Parsa A, Yorgason J,
Luxford W, Urrutia R and Kalinec F: Acetaminophen and NAPQI are
toxic to auditory cells via oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum
stress-dependent pathways. Hear Res. 313:26–37. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Zhang X, Xiong W, Chen LL, Huang JQ and
Lei XG: Selenoprotein V protects against endoplasmic reticulum
stress and oxidative injury induced by pro-oxidants. Free Radic
Biol Med. 160:670–679. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Uzi D, Barda L, Scaiewicz V, Mills M,
Mueller T, Gonzalez-Rodriguez A, Valverde AM, Iwawaki T, Nahmias Y,
Xavier R, et al: CHOP is a critical regulator of
acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. J Hepatol. 59:495–503. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Nagy G, Kardon T, Wunderlich L, Szarka A,
Kiss A, Schaff Z, Bánhegyi G and Mandl J: Acetaminophen induces ER
dependent signaling in mouse liver. Arch Biochem Biophys.
459:273–279. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Jaeschke H, Gujral JS and Bajt ML:
Apoptosis and necrosis in liver disease. Liver Int. 24:85–89. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Henderson CJ, Wolf CR, Kitteringham N,
Powell H, Otto D and Park BK: Increased resistance to acetaminophen
hepatotoxicity in mice lacking glutathione S-transferase pi. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:12741–12745. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Foufelle F and Fromenty B: Role of
endoplasmic reticulum stress in drug-induced toxicity. Pharmacol
Res Perspect. 4:e002112016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Xiao T, Liang X, Liu H, Zhang F, Meng W
and Hu F: Mitochondrial stress protein HSP60 regulates ER
stress-induced hepatic lipogenesis. J Mol Endocrinol. 64:67–75.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Mihm S: Danger-associated molecular
patterns (DAMPs): Molecular triggers for sterile inflammation in
the liver. Int J Mol Sci. 19:31042018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Sanz-Garcia C, Ferrer-Mayorga G,
González-Rodríguez Á, Valverde AM, Martín-Duce A, Velasco-Martín
JP, Regadera J, Fernández M and Alemany S: Sterile inflammation in
acetaminophen-induced liver injury is mediated by Cot/tpl2. J Biol
Chem. 288:15342–15351. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Jaeschke H, Williams CD, Ramachandran A
and Bajt ML: Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity and repair: The role of
sterile inflammation and innate immunity. Liver Int. 32:8–20. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Jaeschke H and Ramachandran A:
Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity: Paradigm for understanding mechanisms
of drug-induced liver injury. Ann Rev Pathol. 19:453–478. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Jaeschke H and Ramachandran A: Mechanisms
and pathophysiological significance of sterile inflammation during
acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Food Chem Toxicol. 138:1112402020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Guo H, Chen S, Xie M and Zheng M: The
complex roles of neutrophils in APAP-induced liver injury. Cell
Prolif. 54:e130402021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Krenkel O and Tacke F: Liver macrophages
in tissue homeostasis and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 17:306–321.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Shan S, Shen Z and Song F: Autophagy and
acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Arch Toxicol. 92:2153–2161.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Mitchell JR, Jollow DJ, Potter WZ, Davis
DC, Gillette JR and Brodie BB: Acetaminophen-induced hepatic
necrosis. I. Role of drug metabolism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
187:185–194. 1973. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Renzi FP, Donovan JW, Martin TG, Morgan L
and Harrison EF: Concomitant use of activated charcoal and
N-acetylcysteine. Ann Emerg Med. 14:568–572. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Saito C, Zwingmann C and Jaeschke H: Novel
mechanisms of protection against acetaminophen hepatotoxicity in
mice by glutathione and N-acetylcysteine. Hepatology. 51:246–254.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Lasram MM, Dhouib IB, Annabi A, El Fazaa S
and Gharbi N: A review on the possible molecular mechanism of
action of N-acetylcysteine against insulin resistance and type-2
diabetes development. Clin Biochem. 48:1200–1208. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Jones AL: Mechanism of action and value of
N-acetylcysteine in the treatment of early and late acetaminophen
poisoning: A critical review. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 36:277–285.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Dell'Aglio DM, Sutter ME, Schwartz MD,
Koch DD, Algren DA and Morgan BW: Acute chloroform ingestion
successfully treated with intravenously administered
N-acetylcysteine. J Med Toxicol. 6:143–146. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Fisher ES and Curry SC: Evaluation and
treatment of acetaminophen toxicity. Adv Pharmacol. 85:263–272.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Park BK, Dear JW and Antoine DJ:
Paracetamol (acetaminophen) poisoning. BMJ Clin Evid.
2015:21012015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Licata A, Minissale MG, Stankevičiūtė S,
Sanabria-Cabrera J, Lucena MI, Andrade RJ and Almasio PL:
N-acetylcysteine for preventing acetaminophen-induced liver injury:
A comprehensive review. Front Pharmacol. 13:8285652022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Akakpo JY, Jaeschke MW, Ramachandran A,
Curry SC, Rumack BH and Jaeschke H: Delayed administration of
N-acetylcysteine blunts recovery after an acetaminophen overdose
unlike 4-methylpyrazole. Arch Toxicol. 95:3377–3391. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Akakpo JY, Ramachandran A, Rumack BH,
Wallace DP and Jaeschke H: Lack of mitochondrial Cyp2E1 drives
acetaminophen-induced ER stress-mediated apoptosis in mouse and
human kidneys: Inhibition by 4-methylpyrazole but not
N-acetylcysteine. Toxicology. 500:1536922023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Matsuzawa-Ishimoto Y, Hwang S and Cadwell
K: Autophagy and inflammation. Annu Rev Immunol. 36:73–101. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Levine B and Klionsky DJ: Development by
self-digestion: Molecular mechanisms and biological functions of
autophagy. Dev Cell. 6:463–477. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Moore MN: Autophagy as a second level
protective process in conferring resistance to
environmentally-induced oxidative stress. Autophagy. 4:254–256.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Chao X, Wang H, Jaeschke H and Ding WX:
Role and mechanisms of autophagy in acetaminophen-induced liver
injury. Liver Int. 38:1363–1374. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Lee J, Giordano S and Zhang J: Autophagy,
mitochondria and oxidative stress: Cross-talk and redox signalling.
Biochem J. 441:523–540. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Khaminets A, Heinrich T, Mari M, Grumati
P, Huebner AK, Akutsu M, Liebmann L, Stolz A, Nietzsche S, Koch N,
et al: Regulation of endoplasmic reticulum turnover by selective
autophagy. Nature. 522:354–358. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Lin Z, Wu F, Lin S, Pan X, Jin L, Lu T,
Shi L, Wang Y, Xu A and Li X: Adiponectin protects against
acetaminophen-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and acute liver
injury by promoting autophagy in mice. J Hepatol. 61:825–831. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Rhodes DG, Sarmiento JG and Herbette LG:
Kinetics of binding of membrane-active drugs to receptor sites.
Diffusion-limited rates for a membrane bilayer approach of
1,4-dihydropyridine calcium channel antagonists to their active
site. Mol Pharmacol. 27:612–623. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Mochida K, Oikawa Y, Kimura Y, Kirisako H,
Hirano H, Ohsumi Y and Nakatogawa H: Receptor-mediated selective
autophagy degrades the endoplasmic reticulum and the nucleus.
Nature. 522:359–362. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Zhou J, Zheng Q and Chen Z: The Nrf2
pathway in liver diseases. Front Cell Dev. 10:8262042022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Wang L, Wei W, Xiao Q, Yang H and Ci X:
Farrerol ameliorates APAP-induced hepatotoxicity via activation of
Nrf2 and autophagy. Int J Biol Sci. 15:788–799. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Li H, Weng Q, Gong S, Zhang W, Wang J,
Huang Y, Li Y, Guo J and Lan T: Kaempferol prevents
acetaminophen-induced liver injury by suppressing hepatocyte
ferroptosis via Nrf2 pathway activation. Food Funct. 14:1884–1896.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Stockwell BR, Friedmann Angeli JP, Bayir
H, Bush AI, Conrad M, Dixon SJ, Fulda S, Gascón S, Hatzios SK,
Kagan VE, et al: Ferroptosis: A regulated cell death nexus linking
metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell. 171:273–285. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Tao J, Xue C, Wang X, Chen H, Liu Q, Jiang
C and Zhang W: GAS1 promotes ferroptosis of liver cells in
acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure. Int J Med Sci.
20:1616–1630. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Wang C, Liu T, Tong Y, Cui R, Qu K, Liu C
and Zhang J: Ulinastatin protects against acetaminophen-induced
liver injury by alleviating ferroptosis via the SIRT1/NRF2/HO-1
pathway. Am J Transl Res. 13:6031–6042. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Cai X, Hua S, Deng J, Du Z, Zhang D, Liu
Z, Khan NU, Zhou M and Chen Z: Astaxanthin activated the Nrf2/HO-1
pathway to enhance autophagy and inhibit ferroptosis, ameliorating
acetaminophen-induced liver injury. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.
14:42887–42903. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Yan M, Huo Y, Yin S and Hu H: Mechanisms
of acetaminophen-induced liver injury and its implications for
therapeutic interventions. Redox Biol. 17:274–283. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Chauhan A, Sheriff L, Hussain MT, Webb GJ,
Patten DA, Shepherd EL, Shaw R, Weston CJ, Haldar D, Bourke S, et
al: The platelet receptor CLEC-2 blocks neutrophil mediated hepatic
recovery in acetaminophen induced acute liver failure. Nat Commun.
11:19392020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
McDonald B and Kubes P: Innate immune cell
trafficking and function during sterile inflammation of the liver.
Gastroenterology. 151:1087–1095. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Calvente CJ, Tameda M, Johnson CD, Del
Pilar H, Lin YC, Adronikou N, De Mollerat Du Jeu X, Llorente C,
Boyer J and Feldstein AE: Neutrophils contribute to spontaneous
resolution of liver inflammation and fibrosis via microRNA-223. J
Clin Invest. 129:4091–4109. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Shibuya M: Vascular endothelial growth
factor-dependent and -independent regulation of angiogenesis. BMB
Rep. 41:278–286. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Fernández M, Semela D, Bruix J, Colle I,
Pinzani M and Bosch J: Angiogenesis in liver disease. J Hepatol.
50:604–620. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Kato T, Ito Y, Hosono K, Suzuki T, Tamaki
H, Minamino T, Kato S, Sakagami H, Shibuya M and Majima M: Vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor-1 signaling promotes liver
repair through restoration of liver microvasculature after
acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Toxicol Sci. 120:218–229. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Li T, Zhu Y and Han L: VEGFR-1
activation-induced MMP-9-dependent invasion in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Future Oncol. 11:3143–3157. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Prescott LF, Illingworth RN, Critchley JA
and Proudfoot AT: Intravenous N-acetylcysteine: Still the treatment
of choice for paracetamol poisoning. Br Med J. 280:46–47. 1980.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Hu C, Zhao L, Wu Z and Li L:
Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells and their derivatives
effectively promotes liver regeneration to attenuate
acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 11:882020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Simpson KJ, Bates CM, Henderson NC,
Wigmore SJ, Garden OJ, Lee A, Pollok A, Masterton G and Hayes PC:
The utilization of liver transplantation in the management of acute
liver failure: Comparison between acetaminophen and
non-acetaminophen etiologies. Liver Transpl. 15:600–609. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Hodgman MJ and Garrard AR: A review of
acetaminophen poisoning. Crit Care Clin. 28:499–516. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Myers RP, Shaheen AAM, Li B, Dean S and
Quan H: Impact of liver disease, alcohol abuse, and unintentional
ingestions on the outcomes of acetaminophen overdose. Clin
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 6:918–925. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Bunchorntavakul C and Reddy KR:
Acetaminophen (APAP or N-acetyl-p-aminophenol) and acute liver
failure. Clin Liver Dis. 22:325–346. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Mohler CR, Nordt SP, Williams SR,
Manoguerra AS and Clark RF: Prospective evaluation of mild to
moderate pediatric acetaminophen exposures. Ann Emerg Med.
35:239–244. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Kociancic T and Reed MD: Acetaminophen
intoxication and length of treatment: How long is long enough?
Pharmacotherapy. 23:1052–1059. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells, .
Physiology and role in liver diseases-PubMed[EB/OL]. [2024-12-29].
Available from:. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27423426/
|
|
119
|
Pathological process of liver sinusoidal
endothelial cells in liver diseases-PubMed[EB/OL]. [2024-12-29].
Available from. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29209108/
|
|
120
|
Peterson RG and Rumack BH: Treating acute
acetaminophen poisoning with acetylcysteine. JAMA. 237:2406–2407.
1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Corcoran GB and Wong BK: Role of
glutathione in prevention of acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity
by N-acetyl-L-cysteine in vivo: Studies with N-acetyl-D-cysteine in
mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 238:54–61. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Smilkstein MJ, Knapp GL, Kulig KW and
Rumack BH: Efficacy of oral N-acetylcysteine in the treatment of
acetaminophen overdose. Analysis of the national multicenter study
(1976 to 1985). N Engl J Med. 319:1557–1562. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Rumack BH: Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity:
The first 35 years. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 40:3–20. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Yarema MC, Johnson DW, Berlin RJ,
Sivilotti ML, Nettel-Aguirre A, Brant RF, Spyker DA, Bailey B,
Chalut D, Lee JS, et al: Comparison of the 20-hour intravenous and
72-hour oral acetylcysteine protocols for the treatment of acute
acetaminophen poisoning. Ann Emerg Med. 54:606–614. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Yang R, Miki K, He X, Killeen ME and Fink
MP: Prolonged treatment with N-acetylcystine delays liver recovery
from acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Crit Care. 13:R552009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Blieden M, Paramore LC, Shah D and
Ben-Joseph R: A perspective on the epidemiology of acetaminophen
exposure and toxicity in the United States. Expert Rev Clin
Pharmacol. 7:341–348. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Waring WS: Novel acetylcysteine regimens
for treatment of paracetamol overdose. Ther Adv Drug Saf.
3:305–315. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
de Andrade KQ, Moura FA, dos Santos JM, de
Araújo OR, de Farias Santos JC and Goulart MO: Oxidative stress and
inflammation in hepatic diseases: Therapeutic possibilities of
N-acetylcysteine. Int J Mol Sci. 16:30269–30308. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Khayyat A, Tobwala S, Hart M and Ercal N:
N-acetylcysteine amide, a promising antidote for acetaminophen
toxicity. Toxicol Lett. 241:133–142. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Downs JW, Cumpston KL, Kershner EK,
Troendle MM, Rose SR and Wills BK: Clinical outcome of massive
acetaminophen overdose treated with standard-dose N-acetylcysteine.
Clin Toxicol (Phila). 59:932–936. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Pang C, Zheng Z, Shi L, Sheng Y, Wei H,
Wang Z and Ji L: Caffeic acid prevents acetaminophen-induced liver
injury by activating the Keap1-Nrf2 antioxidative defense system.
Free Rad Biol Med. 91:236–246. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Yang R, Song C, Chen J, Zhou L, Jiang X,
Cao X, Sun Y and Zhang Q: Limonin ameliorates acetaminophen-induced
hepatotoxicity by activating Nrf2 antioxidative pathway and
inhibiting NF-κB inflammatory response via upregulating Sirt1.
Phytomedicine. 69:1532112020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
An Y, Luo Q, Han D and Guan L: Abietic
acid inhibits acetaminophen-induced liver injury by alleviating
inflammation and ferroptosis through regulating Nrf2/HO-1 axis. Int
Immunopharmacol. 118:1100292023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Lv H, Hong L, Tian Y, Yin C, Zhu C and
Feng H: Corilagin alleviates acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity
via enhancing the AMPK/GSK3β-Nrf2 signaling pathway. Cell Commun
Signal. 17:22019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Wang L, Zhang S, Cheng H, Lv H, Cheng G
and Ci X: Nrf2-mediated liver protection by esculentoside a against
acetaminophen toxicity through the AMPK/akt/GSK3β pathway. Free
Radic Biol Med. 101:401–412. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Zhu L, Fan X, Cao C, Li K, Hou W and Ci X:
Xanthohumol protect against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity
via Nrf2 activation through the AMPK/akt/GSK3β pathway. Biomed
Pharmacother. 165:1150972023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Yao Y, Li R, Liu D, Long L and He N:
Rosmarinic acid alleviates acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity by
targeting Nrf2 and NEK7-NLRP3 signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol Environ
Saf. 241:1137732022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Jiang Z, Yang X, Han Y, Li J, Hu C, Liu C
and Xiao W: Sarmentosin promotes USP17 and regulates Nrf2-mediated
mitophagy and cellular oxidative stress to alleviate APAP-induced
acute liver failure. Phytomedicine. 104:1543372022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|