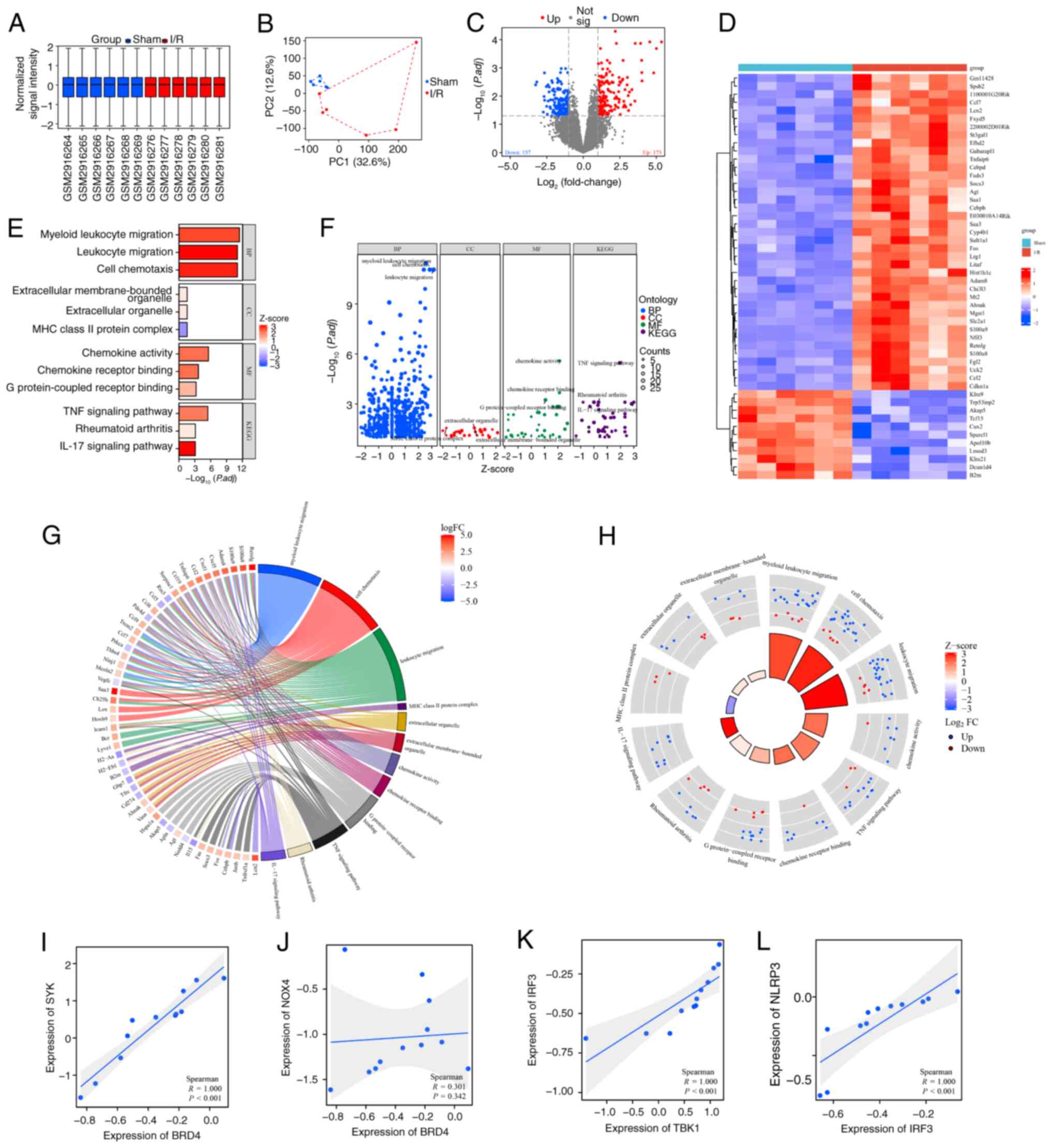
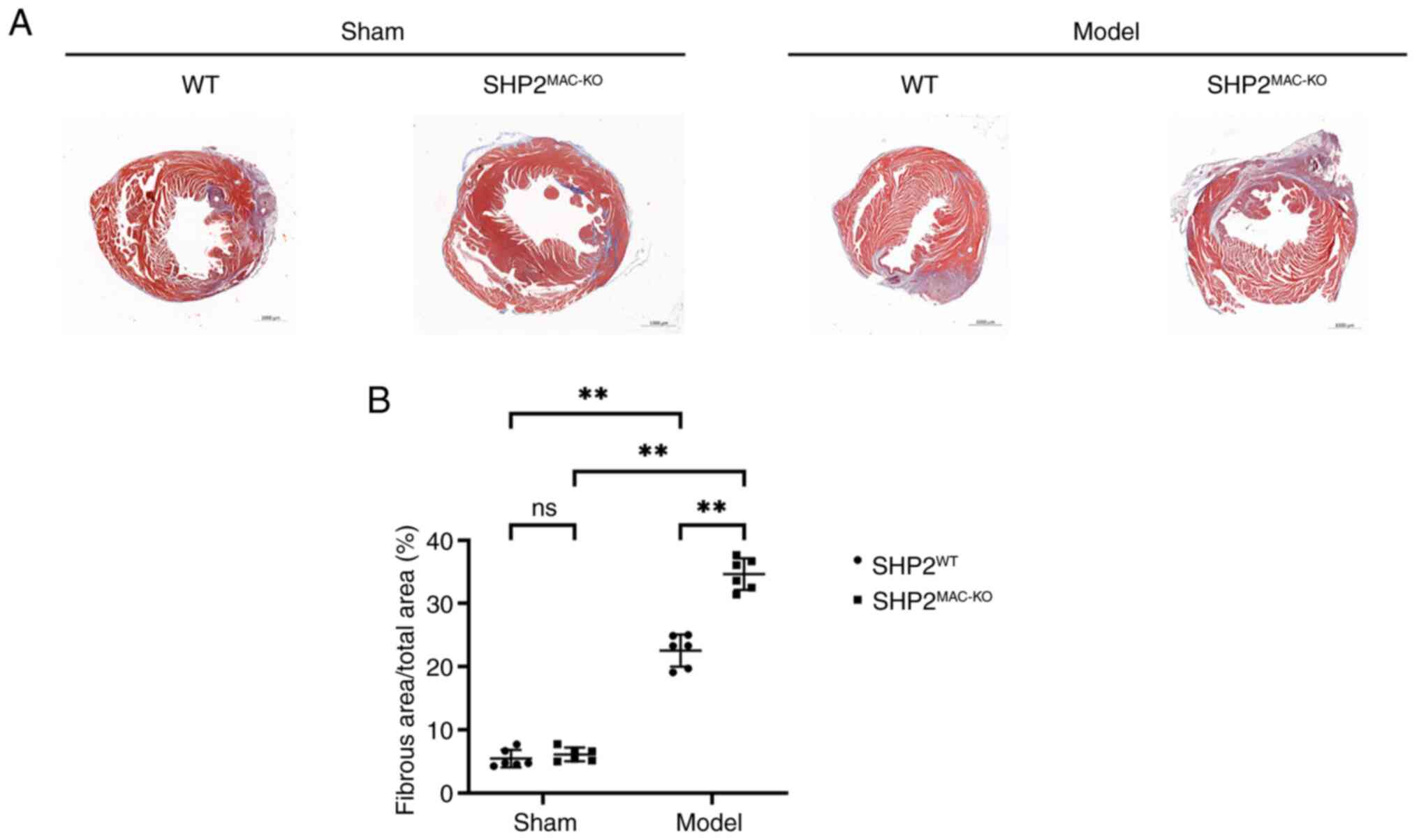
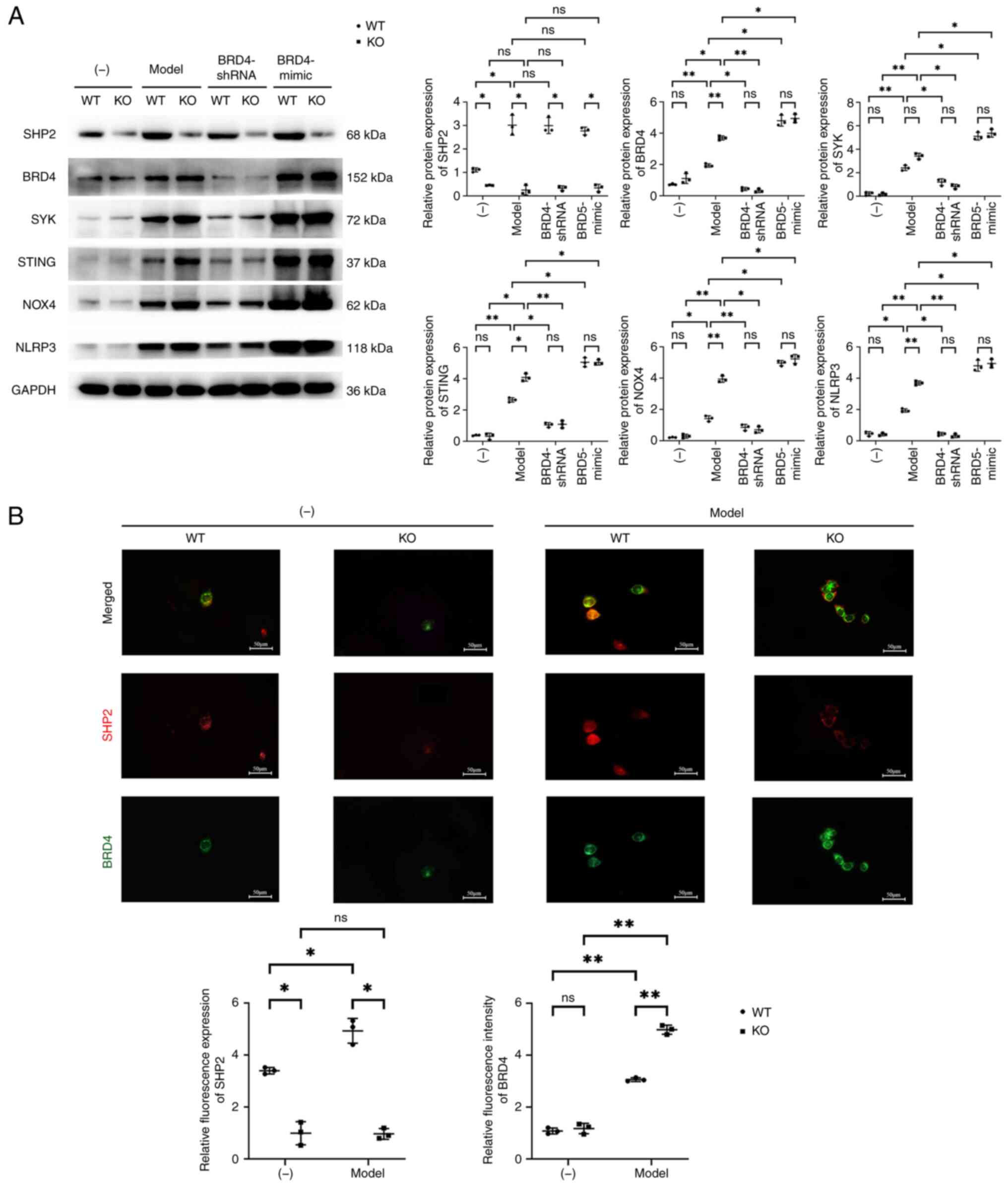
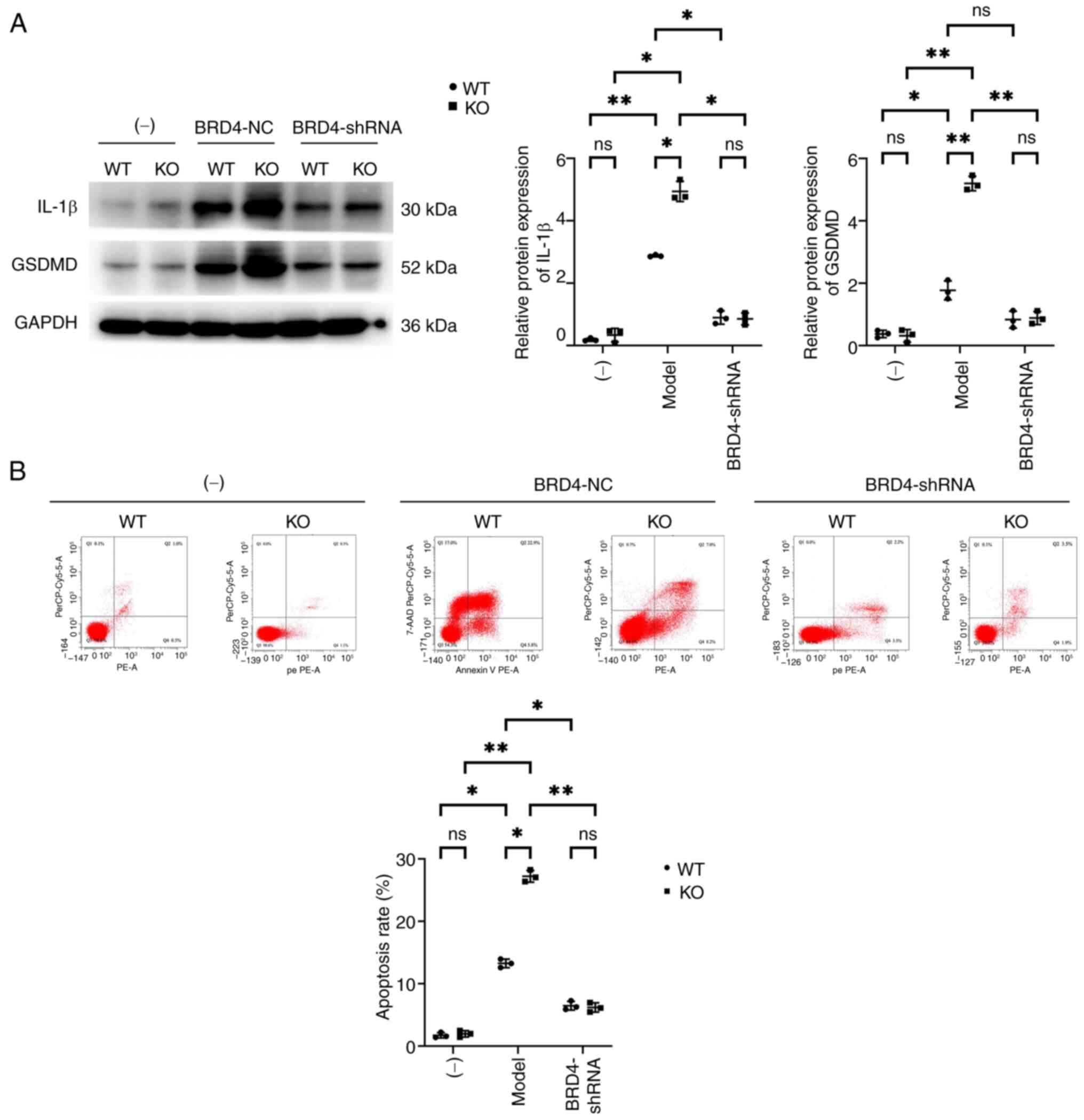
|
1
|
Xu S, Wu B, Zhong B, Lin L, Ding Y, Jin X,
Huang Z, Lin M, Wu H and Xu D: Naringenin alleviates myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating the nuclear
factor-erythroid factor 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)/System
xc-/glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) axis to inhibit ferroptosis.
Bioengineered. 12:10924–10934. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tian H, Zhao X, Zhang Y and Xia Z:
Abnormalities of glucose and lipid metabolism in myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 163:1148272023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang XJ, Liu X, Hu M, Zhao GJ, Sun D,
Cheng X, Xiang H, Huang YP, Tian RF, Shen LJ, et al:
Pharmacological inhibition of arachidonate 12-lipoxygenase
ameliorates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in multiple
species. Cell Metab. 33:2059–2075.e10. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schanze N, Hamad MA, Nührenberg TG, Bode C
and Duerschmied D: Platelets in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion
injury. Hamostaseologie. 43:110–121. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bugger H and Pfeil K: Mitochondrial ROS in
myocardial ischemia reperfusion and remodeling. Biochim Biophys
Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1866:1657682020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shen S, He F, Cheng C, Xu B and Sheng J:
Uric acid aggravates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via
ROS/NLRP3 pyroptosis pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 133:1109902021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hao T, Qian M, Zhang Y, Liu Q, Midgley AC,
Liu Y, Che Y, Hou J and Zhao Q: An injectable dual-function
hydrogel protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by
modulating ROS/NO disequilibrium. Adv Sci (Weinh). 9:e21054082022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu H, Wang L, Weng X, Chen H, Du Y, Diao
C, Chen Z and Liu X: Inhibition of Brd4 alleviates renal
ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced apoptosis and endoplasmic
reticulum stress by blocking FoxO4-mediated oxidative stress. Redox
Biol. 24:1011952019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhu W, Wu RD, Lv YG, Liu YM, Huang H and
Xu JQ: BRD4 blockage alleviates pathological cardiac hypertrophy
through the suppression of fibrosis and inflammation via reducing
ROS generation. Biomed Pharmacother. 121:1093682020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu M, Fu D, Gao T, Jiang H, Yang P and Li
X: The low expression of miR-155 promotes the expression of SHP2 by
inhibiting the activation of the ERK1/2 pathway and improves cell
pyroptosis induced by I/R in mice. Aging (Albany NY). 16:4778–4788.
2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gao T, Liu M, Fu D, Xue Y, Liao J, Yang P
and Li X: Allicin treats myocardial infarction in I/R through the
promotion of the SHP2 axis to inhibit p-PERK-mediated oxidative
stress. Aging (Albany NY). 16:5207–5223. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sha M, Li H, Guo B and Geng X:
Myeloid-specific knockout of SHP2 regulates PI3K/PLCγ signaling
pathway to protect against early myocardial infarction injury.
Aging (Albany NY). 15:9877–9889. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lauriol J, Jaffré F and Kontaridis MI: The
role of the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP2 in cardiac
development and disease. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 37:73–81. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Stratton MS, Bagchi RA, Felisbino MB,
Hirsch RA, Smith HE, Riching AS, Enyart BY, Koch KA, Cavasin MA,
Alexanian M, et al: Dynamic chromatin targeting of BRD4 stimulates
cardiac fibroblast activation. Circ Res. 125:662–677. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao J, Zhang J, Liu Q, Wang Y, Jin Y,
Yang Y, Ni C and Zhang L: Hongjingtian injection protects against
myocardial ischemia reperfusion-induced apoptosis by blocking ROS
induced autophagic-flux. Biomed Pharmacother. 135:1112052021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li X and Jin Y: Inhibition of miR-182-5p
attenuates ROS and protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion
injury by targeting STK17A. Cell Cycle. 21:1639–1650. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu L, Zhang W, Huang C, Liang Q, Bao H,
Gong Z, Xu M, Wang Z, Wen M and Cheng X: FoxO4 promotes myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury: The role of oxidative stress-induced
apoptosis. Am J Transl Res. 10:2890–2900. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Francisco J and Del Re DP: Inflammation in
myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury: Underlying mechanisms and
therapeutic potential. Antioxidants (Basel). 12:19442023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou L, Yang S and Zou X: Farrerol
alleviates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by targeting
macrophages and NLRP3. Front Pharmacol. 13:8792322022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu L, Yang C, Lavayen BP, Tishko RJ,
Larochelle J and Candelario-Jalil E: Targeted BRD4 protein
degradation by dBET1 ameliorates acute ischemic brain injury and
improves functional outcomes associated with reduced
neuroinflammation and oxidative stress and preservation of
blood-brain barrier integrity. J Neuroinflammation. 19:1682022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li X, Chen X, Zheng L, Chen M, Zhang Y,
Zhu R, Chen J, Gu J, Yin Q, Jiang H, et al: Non-canonical
STING-PERK pathway dependent epigenetic regulation of vascular
endothelial dysfunction via integrating IRF3 and NF-κB in
inflammatory response. Acta Pharm Sin B. 13:4765–4784. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Qiao X, Zong Y, Liu Z, Wu Z, Li Y, Wang L
and Song L: The cGAS/STING-TBK1-IRF regulatory axis orchestrates a
primitive interferon-like antiviral mechanism in oyster. Front
Immunol. 12:6897832021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Oduro PK, Zheng X, Wei J, Yang Y, Wang Y,
Zhang H, Liu E, Gao X, Du M and Wang Q: The cGAS-STING signaling in
cardiovascular and metabolic diseases: Future novel target option
for pharmacotherapy. Acta Pharm Sin B. 12:50–75. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zheng Q, Hou J, Zhou Y, Yang Y, Xie B and
Cao X: Siglec1 suppresses antiviral innate immune response by
inducing TBK1 degradation via the ubiquitin ligase TRIM27. Cell
Res. 25:1121–1136. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tian L, Yu Q, Zhang L and Zhang J:
Accelerated fibrosis progression of diabetic nephropathy from high
uric acid's activation of the ROS/NLRP3/SHP2 pathway in renal
tubular epithelial cells under high glucose conditions. Altern Ther
Health Med. June 5–2024.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
27
|
Guo W, Liu W, Chen Z, Gu Y, Peng S, Shen
L, Shen Y, Wang X, Feng GS, Sun Y and Xu Q: Tyrosine phosphatase
SHP2 negatively regulates NLRP3 inflammasome activation via
ANT1-dependent mitochondrial homeostasis. Nat Commun. 8:21682017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lin Q, Li S, Jiang N, Shao X, Zhang M, Jin
H, Zhang Z, Shen J, Zhou Y, Zhou W, et al: PINK1-parkin pathway of
mitophagy protects against contrast-induced acute kidney injury via
decreasing mitochondrial ROS and NLRP3 inflammasome activation.
Redox Boil. 26:1012542019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qiu Z, He Y, Ming H, Lei S, Leng Y and Xia
ZY: Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) aggravates high glucose- and
hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injury through activating
ROS-dependent NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis in H9C2
cardiomyocytes. J Diabetes Res. 2019:81518362019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li S, Sun Y, Song M, Song Y, Fang Y, Zhang
Q, Li X, Song N, Ding J, Lu M and Hu G:
NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis exerts a crucial role in
astrocyte pathological injury in mouse model of depression. JCI
Insight. 6:e1468522021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Coll RC, Schroder K and Pelegrín P: NLRP3
and pyroptosis blockers for treating inflammatory diseases. Trends
Pharmacol Sci. 43:653–668. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|