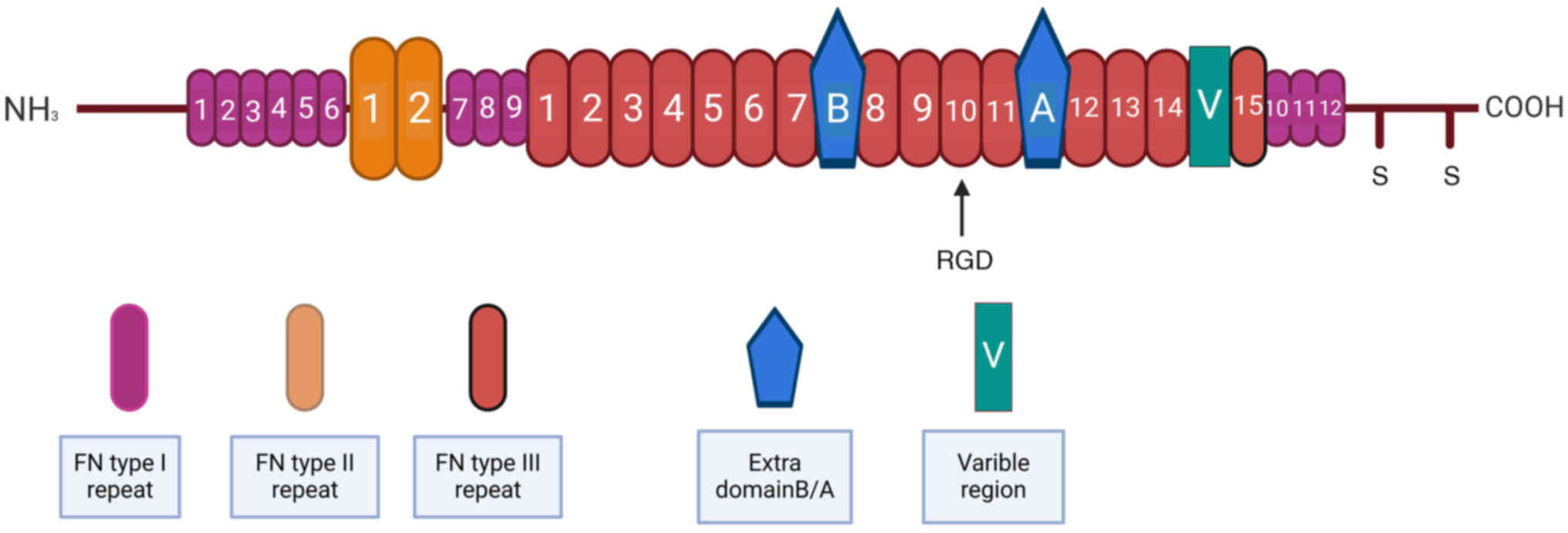
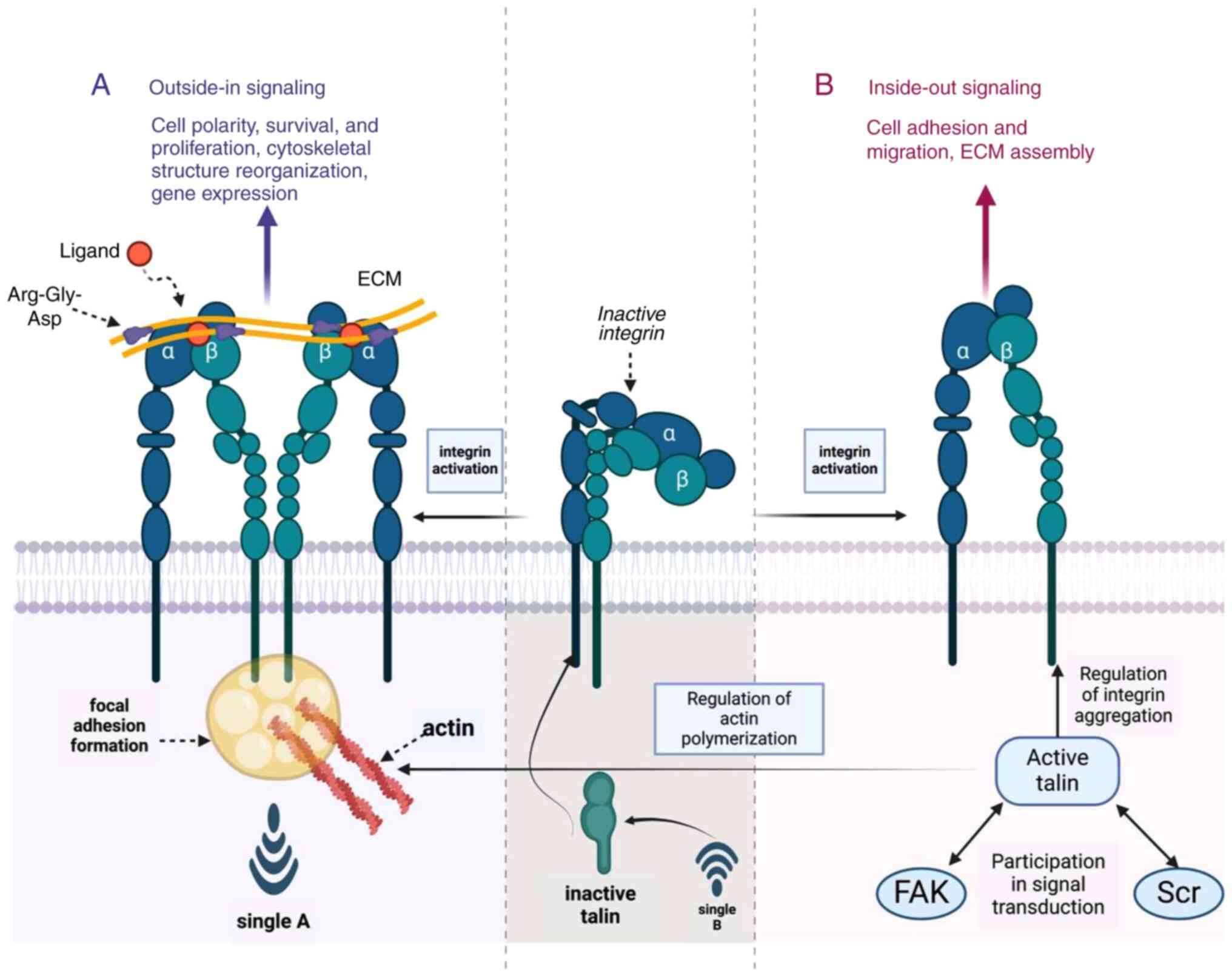
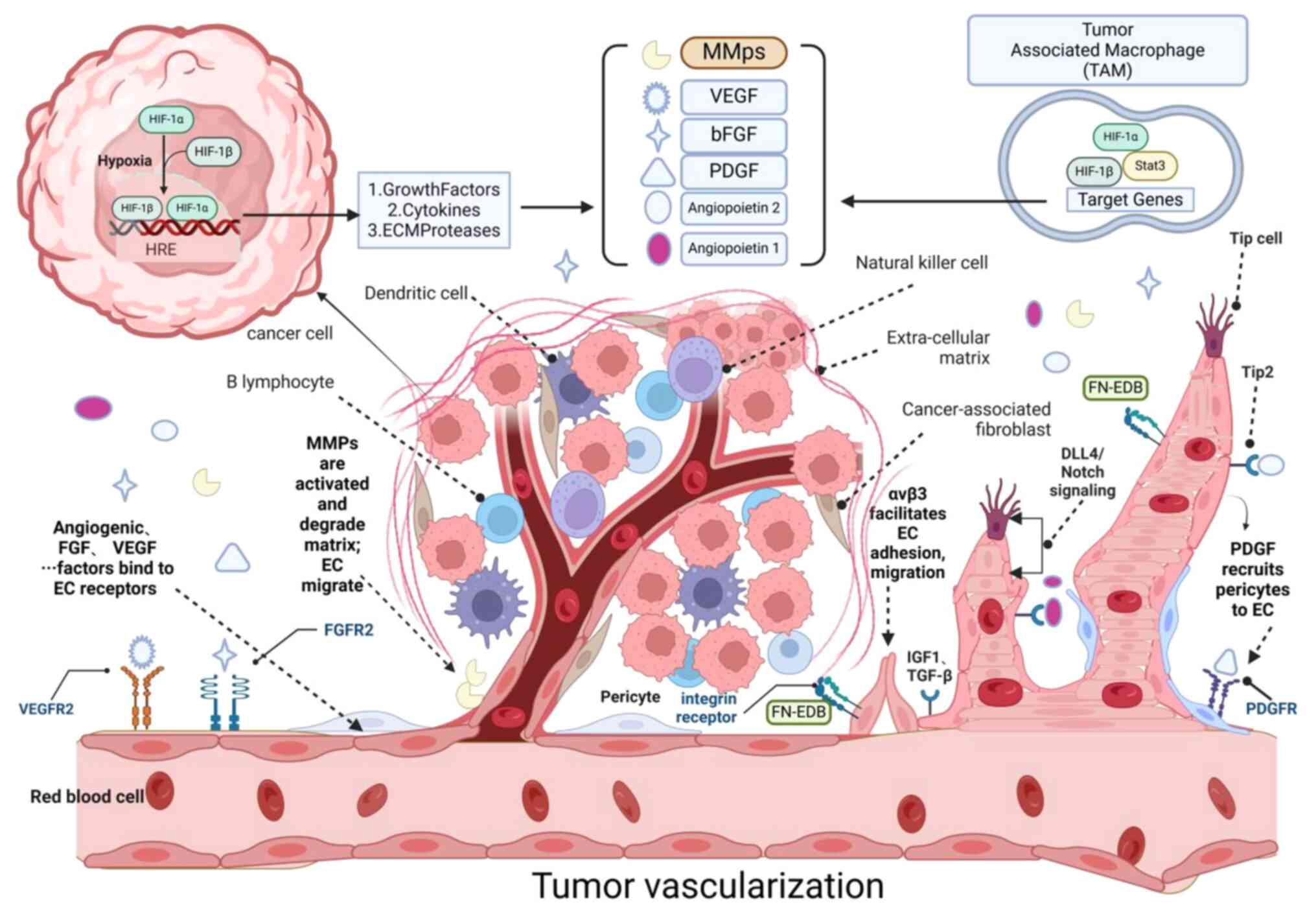
|
1
|
Tiwari A, Trivedi R and Lin SY: Tumor
microenvironment: Barrier or opportunity towards effective cancer
therapy. J Biomed Sci. 29:832022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kolesnikoff N, Chen CH and Samuel MS:
Interrelationships between the extracellular matrix and the immune
microenvironment that govern epithelial tumour progression. Clin
Sci (Lond). 136:361–377. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Efthymiou G, Saint A, Ruff M, Rekad Z,
Ciais D and Van Obberghen-Schilling E: Sha up the tumor
microenvironment with cellular fibronectin. Front Oncol.
10:6412020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kim SE, Yun S and Doh J: Effects of
extracellular adhesion molecules on immune cell mediated solid
tumor cell killing. Front Immunol. 13:10041712022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Parmar D and Apte M: Angiopoietin
inhibitors: A review on targeting tumor angiogenesis. Eur J
Pharmacol. 899:174021. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Peng Z, Lv X and Huang S: Recent progress
on the role of fibronectin in tumor stromal immunity and
immunotherapy. Curr Top Med Chem. 22:2494–2505. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Neri D and Sondel PM: Immunocytokines for
cancer treatment: Past, present and future. Curr Opin Immunol.
40:96–102. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang J, Li R, Li M and Wang C: Fibronectin
and colorectal cancer: Signaling pathways and clinical
implications. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 41:313–320. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wagner J, Wickman E, Shaw TI, Anido AA,
Langfitt D, Zhang J, Porter SN, Pruett-Miller SM, Tillman H,
Krenciute G and Gottschalk S: Antitumor effects of CAR T cells
redirected to the EDB Splice variant of fibronectin. Cancer Immunol
Res. 9:279–290. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhou F, Sun J, Ye L, Jiang T, Li W, Su C,
Ren S, Wu F, Zhou C and Gao G: Fibronectin promotes tumor
angiogenesis and progression of Non-small-cell lung cancer by
elevating WISP3 expression via FAK/MAPK/HIF-1α axis and activating
wnt signaling pathway. Exp Hematol Oncol. 12:612023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pankov R and Yamada KM: Fibronectin at a
glance. J Cell Sci. 115:3861–3863. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kumra H and Reinhardt DP:
Fibronectin-targeted drug delivery in cancer. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.
97:101–110. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang K, Seo BR, Fischbach C and Gourdon D:
Fibronectin mechanobiology regulates tumorigenesis. Cell Mol
Bioeng. 9:1–11. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kraft S, Klemis V, Sens C, Lenhard T,
Jacobi C, Samstag Y, Wabnitz G, Kirschfink M, Wallich R, Hänsch GM
and Nakchbandi IA: Identification and characterization of a unique
role for EDB fibronectin in phagocytosis. J Mol Med (Berl).
94:567–581. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dalton CJ and Lemmon CA: Fibronectin:
Molecular structure, fibrillar structure and mechanochemical
signaling. Cells. 10:24432021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Singh P, Carraher C and Schwarzbauer JE:
Assembly of fibronectin extracellular matrix. Annu Rev Cell Dev
Biol. 26:397–419. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ventura E, Sassi F, Parodi A, Balza E,
Borsi L, Castellani P, Carnemolla B and Zardi L: Alternative
splicing of the angiogenesis associated Extra-domain B of
fibronectin regulates the accessibility of the B-C loop of the type
III repeat 8. PLoS One. 5:e91452010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Barrow-McGee R, Kishi N, Joffre C, Ménard
L, Hervieu A, Bakhouche BA, Noval AJ, Mai A, Guzmán C,
Robbez-Masson L, et al: Beta 1-integrin-c-Met cooperation reveals
an inside-in survival signalling on autophagy-related
endomembranes. Nat Commun. 7:123922016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dinesh NEH, Campeau PM and Reinhardt DP:
Fibronectin isoforms in skeletal development and associated
disorders. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 323:C536–C549. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Guerrero-Barberà G, Burday N and Costell
M: Shaping oncogenic microenvironments: Contribution of
fibronectin. Front Cell Dev Biol. 12:13630042024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rick JW, Chandra A, Dalle Ore C, Nguyen
AT, Yagnik G and Aghi MK: Fibronectin in malignancy:
Cancer-specific alterations, protumoral effects and therapeutic
implications. Semin Oncol. 46:284–290. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Park JH, Ryu JM and Han HJ: Involvement of
caveolin-1 in fibronectin-induced mouse embryonic stem cell
proliferation: Role of FAK, RhoA, PI3K/Akt and ERK 1/2 pathways. J
Cell Physiol. 226:267–275. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fei D, Meng X, Yu W, Yang S, Song N, Cao
Y, Jin S, Dong L, Pan S and Zhao M: Fibronectin (FN) cooperated
with TLR2/TLR4 receptor to promote innate immune responses of
macrophages via binding to integrin β1. Virulence. 9:1588–1600.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Menrad A and Menssen HD: ED-B fibronectin
as a target for antibody-based cancer treatments. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 9:491–500. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hall RC, Vaidya AM, Schiemann WP, Pan Q
and Lu ZR: RNA-Seq analysis of extradomain a and extradomain B
fibronectin as extracellular matrix markers for cancer. Cells.
12:6852023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Faisal SM, Comba A, Varela ML, Argento AE,
Brumley E, Abel C II, Castro MG and Lowenstein PR: The complex
interactions between the cellular and non-cellular components of
the brain tumor microenvironmental landscape and their therapeutic
implications. Front Oncol. 12:10050692022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen CW, Yang CH, Lin YH, Hou YC, Cheng
TJ, Chang ST, Huang YH, Chung ST, Chio CC, Shan YS, et al: The
fibronectin expression determines the distinct progressions of
malignant gliomas via transforming growth Factor-beta pathway. Int
J Mol Sci. 22:3782. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hall RC, Ayat NR, Qiao PL, Vaidya AM, Ma
D, Aminoshariae A, Stojanov I and Lu ZR: Preclinical assessment of
the effectiveness of magnetic resonance molecular imaging of
Extradomain-B fibronectin for detection and characterization of
oral cancer. Mol Imaging Biol. 22:1532–1542. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vaidya A, Wang H, Qian V, Gilmore H and Lu
ZR: Overexpression of Extradomain-B fibronectin is associated with
invasion of breast cancer cells. Cells. 9:18262020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nail HM, Chiu CC, Leung CH, Ahmed MMM and
Wang HD: Exosomal miRNA-mediated intercellular communications and
immunomodulatory effects in tumor microenvironments. J Biomed Sci.
30:692023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yuan Z, Li Y, Zhang S, Wang X, Dou H, Yu
X, Zhang Z, Yang S and Xiao M: Extracellular matrix remodeling in
tumor progression and immune escape: From mechanisms to treatments.
Molecular Cancer. 22:482023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Burrows L, Clark K, Mould AP and Humphries
MJ: Fine mapping of inhibitory anti-α5 monoclonal antibody epitopes
that differentially affect integrin-ligand binding. Biochem J.
344:527. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Farndale RW and Jarvis GE: Integrins in
GtoPdb v.2023.1. IUPHAR/BPS guide to pharmacology CITE. Apr
26–2023.doi:10.2218/gtopdb/f760/2023.1. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Takagi J: Structural basis for ligand
recognition by RGD (Arg-Gly-Asp)-dependent integrins. Biochem Soc
Trans. 32:403–406. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kolasangiani R, Bidone TC and Schwartz MA:
Integrin conformational dynamics and mechanotransduction. Cells.
11:35842022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Moro L, Venturino M, Bozzo C, Silengo L,
Altruda F, Beguinot L, Tarone G and Defilippi P: Integrins induce
activation of EGF receptor: Role in MAP kinase induction and
adhesion-dependent cell survival. EMBO J. 17:6622–6632. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Su Y, Xia W, Li J, Walz T, Humphries MJ,
Vestweber D, Cabañas C, Lu C and Springer TA: Relating conformation
to function in integrin α 5 β 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
113:E3872–E3881. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Widmaier M, Rognoni E, Radovanac K,
Azimifar SB and Fässler R: Integrin-linked kinase at a glance. J
Cell Sci. 125:1839–1843. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Matsuura S, Thompson CR, Kah NS,
Karagianni A, Torres CW, Mazzeo CS, Leiva O, Malara A, Balduini A
and Ravid K: Integrin-mediated adhesion to extracellular matrix
protein fibronectin drives megakaryocytosis in
JAK2V617F+ primary myelofibrosis. Blood. 134 (Suppl
1):S42052019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Andreucci E, Bugatti K, Peppicelli S,
Ruzzolini J, Lulli M, Calorini L, Battistini L, Zanardi F, Sartori
A and Bianchini F: Nintedanib-αVβ6 integrin ligand conjugates
reduce TGFβ-Induced EMT in human Non-small cell lung cancer. Int J
Mol Sci. 24:14752023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Haarmann A, Nowak E, Deiß A, van der Pol
S, Monoranu CM, Kooij G, Müller N, van der Valk P, Stoll G, de
Vries HE, et al: Soluble VCAM-1 impairs human brain endothelial
barrier integrity via integrin α-4-transduced outside-in
signalling. Acta Neuropathologica. 129:639–652. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Su Y, Iacob RE, Li J, Engen JR and
Springer TA: Dynamics of integrin α5β1, fibronectin and their
complex reveal sites of interaction and conformational change. J
Biol Chem. 298:1023232022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Durrant TN, van den Bosch MT and Hers I:
Integrin αIIbβ3 outside-in signaling. Blood. 130:1607–1619. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Pang X, He X, Qiu Z, Zhang H, Xie R, Liu
Z, Gu Y, Zhao N, Xiang Q and Cui Y: Targeting integrin pathways:
Mechanisms and advances in therapy. Signal. 8:12023.
|
|
45
|
Shams H and Mofrad MRK: Molecular
mechanisms underlying the inside-out signaling through focal
adhesions. Biophysical J. 106:574a2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Huang C, Rajfur Z, Yousefi N, Chen Z,
Jacobson K and Ginsberg MH: Talin phosphorylation by Cdk5 regulates
Smurf1-mediated talin head ubiquitylation and cell migration. Nat
Cell Biol. 11:624–630. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Han SB, Lee G, Kim D, Kim JK, Kim IS, Kim
HW and Kim DH: Selective suppression of Integrin-ligand binding by
single molecular tension probes mediates directional cell
migration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 11:e23064972024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kim HJ, You SJ, Yang DH, Chun HJ and Kim
MS: Preparation of novel RGD-conjugated thermosensitive mPEG-PCL
composite hydrogels and in vitro investigation of their impacts on
Adhesion-dependent cellular behavior. J Industrial Engineering
Chemistry. 84:226–235. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Legate KR, Wickström SA and Fässler R:
Genetic and cell biological analysis of integrin outside-in
signaling. Genes Dev. 23:397–418. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Betriu N, Andreeva A, Alonso A and Semino
CE: Increased stiffness downregulates focal adhesion kinase
expression in pancreatic cancer cells cultured in 3D
Self-assembling peptide scaffolds. Biomedicines. 10:1835. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Martinez OE and Sudhamsu J: Abstract A025:
Investigating the molecular mechanisms of regulation of the RAS
guanine nucleotide exchange factor, SOS1 by Grb2 and 14-3-3. Mol
Cancer Res. 21 (5_Suppl):A0252023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lagarrigue F and Gingras AR: Src-mediated
phosphorylation of RIAM promotes integrin activation. Structure.
29:305–307. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kang BW and Chau I: Molecular target:
Pan-AKT in gastric cancer. ESMO Open. 5:e0007282020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wu W, Xue X, Chen Y, Zheng N and Wang J:
Targeting prolyl isomerase Pin1 as a promising strategy to overcome
resistance to cancer therapies. Pharmacol Res. 184:1064562022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Alanko J and Ivaska J: Endosomes: Emerging
platforms for Integrin-mediated FAK signalling. Trends Cell Biol.
26:391–398. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wan J: The regulatory role of the mitotic
checkpoint component Mad1 in interphase and tumor progression.
University of Wisconsin-Madison; 2019
|
|
57
|
Liu J, Lu F, Ithychanda SS, Apostol M, Das
M, Deshpande G, Plow EF and Qin J: A mechanism of platelet integrin
αIIbβ3 outside-in signaling through a novel integrin αIIb
subunit-filamin-actin linkage. Blood. 141:2629–2641.
2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Shams H and Mofrad MRK: α-Actinin induces
a kink in the transmembrane domain of β3-Integrin and impairs
activation via talin. Biophys J. 113:948–956. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Fraser J, Simpson J, Fontana R,
Kishi-Itakura C, Ktistakis NT and Gammoh N: Targeting of early
endosomes by autophagy facilitates EGFR recycling and signalling.
EMBO Rep. 20:e477342019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Miao M, Collins J, Moreira Bahnson ES,
Chubinskaya S and Loeser RF: Reactive oxygen species regulate
fibronectin fragments-induced map kinase signaling and
metalloproteinase 13 release in human chondrocytes through nadph
oxidase 2 and endocytosis of chondrocyte integrins. Osteoarthritis.
28 (Suppl):S45–S46. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Teran OY, Zanotelli MR, Joy Lin MC,
Cerione RA and Wilson KF: Dock7 regulates AKT and mTOR/S6K activity
required for the transformed phenotypes and survival of cancer
cells. bioRxiv. Jan 3–2023.doi: 10.1101/2023.01.03.522657.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Gagné D, Benoit YD, Groulx JF, Vachon PH
and Beaulieu JF: ILK supports RhoA/ROCK-mediated contractility of
human intestinal epithelial crypt cells by inducing the
fibrillogenesis of endogenous soluble fibronectin during the
spreading process. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 21:142020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Nadel G, Maik-Rachline G and Seger R: JNK
Cascade-induced Apoptosis-A unique role in GqPCR signaling. Int J
Mol Sci. 24:13527. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Karunakaran D, Nguyen MA, Geoffrion M,
Vreeken D, Lister Z, Cheng HS, Otte N, Essebier P, Wyatt H, Kandiah
JW, et al: RIPK1 expression associates with inflammation in early
atherosclerosis in humans and can be therapeutically silenced to
reduce NF-κB activation and atherogenesis in mice. Circulation.
143:163–177. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zhang H, Meng F, Wu S, Kreike B, Sethi S,
Chen W, Miller FR and Wu G: Engagement of I-branching {beta}-1,
6-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 2 in breast cancer metastasis and
TGF-{beta} signaling. Cancer Res. 71:4846–4856. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Yang S, Liu Y, Li MY, Ng CSH, Yang SL,
Wang S, Zou C, Dong Y, Du J, Long X, et al: FOXP3 promotes tumor
growth and metastasis by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
and EMT in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer. 16:1242017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Weller M, Silginer M, Goodman SL,
Hasenbach K, Thies S, Schraml P, Tabatabai G, Moch H, Tritschler I
and Roth P: Effect of the integrin inhibitor cilengitide on
TGF-beta signaling. J Clin Oncol. 30 (15_suppl):S20552012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Valdembri D and Serini G: Angiogenesis:
The importance of RHOJ-mediated trafficking of active integrins.
Current Biology. 30:R652–R654. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Nilsson M and Heymach JV: Vascular
endothelial growth factor (VEGF) pathway. J Thorac Oncol.
1:768–770. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Liu Z and Dong Z: A cross talk between HIF
and NF-κB in AKI. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 321:F255–F256. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Zhao Y, Wang J, Qin W, Hu Q, Li J, Qin R,
Ma N, Zheng F, Tian W, Jiang J, et al: Dehydroepiandrosterone
promotes ovarian angiogenesis and improves ovarian function in a
rat model of premature ovarian insufficiency by up-regulating
HIF-1α/VEGF signalling. Reprod Biomed Online. 49:1039142024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Chatterjee S and Naik UP:
Pericyte-endothelial cell interaction. Cell Adh Migr. 6:157–159.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Surazynski A, Donald SP, Cooper SK,
Whiteside MA, Salnikow K, Liu Y and Phang JM: Extracellular matrix
and HIF-1 signaling: The role of prolidase. Int J Cancer.
122:1435–1440. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Caporali A, Martello A, Miscianinov V,
Maselli D, Vono R and Spinetti G: Contribution of pericyte
paracrine regulation of the endothelium to angiogenesis. Pharmacol
Ther. 171:56–64. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Harrell CR, Simovic Markovic B, Fellabaum
C, Arsenijevic A, Djonov V and Volarevic V: Molecular mechanisms
underlying therapeutic potential of pericytes. J Biomed Sci.
25:122028.
|
|
76
|
Simonavicius N, Ashenden M, van Weverwijk
A, Lax S, Huso DL, Buckley CD, Huijbers IJ, Yarwood H and Isacke
CM: Pericytes promote selective vessel regression to regulate
vascular patterning. Blood. 120:1516–1527. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Smart N: Understanding the recruitment
process. Arteriosclerosis Thrombosis Vascular Biol. 40:2564–2565.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Senger DR and Davis GE: Angiogenesis. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 3:a0050902011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Huang Y, Snuderl M and Jain RK:
Polarization of Tumor-associated macrophages: A novel strategy for
vascular normalization and antitumor immunity. Cancer Cell. 19:1–2.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Poto R, Cristinziano L, Modestino L, de
Paulis A, Marone G, Loffredo S, Galdiero MR and Varricchi G:
Neutrophil extracellular traps, angiogenesis and cancer.
Biomedicines. 10:431. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Van Hinsbergh VW and Koolwijk P:
Endothelial sprouting and angiogenesis: Matrix metalloproteinases
in the lead. Cardiovasc Res. 78:203–212. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Zhou X, Zhang J, Lv W, Zhao C, Xia Y, Wu Y
and Zhang Q: The pleiotropic roles of adipocyte secretome in
remodeling breast cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 41:2032022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Tang KH, Ma S, Lee TK, Chan YP, Kwan PS,
Tong CM, Ng IO, Man K, To KF, Lai PB, et al: CD133(+) liver
tumor-initiating cells promote tumor angiogenesis, growth, and
self-renewal through neurotensin/interleukin-8/CXCL1 signaling.
Hepatology. 55:807–820. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Engelmann D, Mayoli-Nüssle D, Mayrhofer C,
Fürst K, Alla V, Stoll A, Spitschak A, Abshagen K, Vollmar B, Ran S
and Pützer BM: E2F1 promotes angiogenesis through the
VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 axis in a feedback loop for cooperative induction of
PDGF-B. J Mol Cell Biol. 5:391–403. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Azizi M, Dianat-Moghadam H, Salehi R,
Farshbaf M, Iyengar D, Sau S, Iyer AK, Valizadeh H, Mehrmohammadi M
and Hamblin MR: Interactions between tumor biology and targeted
nanoplatforms for imaging applications. Adv Funct Mater.
30:19104022020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Vaidya A, Ayat N, Buford M, Wang H,
Shankardass A, Zhao Y, Gilmore H, Wang Z and Lu ZR: Noninvasive
assessment and therapeutic monitoring of drug-resistant colorectal
cancer by MR molecular imaging of extradomain-B fibronectin.
Theranostics. 10:111272020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Lewandowski S, Diao L, Quigley A,
Crochiere M and Pinkas J: EDB+ FN is an attractive therapeutic
target in oncology: Insights from protein expression analysis of
solid tumors. Cancer Res. 84 (6_Suppl):S29082004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Qiao P, Ayat NR, Vaidya A, Gao S, Sun W,
Chou S, Han Z, Gilmore H, Winter JM and Lu ZR: Magnetic resonance
molecular imaging of extradomain B fibronectin improves imaging of
pancreatic cancer tumor xenografts. Front Oncol. 10:5867272020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Feng Y, Hao Y, Wang Y, Song W, Zhang S, Ni
D, Yan F and Sun L: Ultrasound molecular imaging of bladder cancer
via extradomain B Fibronectin-targeted biosynthetic GVs. Int J
Nanomedicine. 18:4871–4884. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Zhang Y, Zheng X, Huang Y, Li S, Li X and
Zhu L: EDB-FN-targeted probes for near infrared fluorescent imaging
and positron emission tomography imaging of breast cancer in mice.
Sci Rep. 14:220562024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Mohammadgholi M, Sadeghzadeh N, Erfani M,
Abediankenari S, Abedi SM, Emrarian I, Jafari N and Behzadi R:
Human fibronectin Extra-domain B (EDB)-Specific aptide (APTEDB)
radiolabelling with technetium-99m as a potent targeted
Tumour-imaging agent. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 18:277–285. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Qiao PL, Gargesha M, Liu Y, Laney VEA,
Hall RC, Vaidya AM, Gilmore H, Gawelek K, Scott BB, Roy D, et al:
Magnetic resonance molecular imaging of extradomain B fibronectin
enables detection of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma metastasis.
Magn Reson Imaging. 86:37–45. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Sergeeva O, Zhang Y, Gao S, Chan ER,
Sergeev M, Iyer R, Sexton S, Avril N, Lu ZR and Lee Z: PET imaging
of hepatocellular carcinoma using ZD2-(Ga-NOTA). J Hepatocell
Carcinoma. 10:291–301. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Han Z, Sergeeva O, Roelle S, Cheng H, Gao
S, Li Y, Lee Z and Lu ZR: Preparation and evaluation of ZD2 peptide
Cu-DOTA conjugate as a positron emission tomography probe for
detection and characterization of prostate cancer. ACS Omega.
4:1185–1190. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Lu ZR, Laney V and Li Y: Targeted contrast
agents for magnetic resonance molecular imaging of cancer. Acc Chem
Res. 55:2833–2847. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Han Z, Sergeeva O, Roelle S, Cheng H, Gao
S, Li Y, Lee Z and Lu ZR: Preparation and evaluation of ZD2 Peptide
64Cu-DOTA conjugate as a positron emission tomography
probe for detection and characterization of prostate cancer. ACS
Omega. 4:1185–1190. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Han Z, Li Y, Roelle S, Zhou Z, Liu Y,
Sabatelle R, DeSanto A, Yu X, Zhu H, Magi-Galluzzi C and Lu ZR:
Targeted contrast agent specific to an oncoprotein in tumor
microenvironment with the potential for detection and risk
stratification of prostate cancer with MRI. Bioconjug Chem.
28:1031–1040. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Ye XX, Zhao YY, Wang Q, Xiao W, Zhao J,
Peng YJ, Cao DH, Lin WJ, Si-Tu MY, Li MZ, et al: EDB
Fibronectin-Specific SPECT Probe 99mTc-HYNIC-ZD2 for breast cancer
detection. ACS Omega. 2:2459–2468. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Zhang W, Liang X, Zhang X, Tong W, Shi G,
Guo H, Jin Z, Tian J, Du Y and Xue H: Magnetic-optical
dual-modality imaging monitoring chemotherapy efficacy of
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with a low-dose
fibronectin-targeting Gd-based contrast agent. Eur J Nucl Med Mol
Imaging. 51:1841–1855. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Yang N, Huang Y, Wang X, Wang D, Yao D and
Ren GL: Fibronectin-targeting Dual-Modal MR/NIRF imaging contrast
agents for diagnosis of gastric cancer and peritoneal metastasis.
Bioconjug Chem. 35:843–854. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Wang MD, Lv GT, An HW, Zhang NY and Wang
H: In Situ Self-assembly of bispecific peptide for cancer
immunotherapy. angewandte chemie international edition. Angew Chem
Int Ed Engl. 61:e2021136492022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Ranjbar L, Maleki F, Sadeghzadeh N,
Abediankenari S, Mardanshahi A and Masteri Farahani A: In vitro/in
vivo assessment of the targeting ability of [99mTc] Tc-labeled an
aptide specific to the extra domain B of fibronectin (APTEDB) for
colorectal cancer. Ann Nucl Med. 34:460–466. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Ghaffari H, Atashzar MR and Abdollahi H:
Molecular imaging in tracking cancer stem cells: A review. Med J
Islam Repub Iran. 34:902020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Noh I, Son Y, Jung W, Kim M, Kim D, Shin
H, Kim YC and Jon S: Targeting the tumor microenvironment with
amphiphilic near-infrared cyanine nanoparticles for potentiated
photothermal immunotherapy. Biomaterials. 275:1209262021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Henze J: Immunotherapy of solid tumors:
Multimodal imaging strategies for chimeric antigen receptor T cell
tracking in the tumor microenvironment. Dissertation Göttingen:
Georg-August Universität; 2021
|
|
106
|
Sun Y, Kim HS, Park J, Li M, Tian L, Choi
Y, Choi BI, Jon S and Moon WK: MRI of breast tumor initiating cells
using the extra domain-B of fibronectin targeting nanoparticles.
Theranostics. 4:845–857. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Sun Y, Kim HS, Kang S, Piao YJ, Jon S and
Moon WK: Magnetic resonance Imaging-guided drug delivery to breast
cancer Stem-like cells. Adv Healthc Mater. 7:e18002662018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Park J, Kim S, Saw PE, Lee IH, Yu MK, Kim
M, Lee K, Kim YC, Jeong YY and Jon S: Fibronectin extra domain
B-specific aptide conjugated nanoparticles for targeted cancer
imaging. J Control Release. 163:111–118. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Jailkhani N, Ingram JR, Rashidian M,
Rickelt S, Tian C, Mak H, Jiang Z, Ploegh HL and Hynes RO:
Noninvasive imaging of tumor progression, metastasis and fibrosis
using a nanobody targeting the extracellular matrix. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 116:187452019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Reeves KM: Applying PET imaging to cancer
immunotherapy to improve clinical outcomes. The University of
Alabama; Birmingham: 2022
|
|
111
|
Rossin R, Berndorff D, Friebe M,
Dinkelborg LM and Welch MJ: Small-animal PET of tumor angiogenesis
using a (76)Br-labeled human recombinant antibody fragment to the
ED-B domain of fibronectin. J Nucl Med. 48:1172–1179. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Berndorff D, Borkowski S, Moosmayer D,
Viti F, Müller-Tiemann B, Sieger S, Friebe M, Hilger CS, Zardi L,
Neri D and Dinkelborg LM: Imaging of tumor angiogenesis using
99mTc-labeled human recombinant anti-ED-B fibronectin antibody
fragments. J Nucl Med. 47:1707–1716. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Zhao Q, Zong H, Zhu P, Su C, Tang W, Chen
Z and Jin S: Crosstalk between colorectal CSCs and immune cells in
tumorigenesis and strategies for targeting colorectal CSCs. Exp
Hematol Oncol. 13:62024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Morgos DT, Stefani C, Miricescu D, Greabu
M, Stanciu S, Nica S, Stanescu-Spinu II, Balan DG,
Balcangiu-Stroescu AE, Coculescu EC, et al: Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR
and MAPK signaling pathways in gastric cancer. Int J Mol Sci.
25:18482024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Yu J, Li S, Chen D, Liu D, Guo H, Yang C,
Zhang W, Zhang L, Zhao G, Tu X, et al: SIRPα-Fc fusion protein
IMM01 exhibits dual anti-tumor activities by targeting CD47/SIRPα
signal pathway via blocking the ‘don't eat me’ signal and
activating the ‘eat me’ signal. J Hematol Oncol. 15:1672022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Li R, Wang Q, She K, Lu F and Yang Y:
CRISPR/Cas systems usher in a new era of disease treatment and
diagnosis. Mol Biomed. 3:312022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Dabas P and Danda A: Revolutionizing
cancer treatment: A comprehensive review of CAR-T cell therapy. Med
Oncol. 40:2752023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Johannsen M, Spitaleri G, Curigliano G,
Roigas J, Weikert S, Kempkensteffen C, Roemer A, Kloeters C,
Rogalla P, Pecher G, et al: The tumour-targeting human L19-IL2
immunocytokine: Preclinical safety studies, phase I clinical trial
in patients with solid tumours and expansion into patients with
advanced renal cell carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 46:2926–2935. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Schliemann C, Börschel N, Schwöppe C,
Liersch R, Kessler T, Dreyling M, Klapper W, Menssen HD, Neri D,
Berdel WE and Mesters RM: Targeting Interleukin-2 to the
neovasculature potentiates Rituximab's activity against mantle cell
lymphoma in mice. Blood. 120:3716. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Orecchia P, Balza E, Pietra G, Conte R,
Bizzarri N, Ferrero S, Mingari MC and Carnemolla B: L19-IL2
immunocytokine in combination with the anti-syndecan-1 46F2SIP
antibody format: A new targeted treatment approach in an ovarian
carcinoma model. Cancers (Basel). 11:12322019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Schliemann C, Palumbo A, Zuberbühler K,
Villa A, Kaspar M, Trachsel E, Klapper W, Menssen HD and Neri D:
Complete eradication of human B-cell lymphoma xenografts using
rituximab in combination with the immunocytokine L19-IL2. Blood.
113:2275–2283. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Weide B, Eigentler T, Catania C, Ascierto
PA, Cascinu S, Becker JC, Hauschild A, Romanini A, Danielli R,
Dummer R, et al: A phase II study of the L19IL2 immunocytokine in
combination with dacarbazine in advanced metastatic melanoma
patients. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 68:1547–1559. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Van Limbergen EJ, Hoeben A, Lieverse RIY,
Houben R, Overhof C, Postma A, Zindler J, Verhelst F, Dubois LJ, De
Ruysscher D, et al: Toxicity of L19-Interleukin 2 Combined with
Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy: A Phase 1 Study. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 109:1421–1430. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Lieverse RIY, Van Limbergen EJ, Oberije
CJG, Troost EGC, Hadrup SR, Dingemans AC, Hendriks LEL, Eckert F,
Hiley C, Dooms C, et al: Stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy
(SABR) combined with immunotherapy (L19-IL2) versus standard of
care in stage IV NSCLC patients, ImmunoSABR: A multicentre,
randomised controlled open-label phase II trial. BMC Cancer.
20:5572020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Zhang S, Mills D, Kim JY, Knudsen N,
Nelson J, Buechler Y and Skidmore L: 41P Evaluation of ARX517: A
next-generation anti-PSMA antibody drug conjugate for prostate
cancer treatment, in preclinical enzalutamide-resistant and
enzalutamide-sensitive pharmacology models and in toxicology
models. Ann Oncol. 34 (Suppl 2):S1992023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Nakada T, Sugihara K, Jikoh T, Abe Y and
Agatsuma T: The latest research and development into the
antibody-drug conjugate, (fam-)Trastuzumab Deruxtecan (DS-8201a),
for HER2 cancer therapy. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 67:173–185. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Ceci C, Lacal PM and Graziani G:
Antibody-drug conjugates: Resurgent anticancer agents with
multi-targeted therapeutic potential. Pharmacol Ther.
236:1081062022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Rudman SM, Jameson MB, McKeage MJ, Savage
P, Jodrell DI, Harries M, Acton G, Erlandsson F and Spicer JF: A
phase 1 study of AS1409, a novel Antibody-cytokine fusion protein,
in patients with malignant melanoma or renal cell carcinoma. Clin
Cancer Res. 17:1998–2005. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Ongaro T, Gouyou B, Stringhini M,
Corbellari R, Neri D and Villa A: A novel format for recombinant
antibody-interleukin-2 fusion proteins exhibits superior
tumor-targeting properties in vivo. Oncotarget. 11:3698–3711. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Wilks S, Carneiro BA, Coté GM, Henry J,
Sen S, Spira AL, Tsai F YC, Wang JS, Crochiere M, He S, et al: 762
A first-in-human phase 1 clinical study evaluating safety,
tolerability, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and efficacy of
the EDB+FN targeting ADC PYX-201 in participants with advanced
solid tumors. J Immunother Cancer. 11 (Suppl 1):A1–A1731. 2023.
|
|
131
|
Hooper AT, Marquette K, Chang CB, Golas J,
Jain S, Lam MH, Guffroy M, Leal M, Falahatpisheh H, Mathur D, et
al: Anti-extra Domain B splice variant of fibronectin antibody-drug
conjugate eliminates tumors with enhanced efficacy when combined
with checkpoint blockade. Mol Cancer Ther. 21:1462–1472. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Trachsel E, Bootz F, Silacci M, Kaspar M,
Kosmehl H and Neri D: Antibody-mediated delivery of IL-10 inhibits
the progression of established collagen-induced arthritis.
Arthritis Res Ther. 9:R92007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Kaspar M, Trachsel E and Neri D: The
antibody-mediated targeted delivery of interleukin-15 and GM-CSF to
the tumor neovasculature inhibits tumor growth and metastasis.
Cancer Res. 67:4940–4948. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Ruan JI: Blocking leptin-STAT3
axis-induced fatty acid oxidation: A novel approach to activate
CD8+ T effector cells in breast cancer. Thoracic Cancer.
11:3422–3424. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Di Nitto C, Gilardoni E, Mock J, Nadal L,
Weiss T, Weller M, Seehusen F, Libbra C, Puca E, Neri D and De Luca
R: An engineered IFNγ-antibody fusion protein with improved
tumor-homing properties. Pharmaceutics. 15:3772023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Niu J, Kaufman HL, Kichenadasse G, Haydon
AM, Barve MA, Ganju V, Iannotti Buchbinder E, Spira AI, Pang W, Fu
W, et al: Updated results from an ongoing phase 1/2a study of
T3011, an oncolytic HSV expressing IL-12 and PD-1 antibody,
administered via IT injection as monotherapy or combined with
pembrolizumab in advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 41
(16_suppl):95352023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Danielli R, Patuzzo R, Di Giacomo AM,
Gallino G, Maurichi A, Di Florio A, Cutaia O, Lazzeri A, Fazio C,
Miracco C, et al: Intralesional administration of L19-IL2/L19-TNF
in stage III or stage IVM1a melanoma patients: Results of a phase
II study. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 64:999–1009. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Papadia F, Basso V, Patuzzo R, Maurichi A,
Di Florio A, Zardi L, Ventura E, González-Iglesias R, Lovato V,
Giovannoni L, et al: Isolated limb perfusion with the
tumor-targeting human monoclonal antibody-cytokine fusion protein
L19-TNF plus melphalan and mild hyperthermia in patients with
locally advanced extremity melanoma. J Surg Oncol. 107:173–179.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Spitaleri G, Berardi R, Pierantoni C, De
Pas T, Noberasco C, Libbra C, González-Iglesias R, Giovannoni L,
Tasciotti A, Neri D, et al: Phase I/II study of the
tumour-targeting human monoclonal antibody-cytokine fusion protein
L19-TNF in patients with advanced solid tumours. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 139:447–455. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Spaeth N, Wyss MT, Pahnke J, Biollaz G,
Trachsel E, Drandarov K, Treyer V, Weber B, Neri D and Buck A:
Radioimmunotherapy targeting the extra domain B of fibronectin in
C6 rat gliomas: A preliminary study about the therapeutic efficacy
of iodine-131-labeled SIP (L19). Nucl Med Biol. 33:661–666. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Saif A, Rossi AJ, Sarnaik A, Hernandez JM
and Zager JS: Efficacy of neoadjuvant intratumoral
Darleukin/Fibromun (L19IL2 + L19TNF) in patients with clinical
stage IIIB/C melanoma (Neo-DREAM). Ann Surg Oncol. 29:3377–3378.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Hauschild A, Hassel JC, Ziemer M,
Rutkowski P, Meier FE, Flatz L, Gaudy-Marqueste C, Santinami M,
Russano F, von Wasielewski I, et al: Phase 3 study (PIVOTAL) of
neoadjuvant intralesional daromun vs. immediate surgery in fully
resectable melanoma with regional skin and/or nodal metastases. J
Clin Oncol. 42 (17_suppl):LBA95012024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
143
|
Borga G, Sucre S, Sucre O, Vivas L,
Salazar H and Sucre CE: Use of tumor mutational burden as a
predictive marker of response to immuno-oncology agents: Initial
experience at an academic center in Venezuela. J Clin Oncol. 41
(16_suppl):e146132023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Park SE: Design and Sythesis of conjugages
of amphiphilic cell-penetrating peptides containing anticancer drug
and ligand for extra cellular matrix biomarker to provide efficient
tumor-targeting. Irvine, CA: Chapman University; 2021
|
|
145
|
Yu B, Hwang D, Jeon H, Kim H, Lee Y, Keum
H, Kim J, Lee DY, Kim Y, Chung J and Jon S: A hybrid platform based
on a bispecific peptide-antibody complex for targeted cancer
therapy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 58:2005–2010. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Park SE, El-Sayed NS, Shamloo K, Lohan S,
Kumar S, Sajid MI and Tiwari RK: Targeted delivery of cabazitaxel
using cyclic cell-penetrating peptide and biomarkers of
extracellular matrix for prostate and breast cancer therapy.
Bioconjug Chem. 32:1898–1914. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Yu B, Yoo D, Kim KH, Kim TW, Park S, Kim
Y, Son Y, Kim J, Noh I, Whang CH, et al: Effective combination
immunotherapy through vessel normalization using a cancer-targeting
antiangiogenic peptide-antibody hybrid. Advanced Therapeutics:.
5:21001512022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
Park SE, Shamloo K, Kristedja TA, Darwish
S, Bisoffi M, Parang K and Tiwari RK: EDB-FN targeted peptide-drug
conjugates for use against prostate cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 20:3291.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Kim H, Hwang D, Choi M, Lee S, Kang S, Lee
Y, Kim S, Chung J and Jon S: Antibody-assisted delivery of a
peptide-drug conjugate for targeted cancer therapy. Mol Pharm.
16:165–172. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Kim YJ, Bae J, Shin TH, Kang SH, Jeong M,
Han Y, Park JH, Kim SK and Kim YS: Immunoglobulin Fc-fused,
neuropilin-1-specific peptide shows efficient tumor tissue
penetration and inhibits tumor growth via anti-angiogenesis. J
Control Release. 216:56–68. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Hong Y, Gao D, Zhao B, Ma J, Yang Z and
Guo H: Thermal immuno-nanomedicine: A new strategy for cancer
treatment. Clin Transl Med. 23:e12562023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Saw PE, Zhang A, Nie Y, Zhang L, Xu Y and
Xu X: Tumor-associated fibronectin targeted liposomal nanoplatform
for cyclophilin A siRNA delivery and targeted malignant
glioblastoma therapy. Front Pharmacol. 9:11942018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Javid H, Oryani MA, Rezagholinejad N,
Hashemzadeh A and Karimi-Shahri M: Unlocking the potential of
RGD-conjugated gold nanoparticles: A new frontier in targeted
cancer therapy, imaging, and metastasis inhibition. J Mater Chem B.
12:10786–10817. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Saw PE, Xu X, Kang BR, Lee J, Lee YS, Kim
C, Kim H, Kang SH, Na YJ, Moon HJ, et al: Extra-domain B of
fibronectin as an alternative target for drug delivery and a cancer
diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for malignant glioma.
Theranostics. 11:941–957. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Yu M, Leitao R, Xu X, Saw PE, Ortega CA,
Si K, Ahn S, Liu J, Lotfi A, Lee I-H, et al: Fibronectin
Extradomain B (FN-EDB) expression is specific to the
atherosclerotic lesion types III, IV, and V, and the FN-EDB
targeting nanomedicine enhances atherosclerotic plaque detection
and local delivery of model drug cargo. Arteriosclerosis Thrombosis
Vascular Biol. 37 (Suppl_1):A4672017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
156
|
Zhou Y, Qian M, Li J, Ruan L, Wang Y, Cai
C, Gu S and Zhao X: The role of tumor-associated macrophages in
lung cancer: From mechanism to small molecule therapy. Biomed
Pharmacother. 170:116014. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Lee JH, Carlino MS and Rizos H: Dosing of
BRAF and MEK inhibitors in melanoma: No point in taking a break.
Cancer Cell. 38:779–781. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Kapoor AR and Mittal V: Immunoregulatory
role of club cell secretory proteins in non-small cell lung cancer.
Cancer Res. 83 (7_Suppl):44242023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
159
|
Ji P, Gong Y, Jin M, Hu X, Di G and Shao
Z: 23P in vivo multi-dimensional CRISPR screens identify LGALS2 as
an immunotherapy target in triple-negative breast cancer. Ann
Oncol. 33:S1332022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
160
|
Canè S, Barouni RM, Fabbi M, Cuozzo J,
Fracasso G, Adamo A, Ugel S, Trovato R, De Sanctis F, Giacca M, et
al: Neutralization of NET-associated human ARG1 enhances cancer
immunotherapy. Sci Transl Med. 15:eabq62212023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Baumgartner CK, Ebrahimi-Nik H,
Iracheta-Vellve A, Hamel KM, Olander KE, Davis TGR, McGuire KA,
Halvorsen GT, Avila OI, Patel CH, et al: The PTPN2/PTPN1 inhibitor
ABBV-CLS-484 unleashes potent anti-tumour immunity. Nature.
622:850–862. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Jogalekar MP, Rajendran RL, Khan F, Dmello
C, Gangadaran P and Ahn BC: CAR T-cell-based gene therapy for
cancers: New perspectives, challenges, and clinical developments.
Front Immunol. 13:9259852022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Tang J, Liu N, Zhu Y, Li Y and Zhao X:
CAR-T therapy targets extra domain b of fibronectin positive solid
tumor cells. Immunol Invest. 52:985–996. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Zhang Z, Liu C, Wang M, Sun R, Yang Z, Hua
Z, Wu Y, Wu M, Wang H, Qiu W, et al: Treating solid tumors with
TCR-based chimeric antigen receptor targeting extra domain
B-containing fibronectin. J Immunother Cancer. 11:e0071992023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Gentile D, Orlandi P, Banchi M and Bocci
G: Preclinical and clinical combination therapies in the treatment
of anaplastic thyroid cancer. Med Oncol. 37:192020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Zhang S, Hao R, Wang H, Yi QY, Yantao Y,
Zhong Y and Sun M: Peri cruiser CAR-T: An innovative platform to
reduce on-target off-tumor toxicity of CAR-T therapy. J Clin Oncol.
41 (16_suppl):25392023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
167
|
Zhang Z, Liu C, Yang Z and Yin H:
CAR-T-cell therapy for solid tumors positive for fibronectin extra
Domain B. Cells. 11:28632022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Martínez Bedoya D, Gustave R, Corlazzoli
F, Dutoit V and Migliorini D: 53P A multispecific non-integrating
RNA CAR T platform to overcome the clinical challenge of
glioblastoma heterogeneity. Ann Oncol. 32:S13952021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
169
|
Parikh RH and Lonial S: Chimeric antigen
receptor T-cell therapy in multiple myeloma: A comprehensive review
of current data and implications for clinical practice. CA Cancer J
Clin. 73:275–285. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Xiong Q, Wang H, Shen Q, Wang Y, Yuan X,
Lin G and Jiang P: The development of chimeric antigen receptor
T-cells against CD70 for renal cell carcinoma treatment. J Transl
Med. 22:3682024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Zhu G, Zhang J, Zhang Q, Jin G, Su X, Liu
S and Liu F: Enhancement of CD70-specific CAR T treatment by IFN-γ
released from oHSV-1-infected glioblastoma. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 71:2433–2448. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Wu G, Guo S, Luo Q, Wang X, Deng W, Ouyang
G, Pu JJ, Lei W and Qian W: Preclinical evaluation of CD70-specific
CAR T cells targeting acute myeloid leukemia. Front Immunol.
14:10937502023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Li X, Zhu T, Wang R, Chen J, Tang L, Huo
W, Huang X and Cao Q: Genetically programmable vesicles for
enhancing CAR-T therapy against solid tumors. Adv Mater.
35:e22111382023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Li Y, Liu Y, Cui Q, Liu L, Li Z, Cui W, Li
M, Zhu X, Kang L, Yu L, et al: Rituximab improves clinical outcomes
of CAR-T therapy for r/r B-ALL via sensitizing leukemia cells to
CAR-T-mediated cytotoxicity and reducing CAR-T exhaustion. Blood.
142 (Suppl 1):68032023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
175
|
Simmons ME, McIntosh J, Zhang T, Li Y, Yan
F, Yao Y, Nie L, Lee HH, Wang W, Jiang VC, et al: The reversible
BTK inhibitor nemtabrutinib demonstrates favorable antitumor
efficacy and enhances the function of CAR T cells in mantle cell
lymphoma. Blood. 142 (Suppl 1):57892023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
176
|
Gholamrezanezhad A, Shooli H, Jokar N,
Nemati R and Assadi M: Radioimmunotherapy (RIT) in brain tumors.
Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 53:374–381. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Leung K: I-Human recombinant anti-ED-B
fibronectin antibody small immunoprotein. Molecular Imaging and
Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) Bethesda (MD): National Center for
Biotechnology Information (US); April 17–2007, PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Borsi L, Balza E, Bestagno M, Castellani
P, Carnemolla B, Biro A, Leprini A, Sepulveda J, Burrone O, Neri D
and Zardi L: Selective targeting of tumoral vasculature: Comparison
of different formats of an antibody (L19) to the ED-B domain of
fibronectin. Int J Cancer. 102:75–85. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Li R, He H, Li X, Zheng X, Li Z, Zhang H,
Ye J, Zhang W, Yu C, Feng G and Fan W: EDB-FN targeted probes for
the surgical navigation, radionuclide imaging and therapy of
thyroid cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 50:2100–2113. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Tijink BM, Perk LR, Budde M, Stigter-van
Walsum M, Visser GW, Kloet RW, Dinkelborg LM, Leemans CR, Neri D
and van Dongen GA: (124)I-L19-SIP for immuno-PET imaging of tumour
vasculature and guidance of (131)I-L19-SIP radioimmunotherapy. Eur
J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 36:1235–1244. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Moosmayer D, Berndorff D, Chang CH,
Sharkey RM, Rother A, Borkowski S, Rossi EA, McBride WJ, Cardillo
TM, Goldenberg DM and Dinkelborg LM: Bispecific antibody
pretargeting of tumor neovasculature for improved systemic
radiotherapy of solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 12:5587–5595. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Del Conte G, Erba PA, Fasolo A, Chiesa C,
Grana C, Menssen H, Neri D, Mariani G, Bombardieri E and Gianni L:
Radioimmunotherapy (RIT) with 131l-L19SIP in solid
cancers (SC) and lymphoproliferative diseases: Final results of the
first human trial. J Clin Oncol. 28 (15_suppl):25232010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
183
|
Petrini I, Sollini M, Bartoli F, Barachini
S, Montali M, Pardini E, Burzi IS and Erba PA: ED-B-containing
isoform of fibronectin in tumor microenvironment of thymomas: A
target for a theragnostic approach. Cancers (Basel). 14:25922022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Miura JT and Zager JS: Neo-DREAM study
investigating Daromun for the treatment of clinical stage IIIB/C
melanoma. Future Oncol. 15:3665–3674. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Vaidya AM, Wang H, Qian V and Lu ZR:
Extradomain-B Fibronectin is a molecular marker of invasive breast
cancer cells. bioRxiv. Aug 22–2019.doi: 10.1101/743500.
|