|
1
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Organization GWH, . Global Breast Cancer
Initiative Implementation Framework: Assessing, strengthening and
scaling-up of services for the early detection and management of
breast cancer. CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. 2023.
|
|
3
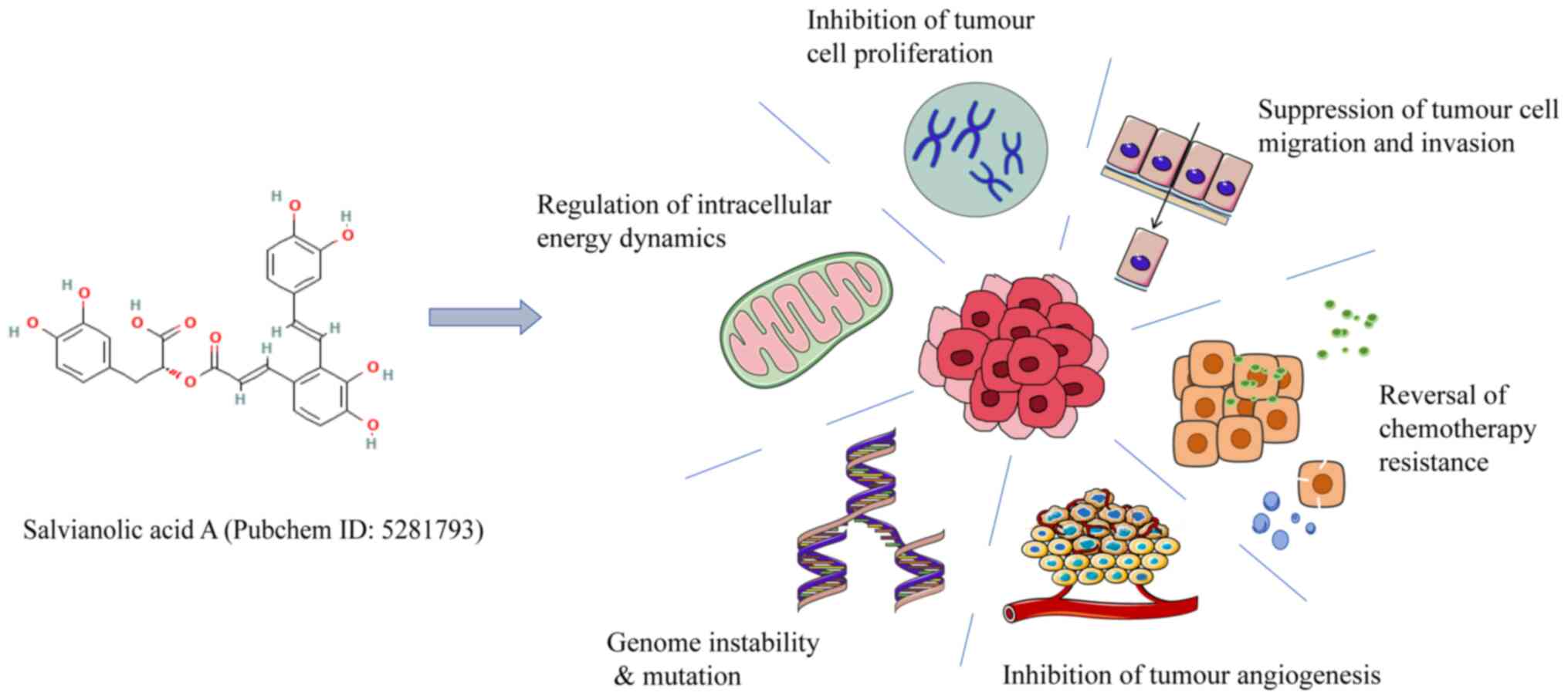
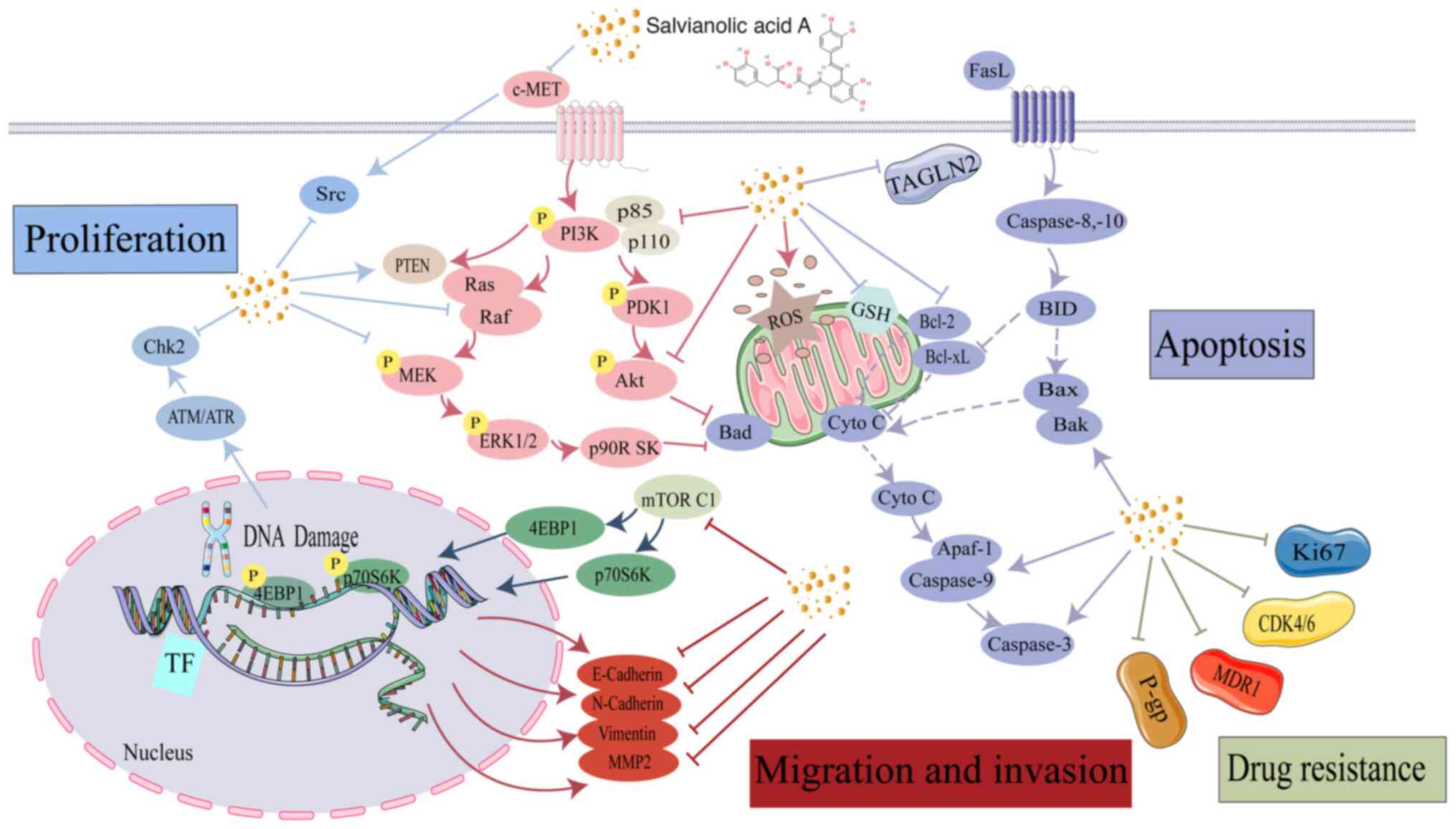
|
Xin J, Song M, Liu X, Zou H, Wang J, Xiao
L, Jia Y, Zhang G, Jiang W, Lei M, et al: A new strategy of using
low-dose caffeic acid carbon nanodots for high resistance to poorly
differentiated human papillary thyroid cancer. J Nanobiotechnology.
22:5712024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Diefenhardt M, Martin D, Hofheinz RD,
Ghadimi M, Fokas E, Rödel C and Fleischmann M: Persistent lymph
node metastases after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy for rectal
cancer. JAMA Netw Open. 7:e24329272024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Guo J, Chen X, Wu M, Wang D, Zhao Y, Li Q,
Tang G, Che F, Xia Z, Liang Z, et al: Traditional Chinese medicine
FYTF-919 (Zhongfeng Xingnao oral prescription) for the treatment of
acute intracerebral haemorrhage: A multicentre, randomised,
placebo-controlled, double-blind, clinical trial. Lancet.
404:2187–2196. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang W, Wang J, Kuang M, Xiao Z, Fan B,
Sun G and Tan Z: Exploring global research status and trends in
anti-obesity effects of traditional Chinese medicine through
intestinal microbiota: A bibliometric study. Front Cell Infect
Microbiol. 13:12714732023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fan Y, Liu J, Miao J, Zhang X, Yan Y, Bai
L, Chang J, Wang Y, Wang L, Bian Y and Zhou H: Anti-inflammatory
activity of the Tongmai Yangxin pill in the treatment of coronary
heart disease is associated with estrogen receptor and NF-κB
signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 276:1141062021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu Y, Fang C, Luo J, Gong C, Wang L and
Zhu S: Traditional Chinese medicine for cancer treatment. Am J Chin
Med. 52:583–604. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li J, Wang S, Wang N, Zheng Y, Yang B,
Wang X, Zhang J, Pan B and Wang Z: Aiduqing formula inhibits breast
cancer metastasis by suppressing TAM/CXCL1-induced Treg
differentiation and infiltration. Cell Commun Signal. 19:892021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yan X, Yao C, Fang C, Han M, Gong C, Hu D,
Shen W, Wang L, Li S and Zhu S: Rocaglamide promotes the
infiltration and antitumor immunity of NK cells by activating
cGAS-STING signaling in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Biol Sci.
18:585–598. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Man S, Liu W, Bi J, Bai J, Wu Q, Hu B, Hu
J and Ma L: Smart mesoporous silica nanoparticles loading curcumin
inhibit liver cancer. J Agric Food Chem. 72:25743–25754. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Islam MS, Wang C, Zheng J, Paudyal N, Zhu
Y and Sun H: The potential role of tubeimosides in cancer
prevention and treatment. Eur J Med Chem. 162:109–121. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ma J, Wang J, Wan Y, Wang S and Jiang C:
Probiotic-fermented traditional Chinese herbal medicine, a
promising approach to maintaining the intestinal microecology. J
Ethnopharmacol. 337:1188152024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou L, Zuo Z and Chow MS: Danshen: An
overview of its chemistry, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and
clinical use. J Clin Pharmacol. 45:1345–1359. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jia Y, Yao D, Bi H, Duan J, Liang W, Jing
Z and Liu M: Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge (Danshen) based
nano-delivery systems for anticancer therapeutics. Phytomedicine.
128:1555212024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang J, Zhang J, Sun C, Yang R, Sheng M,
Hu J, Kai G and Han B: Adjuvant role of Salvia miltiorrhiza
bunge in cancer chemotherapy: A review of its bioactive components,
health-promotion effect and mechanisms. J Ethnopharmacol.
318:1170222024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shan XX, Hong BZ, Liu J, Wang GK, Chen WD,
Yu NJ, Peng DY, Wang L and Zhang CY: Review of chemical
composition, pharmacological effects, and clinical application of
Salviae Miltiorrhizae Radix et Rhizoma and prediction of its
Q-markers. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 46:5496–5511. 2021.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang J, Jin Q, Deng Y, Hou J, Wu W and
Guo D: New depsides from the roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza
and their radical-scavenging capacity and protective effects
against H2O2-induced H9c2 cells. Fitoterapia. 121:46–52. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
National Center for Biotechnology
Information, . ‘PubChem Compound Summary for CID 5281793.
Salvianolic acid A’ PubChem; https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Salvianolic-acid-A2–January.
2024
|
|
20
|
Zhao H, Han B, Li X, Sun C, Zhai Y, Li M,
Jiang M, Zhang W, Liang Y and Kai G: Salvia miltiorrhiza in
breast cancer treatment: A review of its phytochemistry,
derivatives, nanoparticles, and potential mechanisms. Front
Pharmacol. 13:8720852022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim S, Chen J, Cheng T, Gindulyte A, He J,
He S, Li Q, Shoemaker BA, Thiessen PA, Yu B, et al: PubChem 2023
update. Nucleic Acids Res. 51:D1373–D1380. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Diao HY, Zhu W, Liu J, Yin S, Wang JH and
Li CL: Salvianolic acid a improves rat kidney injury by regulating
MAPKs and TGF-β1/Smads signaling pathways. Molecules. 28:36302023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang HF, Wang YL, Gao C, Gu YT, Huang J,
Wang JH, Wang JH and Zhang Z: Salvianolic acid A attenuates kidney
injury and inflammation by inhibiting NF-κB and p38 MAPK signaling
pathways in 5/6 nephrectomized rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
39:1855–1864. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen Z, Li D, Wang T, Li Y, Qin P, Zhu H,
Zhang M, Li W, Yu L, Duan H, et al: Salvianolic acid A inhibits
pseudorabies virus infection by directly inactivating the virus
particle. Phytomedicine. 134:1560152024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Meirelles LEF, Souza MVF, Carobeli LR,
Morelli F, Mari NL, Damke E, Shinobu Mesquita CS, Teixeira JJV,
Consolaro MEL and Silva VRSD: Combination of conventional drugs
with biocompounds derived from cinnamic acid: A promising option
for breast cancer therapy. Biomedicines. 11:2752023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jiang H, Wang S, Liu Y, Zheng C, Chen L,
Zheng K, Xu Z, Dai Y, Jin H, Cheng Z, et al: Targeting EFNA1
suppresses tumor progression via the cMYC-modulated cell cycle and
autophagy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Discov Oncol.
14:642023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang LL, Li DY, Zhang YB, Zhu MY, Chen D
and Xu TD: Salvianolic acid A inhibits angiotensin II-induced
proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells by
attenuating the production of ROS. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 33:41–48.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhong W, Sun B, Gao W, Qin Y, Zhang H,
Huai L, Tang Y, Liang Y, He L, Zhang X, et al: Salvianolic acid A
targeting the transgelin-actin complex to enhance vasoconstriction.
EBioMedicine. 37:246–258. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pu XY, Mei Y, Zheng Q and Ko CY:
Inhibition of melanoma cell growth by salvianolic acid A through
CHK2-CDC25A pathway modulation. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed).
29:2132024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zheng X, Chen S, Yang Q, Cai J, Zhang W,
You H, Xing J and Dong Y: Salvianolic acid A reverses the
paclitaxel resistance and inhibits the migration and invasion
abilities of human breast cancer cells by inactivating transgelin
2. Cancer Biol Ther. 16:1407–1414. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Qin X, Guo J, Li H, He H, Cai F, Chen X,
Chen M, Chen T and Ma L: Selenium electrophilic center responsive
to biological electron donors for efficient chemotherapy. Adv Sci
(Weinh). e24120622025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhao M, Jiang X, Fang J, Lin Y, Li Y, Pei
R, Ye P, Lu Y and Jiang L: The kava chalcone flavokawain B exerts
inhibitory activity and synergizes with BCL-2 inhibition in
malignant B-cell lymphoma. Phytomedicine. 120:1550742023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hseu YC, Huang YC, Thiyagarajan V, Mathew
DC, Lin KY, Chen SC, Liu JY, Hsu LS, Li ML and Yang HL: Anticancer
activities of chalcone flavokawain B from Alpinia pricei Hayata in
human lung adenocarcinoma (A549) cells via induction of reactive
oxygen species-mediated apoptotic and autophagic cell death. J Cell
Physiol. 234:17514–17526. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang W, Dong J, Xu J, Qian Y, Chen D, Fan
Z, Yang H, Xiang J, Xue X, Luo X, et al: Columbianadin suppresses
glioblastoma progression by inhibiting the PI3K-Akt signaling
pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 223:1161122024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jiang S, Wang P, Sun X, Zhang M, Zhang S,
Cao Y, Wang Y, Liu L and Gao X: Mechanistic study of leukopenia
treatment by Qijiao shengbai Capsule via the Bcl2/Bax/CASAPSE3
pathway. Front Pharmacol. 15:14515532024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ye C, Yao Z, Wang Y and Zhang C:
Asiaticoside promoted ferroptosis and suppressed immune escape in
gastric cancer cells by downregulating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
Int Immunopharmacol. 134:1121752024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shin N, Lee HJ, Sim DY, Ahn CH, Park SY,
Koh W, Koh J, Koh BS, Koh B and Koh SH: Anti-warburg mechanism of
ginsenoside F2 in human cervical cancer cells via activation of
miR193a-5p and inhibition of β-Catenin/c-Myc/hexokinase 2 signaling
axis. Int J Mol Sci. 25:94182024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nilkhet S, Vongthip W, Lertpatipanpong P,
Prasansuklab A, Tencomnao T, Chuchawankul S and Baek SJ: Ergosterol
inhibits the proliferation of breast cancer cells by suppressing
AKT/GSK-3beta/beta-catenin pathway. Sci Rep. 14:196642024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pan C, Xu Y, Jiang Z, Fan C, Chi Z, Zhang
Y, Miao M, Ren Y, Wu Z, Xu L, et al: Naringenin relieves
paclitaxel-induced pain by suppressing calcitonin gene-related
peptide signalling and enhances the anti-tumour action of
paclitaxel. Br J Pharmacol. 18:3136–3159. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lin WS, Leland JV, Ho CT and Pan MH:
Occurrence, bioavailability, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer
effects of pterostilbene. J Agric Food Chem. 68:12788–12799. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li Y, Xu C, Weng W and Goel A: Combined
treatment with Aronia berry extract and oligomeric
proanthocyanidins exhibit a synergistic anticancer efficacy through
LMNB1-AKT signaling pathways in colorectal cancer. Mol Carcinog.
63:2145–2157. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Szoka L, Stocki M and Isidorov V:
Dammarane-Type 3,4-seco-triterpenoid from silver birch (Betula
pendula Roth) buds induces melanoma cell death by promotion of
apoptosis and autophagy. Molecules. 29:40912024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cai J, Chen S, Zhang W, Zheng X, Hu S,
Pang C, Lu J, Xing J and Dong Y: Salvianolic acid A reverses
paclitaxel resistance in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells via
targeting the expression of transgelin 2 and attenuating PI3 K/Akt
pathway. Phytomedicine. 21:1725–1732. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Fang CY, Wu CZ, Chen PN, Chang YC, Chuang
CY, Lai CT, Yang SF and Tsai LL: Antimetastatic potentials of
salvianolic acid A on oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting
MMP-2 and the c-Raf/MEK/ERK pathway. Environ Toxicol. 33:545–554.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Pei R, Si T, Lu Y, Zhou JX and Jiang L:
Salvianolic acid A, a novel PI3K/Akt inhibitor, induces cell
apoptosis and suppresses tumor growth in acute myeloid leukemia.
Leuk Lymphoma. 59:1959–1967. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Péczka N, Orgován Z, Ábrányi-Balogh P and
Keserű GM: Electrophilic warheads in covalent drug discovery: An
overview. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 17:413–422. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zheng M, Zhang Y, Xu Y, Han Y, Wu Y and
Kang J: Chemoproteomics and phosphoproteomics profiling reveals
salvianolic acid a as a covalent inhibitor of mTORC1. J Proteome
Res. 22:2450–2459. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yin X, Feng Y and Kang W: Effect of
salvianolic acid A on the proliferation and apoptosis in esophageal
cancer cells and the underlying mechanisms. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue
Bao Yi Xue Ban. 45:1269–1275. 2020.(In English, Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang X, Wang C, Zhang L, Li Y, Wang S,
Wang J, Yuan C, Niu J, Wang C and Lu G: Salvianolic acid A shows
selective cytotoxicity against multidrug-resistant MCF-7 breast
cancer cells. Anticancer Drugs. 26:210–223. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Tang XL, Yan L, Zhu L, Jiao DM, Chen J and
Chen QY: Salvianolic acid A reverses cisplatin resistance in lung
cancer A549 cells by targeting c-met and attenuating Akt/mTOR
pathway. J Pharmacol Sci. 135:1–7. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhang T, Xu J, Li D, Chen J, Shen X, Xu F,
Teng F, Deng Y, Ma H, Zhang L, et al: Salvianolic acid A, a matrix
metalloproteinase-9 inhibitor of Salvia miltiorrhiza,
attenuates aortic aneurysm formation in apolipoprotein E-deficient
mice. Phytomedicine. 21:1137–1145. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Li T, Kong AN, Ma Z, Liu H, Liu P, Xiao Y,
Jiang X and Wang L: Protein arginine methyltransferase 1 may be
involved in pregnane × receptor-activated overexpression of
multidrug resistance 1 gene during acquired multidrug resistant.
Oncotarget. 7:20236–20248. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kebebe D, Wu Y, Zhang B, Yang J, Liu Y, Li
X, Ma Z, Lu P, Liu Z and Li J: Dimeric c(RGD) peptide conjugated
nanostructured lipid carriers for efficient delivery of Gambogic
acid to breast cancer. Int J Nanomedicine. 14:6179–6195. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yang Y, Zhang L, La X, Li Z, Li H and Guo
S: Salvianolic acid A inhibits tumor-associated angiogenesis by
blocking GRP78 secretion. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol.
392:467–480. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhang SH, Su J and Zhen YS: Salvianolic
acid A inhibits nucleoside transport and potentiates the antitumor
activity of chemotherapeutic drugs. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 39:496–499.
2004.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
D'Arcy MS: Cell death: A review of the
major forms of apoptosis, necrosis and autophagy. Cell Biol Int.
43:582–592. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wong RS: Apoptosis in cancer: From
pathogenesis to treatment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 30:872011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Singh SP, Pathuri G, Asch AS, Rao CV and
Madka V: Stat3 inhibitors TTI-101 and SH5-07 suppress bladder
cancer cell survival in 3D tumor models. Cells. 13:14632024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Shaban NZ, Hegazy WA, Abu-Serie MM, Talaat
IM, Awad OM and Habashy NH: Seedless black Vitis vinifera
polyphenols suppress hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo
by targeting apoptosis, cancer stem cells, and proliferation.
Biomed Pharmacother. 175:1166382024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Thinnes FP: Neuroendocrine differentiation
of LNCaP cells suggests: VDAC in the cell membrane is involved in
the extrinsic apoptotic pathway. Mol Genet Metab. 97:241–243. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Conti Nibali S, De Siervi S, Luchinat E,
Magrì A, Messina A, Brocca L, Mantovani S, Oliviero B, Mondelli MU,
De Pinto V, et al: VDAC1-interacting molecules promote cell death
in cancer organoids through mitochondrial-dependent metabolic
interference. iScience. 27:1098532024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kulyar MF, Mo Q, Yao W, Li Y, Nawaz S,
Loon KS, Ahmed AE, Alsaegh AA, Al Syaad KM, Akhtar M, et al:
Modulation of apoptosis and Inflammasome activation in
chondrocytes: Co-regulatory role of Chlorogenic acid. Cell Commun
Signal. 22:22024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Van Opdenbosch N and Lamkanfi M: Caspases
in cell death, inflammation, and disease. Immunity. 50:1352–1364.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Soengas MS, Alarcón RM, Yoshida H, Giaccia
AJ, Hakem R, Mak TW and Lowe SW: Apaf-1 and caspase-9 in
p53-dependent apoptosis and tumor inhibition. Science. 284:156–159.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Pettigrew CA and Cotter TG: Deregulation
of cell death (apoptosis): Implications for tumor development.
Discov Med. 8:61–63. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Carneiro BA and El-Deiry WS: Targeting
apoptosis in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 17:395–417. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Peng H, Yuan X, Shi R, Wei X, Ren S, Yan
C, Ding Y, Lin Y, Fan D, Yang M, et al: PHII-7 inhibits cell growth
and induces apoptosis in leukemia cell line K562 as well as its
MDR-counterpart K562/A02 through producing reactive oxygen species.
Eur J Pharmacol. 718:459–468. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Liu J, Liu Y, Li H, Wei C, Mao A, Liu W
and Pan G: Polyphyllin D induces apoptosis and protective autophagy
in breast cancer cells through JNK1-Bcl-2 pathway. J
Ethnopharmacol. 282:1145912022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Wang S, Yadav AK, Han JY, Ahn KS and Jang
BC: Anti-Growth, Anti-angiogenic, and pro-apoptotic effects by
CX-4945, an inhibitor of casein kinase 2, on HuCCT-1 human
cholangiocarcinoma cells via control of caspase-9/3, DR-4,
STAT-3/STAT-5, Mcl-1, eIF-2α, and HIF-1α. Int J Mol Sci.
23:63532022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Tang Z, Ding J and Xiao X: Salvianolic
acid a induces apoptosis and inhibits the C-Met expression in
hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cell line. Chin J Mod Appl Pharm.
31:537–541. 2014.
|
|
71
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Seront E, Pinto A, Bouzin C, Bertrand L,
Machiels JP and Feron O: PTEN deficiency is associated with reduced
sensitivity to mTOR inhibitor in human bladder cancer through the
unhampered feedback loop driving PI3K/Akt activation. Br J Cancer.
109:1586–1592. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Sun B, Zhao Y, Yang S, Li X, Li N, Wang Y,
Han Q, Liu X, Tu Q, Zheng J and Zhang X: Celecoxib as a potential
treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma in populations exposed to
high PFAS levels. J Hazard Mater. 489:1376132025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Li J, Bian X, Zhang C, Chen Y, Huang S,
Zhao S and Li Y: Identifying prognostic biomarkers and immune
interactions in ovarian cancer associated with perfluorooctanoic
acid exposure: Insights from comparative toxicogenomics and
molecular docking studies. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 291:1178312025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Hu M, Tao P, Wang Y, Zhu C, Ma Y, Liu X
and Cai H: Knockdown of CCNB2 inhibits the tumorigenesis of gastric
cancer by regulation of the PI3K/Akt pathway. Sci Rep. 15:57032025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Noorolyai S, Shajari N, Baghbani E,
Sadreddini S and Baradaran B: The relation between PI3K/AKT
signalling pathway and cancer. Gene. 698:120–128. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Bi L, Chen J, Yuan X, Jiang Z and Chen W:
Salvianolic acid A positively regulates PTEN protein level and
inhibits growth of A549 lung cancer cells. Biomed Rep. 1:213–217.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Wülfing P, Kersting C, Tio J, Fischer RJ,
Wülfing C, Poremba C, Diallo R, Böcker W and Kiesel L:
Endothelin-1-, endothelin-A-, and endothelin-B-receptor expression
is correlated with vascular endothelial growth factor expression
and angiogenesis in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 10:2393–2400.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Zhang Q, Wang S, Yu Y, Sun S, Zhang Y,
Zhang Y, Yang W, Li S and Qiao Y: Salvianolic acid A, as a novel
ETA receptor antagonist, shows inhibitory effects on tumor in
vitro. Int J Mol Sci. 17:12442016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Leng X, Kan H, Wu Q, Li C, Zheng Y and
Peng G: Inhibitory effect of Salvia miltiorrhiza extract and
its active components on cervical intraepithelial neoplastic cells.
Molecules. 27:15822022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Li S, Fang J, Si T, Lu Y and Jiang L:
Salvianolic acid A inhibits the growth of diffuse large B-cell
lymphoma through MAPK pathways. Exp Hematol. 94:60–68.e2. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Li HY, Li Y, Yan CH, Li LN and Chen XG:
Inhibition of tumor growth by S-3-1, a synthetic intermediate of
salvianolic acid A. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 4:271–280. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Xuan Z, Zhang Y, Li D, Wang K, Huang P and
Shi J: PLXNB1/SEMA4D signals mediate interactions between malignant
epithelial and immune cells to promote colorectal cancer liver
metastasis. J Cell Mol Med. 28:e701422024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Xie S, Han S, Gong J, Feng Z, Sun Y, Yao H
and Shi P: Bee venom prompts the inhibition of gefitinib on
proliferation, migration, and invasion of non-small cell lung
cancer cells via EGFR-mediated autophagy. Toxicon. 251:1081492024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Li X, Sun Y, Guo J, Cheng Y, Lu W, Yang W,
Wang L and Cheng Z: Sodium bicarbonate potentiates the antitumor
effects of Olaparib in ovarian cancer via cGMP/PKG-mediated ROS
scavenging and M1 macrophage transformation. Biomed Pharmacother.
180:1175092024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Gupta GP and Massagué J: Cancer
metastasis: Building a framework. Cell. 127:679–695. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Liu L, Meng T, Zheng X, Liu Y, Hao R, Yan
Y, Chen S, You H, Xing J and Dong Y: Transgelin 2 promotes
paclitaxel resistance, migration, and invasion of breast cancer by
directly interacting with PTEN and activating PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β
pathway. Mol Cancer Ther. 18:2457–2468. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Fares J, Fares MY, Khachfe HH, Salhab HA
and Fares Y: Molecular principles of metastasis: A hallmark of
cancer revisited. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 5:282020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Mrozik KM, Blaschuk OW, Cheong CM,
Zannettino ACW and Vandyke K: N-cadherin in cancer metastasis, its
emerging role in haematological malignancies and potential as a
therapeutic target in cancer. BMC Cancer. 18:9392018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Saldanha R, Ho Thanh MT, Krishnan N,
Hehnly H and Patteson A: Vimentin supports cell polarization by
enhancing centrosome function and microtubule acetylation. J R Soc
Interface. 21:202306412024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Xypolita ME, Goolam M, Bikoff EK,
Robertson EJ and Mould AW: The zinc-finger transcription factor
Blimp1/Prdm1 is required for uterine remodelling and repair in the
mouse. Nat Commun. 16:12202025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Curran S and Murray GI: Matrix
metalloproteinases: Molecular aspects of their roles in tumour
invasion and metastasis. Eur J Cancer. 36:1621–1630. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Tong Z, Zhang Y, Guo P, Wang W, Chen Q,
Jin J, Liu S, Yu C, Mo P, Zhang L and Huang J: Steroid receptor
coactivator 1 promotes human hepatocellular carcinoma invasiveness
through enhancing MMP-9. J Cell Mol Med. 28:e181712024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Li K, Li D, Hafez B, Bekhit MMS, Jardan
YAB, Alanazi FK, Taha EI, Auda SH, Ramzan F and Jamil M:
Identifying and validating MMP family members (MMP2, MMP9, MMP12,
and MMP16) as therapeutic targets and biomarkers in kidney renal
clear cell carcinoma (KIRC). Oncol Res. 32:737–752. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Guo J, Song Z, Muming A, Zhang H and Awut
E: Cysteine protease inhibitor S promotes lymph node metastasis of
esophageal cancer cells via VEGF-MAPK/ERK-MMP9/2 pathway. Naunyn
Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 397:6051–6059. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Chuang CY, Ho YC, Lin CW, Yang WE, Yu YL,
Tsai MC, Yang SF and Su SC: Salvianolic acid A suppresses MMP-2
expression and restrains cancer cell invasion through ERK signaling
in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Ethnopharmacol.
252:1126012020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Stasiak P, Sopel J, Lipowicz JM,
Rawłuszko-Wieczorek AA, Korbecki J and Januchowski R: The role of
elacridar, a P-gp inhibitor, in the Re-sensitization of
PAC-resistant ovarian cancer cell lines to cytotoxic drugs in 2D
and 3D cell culture models. Int J Mol Sci. 26:11242025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Nikolaou M, Pavlopoulou A, Georgakilas AG
and Kyrodimos E: The challenge of drug resistance in cancer
treatment: A current overview. Clin Exp Metastasis. 35:309–318.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Jin Q, Ren Q, Chang X, Yu H, Jin X, Lu X,
He N and Wang G: Neuropilin-1 predicts poor prognosis and promotes
tumor metastasis through epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
gastric cancer. J Cancer. 12:3648–3659. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Yao S, Liu X, Feng Y, Li Y, Xiao X, Han Y
and Xia S: Unveiling the role of HGF/c-Met signaling in Non-small
cell lung cancer tumor microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci.
25:91012024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Xu J, Liu S, Yang X, Cao S and Zhou Y:
Paracrine HGF promotes EMT and mediates the effects of PSC on
chemoresistance by activating c-Met/PI3K/Akt signaling in
pancreatic cancer in vitro. Life Sci. 263:1185232020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Shao Z, Pan H, Tu S, Zhang J, Yan S and
Shao A: HGF/c-Met Axis: The advanced development in digestive
system cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. 8:8012020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Bahrami A, Shahidsales S, Khazaei M,
Ghayour-Mobarhan M, Maftouh M, Hassanian SM and Avan A: C-Met as a
potential target for the treatment of gastrointestinal cancer:
Current status and future perspectives. J Cell Physiol.
232:2657–2673. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Pilotto S, Carbognin L, Karachaliou N, Ma
PC, Rosell R, Tortora G and Bria E: Tracking MET de-addiction in
lung cancer: A road towards the oncogenic target. Cancer Treat Rev.
60:1–11. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Wu JC, Wang CT, Hung HC, Wu WJ, Wu DC,
Chang MC, Sung PJ, Chou YW, Wen ZH and Tai MH: Heteronemin is a
Novel c-Met/STAT3 inhibitor against advanced prostate cancer cells.
Prostate. 76:1469–1483. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Zhang Y, Xia M, Jin K, Wang S, Wei H, Fan
C, Wu Y, Li X, Li X, Li G, et al: Function of the c-Met receptor
tyrosine kinase in carcinogenesis and associated therapeutic
opportunities. Mol Cancer. 17:452018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Chen FY, Bi L, Qian L, Gao J, Jiang YC and
Chen WP: Identification of multidrug resistance gene MDR1
associated microRNA of salvianolic acid A reversal in lung cancer.
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 41:3279–3284. 2016.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Li H, Chen J, Xu C, Pang L and Cheng X:
Antitumor effect of salvianolic acid A and on its reversal of
multidrug resisitance in A549/MTX tumor. Chin J Clin Pharmacol
Ther. 22:12442017.
|
|
109
|
Ye T, Chen R, Zhou Y, Zhang J, Zhang Z,
Wei H, Xu Y, Wang Y and Zhang Y: Salvianolic acid A (Sal A)
suppresses malignant progression of glioma and enhances
temozolomide (TMZ) sensitivity via repressing transgelin-2 (TAGLN2)
mediated phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B
(Akt) pathway. Bioengineered. 13:11646–11655. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Zhang B, Zhang Y, Dang W, Xing B, Yu C,
Guo P, Pi J, Deng X, Qi D and Liu Z: The anti-tumor and
renoprotection study of E-[c(RGDfK)(2)]/folic acid co-modified
nanostructured lipid carrier loaded with doxorubicin
hydrochloride/salvianolic acid A. J Nanobiotechnology. 20:4252022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Xue L, Ouyang W, Qi P, Zhu Y, Qi X, Zhang
X, Zhang X, Wang L and Cui L: Key mechanisms of angiogenesis in the
infarct core: Association of macrophage infiltration with
venogenesis. Mol Brain. 18:122025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Yu Yan and Yuan E: Regulatory effect of
N6-methyladenosine on tumor angiogenesis. Front Immunol.
15:14537742024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Sayed ZS, Khattap MG, Madkour MA, Yasen
NS, Elbary HA, Elsayed RA, Abdelkawy DA, Wadan AS, Omar I and
Nafady MH: Circulating tumor cells clusters and their role in
Breast cancer metastasis; a review of literature. Discov Oncol.
15:942024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Lugano R, Ramachandran M and Dimberg A:
Tumor angiogenesis: Causes, consequences, challenges and
opportunities. Cell Mol Life Sci. 77:1745–1770. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Jin R, Neufeld L and McGaha TL: Linking
macrophage metabolism to function in the tumor microenvironment.
Nat Cancer. 6:239–252. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Bergers G and Benjamin LE: Tumorigenesis
and the angiogenic switch. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:401–410. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Lim JX, Yong YK, Dewi FRP, Chan SY and Lim
V: Nanoscale strategies: Doxorubicin resistance challenges and
enhancing cancer therapy with advanced nanotechnological
approaches. Drug Deliv Transl Res. February 15–2025.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Qian C, Zhou Y, Zhang T, Dong G, Song M,
Tang Y, Wei Z, Yu S, Shen Q, Chen W, et al: Targeting PKM2
signaling cascade with salvianic acid A normalizes tumor blood
vessels to facilitate chemotherapeutic drug delivery. Acta Pharm
Sin B. 14:2077–2096. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Kaur T, Weadick B, Mace TA, Desai K, Odom
H and Govindarajan R: Nucleoside transporters and immunosuppressive
adenosine signaling in the tumor microenvironment: Potential
therapeutic opportunities. Pharmacol Ther. 240:1083002022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Tang C, Jiang ST, Li CX, Jia XF and Yang
WL: The Effect of salvianolic acid a on Tumor-associated macrophage
polarization and its mechanisms in the tumor microenvironment of
Triple-negative breast cancer. Molecules. 29:14692024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Nan Y, Wu X, Luo Q, Chang W, Zhao P, Zhang
L and Liu Z: OTUB2 silencing promotes ovarian cancer via
mitochondrial metabolic reprogramming and can be synthetically
targeted by CA9 inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
121:e23153481212024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Liu X, Zhao J, Liu F, Xie Z, Lei X, Wang
Z, Yang Z, Zhou Y and Tang G: A Smart CA IX-targeting and
pH-responsive nano-mixed micelles for delivery of FB15 with
superior anti-breast cancer efficacy. Int J Nanomedicine.
19:10247–10262. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Zhang C, Pan Y, Cai R, Guo S, Zhang X, Xue
Y, Wang J, Huang J, Wang J, Gu Y and Zhang Z: Salvianolic acid A
increases the accumulation of doxorubicin in brain tumors through
Caveolae endocytosis. Neuropharmacology. 167:1079802020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Qiu C, Zhang JZ, Wu B, Xu CC, Pang HH, Tu
QC, Lu YQ, Guo QY, Xia F and Wang JG: Advanced application of
nanotechnology in active constituents of Traditional Chinese
Medicines. J Nanobiotechnology. 21:4562023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Lu L, Zhang H, Qian Y and Yuan Y:
Isolation of salvianolic acid A, a minor phenolic carboxylic acid
of Salvia miltiorrhiza. Nat Prod Commun. 5:805–808.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Yang MY, Liu Y, Yu YW, Gong BF, Ruan J and
Fan HY: Application of targeted liposomes-based salvianolic acid A
for the treatment of ischemic stroke. Neurotherapeutics.
21:e003422024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|