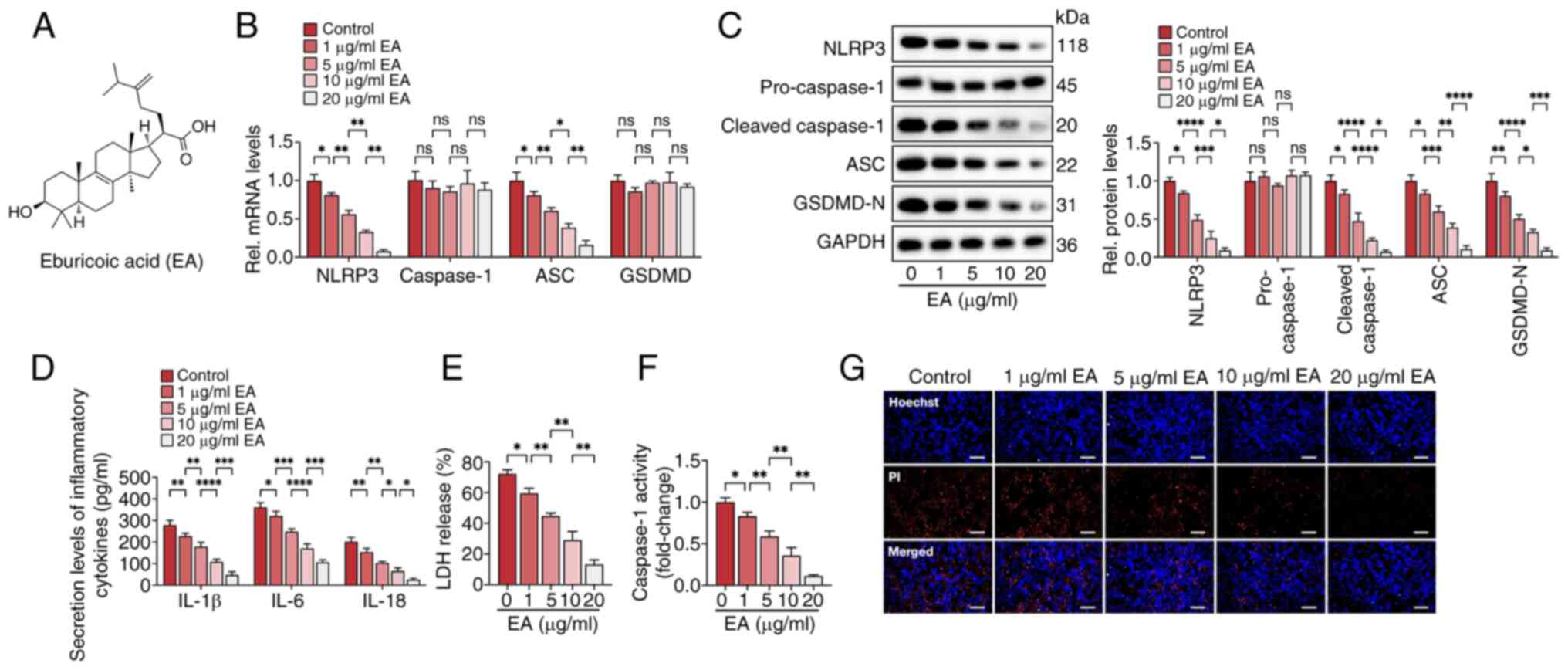
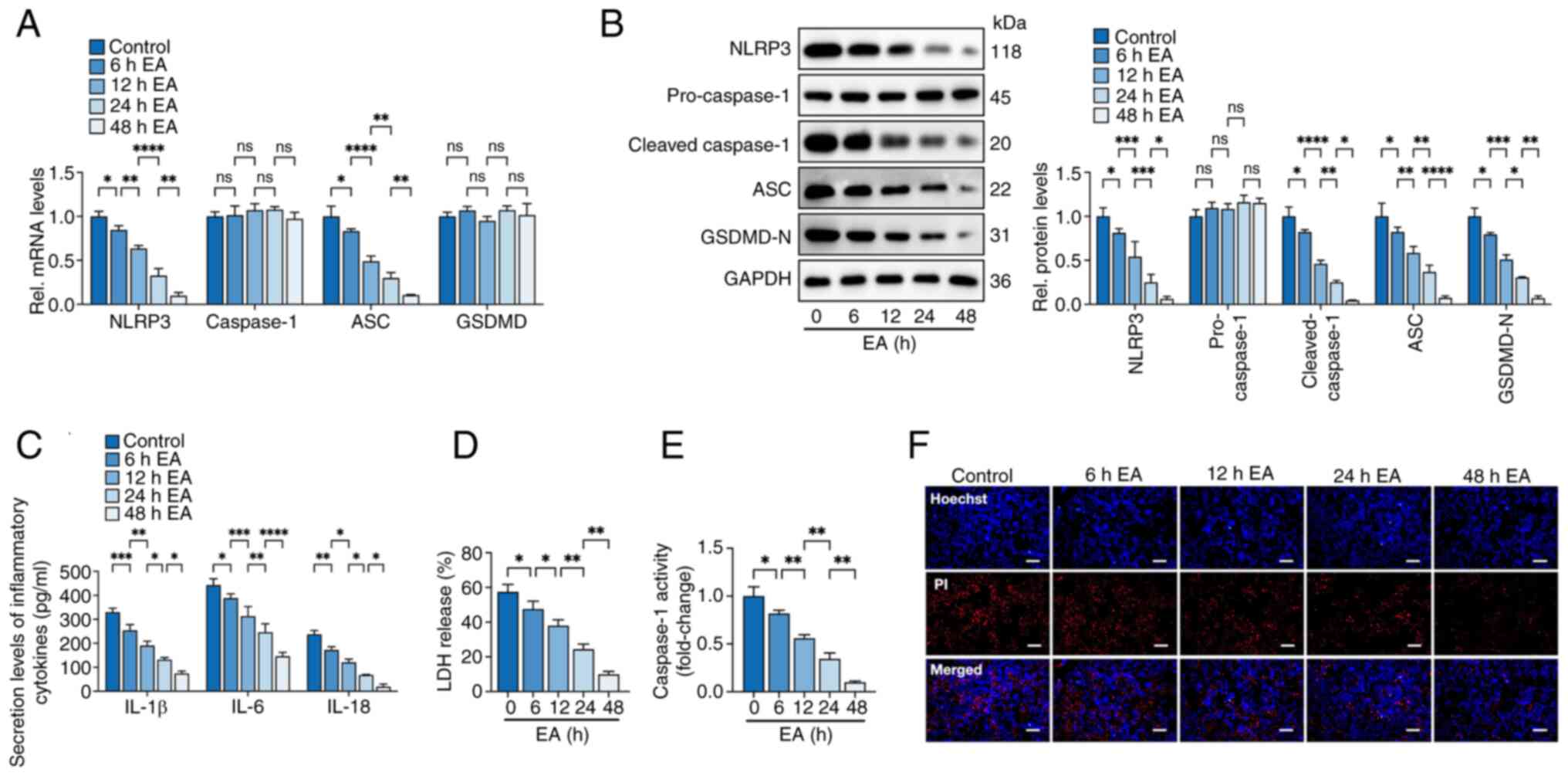
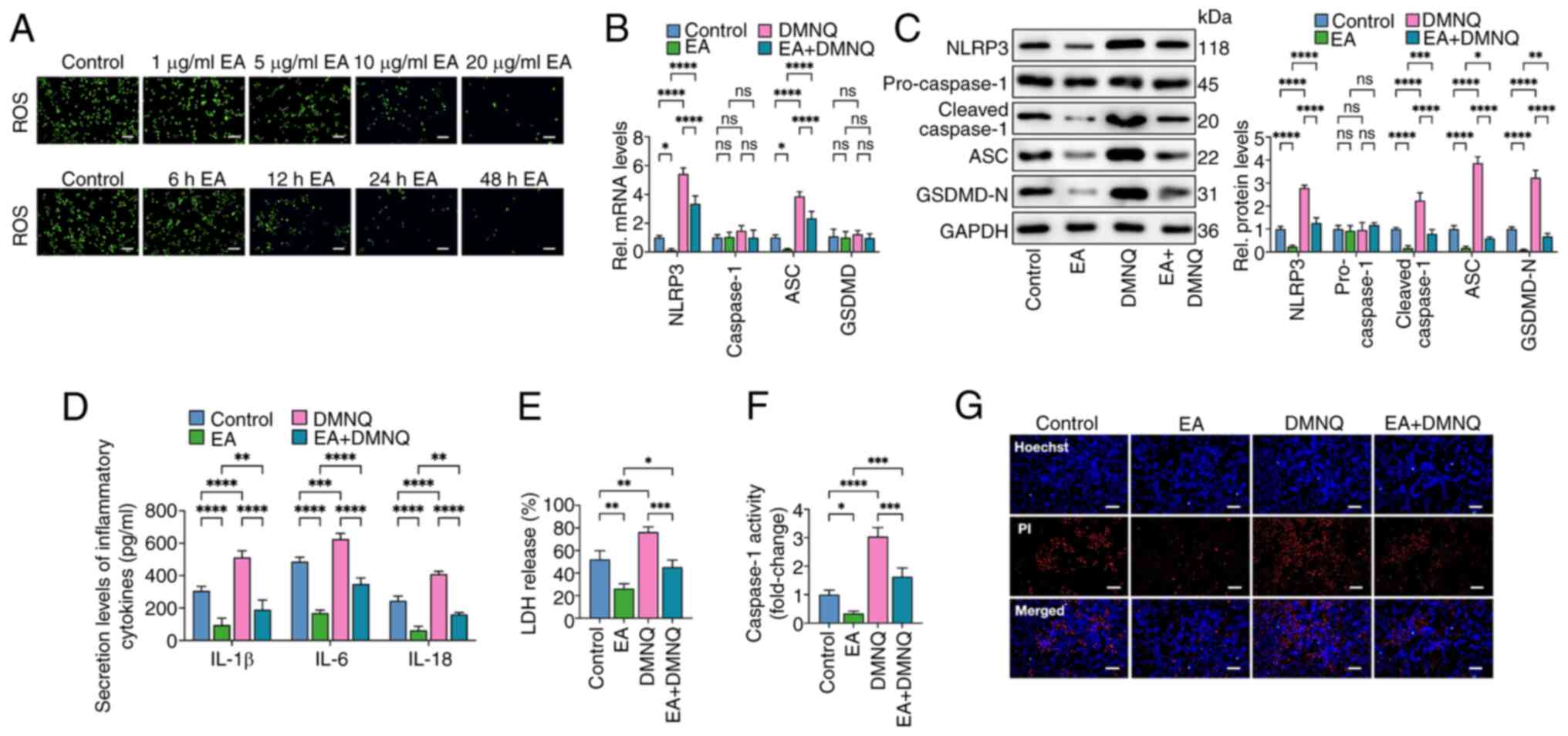
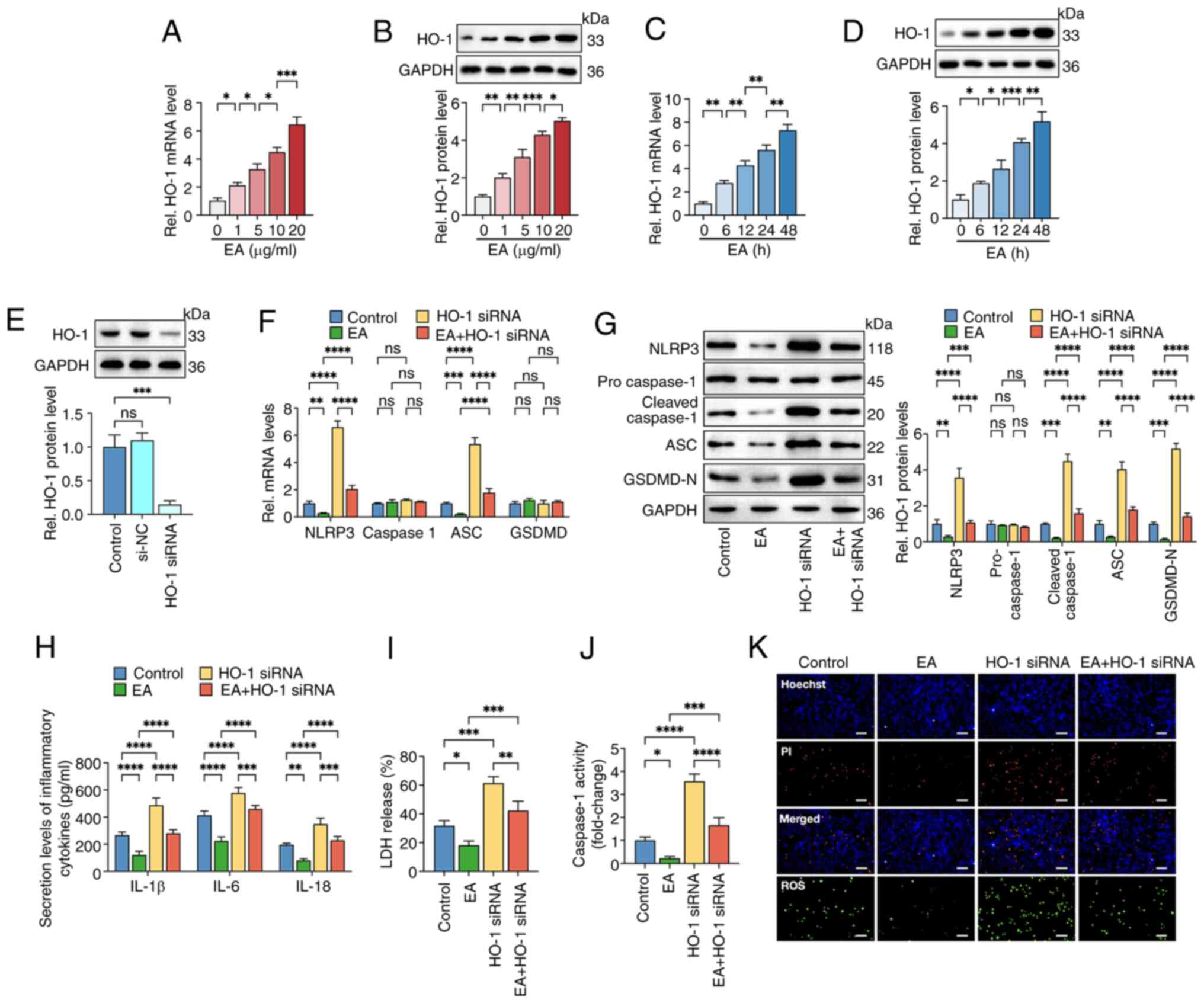
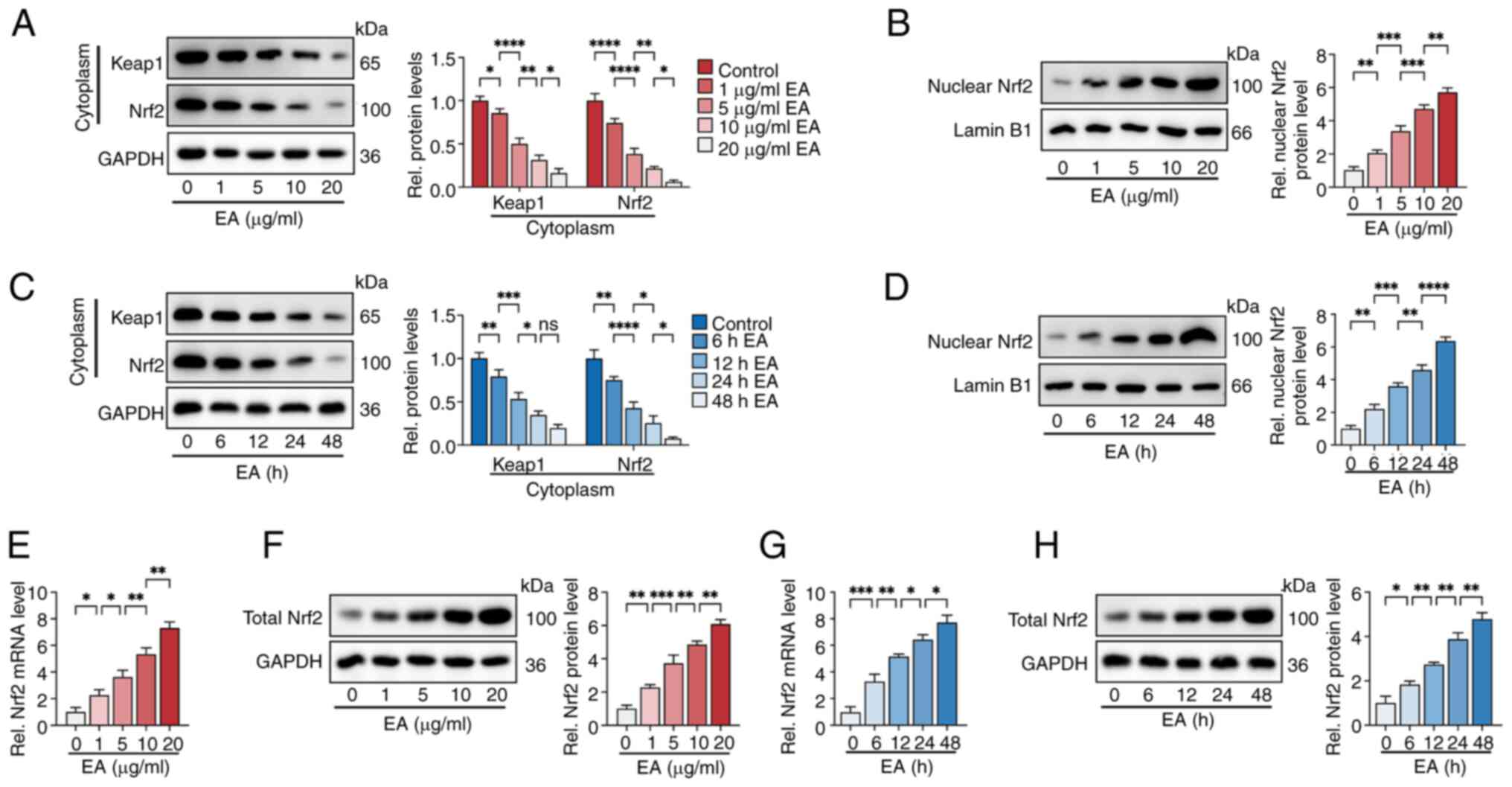
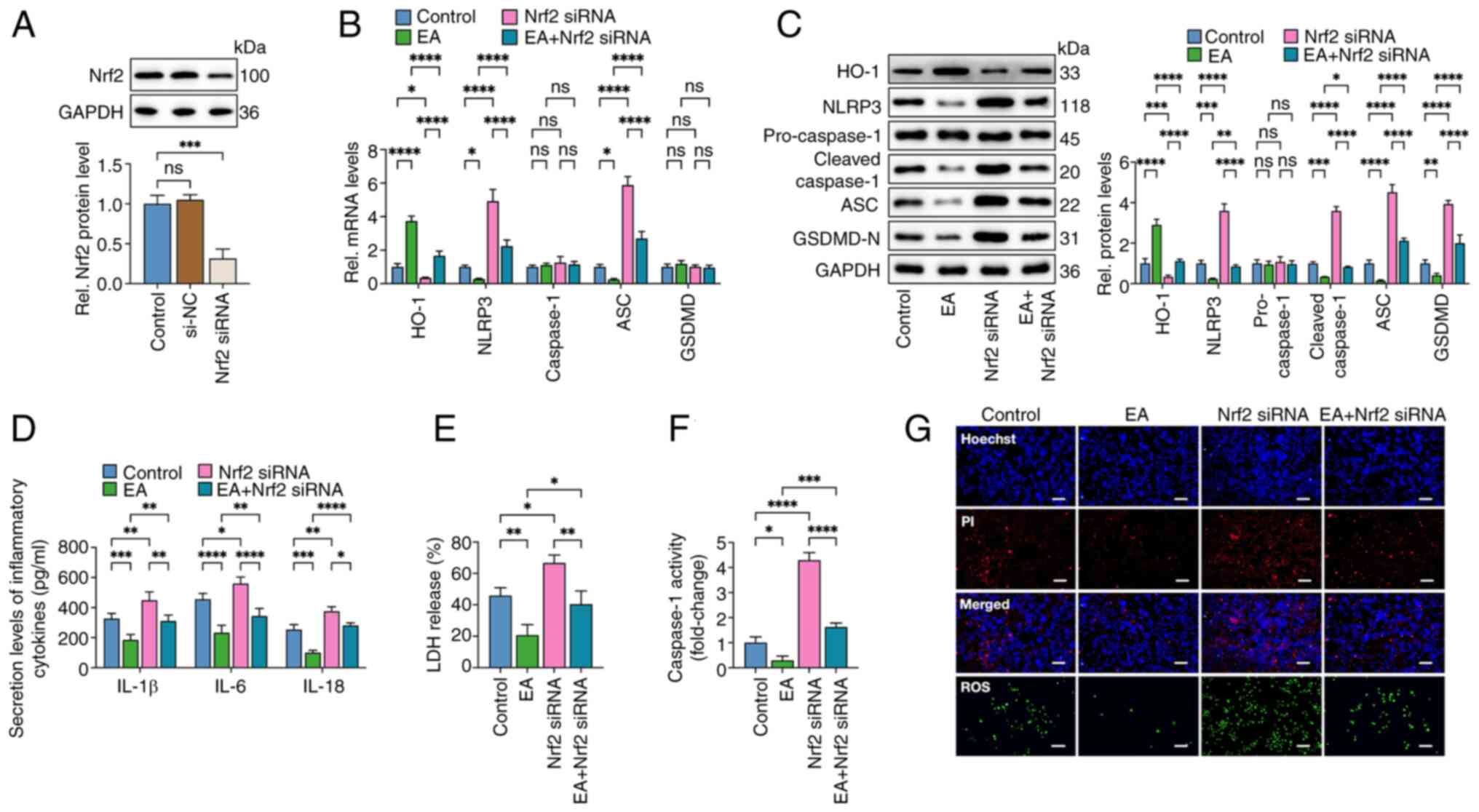
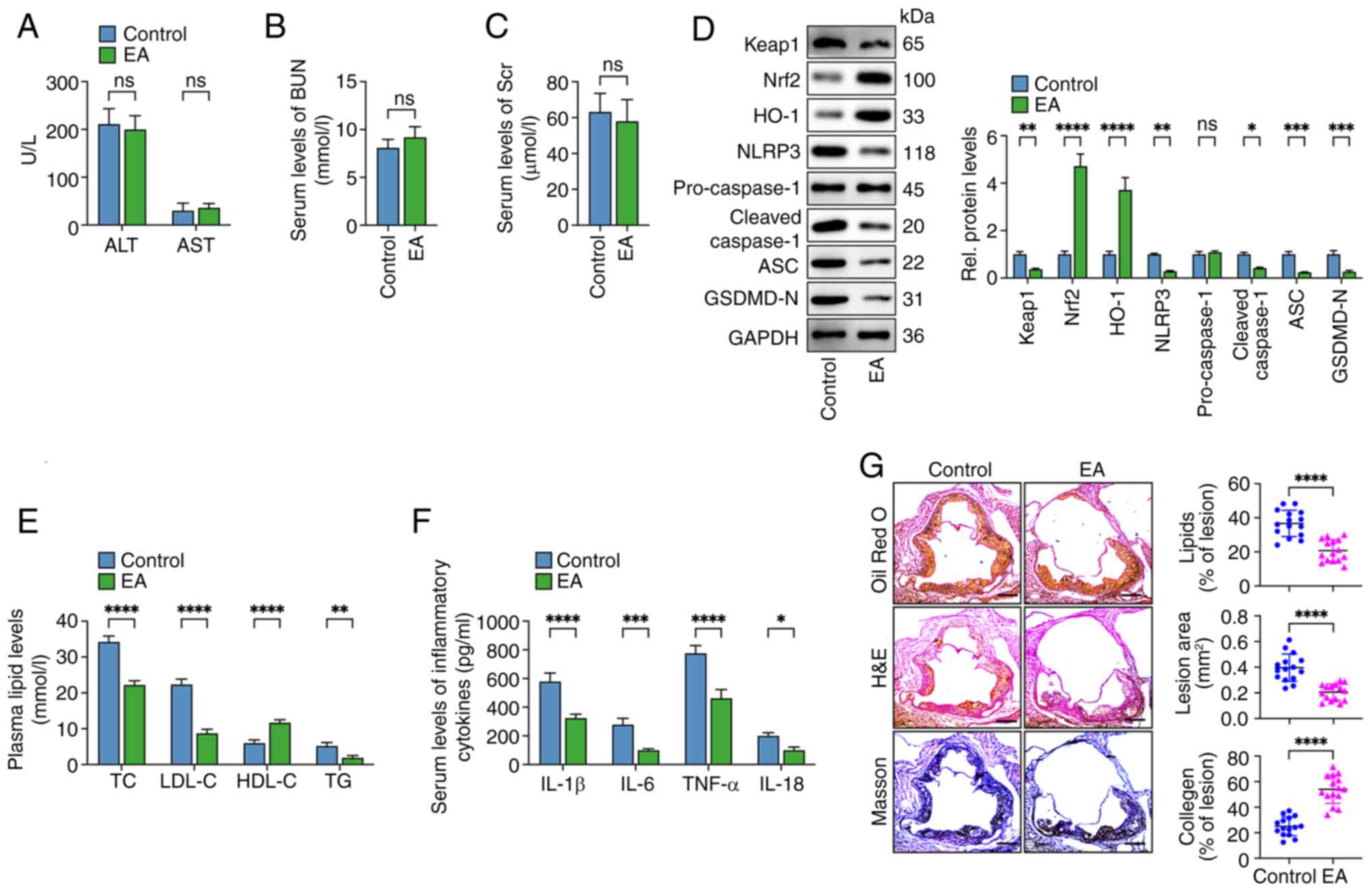
|
1
|
Dibben GO, Faulkner J, Oldridge N, Rees K,
Thompson DR, Zwisler AD and Taylor RS: Exercise-based cardiac
rehabilitation for coronary heart disease: A meta-analysis. Eur
Heart J. 44:452–469. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pan H, Ho SE, Xue C, Cui J, Johanson QS,
Sachs N, Ross LS, Li F, Solomon RA, Connolly ES Jr, et al:
Atherosclerosis is a smooth muscle Cell-Driven Tumor-like disease.
Circulation. 149:1885–1898. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xing Y and Lin X: Challenges and advances
in the management of inflammation in atherosclerosis. J Adv Res.
Jun 21–2024.doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.06.016.
|
|
4
|
Jia M, Li Q, Guo J, Shi W, Zhu L, Huang Y,
Li Y, Wang L, Ma S, Zhuang T, et al: Deletion of BACH1 attenuates
atherosclerosis by reducing endothelial inflammation. Circ Res.
130:1038–1055. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang Q, Han J, Liang Z, Geng X, Du Y, Zhou
J, Yao W and Xu T: FSH is responsible for androgen deprivation
Therapy-associated atherosclerosis in mice by exaggerating
endothelial inflammation and monocyte adhesion. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 44:698–719. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Oladapo A, Jackson T, Menolascino J and
Periyasamy P: Role of pyroptosis in the pathogenesis of various
neurological diseases. Brain Behav Immun. 117:428–446. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Volchuk A, Ye A, Chi L, Steinberg BE and
Goldenberg NM: Indirect regulation of HMGB1 release by gasdermin D.
Nat Commun. 11:45612020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gimbrone MA Jr and García-Cardeña G:
Endothelial cell dysfunction and the pathobiology of
atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 118:620–636. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yin Y, Li X, Sha X, Xi H, Li YF, Shao Y,
Mai J, Virtue A, Lopez-Pastrana J, Meng S, et al: Early
hyperlipidemia promotes endothelial activation via a
caspase-1-sirtuin 1 pathway. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
35:804–816. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lv Y, Jiang Z, Zhou W, Yang H, Jin G, Wang
D, Kong C, Qian Z, Gu Y, Chen S and Zhu L: Low-shear stress
promotes atherosclerosis via inducing endothelial cell pyroptosis
mediated by IKKε/STAT1/NLRP3 pathway. Inflammation. 47:1053–1066.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen Y, Yuan C, Qin W, Yu B, Wei D and Wu
P: TMAO promotes vascular endothelial cell pyroptosis via the
LPEAT-mitophagy pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
703:1496672024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Song L, Zhang J, Lai R, Li Q, Ju J and Xu
H: Chinese herbal medicines and active metabolites: Potential
antioxidant treatments for atherosclerosis. Front Pharmacol.
12:6759992021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jing Y, Hu T, Yuan J, Liu Z, Tao M, Ou M,
Cheng X, Cheng W, Yi Y and Xiong Q: Resveratrol protects against
postmenopausal atherosclerosis progression through reducing PCSK9
expression via the regulation of the ERα-mediated signaling
pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 211:1155412023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gao S, Zhang W, Zhao Q, Zhou J, Wu Y, Liu
Y, Yuan Z and Wang L: Curcumin ameliorates atherosclerosis in
apolipoprotein E deficient asthmatic mice by regulating the balance
of Th2/Treg cells. Phytomedicine. 52:129–135. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xing SS, Yang J, Li WJ, Li J, Chen L, Yang
YT, Lei X, Li J, Wang K and Liu X: Salidroside decreases
atherosclerosis plaque formation via inhibiting endothelial cell
pyroptosis. Inflammation. 43:433–440. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cao H, Jia Q, Yan L, Chen C, Xing S and
Shen D: Quercetin suppresses the progression of atherosclerosis by
regulating MST1-Mediated autophagy in ox-LDL-Induced RAW264.7
macrophage foam cells. Int J Mol Sci. 20:60932019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ma SR, Tong Q, Lin Y, Pan LB, Fu J, Peng
R, Zhang XF, Zhao ZX, Li Y, Yu JB, et al: Berberine treats
atherosclerosis via a vitamine-like effect down-regulating
Choline-TMA-TMAO production pathway in gut microbiota. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 7:2072022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Deng JS, Huang SS, Lin TH, Lee MM, Kuo CC,
Sung PJ, Hou WC, Huang GJ and Kuo YH: Analgesic and
anti-inflammatory bioactivities of eburicoic acid and
dehydroeburicoic acid isolated from Antrodia camphorata on
the inflammatory mediator expression in mice. J Agric Food Chem.
61:5064–5071. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tung YT, Tsai TC, Kuo YH, Yen CC, Sun JY,
Chang WH, Chen HL and Chen CM: Comparison of solid-state-cultured
and wood-cultured Antrodia camphorata in anti-inflammatory
effects using NF-κB/luciferase inducible transgenic mice.
Phytomedicine. 21:1708–1716. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Su YC, Liu CT, Chu YL, Raghu R, Kuo YH and
Sheen LY: Eburicoic acid, an active triterpenoid from the fruiting
bodies of basswood cultivated antrodia cinnamomea, induces ER
Stress-mediated autophagy in human hepatoma cells. J Tradit
Complement Med. 2:312–322. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang GJ, Deng JS, Huang SS, Lee CY, Hou
WC, Wang SY, Sung PJ and Kuo YH: Hepatoprotective effects of
eburicoic acid and dehydroeburicoic acid from Antrodia
camphorata in a mouse model of acute hepatic injury. Food Chem.
141:3020–3027. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang J, Zhang P, He H, Se X, Sun W, Chen
B, Zhang L, Yan X and Zou K: Eburicoic acid from Laetiporus
sulphureus (Bull.:Fr.) Murrill attenuates inflammatory responses
through inhibiting LPS-induced activation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR/NF-κB
pathways in RAW264.7 cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol.
390:845–856. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lin CH, Kuo YH and Shih CC: Eburicoic
acid, a triterpenoid compound from Antrodia camphorata,
displays antidiabetic and antihyperlipidemic effects in
Palmitate-treated C2C12 myotubes and in High-Fat Diet-Fed mice. Int
J Mol Sci. 18:23142017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Andrews CS, Matsuyama S, Lee BC and Li JD:
Resveratrol suppresses NTHi-induced inflammation via up-regulation
of the negative regulator MyD88 short. Sci Rep. 6:344452016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jiang X, Ma C, Gao Y, Zheng Y, Li J, Zong
W and Zhang Q: Tongxinluo attenuates atherosclerosis by inhibiting
ROS/NLRP3/caspase-1-mediated endothelial cell pyroptosis. J
Ethnopharmacol. 304:1160112023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhou Y, Zhang Y, Wang H, Zhang X, Chen Y
and Chen G: Microglial pyroptosis in hippocampus mediates
Sevolfurane-induced cognitive impairment in aged mice via ROS-NLRP3
inflammasome pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 116:1097252023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Luo P, Liu D, Zhang Q, Yang F, Wong YK,
Xia F, Zhang J, Chen J, Tian Y, Yang C, et al: Celastrol induces
ferroptosis in activated HSCs to ameliorate hepatic fibrosis via
targeting peroxiredoxins and HO-1. Acta Pharm Sin B. 12:2300–2314.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang W, Wang Y, Zhang C, Huang Y, Yu J,
Shi L, Zhang P, Yin Y, Li R and Tao K: Maresin1 protect against
ferroptosis-induced liver injury through ROS inhibition and
Nrf2/HO-1/GPX4 activation. Front Pharmacol. 13:8656892022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hong H, Lou S, Zheng F, Gao H, Wang N,
Tian S, Huang G and Zhao H: Hydnocarpin D attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via MAPK/NF-κB and
Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Phytomedicine. 101:1541432022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen H, Fu J, Chen H, Hu Y, Soroka DN,
Prigge JR, Schmidt EE, Yan F, Major MB, Chen X and Sang S: Ginger
compound [6]-shogaol and its cysteine-conjugated metabolite (M2)
activate Nrf2 in colon epithelial cells in vitro and in vivo. Chem
Res Toxicol. 27:1575–1585. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Luo RR, Yang J, Sun YL, Zhou BY, Zhou SX,
Zhang GX and Yang AX: Dexmedetomidine attenuates ferroptosis by
Keap1-Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in LPS-induced acute kidney injury. Naunyn
Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 397:7785–7796. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yan Q, Li P, Liu S, Sun Y, Chen C, Long J,
Lin Y, Liang J, Wang H, Zhang L, et al: Dihydromyricetin treats
pulmonary hypertension by modulating CKLF1/CCR5 axis-induced
pulmonary vascular cell pyroptosis. Biomed Pharmacother.
180:1176142024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang Y, Guan X, Gao CL, Ruan W, Zhao S,
Kai G, Li F and Pang T: Medioresinol as a novel PGC-1α activator
prevents pyroptosis of endothelial cells in ischemic stroke through
PPARα-GOT1 axis. Pharmacol Res. 169:1056402021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhu J, Chen H, Le Y, Guo J, Liu Z, Dou X
and Lu D: Salvianolic acid A regulates pyroptosis of endothelial
cells via directly targeting PKM2 and ameliorates diabetic
atherosclerosis. Front Pharmacol. 13:10092292022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
He J, Deng Y, Ren L, Jin Z, Yang J, Yao F,
Liu Y, Zheng Z, Chen D, Wang B, et al: Isoliquiritigenin from
licorice flavonoids attenuates NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis by SIRT6
in vascular endothelial cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 303:1159522023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu M, Luo G, Liu T, Yang T, Wang R, Ren
W, Liu P, Lai X, Zhou H and Yang S: Zhilong huoxue tongyu capsule
alleviated the pyroptosis of vascular endothelial cells induced by
ox-LDL through miR-30b-5p/NLRP3. Evid Based Complement Alternat
Med. 2022:39813502022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tan C, Chen J, Tu T, Chen L and Zou J:
Lycopene inhibits pyroptosis of endothelial progenitor cells
induced by ox-LDL through the AMPK/mTOR/NLRP3 pathway. Open Med
(Wars). 19:202409732024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Saba E, Son Y, Jeon BR, Kim SE, Lee IK,
Yun BS and Rhee MH: Acetyl eburicoic acid from laetiporus
sulphureus var. miniatus suppresses inflammation in murine
macrophage RAW 264.7 cells. Mycobiology. 43:131–136. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang J, Sun W, Luo H, He H, Deng W, Zou K,
Liu C, Song J and Huang W: Protective effect of eburicoic acid of
the chicken of the woods mushroom, laetiporus sulphureus (Higher
Basidiomycetes), against gastric ulcers in mice. Int J Med
Mushrooms. 17:619–626. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lin CH, Kuo YH and Shih CC: Antidiabetic
and hypolipidemic activities of eburicoic acid, a triterpenoid
compound from Antrodia camphorata, by regulation of Akt
phosphorylation, gluconeogenesis, and PPARα in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. RSC Adv. 8:20462–20476. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
La Chica Lhoëst MT, Martinez A, Claudi L,
Garcia E, Benitez-Amaro A, Polishchuk A, Piñero J, Vilades D,
Guerra JM, Sanz F, et al: Mechanisms modulating foam cell formation
in the arterial intima: Exploring new therapeutic opportunities in
atherosclerosis. Front Cardiovasc Med. 11:13815202024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jin Y, Liu Y, Xu L, Xiong Y, Peng Y, Ding
K, Zheng S, Yang N, Zhang Z, Li L, et al: Novel role for caspase 1
inhibitor VX765 in suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and
atherosclerosis via promoting mitophagy and efferocytosis. Cell
Death Dis. 13:5122022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang Q, Liu J, Duan H, Li R, Peng W and
Wu C: Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling: An important molecular
mechanism of herbal medicine in the treatment of atherosclerosis
via the protection of vascular endothelial cells from oxidative
stress. J Adv Res. 34:43–63. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hu Q, Zhang T, Yi L, Zhou X and Mi M:
Dihydromyricetin inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent pyroptosis
by activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway in vascular endothelial
cells. Biofactors. 44:123–136. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lee SE, Jeong SI, Yang H, Park CS, Jin YH
and Park YS: Fisetin induces Nrf2-mediated HO-1 expression through
PKC-δ and p38 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Cell
Biochem. 112:2352–2360. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhu Z, Li J and Zhang X: Astragaloside IV
protects against oxidized Low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL)-induced
endothelial cell injury by reducing oxidative stress and
inflammation. Med Sci Monit. 25:2132–2140. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li CP, Qin G, Shi RZ, Zhang MS and Lv JY:
Ginsenoside Rg1 reduces toxicity of PM(2.5) on human umbilical vein
endothelial cells by upregulating intracellular antioxidative
state. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 35:21–29. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lu CY, Yang YC, Li CC, Liu KL, Lii CK and
Chen HW: Andrographolide inhibits TNFα-induced ICAM-1 expression
via suppression of NADPH oxidase activation and induction of HO-1
and GCLM expression through the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 and PI3K/Akt/AP-1
pathways in human endothelial cells. Biochemical Pharmacology.
91:40–50. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kong C, Yan X, Zhu Y, Zhu H, Luo Y, Liu P,
Ferrandon S, Kalady MF, Gao R, He J, et al: Fusobacterium nucleatum
promotes the development of colorectal cancer by activating a
cytochrome P450/Epoxyoctadecenoic acid axis via TLR4/Keap1/NRF2
signaling. Cancer Res. 81:4485–4498. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yao Y, Hu S, Zhang C, Zhou Q, Wang H, Yang
Y, Liu C and Ding H: Ginsenoside Rd attenuates cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury by exerting an anti-pyroptotic effect
via the miR-139-5p/FoxO1/Keap1/Nrf2 axis. Int Immunopharmacol.
105:1085822022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Xu J, Xie G, Yang W and Wang W, Zuo Z and
Wang W: Platelet-rich plasma attenuates intervertebral disc
degeneration via delivering miR-141-3p-containing exosomes. Cell
Cycle. 20:1487–1499. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|