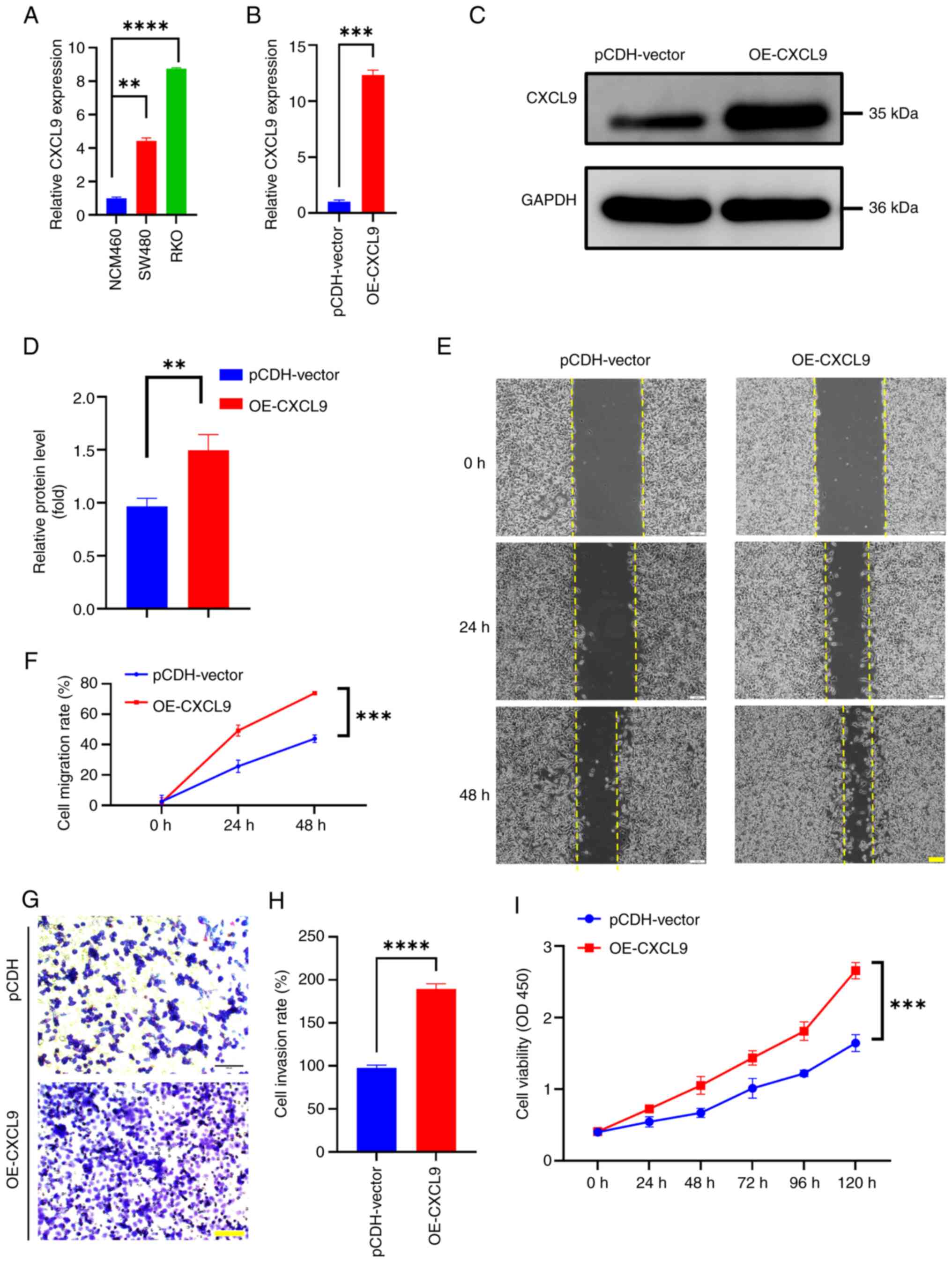
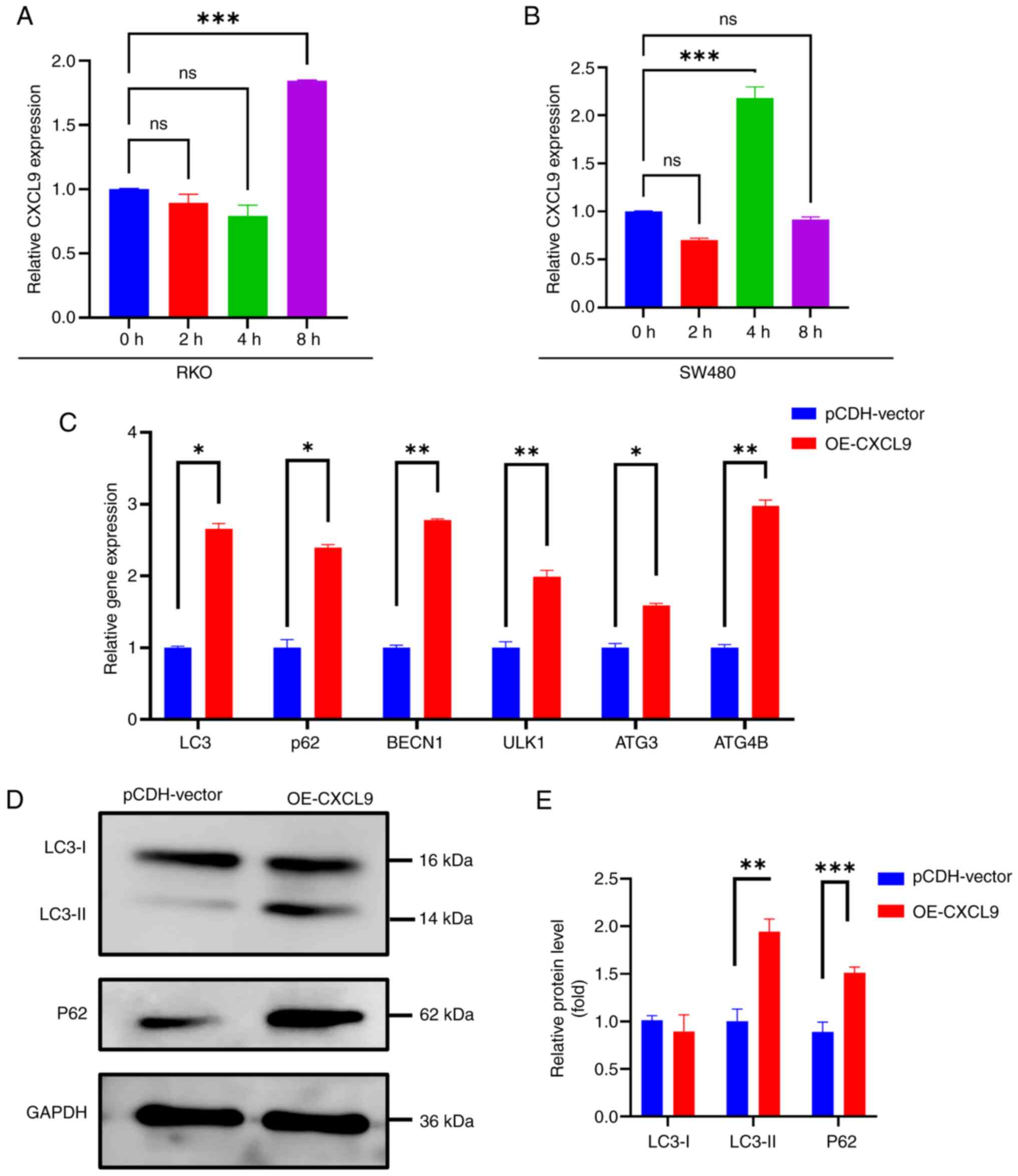
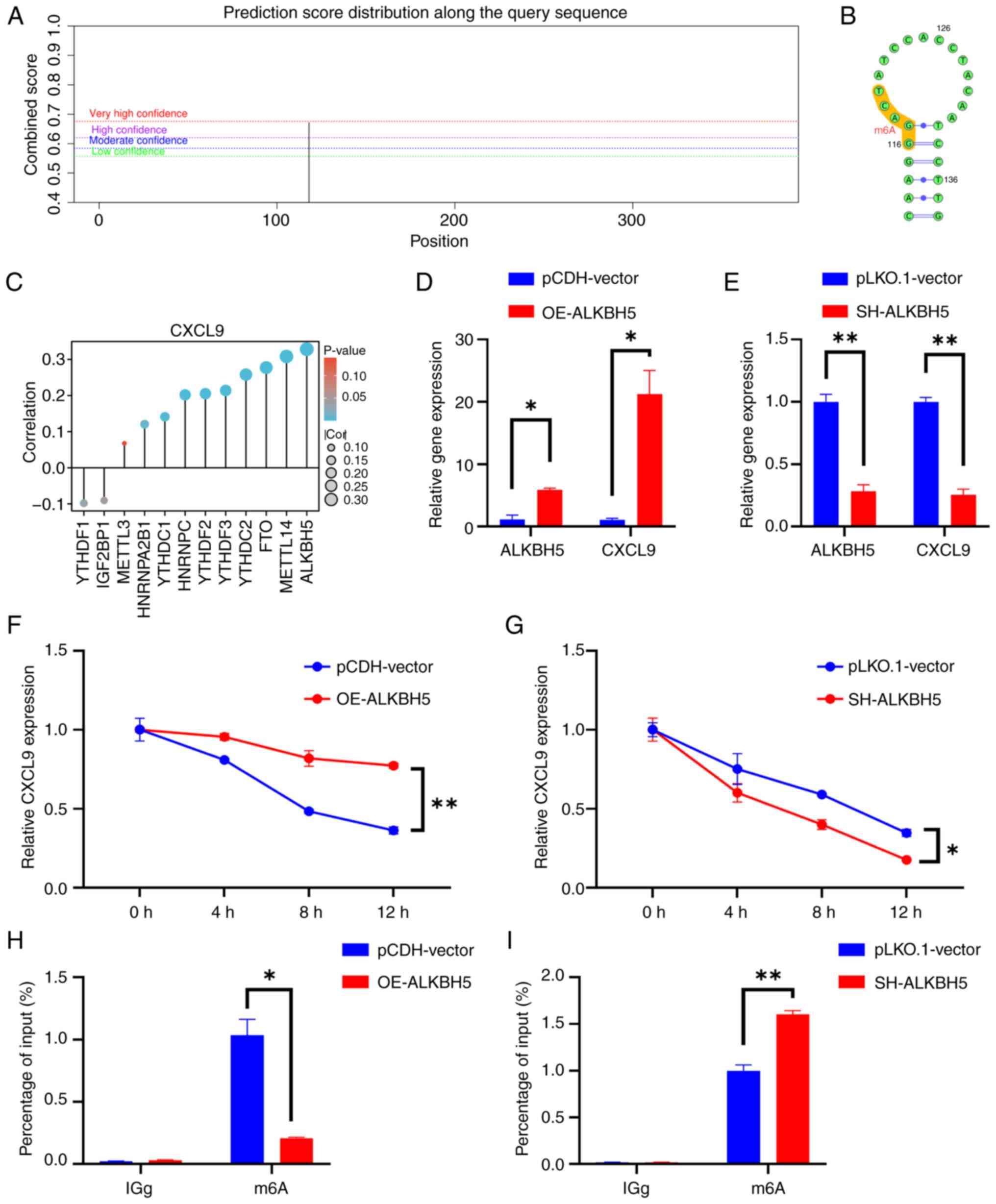
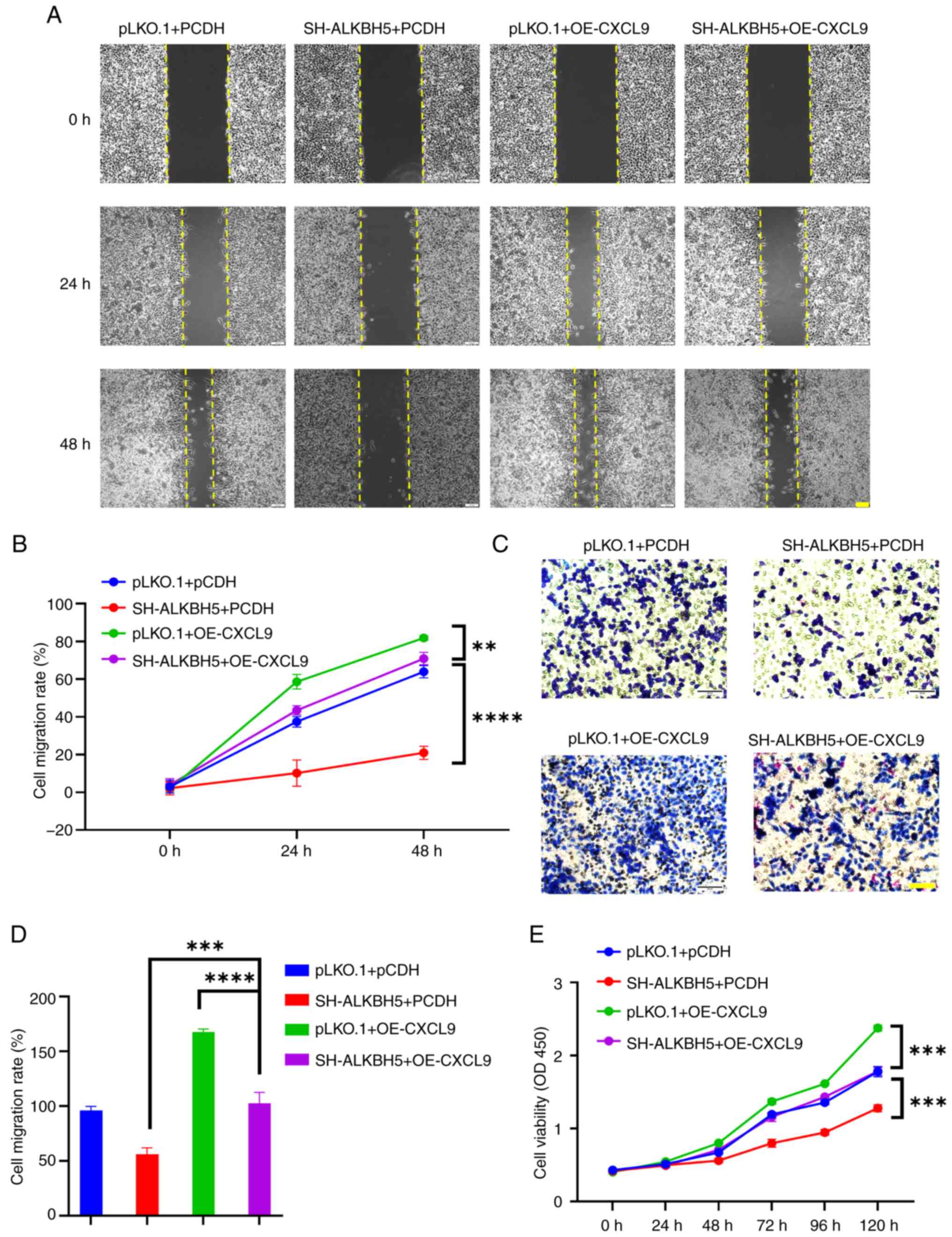
|
1
|
Morgan E, Arnold M, Gini A, Lorenzoni V,
Cabasag CJ, Laversanne M, Vignat J, Ferlay J, Murphy N and Bray F:
Global burden of colorectal cancer in 2020 and 2040: Incidence and
mortality estimates from GLOBOCAN. Gut. 72:338–344. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Housini M, Dariya B, Ahmed N, Stevens A,
Fiadjoe H, Nagaraju GP and Basha R: Colorectal cancer: Genetic
alterations, novel biomarkers, current therapeutic strategies and
clinical trials. Gene. 892:1478572024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Potter JD, Slattery ML, Bostick RM and
Gapstur SM: Colon cancer: A review of the epidemiology. Epidemiol
Rev. 15:499–545. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Benson AB, Venook AP, Al-Hawary MM, Arain
MA, Chen YJ, Ciombor KK, Cohen S, Cooper HS, Deming D, Farkas L, et
al: Colon cancer, version 2.2021, NCCN clinical practice guidelines
in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 19:329–359. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Schlechter BL: Management of rectal
cancer. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 36:521–537. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Schrag D, Shi Q, Weiser MR, Gollub MJ,
Saltz LB, Musher BL, Goldberg J, Al Baghdadi T, Goodman KA,
McWilliams RR, et al: Preoperative treatment of locally advanced
rectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 389:322–334. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Niu SQ, Li RZ, Yuan Y, Xie WH, Wang QX,
Chang H, Lu ZH, Ding PR, Li LR, Wu XJ, et al: Neoadjuvant
chemoradiotherapy in patients with unresectable locally advanced
sigmoid colon cancer: Clinical feasibility and outcome. Radiat
Oncol. 16:932021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
André T, Boni C, Mounedji-Boudiaf L,
Navarro M, Tabernero J, Hickish T, Topham C, Zaninelli M, Clingan
P, Bridgewater J, et al: Oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin
as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer. N Engl J Med.
350:2343–2351. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
André T, Shiu KK, Kim TW, Jensen BV,
Jensen LH, Punt C, Smith D, Garcia-Carbonero R, Benavides M, Gibbs
P, et al: Pembrolizumab in microsatellite-instability-high advanced
colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 383:2207–2218. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kong MY, Li LY, Lou YM, Chi HY and Wu JJ:
Chinese herbal medicines for prevention and treatment of colorectal
cancer: From molecular mechanisms to potential clinical
applications. J Integr Med. 18:369–384. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Underwood PW, Ruff SM and Pawlik TM:
Update on targeted therapy and immunotherapy for metastatic
colorectal cancer. Cells. 13:2452024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cunningham D, Humblet Y, Siena S, Khayat
D, Bleiberg H, Santoro A, Bets D, Mueser M, Harstrick A, Verslype
C, et al: Cetuximab monotherapy and cetuximab plus irinotecan in
irinotecan-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med.
351:337–345. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chalabi M, Fanchi LF, Dijkstra KK, Van den
Berg JG, Aalbers AG, Sikorska K, Lopez-Yurda M, Grootscholten C,
Beets GL, Snaebjornsson P, et al: Neoadjuvant immunotherapy leads
to pathological responses in MMR-proficient and MMR-deficient
early-stage colon cancers. Nat Med. 26:566–576. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ieranò C, Righelli D, D'Alterio C,
Napolitano M, Portella L, Rea G, Auletta F, Santagata S, Trotta AM,
Guardascione G, et al: In PD-1+ human colon cancer cells NIVOLUMAB
promotes survival and could protect tumor cells from conventional
therapies. J Immunother Cancer. 10:e0040322022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Suzuki S, Kawakami H, Miike T and Yamamoto
S: Complete remission of colon cancer with ipilimumab monotherapy.
Intern Med. 60:957–958. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chalabi M, Verschoor YL, Tan PB, Balduzzi
S, Van Lent AU, Grootscholten C, Dokter S, Büller NV, Grotenhuis
BA, Kuhlmann K, et al: Neoadjuvant immunotherapy in locally
advanced mismatch repair-deficient colon cancer. N Engl J Med.
390:1949–1958. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou C, Gao Y, Ding P, Wu T and Ji G: The
role of CXCL family members in different diseases. Cell Death
Discov. 9:2122023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cambier S, Gouwy M and Proost P: The
chemokines CXCL8 and CXCL12: Molecular and functional properties,
role in disease and efforts towards pharmacological intervention.
Cell Mol Immunol. 20:217–251. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
House IG, Savas P, Lai J, Chen AXY, Oliver
AJ, Teo ZL, Todd KL, Henderson MA, Giuffrida L, Petley EV, et al:
Macrophage-derived CXCL9 and CXCL10 are required for antitumor
immune responses following immune checkpoint blockade. Clin Cancer
Res. 26:487–504. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mikucki ME, Fisher DT, Matsuzaki J,
Skitzki JJ, Gaulin NB, Muhitch JB, Ku AW, Frelinger JG, Odunsi K,
Gajewski TF, et al: Non-redundant requirement for CXCR3 signalling
during tumoricidal T-cell trafficking across tumour vascular
checkpoints. Nat Commun. 6:74582015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tokunaga R, Zhang W, Naseem M, Puccini A,
Berger MD, Soni S, McSkane M, Baba H and Lenz HJ: CXCL9, CXCL10,
CXCL11/CXCR3 axis for immune activation-A target for novel cancer
therapy. Cancer Treat Rev. 63:40–47. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Andersson As, Yang SC, Huang M, Zhu L, Kar
UK, Batra RK, Elashoff D, Strieter RM, Dubinett SM and Sharma S:
IL-7 promotes CXCR3 ligand-dependent T cell antitumor reactivity in
lung cancer. J Immunol. 182:6951–6958. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu L, Sun S, Qu F, Sun M, Liu X, Sun Q,
Cheng L, Zheng Y and Su G: CXCL9 influences the tumor immune
microenvironment by stimulating JAK/STAT pathway in triple-negative
breast cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 72:1479–1492. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Santana-Hernández S, Suarez-Olmos J,
Servitja S, Berenguer-Molins P, Costa-Garcia M, Comerma L, Rea A,
Perera-Bel J, Menendez S, Arpí O, et al: NK cell-triggered
CCL5/IFNγ-CXCL9/10 axis underlies the clinical efficacy of
neoadjuvant anti-HER2 antibodies in breast cancer. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 43:102024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bronger H, Karge A, Dreyer T, Zech D,
Kraeft S, Avril S, Kiechle M and Schmitt M: Induction of cathepsin
B by the CXCR3 chemokines CXCL9 and CXCL10 in human breast cancer
cells. Oncol Lett. 13:4224–4230. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang J, Wang Q, Guan Y, Sun Y, Wang X,
Lively K, Wang Y, Luo M, Kim JA, Murphy EA, et al: Breast cancer
cell-derived microRNA-155 suppresses tumor progression via
enhancing immune cell recruitment and antitumor function. J Clin
Invest. 132:e1572482022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Romano G, Paradiso F, Li P, Shukla P,
Barger LN, El Naggar O, Miller JP, Liang RJ, Helms TL, Lazar AJ, et
al: Microparticle-delivered Cxcl9 prolongs braf inhibitor efficacy
in melanoma. Cancer Immunol Res. 11:558–569. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cui Y, Miao Y, Cao L, Guo L, Cui Y, Yan C,
Zeng Z, Xu M and Han T: Activation of melanocortin-1 receptor
signaling in melanoma cells impairs T cell infiltration to dampen
antitumor immunity. Nat Commun. 14:57402023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lim RJ, Salehi-Rad R, Tran LM, Oh MS,
Dumitras C, Crosson WP, Li R, Patel TS, Man S, Yean CE, et al:
CXCL9/10-engineered dendritic cells promote T cell activation and
enhance immune checkpoint blockade for lung cancer. Cell Rep Med.
5:1014792024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Woo SJ, Kim Y, Kang HJ, Jung H, Youn DH,
Hong Y, Lee JJ and Hong JY: Tuberculous pleural effusion-induced
Arg-1+ macrophage polarization contributes to lung
cancer progression via autophagy signaling. Respir Res. 25:1982024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Assenov Y, Ramírez F, Schelhorn SE,
Lengauer T and Albrecht M: Computing topological parameters of
biological networks. Bioinformatics. 24:282–284. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Győrffy B: Integrated analysis of public
datasets for the discovery and validation of survival-associated
genes in solid tumors. Innovation (Camb). 5:1006252024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ru B, Wong CN, Tong Y, Zhong JY, Zhong
SSW, Wu WC, Chu KC, Wong CY, Lau CY, Chen I, et al: TISIDB: An
integrated repository portal for tumor-immune system interactions.
Bioinformatics. 35:4200–4202. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhou Y, Zeng P, Li YH, Zhang Z and Cui Q:
SRAMP: Prediction of mammalian N6-methyladenosine (m6A) sites based
on sequence-derived features. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:e912016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Luo X, Tai J, Zhao Y, Zhao P, Sun D and
Wang L: Associations of C-X-C motif chemokine ligands 1/2/8/13/14
with clinicopathological features and survival profile in patients
with colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett. 24:3482022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhuo C, Ruan Q, Zhao X, Shen Y and Lin R:
CXCL1 promotes colon cancer progression through activation of
NF-κB/P300 signaling pathway. Biol Direct. 17:342022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lepsenyi M, Algethami N, Al-Haidari AA,
Algaber A, Syk I, Rahman M and Thorlacius H: CXCL2-CXCR2 axis
mediates αV integrin-dependent peritoneal metastasis of colon
cancer cells. Clin Exp Metastasis. 38:401–410. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Han B, Feng D, Yu X, Liu Y, Yang M, Luo F,
Zhou L and Liu F: MicroRNA-144 mediates chronic inflammation and
tumorigenesis in colorectal cancer progression via regulating C-X-C
motif chemokine ligand 11. Exp Ther Med. 16:1935–1943.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cao Y, Jiao N, Sun T, Ma Y, Zhang X, Chen
H, Hong J and Zhang Y: CXCL11 correlates with antitumor immunity
and an improved prognosis in colon cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol.
9:6462522021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li X, Lu M, Yuan M, Ye J, Zhang W, Xu L,
Wu X, Hui B, Yang Y, Wei B, et al: CXCL10-armed oncolytic
adenovirus promotes tumor-infiltrating T-cell chemotaxis to enhance
anti-PD-1 therapy. Oncoimmunology. 11:21182102022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang B, Wang M, Ao D and Wei X:
CXCL13-CXCR5 axis: Regulation in inflammatory diseases and cancer.
Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1877:1887992022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hussain M, Liu J, Wang GZ and Zhou GB:
CXCL13 signaling in the tumor microenvironment. Adv Exp Med Biol.
1302:71–90. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liu G, Sun J, Yang ZF, Zhou C, Zhou PY,
Guan RY, Sun BY, Wang ZT, Zhou J, Fan J, et al: Cancer-associated
fibroblast-derived CXCL11 modulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell
migration and tumor metastasis through the
circUBAP2/miR-4756/IFIT1/3 axis. Cell Death Dis. 12:2602021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wang J, Ouyang X, Zhu W, Yi Q and Zhong J:
The Role of CXCL11 and its receptors in cancer: Prospective but
challenging clinical targets. Cancer Control.
31:107327482412411622024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wu X, Sun A, Yu W, Hong C and Liu Z:
CXCL10 mediates breast cancer tamoxifen resistance and promotes
estrogen-dependent and independent proliferation. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 512:1108662020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zuo H and Wan Y: Inhibition of myeloid
PD-L1 suppresses osteoclastogenesis and cancer bone metastasis.
Cancer Gene Ther. 29:1342–1354. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Han Y, Liu D and Li L: PD-1/PD-L1 pathway:
Current researches in cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 10:727–742.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang Z, Zhang H, Cui L, Wang X, Wang D,
Liu Z, Zhang X and Tang Z: An MMAE-loaded PDL1 active targeting
nanomedicine for the precision treatment of colon cancer. Biomater
Sci. 11:5195–5204. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wang S, Song Y, Cao K, Zhang L, Fang X,
Chen F, Feng S and Yan F: Photothermal therapy mediated by gold
nanocages composed of anti-PDL1 and galunisertib for improved
synergistic immunotherapy in colorectal cancer. Acta Biomater.
134:621–632. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Gao Y, Zhao K, Huang Y, Zhang D, Luo N,
Peng X, Yang F, Xiao W, Wang M, Shi R and Miao H: Lanosterol
synthase deficiency promotes tumor progression by orchestrating
PDL1-dependent tumor immunosuppressive microenvironment. MedComm
(2020). 5:e5282024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Limagne E and Ghiringhelli F: Mitophagy: A
new actor in the efficacy of chemo-immunotherapy. Autophagy.
18:3033–3034. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wang T, Gao T, Fujisawa M, Ohara T,
Sakaguchi M, Yoshimura T and Matsukawa A: SPRED2 is a novel
regulator of autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma cells and normal
hepatocytes. Int J Mol Sci. 25:62692024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Guido C, Whitaker-Menezes D, Lin Z,
Pestell RG, Howell A, Zimmers TA, Casimiro MC, Aquila S, Ando' S,
Martinez-Outschoorn UE, et al: Mitochondrial fission induces
glycolytic reprogramming in cancer-associated myofibroblasts,
driving stromal lactate production, and early tumor growth.
Oncotarget. 3:798–810. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Qiu Y, Wang J, Li H, Yang B, Wang J, He Q
and Weng Q: Emerging views of OPTN (optineurin) function in the
autophagic process associated with disease. Autophagy. 18:73–85.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Liu X, Li P, Huang Y, Li H, Liu X, Du Y,
Lin X, Chen D, Liu H and Zhou Y: M6A demethylase ALKBH5
regulates FOXO1 mRNA stability and chemoresistance in
triple-negative breast cancer. Redox Biol. 69:1029932024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Liu M and Chen X: N6-methyladenosine
demethylase ALKBH5 promotes pyroptosis by modulating PTBP1 mRNA
stability in LPS-induced myocardial dysfunction. Acta Cardiol Sin.
40:312–321. 2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Wang YY, Ye LH, Zhao AQ, Gao WR, Dai N,
Yin Y and Zhang X: M6A modification regulates tumor suppressor
DIRAS1 expression in cervical cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther.
25:23066742024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|