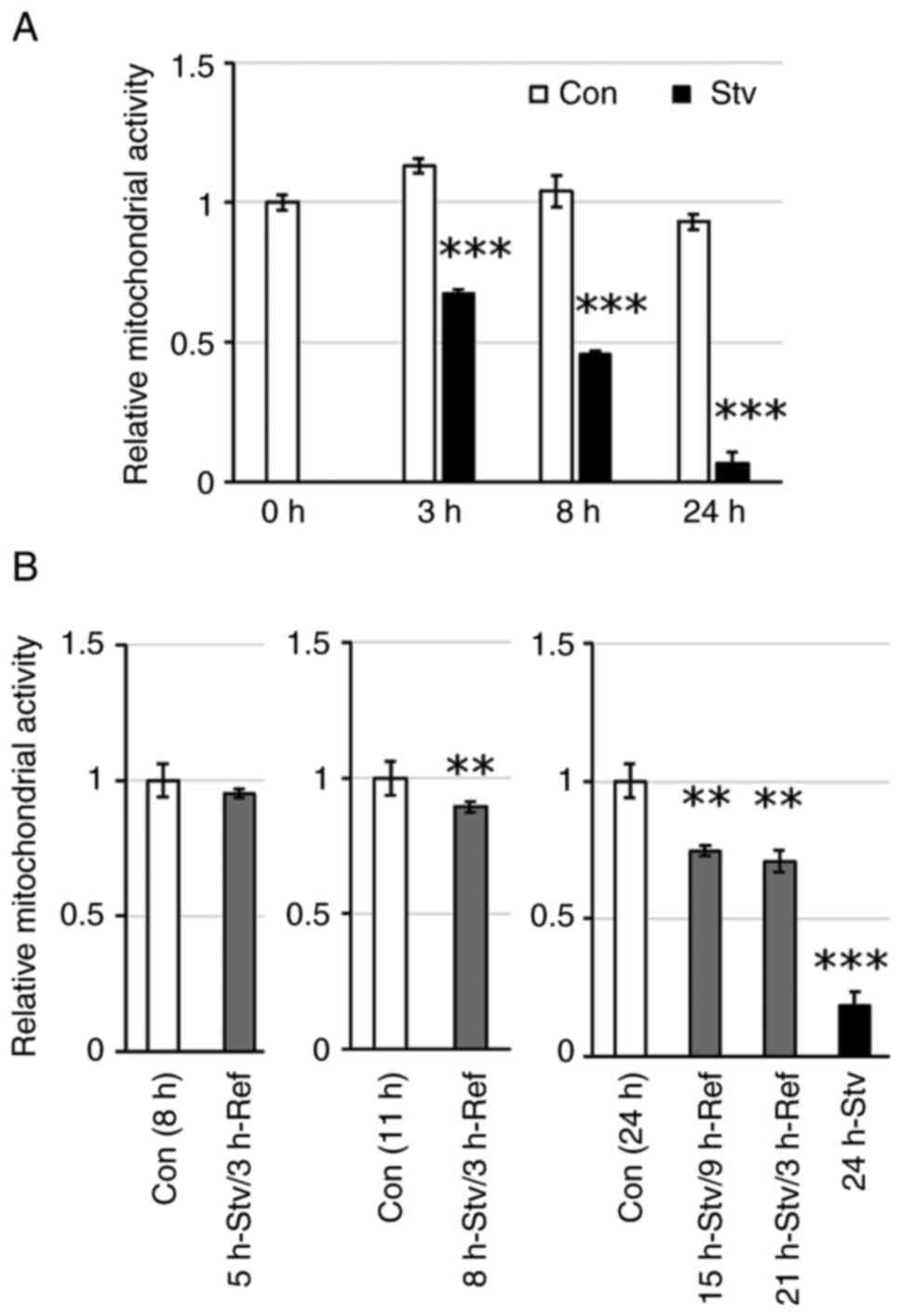
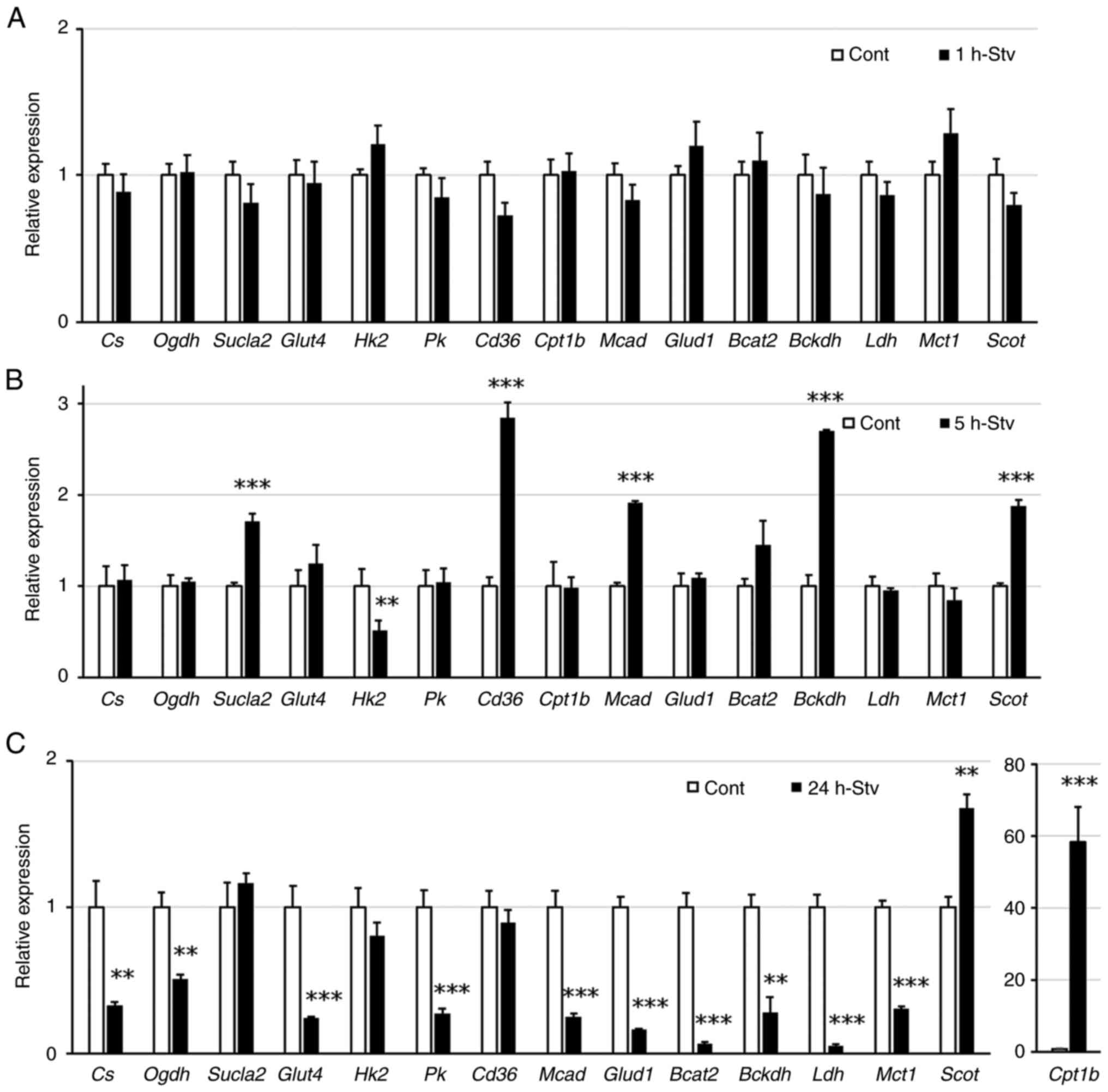
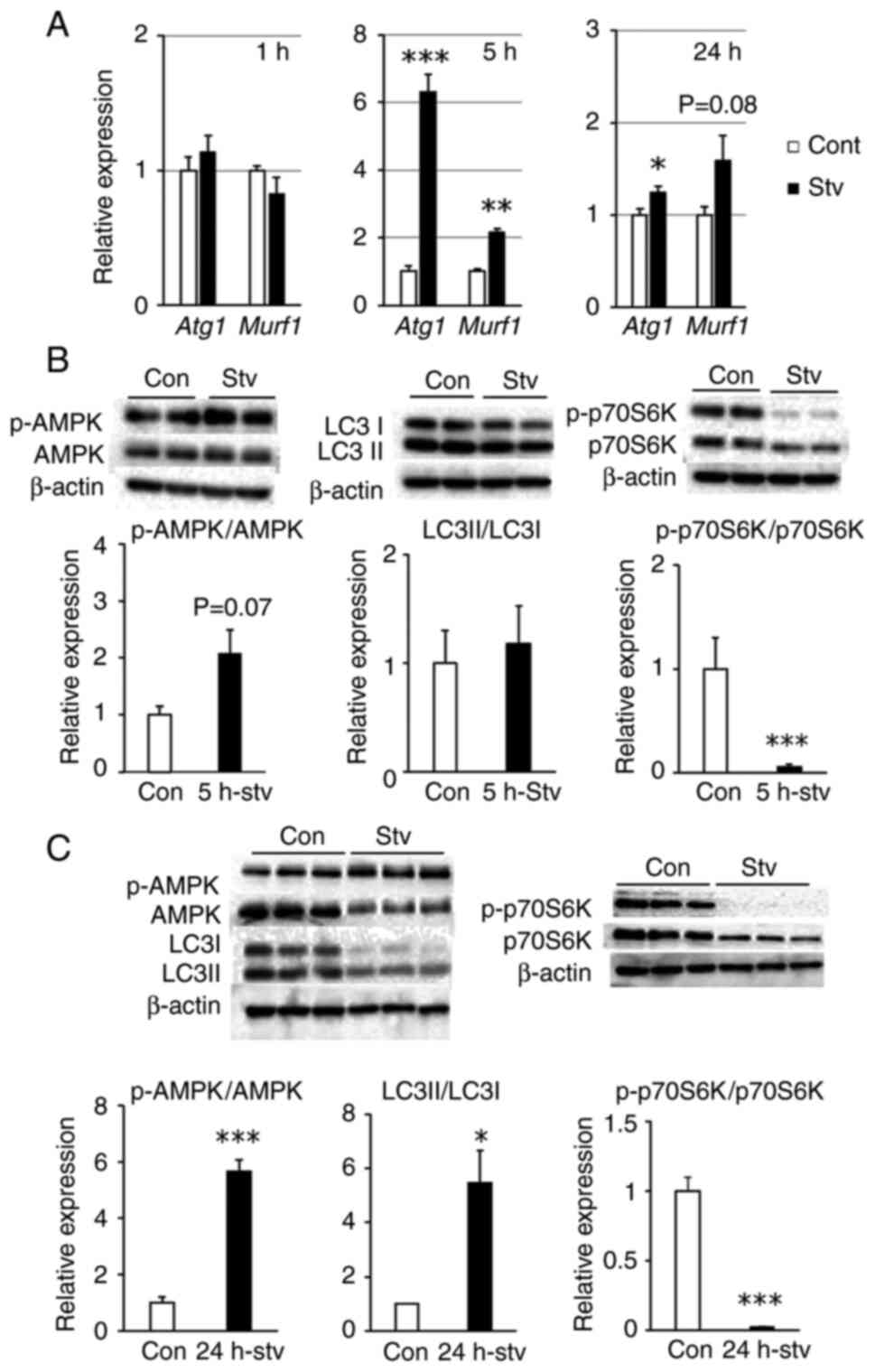
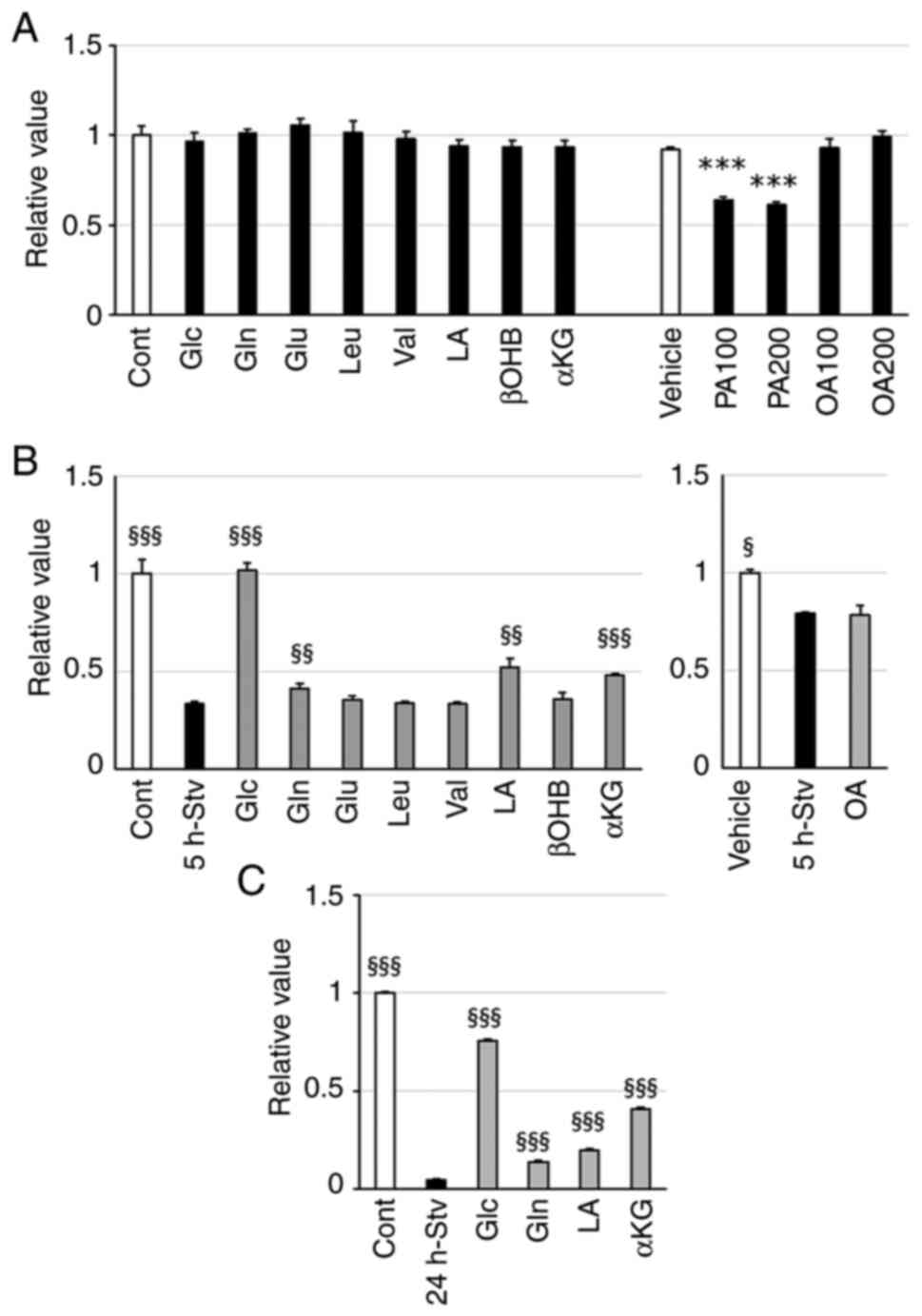
|
1
|
Frontera WR and Ochala J: Skeletal muscle:
A brief review of structure and function. Calcif Tissue Int.
96:183–195. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sieber CC: Malnutrition and sarcopenia.
Aging Clin Exp Res. 31:793–798. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yuan S and Larsson SC: Epidemiology of
sarcopenia: Prevalence, risk factors, and consequences. Metabolism.
144:1555332023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Owens DJ: Nutritional support to
counteract muscle atrophy. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1088:483–495. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang Y, Liu Q, Quan H, Kang SG, Huang K
and Tong T: Nutraceuticals in the prevention and treatment of the
muscle atrophy. Nutrients. 13:19142021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hoffman EP and Nader GA: Balancing muscle
hypertrophy and atrophy. Nat Med. 10:584–585. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sartori R, Romanello V and Sandri M:
Mechanisms of muscle atrophy and hypertrophy: Implications in
health and disease. Nat Commun. 12:3302021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Carbone JW, Margolis LM, McClung JP, Cao
JJ, Murphy NE, Sauter ER, Combs GF Jr, Young AJ and Pasiakos SM:
Effects of energy deficit, dietary protein, and feeding on
intracellular regulators of skeletal muscle proteolysis. FASEB J.
27:5104–5111. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pasiakos SM, Margolis LM and Orr JS:
Optimized dietary strategies to protect skeletal muscle mass during
periods of unavoidable energy deficit. FASEB J. 29:1136–1142. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gielen E, Beckwée D, Delaere A, De
Breucker S, Vandewoude M and Bautmans I; Sarcopenia Guidelines
Development Group of the Belgian Society of Gerontology Geriatrics
(BSGG), : Nutritional interventions to improve muscle mass, muscle
strength, and physical performance in older people: An umbrella
review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Nutr Rev.
79:121–147. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bertero E and Maack C: Metabolic
remodelling in heart failure. Nat Rev Cardiol. 15:457–470. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lopaschuk GD, Karwi QG, Tian R, Wende AR
and Abel ED: Cardiac energy metabolism in heart failure. Circ Res.
128:1487–1513. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Olson B, Marks DL and Grossberg AJ:
Diverging metabolic programmes and behaviours during states of
starvation, protein malnutrition, and cachexia. J Cachexia
Sarcopenia Muscle. 11:1429–1446. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mengeste AM, Rustan AC and Lund J:
Skeletal muscle energy metabolism in obesity. Obesity (Silver
Spring). 29:1582–1595. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Boya P, Reggiori F and Codogno P: Emerging
regulation and functions of autophagy. Nat Cell Biol. 15:713–720.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Deshmukh AS, Murgia M, Nagaraj N, Treebak
JT, Cox J and Mann M: Deep proteomics of mouse skeletal muscle
enables quantitation of protein isoforms, metabolic pathways, and
transcription factors. Mol Cell Proteomics. 14:841–853. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pavlovic K, Krako Jakovljevic N, Isakovic
AM, Ivanovic T, Markovic I and Lalic NM: Therapeutic vs
suprapharmacological metformin concentrations: Different effects on
energy metabolism and mitochondrial function in skeletal muscle
cells in vitro. Front Pharmacol. 13:9303082022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Akhtar J, Han Y, Han S, Lin W, Cao C, Ge
R, Babarinde IA, Jia Q, Yuan Y, Chen G, et al: Bistable insulin
response: The win-win solution for glycemic control. iScience.
25:1055612022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang B, Liu Y and Steinacker JM:
α-Ketoglutarate stimulates cell growth through the improvement of
glucose and glutamine metabolism in C2C12 cell culture. Front Nutr.
10:11452362023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Desgeorges MM, Freyssenet D, Chanon S,
Castells J, Pugnière P, Béchet D, Peinnequin A, Devillard X and
Defour A: Post-transcriptional regulation of autophagy in C2C12
myotubes following starvation and nutrient restoration. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 54:208–216. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li F, Li X, Peng X, Sun L, Jia S, Wang P,
Ma S, Zhao H, Yu Q and Huo H: Ginsenoside Rg1 prevents
starvation-induced muscle protein degradation via regulation of
AKT/mTOR/FoxO signaling in C2C12 myotubes. Exp Ther Med.
14:1241–1247. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Matsuba I, Fujita R and Iida K: Palmitic
acid inhibits myogenic activity and expression of myosin heavy
chain MHC IIb in muscle cells through phosphorylation-dependent
MyoD inactivation. Int J Mol Sci. 24:58472023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Musser DA and Oseroff AR: The use of
tetrazolium salts to determine sites of damage to the mitochondrial
electron transport chain in intact cells following in vitro
photodynamic therapy with photofrin II. Photochem Photobiol.
59:621–626. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dice JF: Selective degradation of
cytosolic proteins by lysosomes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 674:58–64. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dice JF: Molecular determinants of protein
half-lives in eukaryotic cells. FASEB J. 1:349–357. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Duan Y, Li F, Guo Q, Wang W, Zhang L, Wen
C, Chen X and Yin Y: β-Hydroxy-β-methyl butyrate is more potent
than leucine in inhibiting starvation-induced protein degradation
in C2C12 myotubes. J Agric Food Chem. 66:170–176. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Caldow MK, Ham DJ, Trieu J, Chung JD,
Lynch GS and Koopman R: Glycine protects muscle cells from wasting
in vitro via mTORC1 signaling. Front Nutr. 6:1722019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang H, Wang F, Pang X, Zhou Y, Li S, Li
W, Zhang P and Chen X: Decreased expression of H19/miR-675
ameliorates muscle atrophy by regulating the IGF1R/Akt/FoxO
signaling pathway. Mol Med. 29:782023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nakai N, Kitai S, Iida N, Inoue S and
Higashida K: Autophagy under glucose starvation enhances protein
translation initiation in response to re-addition of glucose in
C2C12 myotubes. FEBS Open Bio. 10:2149–2156. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zeidler JD, Fernandes-Siqueira LO,
Carvalho AS, Cararo-Lopes E, Dias MH, Ketzer LA, Galina A and Da
Poian AT: Short-term starvation is a strategy to unravel the
cellular capacity of oxidizing specific exogenous/endogenous
substrates in mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 292:14176–14187. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
de Lange P, Moreno M, Silvestri E,
Lombardi A, Goglia F and Lanni A: Fuel economy in food-deprived
skeletal muscle: Signaling pathways and regulatory mechanisms.
FASEB J. 21:3431–3441. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Samec S, Seydoux J, Russell AP, Montani JP
and Dulloo AG: Skeletal muscle heterogeneity in fasting-induced
upregulation of genes encoding UCP2, UCP3, PPARgamma and key
enzymes of lipid oxidation. Pflugers Arch. 445:80–86. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Frier BC, Jacobs RL and Wright DC:
Interactions between the consumption of a high-fat diet and fasting
in the regulation of fatty acid oxidation enzyme gene expression:
An evaluation of potential mechanisms. Am J Physiol Regul Integr
Comp Physiol. 300:R212–R221. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Saneyasu T, Kimura S, Kitashiro A, Tsuchii
N, Tsuchihashi T, Inui M, Honda K and Kamisoyama H: Differential
regulation of the expression of lipid metabolism-related genes with
skeletal muscle type in growing chickens. Comp Biochem Physiol B
Biochem Mol Biol. 189:1–5. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jagoe RT, Lecker SH, Gomes M and Goldberg
AL: Patterns of gene expression in atrophying skeletal muscles:
Response to food deprivation. FASEB J. 16:1697–1712. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lecker SH, Jagoe RT, Gilbert A, Gomes M,
Baracos V, Bailey J, Price SR, Mitch WE and Goldberg AL: Multiple
types of skeletal muscle atrophy involve a common program of
changes in gene expression. FASEB J. 18:39–51. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Harvald EB, Sprenger RR, Dall KB, Ejsing
CS, Nielsen R, Mandrup S, Murillo AB, Larance M, Gartner A, Lamond
AI and Færgeman NJ: Multi-omics analyses of starvation responses
reveal a central role for lipoprotein metabolism in acute
starvation survival in C. elegans. Cell Syst. 5:38–52.e4. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Dall KB, Havelund JF, Harvald EB, Witting
M and Faergeman NJ: HLH-30-dependent rewiring of metabolism during
starvation in C. elegans. Aging Cell. 20:e133422021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Skiba-Cassy S, Collin A, Chartrin P,
Médale F, Simon J, Duclos MJ and Tesseraud S: Chicken liver and
muscle carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1: Nutritional regulation of
messengers. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 147:278–287.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Benjamin DI, Both P, Benjamin JS, Nutter
CW, Tan JH, Kang J, Machado LA, Klein JDD, de Morree A, Kim S, et
al: Fasting induces a highly resilient deep quiescent state in
muscle stem cells via ketone body signaling. Cell Metab.
34:902–918.e6. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gwinn DM, Shackelford DB, Egan DF,
Mihaylova MM, Mery A, Vasquez DS, Turk BE and Shaw RJ: AMPK
phosphorylation of raptor mediates a metabolic checkpoint. Mol
Cell. 30:214–226. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tavares MR, Pavan IC, Amaral CL,
Meneguello L, Luchessi AD and Simabuco FM: The S6K protein family
in health and disease. Life Sci. 131:1–10. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Diaz-Troya S, Pérez-Pérez ME, Florencio FJ
and Crespo JL: The role of TOR in autophagy regulation from yeast
to plants and mammals. Autophagy. 4:851–865. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Mugume Y, Kazibwe Z and Bassham DC: Target
of rapamycin in control of autophagy: Puppet master and signal
integrator. Int J Mol Sci. 21:82592020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Durán RV, Oppliger W, Robitaille AM,
Heiserich L, Skendaj R, Gottlieb E and Hall MN: Glutaminolysis
activates Rag-mTORC1 signaling. Mol Cell. 47:349–358. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Dodd KM and Tee AR: Leucine and mTORC1: A
complex relationship. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
302:E1329–E1342. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Han JM, Jeong SJ, Park MC, Kim G, Kwon NH,
Kim HK, Ha SH, Ryu SH and Kim S: Leucyl-tRNA synthetase is an
intracellular leucine sensor for the mTORC1-signaling pathway.
Cell. 149:410–424. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Leenders M and van Loon LJ: Leucine as a
pharmaconutrient to prevent and treat sarcopenia and type 2
diabetes. Nutr Rev. 69:675–689. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ham DJ, Caldow MK, Lynch GS and Koopman R:
Leucine as a treatment for muscle wasting: A critical review. Clin
Nutr. 33:937–945. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Mobley CB, Fox CD, Ferguson BS, Amin RH,
Dalbo VJ, Baier S, Rathmacher JA, Wilson JM and Roberts MD:
L-leucine, beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyric acid (HMB) and creatine
monohydrate prevent myostatin-induced Akirin-1/Mighty mRNA
down-regulation and myotube atrophy. J Int Soc Sports Nutr.
11:382014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Oelkrug C, Horn K, Makert GR and Schubert
A: Novel in vitro platform to investigate myotube atrophy.
Anticancer Res. 35:2085–2091. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wang L, Yi D, Hou Y, Ding B, Li K, Li B,
Zhu H, Liu Y and Wu G: Dietary supplementation with α-ketoglutarate
activates mTOR signaling and enhances energy status in skeletal
muscle of lipopolysaccharide-challenged piglets. J Nutr.
146:1514–1520. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Cai X, Yuan Y, Liao Z, Xing K, Zhu C, Xu
Y, Yu L, Wang L, Wang S, Zhu X, et al: α-Ketoglutarate prevents
skeletal muscle protein degradation and muscle atrophy through
PHD3/ADRB2 pathway. FASEB J. 32:488–499. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Tsukamoto S, Shibasaki A, Naka A, Saito H
and Iida K: Lactate promotes myoblast differentiation and myotube
hypertrophy via a pathway involving MyoD in vitro and enhances
muscle regeneration in vivo. Int J Mol Sci. 19:36492018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ohno Y, Oyama A, Kaneko H, Egawa T,
Yokoyama S, Sugiura T, Ohira Y, Yoshioka T and Goto K: Lactate
increases myotube diameter via activation of MEK/ERK pathway in
C2C12 cells. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 223:e130422018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ohno Y, Nakatani M, Ito T, Matsui Y, Ando
K, Suda Y, Ohashi K, Yokoyama S and Goto K: Activation of lactate
receptor positively regulates skeletal muscle mass in mice. Physiol
Res. 72:465–473. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Goodpaster BH and Sparks LM: Metabolic
flexibility in health and disease. Cell Metab. 25:1027–1036. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Hui S, Ghergurovich JM, Morscher RJ, Jang
C, Teng X, Lu W, Esparza LA, Reya T, Zhan L, Yanxiang Guo J, et al:
Glucose feeds the TCA cycle via circulating lactate. Nature.
551:115–118. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Li M, Wang Y, Wei X, Cai WF, Wu J, Zhu M,
Wang Y, Liu YH, Xiong J, Qu Q, et al: AMPK targets PDZD8 to trigger
carbon source shift from glucose to glutamine. Cell Res.
34:683–706. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|