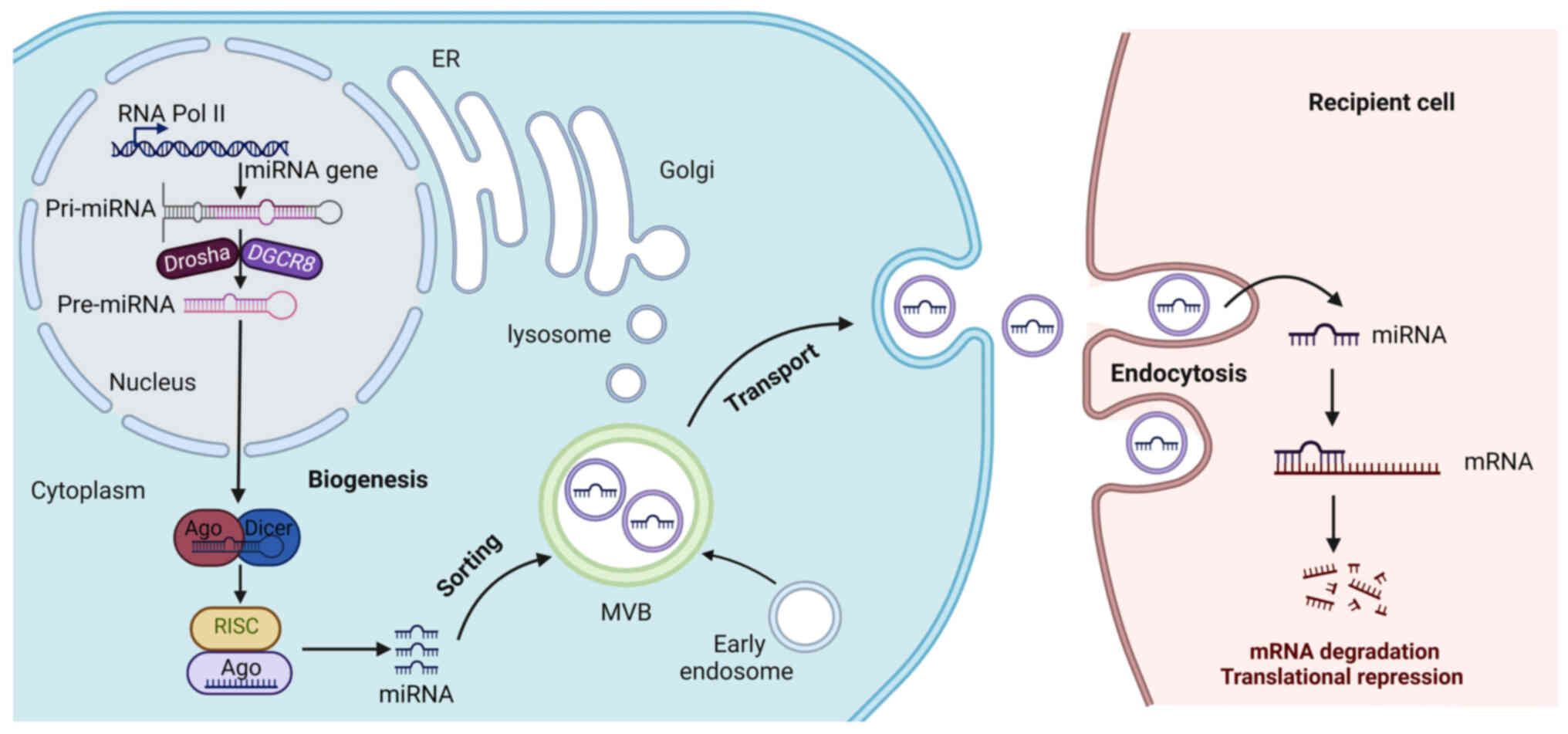
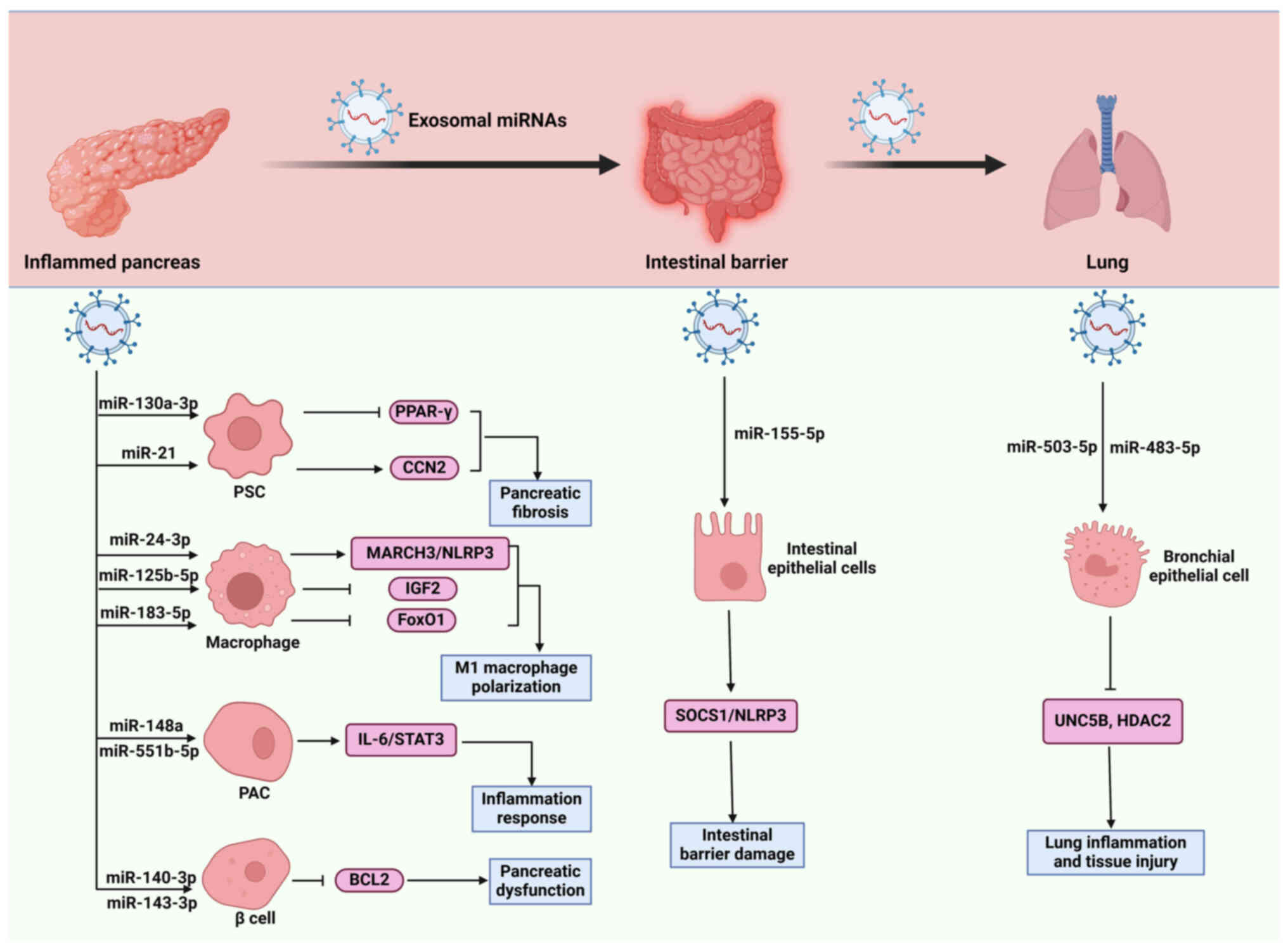
|
1
|
Trikudanathan G, Yazici C, Evans Phillips
A and Forsmark CE: Diagnosis and management of acute pancreatitis.
Gastroenterology. 167:673–688. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hines OJ and Pandol SJ: Management of
chronic pancreatitis. BMJ. 384:e0709202024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Saluja A, Dudeja V, Dawra R and Sah RP:
Early Intra-acinar events in pathogenesis of pancreatitis.
Gastroenterology. 156:1979–1993. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Capurso G, Tacelli M, Vanella G, Ponz de
Leon Pisani R, Dell'Anna G, Abati M, Mele R, Lauri G, Panaitescu A,
Nunziata R, et al: Managing complications of chronic pancreatitis:
A guide for the gastroenterologist. Expert Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 17:1267–1283. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Szatmary P, Grammatikopoulos T, Cai W,
Huang W, Mukherjee R, Halloran C, Beyer G and Sutton R: Acute
pancreatitis: Diagnosis and treatment. Drugs. 82:1251–1276. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Barreto SG, Habtezion A, Gukovskaya A,
Lugea A, Jeon C, Yadav D, Hegyi P, Venglovecz V, Sutton R and
Pandol SJ: Critical thresholds: Key to unlocking the door to the
prevention and specific treatments for acute pancreatitis. Gut.
70:194–203. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li Y, Sui S and Goel A: Extracellular
vesicles associated microRNAs: Their biology and clinical
significance as biomarkers in gastrointestinal cancers. Semin
Cancer Biol. 99:5–23. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bayat M and Sadri Nahand J: Exosomal
miRNAs: The tumor's trojan horse in selective metastasis. Mol
Cancer. 23:1672024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ghafouri-Fard S, Shoorei H, Dong P,
Poornajaf Y, Hussen BM, Taheri M and Akbari Dilmaghani N: Emerging
functions and clinical applications of exosomal microRNAs in
diseases. Noncoding RNA Res. 8:350–362. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li S, Lv D, Yang H, Lu Y and Jia Y: A
review on the current literature regarding the value of exosome
miRNAs in various diseases. Ann Med. 55:22329932023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wei H, Zhao H, Cheng D, Zhu Z, Xia Z, Lu
D, Yu J, Dong R and Yue J: miR-148a and miR-551b-5p regulate
inflammatory responses via regulating autophagy in acute
pancreatitis. Int Immunopharmacol. 127:1114382024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang Q, Wang H, Jing Q, Yang Y, Xue D, Hao
C and Zhang W: Regulation of pancreatic fibrosis by acinar
Cell-derived exosomal miR-130a-3p via targeting of stellate cell
PPAR-γ. J Inflamm Res. 14:461–477. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jia YC, Ding YX, Mei WT, Wang YT, Zheng Z,
Qu YX, Liang K, Li J, Cao F and Li F: Extracellular vesicles and
pancreatitis: Mechanisms, status and perspectives. Int J Biol Sci.
17:549–561. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mihoc T, Latcu SC, Secasan CC, Dema V,
Cumpanas AA, Selaru M, Pirvu CA, Valceanu AP, Zara F, Dumitru CS,
et al: Pancreatic morphology, immunology, and the pathogenesis of
acute pancreatitis. Biomedicines. 12:26272024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zaman S and Gorelick F: Acute
pancreatitis: Pathogenesis and emerging therapies. J Pancreatol.
7:10–20. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mederos MA, Reber HA and Girgis MD: Acute
pancreatitis: A review. JAMA. 325:382–390. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang S, Ni HM, Chao X, Ma X, Kolodecik T,
De Lisle R, Ballabio A, Pacher P and Ding WX: Critical role of
TFEB-mediated lysosomal biogenesis in Alcohol-induced pancreatitis
in mice and humans. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 10:59–81. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Qiu M, Zhou X, Zippi M, Goyal H, Basharat
Z, Jagielski M and Hong W: Comprehensive review on the pathogenesis
of Hypertriglyceridaemia-associated acute pancreatitis. Ann Med.
55:22659392023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang H, Gao J, Wen L, Huang K, Liu H, Zeng
L, Zeng Z, Liu Y and Mo Z: Ion channels in acinar cells in acute
pancreatitis: Crosstalk of calcium, iron, and copper signals. Front
Immunol. 15:14442722024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
An J, Jiang T, Qi L and Xie K: Acinar
cells and the development of pancreatic fibrosis. Cytokine Growth
Factor Rev. 71-72:40–53. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ge P, Luo Y, Okoye CS and Chen H, Liu J,
Zhang G, Xu C and Chen H: Intestinal barrier damage, systemic
inflammatory response syndrome, and acute lung injury: A
troublesome trio for acute pancreatitis. Biomed Pharmacother.
132:1107702020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kang H, Yang Y, Zhu L, Zhao X, Li J, Tang
W and Wan M: Role of neutrophil extracellular traps in inflammatory
evolution in severe acute pancreatitis. Chin Med J (Engl).
135:2773–2784. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Papantoniou K, Aggeletopoulou I,
Michailides C, Pastras P and Triantos C: Understanding the role of
NLRP3 inflammasome in acute pancreatitis. Biology (Basel).
13:9452024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kong F, Pan Y and Wu D: Activation and
regulation of pancreatic stellate cells in chronic pancreatic
fibrosis: A potential therapeutic approach for chronic
pancreatitis. Biomedicines. 12:1082024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nail HM, Chiu CC, Leung CH, Ahmed MMM and
Wang HD: Exosomal miRNA-mediated intercellular communications and
immunomodulatory effects in tumor microenvironments. J Biomed Sci.
30:692023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Melzer MK and Kleger A: Acute
pancreatitis: Murine model systems unravel disease-modifying genes
with potential implications for diagnostics and patient
stratification. United European Gastroenterol J. 10:618–619. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Patel HR, Diaz Almanzar VM, LaComb JF, Ju
J and Bialkowska AB: The role of MicroRNAs in pancreatitis
development and progression. Int J Mol Sci. 24:10572023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim H, Lee YY and Kim VN: The biogenesis
and regulation of animal microRNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
26:276–296. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shang R, Lee S, Senavirathne G and Lai EC:
microRNAs in action: Biogenesis, function and regulation. Nat Rev
Genet. 24:816–833. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang Y, Huang Q, Luo C, Wen Y, Liu R, Sun
H and Tang L: MicroRNAs in acute pancreatitis: From pathogenesis to
novel diagnosis and therapy. J Cell Physiol. 235:1948–1961. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Correia de Sousa M, Gjorgjieva M, Dolicka
D, Sobolewski C and Foti M: Deciphering miRNAs' Action through
miRNA Editing. Int J Mol Sci. 20:62492019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Treiber T, Treiber N and Meister G:
Regulation of microRNA biogenesis and its crosstalk with other
cellular pathways. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 20:5–20. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu K, He J, Pu W and Peng Y: The role of
Exportin-5 in MicroRNA biogenesis and cancer. Genomics Proteomics
Bioinformatics. 16:120–126. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hynes C and Kakumani PK: Regulatory role
of RNA-binding proteins in microRNA biogenesis. Front Mol Biosci.
11:13748432024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rani V and Sengar RS: Biogenesis and
mechanisms of microRNA-mediated gene regulation. Biotechnol Bioeng.
119:685–692. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Komatsu S, Kitai H and Suzuki HI: Network
regulation of microRNA biogenesis and target interaction. Cells.
12:3062023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cánovas-Márquez JT, Falk S, Nicolás FE,
Padmanabhan S, Zapata-Pérez R, Sánchez-Ferrer Á, Navarro E and
Garre V: A ribonuclease III involved in virulence of Mucorales
fungi has evolved to cut exclusively single-stranded RNA. Nucleic
Acids Res. 49:5294–5307. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Slezak-Prochazka I, Kluiver J, de Jong D,
Kortman G, Halsema N, Poppema S, Kroesen BJ and van den Berg A:
Cellular localization and processing of primary transcripts of
exonic microRNAs. PLoS One. 8:e766472013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Arya SB, Collie SP and Parent CA: The
ins-and-outs of exosome biogenesis, secretion, and internalization.
Trends Cell Biol. 34:90–108. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wozniak AL, Adams A, King KE, Dunn W,
Christenson LK, Hung WT and Weinman SA: The RNA binding protein
FMR1 controls selective exosomal miRNA cargo loading during
inflammation. J Cell Biol. 219:e2019120742020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Villarroya-Beltri C, Gutiérrez-Vázquez C,
Sánchez-Cabo F, Pérez-Hernández D, Vázquez J, Martin-Cofreces N,
Martinez-Herrera DJ, Pascual-Montano A, Mittelbrunn M and
Sánchez-Madrid F: Sumoylated hnRNPA2B1 controls the sorting of
miRNAs into exosomes through binding to specific motifs. Nat
Commun. 4:29802013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sonoda Y, Kano F and Murata M:
Applications of cell resealing to reconstitute microRNA loading to
extracellular vesicles. Sci Rep. 11:29002021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jaé N, McEwan DG, Manavski Y, Boon RA and
Dimmeler S: Rab7a and Rab27b control secretion of endothelial
microRNA through extracellular vesicles. FEBS Lett. 589:3182–3188.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ostrowski M, Carmo NB, Krumeich S, Fanget
I, Raposo G, Savina A, Moita CF, Schauer K, Hume AN, Freitas RP, et
al: Rab27a and Rab27b control different steps of the exosome
secretion pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 12:19–30. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Payandeh Z, Tangruksa B, Synnergren J,
Heydarkhan-Hagvall S, Nordin JZ, Andaloussi SE, Borén J, Wiseman J,
Bohlooly YM, Lindfors L and Valadi H: Extracellular vesicles
transport RNA between cells: Unraveling their dual role in
diagnostics and therapeutics. Mol Aspects Med. 99:1013022024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Robinson H, Ruelcke JE, Lewis A, Bond CS,
Fox AH, Bharti V, Wani S, Cloonan N, Lai A, Margolin D, et al:
Caveolin-1-driven membrane remodelling regulates hnRNPK-mediated
exosomal microRNA sorting in cancer. Clin Transl Med. 11:e3812021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sun H, Bhandari K, Burrola S, Wu J and
Ding WQ: Pancreatic ductal Cell-derived extracellular vesicles are
effective drug carriers to enhance Paclitaxel's efficacy in
pancreatic cancer cells through Clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Int
J Mol Sci. 23:47732022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Groot M and Lee H: Sorting mechanisms for
MicroRNAs into extracellular vesicles and their associated
diseases. Cells. 9:10442020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Minhua Q, Bingzheng F, Zhiran X, Yingying
Z, Yuwei Y, Ting Z, Jibing C and Hongjun G: Exosomal-microRNAs
improve islet cell survival and function in islet transplantation.
Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 19:669–677. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Park EJ, Shimaoka M and Kiyono H:
Functional flexibility of exosomes and micrornas of intestinal
epithelial cells in affecting inflammation. Front Mol Biosci.
9:8544872022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
He K, Yang T, Yu J, Zang X, Jiang S, Xu S,
Liu J, Xu Z, Wang W and Hong S: Dermatophagoides farinae microRNAs
released to external environments via exosomes regulate
inflammation-related gene expression in human bronchial epithelial
cells. Front Immunol. 14:13032652023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Isaac R, Reis FCG, Ying W and Olefsky JM:
Exosomes as mediators of intercellular crosstalk in metabolism.
Cell Metab. 33:1744–1762. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Otahal A, Kuten-Pella O, Kramer K,
Neubauer M, Lacza Z, Nehrer S and De Luna A: Functional repertoire
of EV-associated miRNA profiles after lipoprotein depletion via
ultracentrifugation and size exclusion chromatography from
autologous blood products. Sci Rep. 11:58232021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Gemoll T, Rozanova S, Roder C, Hartwig S,
Kalthoff H, Lehr S, ElSharawy A and Habermann JK: Protein profiling
of serum extracellular vesicles reveals qualitative and
quantitative differences after differential ultracentrifugation and
exoquickTM isolation. J Clin Med. 9:14292020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Rekker K, Saare M, Roost AM, Kubo AL,
Zarovni N, Chiesi A, Salumets A and Peters M: Comparison of serum
exosome isolation methods for microRNA profiling. Clin Biochem.
47:135–138. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Liu K, Lv T, He L, Tang W, Zhang Y, Xiao
X, Li Y, Chang X, Wang S, Pandol SJ, et al: Endocrine-exocrine
miR-503-322 drives aging-associated pancreatitis via targeting
MKNK1 in acinar cells. Nat Commun. 16:26132025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Shao Y, Wu W, Fan F, Liu H, Ming Y, Liao
W, Bai C and Gao Y: Extracellular vesicle content changes induced
by melatonin promote functional recovery of pancreatic beta cells
in acute pancreatitis. J Inflamm Res. 16:6397–6413. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Liu J, Niu Z, Zhang R, Peng Z, Wang L, Liu
Z, Gao Y, Pei H and Pan L: MALAT1 shuttled by extracellular
vesicles promotes M1 polarization of macrophages to induce acute
pancreatitis via miR-181a-5p/HMGB1 axis. J Cell Mol Med.
25:9241–9254. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ryu S and Lee EK: The pivotal role of
macrophages in the pathogenesis of pancreatic diseases. Int J Mol
Sci. 25:57652024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Iyer S, Enman M, Sahay P and Dudeja V:
Novel therapeutics to treat chronic pancreatitis: Targeting
pancreatic stellate cells and macrophages. Expert Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 18:171–183. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Xiang H, Yu H, Zhou Q, Wu Y, Ren J, Zhao
Z, Tao X and Dong D: Macrophages: A rising star in immunotherapy
for chronic pancreatitis. Pharmacol Res. 185:1065082022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhao Y, Wang H, Lu M, Qiao X, Sun B, Zhang
W and Xue D: Pancreatic acinar cells employ miRNAs as mediators of
intercellular communication to participate in the regulation of
Pancreatitis-associated macrophage activation. Mediators Inflamm.
2016:63404572016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Jimenez-Alesanco A, Marcuello M,
Pastor-Jimenez M, Lopez-Puerto L, Bonjoch L, Gironella M, Carrascal
M, Abian J, de-Madaria E and Closa D: Acute pancreatitis promotes
the generation of two different exosome populations. Sci Rep.
9:198872019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhang X, Chu J, Sun H, Zhao D, Ma B, Xue
D, Zhang W and Li Z: MiR-155 aggravates impaired autophagy of
pancreatic acinar cells through targeting Rictor. Acta Biochim
Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 52:192–199. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Wan J, Yang X, Ren Y, Li X, Zhu Y, Haddock
AN, Ji B, Xia L and Lu N: Inhibition of mir-155 reduces impaired
autophagy and improves prognosis in an experimental pancreatitis
mouse model. Cell Death Dis. 10:3032019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wang D, Tang M, Zong P, Liu H, Zhang T,
Liu Y and Zhao Y: MiRNA-155 regulates the Th17/Treg ratio by
targeting SOCS1 in severe acute pancreatitis. Front Physiol.
9:6862018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Tang DS, Cao F, Yan CS, Cui JT, Guo XY,
Cheng L, Li L, Li YL, Ma JM, Fang K, et al: Acinar Cell-derived
extracellular vesicle MiRNA-183-5p aggravates acute pancreatitis by
promoting M1 macrophage polarization through downregulation of
FoxO1. Front Immunol. 13:8692072022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zheng Z, Cao F, Ding YX, Lu JD, Fu YQ, Liu
L, Guo YL, Liu S, Sun HC, Cui YQ and Li F: Acinous cell
AR42J-derived exosome miR125b-5p promotes acute pancreatitis
exacerbation by inhibiting M2 macrophage polarization via PI3K/AKT
signaling pathway. World J Gastrointest Surg. 15:600–620. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Su XJ, Chen Y, Zhang QC, Peng XB, Liu YP,
Wang L and Du YQ: Exosomes derived from cerulein-stimulated
pancreatic acinar cells mediate peritoneal macrophage M1
polarization and pyroptosis via an miR-24-3p/MARCH3/NLRP3 axis in
acute pancreatitis. Pancreas. 53:e641–e651. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Chen F, Xu K, Han Y, Ding J, Ren J, Wang
Y, Ma Z and Cao F: Mitochondrial dysfunction in pancreatic acinar
cells: Mechanisms and therapeutic strategies in acute pancreatitis.
Front Immunol. 15:15030872024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Cai SW, Han Y and Wang GP: miR-148a-3p
exhaustion inhibits necrosis by regulating PTEN in acute
pancreatitis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 11:5647–5657. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Zhang Y, Yan L and Han W: Elevated level
of miR-551b-5p is associated with inflammation and disease
progression in patients with severe acute pancreatitis. Ther Apher
Dial. 22:649–655. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Kusnierz-Cabala B, Nowak E, Sporek M,
Kowalik A, Kuzniewski M, Enguita FJ and Stepien E: Serum levels of
unique miR-551-5p and endothelial-specific miR-126a-5p allow
discrimination of patients in the early phase of acute
pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 15:344–351. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Hu C, Yin L, Chen Z, Waldron RT, Lugea A,
Lin Y, Zhai X, Wen L, Han YP, Pandol SJ, et al: The unique
pancreatic stellate cell gene expression signatures are associated
with the progression from acute to chronic pancreatitis. Comput
Struct Biotechnol J. 19:6375–6385. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Chan LK, Tsesmelis M, Gerstenlauer M,
Leithäuser F, Kleger A, Frick LD, Maier HJ and Wirth T: Functional
IKK/NF-κB signaling in pancreatic stellate cells is essential to
prevent autoimmune pancreatitis. Commun Biol. 5:5092022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Zhao Y, Feng Y, Sun F, Li L, Chen J, Song
Y, Zhu W, Hu X, Li Z, Kong F, et al: Optimized rAAV8 targeting
acinar KLF4 ameliorates fibrosis in chronic pancreatitis via
exosomes-enriched let-7s suppressing pancreatic stellate cells
activation. Mol Ther. 32:2624–2640. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Charrier A, Chen R, Chen L, Kemper S,
Hattori T, Takigawa M and Brigstock DR: Connective tissue growth
factor (CCN2) and microRNA-21 are components of a positive feedback
loop in pancreatic stellate cells (PSC) during chronic pancreatitis
and are exported in PSC-derived exosomes. J Cell Commun Signal.
8:147–156. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Li X, Lin Z, Wang L, Liu Q, Cao Z, Huang
Z, Zhong M, Peng S, Zhang Y, Li Y and Ma X: RNA-Seq analyses of the
role of miR-21 in acute pancreatitis. Cell Physiol Biochem.
51:2198–2211. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Yan B, Cheng L, Jiang Z, Chen K, Zhou C,
Sun L, Cao J, Qian W, Li J, Shan T, et al: Resveratrol inhibits
ROS-Promoted activation and glycolysis of pancreatic stellate cells
via suppression of miR-21. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018:13469582018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Ciccarelli G, Di Giuseppe G, Soldovieri L,
Quero G, Nista EC, Brunetti M, Cinti F, Moffa S, Capece U, Tondolo
V, et al: Beta-cell function and glucose metabolism in patients
with chronic pancreatitis. Eur J Intern Med. 128:112–118. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Gao Y, Mi N, Wu W, Zhao Y, Fan F, Liao W,
Ming Y, Guan W and Bai C: Transfer of inflammatory mitochondria via
extracellular vesicles from M1 macrophages induces ferroptosis of
pancreatic beta cells in acute pancreatitis. J Extracell Vesicles.
13:e124102024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Zhu X, Liu D, Li G, Zhi M, Sun J, Qi L, Li
J, Pandol SJ and Li L: Exosomal miR-140-3p and miR-143-3p from
TGF-β1-treated pancreatic stellate cells target BCL2 mRNA to
increase β-cell apoptosis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 551:1116532022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Lu XG, Kang X, Zhan LB, Kang LM, Fan ZW
and Bai LZ: Circulating miRNAs as biomarkers for severe acute
pancreatitis associated with acute lung injury. World J
Gastroenterol. 23:7440–7449. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Liu C, Feng H, Zhang L, Guo Y, Ma J and
Yang L: MicroRNA-143-3p levels are reduced in the peripheral blood
of patients with gestational diabetes mellitus and influences
pancreatic β-cell function and viability. Exp Ther Med. 25:812023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Liu Q, Zhu X and Guo S: From pancreas to
lungs: The role of immune cells in severe acute pancreatitis and
acute lung injury. Immun Inflamm Dis. 12:e13512024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Xiong Y, Chen X, Yang X, Zhang H, Li X,
Wang Z, Feng S, Wen W and Xiong X: miRNA transcriptomics analysis
shows miR-483-5p and miR-503-5p targeted miRNA in extracellular
vesicles from severe acute pancreatitis-associated lung injury
patients. Int Immunopharmacol. 125:1110752023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Li F, Wang Z, Cao Y, Pei B, Luo X, Liu J,
Ge P, Luo Y, Ma S and Chen H: Intestinal mucosal immune barrier: A
powerful firewall against severe acute pancreatitis-associated
acute lung injury via the Gut-lung axis. J Inflamm Res.
17:2173–2193. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Shao Y, Li Y, Jiang Y, Li H, Wang J and
Zhang D: Circulating exosomal miR-155-5p contributes to severe
acute pancreatitis-associated intestinal barrier injury by
targeting SOCS1 to activate NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis.
FASEB J. 37:e230032023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Wang L, Yuan N, Li Y, Ma Q, Zhou Y, Qiao
Z, Li S, Liu C, Zhang L, Yuan M and Sun J: Stellate ganglion block
relieves acute lung injury induced by severe acute pancreatitis via
the miR-155-5p/SOCS5/JAK2/STAT3 axis. Eur J Med Res. 27:2312022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Balaraman AK, Moglad E, Afzal M, Babu MA,
Goyal K, Roopashree R, Kaur I, Kumar S, Kumar M, Chauhan AS, et al:
Liquid biopsies and exosomal ncRNA: Transforming pancreatic cancer
diagnostics and therapeutics. Clin Chim Acta. 567:1201052025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Xu C, Jiang C, Li Z, Gao H, Xian J, Guo W,
He D, Peng X, Zhou D and Li D: Exosome nanovesicles: Biomarkers and
new strategies for treatment of human diseases. MedComm (2020).
5:e6602024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Preethi KA, Selvakumar SC, Ross K,
Jayaraman S, Tusubira D and Sekar D: Liquid biopsy: Exosomal
microRNAs as novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in cancer.
Mol Cancer. 21:542022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Xu Y, Sun Y, Yin R, Dong T, Song K, Fang
Y, Liu G, Shen B and Li H: Differential expression of plasma
exosomal microRNA in severe acute pancreatitis. Front Pharmacol.
13:9809302022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Qu Y, Ding Y, Lu J, Jia Y, Bian C, Guo Y,
Zheng Z, Mei W, Cao F and Li F: Identification of key microRNAs in
exosomes derived from patients with the severe acute pancreatitis.
Asian J Surg. 46:337–347. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Desai CS, Khan A, Bellio MA, Willis ML,
Mahung C, Ma X, Baldwin X, Williams BM, Baron TH, Coleman LG, et
al: Characterization of extracellular vesicle miRNA identified in
peripheral blood of chronic pancreatitis patients. Mol Cell
Biochem. 476:4331–4341. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Nakamaru K, Tomiyama T, Kobayashi S,
Ikemune M, Tsukuda S, Ito T, Tanaka T, Yamaguchi T, Ando Y, Ikeura
T, et al: Extracellular vesicles microRNA analysis in type 1
autoimmune pancreatitis: Increased expression of microRNA-21.
Pancreatology. 20:318–324. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Li L, Zhang Q, Feng Y, Kong F, Sun F, Xie
P, Zhao J, Yu H, Zhou J, Wu S, et al: A novel serum exosomal miRNA
signature in the early prediction of persistent organ failure in
patients with acute pancreatitis. Ann Surg. Feb 7–2024.(Epub ahead
of print) doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000006229. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Zerem E, Kurtcehajic A, Kunosic S, Zerem
Malkocevic D and Zerem O: Current trends in acute pancreatitis:
Diagnostic and therapeutic challenges. World J Gastroenterol.
29:2747–2763. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Zhu H, Zhou X, Sun X, Fu C, Li G, Dong X,
Kong X, Su X and Du Y: Serum exosomal miR-216a contributes to acute
pancreatitis-associated acute lung injury by enhancing endothelial
cell vascular permeability via downregulating LAMC1. Pancreas. Feb
13–2025.(Epub ahead of print). doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000002467.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Han SB and Lee SS: Simultaneous detection
of exosomal microRNAs isolated from cancer cells using surface
acoustic wave sensor array with high sensitivity and
reproducibility. Micromachines (Basel). 15:2492024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Trigo CM, Rodrigues JS, Camoes SP, Sola S
and Miranda JP: Mesenchymal stem cell secretome for regenerative
medicine: Where do we stand? J Adv Res. 70:103–124. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Rahimian S, Mirkazemi K, Nejad AK and
Doroudian M: Exosome-based advances in pancreatic cancer: The
potential of mesenchymal stem cells. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
207:1045942025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Galgaro BC, Beckenkamp LR, van den MNM,
Korb VG, Naasani LIS, Roszek K and Wink MR: The adenosinergic
pathway in mesenchymal stem cell fate and functions. Med Res Rev.
41:2316–2349. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Xie Q, Liu R, Jiang J, Peng J, Yang C,
Zhang W, Wang S and Song J: What is the impact of human umbilical
cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on clinical treatment?
Stem Cell Res Ther. 11:5192020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Pang K, Kong F and Wu D: Prospect of
mesenchymal Stem-cell-conditioned medium in the treatment of acute
pancreatitis: A systematic review. Biomedicines. 11:23432023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Oveili E, Vafaei S, Bazavar H, Eslami Y,
Mamaghanizadeh E, Yasamineh S and Gholizadeh O: The potential use
of mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes as microRNAs delivery
systems in different diseases. Cell Commun Signal. 21:202023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Li H, Du R, Xiang A, Liu Y, Guan M and He
H: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-181a-5p
promotes M2 macrophage polarization to alleviate acute pancreatitis
through ZEB2-mediated RACK1 ubiquitination. FASEB J. 38:e700422024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Li HY, He HC, Song JF, Du YF, Guan M and
Wu CY: Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells repair severe
acute pancreatitis by secreting miR-181a-5p to target
PTEN/Akt/TGF-β1 signaling. Cell Signal. 66:1094362020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Ren S, Pan L, Yang L, Niu Z, Wang L, Feng
H and Yuan M: miR-29a-3p transferred by mesenchymal stem
cells-derived extracellular vesicles protects against myocardial
injury after severe acute pancreatitis. Life Sci. 272:1191892021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Sharifi-Rad J, Herrera-Bravo J, Kamiloglu
S, Petroni K, Mishra AP, Monserrat-Mesquida M, Sureda A, Martorell
M, Aidarbekovna DS, Yessimsiitova Z, et al: Recent advances in the
therapeutic potential of emodin for human health. Biomed
Pharmacother. 154:1135552022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Yang Q, Luo Y, Ge P, Lan B, Liu J, Wen H,
Cao Y, Sun Z, Zhang G, Yuan H, et al: Emodin ameliorates severe
acute Pancreatitis-associated acute lung injury in rats by
modulating Exosome-specific miRNA expression profiles. Int J
Nanomedicine. 18:6743–6761. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|