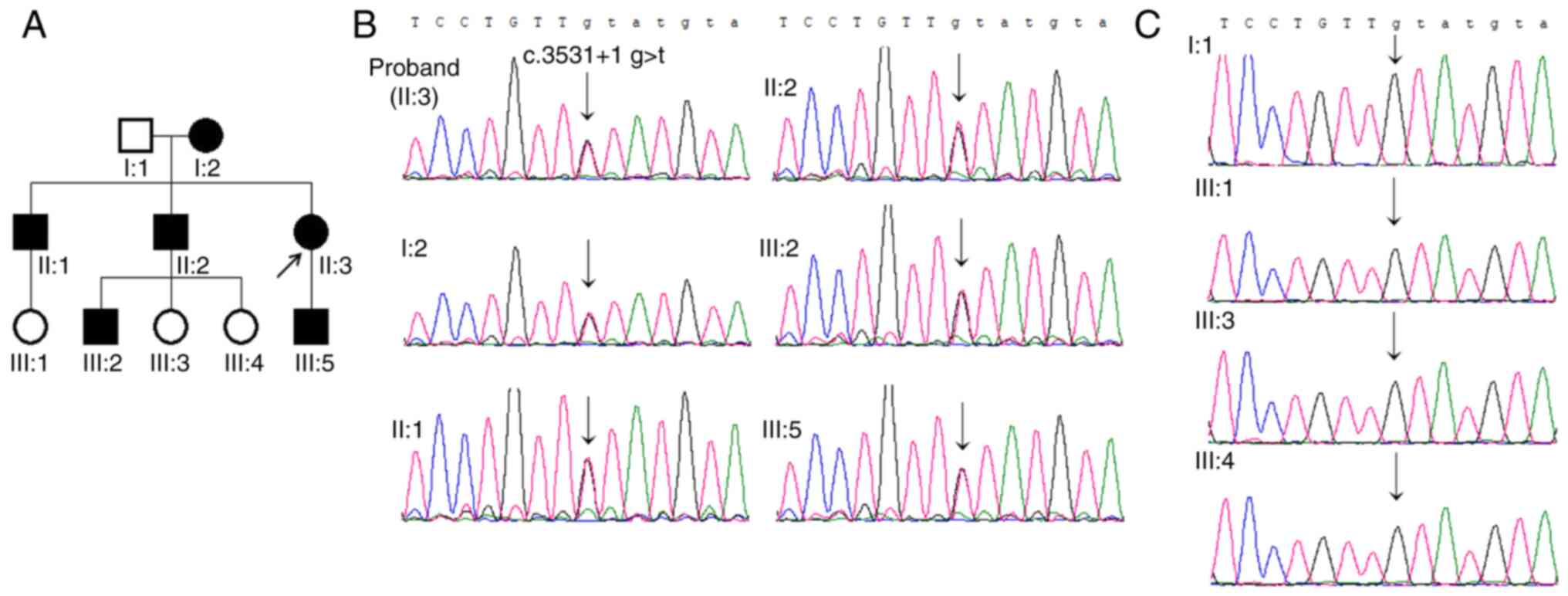
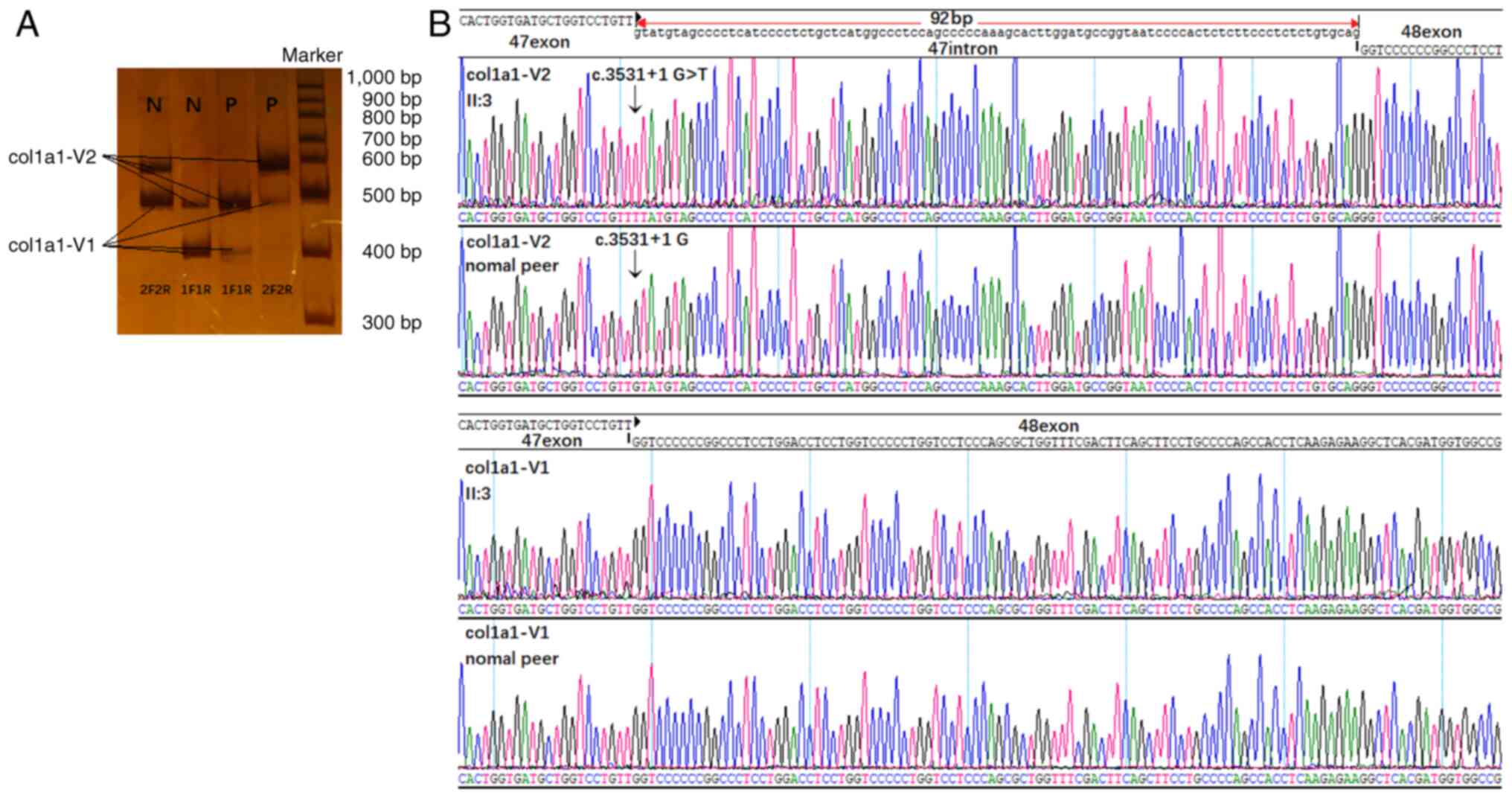
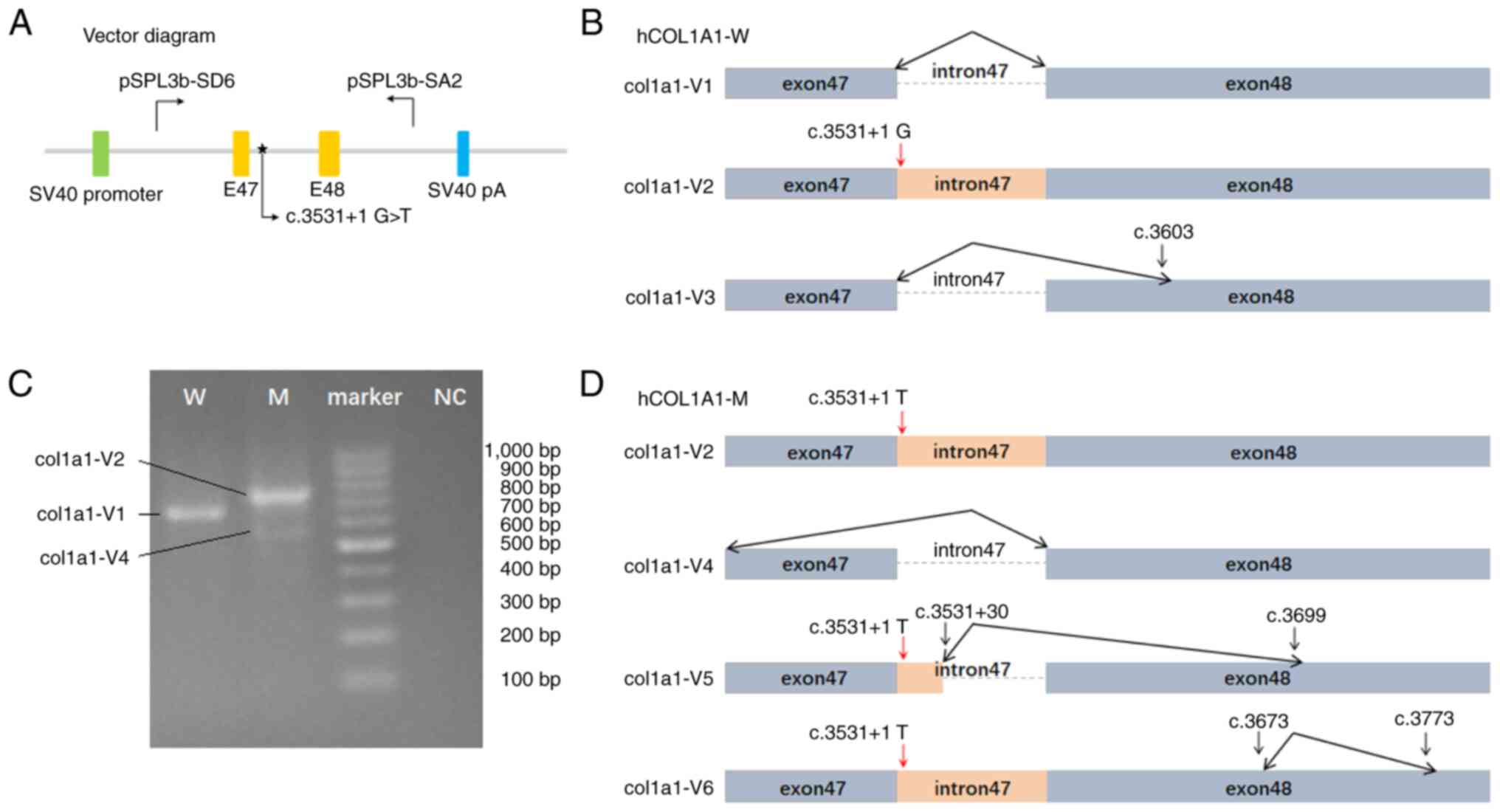
|
1
|
Uttarilli A, Shah H, Bhavani GS, Upadhyai
P, Shukla A and Girisha KM: Phenotyping and genotyping of skeletal
dysplasias: Evolution of a center and a decade of experience in
India. Bone. 120:204–211. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nicol L, Morar P, Wang Y, Henriksen K, Sun
S, Karsdal M, Smith R, Nagamani SCS, Shapiro J, Lee B and Orwoll E:
Alterations in non-type I collagen biomarkers in osteogenesis
imperfecta. Bone. 120:70–74. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Forlino A, Cabral WA, Barnes AM and Marini
JC: New perspectives on osteogenesis imperfecta. Nat Rev
Endocrinol. 7:540–557. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ablin DS: Osteogenesis imperfecta: A
review. Can Assoc Radiol J. 49:110–123. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Marini JC, Forlino A, Bächinger HP, Bishop
NJ, Byers PH, Paepe A, Fassier F, Fratzl-Zelman N, Kozloff KM,
Krakow D, et al: Osteogenesis imperfecta. Nat Rev Dis Primers.
3:170522017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li L, Mao B, Li S, Xiao J, Wang H, Zhang
J, Ren X, Wang Y, Wu Y, Cao Y, et al: Genotypic and phenotypic
characterization of Chinese patients with osteogenesis imperfecta.
Hum Mutat. 40:588–600. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tromp G, Kuivaniemi H, Stacey A, Shikata
H, Baldwin CT, Jaenisch R and Prockop DJ: Structure of a
full-length cDNA clone for the prepro alpha 1(I) chain of human
type I procollagen. Biochem J. 253:919–922. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Essawi O, Symoens S, Fannana M, Darwish M,
Farraj M, Willaert A, Essawi T, Callewaert B, De Paepe A, Malfait F
and Coucke PJ: Genetic analysis of osteogenesis imperfecta in the
Palestinian population: Molecular screening of 49 affected
families. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 6:15–26. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Plagnol V, Curtis J, Epstein M, Mok KY,
Stebbings E, Grigoriadou S, Wood NW, Hambleton S, Burns SO,
Thrasher AJ, et al: A robust model for read count data in exome
sequencing experiments and implications for copy number variant
calling. Bioinformatics. 28:2747–2754. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S,
Gastier-Foster J, Grody WW, Hegde M, Lyon E, Spector E, et al: ACMG
laboratory quality assurance committee. Standards and guidelines
for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus
recommendation of the American college of medical genetics and
genomics and the association for molecular pathology. Genet Med.
17:405–424. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Biesecker LG and Harrison SM: ClinGen
sequence variant interpretation working group. The ACMG/AMP
reputable source criteria for the interpretation of sequence
variants. Genet Med. 20:1687–1688. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Abou Tayoun AN, Pesaran T, DiStefano MT,
Oza A, Rehm HL, Biesecker LG and Harrison SM: ClinGen sequence
variant interpretation working group (ClinGen SVI). Recommendations
for interpreting the loss of function PVS1 ACMG/AMP variant
criterion. Hum Mutat. 39:1517–1524. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang Z, Zhao G, Zhu Z, Wang Y, Xiang X,
Zhang S, Luo T, Zhou Q, Qiu J, Tang B, et al: VarCards2: An
integrated genetic and clinical database for ACMG-AMP
variant-interpretation guidelines in the human whole genome.
Nucleic Acids Res. 52:D1478–D1489. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Neitzel H: A routine method for the
establishment of permanent growing lymphoblastoid cell lines. Hum
Genet. 73:320–326. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Van Dijk FS, Semler O, Etich J, Köhler A,
Jimenez-Estrada JA, Bravenboer N, Claeys L, Riesebos E, Gegic S,
Piersma SR, et al: Interaction between KDELR2 and HSP47 as a key
determinant in osteogenesis imperfecta caused by bi-allelic
variants in KDELR2. Am J Hum Genet. 107:989–999. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tuysuz B, Uludag Alkaya D, Geyik F,
Alaylıoğlu M, Kasap B, Kurugoğlu S, Akman YE, Vural M and Bilguvar
K: Biallelic frameshift variants in PHLDB1 cause mild-type
osteogenesis imperfecta with regressive spondylometaphyseal
changes. J Med Genet. 60:819–826. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Umair M, Hassan A, Jan A, Ahmad F, Imran
M, Samman MI, Basit S and Ahmad W: Homozygous sequence variants in
the FKBP10 gene underlie osteogenesis imperfecta in consanguineous
families. J Hum Genet. 61:207–213. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Umair M, Alhaddad B, Rafique A, Jan A,
Haack TB, Graf E, Ullah A, Ahmad F, Strom TM, Meitinger T and Ahmad
W: Exome sequencing reveals a novel homozygous splice site variant
in the WNT1 gene underlying osteogenesis imperfecta type 3. Pediatr
Res. 82:753–758. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hayat A, Hussain S, Bilal M, Kausar M,
Almuzzaini B, Abbas S, Tanveer A, Khan A, Siddiqi S, Foo JN, et al:
Biallelic variants in four genes underlying recessive osteogenesis
imperfecta. Eur J Med Genet. 63:1039542020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rauch F and Glorieux FH: Osteogenesis
imperfecta. Lancet. 363:1377–1385. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Malfait F, Symoens S, De Backer J,
Hermanns-Lê T, Sakalihasan N, Lapière CM, Coucke P and De Paepe A:
Three arginine to cysteine substitutions in the pro-alpha
(I)-collagen chain cause Ehlers-Danlos syndrome with a propensity
to arterial rupture in early adulthood. Hum Mutat. 28:387–395.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jovanovic M, Guterman-Ram G and Marini JC:
Osteogenesis imperfecta: Mechanisms and signaling pathways
connecting classical and rare OI types. Endocr Rev. 43:61–90. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Marini JC, Forlino A, Cabral WA, Barnes
AM, San Antonio JD, Milgrom S, Hyland JC, Körkkö J, Prockop DJ, De
Paepe A, et al: Consortium for osteogenesis imperfecta mutations in
the helical domain of type I collagen: Regions rich in lethal
mutations align with collagen binding sites for integrins and
proteoglycans. Hum Mutat. 28:209–221. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wei S, Yao Y, Shu M, Gao L, Zhao J, Li T,
Wang Y and Xu C: Genotype-phenotype relationship and follow-up
analysis of a Chinese cohort with osteogenesis imperfecta. Endocr
Pract. 28:760–766. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Aliyeva L, Ongen YD, Eren E, Sarisozen MB,
Alemdar A, Temel SG and Sag SO: Genotype and phenotype correlation
of patients with osteogenesis imperfecta. J Mol Diagn. 26:754–769.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Willing MC, Deschenes SP, Scott DA, Byers
PH, Slayton RL, Pitts SH, Arikat H and Roberts EJ: Osteogenesis
imperfecta type I: Molecular heterogeneity for COL1A1 null alleles
of type I collagen. Am J Hum Genet. 55:638–647. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Vandersteen AM, Lund AM, Ferguson DJ,
Sawle P, Pollitt RC, Holder SE, Wakeling E, Moat N and Pope FM:
Four patients with Sillence type I osteogenesis imperfecta and mild
bone fragility, complicated by left ventricular cardiac valvular
disease and cardiac tissue fragility caused by type I collagen
mutations. Am J Med Genet A. 164A:386–391. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Malmgren B, Andersson K, Lindahl K,
Kindmark A, Grigelioniene G, Zachariadis V, Dahllöf G and Åström E:
Tooth agenesis in osteogenesis imperfecta related to mutations in
the collagen type I genes. Oral Dis. 23:42–49. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Van Dijk FS: Genetics of osteoporosis in
children. Endocr Dev. 28:196–209. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Swinnen FK, Coucke PJ, De Paepe AM,
Symoens S, Malfait F, Gentile FV, Sangiorgi L, D'Eufemia P, Celli
M, Garretsen TJ, et al: Osteogenesis imperfecta: The audiological
phenotype lacks correlation with the genotype. Orphanet J Rare Dis.
6:882011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Byers PH, Duvic M, Atkinson M, Robinow M,
Smith LT, Krane SM, Greally MT, Ludman M, Matalon R, Pauker S, et
al: Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VIIA and VIIB result from
splice-junction mutations or genomic deletions that involve exon 6
in the COL1A1 and COL1A2 genes of type I collagen. Am J Med Genet.
72:94–105. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Körkkö J, Ala-Kokko L, De Paepe A,
Nuytinck L, Earley J and Prockop DJ: Analysis of the COL1A1 and
COL1A2 genes by PCR amplification and scanning by
conformation-sensitive gel electrophoresis identifies only COL1A1
mutations in 15 patients with osteogenesis imperfecta type I:
Identification of common sequences of null-allele mutations. Am J
Hum Genet. 62:98–110. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Baralle D and Baralle M: Splicing in
action: Assessing disease causing sequence changes. J Med Genet.
42:737–748. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bardai G, Moffatt P, Glorieux FH and Rauch
F: DNA sequence analysis in 598 individuals with a clinical
diagnosis of osteogenesis imperfecta: Diagnostic yield and mutation
spectrum. Osteoporos Int. 27:3607–3613. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Stover ML, Primorac D, Liu SC, McKinstry
MB and Rowe DW: Defective splicing of mRNA from one COL1A1 allele
of type I collagen in nondeforming (type I) osteogenesis
imperfecta. J Clin Invest. 92:1994–2002. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ito K, Patel PN, Gorham JM, McDonough B,
DePalma SR, Adler EE, Lam L, MacRae CA, Mohiuddin SM, Fatkin D, et
al: Identification of pathogenic gene mutations in LMNA and MYBPC3
that alter RNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:7689–7694.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dong Z, Wang Y, Zhang J, Zhu F, Liu Z,
Kang Y, Lin M and Shi H: Analyzing the effects of BRCA1/2 variants
on mRNA splicing by minigene assay. J Hum Genet. 68:65–71. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang Y, Luo H, Pan L, Feng C, Guo Z, Zou
Y, Zeng B, Huang S, Yuan H, Wu P, et al: Reevaluating the
splice-altering variant in TECTA as a cause of nonsyndromic hearing
loss DFNA8/12 by functional analysis of RNA. Hum Mol Genet. Apr
27–2024.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|