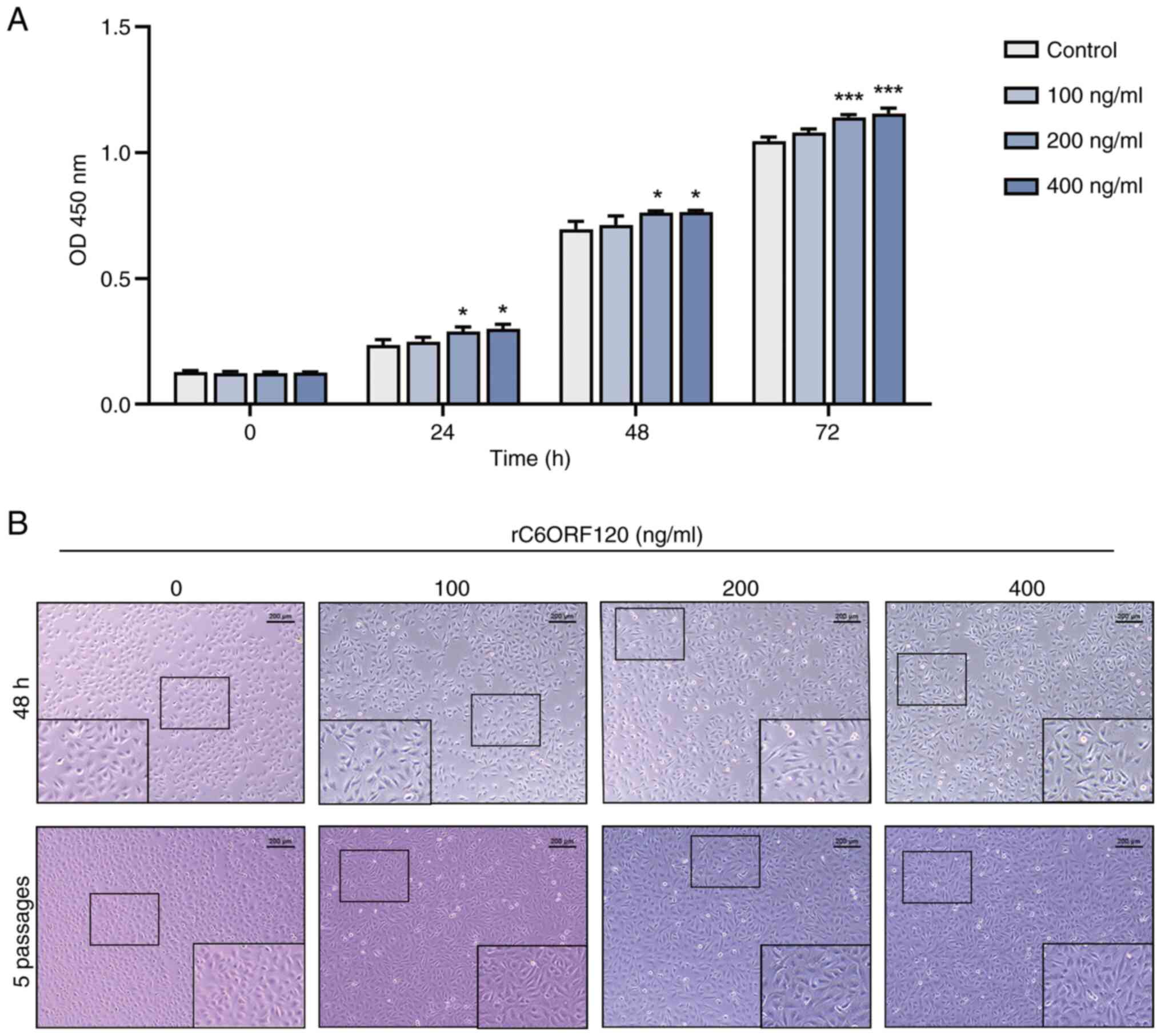
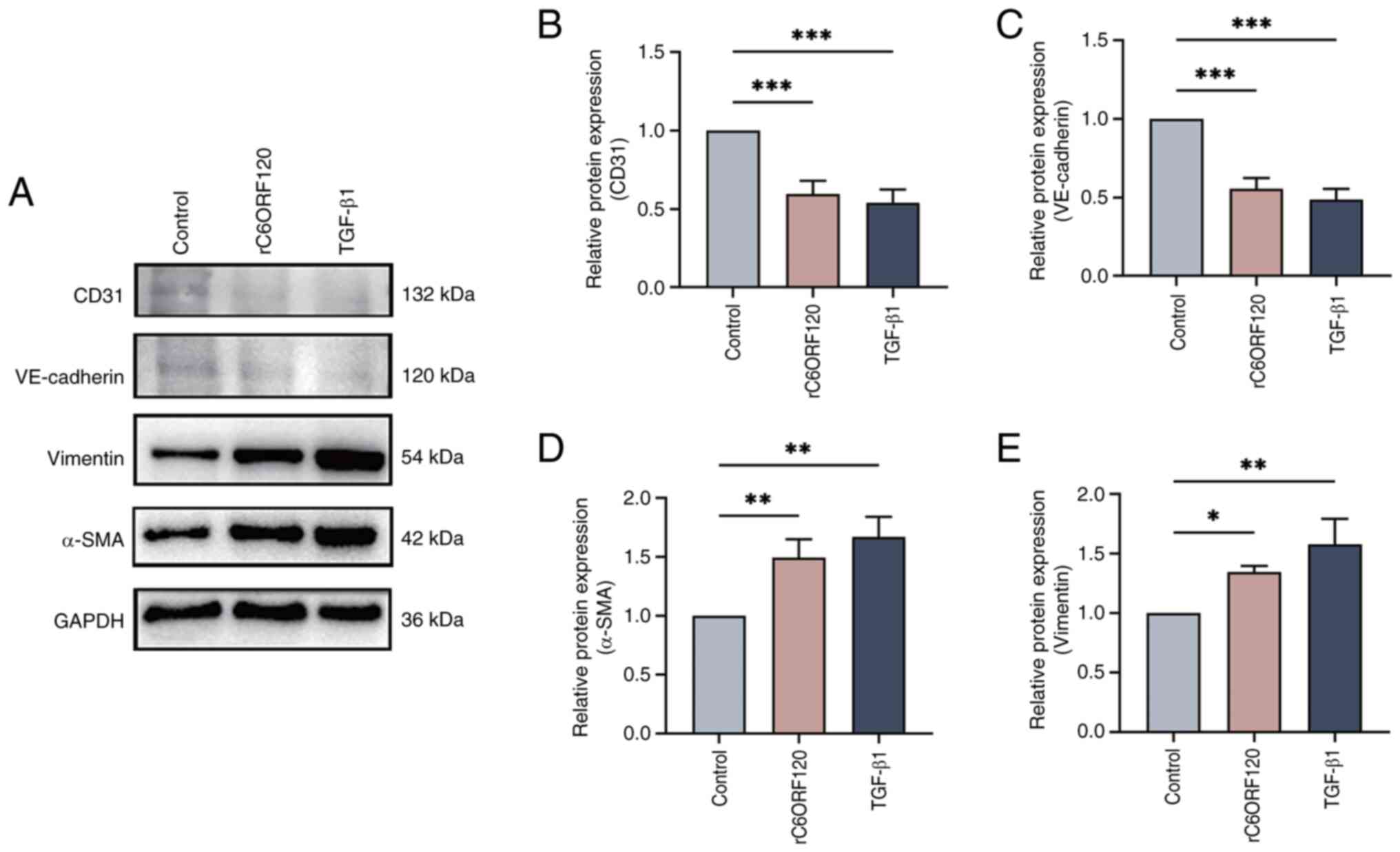
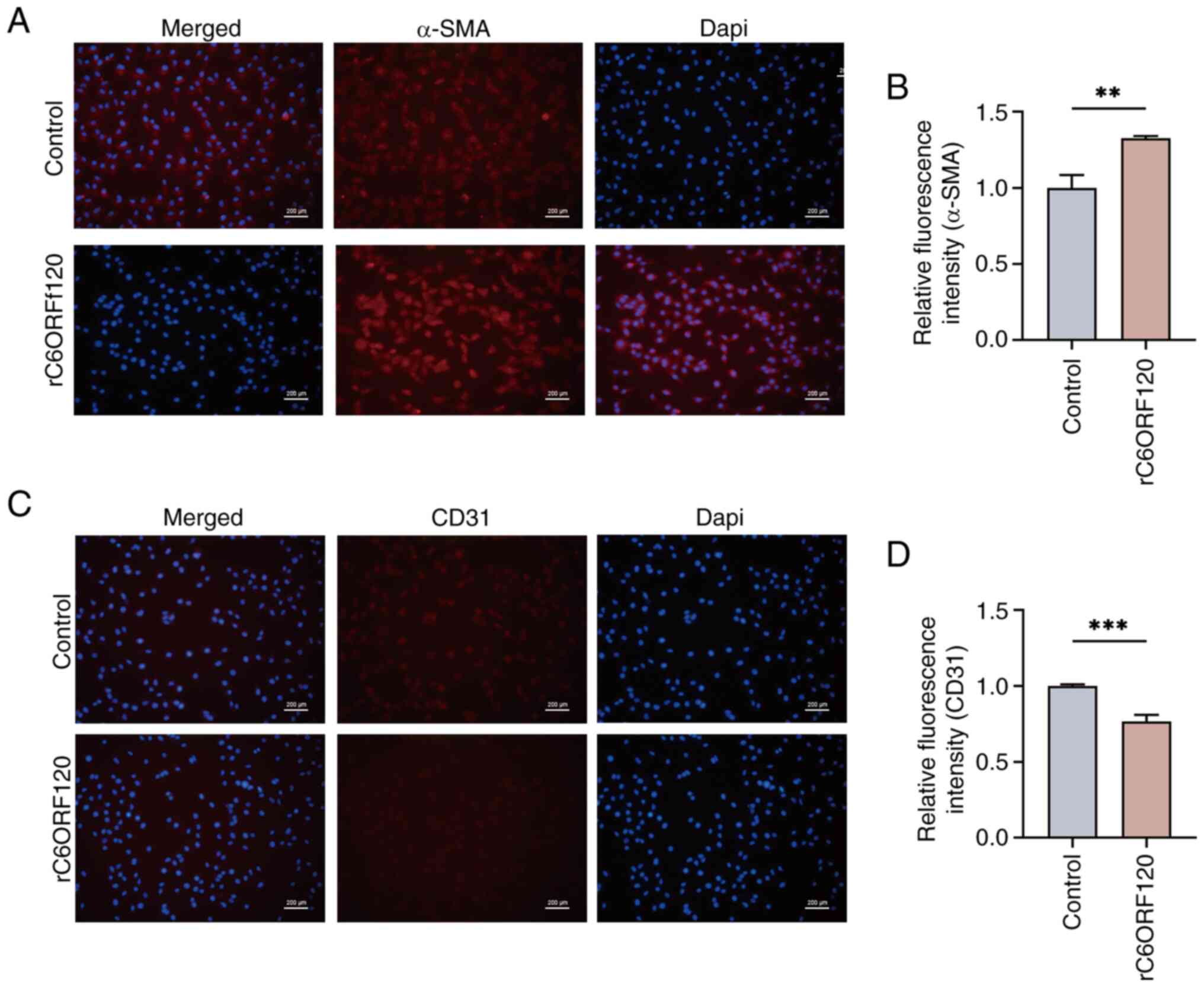
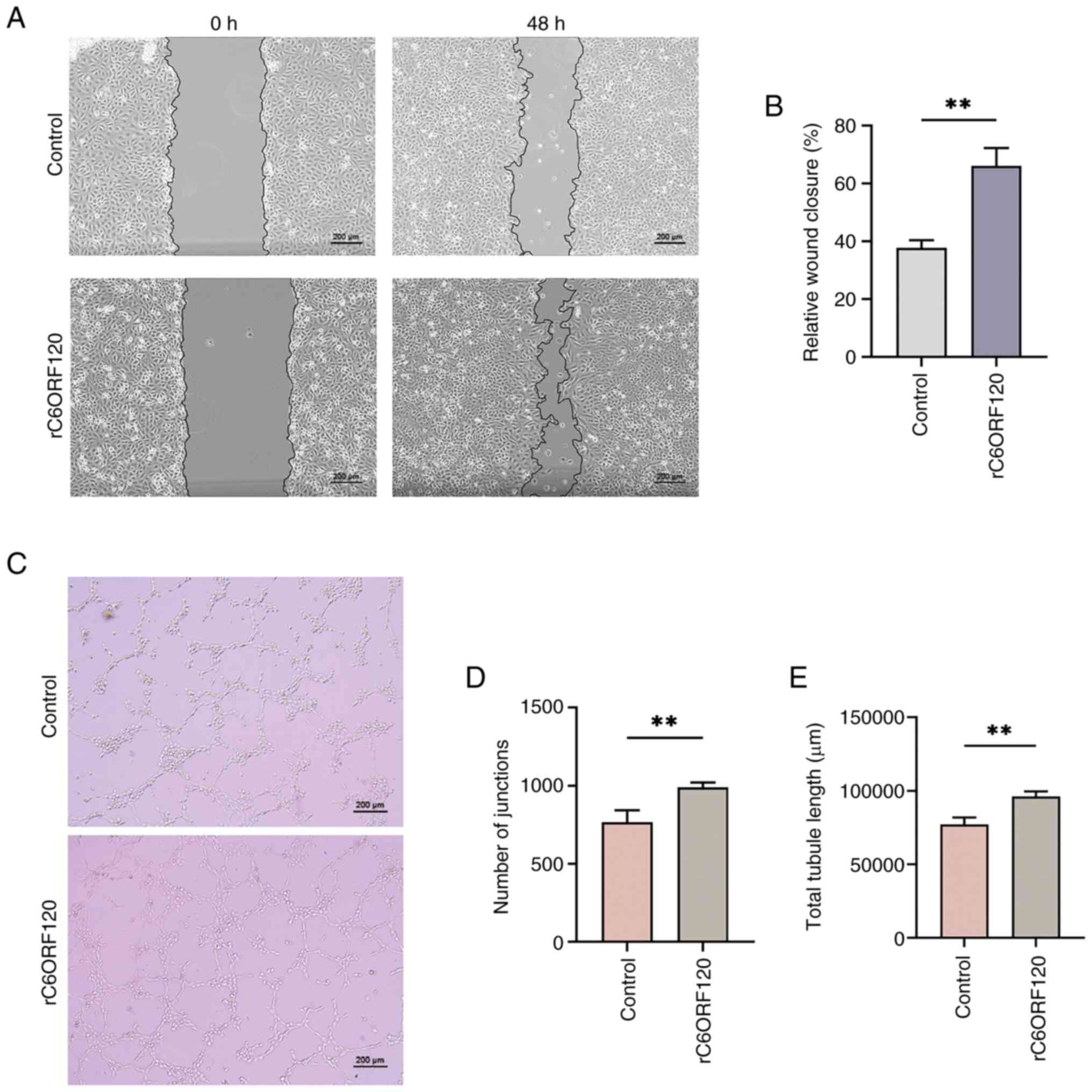
|
1
|
Xu Y and Kovacic JC: Endothelial to
mesenchymal transition in health and disease. Annu Rev Physiol.
85:245–267. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang L, Wu X and Hong L: Endothelial
reprogramming in atherosclerosis. Bioengineering (Basel).
11:3252024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu Y, Wu Z, Li Y, Chen Y, Zhao X, Wu M
and Xia Y: Metabolic reprogramming and interventions in
angiogenesis. J Adv Res. 70:323–338. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Piera-Velazquez S and Jimenez SA:
Endothelial to mesenchymal transition: Role in physiology and in
the pathogenesis of human diseases. Physiol Rev. 99:1281–1324.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Naderi-Meshkin H and Setyaningsih WAW:
Endothelial cell dysfunction: Onset, progression, and consequences.
Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 29:2232024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Singh A, Bhatt KS, Nguyen HC, Frisbee JC
and Singh KK: Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in
cardiovascular pathophysiology. Int J Mol Sci. 25:61802024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Clere N, Renault S and Corre I:
Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer. Front Cell Dev
Biol. 8:7472020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Poisson J, Lemoinne S, Boulanger C, Durand
F, Moreau R, Valla D and Rautou PE: Liver sinusoidal endothelial
cells: Physiology and role in liver diseases. J Hepatol.
66:212–227. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Medici D and Kalluri R:
Endothelial-mesenchymal transition and its contribution to the
emergence of stem cell phenotype. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:379–384.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Man S, Duffhues GS, Dijke PT and Baker D:
The therapeutic potential of targeting the
endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Angiogenesis. 22:3–13. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li X, Qiao Y, Chang LS, Xiao F, Lu LH, Hao
XH, Zhang RW, Wu H and Wei HS: Role of C6ORF120, an N-glycosylated
protein, is implicated in apoptosis of CD4+ T lymphocytes. Chin Med
J (Engl). 124:3560–3567. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bradfield JP, Qu HQ, Wang K, Zhang H,
Sleiman PM, Kim CE, Mentch FD, Qiu H, Glessner JT, Thomas KA, et
al: A genome-wide meta-analysis of six type 1 diabetes cohorts
identifies multiple associated loci. PLoS Genet. 7:e10022932011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wu Y, Zhang R, Song X, Han X, Zhang J and
Li X: C6orf120 gene knockout in rats mitigates concanavalin
A-induced autoimmune hepatitis via regulating NKT cells. Cell
Immunol. 371:1044672022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang M, Ma H, Zhang J, Song XC, Ye XH, Li
YF, Zhang YF, He LL, Wei HS and Li X: Deletion of the C6orf120 gene
with unknown function ameliorates autoimmune hepatitis induced by
concanavalin A. Cell Immunol. 331:9–15. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu H, Wang X, Wang P, Wang YQ, Yi YY and
Li X: Novel protein C6ORF120 promotes apoptosis through
mitochondria-dependent pathway in CD4 +T lymphocytes. Biomed
Environ Sci. 36:639–643. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang X, Liu H, Wang Y, Wang P, Yi Y, Lin Y
and Li X: Novel protein C6ORF120 promotes liver fibrosis by
activating hepatic stellate cells through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR
pathway. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 39:1422–1430. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang J, Zhang M, Ma H, Song XC, Wu YN,
Zhang R, He LL, Ye XH, Gao MX and Li X: C6orf120 gene deficiency
may be vulnerable to carbon tetra-chloride induced acute hepatic
injury in rats. Arch Med Sci. 18:1626–1637. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jin X, Fu W, Zhou J, Shuai N, Yang Y and
Wang B: Oxymatrine attenuates oxidized low-density
lipoprotein-induced HUVEC injury by inhibiting NLRP3
inflammasome-mediated pyrop-tosis via the activation of the
SIRT1/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 48:1872021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Arakelian L, Lion J, Churlaud G, Bargui R,
Thierry B, Mutabazi E, Bruneval P, Alberdi AJ, Doliger C, Veyssiere
M, et al: 20-Endothelial CD34 expression and regulation of immune
cell response in-vitro. Sci Rep. 13:135122023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Duranova H, Kuzelova L, Borotova P, Simora
V and Fialkova V: Human umbilical vein endothelial cells as a
versatile cellular model system in diverse experimental paradigms:
An ultrastructural perspective. Microsc Microanal. 30:419–439.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gong L, Lei Y, Liu Y, Tan F, Li S, Wang X,
Xu M, Cai W, Du B, Xu F, et al: Vaccarin prevents ox-LDL-induced
HUVEC EndMT, inflammation and apoptosis by suppressing ROS/p38 MAPK
signaling. Am J Transl Res. 11:2140–2154. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang Y, Liu J, Zou T, Qi Y, Yi B,
Dissanayaka WL and Zhang C: DPSCs treated by TGF-β1 regulate
angiogenic sprouting of three-dimensionally co-cultured HUVECs and
DPSCs through VEGF-Ang-Tie2 signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther.
12:2812021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu X, Pu L, Chen W, Zhao Q, Wu G, Li D and
Zhu H: LY294002 attenuates inflammatory response in
endotoxin-induced uveitis by downregulating JAK3 and inactivating
the PI3K/Akt signaling. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 44:510–518.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Eskiler GG and Ozturk M: Therapeutic
potential of the PI3K inhibitor LY294002 and PARP inhibitor
talazoparib combination in BRCA-deficient triple negative breast
cancer cells. Cell Signal. 91:1102292022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ma Q, Yang F, Huang B, Pan X, Li W, Yu T,
Wang X, Ran L, Qian K, Li H, et al: CircARID1A binds to IGF2BP3 in
gastric cancer and promotes cancer proliferation by forming a
circARID1A-IGF2BP3-SLC7A5 RNA-protein ternary complex. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 41:2512022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zeng Z, Inoue K, Sun H, Leng T, Feng X,
Zhu L and Xiong ZG: TRPM7 regulates vascular endothelial cell
adhesion and tube formation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
308:C308–C318. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang W, Li Y and Zhang Y, Ye T, Wang K, Li
S and Zhang Y: SIRT1 mediates the inhibitory ef-fect of
Dapagliflozin on EndMT by inhibiting the acetylation of endothelium
notch1. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 22:3312023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang Z, Guo Q, Ma C, Zhao Z, Shi Q, Yu H,
Rao L and Li M: USF1 transcriptionally activates USP14 to drive
atherosclerosis by promoting EndMT through NLRC5/Smad2/3 axis. Mol
Med. 30:322024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xie X, Qu P, Wu H, Liu P, Luo J, Chi J,
Liu X, Chen X and Xu C: Circulating exosomal miR-21 mediates HUVEC
proliferation and migration through PTEN/PI3K/AKT in Crohn's
disease. Ann Transl Med. 10:2582022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang W, Li H, Qian Y, Li M, Deng M, Bi D
and Zou J: ALKBH5 regulates corneal neovascularization by Mediating
FOXM1 M6A demethylation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 65:342024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Sobierajska K, Wawro ME, Ciszewski WM and
Niewiarowska J: Transforming growth Factor-β receptor
internalization via caveolae is regulated by tubulin-β2 and
tubulin-β3 during endothelial-mesenchymal transition. Am J Pathol.
189:2531–2546. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang L, Ge T and Cui J: FLI-1-driven
regulation of endothelial cells in human diseases. J Transl Med.
22:7402024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ciszewski WM, Woźniak LA and Sobierajska
K: Diverse roles of SARS-CoV-2 spike and nucleocapsid proteins in
EndMT stimulation through the TGF-β-MRTF axis inhibited by aspirin.
Cell Commun Signal. 22:2962024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wu X, Du X, Yang Y, Liu X, Liu X, Zhang N,
Li Y, Jiang X, Jiang Y and Yang Z: Inhibition of miR-122 reduced
atherosclerotic lesion formation by regulating NPAS3-mediated
endothelial to mesenchymal transition. Life Sci. 265:1188162021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hu Z, Wang J, Pan T, Li X, Tao C, Wu Y,
Wang X, Zhang Z, Liu Y, Zhang W, et al: The exosome-transmitted
lncRNA LOC100132249 induces endothelial dysfunction in diabetic
retinopathy. Diabetes. 72:1307–1319. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bischoff J: Endothelial to mesenchymal
transition-purposeful versus maladaptive differentiation. Circ Res.
124:1163–1165. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhou WW, Dai C, Liu WZ, Zhang C, Zhang Y,
Yang GS, Guo QH, Li S, Yang HX and Li AY: Gentianella acuta
improves TAC-induced cardiac remodel-ling by regulating the notch
and PI3K/Akt/FOXO1/3 pathways. Biomed Pharmacother. 154:1135642022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
He Y, Dan Y, Gao X, Huang L, Lv H and Chen
J: DNMT1-mediated lncRNA MEG3 methylation accelerates
endothelial-mesenchymal transition in diabetic retinopathy through
the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
320:E598–E608. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
La Mendola D, Trincavelli ML and Martini
C: Angiogenesis in disease. Int J Mol Sci. 23:109622022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gentile MT, Pastorino O, Bifulco M and
Colucci-D'Amato L: HUVEC tube-formation assay to evaluate the
impact of natural products on angiogenesis. J Vis Exp.
24:e585912019.
|
|
41
|
Yang DR, Wang MY, Zhang CL and Wang Y:
Endothelial dysfunction in vascular complications of diabetes: A
comprehensive review of mechanisms and implications. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 15:13592552024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hall IF, Kishta F, Xu Y, Baker AH and
Kovacic JC: Endothelial to mesenchymal transition: At the axis of
cardiovascular health and disease. Cardiovasc Res. 120:223–236.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Romano E, Rosa I, Fioretto BS and Manetti
M: The contribution of endothelial cells to tissue fibrosis. Curr
Opin Rheumatol. 36:52–60. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ciszewski WM, Wawro ME, Sacewicz-Hofman I
and Sobierajska K: Cytoskeleton reorganization in EndMT-the role in
cancer and fibrotic diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 22:116072021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Song C, Wang Z, Cao J, Dong Y and Chen Y:
Hesperetin alleviates aflatoxin B1 induced liver toxicity in mice:
Modulating lipid peroxidation and ferritin autophagy. Ecotoxicol
Environ Saf. 284:1168542024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhou K, Xiao S, Cao S, Zhao C, Zhang M and
Fu Y: Improvement of glucolipid metabolism and oxidative stress via
modulating PI3K/Akt pathway in insulin resistance HepG2 cells by
chickpea flavonoids. Food Chem X. 23:1016302024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Cao Y: 34-Lack of basic rationale in
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its related concepts. Cell
Biosci. 14:1042024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hamm MJ, Kirchmaier BC and Herzog W:
Sema3d controls collective endothelial cell migration by distinct
mechanisms via Nrp1 and PlxnD1. J Cell Biol. 215:415–430. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|