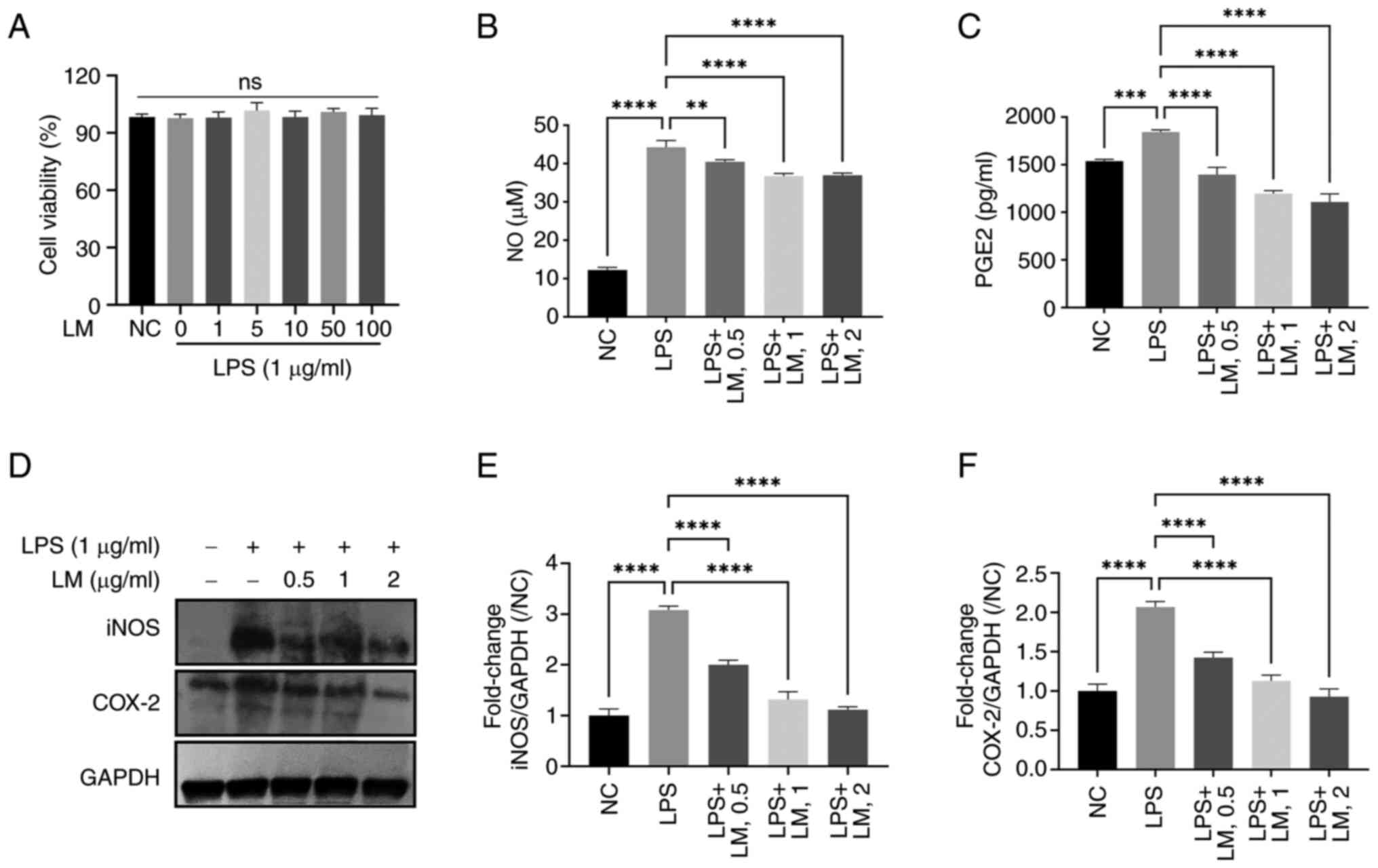
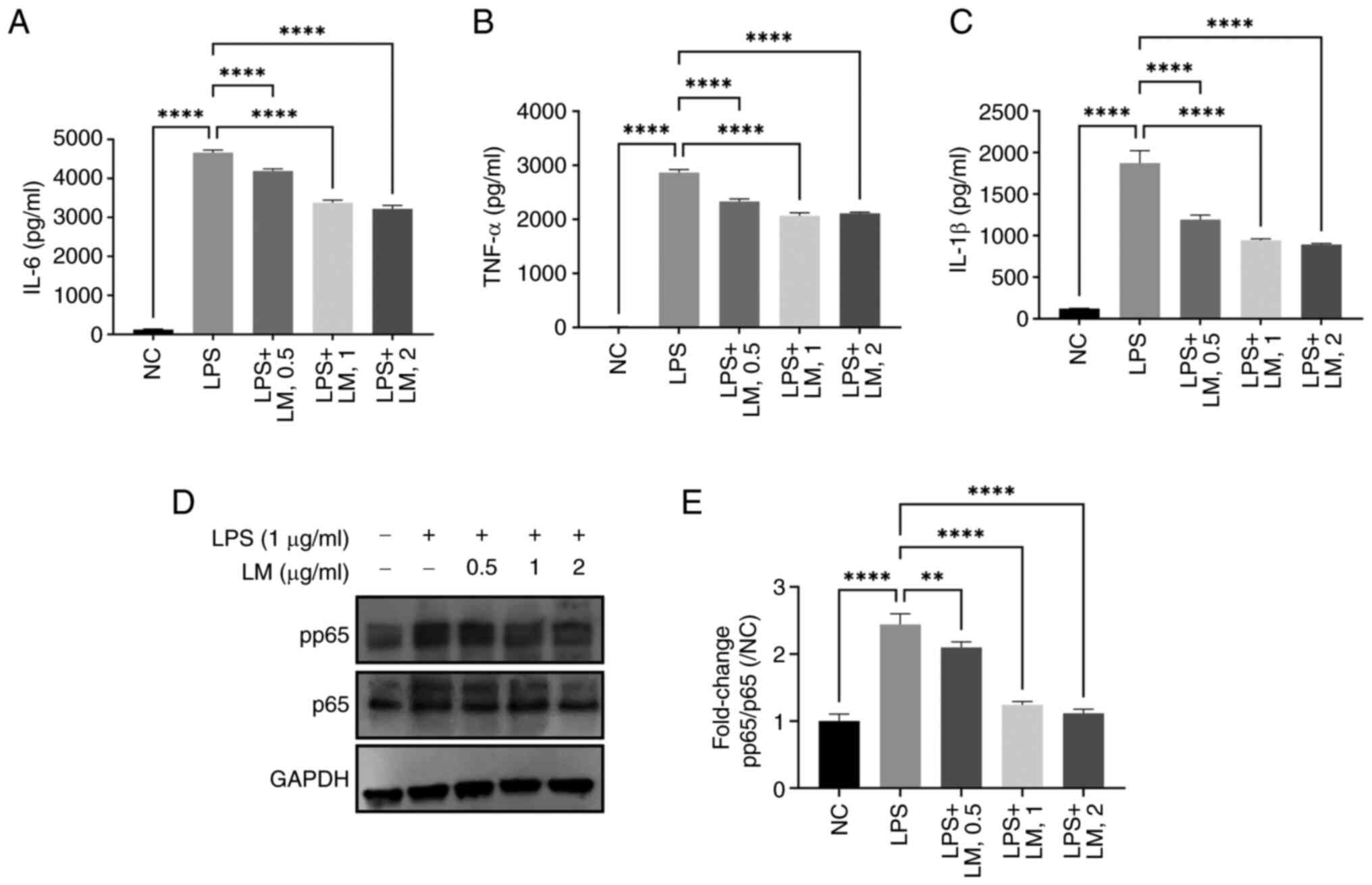
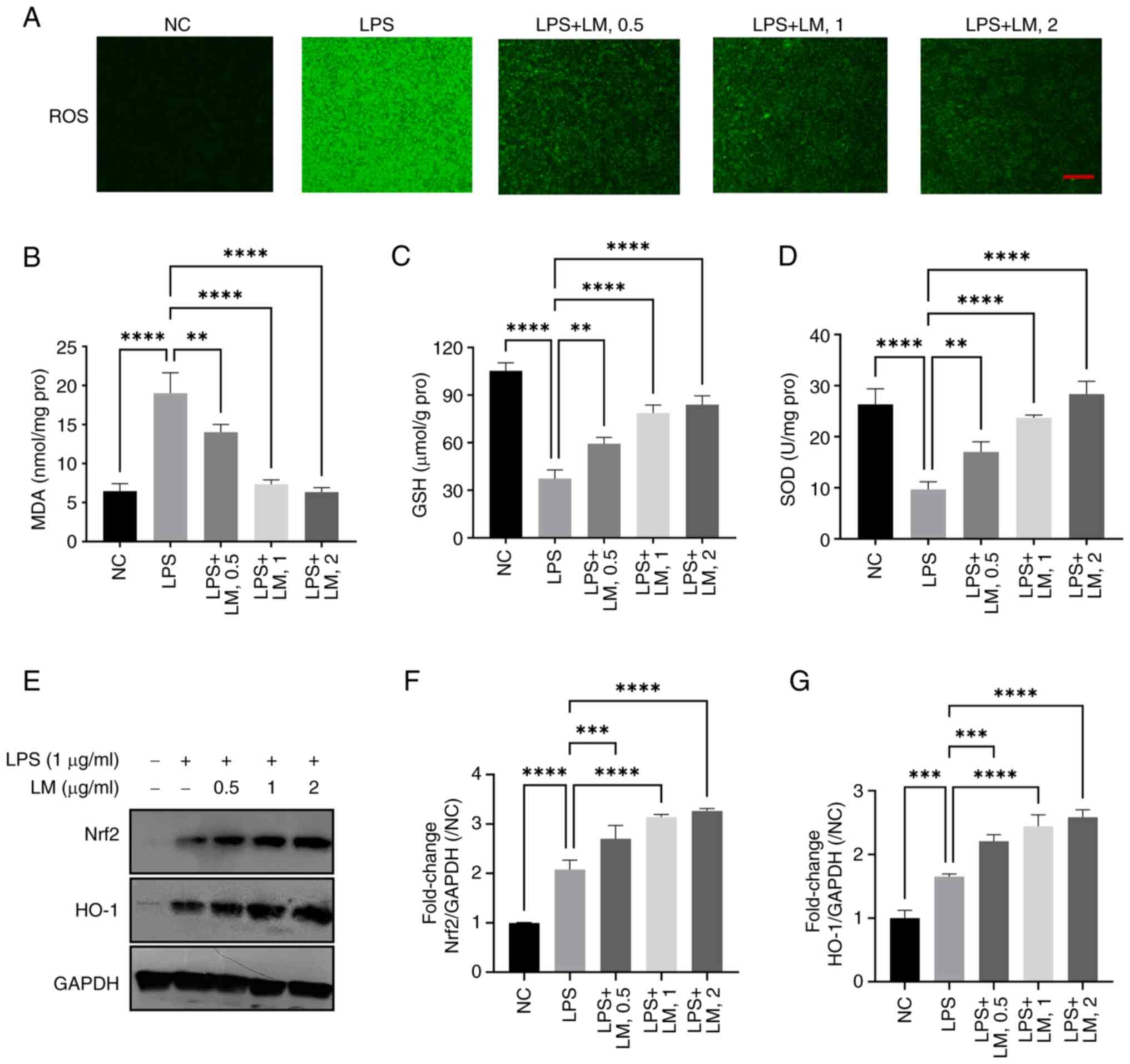
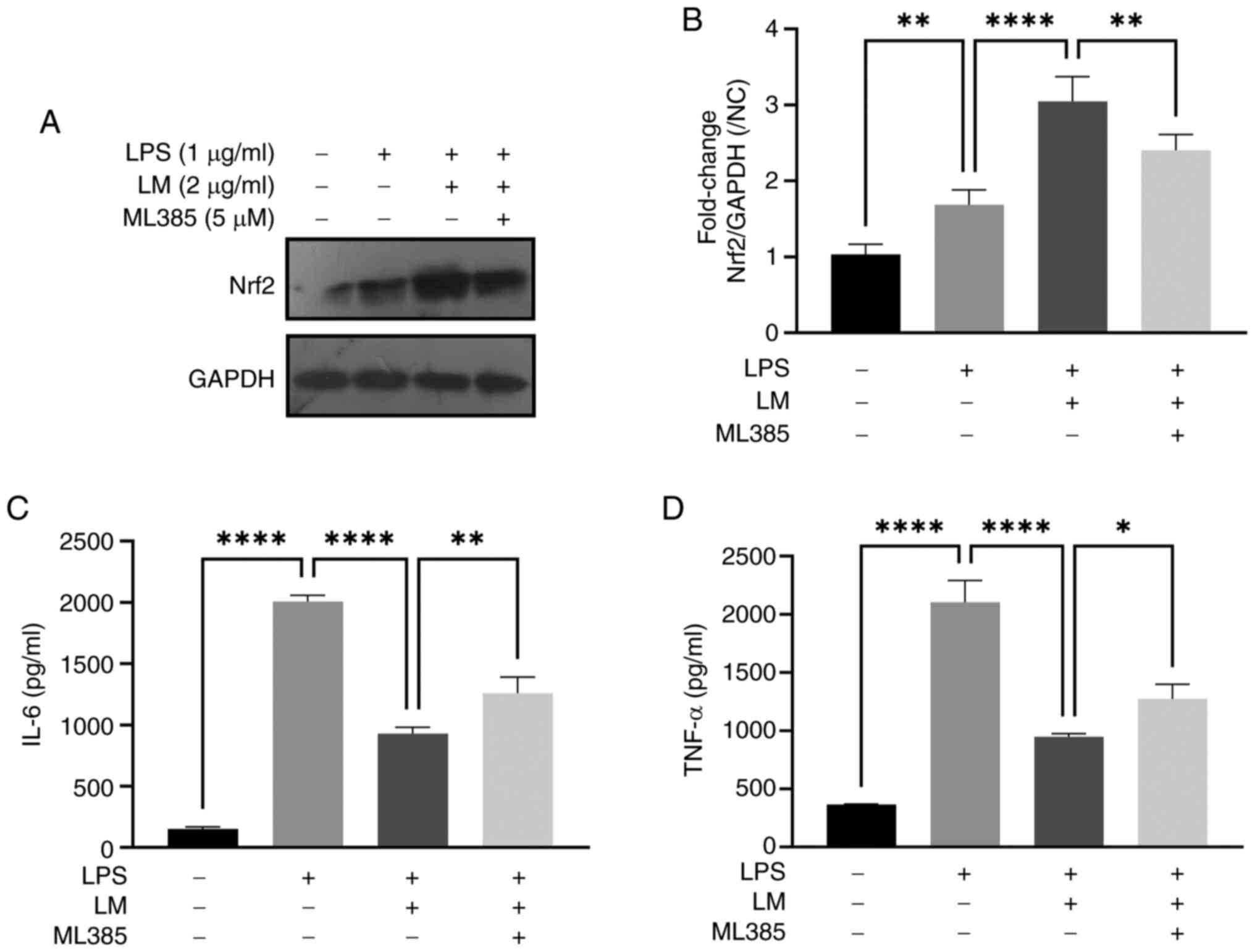
|
1
|
Ortiz-Diaz E, Festic E, Gajic O and Levitt
J: Emerging Pharmacological therapies for prevention and early
treatment of acute lung injury. Semin Respir Crit Care Med.
34:448–458. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lv H, Liu Q, Wen Z, Feng H, Deng X and Ci
X: Xanthohumol ameliorates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute
lung injury via induction of AMPK/GSK3β-Nrf2 signal axis. Redox
Biol. 12:311–324. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zimmermann K, Baldinger J, Mayerhofer B,
Atanasov AG, Dirsch VM and Heiss EH: Activated AMPK boosts the
Nrf2/HO-1 signaling axis-A role for the unfolded protein response.
Free Radic Biol Med. 88:417–426. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhao XL, Yu L, Zhang SD, Ping K, Ni HY,
Qin XY, Zhao CJ, Wang W, Efferth T and Fu YJ: Cryptochlorogenic
acid attenuates LPS-induced inflammatory response and oxidative
stress via upregulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in RAW
264.7 macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol. 83:1064362020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang H, Lv H, Li H, Ci X and Peng L:
Oridonin protects LPS-induced acute lung injury by modulating
Nrf2-mediated oxidative stress and Nrf2-independent NLRP3 and NF-κB
pathways. Cell Commun Signal. 17:622019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Su ZQ, Mo ZZ, Liao JB, Feng XX, Liang YZ,
Zhang X, Liu YH, Chen XY, Chen ZW, Su ZR and Lai XP: Usnic acid
protects LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice through attenuating
inflammatory responses and oxidative stress. Int Immunopharmacol.
22:371–378. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang Y, Han Z, Jiang A, Wu D, Li S, Liu
Z, Wei Z, Yang Z and Guo C: Protective effects of pterostilbene on
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice by inhibiting
NF-κB and activating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways. Front Pharmacol.
11:5918362021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Conti G, Tambalo S, Villetti G, Catinella
S, Carnini C, Bassani F, Sonato N, Sbarbati A and Marzola P:
Evaluation of lung inflammation induced by intratracheal
administration of LPS in mice: Comparison between MRI and
histology. MAGMA. 23:93–101. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Stangherlin A and Reddy AB: Regulation of
circadian clocks by redox homeostasis. J Biol Chem.
288:26505–26511. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hsu AT, Barrett CD, DeBusk GM, Ellson CD,
Gautam S, Talmor DS, Gallagher DC and Yaffe MB: Kinetics and role
of plasma matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in acute lung
injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Shock.
44:128–136. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li C, Yang D, Cao X, Wang F, Jiang H, Guo
H, Du L, Guo Q and Yin X: LFG-500, a newly synthesized flavonoid,
attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury and
inflammation in mice. Biochem Pharmacol. 113:57–69. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zamora R, Vodovotz Y and Billiar TR:
Inducible nitric oxide synthase and inflammatory diseases. Mol Med.
6:347–373. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hayden MS and Ghosh S: Shared principles
in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell. 132:344–362. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang X, Liu W, Zhou Y, Hao CX, Zhou Y,
Zhang CY, Sun CC, Luo ZQ and Tang SY: Dihydroartemisinin attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice by suppressing
NF-κB signaling in an Nrf2-dependent manner. Int J Mol Med.
44:2213–2222. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhao M, Li C, Shen F, Wang M, Jia N and
Wang C: Naringenin ameliorates LPS-induced acute lung injury
through its anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory activity and by
inhibition of the PI3K/AKT pathway. Exp Ther Med. 14:2228–2234.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ward PA: Oxidative stress: Acute and
progressive lung injury. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1203:53–59. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang CY, Deng JS, Huang WC, Jiang WP and
Huang GJ: Attenuation of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung
injury by hispolon in mice, through regulating the
TLR4/PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathways and suppressing
oxidative stress-mediated ER stress-induced apoptosis and
autophagy. Nutrients. 12:17422020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li T, Wu YN, Wang H, Ma JY, Zhai SS and
Duan J: Dapk1 improves inflammation, oxidative stress and autophagy
in LPS-induced acute lung injury via p38MAPK/NF-κB signaling
pathway. Mol Immunol. 120:13–22. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rojo de la Vega M, Dodson M, Gross C,
Mansour HM, Lantz RC, Chapman E, Wang T, Black SM, Garcia JG and
Zhang DD: Role of Nrf2 and autophagy in acute lung injury. Curr
Pharmacol Rep. 2:91–101. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hou L, Zhang J, Liu Y, Fang H, Liao L,
Wang Z, Yuan J, Wang X, Sun J, Tang B, et al: MitoQ alleviates
LPS-mediated acute lung injury through regulating Nrf2/Drp1
pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 165:219–228. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang X, Ding M, Zhu P, Huang H, Zhuang Q,
Shen J, Cai Y, Zhao M and He Q: New insights into the Nrf-2/HO-1
signaling axis and its application in pediatric respiratory
diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019:32141962019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Su Y, Choi HS, Choi JH, Kim HS, Lee GY,
Cho HW, Choi H, Jang YS and Seo JW: Effects of fish oil, lipid
mediators, derived from docosahexaenoic acid and their co-treatment
against lipid metabolism dysfunction and inflammation in HFD mice
and HepG2 cells. Nutrients. 15:4272023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Su Y, Han Y, Choi HS, Lee GY, Cho HW, Choi
H, Jang YS, Choi JH and Seo JW: Lipid mediators derived from DHA
alleviate DNCB-induced atopic dermatitis and improve the gut
microbiome in BALB/c mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 124((Pt A)):
1109002023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu YX, Wang YY, Gao ZQ, Chen D, Liu G, Wan
BB, Jiang FJ, Wei MX, Zuo J, Zhu J, et al: Ethyl ferulate protects
against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by activating
AMPK/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 42:2069–2081.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shi Q, Cao J, Fang L, Zhao H, Liu Z, Ran
J, Zheng X, Li X, Zhou Y, Ge D, et al: Geniposide suppresses
LPS-induced nitric oxide, PGE2 and inflammatory cytokine by
downregulating NF-κB, MAPK and AP-1 signaling pathways in
macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol. 20:298–306. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Beasley MB: The pathologist's approach to
acute lung injury. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 134:719–727. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tsushima K, King LS, Aggarwal NR, De
Gorordo A, D'Alessio FR and Kubo K: Acute lung injury review.
Intern Med. 48:621–630. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jiang L, Fei D, Gong R, Yang W, Yu W, Pan
S and Zhao M and Zhao M: CORM-2 inhibits TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome
pathway in LPS-induced acute lung injury. Inflamm Res. 65:905–915.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Duvall MG and Levy BD: DHA- and
EPA-derived resolvins, protectins and maresins in airway
inflammation. Eur J Pharmacol. 785:144–155. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang A, Wu Y, Yu G and Wang H: Role of
specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators in pulmonary inflammation
diseases: Mechanisms and development. Respir Res. 22:2042021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Recchiuti A and Serhan CN: Pro-resolving
lipid mediators (SPMs) and their actions in regulating miRNA in
novel resolution circuits in inflammation. Front Immunol.
3:2982012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Flak MB, Koenis DS, Sobrino A, Smith J,
Pistorius K, Palmas F and Dalli J: GPR101 mediates the
pro-resolving actions of RvD5n-3 DPA in arthritis and infections. J
Clin Invest. 130:359–373. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Brennan E, Kantharidis P, Cooper ME and
Godson C: Pro-resolving lipid mediators: Regulators of
inflammation, metabolism and kidney function. Nat Rev Nephrol.
17:725–739. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ji RR: Specialized pro-resolving mediators
as resolution pharmacology for the control of pain and itch. Annu
Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 63:273–293. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Su Y, Han Y, Choi HS, Lee GY, Cho HW, Choi
H, Choi JH, Jang YS and Seo JW: Lipid mediators obtained from
docosahexaenoic acid by soybean lipoxygenase attenuate
RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation and rheumatoid arthritis.
Biomed Pharmacother. 171:1161532024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Raetz CR and Whitfield C:
Lipopolysaccharide endotoxins. Annu Rev Biochem. 71:635–700. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shen W, Gan J, Xu S, Jiang G and Wu H:
Penehyclidine hydrochloride attenuates LPS-induced acute lung
injury involvement of NF-kappaB pathway. Pharmacol Res. 60:296–302.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Grommes J and Soehnlein O: Contribution of
neutrophils to acute lung injury. Mol Med. 17:293–307. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rojas M, Woods CR, Mora AL, Xu J and
Brigham KL: Endotoxin-induced lung injury in mice: Structural,
functional and biochemical responses. Am J Physiol-Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 288:L333–L341. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Krajka-Kuźniak V, Paluszczak J and
Baer-Dubowska W: Xanthohumol induces phase II enzymes via Nrf2 in
human hepatocytes in vitro. Toxicol In Vitro. 27:149–156. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kim EA, Kim SY, Ye BR, Kim J, Ko SC, Lee
WW, Kim KN, Choi IW, Jung WK and Heo SJ: Anti-inflammatory effect
of Apo-9′-fucoxanthinone via inhibition of MAPKs and NF-kB
signaling pathway in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages and
zebrafish model. Int Immunopharmacol. 59:339–346. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang R, Yang L, Shen X, Cheng W, Zhao B,
Ali KH, Qian Z and Ji H: Suppression of NF-κB pathway by crocetin
contributes to attenuation of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung
injury in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 674:391–396. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tang J, Xu L, Zeng Y and Gong F: Effect of
gut microbiota on LPS-induced acute lung injury by regulating the
TLR4/NF-kB signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 91:1072722021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Matthay MA, Ware LB and Zimmerman GA: The
acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Clin Invest. 122:2731–2740.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Matthay MA, Zemans RL, Zimmerman GA, Arabi
YM, Beitler JR, Mercat A, Herridge M, Randolph AG and Calfee CS:
Acute respiratory distress syndrome. Nat Rev Dis Primer. 5:182019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Jiang W, Luo F, Lu Q, Liu J, Li P, Wang X,
Fu Y, Hao K, Yan T and Ding X: The protective effect of Trillin
LPS-induced acute lung injury by the regulations of inflammation
and oxidative state. Chem Biol Interact. 243:127–134. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Li J, Lu K, Sun F, Tan S, Zhang X, Sheng
W, Hao W, Liu M, Lv W and Han W: Panaxydol attenuates ferroptosis
against LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice by Keap1-Nrf2/HO-1
pathway. J Transl Med. 19:962021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kang JY, Xu MM, Sun Y, Ding ZX, Wei YY,
Zhang DW, Wang YG, Shen JL, Wu HM and Fei GH: Melatonin attenuates
LPS-induced pyroptosis in acute lung injury by inhibiting
NLRP3-GSDMD pathway via activating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling axis. Int
Immunopharmacol. 109:1087822022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kansanen E, Jyrkkänen HK and Levonen AL:
Activation of stress signaling pathways by electrophilic oxidized
and nitrated lipids. Free Radic Biol Med. 52:973–982. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Niu X, Zang L and Li W, Xiao X, Yu J, Yao
Q, Zhao J, Ye Z, Hu Z and Li W: Anti-inflammatory effect of Yam
Glycoprotein on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via
the NLRP3 and NF-κB/TLR4 signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol.
81:1060242020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhang Y, Wei Z, Liu W, Wang J, He X, Huang
H, Zhang J and Yang Z: Melatonin protects against arsenic
trioxide-induced liver injury by the upregulation of Nrf2
expression through the activation of PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncotarget.
8:3773–3780. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Abdulaal WH, Omar UM, Zeyadi M, El-Agamy
DS, Alhakamy NA, A R Almalki N, Asfour HZ, Al-Rabia MW, Alzain AA,
Mohamed GA and Ibrahim SRM: Protective effect of kaempferol
glucoside against lipopolysaccharide-caused acute lung injury via
targeting Nrf2/NF-κB/NLRP3/GSDMD: Integrating experimental and
computational studies. Saudi Pharm J. 32:1020732024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jiang F, Hua C, Pan J, Peng S, Ning D,
Chen C, Li S, Xu X, Wang L, Zhang C and Li M: Effect fraction of
Bletilla striata (Thunb.) Reichb.f. alleviates LPS-induced acute
lung injury by inhibiting p47phox/NOX2 and promoting the Nrf2/HO-1
signaling pathway. Phytomedicine. 126:1551862024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhang J, Chen J, Jiang Q, Feng R, Zhao X,
Li H, Yang C and Hua X: Resolvin D1 attenuates inflammation and
pelvic pain associated with EAP by inhibiting oxidative stress and
NLRP3 inflammasome activation via the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. J Inflamm
Res. 16:3365–3379. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Sun Q, Wu Y, Zhao F and Wang J: Maresin 1
ameliorates lung ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing
oxidative stress via activation of the Nrf-2-mediated HO-1
signaling pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017:96348032017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Khodakarami A, Adibfar S, Karpisheh V,
Abolhasani S, Jalali P, Mohammadi H, Gholizadeh Navashenaq J,
Hojjat-Farsangi M and Jadidi-Niaragh F: The molecular biology and
therapeutic potential of Nrf2 in leukemia. Cancer Cell Int.
22:2412022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Casper E: The crosstalk between Nrf2 and
NF-κB pathways in coronary artery disease: Can it be regulated by
SIRT6? Life Sci. 330:1220072023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|