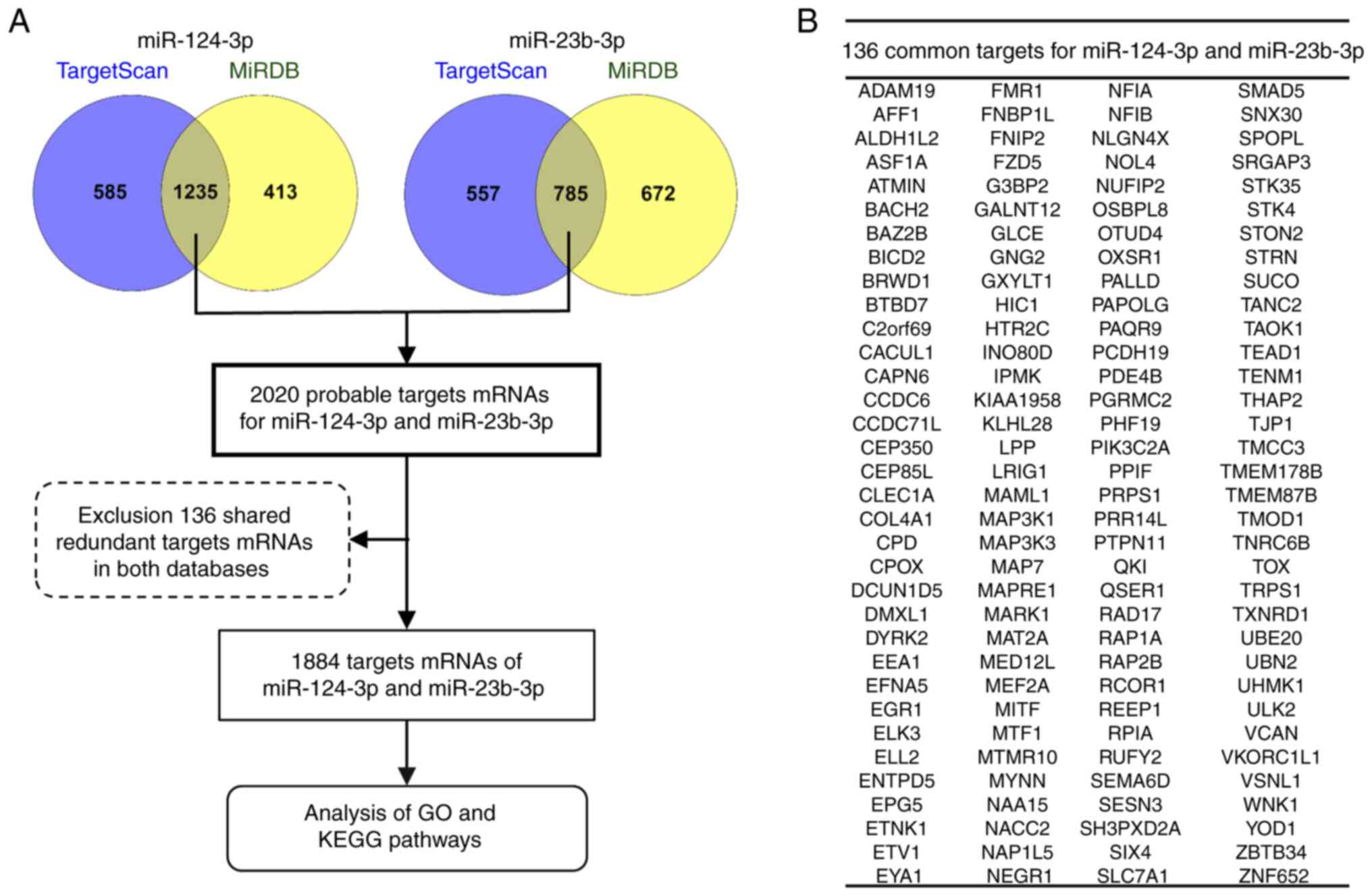
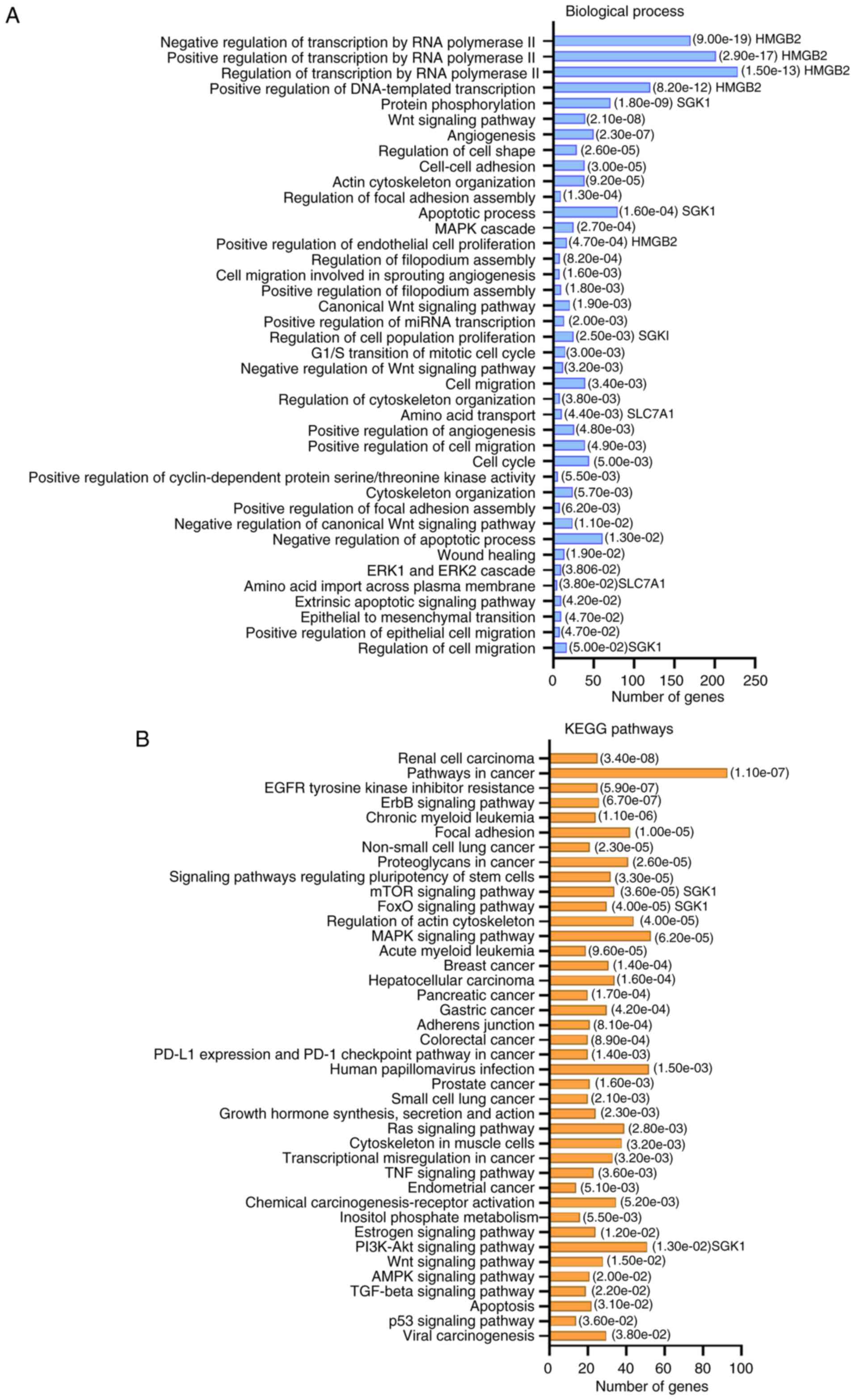
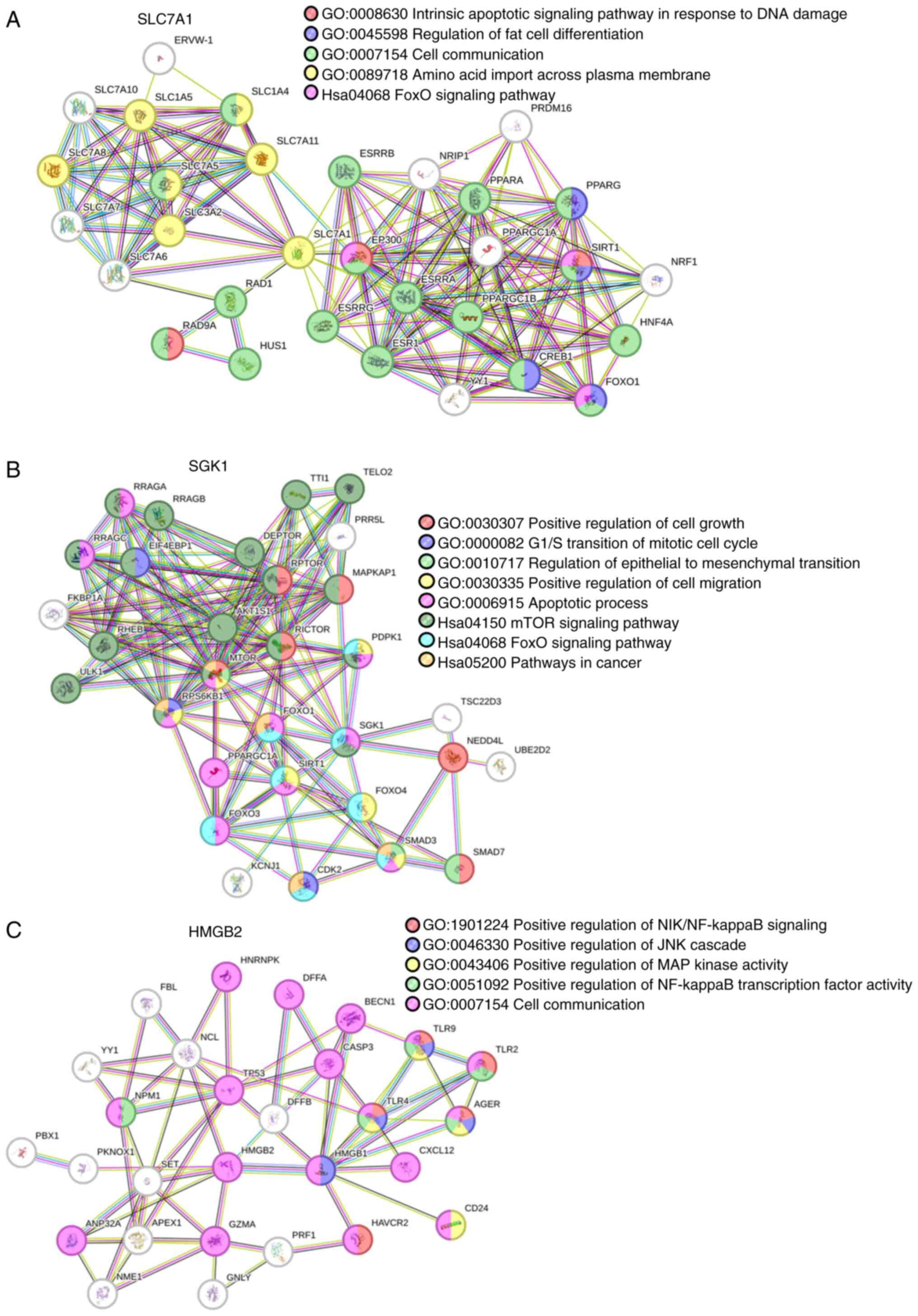
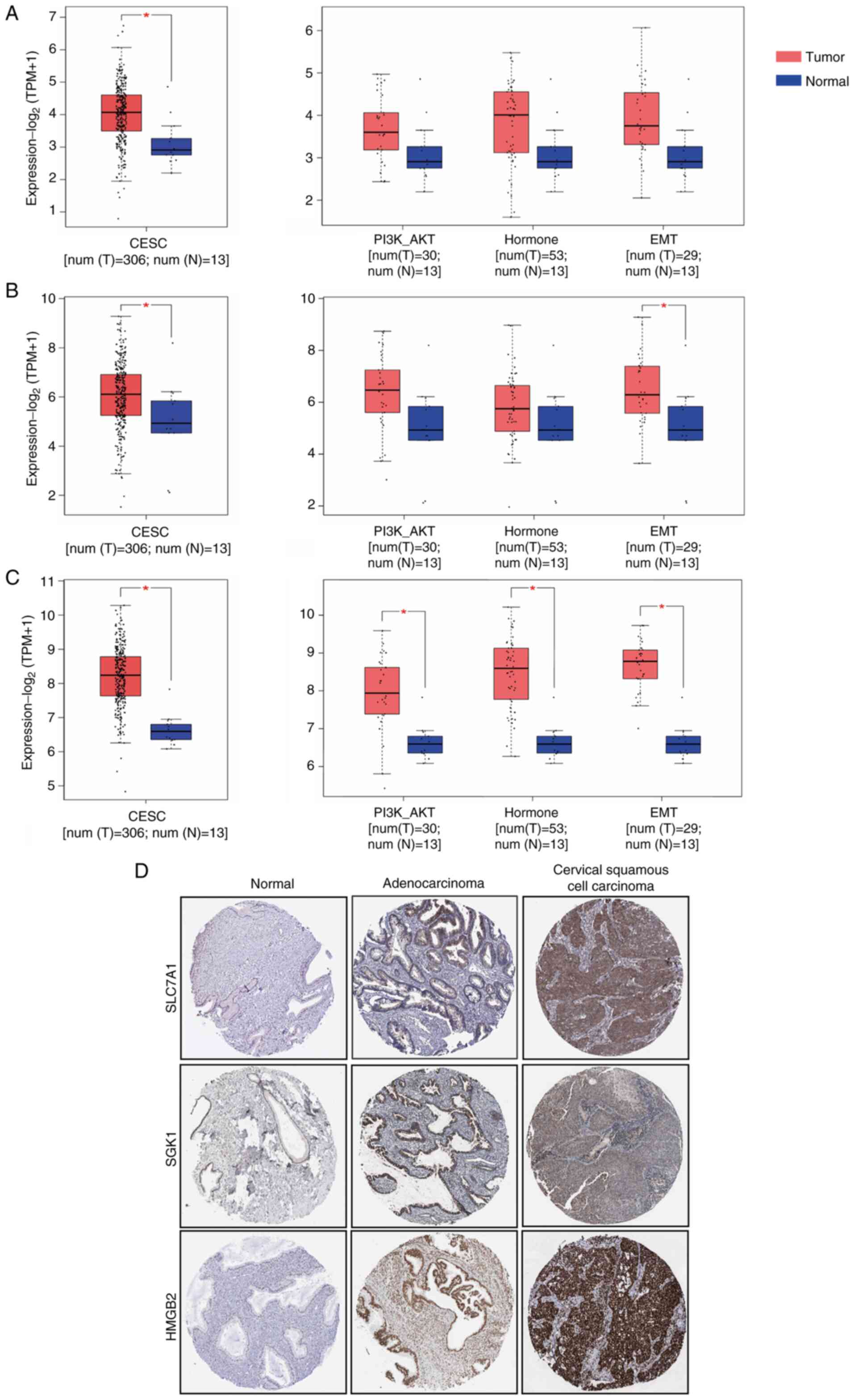
|
1
|
Buskwofie A, David-West G and Clare CA: A
review of cervical cancer: Incidence and disparities. J Natl Med
Assoc. 112:229–232. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Servayge J, Olthof EP, Mom CH, van der Aa
MA, Wenzel HHB, van der Velden J, Nout RA, Boere IA, van Doorn HC
and van Beekhuizen HJ: Survival of women with advanced stage
cervical cancer: Neo-adjuvant chemotherapy followed by radiotherapy
and hyperthermia versus chemoradiotherapy. Cancers (Basel).
16:6352024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gardner AB, Charo LM, Mann AK, Kapp DS,
Eskander RN and Chan JK: Ovarian, uterine, and cervical cancer
patients with distant metastases at diagnosis: Most common
locations and outcomes. Clin Exp Metastasis. 37:107–113. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Romero-López MJ, Jiménez-Wences H, Cruz-De
La Rosa MI, Román-Fernández IV and Fernández-Tilapa G: miR-23b-3p,
miR-124-3p and miR-218-5p synergistic or additive effects on
cellular processes that modulate cervical cancer progression? A
molecular balance that needs attention. Int J Mol Sci.
23:135512022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ruan Y, Liu M, Guo J, Zhao J, Niu S and Li
F: Evaluation of the accuracy of colposcopy in detecting high-grade
squamous intraepithelial lesion and cervical cancer. Arch Gynecol
Obstet. 302:1529–1538. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yan X, Huang Y, Zhang M, Hu X, Li K and
Jing M: Prevalence of human papillomavirus infection and type
distribution among Uyghur females in Xinjiang, northwest China.
Oncol Lett. 20:252020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ben W, Yang Y, Yuan J, Sun J, Huang M,
Zhang D and Zheng J: Human papillomavirus 16 E6 modulates the
expression of host microRNAs in cervical cancer. Taiwan J Obstet
Gynecol. 54:364–370. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Castro-Oropeza R and Piña-Sánchez P:
Epigenetic and transcriptomic regulation landscape in HPV+ cancers:
Biological and clinical implications. Front Genet. 13:8866132022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Saliminejad K, Khorram Khorshid HR,
Soleymani Fard S and Ghaffari SH: An overview of microRNAs:
Biology, functions, therapeutics, and analysis methods. J Cell
Physiol. 234:5451–5465. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang X, Cai D, Meng L and Wang B:
MicroRNA-124 inhibits proliferation, invasion, migration and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of cervical carcinoma cells by
targeting astrocyte-elevated gene-1. Oncol Rep. 36:2321–2328. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Campos-Viguri GE, Peralta-Zaragoza O,
Jiménez-Wences H, Longinos-González AE, Castañón-Sánchez CA,
Ramírez-Carrillo M, Camarillo CL, Castañeda-Saucedo E,
Jiménez-López MA, Martínez-Carrillo DN and Fernández-Tilapa G:
MiR-23b-3p reduces the proliferation, migration and invasion of
cervical cancer cell lines via the reduction of c-Met expression.
Sci Rep. 10:32562020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhu Q, Zhang Y, Li M, Zhang Y, Zhang H,
Chen J, Liu Z, Yuan P, Yang Z and Wang X: MiR-124-3p impedes the
metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer via extracellular exosome
transport and intracellular PI3K/AKT signaling. Biomark Res.
11:12023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhao Q, Jiang F, Zhuang H, Chu Y, Zhang F
and Wang C: MicroRNA miR-124-3p suppresses proliferation and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma via
ARRDC1 (arrestin domain containing 1). Bioengineered. 13:8255–8265.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Song B, Xu L, Jiang K and Cheng F:
MiR-124-3p inhibits tumor progression in prostate cancer by
targeting EZH2. Funct Integr Genomics. 23:802023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Song E, Yu W and Xiong X, Kuang X, Ai Y
and Xiong X: Astrocyte elevated gene-1 promotes progression of
cervical squamous cell carcinoma by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal
transition via Wnt signaling. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 25:345–355.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Grossi I, Arici B, Portolani N, Petro GD
and Salvi A: Clinical and biological significance of miR-23b and
miR-193a in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget.
8:6955–6969. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pimenta RC, Viana NI, Amaral GQ, Park R,
Morais DR, Pontes J Jr, Guimaraes VR, Camargo JA, Leite KR, Nahas
WC, et al: MicroRNA-23b and microRNA-27b plus flutamide treatment
enhances apoptosis rate and decreases CCNG1 expression in a
castration-resistant prostate cancer cell line. Tumour Biol.
40:10104283188030112018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu H, Wei W, Wang X, Guan X, Chen Q, Pu
Z, Xu X and Wei A: miR-23b-3p promotes the apoptosis and inhibits
the proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma cells by targeting
SIX1. Mol Med Rep. 18:5683–5692. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li YM, Li XJ, Yang HL, Zhang YB and Li JC:
MicroRNA-23b suppresses cervical cancer biological progression by
directly targeting six1 and affecting epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition and AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol
Sci. 23:4688–4697. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang W, Li Y, Liu N, Gao Y and Li L:
MiR-23b controls ALDH1A1 expression in cervical cancer stem cells.
BMC Cancer. 17:2922017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
You S, Zhu X, Yang Y, Du X, Song K, Zheng
Q, Zeng P and Yao Q: SLC7A1 overexpression is involved in energy
metabolism reprogramming to induce tumor progression in epithelial
ovarian cancer and is associated with immune-infiltrating cells. J
Oncol. 2022:58648262022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Missiaen R, Anderson NM, Kim LC, Nance B,
Burrows M, Skuli N, Carens M, Riscal R, Steensels A, Li F and Simon
MC: GCN2 inhibition sensitizes arginine-deprived hepatocellular
carcinoma cells to senolytic treatment. Cell Metab.
34:1151–1167.e7. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kishikawa T, Otsuka M, Seng Tan P, Ohno M,
Sun X, Yoshikawa T, Shibata C, Takata A, Kojima K, Takehana K, et
al: Decreased miR122 in hepatocellular carcinoma leads to
chemoresistance with increased arginine. Oncotarget. 6:8339–8352.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhu R, Yang G, Cao Z, Shen K, Zheng L,
Xiao J, You L and Zhang T: The prospect of serum and
glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 1 (SGK1) in cancer therapy: A
rising star. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 12:17588359209409462020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ghani MJ: SGK1, autophagy and cancer: An
overview. Mol Biol Rep. 49:675–685. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cicenas J, Meskinyte-Kausiliene E, Jukna
V, Rimkus A, Simkus J and Soderholm D: SGK1 in cancer: Biomarker
and drug target. Cancers (Basel). 14:23852022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu W, Wang X, Wang Y, Dai Y, Xie Y, Ping
Y, Yin B, Yu P, Liu Z, Duan X, et al: SGK1 inhibition-induced
autophagy impairs prostate cancer metastasis by reversing EMT. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:732018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang M, Xue Y, Shen L, Qin P, Sang X, Tao
Z, Yi J, Wang J, Liu P and Cheng H: Inhibition of SGK1 confers
vulnerability to redox dysregulation in cervical cancer. Redox
Biol. 24:1012252019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang Y, Zhao Z, Zhao X, Xie H, Zhang C,
Sun X and Zhang J: HMGB2 causes photoreceptor death via
down-regulating Nrf2/HO-1 and up-regulating NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling
pathways in light-induced retinal degeneration model. Free Radic
Biol Med. 181:14–28. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang P, Lu Y and Gao S: High-mobility
group box 2 promoted proliferation of cervical cancer cells by
activating AKT signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem. 120:17345–17353.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shaw RJ and Cantley LC: Ras, PI(3)K and
mTOR signalling controls tumour cell growth. Nature. 441:424–430.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ma L, Huang K, Zhang H, Kim E, Kim H, Liu
Z, Kim CY, Park K, Raza MA, Kim K, et al: Imatinib inhibits oral
squamous cell carcinoma by suppressing the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling
pathway. J Cancer. 15:659–670. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Boccardo E, Manzini Baldi CV, Carvalho AF,
Rabachini T, Torres C, Barreta LA, Brentani H and Villa LL:
Expression of human papillomavirus type 16 E7 oncoprotein alters
keratinocytes expression profile in response to tumor necrosis
factor-alpha. Carcinogenesis. 31:521–531. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tian R, Li H, Ren S, Li S, Fang R and Liu
Y: circRNA THBS1 silencing inhibits the malignant biological
behavior of cervical cancer cells via the regulation of
miR-543/HMGB2 axis. Open Med (Wars). 18:202307092023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
An Y, Zhang Z, Shang Y, Jiang X, Dong J,
Yu P, Nie Y and Zhao Q: miR-23b-3p regulates the chemoresistance of
gastric cancer cells by targeting ATG12 and HMGB2. Cell Death Dis.
6:e17662015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C and
Zhang Z: GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression
profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 45:W98–W102.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Lyon D, Junge A,
Wyder S, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Doncheva NT, Morris JH, Bork
P, et al: STRING v11: Protein-protein association networks with
increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide
experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 47:D607–D613. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nagandla K, Lin KH, Chitra E and Jamli
MFBM: Role of microRNAs as biomarkers of cervical carcinogenesis: A
systematic review. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 64:419–436. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu S, Song L, Zeng S and Zhang L:
MALAT1-miR-124-RBG2 axis is involved in growth and invasion of
HR-HPV-positive cervical cancer cells. Tumor Biol. 37:633–640.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Liu F, Hu H, Zhao J, Zhang Z, Ai X, Tang L
and Xie L: miR-124-3p acts as a potential marker and suppresses
tumor growth in gastric cancer. Biomed Rep. 9:147–155.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yan G, Li Y, Zhan L, Sun S, Yuan J, Wang
T, Yin Y, Dai Z, Zhu Y, Jiang Z, et al: Decreased miR-124-3p
promoted breast cancer proliferation and metastasis by targeting
MGAT5. Am J Cancer Res. 9:585–596. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yan J, Jiang J, Meng XN, Xiu YL and Zong
ZH: MiR-23b targets cyclin G1 and suppresses ovarian cancer
tumorigenesis and progression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 35:312016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hao L and Yu H: MiR-23b inhibits cell
migration and invasion through targeting PDE7A in colon cancer
cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 10:9436–9443. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Jiramongkol Y and Lam EWF: FOXO
transcription factor family in cancer and metastasis. Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 39:681–709. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Liu B, Feng Y, Xie N, Yang Y and Yang D:
FERMT1 promotes cell migration and invasion in non-small cell lung
cancer via regulating PKP3-mediated activation of p38 MAPK
signaling. BMC Cancer. 24:582024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wu Z, Zhuang X, Liang M, Sheng L, Huang L,
Li Y and Ke Y: Identification of an inflammatory response-related
gene prognostic signature and immune microenvironment for cervical
cancer. Front Mol Biosci. 11:13949022024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Cormerais Y, Vučetić M, Parks SK and
Pouyssegur J: Amino acid transporters are a vital focal point in
the control of mTORC1 signaling and cancer. Int J Mol Sci.
22:232020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Narayanankutty A: Phytochemicals as
PI3K/Akt/mTOR Inhibitors and their role in breast cancer treatment.
Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 15:188–199. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hémon A, Louandre C, Lailler C, Godin C,
Bottelin M, Morel V, François C, Galmiche A and Saidak Z: SLC7A11
as a biomarker and therapeutic target in HPV-positive head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 533:1083–1087.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
You S, Han X, Xu Y, Sui L, Song K and Yao
Q: High expression of SLC7A1 in high-grade serous ovarian cancer
promotes tumor progression and is involved in MAPK/ERK pathway and
EMT. Cancer Med. 13:e72172024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Sætrom P, Heale BSE, Snøve O, Aagaard L,
Alluin J and Rossi JJ: Distance constraints between microRNA target
sites dictate efficacy and cooperativity. Nucleic Acids Res.
35:2333–2342. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Gupta S, Kumar P and Das BC: HPV:
Molecular pathways and targets. Curr Probl Cancer. 42:161–174.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Bossler F, Hoppe-Seyler K and Hoppe-Seyler
F: PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling regulates the virus/host cell crosstalk
in HPV-positive cervical cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 20:21882019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Greenawalt EJ, Edmonds MD, Jain N, Adams
CM, Mitra R and Eischen CM: Targeting of SGK1 by miR-576-3p
inhibits lung adenocarcinoma migration and invasion. Mol Cancer
Res. 17:289–298. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yadav J, Chaudhary A, Tripathi T, Janjua
D, Joshi U, Aggarwal N, Chhokar A, Keshavam CC, Senrung A and
Bharti AC: Exosomal transcript cargo and functional correlation
with HNSCC patients' survival. BMC Cancer. 24:11442024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Liang T, Lu T, Jia W, Li R, Jiang M, Jiao
Y, Wang Y, Cong S, Jiang X, Dong L, et al: Knockdown of lncRNA
MALAT1 induces pyroptosis by regulating the miR-124/SIRT1 axis in
cervical cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 63:1382023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhang Y, Li X, Zhang J and Liang H:
Natural killer T cell cytotoxic activity in cervical cancer is
facilitated by the LINC00240/microRNA-124-3p/STAT3/MICA axis.
Cancer Lett. 474:63–73. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Li X, Huang C, Li Y and Zheng D: MiR-124
inhibits the proliferation of human hepatic L02 cells by targeting
SGK1. Int J Clin Exp Med. 12:1570–1576. 2019.
|
|
60
|
Alaaeldin R, Ali FEM, Bekhit AA, Zhao QL
and Fathy M: Inhibition of NF-kB/IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 pathway and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells by
Azilsartan. Molecules. 27:78252022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Sui H, Zhu L, Deng W and Li Q:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and drug resistance: Role,
molecular mechanisms, and therapeutic strategies. Oncol Res Treat.
37:584–589. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhang ZB and Liu N: Long non-coding RNA
KTN1-AS1 promotes progression in pancreatic cancer through
regulating microRNA-23b-3p/high-mobility group box 2 axis. Aging
(Albany NY). 13:20820–20835. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
He ZH, Guo F, Hu XX, Luo ZY and Yi JW:
Knockdown of HMGB2 inhibits proliferation and invasion of renal
tumor cells via the p-38MAPK pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
24:4729–4737. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Huang Y, Hong W and Wei X: The molecular
mechanisms and therapeutic strategies of EMT in tumor progression
and metastasis. J Hematol Oncol. 15:1292022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Lee SA, Baik S and Chung SH: Functional
roles of female sex hormones and their nuclear receptors in
cervical cancer. Essays Biochem. 65:941–950. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Chen R, Gan Q, Zhao S, Zhang D, Wang S,
Yao L, Yuan M and Cheng J: DNA methylation of miR-138 regulates
cell proliferation and EMT in cervical cancer by targeting EZH2.
BMC Cancer. 22:4882022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Zheng P, Wu Y, Wang Y and Hu F: Disulfiram
suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), migration and
invasion in cervical cancer through the HSP90A/NDRG1 pathway. Cell
Signal. 109:1107712023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Sun Q, Liang Y, Zhang T, Wang K and Yang
X: ER-α36 mediates estrogen-stimulated MAPK/ERK activation and
regulates migration, invasion, proliferation in cervical cancer
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 487:625–632. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Zhang X, Zhang A, Zhang X, Hu S, Bao Z,
Zhang Y, Jiang X, He H and Zhang TC: ERa-36 instead of ERa mediates
the stimulatory effects of estrogen on the expression of viral
oncogenes HPV E6/E7 and the malignant phenotypes in cervical cancer
cells. Virus Res. 306:1986022021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|