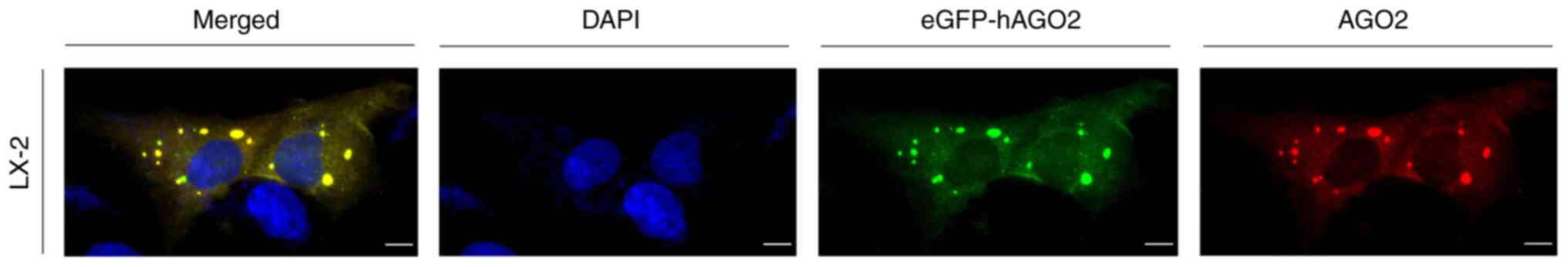
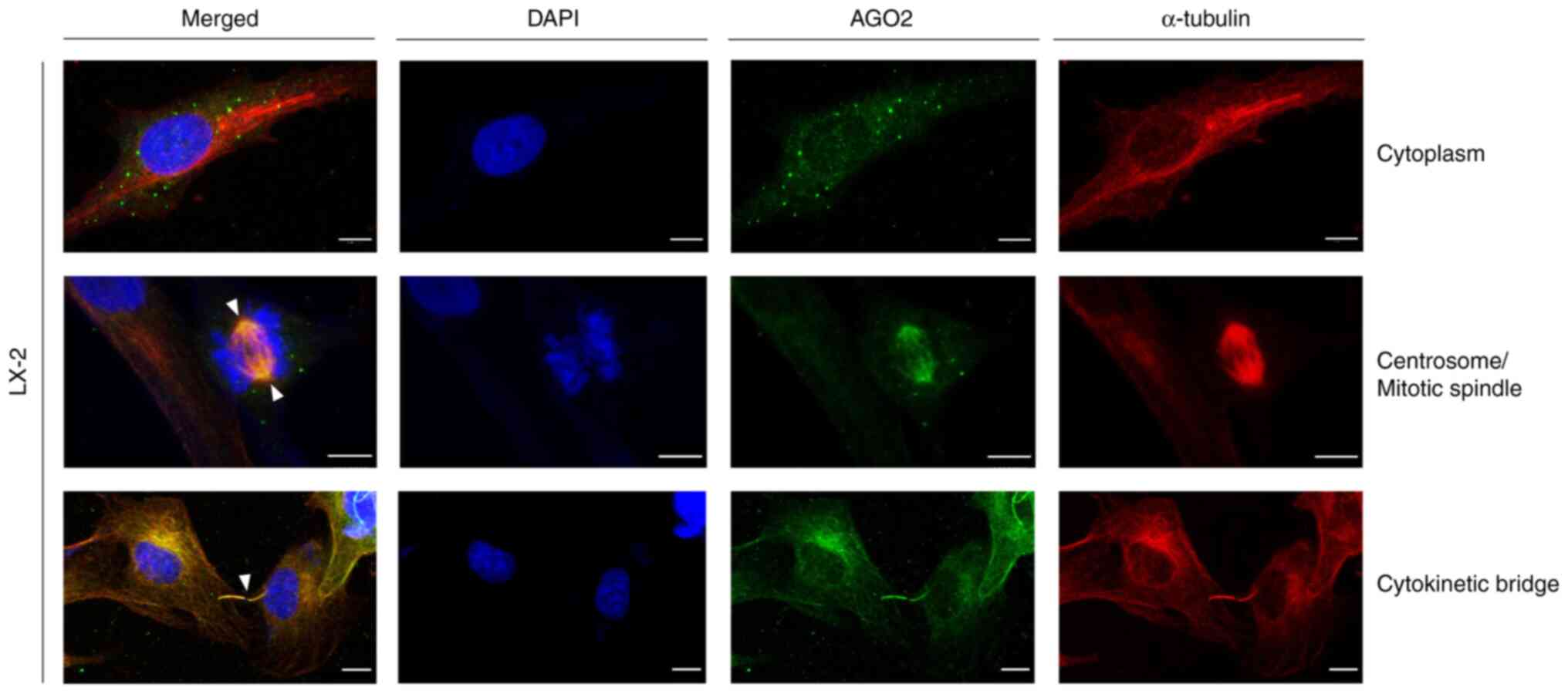
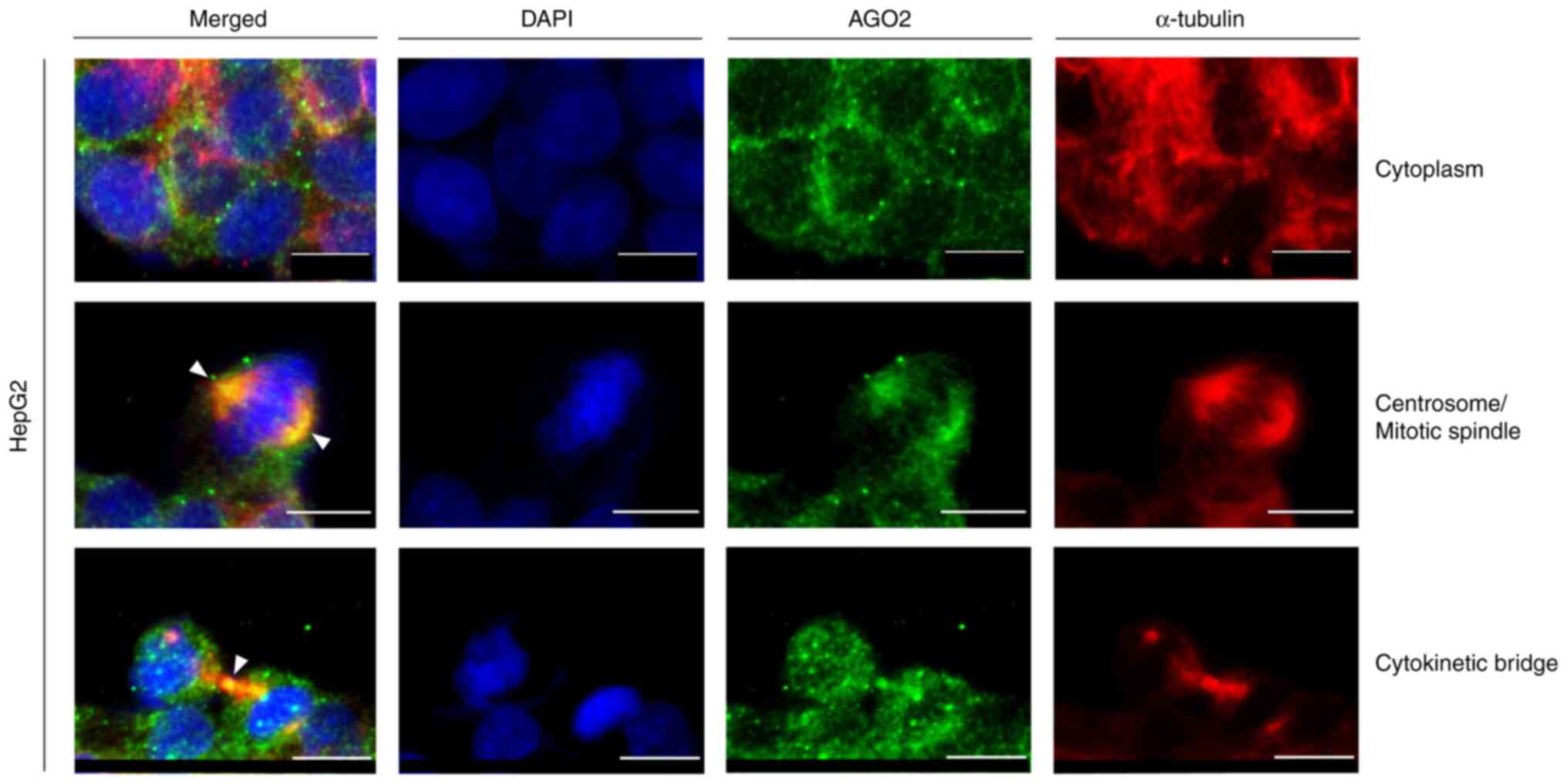
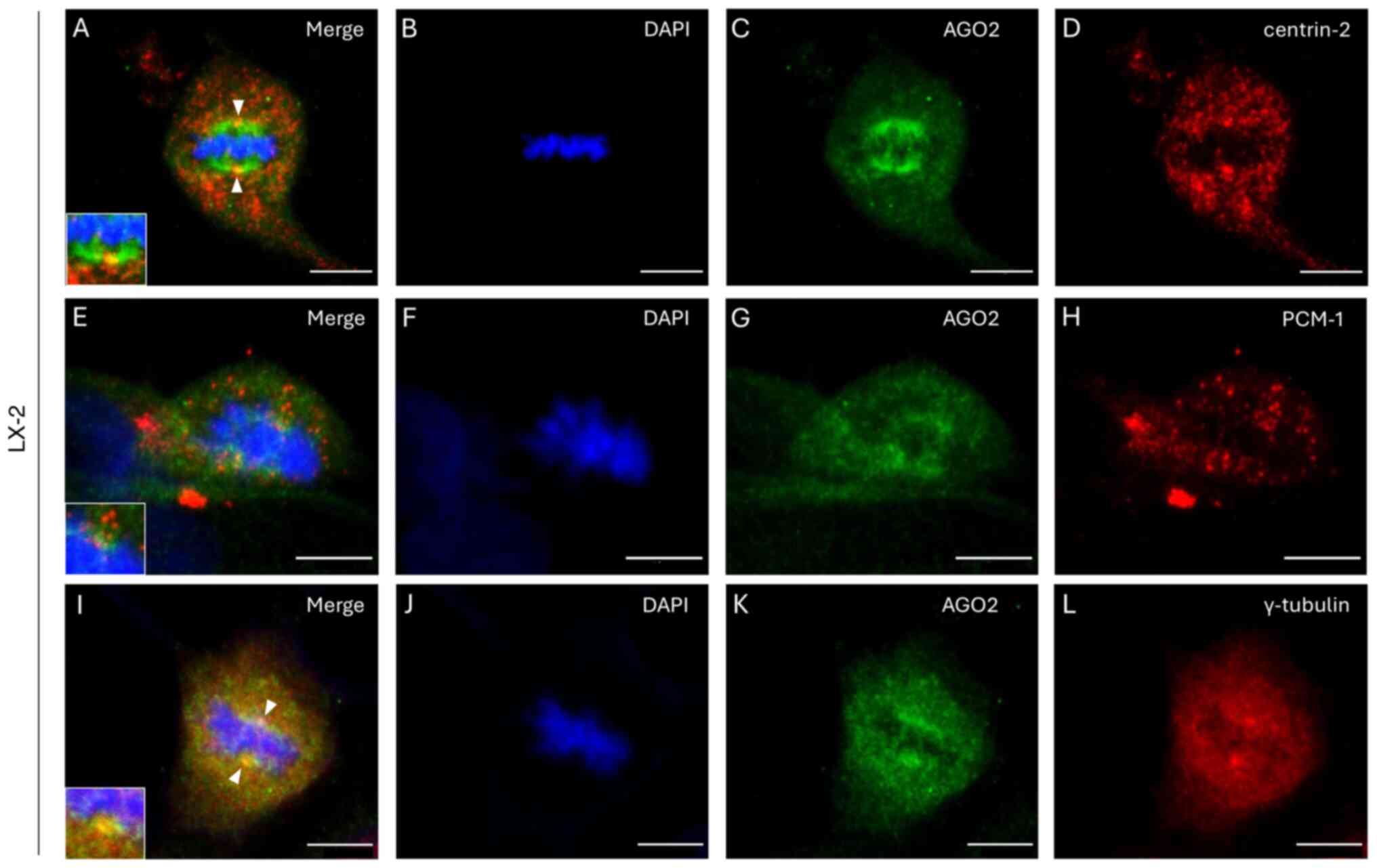
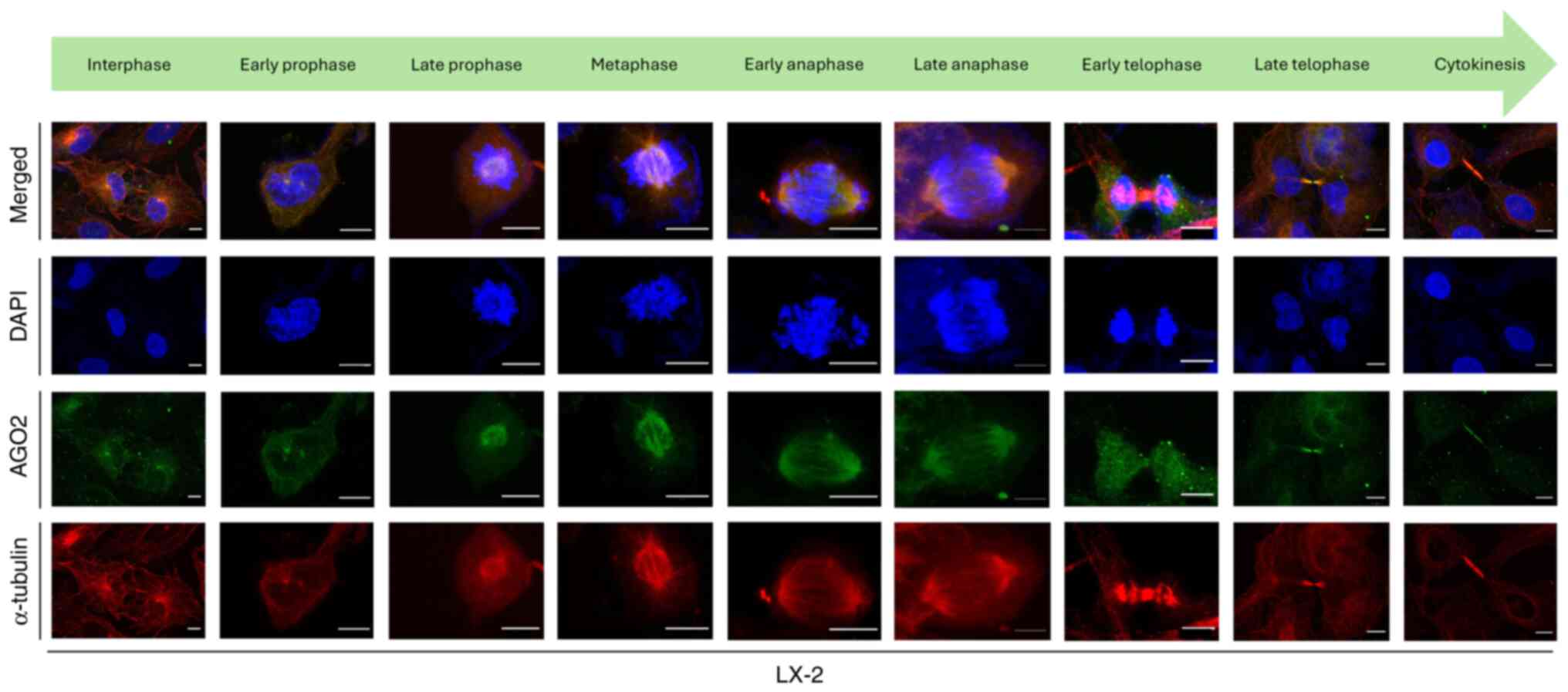
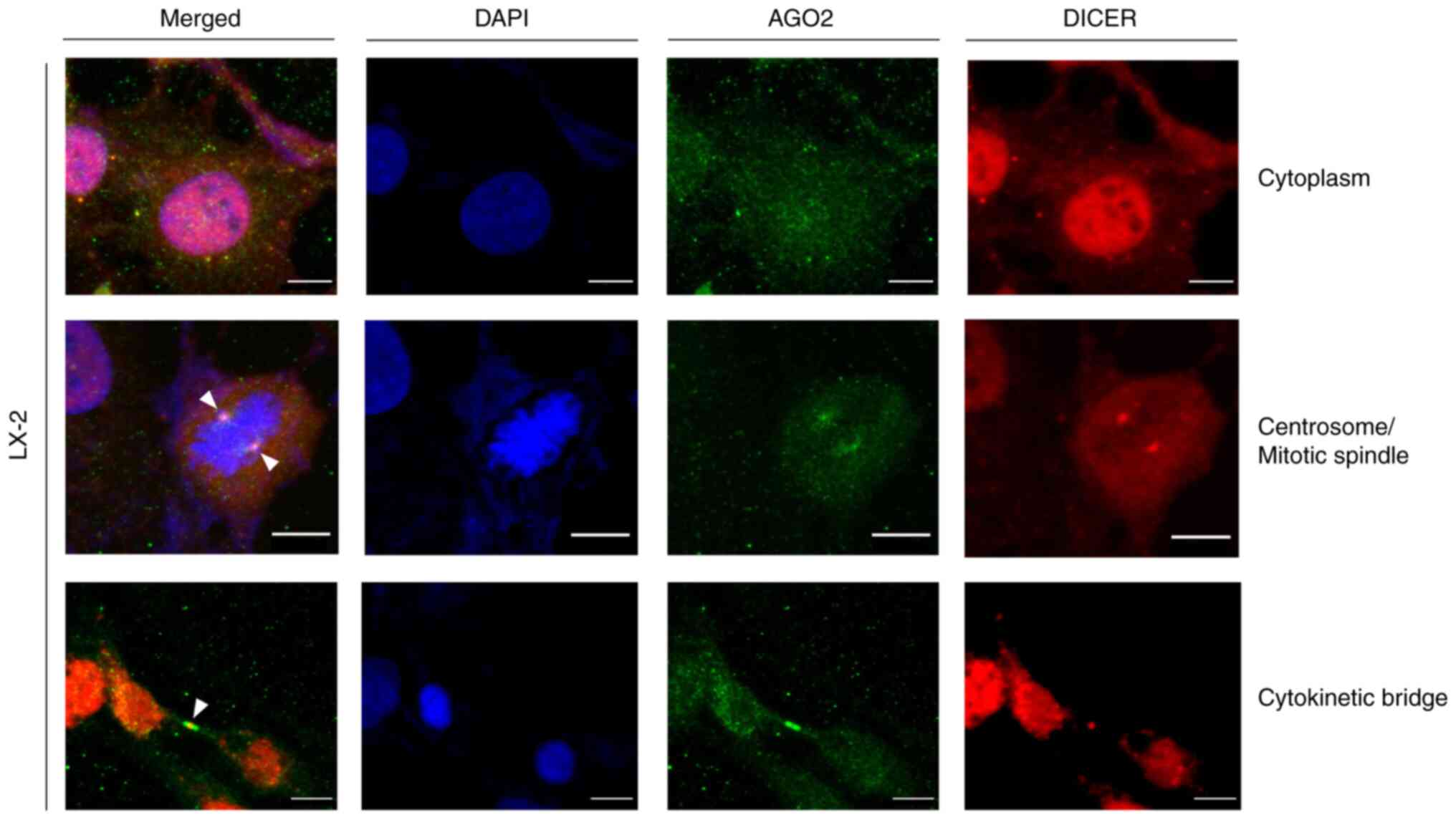
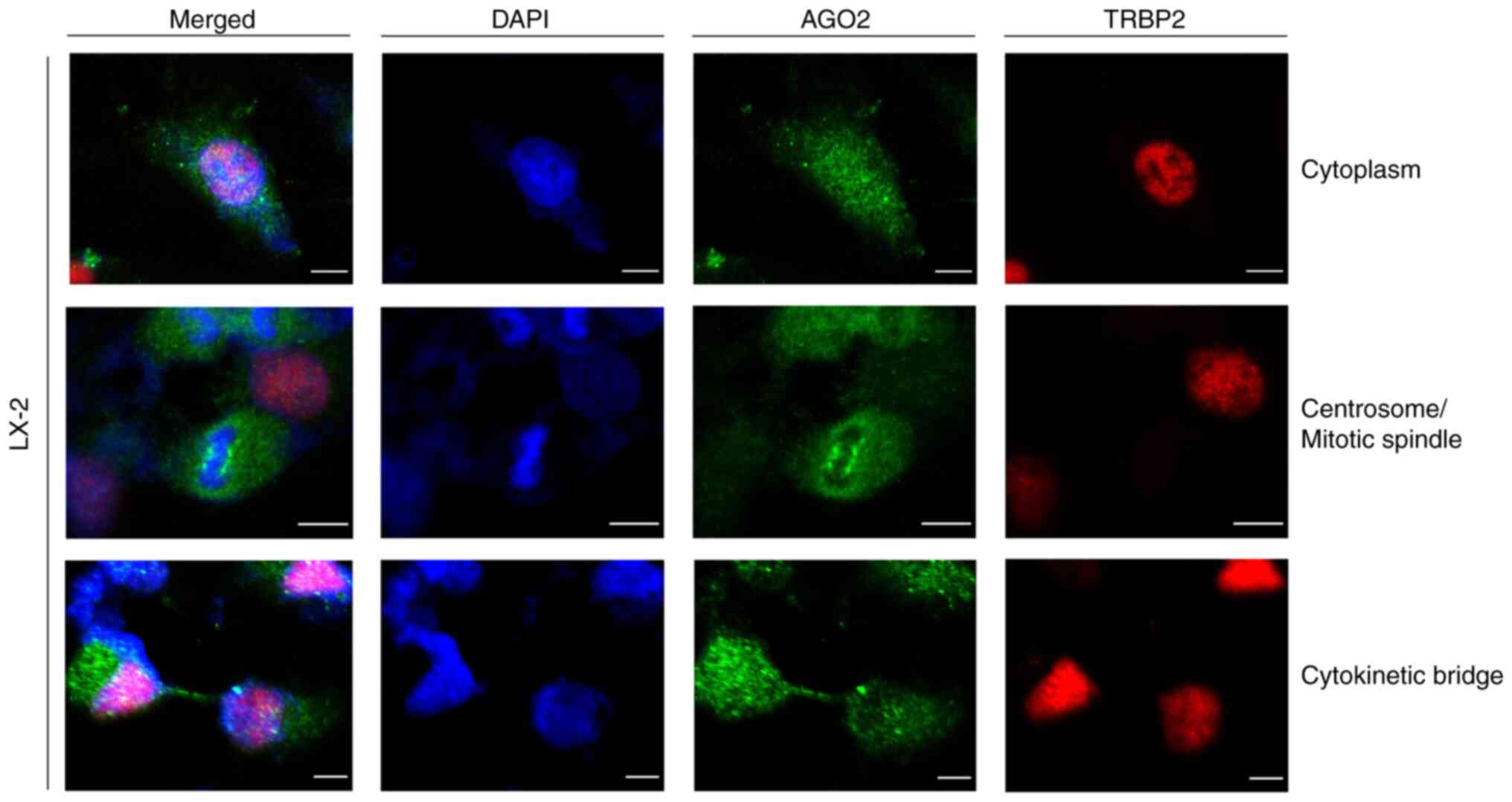
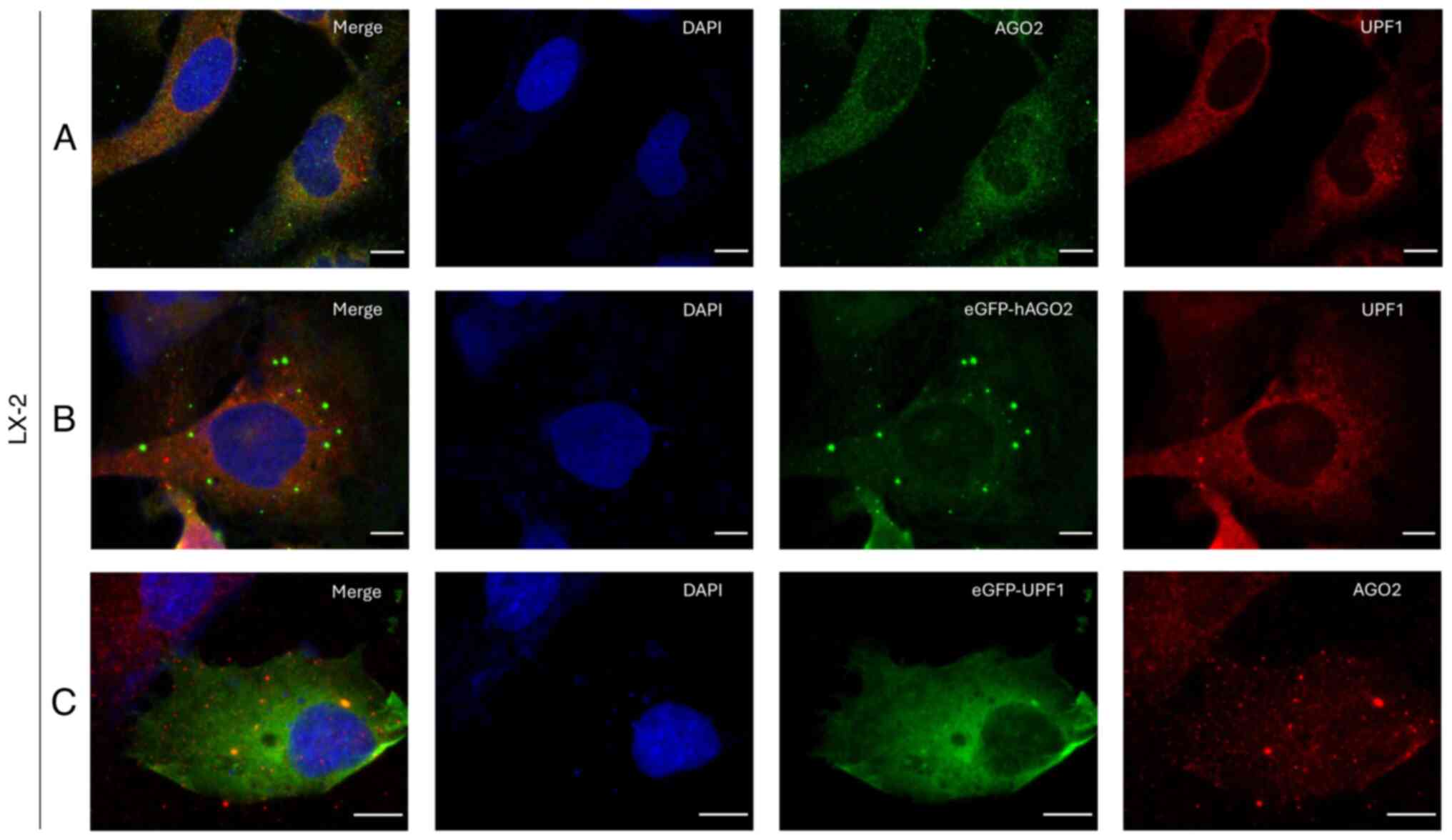
|
1
|
Oliveto S, Mancino M, Manfrini N and Biffo
S: Role of microRNAs in translation regulation and cancer. World J
Biol Chem. 8:45–56. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Croce CM: Causes and consequences of
microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 10:704–714. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W
and Tuschl T: Identification of novel genes coding for small
expressed RNAs. Science. 294:853–858. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Beermann J, Piccoli MT, Viereck J and Thum
T: Non-coding RNAs in development and disease: Background,
mechanisms, and therapeutic approaches. Physiol Rev. 96:1297–1325.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Clark BS and Blackshaw S: Long non-coding
RNA-dependent transcriptional regulation in neuronal development
and disease. Front Genet. 5:1642014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Sayed D and Abdellatif M: MicroRNAs in
development and disease. Physiol Rev. 91:827–887. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Quévillon Huberdeau M, Zeitler DM,
Hauptmann J, Bruckmann A, Fressigné L, Danner J, Piquet S, Strieder
N, Engelmann JC, Jannot G, et al: Phosphorylation of argonaute
proteins affects mRNA binding and is essential for microRNA-guided
gene silencing in vivo. EMBO J. 36:2088–2106. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Hutvagner G and Simard MJ: Argonaute
proteins: Key players in RNA silencing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
9:22–32. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Meister G: Argonaute proteins: Functional
insights and emerging roles. Nat Rev Genet. 14:447–459. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Nowak I and Sarshad AA: Argonaute proteins
take center stage in cancers. Cancers (Basel). 13:7882021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bartel DP: Metazoan MicroRNAs. Cell.
173:20–51. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hutvágner G and Zamore PD: A microRNA in a
multiple-turnover RNAi enzyme complex. Science. 297:2056–2060.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zeng Y and Cullen BR: Sequence
requirements for micro RNA processing and function in human cells.
RNA. 9:112–123. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Doench JG, Petersen CP and Sharp PA:
siRNAs can function as miRNAs. Genes Dev. 17:438–442. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pantazopoulou VI, Delis AD, Georgiou S,
Pagakis SN, Filippa V, Dragona E, Kloukina I, Chatzitheodoridis E,
Trebicka J, Velentzas AD, et al: AGO2 localizes to cytokinetic
protrusions in a p38-dependent manner and is needed for accurate
cell division. Commun Biol. 4:7262021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Li X, Wang X, Cheng Z and Zhu Q: AGO2 and
its partners: A silencing complex, a chromatin modulator, and new
features. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 55:33–53. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Carmell MA, Xuan Z, Zhang MQ and Hannon
GJ: The argonaute family: Tentacles that reach into RNAi,
developmental control, stem cell maintenance, and tumorigenesis.
Genes Dev. 16:2733–2742. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nakanishi K: Anatomy of four human
argonaute proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 50:6618–6638. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Song JJ, Smith SK, Hannon GJ and
Joshua-Tor L: Crystal structure of argonaute and its implications
for RISC slicer activity. Science. 305:1434–1437. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yuan YR, Pei Y, Ma JB, Kuryavyi V, Zhadina
M, Meister G, Chen HY, Dauter Z, Tuschl T and Patel DJ: Crystal
structure of A. aeolicus argonaute, a site-specific DNA-guided
endoribonuclease, provides insights into RISC-mediated mRNA
cleavage. Mol Cell. 19:405–419. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ma JB, Ye K and Patel DJ: Structural basis
for overhang-specific small interfering RNA recognition by the PAZ
domain. Nature. 429:318–322. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ma JB, Yuan YR, Meister G, Pei Y, Tuschl T
and Patel DJ: Structural basis for 5′-end-specific recognition of
guide RNA by the A. fulgidus Piwi protein. Nature. 434:666–670.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Höck J and Meister G: The argonaute
protein family. Genome Biol. 9:2102008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Chu Y, Yokota S, Liu J, Kilikevicius A,
Johnson KC and Corey DR: Argonaute binding within human nuclear RNA
and its impact on alternative splicing. RNA. 27:991–1003. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Park MS, Sim G, Kehling AC and Nakanishi
K: Human argonaute2 and argonaute3 are catalytically activated by
different lengths of guide RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
117:28576–28578. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Robb GB, Brown KM, Khurana J and Rana TM:
Specific and potent RNAi in the nucleus of human cells. Nat Struct
Mol Biol. 12:133–137. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Rüdel S, Flatley A, Weinmann L, Kremmer E
and Meister G: A multifunctional human argonaute2-specific
monoclonal antibody. RNA. 14:1244–1253. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wu J, Yang J, Cho WC and Zheng Y:
Argonaute proteins: Structural features, functions and emerging
roles. J Adv Res. 24:317–324. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ameyar-Zazoua M, Rachez C, Souidi M, Robin
P, Fritsch L, Young R, Morozova N, Fenouil R, Descostes N, Andrau
JC, et al: Argonaute proteins couple chromatin silencing to
alternative splicing. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 19:998–1004. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Perron MP and Provost P: Protein
components of the microRNA pathway and human diseases. Methods Mol
Biol. 487:369–385. 2009.
|
|
33
|
Liu J, Carmell MA, Rivas FV, Marsden CG,
Thomson JM, Song JJ, Hammond SM, Joshua-Tor L and Hannon GJ:
Argonaute2 is the catalytic engine of mammalian RNAi. Science.
305:1437–1441. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Morita S, Horii T, Kimura M, Goto Y,
Ochiya T and Hatada I: One argonaute family member, Eif2c2 (Ago2),
is essential for development and appears not to be involved in DNA
methylation. Genomics. 89:687–696. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
O'Carroll D, Mecklenbrauker I, Das PP,
Santana A, Koenig U, Enright AJ, Miska EA and Tarakhovsky A: A
slicer-independent role for argonaute 2 in hematopoiesis and the
microRNA pathway. Genes Dev. 21:1999–2004. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Schirle NT, Sheu-Gruttadauria J,
Chandradoss SD, Joo C and MacRae IJ: Water-mediated recognition of
t1-adenosine anchors argonaute2 to microRNA targets. Elife.
4:e076462015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
de Vries I, Kwakman T, Lu XJ, Hekkelman
ML, Deshpande M, Velankar S, Perrakis A and Joosten RP: New
restraints and validation approaches for nucleic acid structures in
PDB-REDO. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 77:1127–1141. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Sastry GM, Adzhigirey M, Day T,
Annabhimoju R and Sherman W: Protein and ligand preparation:
Parameters, protocols, and influence on virtual screening
enrichments. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 27:221–234. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jones G, Jindal A, Ghani U, Kotelnikov S,
Egbert M, Hashemi N, Vajda S, Padhorny D and Kozakov D: Elucidation
of protein function using computational docking and hotspot
analysis by ClusPro and FTMap. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol.
78:690–697. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Gowravaram M, Bonneau F, Kanaan J, Maciej
VD, Fiorini F, Raj S, Croquette V, Le Hir H and Chakrabarti S: A
conserved structural element in the RNA helicase UPF1 regulates its
catalytic activity in an isoform-specific manner. Nucleic Acids
Res. 46:2648–2659. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kim J, Li CL, Chen X, Cui Y, Golebiowski
FM, Wang H, Hanaoka F, Sugasawa K and Yang W: Lesion recognition by
XPC, TFIIH and XPA in DNA excision repair. Nature. 617:170–175.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Theotoki EI, Kakoulidis P, Velentzas AD,
Nikolakopoulos KS, Angelis NV, Tsitsilonis OE, Anastasiadou E and
Stravopodis DJ: TRBP2, a major component of the RNAi machinery, is
subjected to cell cycle-dependent regulation in human cancer cells
of diverse tissue origin. Cancers (Basel). 16:37012024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li F, Li Y, Ye X, Gao H, Shi Z, Luo X,
Rice LM and Yu H: Cryo-EM structure of VASH1-SVBP bound to
microtubules. Elife. 9:e581572020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wieczorek M, Urnavicius L, Ti SC, Molloy
KR, Chait BT and Kapoor TM: Asymmetric molecular architecture of
the human γ-tubulin ring complex. Cell. 180:165–175.e16. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Rice LM, Montabana EA and Agard DA: The
lattice as allosteric effector: Structural studies of alphabeta-
and gamma-tubulin clarify the role of GTP in microtubule assembly.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:5378–5383. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Burley SK, Bhatt R, Bhikadiya C, Bi C,
Biester A, Biswas P, Bittrich S, Blaumann S, Brown R, Chao H, et
al: Updated resources for exploring experimentally-determined PDB
structures and computed structure models at the RCSB protein data
bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 53(D1): D564–D574. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Eastman P, Galvelis R, Peláez RP, Abreu
CRA, Farr SE, Gallicchio E, Gorenko A, Henry MM, Hu F, Huang J, et
al: OpenMM 8: Molecular dynamics simulation with machine learning
potentials. J Phys Chem B. 128:109–116. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jurrus E, Engel D, Star K, Monson K,
Brandi J, Felberg LE, Brookes DH, Wilson L, Chen J, Liles K, et al:
Improvements to the APBS biomolecular solvation software suite.
Protein Sci. 27:112–128. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Lee YY, Lee H, Kim H, Kim VN and Roh SH:
Structure of the human DICER-pre-miRNA complex in a dicing state.
Nature. 615:331–338. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Arab SS and Dantism A: EasyModel: A
user-friendly web-based interface based on MODELLER. Sci Rep.
13:171852023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Webb B and Sali A: Comparative protein
structure modeling using MODELLER. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics.
54:5.6.1–5.6.37. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Deshmukh P, Markande S, Fandade V,
Ramtirtha Y, Madhusudhan MS and Joseph J: The miRISC component AGO2
has multiple binding sites for Nup358 SUMO-interacting motif.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 556:45–52. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Laskowski RA and Thornton JM: PDBsum
extras: SARS-CoV-2 and AlphaFold models. Protein Sci. 31:283–289.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Honorato RV, Koukos PI, Jiménez-García B,
Tsaregorodtsev A, Verlato M, Giachetti A, Rosato A and Bonvin AMJJ:
Structural biology in the clouds: The WeNMR-EOSC ecosystem. Front
Mol Biosci. 8:7295132021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Abramson J, Adler J, Dunger J, Evans R,
Green T, Pritzel A, Ronneberger O, Willmore L, Ballard AJ, Bambrick
J, et al: Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular
interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature. 630:493–500. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
UniProt Consortium: UniProt: The universal
protein knowledgebase in 2025. Nucleic Acids Res. 53(D1):
D609–D617. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yamashita K, Wojdyr M, Long F, Nicholls RA
and Murshudov GN: GEMMI and Servalcat restrain REFMAC5. Acta
Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 79:368–373. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Humphrey W, Dalke A and Schulten K: VMD:
Visual molecular dynamics. J Mol Graph. 14:33–38. 27–28. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Meng EC, Goddard TD, Pettersen EF, Couch
GS, Pearson ZJ, Morris JH and Ferrin TE: UCSF ChimeraX: Tools for
structure building and analysis. Protein Sci. 32:e47922023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Orchard S, Ammari M, Aranda B, Breuza L,
Briganti L, Broackes-Carter F, Campbell NH, Chavali G, Chen C,
del-Toro N, et al: The MIntAct project-IntAct as a common curation
platform for 11 molecular interaction databases. Nucleic Acids Res.
42((Database Issue)): D358–D363. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Liu J, Valencia-Sanchez MA, Hannon GJ and
Parker R: MicroRNA-dependent localization of targeted mRNAs to
mammalian P-bodies. Nat Cell Biol. 7:719–723. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Salisbury JL, Suino KM, Busby R and
Springett M: Centrin-2 is required for centriole duplication in
mammalian cells. Curr Biol. 12:1287–1292. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Bettencourt-Dias M and Glover DM:
Centrosome biogenesis and function: Centrosomics brings new
understanding. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:451–463. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Buhler M and Stolz A: Estrogens-origin of
centrosome defects in human cancer? Cells. 11:4322022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Moritz M, Braunfeld MB, Sedat JW, Alberts
B and Agard DA: Microtubule nucleation by gamma-tubulin-containing
rings in the centrosome. Nature. 378:638–640. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Pihan GA: Centrosome dysfunction
contributes to chromosome instability, chromoanagenesis, and genome
reprograming in cancer. Front Oncol. 3:2772013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Dammermann A and Merdes A: Assembly of
centrosomal proteins and microtubule organization depends on PCM-1.
J Cell Biol. 159:255–266. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Hames RS, Crookes RE, Straatman KR, Merdes
A, Hayes MJ, Faragher AJ and Fry AM: Dynamic recruitment of Nek2
kinase to the centrosome involves microtubules, PCM-1, and
localized proteasomal degradation. Mol Biol Cell. 16:1711–1724.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Staszewski J, Lazarewicz N, Konczak J,
Migdal I and Maciaszczyk-Dziubinska E: UPF1-From mRNA degradation
to human disorders. Cells. 12:4192023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Jin H, Suh MR, Han J, Yeom KH, Lee Y, Heo
I, Ha M, Hyun S and Kim VN: Human UPF1 participates in small
RNA-induced mRNA downregulation. Mol Cell Biol. 29:5789–5799. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Welte T, Goulois A, Stadler MB, Hess D,
Soneson C, Neagu A, Azzi C, Wisser MJ, Seebacher J, Schmidt I, et
al: Convergence of multiple RNA-silencing pathways on GW182/TNRC6.
Mol Cell. 83:2478–2492.e8. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Fiorini F, Bagchi D, Le Hir H and
Croquette V: Human Upf1 is a highly processive RNA helicase and
translocase with RNP remodelling activities. Nat Commun.
6:75812015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Cerulo L, Pezzella N, Caruso FP, Parente
P, Remo A, Giordano G, Forte N, Busselez J, Boschi F, Galiè M, et
al: Single-cell proteo-genomic reveals a comprehensive map of
centrosome-associated spliceosome components. iScience.
26:1066022023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Wynn TA: Cellular and molecular mechanisms
of fibrosis. J Pathol. 214:199–210. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Völler D, Linck L, Bruckmann A, Hauptmann
J, Deutzmann R, Meister G and Bosserhoff AK: Argonaute family
protein expression in normal tissue and cancer entities. PLoS One.
11:e01611652016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Shen EZ, Chen H, Ozturk AR, Tu S,
Shirayama M, Tang W, Ding YH, Dai SY, Weng Z and Mello CC:
Identification of piRNA binding sites reveals the argonaute
regulatory landscape of the C. elegans germline. Cell.
172:937–951.e18. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Sasaki T, Kuwata R, Hoshino K, Isawa H,
Sawabe K and Kobayashi M: Argonaute 2 suppresses japanese
encephalitis virus infection in aedes aegypti. Jpn J Infect Dis.
70:38–44. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Gou LT, Kang JY, Dai P, Wang X, Li F, Zhao
S, Zhang M, Hua MM, Lu Y, Zhu Y, et al: Ubiquitination-deficient
mutations in human Piwi cause male infertility by impairing
histone-to-protamine exchange during spermiogenesis. Cell.
169:1090–1104.e13. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Lessel D, Zeitler DM, Reijnders MRF,
Kazantsev A, Hassani Nia F, Bartholomäus A, Martens V, Bruckmann A,
Graus V, McConkie-Rosell A, et al: Germline AGO2 mutations impair
RNA interference and human neurological development. Nat Commun.
11:57972020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Detzer A, Engel C, Wünsche W and Sczakiel
G: Cell stress is related to re-localization of argonaute 2 and to
decreased RNA interference in human cells. Nucleic Acids Res.
39:2727–2741. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Leung AKL and Sharp PA: Quantifying
Argonaute proteins in and out of GW/P-bodies: Implications in
microRNA activities. Adv Exp Med Biol. 768:165–182. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Patel PH, Barbee SA and Blankenship JT:
GW-bodies and P-bodies constitute two separate pools of sequestered
non-translating RNAs. PLoS One. 11:e01502912016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Karlikow M, Goic B, Mongelli V, Salles A,
Schmitt C, Bonne I, Zurzolo C and Saleh MC: Drosophila cells use
nanotube-like structures to transfer dsRNA and RNAi machinery
between cells. Sci Rep. 6:270852016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Antoniou A, Baptista M, Carney N and
Hanley JG: PICK1 links argonaute 2 to endosomes in neuronal
dendrites and regulates miRNA activity. EMBO Rep. 15:548–556. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Zhang Y, Wang B, Chen X, Li W and Dong P:
AGO2 involves the malignant phenotypes and FAK/PI3K/AKT signaling
pathway in hypopharyngeal-derived FaDu cells. Oncotarget.
8:54735–54746. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Zhang K, Pomyen Y, Barry AE, Martin SP,
Khatib S, Knight L, Forgues M, Dominguez DA, Parhar R, Shah AP, et
al: AGO2 mediates MYC mRNA stability in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Mol Cancer Res. 18:612–622. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Ye Z, Jin H and Qian Q: Argonaute 2: A
novel rising star in cancer research. J Cancer. 6:877–882. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Li L, Yu C, Gao H and Li Y: Argonaute
proteins: Potential biomarkers for human colon cancer. BMC Cancer.
10:382010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Vaksman O, Hetland TE, Trope CG, Reich R
and Davidson B: Argonaute, Dicer, and Drosha are up-regulated along
tumor progression in serous ovarian carcinoma. Hum Pathol.
43:2062–2069. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Gao CL, Sun R, Li DH and Gong F: PIWI-like
protein 1 upregulation promotes gastric cancer invasion and
metastasis. Onco Targets Ther. 11:8783–8789. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Feng B, Hu P, Lu SJ, Chen JB and Ge RL:
Increased argonaute 2 expression in gliomas and its association
with tumor progression and poor prognosis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:4079–4083. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Shankar S, Pitchiaya S, Malik R, Kothari
V, Hosono Y, Yocum AK, Gundlapalli H, White Y, Firestone A, Cao X,
et al: KRAS engages AGO2 to enhance cellular transformation. Cell
Rep. 14:1448–1461. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Zhang X, Graves P and Zeng Y:
Overexpression of human argonaute2 inhibits cell and tumor growth.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1830:2553–2561. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Casey MC, Prakash A, Holian E, McGuire A,
Kalinina O, Shalaby A, Curran C, Webber M, Callagy G, Bourke E, et
al: Quantifying argonaute 2 (Ago2) expression to stratify breast
cancer. BMC Cancer. 19:7122019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Baldarelli RM, Smith CL, Ringwald M,
Richardson JE and Bult CJ; Mouse Genome Informatics Group, : Mouse
genome informatics: An integrated knowledgebase system for the
laboratory mouse. Genetics. 227:iyae0312024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Baldarelli RM, Smith CM, Finger JH,
Hayamizu TF, McCright IJ, Xu J, Shaw DR, Beal JS, Blodgett O,
Campbell J, et al: The mouse gene expression database (GXD): 2021
Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 49(D1): D924–D931. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Krupke DM, Begley DA, Sundberg JP,
Richardson JE, Neuhauser SB and Bult CJ: The mouse tumor biology
database: A comprehensive resource for mouse models of human
cancer. Cancer Res. 77:e67–e70. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Aizer A, Brody Y, Ler LW, Sonenberg N,
Singer RH and Shav-Tal Y: The dynamics of mammalian P body
transport, assembly, and disassembly in vivo. Mol Biol Cell.
19:4154–4166. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Moser JJ, Fritzler MJ and Rattner JB:
Repression of GW/P body components and the RNAi microprocessor
impacts primary ciliogenesis in human astrocytes. BMC Cell Biol.
12:372011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Alliegro MC, Alliegro MA and Palazzo RE:
Centrosome-associated RNA in surf clam oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 103:9034–9038. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Chichinadze K, Lazarashvili A and
Tkemaladze J: RNA in centrosomes: Structure and possible functions.
Protoplasma. 250:397–405. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Alliegro MC and Alliegro MA: Centrosomal
RNA correlates with intron-poor nuclear genes in Spisula oocytes.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:6993–6997. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Alliegro MC: The implications of
centrosomal RNA. RNA Biol. 5:198–200. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Safieddine A, Coleno E, Salloum S, Imbert
A, Traboulsi AM, Kwon OS, Lionneton F, Georget V, Robert MC, Gostan
T, et al: A choreography of centrosomal mRNAs reveals a conserved
localization mechanism involving active polysome transport. Nat
Commun. 12:13522021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Fareh M, Yeom KH, Haagsma AC, Chauhan S,
Heo I and Joo C: TRBP ensures efficient Dicer processing of
precursor microRNA in RNA-crowded environments. Nat Commun.
7:136942016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Griffin KN, Walters BW, Li H, Wang H,
Biancon G, Tebaldi T, Kaya CB, Kanyo J, Lam TT, Cox AL, et al:
Widespread association of the argonaute protein AGO2 with meiotic
chromatin suggests a distinct nuclear function in mammalian male
reproduction. Genome Res. 32:1655–1668. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Atwood BL, Woolnough JL, Lefevre GM, Saint
Just Ribeiro M, Felsenfeld G and Giles KE: Human ARGONAUTE 2 IS
TETHERED TO RIBOSOmal RNA through MicroRNA interactions. J Biol
Chem. 291:17919–17928. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Woolnough JL, Atwood BL and Giles KE:
Argonaute 2 binds directly to tRNA genes and promotes gene
repression in cis. Mol Cell Biol. 35:2278–2294. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Nazer E, Gómez Acuña L and Kornblihtt AR:
Seeking the truth behind the myth: Argonaute tales from
‘nuclearland’. Mol Cell. 82:503–513. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Li J, Kim T, Nutiu R, Ray D, Hughes TR and
Zhang Z: Identifying mRNA sequence elements for target recognition
by human argonaute proteins. Genome Res. 24:775–785. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Remo A, Li X, Schiebel E and Pancione M:
The centrosome linker and its role in cancer and genetic disorders.
Trends Mol Med. 26:380–393. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|