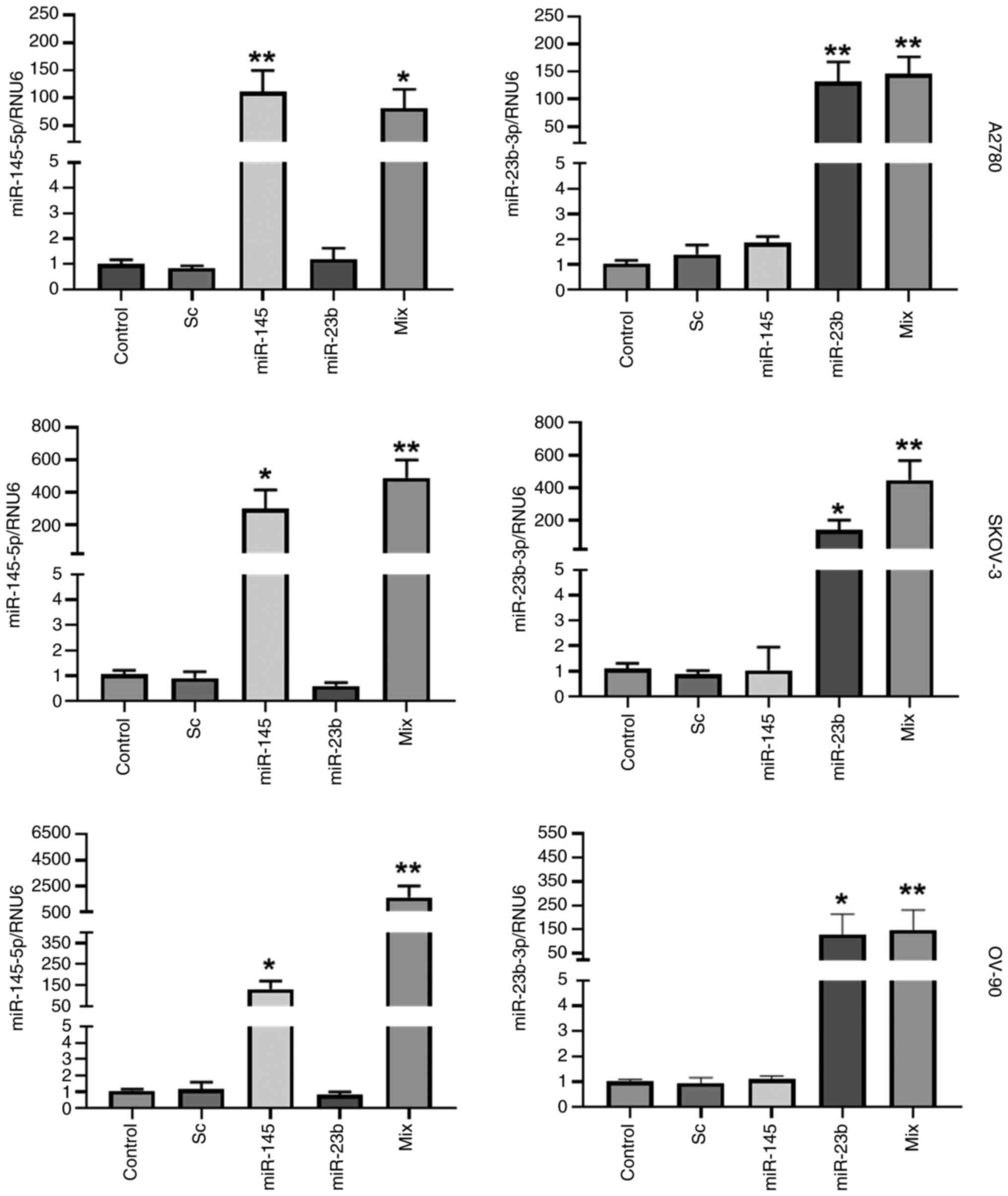
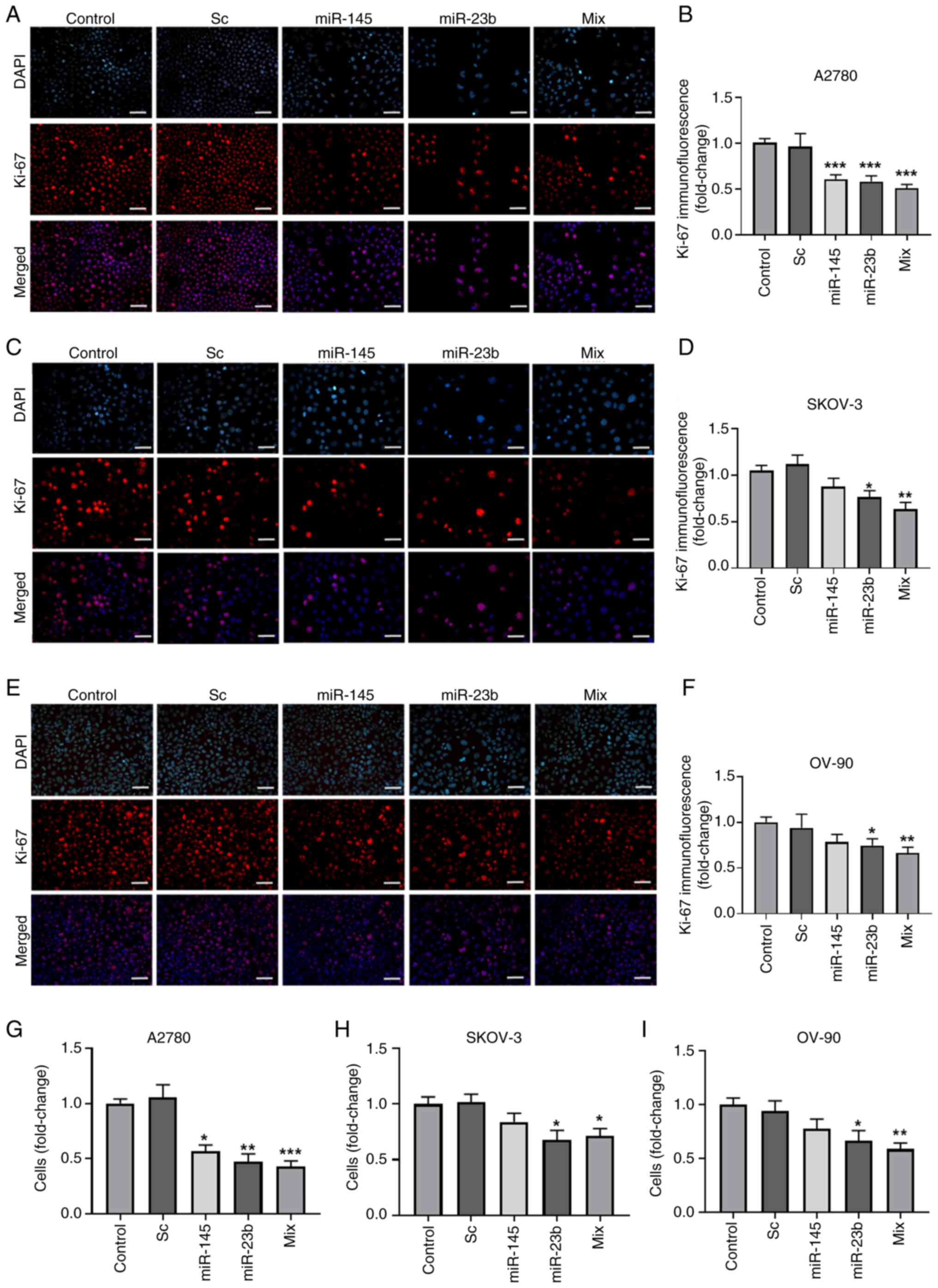
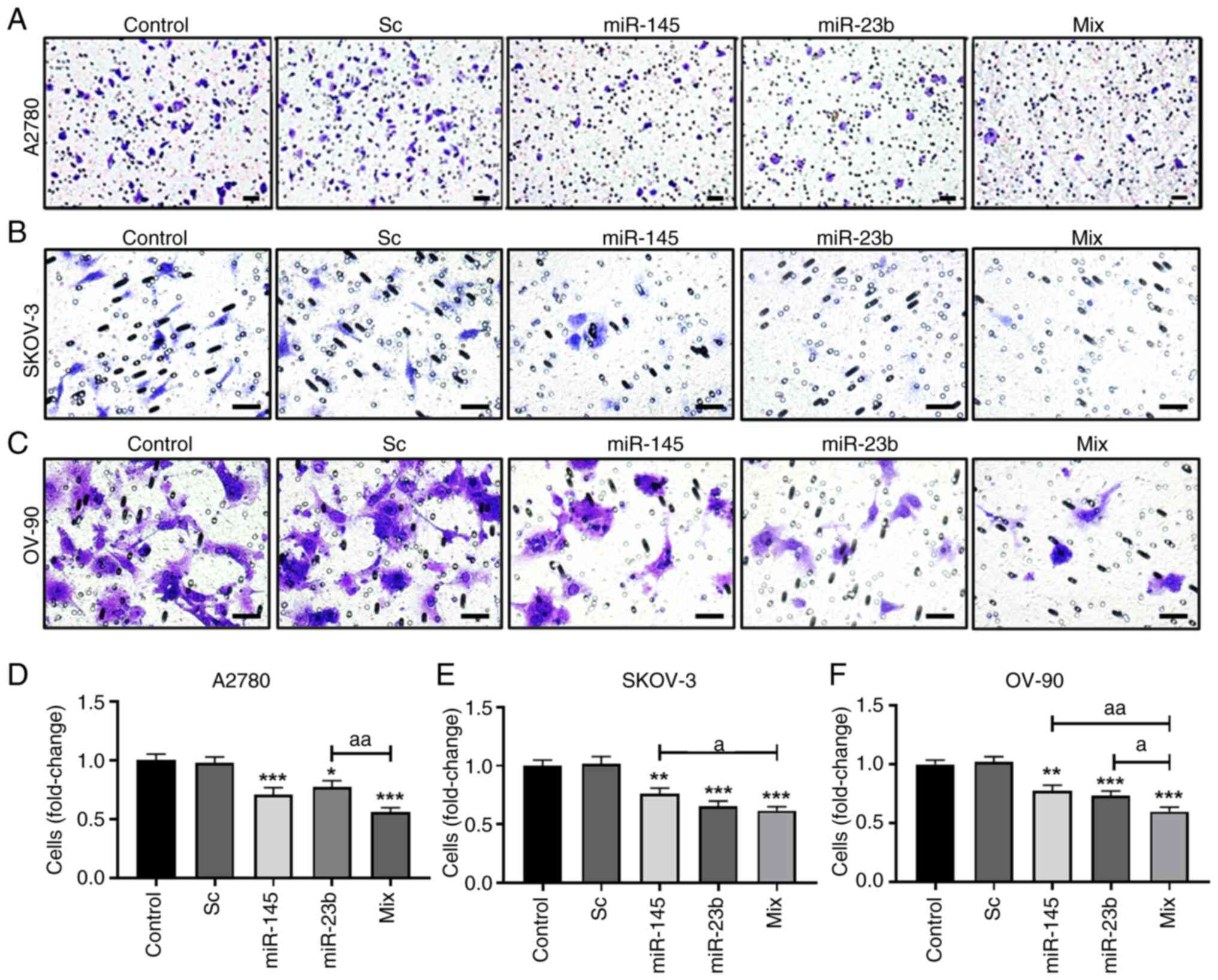
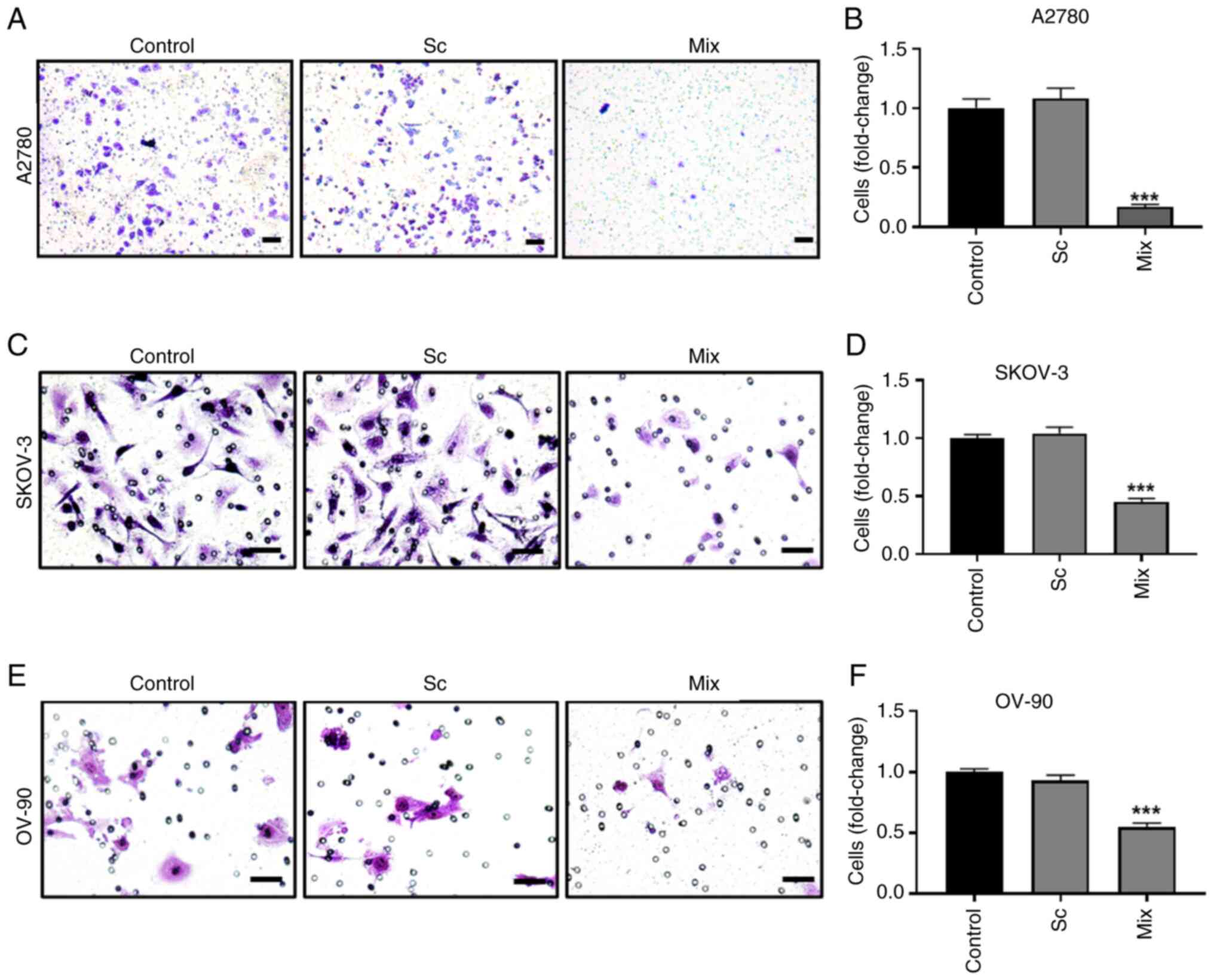
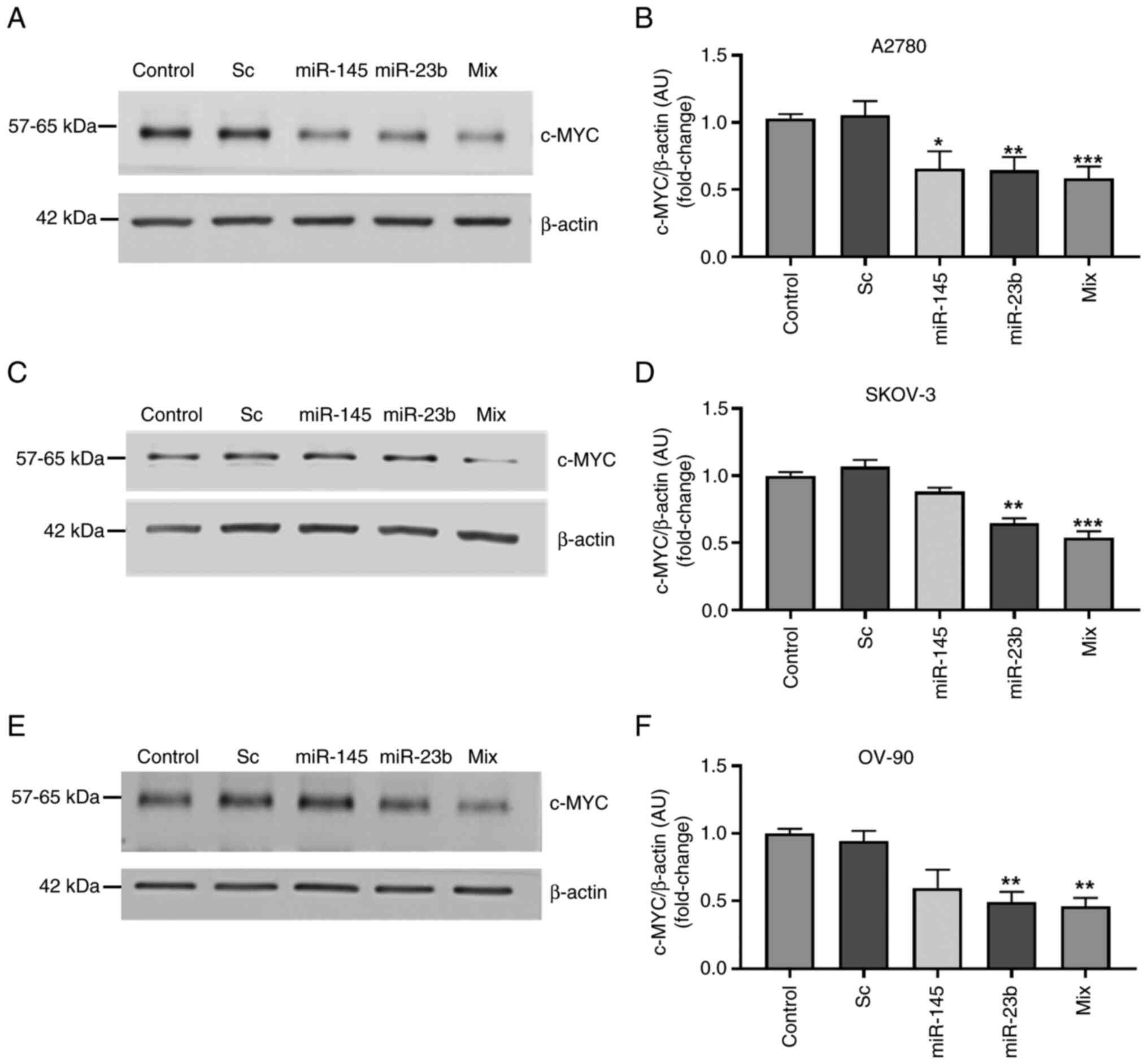
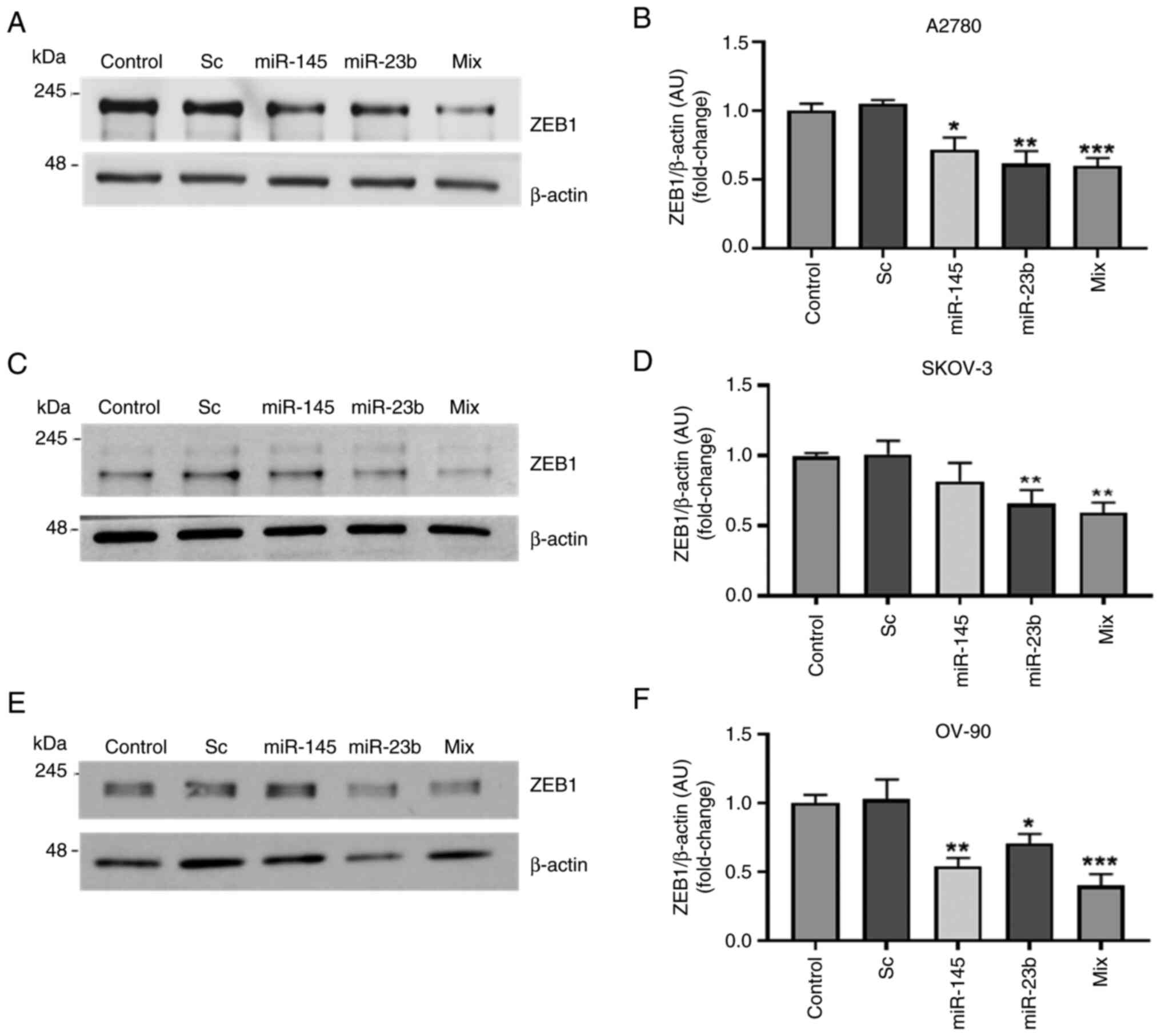
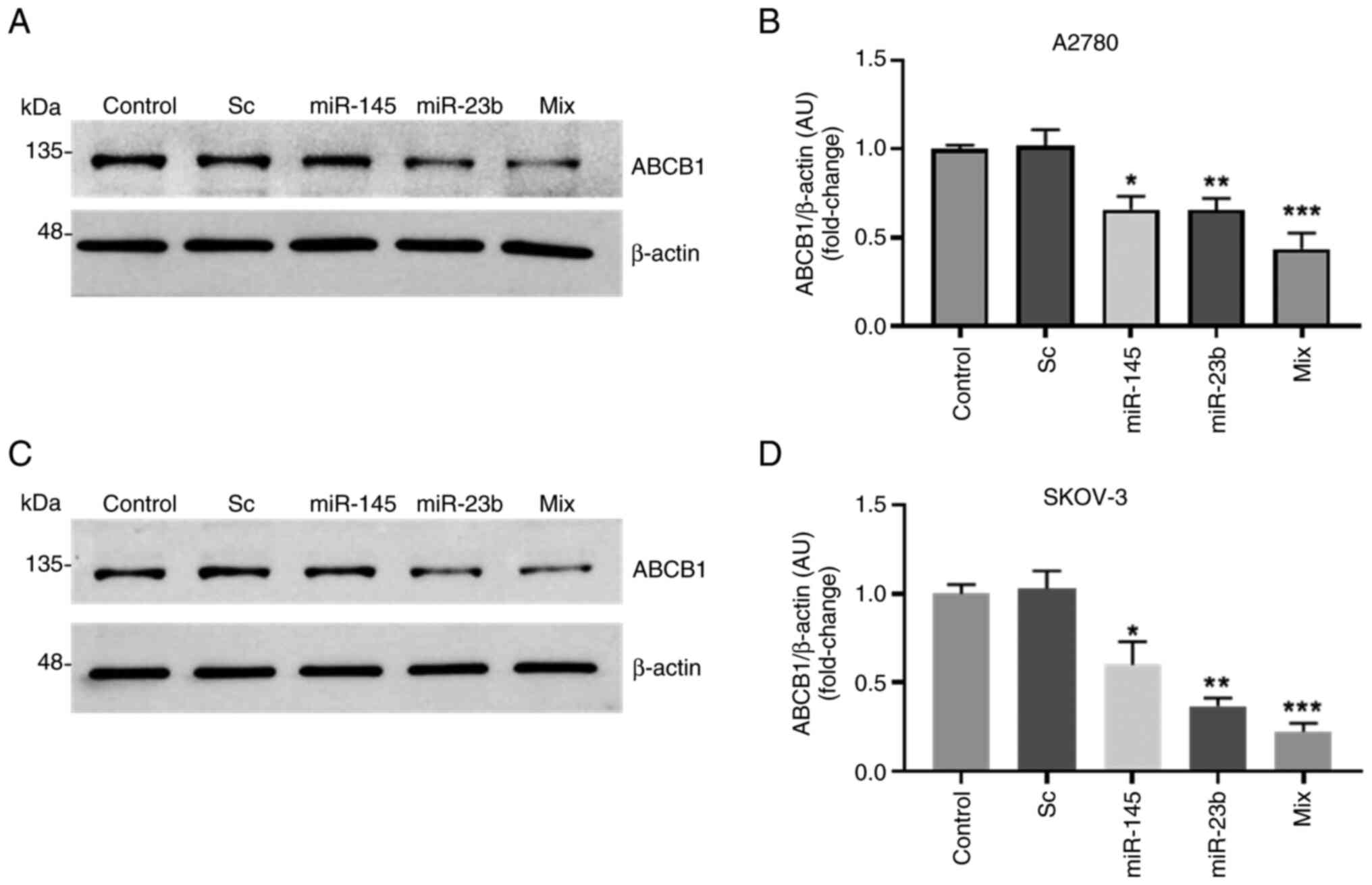
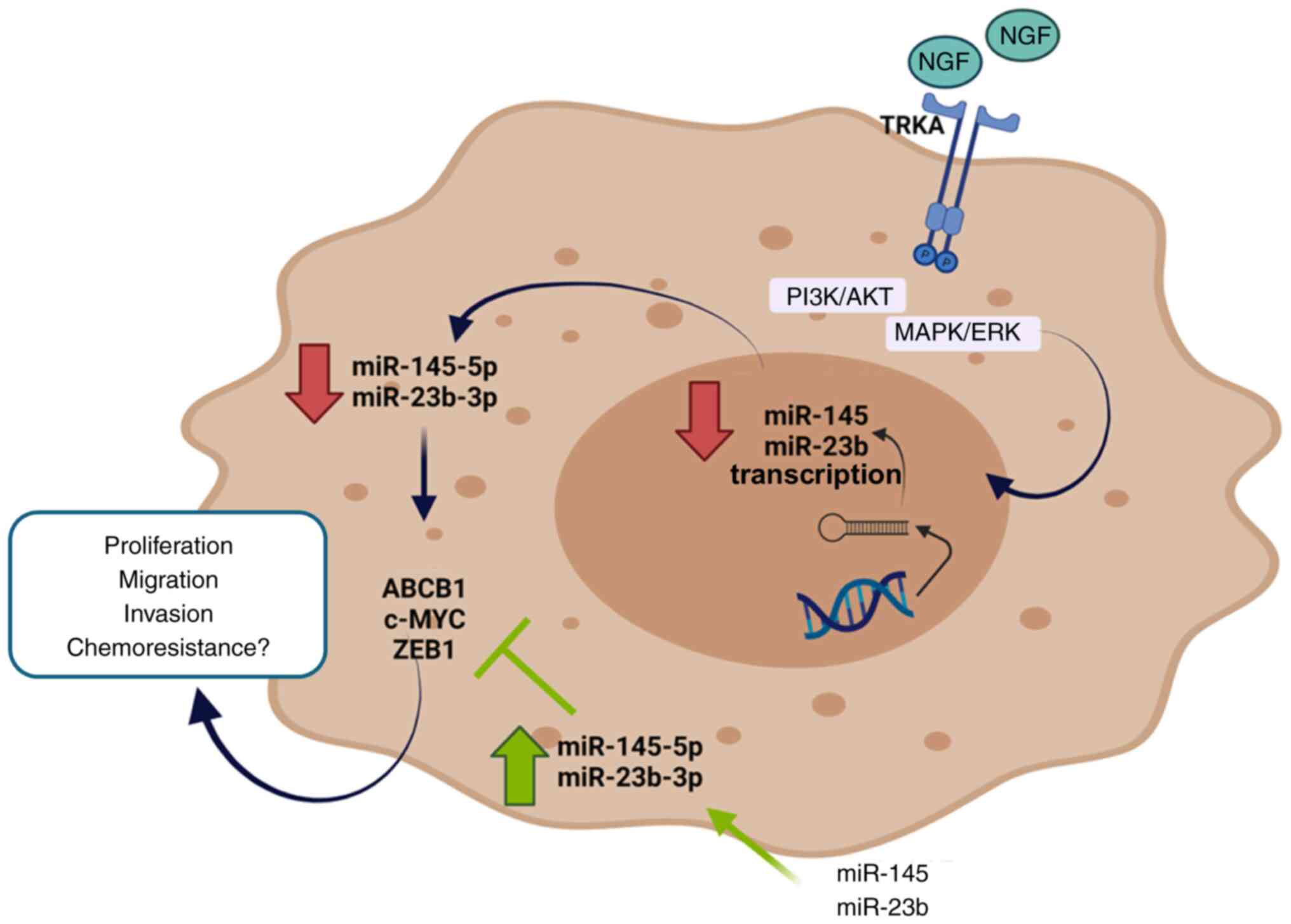
|
1
|
Torre LA, Trabert B, DeSantis CE, Miller
KD, Samimi G, Runowicz CD, Gaudet MM, Jemal A and Siegel RL:
Ovarian cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:284–296.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
World Ovarian Cancer Coalition, . The
World Ovarian Cancer Coalition Atlas, Global Trends in Incidence,
Mortality and Survival. 2023.
|
|
3
|
World Ovarian Cancer Coalition, . The
World Ovarian Cancer Coalition Atlas, Global Trends in Incidence,
Mortality and Survival. 2020.
|
|
4
|
Jessmon P, Boulanger T, Zhou W and
Patwardhan P: Epidemiology and treatment patterns of epithelial
ovarian cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 17:427–437. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rojas V, Hirshfield KM, Ganesan S and
Rodriguez-Rodriguez L: Molecular characterization of epithelial
ovarian cancer: Implications for diagnosis and treatment. Int J Mol
Sci. 17:21132016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ledermann JA: First-line treatment of
ovarian cancer: Questions and controversies to address. Ther Adv
Med Oncol. 10:17588359187682322018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Beesley VL, Ross TL, King MT, Campbell R,
Nagle CM, Obermair A, Grant P, DeFazio A, Webb PM and Friedlander
ML; OPAL Study Group, : Evaluating patient-reported symptoms and
late adverse effects following completion of first-line
chemotherapy for ovarian cancer using the MOST (Measure of Ovarian
Symptoms and Treatment concerns). Gynecol Oncol. 164:437–445. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Garrido MP, Fredes AN, Lobos-González L,
Valenzuela-Valderrama M, Vera DB and Romero C: Current treatments
and new possible complementary therapies for epithelial ovarian
cancer. Biomedicines. 10:772022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ha M and Kim VN: Regulation of microRNA
biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:509–524. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Garrido MP, Torres I, Avila A, Chnaiderman
J, Valenzuela-Valderrama M, Aramburo J, Oróstica L, Durán-Jara E,
Lobos-Gonzalez L and Romero C: NGF/TRKA Decrease miR-145-5p levels
in epithelial ovarian cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 21:76572020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Vera C, Retamales-Ortega R, Garrido M,
Vega M and Romero C: Signaling pathways related to nerve growth
factor and miRNAs in epithelial ovarian cancer. Ovarian Cancer:
From Pathogenesis to Treatment. pp392018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Croce CM: Causes and consequences of
microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 10:704–714. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Julio-Pieper M, Lozada P, Tapia V, Vega M,
Miranda C, Vantman D, Ojeda SR and Romero C: Nerve growth factor
induces vascular endothelial growth factor expression in granulosa
cells via a trkA Receptor/Mitogen-Activated protein
Kinase-extracellularly regulated kinase 2-Dependent pathway. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 94:3065–3071. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Garrido MP, Hurtado I,
Valenzuela-Valderrama M, Salvatierra R, Hernández A, Vega M, Selman
A, Quest AFG and Romero C: NGF-Enhanced vasculogenic properties of
epithelial ovarian cancer cells is reduced by inhibition of the
COX-2/PGE2 signaling axis. Cancers. 11:19702019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tapia V, Gabler F, Muñoz M, Yazigi R,
Paredes A, Selman A, Vega M and Romero C: Tyrosine kinase A
receptor (trkA): A potential marker in epithelial ovarian cancer.
Gynecol Oncol. 121:13–23. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Urzua U, Tapia V, Geraldo MP, Selman A,
Vega M and Romero C: Nerve growth factor stimulates cellular
proliferation of human epithelial ovarian cancer. Horm Metab Res.
44:656–661. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Campos X, Muñoz Y, Selman A, Yazigi R,
Moyano L, Weinstein-Oppenheimer C, Lara HE and Romero C: Nerve
growth factor and its high-affinity receptor trkA participate in
the control of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in
epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 104:168–175. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Smolarz B, Durczyński A, Romanowicz H,
Szyłło K and Hogendorf P: miRNAs in Cancer (Review of Literature).
Int J Mol Sci. 23:28052022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Adams BD, Kasinski AL and Slack FJ:
Aberrant regulation and function of microRNAs in cancer. Current
Biology. 24:R762–R776. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Svoronos AA, Engelman DM and Slack FJ:
OncomiR or tumor suppressor? The duplicity of MicroRNAs in cancer.
Cancer Res. 76:3666–3670. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tian S, Zhang M, Chen X, Liu Y and Lou G:
MicroRNA-595 sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin by
targeting ABCB1. Oncotarget. 7:87091–87099. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
An X, Sarmiento C, Tan T and Zhu H:
Regulation of multidrug resistance by microRNAs in anti-cancer
therapy. Acta Pharm Sin B. 7:38–51. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang W, Wang Q, Yu M, Wu N and Wang H:
MicroRNA-145 function as a cell growth repressor by directly
targeting c-Myc in human ovarian cancer. Technol Cancer Res Treat.
13:161–168. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Romero-Pérez L, López-García MÁ,
Díaz-Martín J, Biscuola M, Castilla MÁ, Tafe LJ, Garg K, Oliva E,
Matias-Guiu X, Soslow RA and Palacios J: ZEB1 overexpression
associated with E-cadherin and microRNA-200 downregulation is
characteristic of undifferentiated endometrial carcinoma. Mod
Pathol. 26:1514–1524. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Retamales-Ortega R, Oróstica L, Vera C,
Cuevas P, Hernández A, Hurtado I, Vega M and Romero C: Role of
nerve growth factor (NGF) and miRNAs in epithelial ovarian cancer.
Int J Mol Sci. 18:5072017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Romero-López MJ, Jiménez-Wences H, Cruz-De
la Rosa MI, Román-Fernández IV and Fernández-Tilapa G: miR-23b-3p,
miR-124-3p and miR-218-5p synergistic or additive effects on
cellular processes that modulate cervical cancer progression? A
molecular balance that needs attention. Int J Mol Sci.
23:135512022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Grossi I, Arici B, Portolani N, Petro GD
and Salvi A: Clinical and biological significance of miR-23b and
miR-193a in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget.
8:6955–6969. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Pimenta RC, Viana NI, Amaral GQ, Park R,
Morais DR, Pontes J Jr, Guimaraes VR, Camargo JA, Leite KR, Nahas
WC, et al: MicroRNA-23b and microRNA-27b plus flutamide treatment
enhances apoptosis rate and decreases CCNG1 expression in a
castration-resistant prostate cancer cell line. Tumour Biol.
40:10104283188030112018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Qiu T, Zhou X, Wang J, Du Y, Xu J, Huang
Z, Zhu W, Shu Y and Liu P: MiR-145, miR-133a and miR-133b inhibit
proliferation, migration, invasion and cell cycle progression via
targeting transcription factor Sp1 in gastric cancer. FEBS Lett.
588:1168–1177. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Fulciniti M, Amodio N, Bandi RL, Cagnetta
A, Samur MK, Acharya C, Prabhala R, D'Aquila P, Bellizzi D,
Passarino G, et al: miR-23b/SP1/c-myc forms a feed-forward loop
supporting multiple myeloma cell growth. Blood Cancer J.
6:e3802016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhu X, Li Y, Xie C, Yin X, Liu Y, Cao Y,
Fang Y, Lin X, Xu Y, Xu W, et al: miR-145 sensitizes ovarian cancer
cells to paclitaxel by targeting Sp1 and Cdk6. Int J Cancer.
135:1286–1296. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Vaidyanathan A, Sawers L, Gannon AL,
Chakravarty P, Scott AL, Bray SE, Ferguson MJ and Smith G: ABCB1
(MDR1) induction defines a common resistance mechanism in
paclitaxel- and olaparib-resistant ovarian cancer cells. Br J
Cancer. 115:431–441. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Engle K and Kumar G: Cancer
multidrug-resistance reversal by ABCB1 inhibition: A recent update.
Eur J Med Chem. 239:1145422022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xu W, Hua Y, Deng F, Wang D, Wu Y, Zhang W
and Tang J: MiR-145 in cancer therapy resistance and sensitivity: A
comprehensive review. Cancer Sci. 111:3122–3131. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Sheng Q, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Ding J, Song Y
and Zhao W: Cisplatin-mediated down-regulation of miR-145
contributes to up-regulation of PD-L1 via the c-Myc transcription
factor in cisplatin-resistant ovarian carcinoma cells. Clin Exp
Immunol. 200:45–52. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Majid S, Dar AA, Saini S, Deng G, Chang I,
Greene K, Tanaka Y, Dahiya R and Yamamura S: MicroRNA-23b functions
as a tumor suppressor by regulating Zeb1 in bladder cancer. PLoS
One. 8:e676862013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yao D, Dai C and Peng S: Mechanism of the
Mesenchymal-epithelial transition and its relationship with
metastatic tumor formation. Mol Cancer Res. 9:1608–1620. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fan H, Atiya HI, Wang Y, Pisanic TR, Wang
TH, Shih IM, Foy KK, Frisbie L, Buckanovich RJ, Chomiak AA, et al:
Epigenomic reprogramming toward Mesenchymal-epithelial transition
in ovarian-Cancer-associated mesenchymal stem cells drives
metastasis. Cell Rep. 33:1084732020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cui Y, Qin L, Tian D, Wang T, Fan L, Zhang
P and Wang Z: ZEB1 promotes chemoresistance to cisplatin in ovarian
cancer cells by suppressing SLC3A2. Chemotherapy. 63:262–271. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Garrido MP, Salvatierra R,
Valenzuela-Valderrama M, Vallejos C, Bruneau N, Hernández A, Vega
M, Selman A, Quest AFG and Romero C: Metformin reduces NGF-induced
tumour promoter effects in epithelial ovarian cancer cells.
Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 13:3152020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Behrens BC, Hamilton TC, Masuda H,
Grotzinger KR, Whang-Peng J, Louie KG, Knutsen T, McKoy WM, Young
RC and Ozols RF: Characterization of a
cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II)-resistant human ovarian cancer
cell line and its use in evaluation of platinum analogues. Cancer
Res. 47:414–418. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tudrej P, Olbryt M, Zembala-Nożyńska E,
Kujawa KA, Cortez AJ, Fiszer-Kierzkowska A, Pigłowski W, Nikiel B,
Głowala-Kosińska M, Bartkowska-Chrobok A, et al: Establishment and
characterization of the novel High-grade serous ovarian cancer cell
line OVPA8. Int J Mol Sci. 19:20802018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Cowley GS, Weir BA, Vazquez F, Tamayo P,
Scott JA, Rusin S, East-Seletsky A, Ali LD, Gerath WF, Pantel SE,
et al: Parallel genome-scale loss of function screens in 216 cancer
cell lines for the identification of context-specific genetic
dependencies. Sci Data. 1:1400352014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Llorens MC, Lorenzatti G, Cavallo NL,
Vaglienti MV, Perrone AP, Carenbauer AL, Darling DS and Cabanillas
AM: Phosphorylation regulates functions of ZEB1 transcription
factor. J Cell Physiol. 231:2205–2217. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Perez-Oquendo M, Manshouri R, Tian Y,
Fradette JJ, Rodriguez BL, Kundu ST and Gibbons DL: ZEB1 is
regulated by K811 acetylation to promote stability, NuRD complex
interactions, EMT, and NSCLC metastasis. Mol Cancer Res.
21:779–794. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhou F, Du C, Xu D, Lu J, Zhou L, Wu C, Wu
B and Huang J: Knockdown of ubiquitin-specific protease 51
attenuates cisplatin resistance in lung cancer through
ubiquitination of zinc-finger E-box binding homeobox 1. Mol Med
Rep. 22:1382–1390. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhang H, Tang H, Tu W and Peng F:
Regulatory role of non-coding RNAs in 5-Fluorouracil resistance in
gastrointestinal cancers. Cancer Drug Resist. 8:42025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Yi J, Li B, Yin X, Liu L, Song C, Zhao Y,
Cai M, Tang H, Chen D and Lyu N: CircMYBL2 facilitates
hepatocellular carcinoma progression by regulating E2F1 expression.
Oncol Res. 32:1129–1139. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wu S, Lu J, Zhu H, Wu F, Mo Y, Xie L, Song
C, Liu L, Xie X, Li Y, et al: A novel axis of
circKIF4A-miR-637-STAT3 promotes brain metastasis in
triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 581:2165082024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Pei X, Chen SW, Long X, Zhu SQ, Qiu BQ,
Lin K, Lu F, Xu JJ, Zhang PF and Wu YB: circMET promotes NSCLC cell
proliferation, metastasis, and immune evasion by regulating the
miR-145-5p/CXCL3 axis. Aging (Albany NY). 12:13038–13058. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhu Z, Wu Q, Zhang M, Tong J, Zhong B and
Yuan K: Hsa_circ_0016760 exacerbates the malignant development of
Non-small cell lung cancer by sponging miR-145-5p/FGF5. Oncol Rep.
45:501–512. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Singh S, Saxena S, Sharma H, Paudel KR,
Chakraborty A, MacLoughlin R, Oliver BG, Gupta G, Negi P, Singh SK
and Dua K: Emerging role of tumor suppressing microRNAs as
therapeutics in managing non-small cell lung cancer. Pathol Res
Pract. 256:1552222024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Yan J, Jiang J, Meng XN, Xiu YL and Zong
ZH: MiR-23b targets cyclin G1 and suppresses ovarian cancer
tumorigenesis and progression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 35:312016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhou J, Zhang X, Li W and Chen Y:
MicroRNA-145-5p regulates the proliferation of epithelial ovarian
cancer cells via targeting SMAD4. J Ovarian Res. 13:542020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kubickova A, De Sanctis JB and Hajduch M:
Isoform-directed control of c-Myc Functions: Understanding the
balance from proliferation to growth arrest. Int J Mol Sci.
24:175242023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Perez-Oquendo M and Gibbons DL: Regulation
of ZEB1 function and molecular associations in tumor progression
and metastasis. Cancers (Basel). 14:18642022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Shao Y, Qu Y, Dang S, Yao B and Ji M:
MiR-145 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cell growth by
targeting c-Myc and Cdk6. Cancer Cell Int. 13:512013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Xu WX, Liu Z, Deng F, Wang DD, Li XW, Tian
T, Zhang J and Tang JH: MiR-145: A potential biomarker of cancer
migration and invasion. Am J Transl Res. 11:6739–6753.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Seyfried TN and Huysentruyt LC: On the
origin of cancer metastasis. Crit Rev Oncog. 18:43–73. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Bravo-Cordero JJ, Hodgson L and Condeelis
J: Directed cell invasion and migration during metastasis. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 24:277–283. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Cai W and Zhang Q: The transcription
factor ZEB1 mediates the progression of epithelial ovarian cancer
by promoting the transcription of CircANKRD17. J Biochem Mol
Toxicol. 36:e230862022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Hashiguchi M, Ueno S, Sakoda M, Iino S,
Hiwatashi K, Minami K, Ando K, Mataki Y, Maemura K, Shinchi H, et
al: Clinical implication of ZEB-1 and E-cadherin expression in
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). BMC Cancer. 13:5722013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zhang J, Lu C, Zhang J, Kang J, Cao C and
Li M: Involvement of ZEB1 and E-cadherin in the invasion of lung
squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Biol Rep. 40:949–956. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Campos-Viguri GE, Jiménez-Wences H,
Peralta-Zaragoza O, Torres-Altamirano G, Soto-Flores DG,
Hernández-Sotelo D, Alarcón-Romero Ldel C, Jiménez-López MA,
Illades-Aguiar B and Fernández-Tilapa G: miR-23b as a potential
tumor suppressor and its regulation by DNA methylation in cervical
cancer. Infect Agents Cancer. 10:422015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Xue M, Pang H, Li X, Li H, Pan J and Chen
W: Long non-coding RNA urothelial cancer-associated 1 promotes
bladder cancer cell migration and invasion by way of the
hsa-miR-145-ZEB1/2-FSCN1 pathway. Cancer Sci. 107:18–27. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Lei H, Gao Y and Xu X: LncRNA TUG1
influences papillary thyroid cancer cell proliferation, migration
and EMT formation through targeting miR-145. Acta Biochim Biophys
Sin (Shanghai). 49:588–597. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Rice MA, Ishteiwy RA, Magani F, Udayakumar
T, Reiner T, Yates TJ, Miller P, Perez-Stable C, Rai P, Verdun R,
et al: The microRNA-23b/-27b cluster suppresses prostate cancer
metastasis via Huntingtin-interacting protein 1-related. Oncogene.
35:4752–4761. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Zeinali T, Mansoori B, Mohammadi A and
Baradaran B: Regulatory mechanisms of miR-145 expression and the
importance of its function in cancer metastasis. Biomed
Pharmacother. 109:195–207. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Chen Q, Zhou L, Ye X, Tao M and Wu J:
miR-145-5p suppresses proliferation, metastasis and EMT of
colorectal cancer by targeting CDCA3. Pathol Res Pract.
216:1528722020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Lin H, Xu X, Chen K, Fu Z, Wang S, Chen Y,
Zhang H, Niu Y, Chen H, Yu H, et al: LncRNA CASC15, MiR-23b cluster
and SMAD3 form a novel positive feedback loop to promote
Epithelial-Mesenchymal transition and metastasis in ovarian cancer.
Int J Biol Sci. 18:1989–2002. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Gao M, Miao L, Liu M, Li C, Yu C, Yan H,
Yin Y, Wang Y, Qi X and Ren J: miR-145 sensitizes breast cancer to
doxorubicin by targeting multidrug resistance-associated protein-1.
Oncotarget. 7:59714–59726. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Gao R, Fang C, Xu J, Tan H, Li P and Ma L:
LncRNA CACS15 contributes to oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal
cancer by positively regulating ABCC1 through sponging miR-145.
Arch Biochem Biophys. 663:183–191. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Wang Y, Tu MJ and Yu AM: Efflux ABC
transporters in drug disposition and their posttranscriptional gene
regulation by microRNAs. Front Pharmacol. 15:14234162024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Wang Y, Wang Y, Qin Z, Cai S, Yu L, Hu H
and Zeng S: The role of non-coding RNAs in ABC transporters
regulation and their clinical implications of multidrug resistance
in cancer. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 17:291–306. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
An Y, Zhang Z, Shang Y, Jiang X, Dong J,
Yu P, Nie Y and Zhao Q: miR-23b-3p regulates the chemoresistance of
gastric cancer cells by targeting ATG12 and HMGB2. Cell Death Dis.
6:e17662015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Norouzi-Barough L, Sarookhani M, Salehi R,
Sharifi M and Moghbelinejad S: CRISPR/Cas9, a new approach to
successful knockdown of ABCB1/P-glycoprotein and reversal of
chemosensitivity in human epithelial ovarian cancer cell line. Iran
J Basic Med Sci. 21:181–187. 2018.
|
|
79
|
Lei ZN, Teng QX, Wu ZX, Ping FF, Song P,
Wurpel JND and Chen ZS: Overcoming multidrug resistance by knockout
of ABCB1 gene using CRISPR/Cas9 system in SW620/Ad300 colorectal
cancer cells. MedComm (2020). 2:765–777. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|