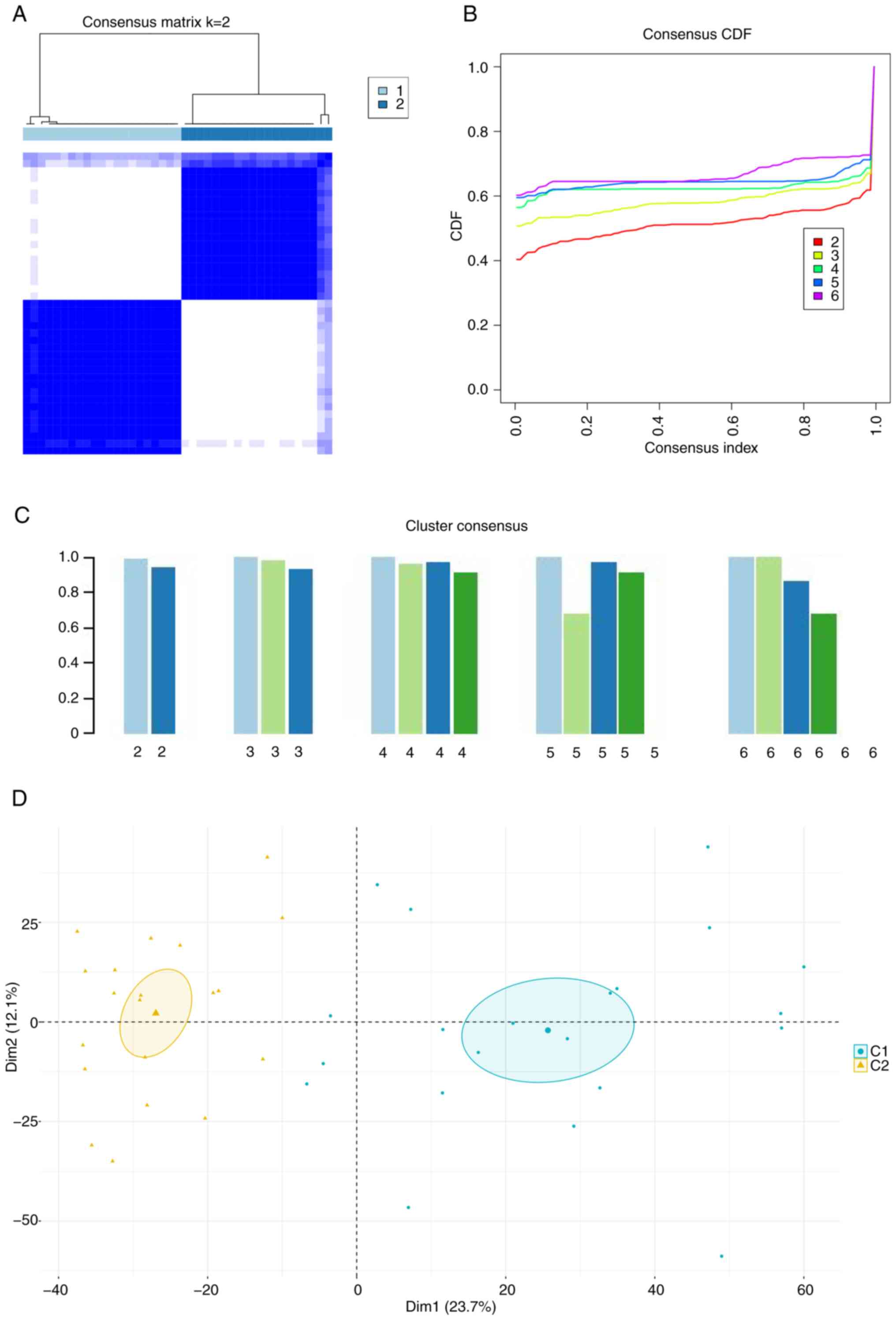
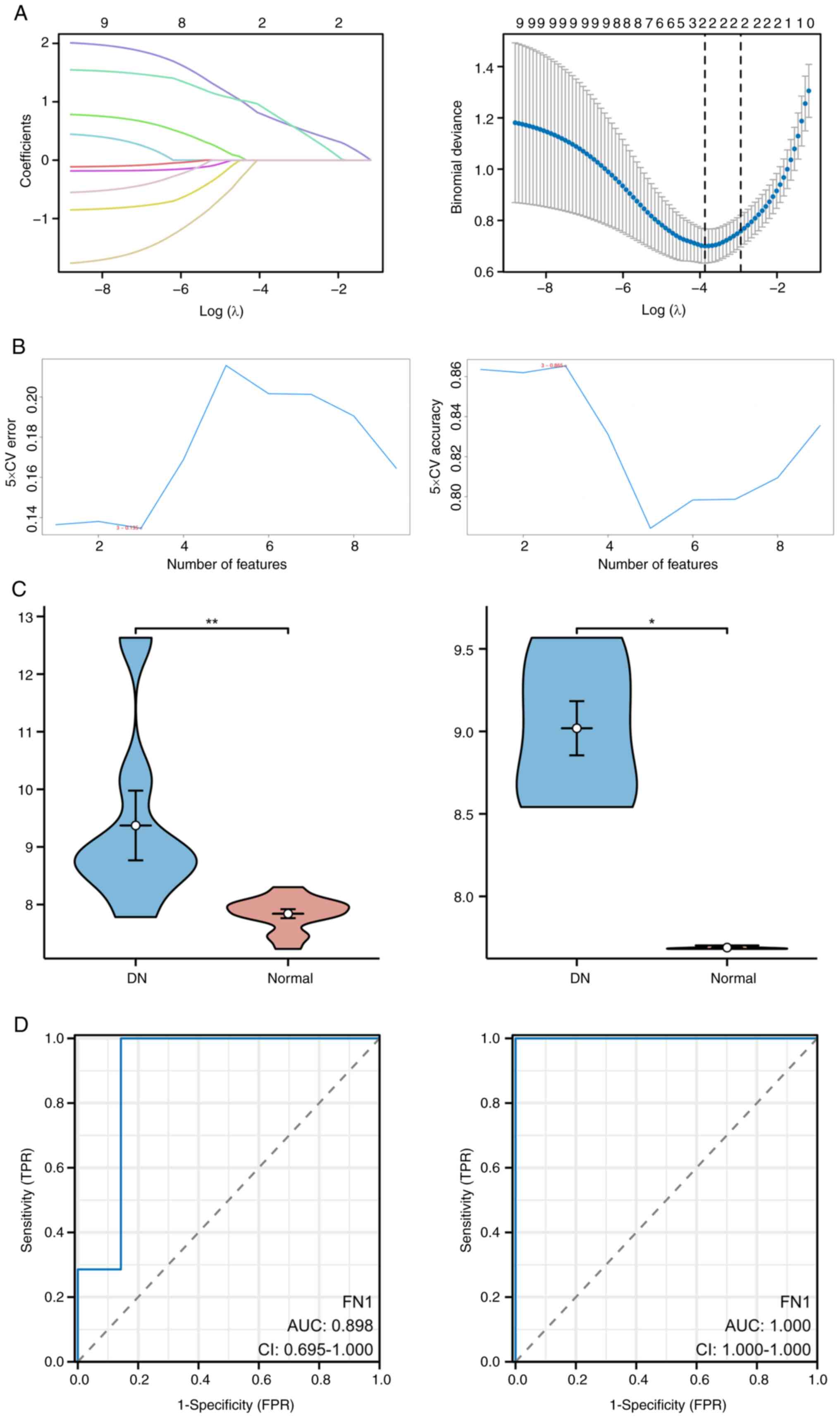
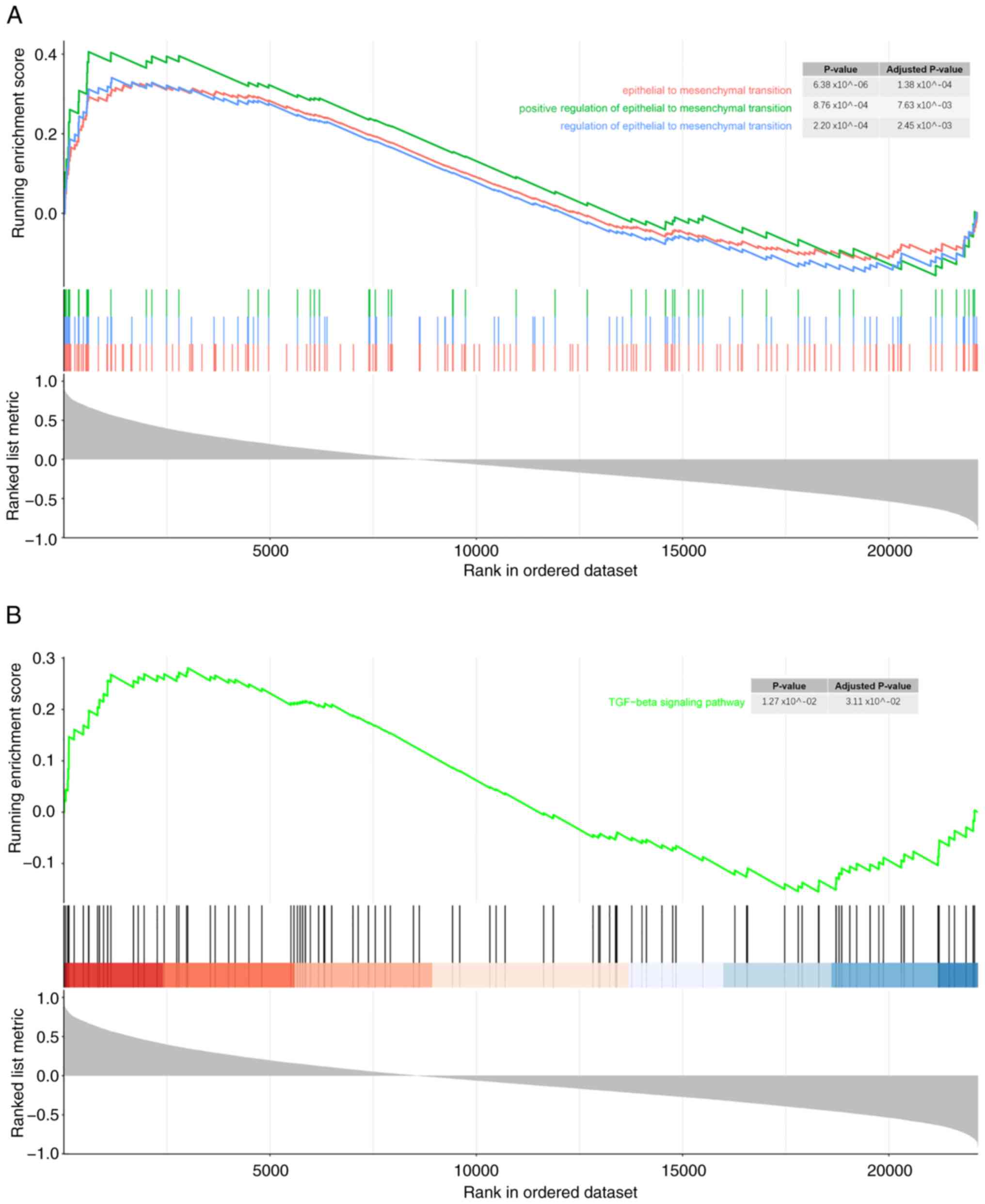
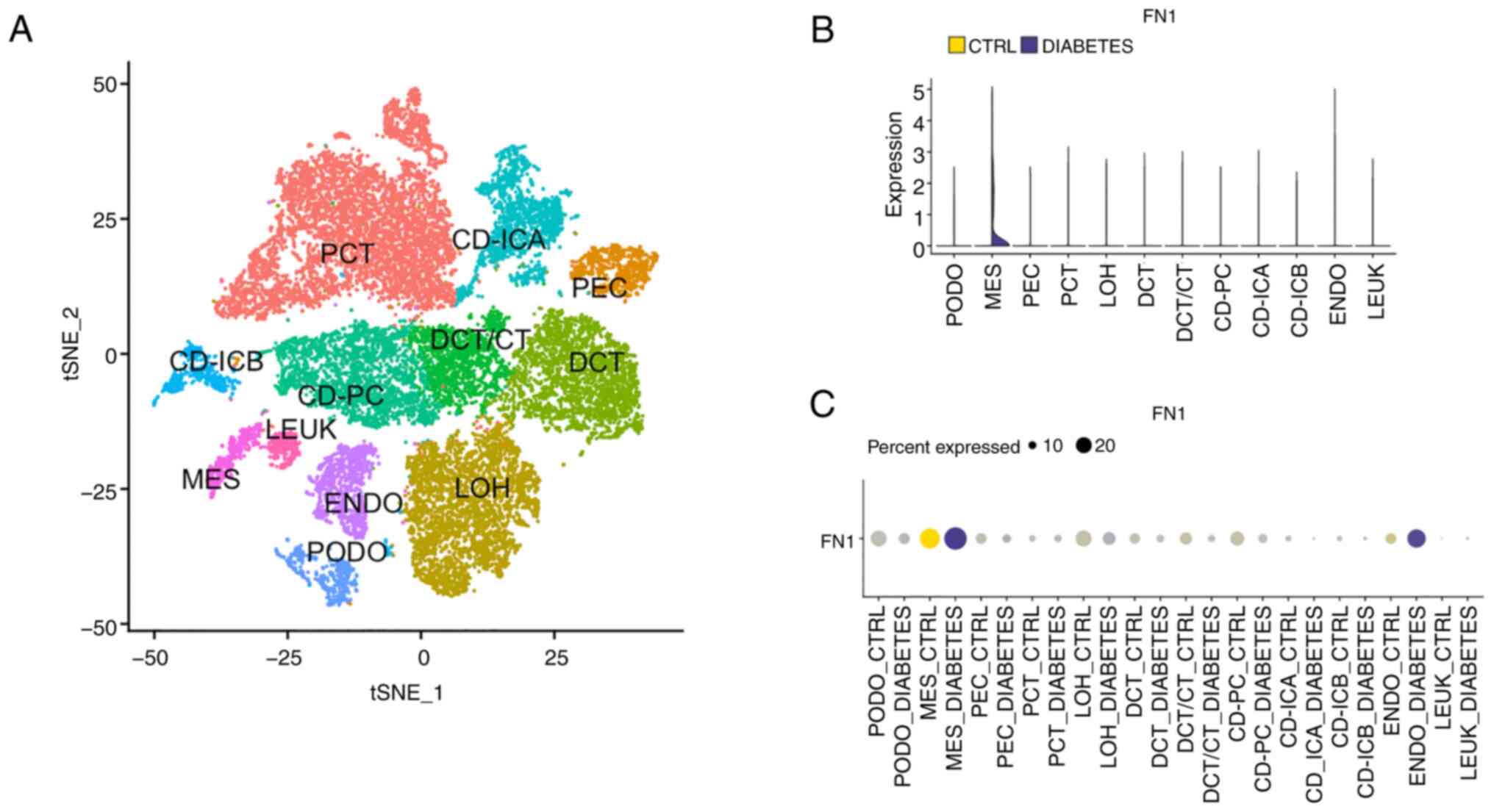
|
1
|
Webster AC, Nagler EV, Morton RL and
Masson P: Chronic kidney disease. Lancet. 389:1238–1252. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Pozo Garcia L, Thomas SS, Rajesh H and
Navaneethan SD: Progress in the management of patients with
diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens.
31:456–463. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Umanath K and Lewis JB: Update on diabetic
nephropathy: Core curriculum 2018. Am J Kidney Dis. 71:884–895.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Flyvbjerg A: The role of the complement
system in diabetic nephropathy. Nat Rev Nephrol. 13:311–318. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Tung CW, Hsu YC, Shih YH, Chang PJ and Lin
CL: Glomerular mesangial cell and podocyte injuries in diabetic
nephropathy. Nephrology (Carlton). 23 (Suppl 4):S32–S37. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Mandelbrot DA, Reese PP, Garg N, Thomas
CP, Rodrigue JR, Schinstock C, Doshi M, Cooper M, Friedewald J,
Naik AS, et al: KDOQI US Commentary on the 2017 KDIGO clinical
practice guideline on the evaluation and care of living kidney
donors. Am J Kidney Dis. 75:299–316. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Radcliffe NJ, Seah JM, Clarke M, MacIsaac
RJ, Jerums G and Ekinci EI: Clinical predictive factors in diabetic
kidney disease progression. J Diabetes Investig. 8:6–18. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang K, Hu J, Luo T, Wang Y, Yang S, Qing
H, Cheng Q and Li Q: Effects of Angiotensin-converting enzyme
inhibitors and Angiotensin II receptor blockers on All-Cause
mortality and renal outcomes in patients with diabetes and
albuminuria: A systematic review and Meta-analysis. Kidney Blood
Press Res. 43:768–779. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Palmer SC, Tendal B, Mustafa RA, Vandvik
PO, Li S, Hao Q, Tunnicliffe D, Ruospo M, Natale P, Saglimbene V,
et al: Sodium-glucose cotransporter protein-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors
and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists for type 2
diabetes: Systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised
controlled trials. BMJ. 372:m45732021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
American Diabetes Association. 6. Glycemic
Targets, . Standards of medical care in diabetes-2020. Diabetes
Care. 43 (Suppl 1):S66–S76. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Taylor SI: GLP-1 receptor agonists:
Differentiation within the class. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.
6:83–85. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ayodele OE, Alebiosu CO and Salako BL:
Diabetic nephropathy-a review of the natural history, burden, risk
factors and treatment. J Natl Med Assoc. 96:1445–1454. 2004.
|
|
13
|
Saito N, Toyoda M, Kondo M, Abe M,
Sanechika N, Kimura M, Sawada K and Fukagawa M: Regulation of renin
expression by Β1-Integrin in As4.1 juxtaglomerular line cells.
Biomedicines. 11:5012023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Writing Group of 2018 Chinese Guidelines
for the Management of Hypertension, Chinese Hypertension League,
Chinese Society of Cardiology, Chinese Medical Doctor Association
Hypertension Committee, Hypertension Branch of China International
Exchange, Promotive Association for Medical, Health Care and the
Hypertension Branch of Chinese Geriatric Medical Association, .
2018 Chinese guidelines for the management of hypertension. Chin J
Cardiovasc Med. 24:24–56. 2019.(In Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Han H, Chen Y, Yang H, Cheng W, Zhang S,
Liu Y, Liu Q, Liu D, Yang G and Li K: Identification and
verification of diagnostic biomarkers for glomerular injury in
diabetic nephropathy based on machine learning algorithms. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 13:8769602022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–1796. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Cruz-Solbes AS and Youker K: Epithelial to
mesenchymal transition (EMT) and endothelial to mesenchymal
transition (EndMT): Role and implications in kidney fibrosis.
Results Probl Cell Differ. 60:345–372. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu R, Mu J, Chen X, Zhang Y, Gao X, Li L,
Luo Q, Feng Q, He S and Pu D: miR-126-5p influences
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal tubular epithelial cells
of diabetic nephropathy by targeting Peli2. Anhui Med
Pharmaceutical J. 25:1428–1432
|
|
19
|
Guo HB, Liu YX, Jia JY and Yan TK: miR-451
negatively regulates EMT of the diabetic nephropathy by Akt. Basic
Clin Med. 40:469–472. 2020.
|
|
20
|
Li Y, Zhang Y, Shi H, Liu X, Li Z, Zhang
J, Wang X, Wang W and Tong X: CRTC2 activates the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of diabetic kidney disease
through the CREB-Smad2/3 pathway. Mol Med. 29:1462023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jia J, Tan R, Xu L, Wang H, Li J, Su H,
Zhong X, Liu P and Wang L: Hederagenin improves renal fibrosis in
diabetic nephropathy by regulating Smad3/NOX4/SLC7A11
signaling-mediated tubular cell ferroptosis. Int Immunopharmacol.
135:1123032024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Li Y, Hu Q, Li C, Liang K, Xiang Y, Hsiao
H, Nguyen TK, Park PK, Egranov SD, Ambati CR, et al: PTEN-induced
partial epithelial-mesenchymal transition drives diabetic kidney
disease. J Clin Invest. 129:1129–1151. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Li X, Miao Y, Li T, Liu X, Xu L, Guo J, Yu
X, Sun B, Zhu Y, Ai D and Chen L: Integrin β6 mediates
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in diabetic kidney disease. Mol
Cell Endocrinol. 572:1119552023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Daniels Gatward LF, Kennard MR, Smith LIF
and King AJF: The use of mice in diabetes research: The impact of
physiological characteristics, choice of model and husbandry
practices. Diabet Med. 38:e147112021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Leary S, Underwood W, Anthony R, Cartner
S, Grandin T, Greenacre C, Gwaltney-Brant S, McCrackin MA, Meyer R,
Miller D, et al: AVMA Guidelines for the Euthanasia of Animals:
2020 edition. Available from:. https://www.avma.org/sites/default/files/2020-02/Guidelines-on-Euthanasia-2020.pdf
|
|
26
|
Pan Y, Jiang S, Hou Q, Qiu D, Shi J, Wang
L, Chen Z, Zhang M, Duan A, Qin W, et al: Dissection of glomerular
transcriptional profile in patients with diabetic nephropathy:
SRGAP2a protects podocyte structure and function. Diabetes.
67:717–730. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ju W, Greene CS, Eichinger F, Nair V,
Hodgin JB, Bitzer M, Lee YS, Zhu Q, Kehata M, Li M, et al: Defining
cell-type specificity at the transcriptional level in human
disease. Genome Res. 23:1862–1873. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Grayson PC, Eddy S, Taroni JN, Lightfoot
YL, Mariani L, Parikh H, Lindenmeyer MT, Ju W, Greene CS, Godfrey
B, et al: Metabolic pathways and immunometabolism in rare kidney
diseases. Ann Rheum Dis. 77:1226–1233. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang C, Delcher C, Shenkman E and Ranka S:
Machine learning approaches for predicting high cost high need
patient expenditures in health care. Biomed Eng Online. 17 (Suppl
1):S1312018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhang J, Yu R, Guo X, Zou Y, Chen S, Zhou
K, Chen Y, Li Y, Gao S and Wu Y: Identification of TYR, TYRP1, DCT
and LARP7 as related biomarkers and immune infiltration
characteristics of vitiligo via comprehensive strategies.
Bioengineered. 12:2214–2227. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lin X, Li C, Zhang Y, Su B, Fan M and Wei
H: Selecting feature subsets based on SVM-RFE and the overlapping
ratio with applications in bioinformatics. Molecules. 23:522017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li K, Tang H, Cao X, Zhang X and Wang X:
PTEN: A novel diabetes nephropathy protective gene related to
cellular senescence. Int J Mol Sci. 26:30882025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wilson PC, Wu H, Kirita Y, Uchimura K,
Ledru N, Rennke HG, Welling PA, Waikar SS and Humphreys BD: The
single-cell transcriptomic landscape of early human diabetic
nephropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 116:19619–19625. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Newman AM, Liu CL, Green MR, Gentles AJ,
Feng W, Xu Y, Hoang CD, Diehn M and Alizadeh AA: Robust enumeration
of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat Methods.
12:453–457. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fu Y, Sun Y, Wang M, Hou Y, Huang W, Zhou
D, Wang Z, Yang S, Tang W, Zhen J, et al: Elevation of JAML
promotes diabetic kidney disease by modulating podocyte lipid
metabolism. Cell Metab. 32:1052–1062.e8. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li Y, Duan Y, Chu Q, Lv H, Li J, Guo X,
Gao Y, Liu M, Tang W, Hu H, et al: G-protein coupled receptor
GPR124 protects against podocyte senescence and injury in diabetic
kidney disease. Kidney Int. 107:652–665. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Xu Z, Jia K, Wang H, Gao F, Zhao S, Li F
and Hao J: METTL14-regulated PI3K/Akt signaling pathway via PTEN
affects HDAC5-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition of renal
tubular cells in diabetic kidney disease. Cell Death Dis.
12:322021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Singh M, Yelle N, Venugopal C and Singh
SK: EMT: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Pharmacol Ther.
182:80–94. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Aiello NM and Kang Y: Context-dependent
EMT programs in cancer metastasis. J Exp Med. 216:1016–1026. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Alicic RZ, Rooney MT and Tuttle KR:
Diabetic kidney disease: Challenges, progress, and possibilities.
Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 12:2032–2045. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Li A, Peng R, Sun Y, Liu H, Peng H and
Zhang Z: LincRNA 1700020I14Rik alleviates cell proliferation and
fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy via miR-34a-5p/Sirt1/HIF-1α
signaling. Cell Death Dis. 9:4612018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang LH, Liu JY and Wang RX: Research
progress on the regulatory mechanism of epithelial mesenchymal
transformation and its role in renal fibrosis. J Gannan Med Univ.
44:634–640. 2024.
|
|
44
|
Zhang L, Shen ZY, Wang K, Li W, Shi JM,
Osoro EK, Ullah N, Zhou Y and Ji SR: C-reactive protein exacerbates
epithelial-mesenchymal transition through Wnt/β-catenin and ERK
signaling in streptozocin-induced diabetic nephropathy. FASEB J.
33:6551–6563. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Teng S, Liu G, Li L, Ou J and Yu Y: CUX1
promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in renal fibrosis
of UUO model by targeting MMP7. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
608:128–134. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Juin SK, Pushpakumar S, Tyagi SC and Sen
U: Glucosidase inhibitor, Nimbidiol ameliorates renal fibrosis and
dysfunction in type-1 diabetes. Sci Rep. 12:217072022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yang G, Zhao Z, Zhang X, Wu A, Huang Y,
Miao Y and Yang M: Effect of berberine on the renal tubular
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by inhibition of the
Notch/snail pathway in diabetic nephropathy model KKAy mice. Drug
Des Devel Ther. 11:1065–1079. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li Z, Feng J, Zhong J, Lu M, Gao X and
Zhang Y: Screening of the key genes and signalling pathways for
diabetic nephropathy using bioinformatics analysis. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 13:8644072022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Gui H, Chen X, Ye L and Ma H: Seven
basement membrane-specific expressed genes are considered potential
biomarkers for the diagnosis and treatment of diabetic nephropathy.
Acta Diabetol. 60:493–505. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Speziale P, Arciola CR and Pietrocola G:
Fibronectin and its role in human infective diseases. Cells.
8:15162019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Patten J and Wang K: Fibronectin in
development and wound healing. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 170:353–368.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhang H, Chen X, Xue P, Ma X, Li J and
Zhang J: FN1 promotes chondrocyte differentiation and collagen
production via TGF-β/PI3K/Akt pathway in mice with femoral
fracture. Gene. 769:1452532021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yen CY, Huang CY, Hou MF, Yang YH, Chang
CH, Huang HW, Chen CH and Chang HW: Evaluating the performance of
fibronectin 1 (FN1), integrin α4β1 (ITGA4), syndecan-2 (SDC2), and
glycoprotein CD44 as the potential biomarkers of oral squamous cell
carcinoma (OSCC). Biomarkers. 18:63–72. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ma LJ, Lee SW, Lin LC, Chen TJ, Chang IW,
Hsu HP, Chang KY, Huang HY and Li CF: Fibronectin overexpression is
associated with latent membrane protein 1 expression and has
independent prognostic value for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Tumour
Biol. 35:1703–1712. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Lou X, Han X, Jin C, Tian W, Yu W, Ding D,
Cheng L, Huang B, Jiang H and Lin B: SOX2 targets fibronectin 1 to
promote cell migration and invasion in ovarian cancer: New
molecular leads for therapeutic intervention. OMICS. 17:510–518.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Waalkes S, Atschekzei F, Kramer MW,
Hennenlotter J, Vetter G, Becker JU, Stenzl A, Merseburger AS,
Schrader AJ, Kuczyk MA and Serth J: Fibronectin 1 mRNA expression
correlates with advanced disease in renal cancer. BMC Cancer.
10:5032010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Cai X, Liu C, Zhang TN, Zhu YW, Dong X and
Xue P: Down-regulation of FN1 inhibits colorectal carcinogenesis by
suppressing proliferation, migration and invasion. J Cell Biochem.
119:4717–4728. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Zhou LT, Qiu S, Lv LL, Li ZL, Liu H, Tang
RN, Ma KL and Liu BC: Integrative bioinformatics analysis provides
insight into the molecular mechanisms of chronic kidney disease.
Kidney Blood Press Res. 43:568–581. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Chowdhury B, Zhang Z and Mukherjee AB:
Uteroglobin interacts with the heparin-binding site of fibronectin
and prevents fibronectin-IgA complex formation found in
IgA-nephropathy. FEBS Lett. 582:611–615. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Stehr AM, Wang G, Demmler R, Stemmler MP,
Krug J, Tripal P, Schmid B, Geppert CI, Hartmann A, Muñoz LE, et
al: Neutrophil extracellular traps drive epithelial-mesenchymal
transition of human colon cancer. J Pathol. 256:455–467. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Brabletz T, Kalluri R, Nieto MA and
Weinberg RA: EMT in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 18:128–134. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Li B, Shen W, Peng H, Li Y, Chen F, Zheng
L, Xu J and Jia L: Fibronectin 1 promotes melanoma proliferation
and metastasis by inhibiting apoptosis and regulating EMT. Onco
Targets Ther. 12:3207–3221. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Dallas SL, Keene DR, Bruder SP, Saharinen
J, Sakai LY, Mundy GR and Bonewald LF: Role of the latent
transforming growth factor beta binding protein 1 in
fibrillin-containing microfibrils in bone cells in vitro and in
vivo. J Bone Miner Res. 15:68–81. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Dallas SL, Sivakumar P, Jones CJ, Chen Q,
Peters DM, Mosher DF, Humphries MJ and Kielty CM: Fibronectin
regulates latent transforming growth factor-beta (TGF beta) by
controlling matrix assembly of latent TGF beta-binding protein-1. J
Biol Chem. 280:18871–18880. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Massagué J: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in development and pathologies. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
15:740–746. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Derynck R and Akhurst RJ: Differentiation
plasticity regulated by TGF-beta family proteins in development and
disease. Nat Cell Biol. 9:1000–1004. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Hills CE and Squires PE: The role of TGF-β
and epithelial-to mesenchymal transition in diabetic nephropathy.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 22:131–139. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Griggs LA, Hassan NT, Malik RS, Griffin
BP, Martinez BA, Elmore LW and Lemmon CA: Fibronectin fibrils
regulate TGF-β1-induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal transition. Matrix
Biol. 60-61:157–175. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Yu SM and Bonventre JV: Acute kidney
injury and progression of diabetic kidney disease. Adv Chronic
Kidney Dis. 25:166–180. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Wada J and Makino H: Innate immunity in
diabetes and diabetic nephropathy. Nat Rev Nephrol. 12:13–26. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Zhu HM, Liu N, Sun DX and Luo L:
Machine-learning algorithm-based prediction of a diagnostic model
based on oxidative stress-related genes involved in immune
infiltration in diabetic nephropathy patients. Front Immunol.
14:12022982023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Xu M, Zhou H, Hu P, Pan Y, Wang S, Liu L
and Liu X: Identification and validation of immune and oxidative
stress-related diagnostic markers for diabetic nephropathy by WGCNA
and machine learning. Front Immunol. 14:10845312023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Ji L, Chen Y, Wang H, Zhang W, He L, Wu J
and Liu Y: Overexpression of Sirt6 promotes M2 macrophage
transformation, alleviating renal injury in diabetic nephropathy.
Int J Oncol. 55:103–115. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Chow F, Ozols E, Nikolic-Paterson DJ,
Atkins RC and Tesch GH: Macrophages in mouse type 2 diabetic
nephropathy: Correlation with diabetic state and progressive renal
injury. Kidney Int. 65:116–128. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Tesch GH: Macrophages and diabetic
nephropathy. Semin Nephrol. 30:290–301. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Hofkens W, Storm G, Berg WVD and Lent PV:
Inhibition of M1 macrophage activation in favour of M2
differentiation by liposomal targeting of glucocorticoids to the
synovial lining during experimental arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 70
(Suppl 2):S702011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Gordon S: Alternative activation of
macrophages. Nat Rev Immunol. 3:23–35. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Kim H, Kim1 M, Lee HY, Park HY, Jhun H and
Kim S: Role of dendritic cell in diabetic nephropathy. Int J Mol
Sci. 22:75542021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Li HD, You YK, Shao BY, Wu WF, Wang YF,
Guo JB, Meng XM and Chen H: Roles and crosstalks of macrophages in
diabetic nephropathy. Front Immunol. 13:10151422022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Liang D, Liu L, Qi Y, Nan F, Huang J, Tang
S, Tang J and Chen N: Jin-Gui-Shen-Qi Wan alleviates fibrosis in
mouse diabetic nephropathy via MHC class II. J Ethnopharmacol.
324:1177452024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Zhou Y, Luo Z, Liao C, Cao R, Hussain Z,
Wang J, Zhou Y, Chen T, Sun J, Huang Z, et al: MHC class II in
renal tubules plays an essential role in renal fibrosis. Cell Mol
Immunol. 18:2530–2540. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|