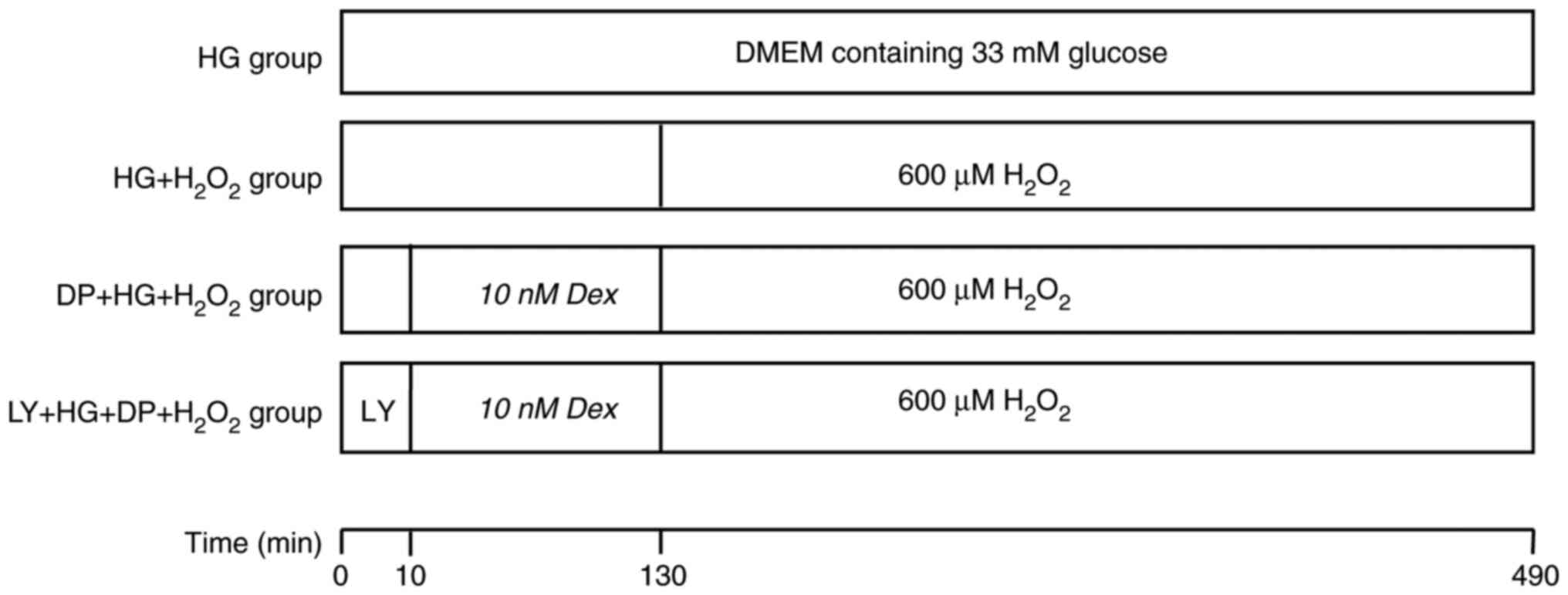
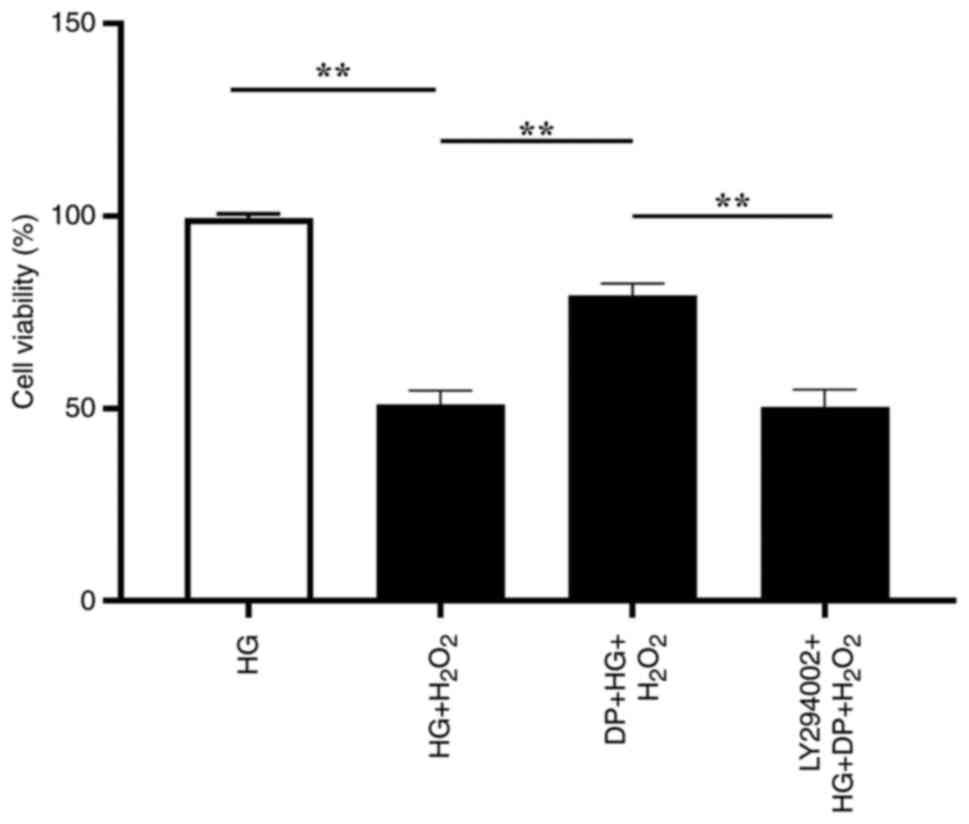
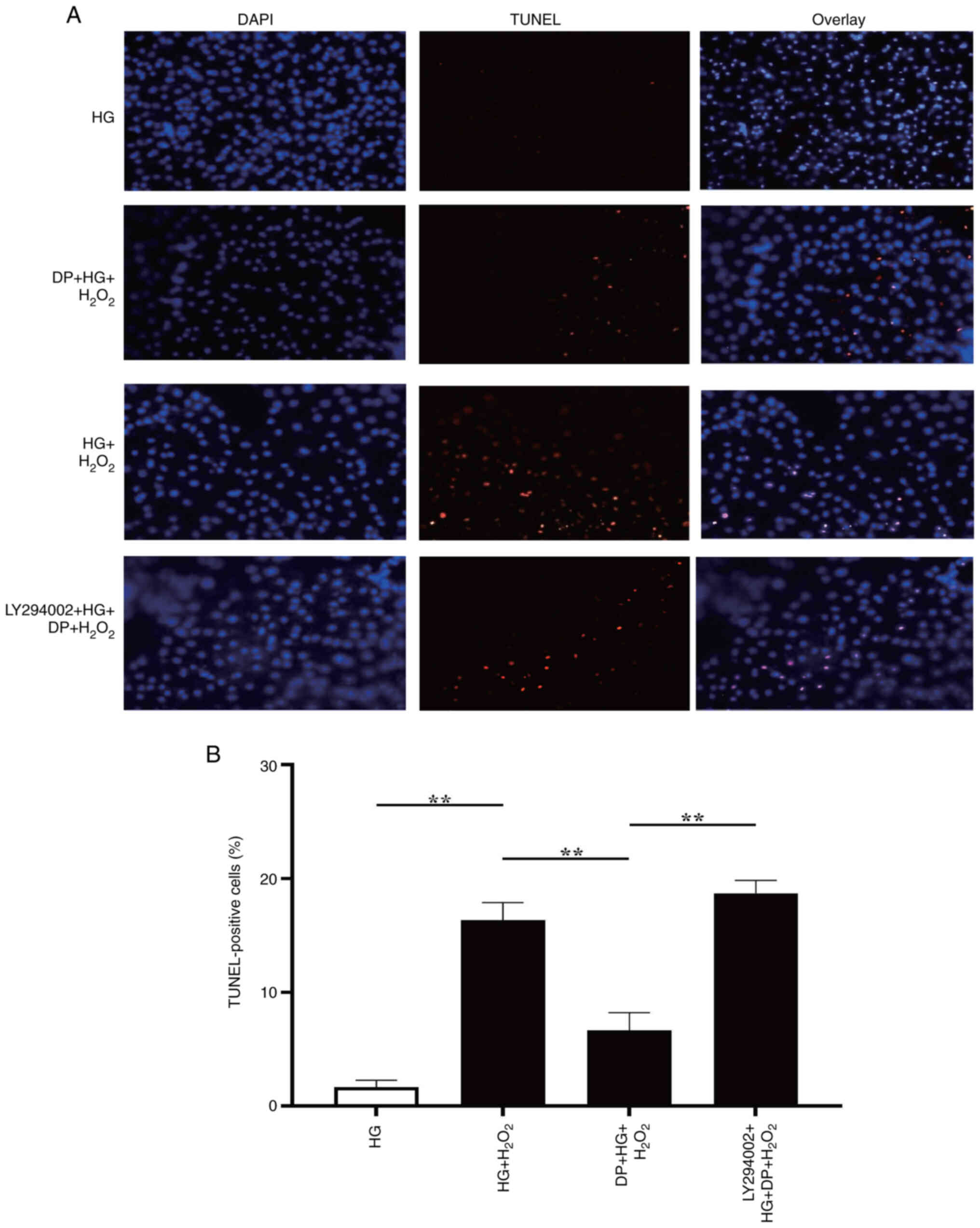
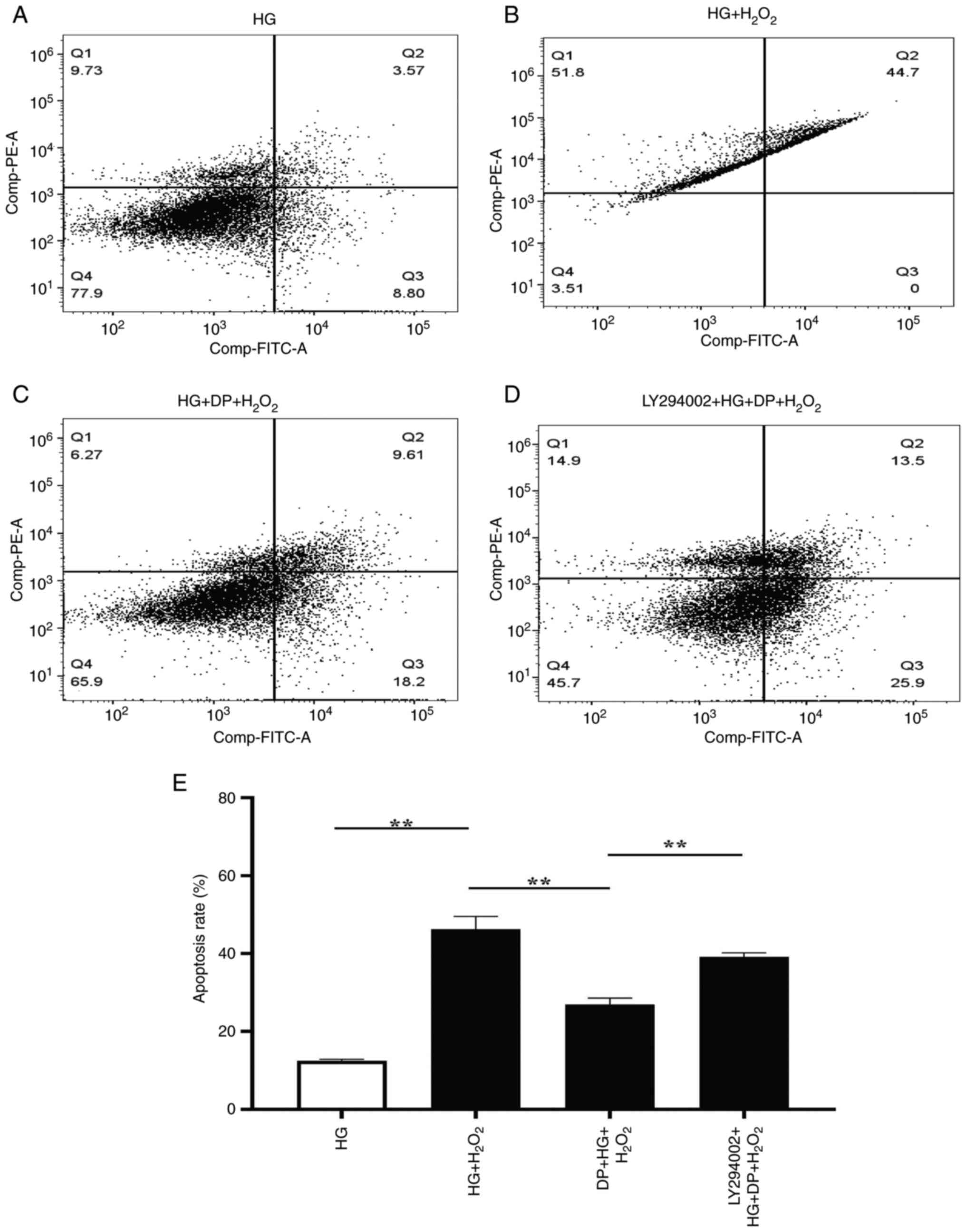
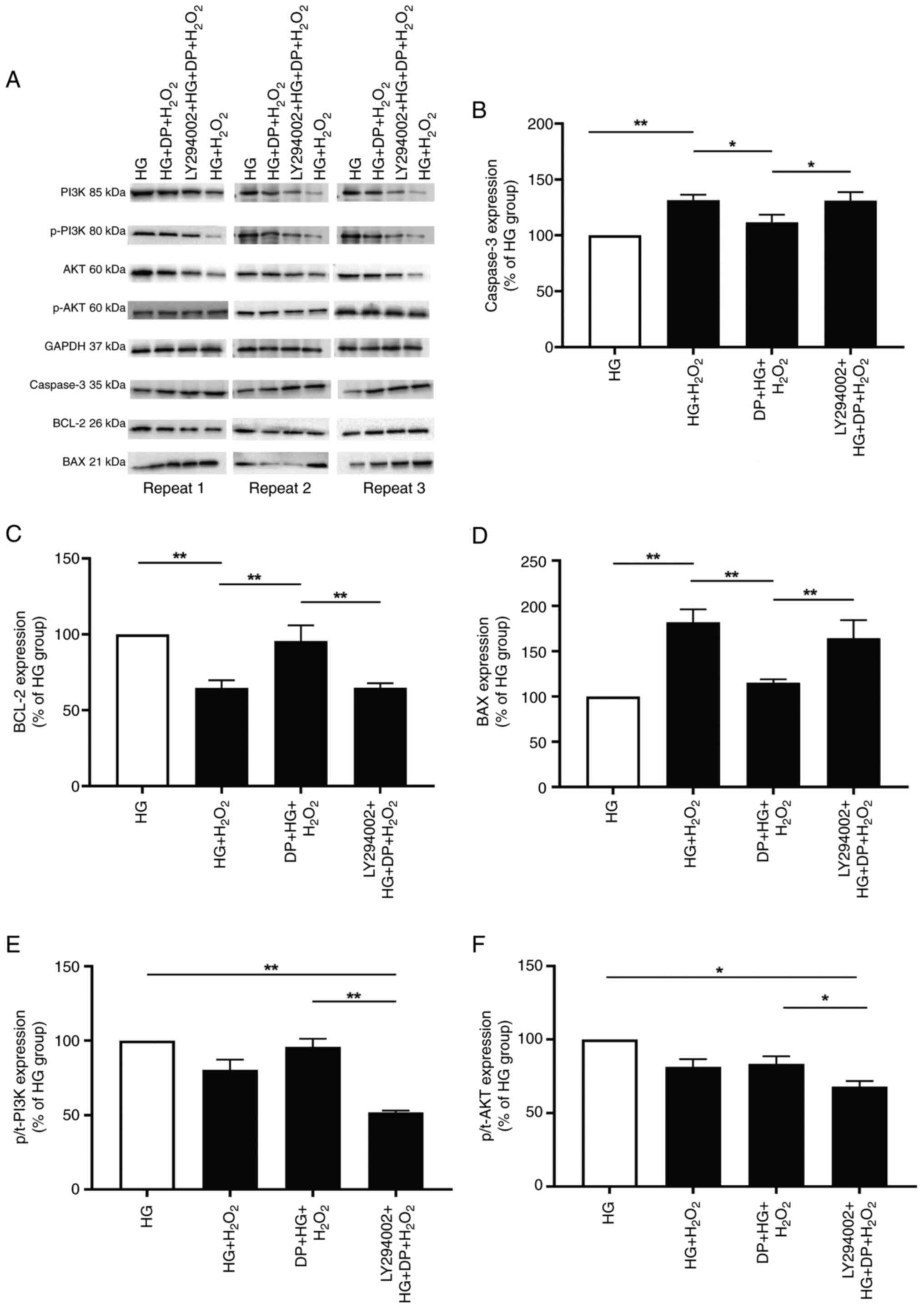
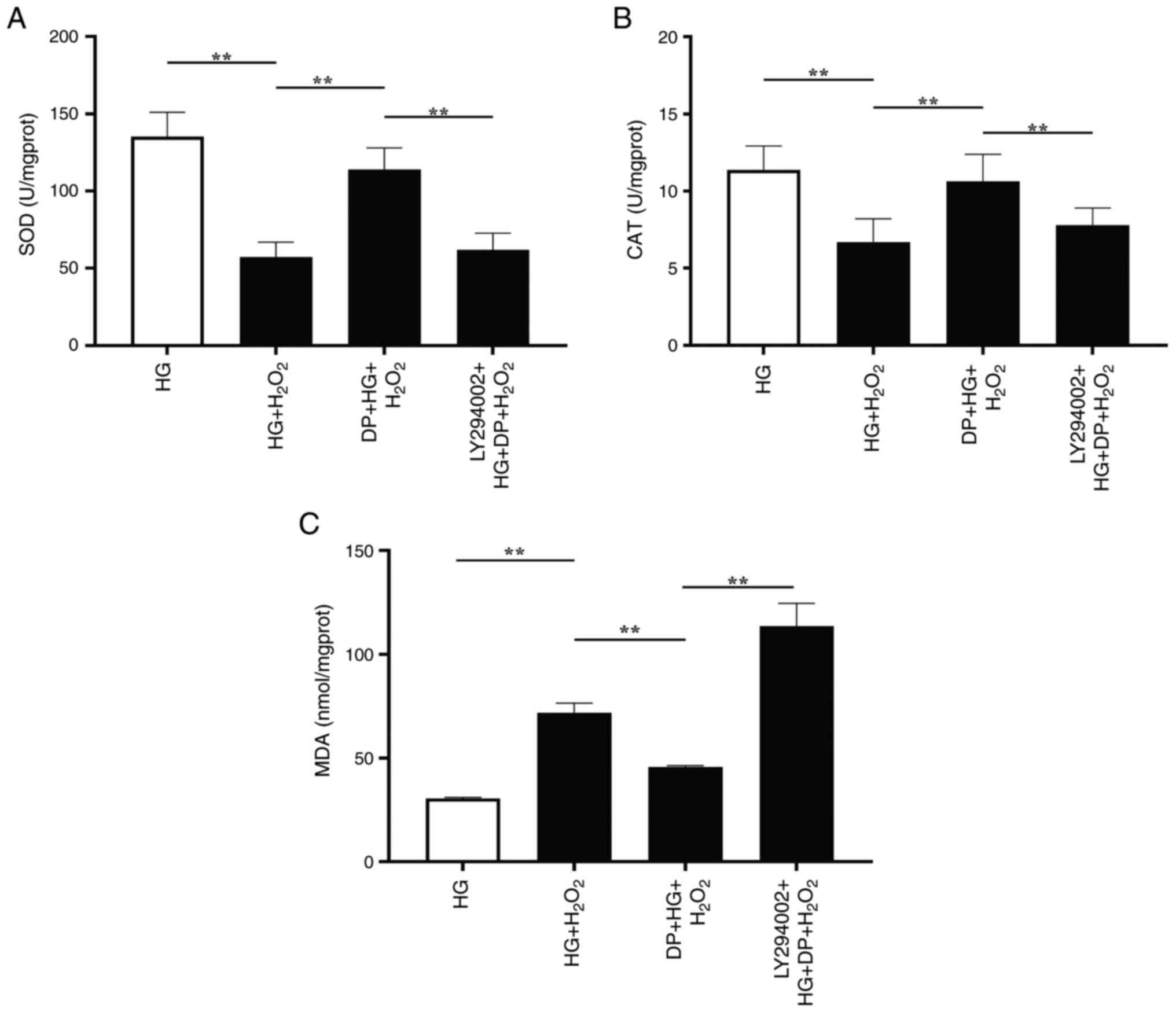
|
1
|
World Health Organization, . The top 10
causes of death, 2024. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-deathJune
18–2025
|
|
2
|
Frangogiannis NG: Pathophysiology of
myocardial infarction. Compr Physiol. 5:1841–1875. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Norhammar A, Kjellström B, Habib N,
Gustafsson A, Klinge B, Nygren Å, Näsman P, Svenungsson E and Rydén
L: Undetected dysglycemia is an important risk factor for two
common diseases, myocardial infarction and periodontitis: A report
from the PAROKRANK study. Diabetes Care. 42:1504–1511. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nepogodiev D, Martin J, Biccard B, Makupe
A and Bhangu A: Global burden of postoperative death. Lancet.
393:4012019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Liang S, Wang Y and Liu Y: Dexmedetomidine
alleviates lung ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by activating
PI3K/Akt pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:370–377. 2019.
|
|
6
|
Xiong W, Zhou R, Qu Y, Yang Y, Wang Z,
Song N, Liang R and Qian J: Dexmedetomidine preconditioning
mitigates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via inhibition of
mast cell degranulation. Biomed Pharmacother. 141:1118532021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu Y, Qiu G, Zhang H, Zhu L, Cheng G, Wang
Y, Li Y and Wu W: Dexmedetomidine alleviates hepatic
ischaemia-reperfusion injury via the PI3K/AKT/Nrf2-NLRP3 pathway. J
Cell Mol Med. 25:9983–9994. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hou M, Chen F, He Y, Tan Z, Han X, Shi Y,
Xu Y and Leng Y: Dexmedetomidine against intestinal
ischemia/reperfusion injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis
of preclinical studies. Eur J Pharmacol. 959:1760902023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Feng J, Li Y, Li Y, Yin Q, Li H, Li J,
Zhou B, Meng J, Lian H, Wu M, et al: Versican promotes
cardiomyocyte proliferation and cardiac repair. Circulation.
149:1004–1015. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li YZ, Wu XD, Liu XH and Li PF: Mitophagy
imbalance in cardiomyocyte ischaemia/reperfusion injury. Acta
Physiol (Oxf). 225:e132282019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Su H, Ji L, Xing W, Zhang W, Zhou H, Qian
X, Wang X, Gao F, Sun X and Zhang H: Acute hyperglycaemia enhances
oxidative stress and aggravates myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion
injury: Role of thioredoxin-interacting protein. J Cell Mol Med.
17:181–191. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Forman HJ and Zhang H: Targeting oxidative
stress in disease: Promise and limitations of antioxidant therapy.
Nat Rev Drug Discov. 20:689–709. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Teleanu DM, Niculescu AG, Lungu II, Radu
CI, Vladâcenco O, Roza E, Costăchescu B, Grumezescu AM and Teleanu
RI: An overview of oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and
neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 23:59382022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yu J, Yang W, Wang W, Wang Z, Pu Y, Chen
H, Wang F and Qian J: Involvement of miR-665 in protection effect
of dexmedetomidine against oxidative stress injury in myocardial
cells via CB2 and CK1. Biomed Pharmacother. 115:1088942019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu J, Wu P, Xu Z, Zhang J, Liu J and Yang
Z: Ginkgolide B inhibits hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis and
attenuates cytotoxicity via activating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling
pathway in H9c2 cells. Mol Med Rep. 22:310–316. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mao CY, Lu HB, Kong N, Li JY, Liu M, Yang
CY and Yang P: Levocarnitine protects H9c2 rat cardiomyocytes from
H2O2-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis. Int J Med
Sci. 11:1107–1115. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wong SSC and Irwin MG: Peri-operative
cardiac protection for non-cardiac surgery. Anaesthesia. 71 (Suppl
1):S29–S39. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ollila A, Vikatmaa L, Sund R, Pettilä V
and Wilkman E: Efficacy and safety of intravenous esmolol for
cardiac protection in non-cardiac surgery. A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Ann Med. 51:17–27. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Davidson SM, Ferdinandy P, Andreadou I,
Bøtker HE, Heusch G, Ibáñez B, Ovize M, Schulz R, Yellon DM,
Hausenloy DJ, et al: Multitarget strategies to reduce myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury: JACC review topic of the week. J Am
Coll Cardiol. 73:89–99. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Thompson A, Fleischmann KE, Smilowitz NR,
de Las Fuentes L, Mukherjee D, Aggarwal NR, Ahmad FS, Allen RB,
Altin SE, Auerbach A, et al: 2024
AHA/ACC/ACS/ASNC/HRS/SCA/SCCT/SCMR/SVM guideline for perioperative
cardiovascular management for noncardiac surgery: A report of the
american college of cardiology/American heart association joint
committee on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation.
150:e351–e442. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Miki T, Itoh T, Sunaga D and Miura T:
Effects of diabetes on myocardial infarct size and cardioprotection
by preconditioning and postconditioning. Cardiovasc Diabetol.
11:672012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Torregroza C, Feige K, Schneider L, Bunte
S, Stroethoff M, Heinen A, Hollmann MW, Huhn R and Raupach A:
Influence of hyperglycemia on dexmedetomidine-induced
cardioprotection in the isolated perfused rat heart. J Clin Med.
9:14452020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Harding JL, Pavkov ME, Magliano DJ, Shaw
JE and Gregg EW: Global trends in diabetes complications: A review
of current evidence. Diabetologia. 62:3–16. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Xie Y, Shi X, Sheng K, Han G, Li W, Zhao
Q, Jiang B, Feng J, Li J and Gu Y: PI3K/Akt signaling transduction
pathway, erythropoiesis and glycolysis in hypoxia (review). Mol Med
Rep. 19:783–791. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Abdelmoneim SS, Hagen ME, Mendrick E,
Pattan V, Wong B, Norby B, Roberson T, Szydel T, Basu R, Basu A and
Mulvagh SL: Acute hyperglycemia reduces myocardial blood flow
reserve and the magnitude of reduction is associated with insulin
resistance: A study in nondiabetic humans using contrast
echocardiography. Heart Vessels. 28:757–768. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Muniyappa R and Quon MJ: Insulin action
and insulin resistance in vascular endothelium. Curr Opin Clin Nutr
Metab Care. 10:523–530. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huang X, Liu G, Guo J and Su Z: The
PI3K/AKT pathway in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Int J Biol Sci.
14:1483–1496. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yao M, Wang Z, Jiang L, Wang L, Yang Y,
Wang Q, Qian X, Zeng W, Yang W, Liang R and Qian J: Oxytocin
ameliorates high glucose- and ischemia/reperfusion-induced
myocardial injury by suppressing pyroptosis via AMPK signaling
pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 153:1134982022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kristiansen SB, Pælestik KB, Johnsen J,
Jespersen NR, Pryds K, Hjortbak MV, Jensen RV and Bøtker HE: Impact
of hyperglycemia on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion susceptibility
and ischemic preconditioning in hearts from rats with type 2
diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 18:662019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wang T, Li Z, Xia S, Xu Z, Chen X and Sun
H: Dexmedetomidine promotes cell proliferation and inhibits cell
apoptosis by regulating LINC00982 and activating the
phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) signaling
in hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced H9c2 cells. Bioengineered.
13:10159–10167. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yu T, Liu D, Gao M, Yang P, Zhang M, Song
F, Zhang X and Liu Y: Dexmedetomidine prevents septic myocardial
dysfunction in rats via activation of α7nAChR and PI3K/Akt-mediated
autophagy. Biomed Pharmacother. 120:1092312019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li H, Xu C, Li Q, Gao X, Sugano E, Tomita
H, Yang L and Shi S: Thioredoxin 2 offers protection against
mitochondrial oxidative stress in H9c2 cells and against myocardial
hypertrophy induced by hyperglycemia. Int J Mol Sci. 18:19582017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
World Health Organization, . Diabetes.
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetesJune
18–2025
|
|
34
|
Qamar F, Sultana S and Sharma M: Animal
models for induction of diabetes and its complications. J Diabetes
Metab Disord. 22:1021–1028. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mapanga R and FEssop MF: Damaging effects
of hyperglycemia on cardiovascular function: Spotlight on glucose
metabolic pathways. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 310:H153–H173.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Mapanga RF, Joseph D, Symington B, Garson
KL, Kimar C, Kelly-Laubscher R and Essop MF: Detrimental effects of
acute hyperglycaemia on the rat heart. Acta Physiol (Oxf).
210:546–564. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mapanga RF, Rajamani U, Dlamini N,
Zungu-Edmondson M, Kelly-Laubscher R, Shafiullah M, Wahab A, Hasan
MY, Fahim MA, Rondeau P, et al: Oleanolic acid: A novel
cardioprotective agent that blunts hyperglycemia-induced
contractile dysfunction. PLoS One. 7:e473222012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cui J, Zhang F, Wang Y, Liu J, Ming X, Hou
J, Lv B, Fang S and Yu B: Macrophage migration inhibitory factor
promotes cardiac stem cell proliferation and endothelial
differentiation through the activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR and
AMPK pathways. Int J Mol Med. 37:1299–1309. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hong F, Kwon SJ, Jhun BS, Kim SS, Ha J,
Kim SJ, Sohn NW, Kang C and Kang I: Insulin-like growth factor-1
protects H9c2 cardiac myoblasts from oxidative stress-induced
apoptosis via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and extracellular
signal-regulated kinase pathways. Life Sci. 68:1095–1105. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|