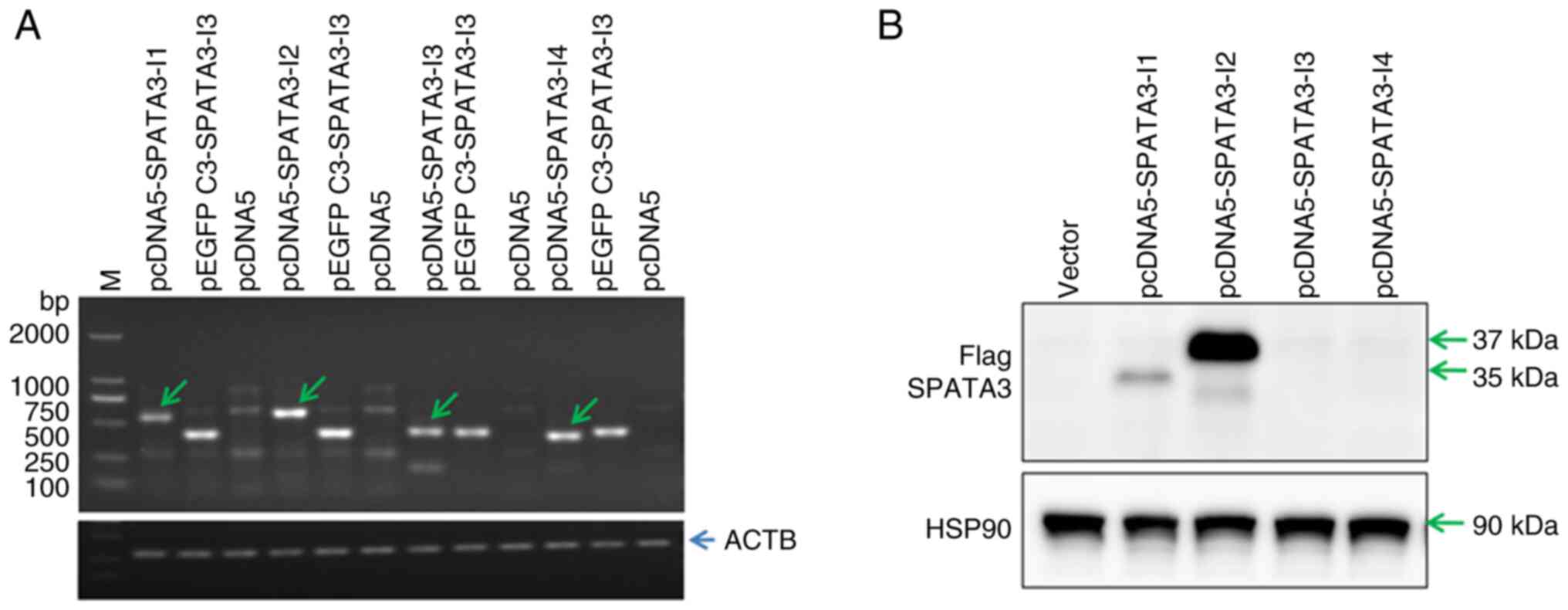
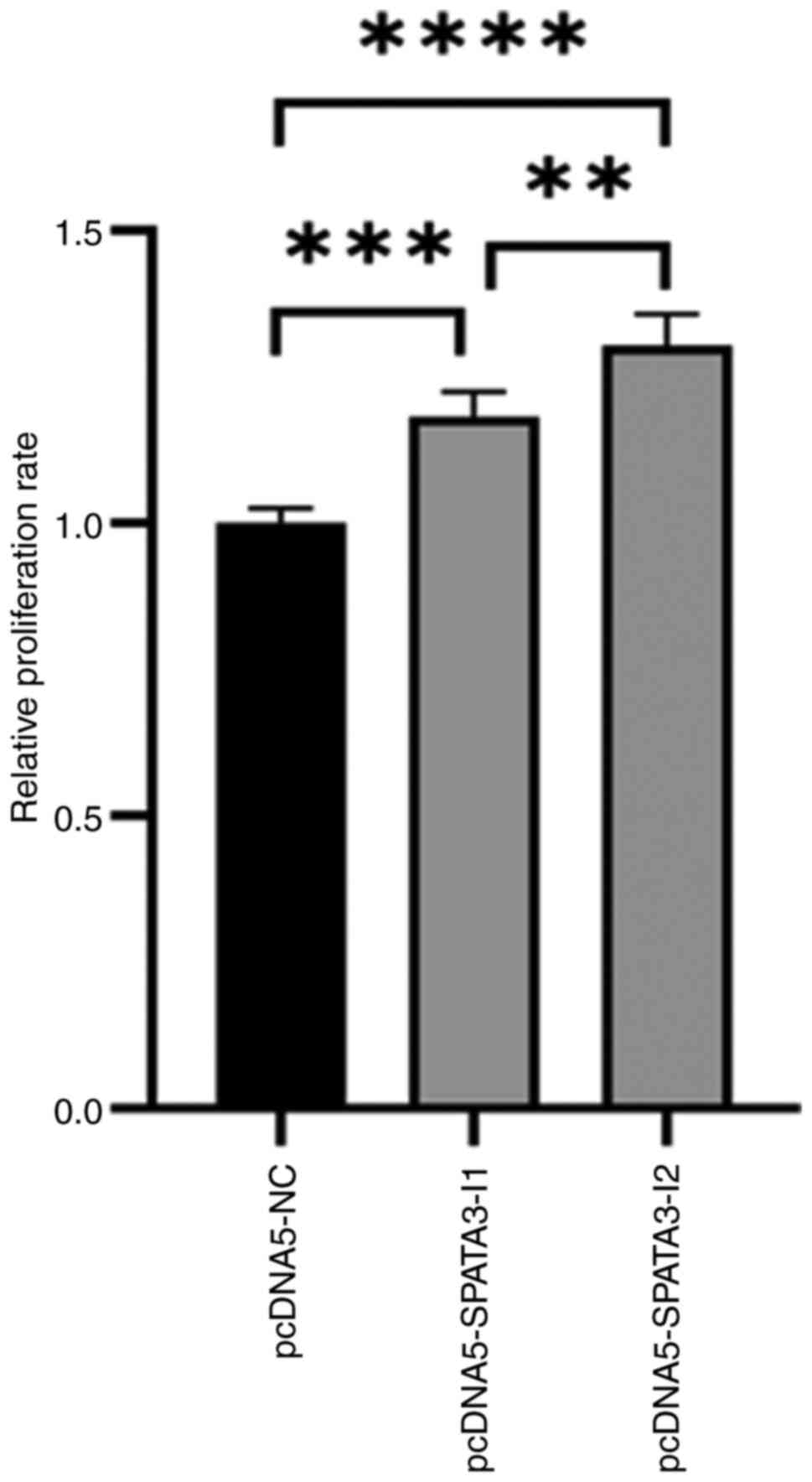
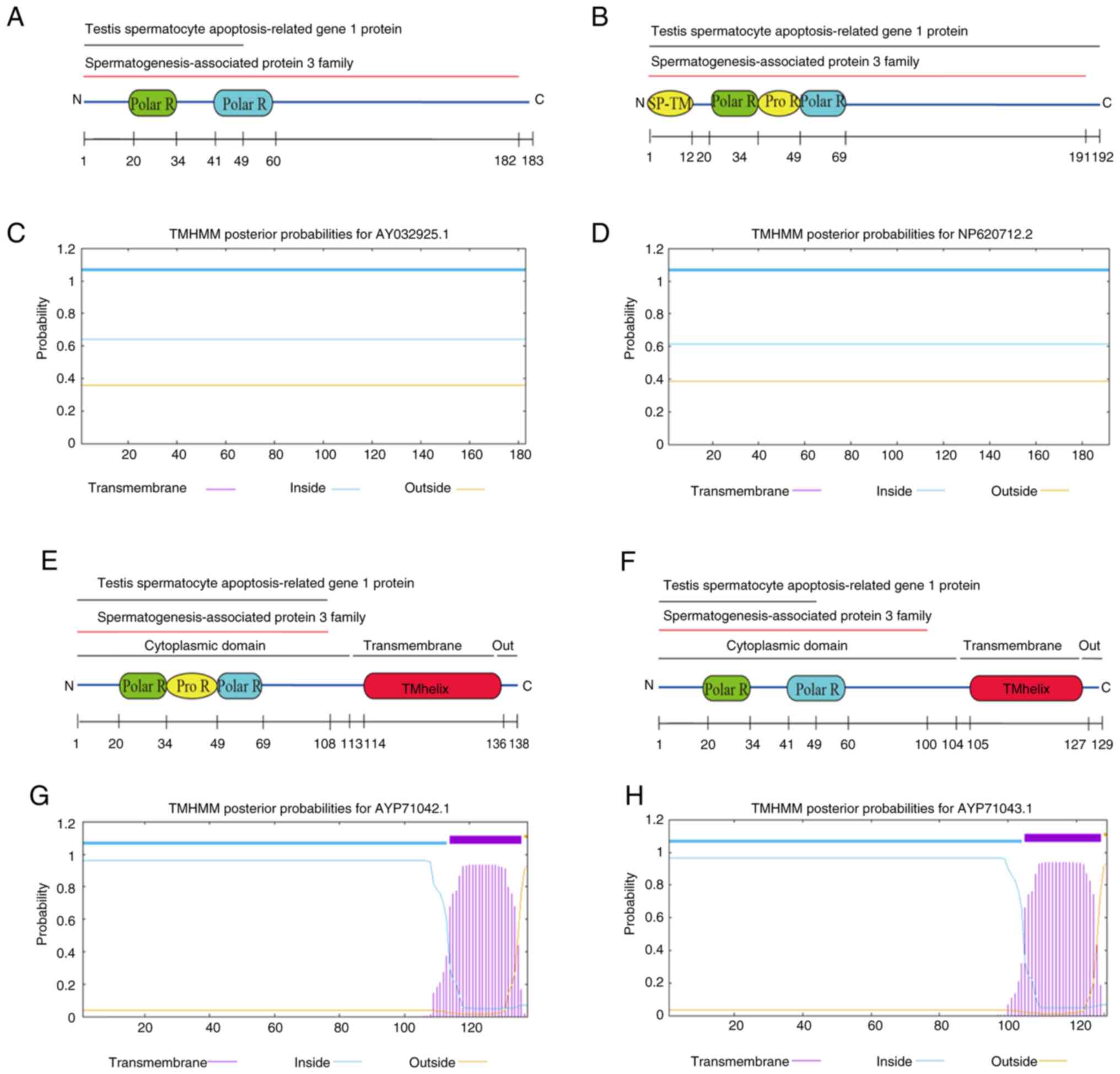
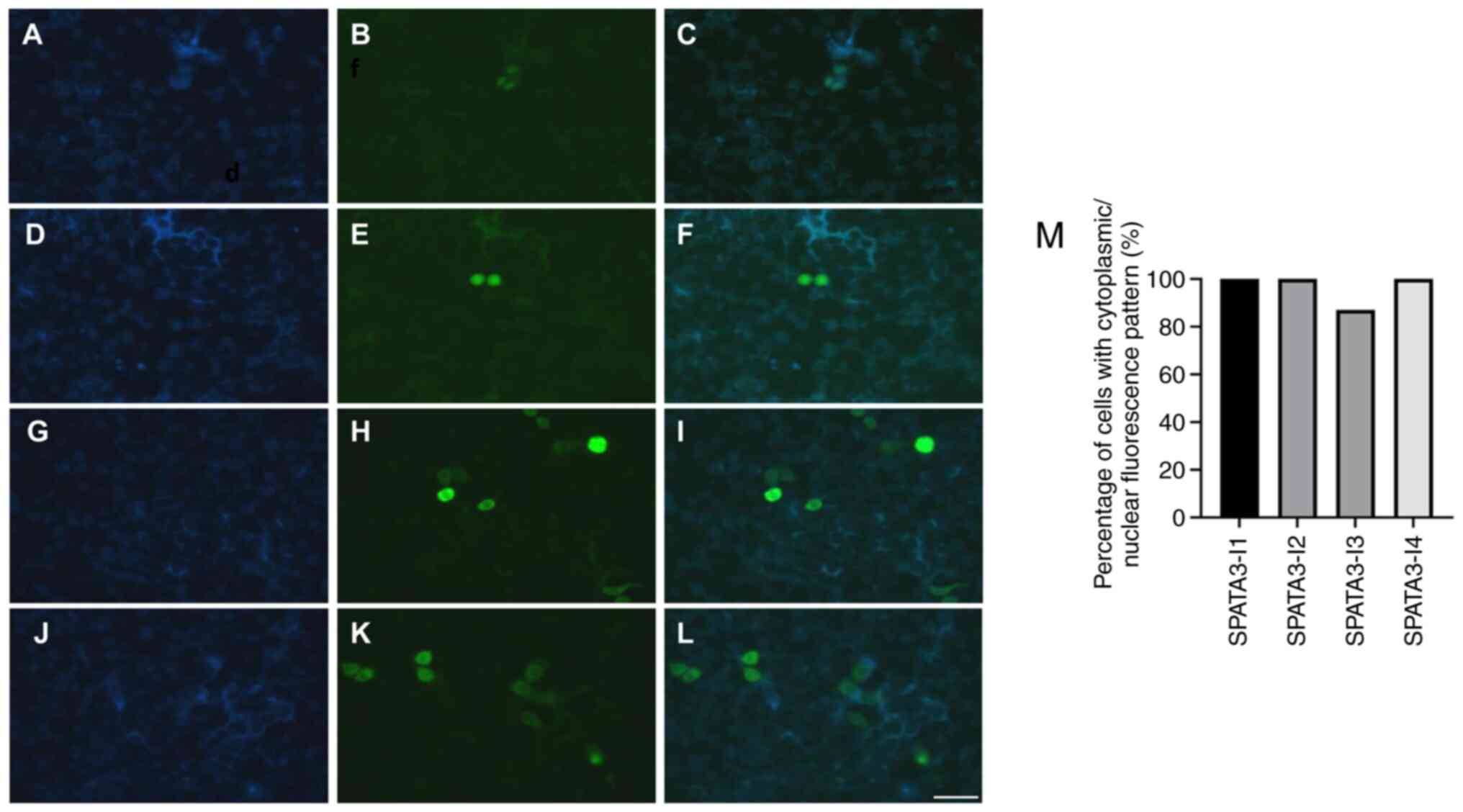
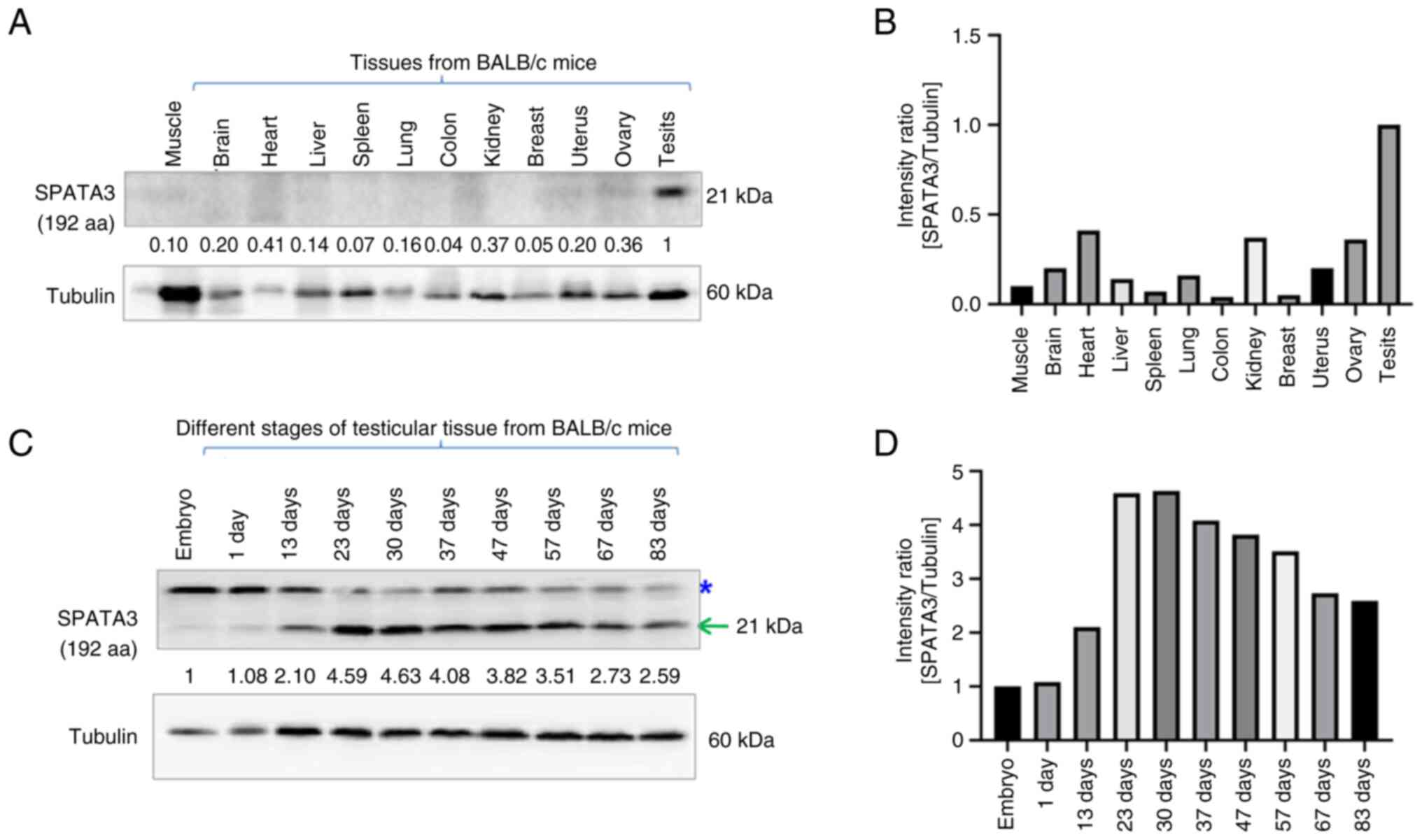
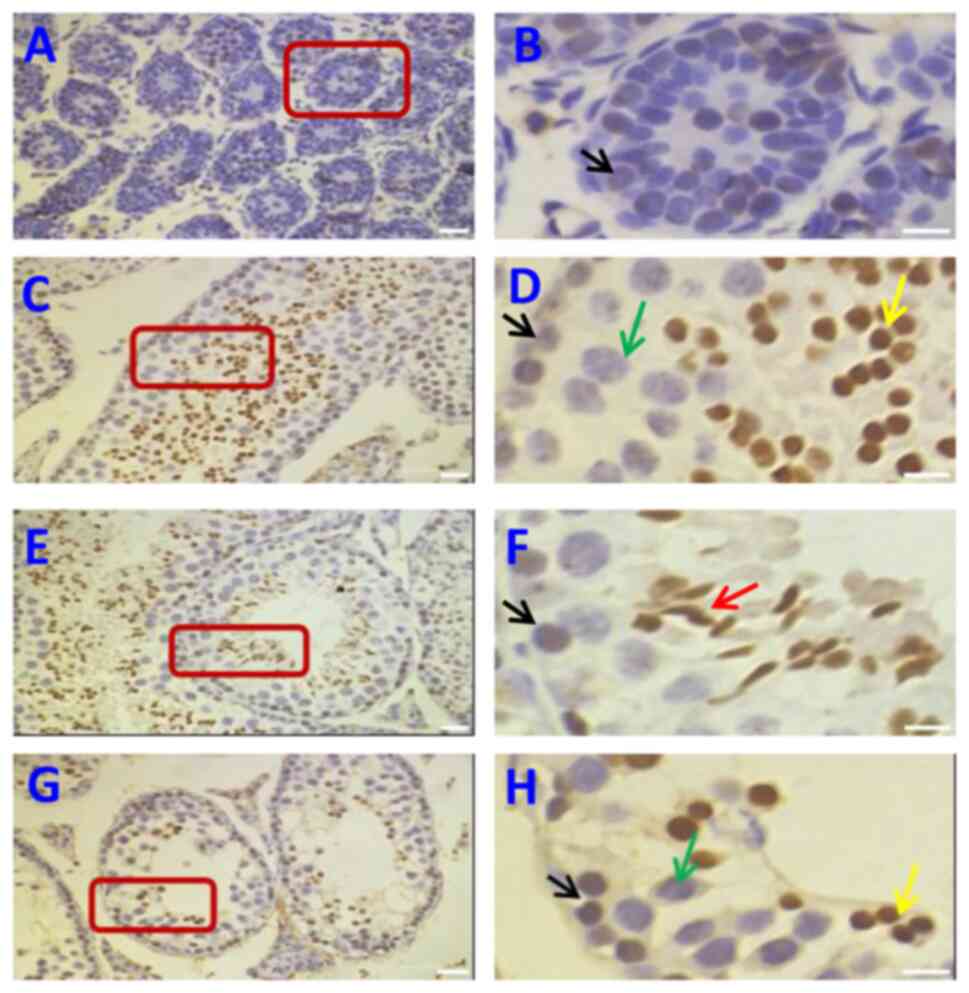
|
1
|
Rowe PJ, Comhaire FH, Hargreave B and
Mahmoud AMA: WHO Manual for the Standardized Investigation,
Diagnosis and Management of the Infertile Male. Cambridge
University Press; Cambridge, UK: pp. pp912000
|
|
2
|
Minhas S, Bettocchi C, Boeri L, Capogrosso
P, Carvalho J, Cilesiz NC, Cocci A, Corona G, Dimitropoulos K, Gül
M, et al: European association of urology guidelines on male sexual
and reproductive health: 2021 update on male infertility. Eur Urol.
80:603–620. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Agarwal A, Baskaran S, Parekh N, Cho CL,
Henkel R, Vij S, Arafa M, Panner Selvam MK and Shah R: Male
infertility. Lancet. 397:319–333. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fu L, Wu Q and Fu J: Exploring the
biological roles of DHX36, a DNA/RNA G-quadruplex helicase,
highlights functions in male infertility: A comprehensive review.
Int J Biol Macromol. 268((Pt 2)): 1318112024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Eisenberg ML, Esteves SC, Lamb DJ,
Hotaling JM, Giwercman A, Hwang K and Cheng YS: Male infertility.
Nat Rev Dis Primers. 9:492023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fu J, Li L and Lu G: Relationship between
microdeletion on Y chromosome and patients with idiopathic
azoospermia and severe oligozoospermia in the Chinese. Chin Med J
(Engl). 115:72–75. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fu L, Xiong DK, Ding XP, Li C, Zhang LY,
Ding M, Nie SS and Quan Q: Genetic screening for chromosomal
abnormalities and Y chromosome microdeletions in Chinese infertile
men. J Assist Reprod Genet. 29:521–527. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kuroda S, Usui K, Sanjo H, Takeshima T,
Kawahara T, Uemura H and Yumura Y: Genetic disorders and male
infertility. Reprod Med Biol. 19:314–322. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tüttelmann F, Ruckert C and Röpke A:
Disorders of spermatogenesis: Perspectives for novel genetic
diagnostics after 20 years of unchanged routine. Med Genet.
30:12–20. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gül M, Russo GI, Kandil H, Boitrelle F,
Saleh R, Chung E, Kavoussi P, Mostafa T, Shah R and Agarwal A: Male
infertility: New developments, current challenges, and future
directions. World J Mens Health. 42:502–517. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Y, Li R, Yang R, Zheng D, Zeng L,
Lian Y, Zhu Y, Zhao J, Liang X, Li W, et al: Intracytoplasmic sperm
injection versus conventional in-vitro fertilisation for couples
with infertility with non-severe male factor: A multicentre,
open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 403:924–934. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Palermo G, Joris H, Devroey P and Van
Steirteghem AC: Pregnancies after intracytoplasmic injection of
single spermatozoon into an oocyte. Lancet. 340:17–18. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Schlegel PN: Testicular sperm extraction:
Microdissection improves sperm yield with minimal tissue excision.
Hum Reprod. 14:131–135. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Griswold MD: Spermatogenesis: The
commitment to meiosis. Physiol Rev. 96:1–17. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhu X, Hu K, Cheng H, Wu H, Li K, Gao Y,
Lv M, Xu C, Geng H, Shen Q, et al: Novel MEIOB pathogenic variants
including a homozygous non-canonical splicing variant, cause
meiotic arrest and human non-obstructive azoospermia. Clin Genet.
105:99–105. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee TH, Song SH, Kim DK, Shim SH, Jeong D
and Kim DS: An analysis of Y-chromosome microdeletion in infertile
Korean men with severe oligozoospermia or azoospermia. Investig
Clin Urol. 65:77–83. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tsai-Morris CH, Sheng Y, Lee E, Lei KJ and
Dufau ML: Gonadotropin-regulated testicular RNA helicase
(GRTH/Ddx25) is essential for spermatid development and completion
of spermatogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:6373–6378. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liman N: Heat shock proteins are
differentially expressed in the domestic cat (Felis catus) testis,
epididymis, and vas deferens. Microsc Microanal. 29:713–738. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang X, Wang L, Ma Y, Wang Y, Liu H, Liu
M, Qin L, Li J, Jiang C, Zhang X, et al: CEP128 is involved in
spermatogenesis in humans and mice. Nat Commun. 13:13952022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Song H, Wang L, Chen D and Li F: The
function of Pre-mRNA alternative splicing in mammal
spermatogenesis. Int J Biol Sci. 16:38–48. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yan W, Suominen J, Samson M, Jégou B and
Toppari J: Involvement of Bcl-2 family proteins in germ cell
apoptosis during testicular development in the rat and pro-survival
effect of stem cell factor on germ cells in vitro. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 165:115–129. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xiao B, Li X, Feng XY, Gong S, Li ZB,
Zhang J, Yuan HJ and Tan JH: Restraint stress of male mice induces
apoptosis in spermatozoa and spermatogenic cells: role of the
FasL/Fas system†. Biol Reprod. 101:235–247. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li YQ, He QH, Zhou Q, Zhou X, Bin DH, Liu
CS and Guo JH: Impact of Ureaplasma urealyticum infection on the
MRPS22 protein expression in rat spermatogenic cells and
intervening effect of Zhibai Dihuang Decoction. Zhonghua Nan Ke
Xue. 25:55–61. 2019.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Feng Y, Shi J, Li M, Duan H and Shao B:
Evaluation of the cytotoxic activity of triphenyl phosphate on
mouse spermatocytes cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 90:1056072023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Turunen HT, Sipilä P, Strauss L, Björkgren
I, Huhtaniemi I and Poutanen M: Loss of Bmyc results in increased
apoptosis associated with upregulation of Myc expression in
juvenile murine testis. Reproduction. 144:495–503. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fu JJ, Lu GX, Li LY, Liu G, Xing XW and
Liu SF: Molecular cloning for testis spermatogenesis cell apoptosis
related gene TSARG1 and Mtsarg1 and expression analysis for Mtsarg1
gene. Yi Chuan Xue Bao. 30:25–29. 2003.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Malcher A, Rozwadowska N, Stokowy T,
Kolanowski T, Jedrzejczak P, Zietkowiak W and Kurpisz M: Potential
biomarkers of nonobstructive azoospermia identified in microarray
gene expression analysis. Fertil Steril. 100:1686–1694.e1-7. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou B, Wei C, Khan MA, Chen H and Fu J:
Characterization and molecular cloning of novel isoforms of human
spermatogenesis associated gene SPATA3. Mol Biol Rep. 46:3827–3834.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Girault MS, Dupuis S, Ialy-Radio C,
Stouvenel L, Viollet C, Pierre R, Favier M, Ziyyat A and Barbaux S:
Deletion of the Spata3 gene induces sperm alterations and in vitro
hypofertility in mice. Int J Mol Sci. 22:19592021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li M, Ma Q, Gong T, Zhang Y, Yan P, Zhai X
and Guo R: Bioinformatics analysis and primary identification of
the structure and function of mouse Spata3 protein. Acta
Laboratorium Animalis Scientia Sinica. 30:767–776. 2022.(In
Chinese).
|
|
31
|
Li L, Liu G, Fu JJ, Li LY, Tan XJ, Yang S
and Lu GX: Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel
transcript variant of Mtsarg1 gene. Mol Biol Rep. 36:1023–1032.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang Y, Wen L, Bai X, Cao R, Wang H and
Guo R: Novel expression of spermatogenesis-associated protein 3
gene in mouse spermatogenic cells and its influence upon apoptosis
and autophagy in HEK 293T cells. Acta Anatomica Sinica. 1:41–48.
2018.(In Chinese).
|
|
33
|
Choi S, Cho N and Kim KK: The implications
of alternative pre-mRNA splicing in cell signal transduction. Exp
Mol Med. 55:755–766. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Carey KT and Wickramasinghe VO: Regulatory
potential of the RNA processing machinery: Implications for human
disease. Trends Genet. 34:279–290. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Venables JP: Alternative splicing in the
testes. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 12:615–619. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhao F, Yan Y, Wang Y, Liu Y and Yang R:
Splicing complexity as a pivotal feature of alternative exons in
mammalian species. BMC Genomics. 24:1982023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yang X, Coulombe-Huntington J, Kang S,
Sheynkman GM, Hao T, Richardson A, Sun S, Yang F, Shen YA, Murray
RR, et al: Widespread expansion of protein interaction capabilities
by alternative splicing. Cell. 164:805–817. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Romeo-Cardeillac C, Trovero MF, Radío S,
Smircich P, Rodríguez-Casuriaga R, Geisinger A and Sotelo-Silveira
J: Uncovering a multitude of stage-specific splice variants and
putative protein isoforms generated along mouse spermatogenesis.
BMC Genomics. 25:2952024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Baralle FE and Giudice J: Alternative
splicing as a regulator of development and tissue identity. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 18:437–451. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Naro C, Cesari E and Sette C: Splicing
regulation in brain and testis: Common themes for highly
specialized organs. Cell Cycle. 20:480–489. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li Q, Li T, Xiao X, Ahmad DW, Zhang N, Li
H, Chen Z, Hou J and Liao M: Specific expression and alternative
splicing of mouse genes during spermatogenesis. Mol Omics.
16:258–267. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Legrand JMD and Hobbs RM: RNA processing
in the male germline: Mechanisms and implications for fertility.
Semin Cell Dev Biol. 79:80–91. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Fu J, Cheng J, Zhou Q, Khan MA, Duan C,
Peng J, Lv H and Fu J: Novel compound heterozygous nonsense
variants, p.L150* and p.Y3565*, of the USH2A gene in a Chinese
pedigree are associated with Usher syndrome type IIA. Mol Med Rep.
22:3464–3472. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Alzahayqa M, Jamous A, Khatib AAH and
Salah Z: TET1 isoforms have distinct expression pattern,
localization and regulation in breast cancer. Front Oncol.
12:8485442022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Pereira CD, Serrano JB, Martins F, da Cruz
E Silva OAB and Rebelo S: Nuclear envelope dynamics during
mammalian spermatogenesis: New insights on male fertility. Biol Rev
Camb Philos Soc. 94:1195–1219. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ohkura H: Meiosis: An overview of key
differences from mitosis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
7:a0158592015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Waclawska A and Kurpisz M: Key functional
genes of spermatogenesis identified by microarray analysis. Syst
Biol Reprod Med. 58:229–235. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ramm SA, Schärer L, Ehmcke J and Wistuba
J: Sperm competition and the evolution of spermatogenesis. Mol Hum
Reprod. 20:1169–1179. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Guo X: Localized proteasomal degradation:
From the nucleus to cell periphery. Biomolecules. 12:2292022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Brooks P, Fuertes G, Murray RZ, Bose S,
Knecht E, Rechsteiner MC, Hendil KB, Tanaka K, Dyson J and Rivett
J: Subcellular localization of proteasomes and their regulatory
complexes in mammalian cells. Biochem J. 346((Pt 1)): 155–161.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Morgan M, Kumar L, Li Y and Baptissart M:
Post-transcriptional regulation in spermatogenesis: All RNA
pathways lead to healthy sperm. Cell Mol Life Sci. 78:8049–8071.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Bettegowda A and Wilkinson MF:
Transcription and post-transcriptional regulation of
spermatogenesis. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 365:1637–1651.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Boulikas T: Putative nuclear localization
signals (NLS) in protein transcription factors. J Cell Biochem.
55:32–58. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Jiang X, Wu M, Albo J and Rao Q:
Non-specific binding and cross-reaction of ELISA: A case study of
porcine hemoglobin detection. Foods. 10:17082021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B, Nusbaum C,
Zody MC, Baldwin J, Devon K, Dewar K, Doyle M, FitzHugh W, et al:
Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature.
409:860–921. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Moritz L and Hammoud SS: The art of
packaging the sperm genome: Molecular and structural basis of the
histone-to-protamine exchange. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
13:8955022022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhou J, Du YR, Qin WH, Hu YG, Huang YN,
Bao L, Han D, Mansouri A and Xu GL: RIM-BP3 is a
manchette-associated protein essential for spermiogenesis.
Development. 136:373–382. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Piechka A, Sparanese S, Witherspoon L,
Hach F and Flannigan R: Molecular mechanisms of cellular
dysfunction in testes from men with non-obstructive azoospermia.
Nat Rev Urol. 21:67–90. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Martianov I, Fimia GM, Dierich A, Parvinen
M, Sassone-Corsi P and Davidson I: Late arrest of spermiogenesis
and germ cell apoptosis in mice lacking the TBP-like TLF/TRF2 gene.
Mol Cell. 7:509–515. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Xu L, Lu Y, Han D, Yao R, Wang H, Zhong S,
Luo Y, Han R, Li K, Fu J, et al: Rnf138 deficiency promotes
apoptosis of spermatogonia in juvenile male mice. Cell Death Dis.
8:e27952017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Siebert-Kuss LM, Krenz H, Tekath T, Wöste
M, Di Persio S, Terwort N, Wyrwoll MJ, Cremers JF, Wistuba J, Dugas
M, et al: Transcriptome analyses in infertile men reveal germ
cell-specific expression and splicing patterns. Life Sci Alliance.
6:e2022016332022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Giassetti MI, Miao D, Law NC, Oatley MJ,
Park J, Robinson LD, Maddison LA, Bernhardt ML and Oatley JM:
ARRDC5 expression is conserved in mammalian testes and required for
normal sperm morphogenesis. Nat Commun. 14:21112023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Hermann BP, Cheng K, Singh A, Roa-De La
Cruz L, Mutoji KN, Chen IC, Gildersleeve H, Lehle JD, Mayo M,
Westernströer B, et al: The mammalian spermatogenesis single-cell
transcriptome, from spermatogonial stem cells to spermatids. Cell
Rep. 25:1650–1667.e1658. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Anbazhagan R, Kavarthapu R, Dale R,
Campbell K, Faucz FR and Dufau ML: miRNA expression profiles of
mouse round spermatids in GRTH/DDX25-mediated spermiogenesis:
mRNA-miRNA network analysis. Cells. 12:7562023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|