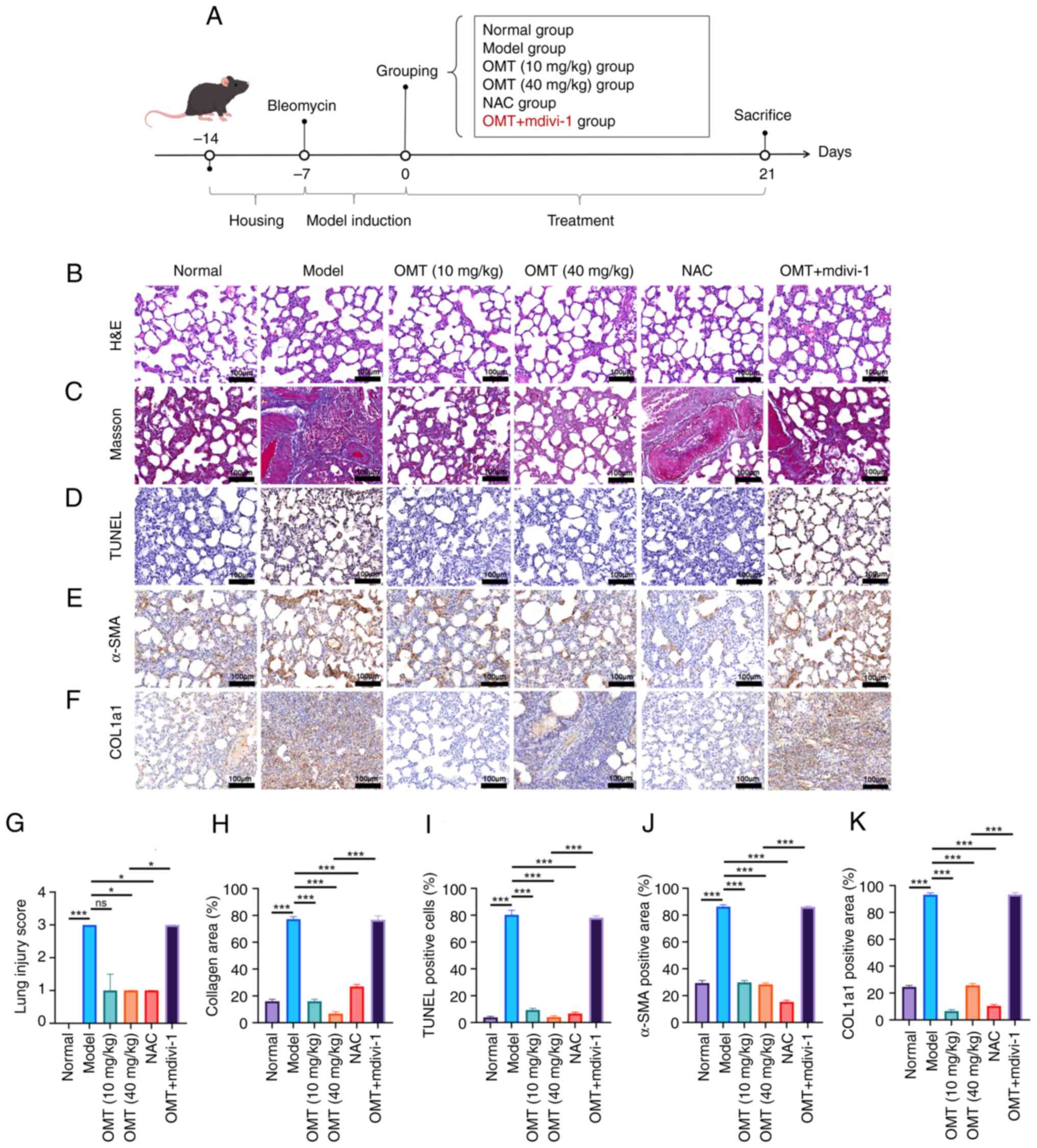
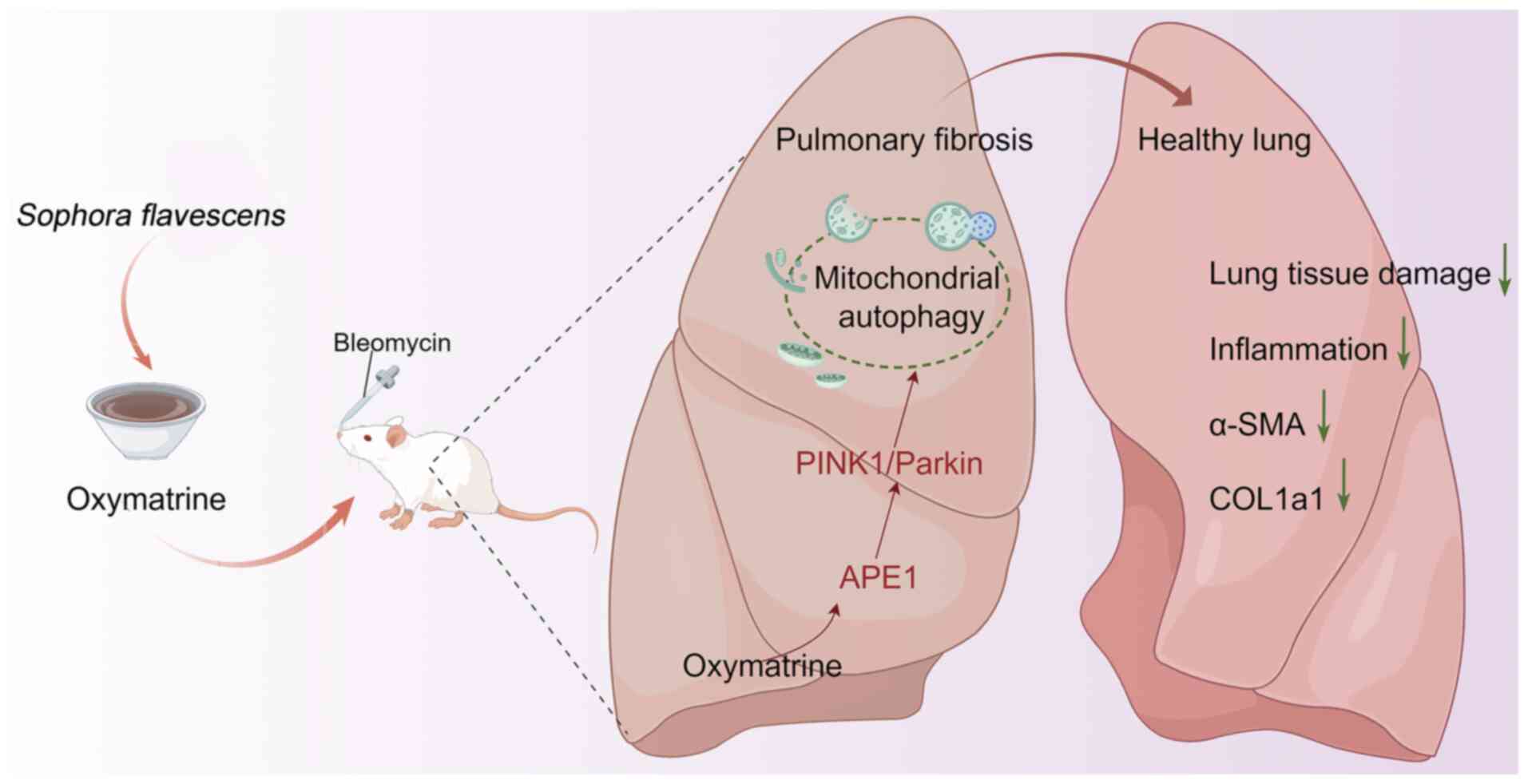
|
1
|
Koudstaal T, Funke-Chambour M, Kreuter M,
Molyneaux PL and Wijsenbeek MS: Pulmonary fibrosis: From
pathogenesis to clinical decision-making. Trends Mol Med.
29:1076–1087. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ishida Y, Kuninaka Y, Mukaida N and Kondo
T: Immune mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis with bleomycin. Int J
Mol Sci. 24:31492023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Selvarajah B, Platé M and Chambers RC:
Pulmonary fibrosis: Emerging diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
Mol Aspects Med. 94:1012272023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kim MJ, Yang J and Song JW: Acute
exacerbation of progressive pulmonary fibrosis: incidence and
outcomes. Respir Res. 25:4152024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang Y, Ji Z, Xu B, Li S and Xie Y: The
incidence of acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A
systematic review and Meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 14:210802024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee H and Yoon HY: Association between
inhaled corticosteroids and incidence of idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis: Nationwide population-based study. BMJ Open Respir Res.
12:e0025662025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Aggarwal K, Arora S and Nagpal K:
Pulmonary fibrosis: Unveiling the pathogenesis, exploring
therapeutic targets, and advancements in drug delivery strategies.
AAPS PharmSciTech. 24:1522023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Diwan R, Bhatt HN, Beaven E and Nurunnabi
M: Emerging delivery approaches for targeted pulmonary fibrosis
treatment. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 204:1151472024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Otoupalova E, Smith S, Cheng G and
Thannickal VJ: Oxidative stress in pulmonary fibrosis. Compr
Physiol. 10:509–547. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mattoo H, Bangari DS, Cummings S, Humulock
Z, Habiel D, Xu EY, Pate N, Resnick R, Savova V, Qian G, et al:
Molecular features and stages of pulmonary fibrosis driven by type
2 inflammation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 69:404–421. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Barchiesi A, Bazzani V, Jabczynska A,
Borowski LS, Oeljeklaus S, Warscheid B, Chacinska A, Szczesny RJ
and Vascotto C: DNA Repair protein APE1 degrades dysfunctional
abasic mRNA in mitochondria affecting oxidative phosphorylation. J
Mol Biol. 433:1671252021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Peng L, Liu Y, Chen J, Cheng M, Wu Y, Chen
M, Zhong Y, Shen D, Chen L and Ye X: APEX1 regulates alternative
splicing of key tumorigenesis genes in non-small-cell lung cancer.
BMC Med Genomics. 15:1472022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Long K, Gu L, Li L, Zhang Z, Li E, Zhang
Y, He L, Pan F, Guo Z and Hu Z: Small-molecule inhibition of APE1
induces apoptosis, pyroptosis, and necroptosis in non-small cell
lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. 12:5032021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang Z, Lin Y, Pan X and Chen S:
Inhibition of Non-small cell lung cancer metastasis by knocking
down APE1 through regulating myeloid-derived suppressor
cells-induced immune disorders. Aging (Albany NY). 16:10435–10445.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Huan DQ, Hop NQ and Son NT: Oxymatrine: A
current overview of its health benefits. Fitoterapia.
168:1055652023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lan X, Zhao J, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Liu Y and
Xu F: Oxymatrine exerts organ- and tissue-protective effects by
regulating inflammation, oxidative stress, apoptosis, and fibrosis:
From bench to bedside. Pharmacol Res. 151:1045412020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Feng T, Duan R, Zheng P, Qiu J, Li Q and
Li W: Oxymatrine inhibits TGF-β1-mediated mitochondrial apoptotic
signaling in alveolar epithelial cells via activation of PI3K/AKT
signaling. Exp Ther Med. 25:1982023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pokharel MD, Garcia-Flores A, Marciano D,
Franco MC, Fineman JR, Aggarwal S, Wang T and Black SM:
Mitochondrial network dynamics in pulmonary disease: Bridging the
gap between inflammation, oxidative stress, and bioenergetics.
Redox Biol. 70:1030492024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tong Z, Du X, Zhou Y, Jing F, Ma J, Feng
Y, Lou S, Wang Q and Dong Z: Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission
promotes pulmonary fibrosis progression through the regulation of
lipid metabolic reprogramming by ROS/HIF-1α. Cell Signal.
117:1110752024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li H, Dai X, Zhou J, Wang Y, Zhang S, Guo
J, Shen L, Yan H and Jiang H: Mitochondrial dynamics in pulmonary
disease: Implications for the potential therapeutics. J Cell
Physiol. 239:e313702024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang T, Lin R, Su Y, Sun H, Zheng X,
Zhang J, Lu X, Zhao B, Jiang X, Huang L, et al: Efficient
intervention for pulmonary fibrosis via mitochondrial transfer
promoted by mitochondrial biogenesis. Nat Commun. 14:57812023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu J, Wang J, Xiong A, Zhang L, Zhang Y,
Liu Y, Xiong Y, Li G and He X: Mitochondrial quality control in
lung diseases: Current research and future directions. Front
Physiol. 14:12366512023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liang L, Sun W, Wei X, Wang L, Ruan H,
Zhang J, Li S, Zhao B, Li M, Cai Z and Huang J: Oxymatrine
suppresses colorectal cancer progression by inhibiting NLRP3
inflammasome activation through mitophagy induction in vitro and in
vivo. Phytother Res. 37:3342–3362. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
National Research Council Committee for
the Update of the Guide for the C and Use of Laboratory A, . The
National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National
Institutes of Health. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals. National Academies Press, National Academy of Sciences;
Washington, DC: 2011, PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Percie du Sert N, Hurst V, Ahluwalia A,
Alam S, Avey MT, Baker M, Browne WJ, Clark A, Cuthill IC, Dirnagl
U, et al: The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: Updated guidelines for
reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 18:e30004102020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Guo B, Liu W, Ji X, Xi B, Meng X, Xie W,
Sun Y, Zhang M, Liu P, Zhang W, et al: CSF3 aggravates acute
exacerbation of pulmonary fibrosis by disrupting alveolar
epithelial barrier integrity. Int Immunopharmacol. 135:1123222024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Peng J, Wang Q, Guo M, Liu C, Chen X, Tao
L, Zhang K and Shen X: Development of inhalable Chitosan-Coated
oxymatrine liposomes to alleviate RSV–Infected Mice. Int J Mol Sci.
23:159092022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Deng W, Zhang Y, Fang P, Shi H and Yang S:
Silencing lncRNA Snhg6 mitigates bleomycin-induced pulmonary
fibrosis in mice via miR-26a-5p/TGF-β1-smads axis. Environ Toxicol.
37:2375–2387. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pang D and Laferriere C: Review of
intraperitoneal injection of sodium pentobarbital as a method of
euthanasia in laboratory rodents. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci.
59:3462020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shariati S, Kalantar H, Pashmforoosh M,
Mansouri E and Khodayar MJ: Epicatechin protective effects on
bleomycin-induced pulmonary oxidative stress and fibrosis in mice.
Biomed Pharmacother. 114:1087762019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dong L, Wang Y, Zheng T, Pu Y, Ma Y, Qi X,
Zhang W, Xue F, Shan Z, Liu J, et al: Hypoxic hUCMSC-derived
extracellular vesicles attenuate allergic airway inflammation and
airway remodeling in chronic asthma mice. Stem Cell Res Ther.
12:42021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen G, Li J, Liu H, Zhou H, Liu M, Liang
D, Meng Z, Gan H, Wu Z, Zhu X, et al: Cepharanthine ameliorates
pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway,
fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transition and inflammation. Molecules.
28:7532023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang J, Zhang Y, Chen Q, Qi Y and Zhang
X: The XPO1 inhibitor selinexor ameliorates bleomycin-induced
pulmonary fibrosis in mice via GBP5/NLRP3 inflammasome signaling.
Int Immunopharmacol. 130:1117342024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Andugulapati SB, Gourishetti K,
Tirunavalli SK, Shaikh TB and Sistla R: Biochanin-A ameliorates
pulmonary fibrosis by suppressing the TGF-β mediated EMT,
myofibroblasts differentiation and collagen deposition in in vitro
and in vivo systems. Phytomedicine. 78:1532982020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hamidi N, Feizi F, Azadmehr A, Zabihi E,
Khafri S, Zarei-Behjani Z and Babazadeh Z: Disulfiram ameliorates
bleomycin induced pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis in rats.
Biotech Histochem. 98:584–592. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yang Y, Sun M, Li W, Liu C, Jiang Z, Gu P,
Li J, Wang W, You R, Ba Q, et al: Rebalancing TGF-β/Smad7 signaling
via Compound kushen injection in hepatic stellate cells protects
against liver fibrosis and hepatocarcinogenesis. Clin Transl Med.
11:e4102021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xiao Y, Peng C, Xiao Y, Liang D, Yuan Z,
Li Z, Shi M, Wang Y, Zhang F and Guo B: Oxymatrine inhibits
Twist-mediated renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis by upregulating
Id2 expression. Front Physiol. 11:5992020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lu J, Bian J, Wang Y, Zhao Y, Zhao X, Wang
G and Yang J: Oxymatrine protects articular chondrocytes from
IL-1β-induced damage through autophagy activation via AKT/mTOR
signaling pathway inhibition. J Orthop Surg Res. 19:1782024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Maharajan N, Lee CM, Vijayakumar KA and
Cho GW: Oxymatrine improves oxidative Stress-induced senescence in
HT22 cells and mice via the activation of AMP-activated protein
kinase. Antioxidants (Basel). 12:20782023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Deng X, Zhao F, Zhao D, Zhang Q, Zhu Y,
Chen Q, Qiang L, Xie N, Ma J, Pan X, et al: Oxymatrine promotes
hypertrophic scar repair through reduced human scar fibroblast
viability, collagen and induced apoptosis via autophagy inhibition.
Int Wound J. 19:1221–1231. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Pan L, Cheng Y, Yang W, Wu X, Zhu H, Hu M,
Zhang Y and Zhang M: Nintedanib ameliorates Bleomycin-induced
pulmonary fibrosis, inflammation, apoptosis, and oxidative stress
by modulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in mice. Inflammation.
46:1531–1542. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Xu Y, Wang X, Han D, Wang J, Luo Z, Jin T,
Shi C, Zhou X, Lin L and Shan J: Revealing the mechanism of Jiegeng
decoction attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis via
PI3K/Akt signaling pathway based on lipidomics and transcriptomics.
Phytomedicine. 102:1542072022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang S, Long H, Hou L, Feng B, Ma Z, Wu Y,
Zeng Y, Cai J, Zhang DW and Zhao G: The mitophagy pathway and its
implications in human diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
8:3042023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Eldeeb MA, Bayne AN, Fallahi A, Goiran T,
MacDougall EJ, Soumbasis A, Zorca CE, Tabah JJ, Thomas RA,
Karpilovsky N, et al: Tom20 gates PINK1 activity and mediates its
tethering of the TOM and TIM23 translocases upon mitochondrial
stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 121:e23135401212024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Poole LP and Macleod KF: Mitophagy in
tumorigenesis and metastasis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 78:3817–3851.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Li J, Zhao H, McMahon A and Yan S: APE1
assembles biomolecular condensates to promote the ATR-Chk1 DNA
damage response in nucleolus. Nucleic Acids Res. 50:10503–10525.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Diao J, Fan H, Zhang J, Fu X, Liao R, Zhao
P, Huang W, Huang S, Liao H, Yu J, et al: Activation of APE1
modulates Nrf2 protected against acute liver injury by inhibit
hepatocyte ferroptosis and promote hepatocyte autophagy. Int
Immunopharmacol. 128:1115292024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li Z, Wang Y, Wu L, Dong Y, Zhang J, Chen
F, Xie W, Huang J and Lu N: Apurinic endonuclease 1 promotes the
cisplatin resistance of lung cancer cells by inducing
Parkin-mediated mitophagy. Oncol Rep. 42:2245–2254. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Tang W, Lin D, Chen M, Li Z, Zhang W, Hu W
and Li F: PTEN-mediated mitophagy and APE1 overexpression protects
against cardiac hypoxia/reoxygenation injury. In Vitro Cell Dev
Biol Anim. 55:741–748. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|