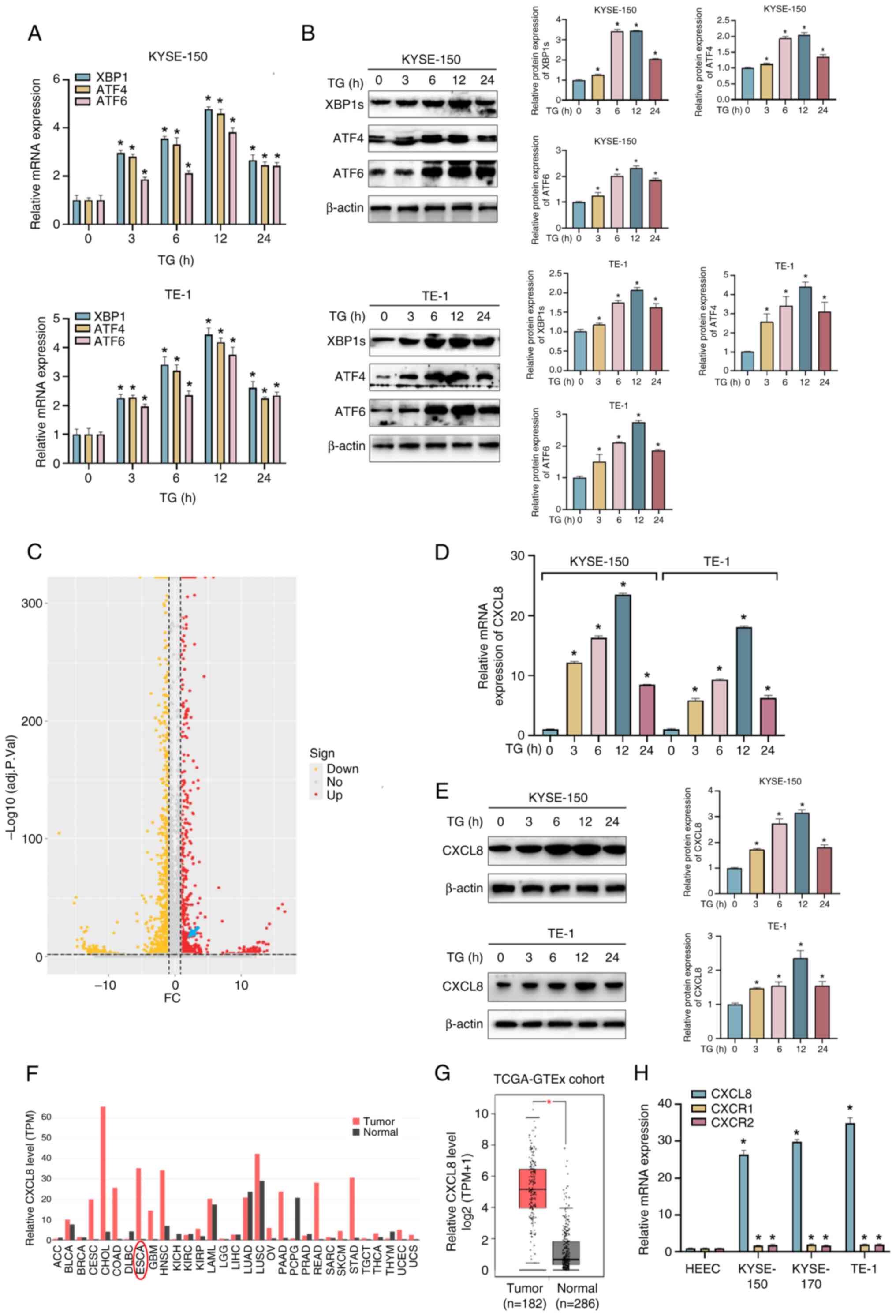
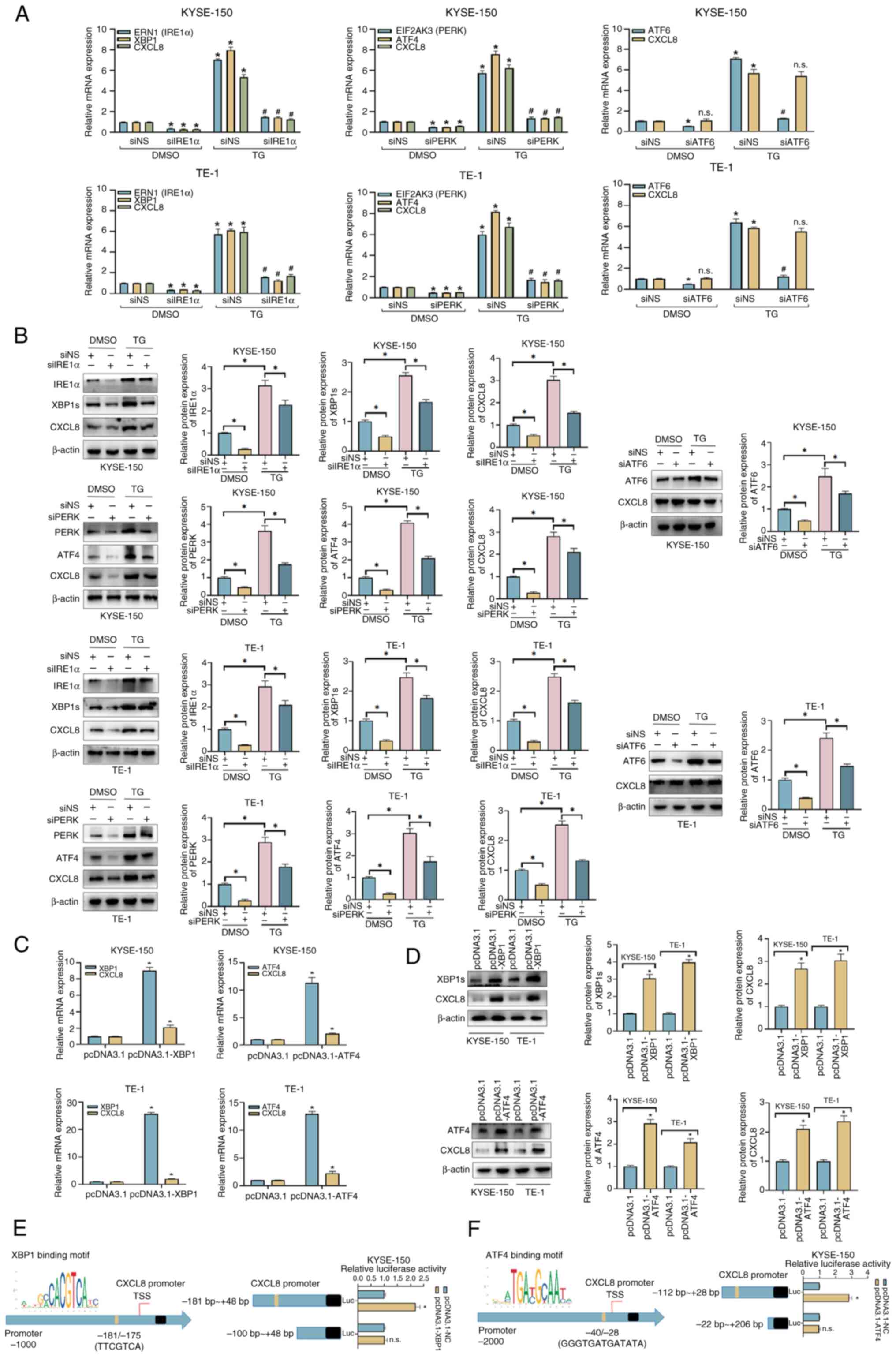
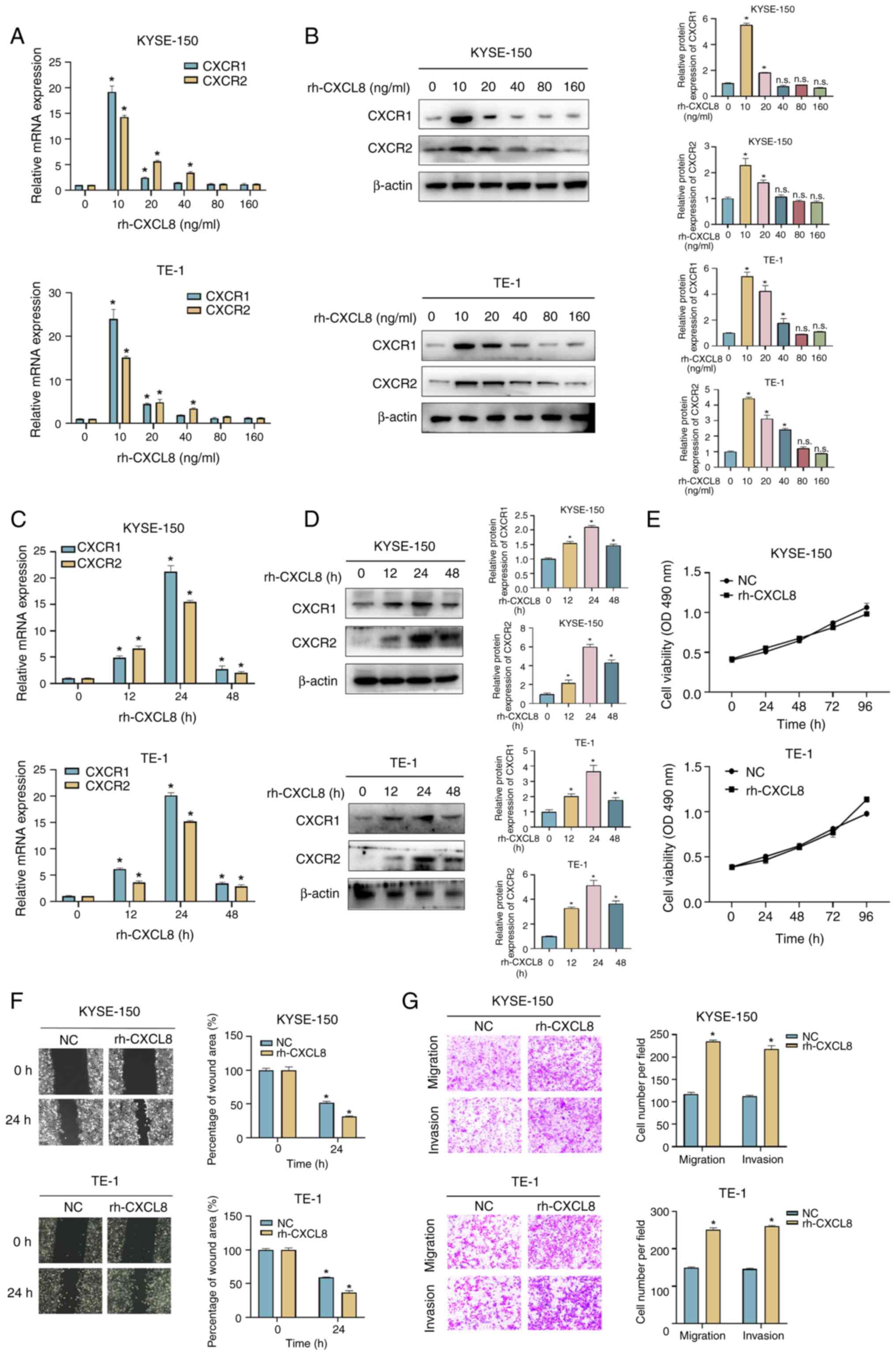
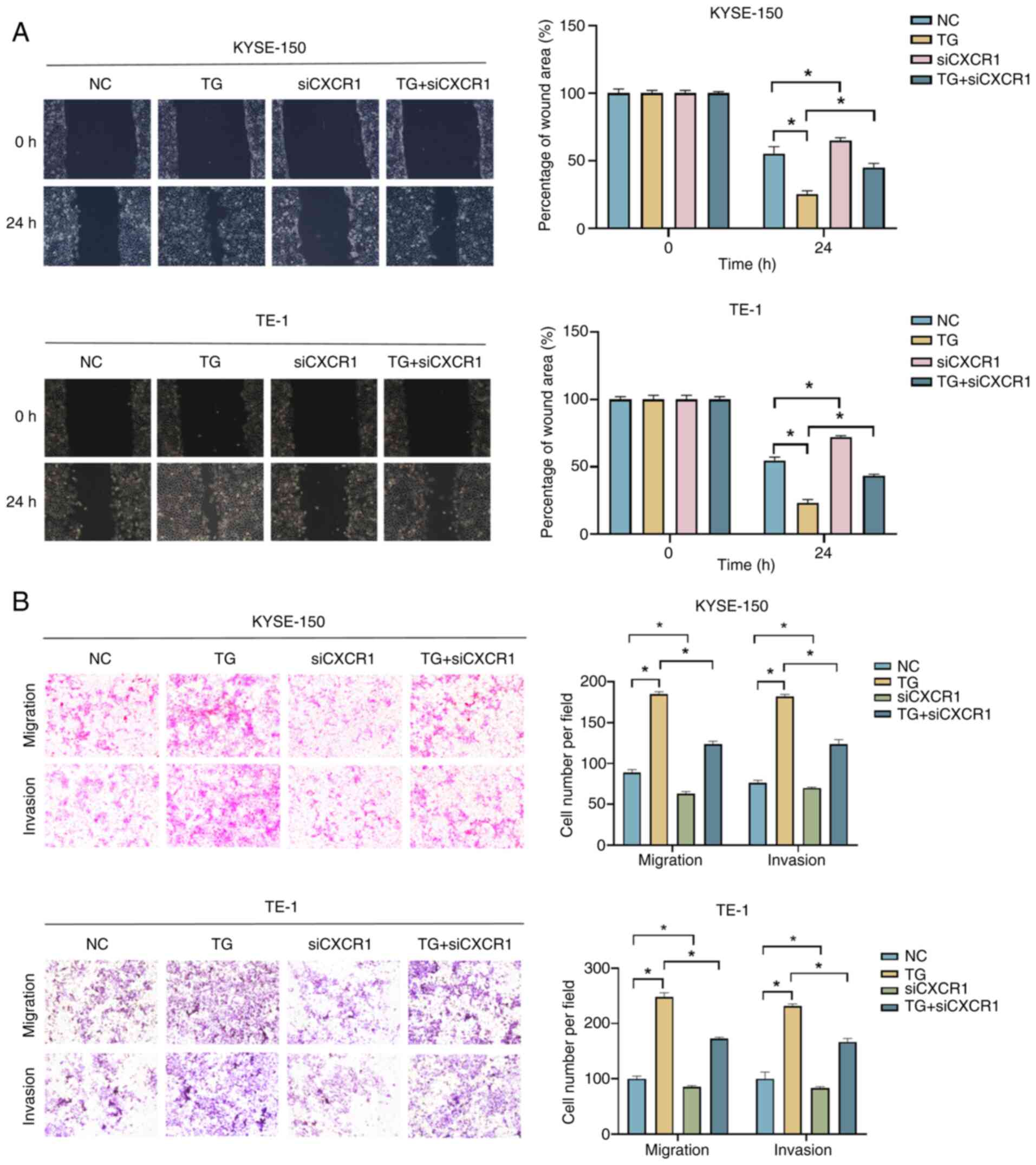
|
1
|
Jin W, Huang K, Ding Z, Zhang M, Li C,
Yuan Z, Ma K and Ye X: Global, regional, and national burden of
esophageal cancer: A systematic analysis of the Global Burden of
Disease Study 2021. Biomark Res. 13:32025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ilic I, Zivanovic Macuzic I, Ravic-Nikolic
A, Ilic M and Milicic V: Global burden of esophageal cancer and its
risk factors: A systematic analysis of the global burden of disease
study 2019. Life (Basel). 15:242024.
|
|
3
|
Qi L, Sun M, Liu W, Zhang X, Yu Y, Tian Z,
Ni Z, Zheng R and Li Y: Global esophageal cancer epidemiology in
2022 and predictions for 2050: A comprehensive analysis and
projections based on GLOBOCAN data. Chin Med J (Engl).
137:3108–3116. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Yokoyama A, Tsutsumi E, Imazeki H, Suwa Y,
Nakamura C, Mizukami T and Yokoyama T: Salivary acetaldehyde
concentration according to alcoholic beverage consumed and aldehyde
dehydrogenase-2 genotype. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 32:1607–1614. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Prabhu A, Obi KO and Rubenstein JH: The
synergistic effects of alcohol and tobacco consumption on the risk
of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Am J
Gastroenterol. 109:822–827. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Blaydon DC, Etheridge SL, Risk JM, Hennies
HC, Gay LJ, Carroll R, Plagnol V, McRonald FE, Stevens HP, Spurr
NK, et al: RHBDF2 mutations are associated with tylosis, a familial
esophageal cancer syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 90:340–346. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ludmir EB, Stephens SJ, Palta M, Willett
CG and Czito BG: Human papillomavirus tumor infection in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. J Gastrointest Oncol. 6:287–295. 2015.
|
|
8
|
Kato K, Ito Y, Nozaki I, Daiko H, Kojima
T, Yano M, Ueno M, Nakagawa S, Takagi M, Tsunoda S, et al:
Parallel-group controlled trial of surgery versus chemoradiotherapy
in patients with stage I esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Gastroenterology. 161:1878–1886.e2. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Sun JM, Shen L, Shah MA, Enzinger P,
Adenis A, Doi T, Kojima T, Metges JP, Li Z, Kim SB, et al:
Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for
first-line treatment of advanced oesophageal cancer (KEYNOTE-590):
A randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet.
398:759–771. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Fan X, Wang J, Xia L, Qiu H, Tian Y,
Zhangcai Y, Luo X, Gao Y, Li C, Wu Y, et al: Efficacy of endoscopic
therapy for T1b esophageal cancer and construction of prognosis
prediction model: A retrospective cohort study. Int J Surg.
109:1708–1719. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Li Y, Li Y and Chen X: NOTCH and
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1287:59–68.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ron D and Walter P: Signal integration in
the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 8:519–529. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Bobrovnikova-Marjon E, Grigoriadou C,
Pytel D, Zhang F, Ye J, Koumenis C, Cavener D and Diehl JA: PERK
promotes cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth by limiting
oxidative DNA damage. Oncogene. 29:3881–3895. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Urra H, Henriquez DR, Cánovas J,
Villarroel-Campos D, Carreras-Sureda A, Pulgar E, Molina E, Hazari
YM, Limia CM, Alvarez-Rojas S, et al: IRE1α governs cytoskeleton
remodelling and cell migration through a direct interaction with
filamin A. Nat Cell Biol. 20:942–953. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hart LS, Cunningham JT, Datta T, Dey S,
Tameire F, Lehman SL, Qiu B, Zhang H, Cerniglia G, Bi M, et al: ER
stress-mediated autophagy promotes Myc-dependent transformation and
tumor growth. J Clin Invest. 122:4621–4634. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Avivar-Valderas A, Salas E,
Bobrovnikova-Marjon E, Diehl JA, Nagi C, Debnath J and
Aguirre-Ghiso JA: PERK integrates autophagy and oxidative stress
responses to promote survival during extracellular matrix
detachment. Mol Cell Biol. 31:3616–3629. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Notte A, Rebucci M, Fransolet M, Roegiers
E, Genin M, Tellier C, Watillon K, Fattaccioli A, Arnould T and
Michiels C: Taxol-induced unfolded protein response activation in
breast cancer cells exposed to hypoxia: ATF4 activation regulates
autophagy and inhibits apoptosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 62:1–14.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lu M, Lawrence DA, Marsters S,
Acosta-Alvear D, Kimmig P, Mendez AS, Paton AW, Paton JC, Walter P
and Ashkenazi A: Opposing unfolded-protein-response signals
converge on death receptor 5 to control apoptosis. Science.
345:98–101. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Li G, Mongillo M, Chin KT, Harding H, Ron
D, Marks AR and Tabas I: Role of ERO1-alpha-mediated stimulation of
inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor activity in endoplasmic
reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 186:783–792. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Prieto K, Cao Y, Mohamed E, Trillo-Tinoco
J, Sierra RA, Urueña C, Sandoval TA, Fiorentino S, Rodriguez PC and
Barreto A: Polyphenol-rich extract induces apoptosis with
immunogenic markers in melanoma cells through the ER
stress-associated kinase PERK. Cell Death Discov. 5:1342019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Alfaro C, Sanmamed MF, Rodríguez-Ruiz ME,
Teijeira Á, Oñate C, González Á, Ponz M, Schalper KA, Pérez-Gracia
JL and Melero I: Interleukin-8 in cancer pathogenesis, treatment
and follow-up. Cancer Treat Rev. 60:24–31. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Raghuwanshi SK, Su Y, Singh V, Haynes K,
Richmond A and Richardson RM: The chemokine receptors CXCR1 and
CXCR2 couple to distinct G protein-coupled receptor kinases to
mediate and regulate leukocyte functions. J Immunol. 189:2824–2832.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Shen T, Yang Z, Cheng X, Xiao Y, Yu K, Cai
X, Xia C and Li Y: CXCL8 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition
in colon cancer cells via the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway.
Oncol Rep. 37:2095–2100. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Liubomirski Y, Lerrer S, Meshel T,
Rubinstein-Achiasaf L, Morein D, Wiemann S, Körner C and Ben-Baruch
A: Tumor-stroma-inflammation networks promote pro-metastatic
chemokines and aggressiveness characteristics in triple-negative
breast cancer. Front Immunol. 10:7572019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhu YM, Webster SJ, Flower D and Woll PJ:
Interleukin-8/CXCL8 is a growth factor for human lung cancer cells.
Br J Cancer. 91:1970–1976. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yi M, Peng C, Xia B and Gan L: CXCL8
facilitates the survival and paclitaxel-resistance of
triple-negative breast cancers. Clin Breast Cancer. 22:e191–e198.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zhai J, Shen J, Xie G, Wu J, He M, Gao L,
Zhang Y, Yao X and Shen L: Cancer-associated fibroblasts-derived
IL-8 mediates resistance to cisplatin in human gastric cancer.
Cancer Lett. 454:37–43. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Xue J, Song Y, Xu W and Zhu Y: The
CDK1-related lncRNA and CXCL8 mediated immune resistance in lung
adenocarcinoma. Cells. 11:26882022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhang H, Yu QL, Meng L, Huang H, Liu H,
Zhang N, Liu N, Yang J, Zhang YZ and Huang Q: TAZ-regulated
expression of IL-8 is involved in chemoresistance of hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 693:1085712020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Liu Q, Li A, Tian Y, Wu JD, Liu Y, Li T,
Chen Y, Han X and Wu K: The CXCL8-CXCR1/2 pathways in cancer.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 31:61–71. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ogura M, Takeuchi H, Kawakubo H, Nishi T,
Fukuda K, Nakamura R, Takahashi T, Wada N, Saikawa Y, Omori T, et
al: Clinical significance of CXCL-8/CXCR-2 network in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Surgery. 154:512–520. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Hosono M, Koma YI, Takase N, Urakawa N,
Higashino N, Suemune K, Kodaira H, Nishio M, Shigeoka M, Kakeji Y
and Yokozaki H: CXCL8 derived from tumor-associated macrophages and
esophageal squamous cell carcinomas contributes to tumor
progression by promoting migration and invasion of cancer cells.
Oncotarget. 8:106071–106088. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Hayakawa K, Nakajima S, Hiramatsu N,
Okamura M, Huang T, Saito Y, Tagawa Y, Tamai M, Takahashi S, Yao J
and Kitamura M: ER stress depresses NF-kappaB activation in
mesangial cells through preferential induction of C/EBP beta. J Am
Soc Nephrol. 21:73–81. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Knall C, Young S, Nick JA, Buhl AM,
Worthen GS and Johnson GL: Interleukin-8 regulation of the
Ras/Raf/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in human
neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 271:2832–2838. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Cheng GZ, Park S, Shu S, He L, Kong W,
Zhang W, Yuan Z, Wang LH and Cheng JQ: Advances of AKT pathway in
human oncogenesis and as a target for anti-cancer drug discovery.
Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 8:2–6. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Waugh DJJ and Wilson C: The interleukin-8
pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 14:6735–6741. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Cheng K and Hao M: Metformin inhibits
TGF-β1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via PKM2
relative-mTOR/p70s6k signaling pathway in cervical carcinoma cells.
Int J Mol Sci. 17:20002016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Hetz C and Papa FR: The unfolded protein
response and cell fate control. Mol Cell. 69:169–181. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
He J, Zhou Y and Sun L: Emerging
mechanisms of the unfolded protein response in therapeutic
resistance: From chemotherapy to Immunotherapy. Cell Commun Signal.
22:892024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Dong D, Ni M, Li J, Xiong S, Ye W, Virrey
JJ, Mao C, Ye R, Wang M, Pen L, et al: Critical role of the stress
chaperone GRP78/BiP in tumor proliferation, survival, and tumor
angiogenesis in transgene-induced mammary tumor development. Cancer
Res. 68:498–505. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Li J and Lee AS: Stress induction of
GRP78/BiP and its role in cancer. Curr Mol Med. 6:45–54. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Tan Y, Dourdin N, Wu C, De Veyra T, Elce
JS and Greer PA: Ubiquitous calpains promote caspase-12 and JNK
activation during endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. J
Biol Chem. 281:16016–16024. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Yuan YJ, Liu S, Yang H, Xu JL, Zhai J,
Jiang HM and Sun B: Acetylshikonin induces apoptosis through the
endoplasmic reticulum stress-activated PERK/eIF2α/CHOP
axis in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Cell Mol Med.
28:e180302024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Hetz C, Zhang K and Kaufman RJ:
Mechanisms, regulation and functions of the unfolded protein
response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 21:421–438. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Yin X, Zhang P, Xia N, Wu S, Liu B, Weng L
and Shang M: GPx8 regulates apoptosis and autophagy in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma through the IRE1/JNK pathway. Cell Signal.
93:1103072022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Wang YM, Xu X, Tang J, Sun ZY, Fu YJ, Zhao
XJ, Ma XM and Ye Q: Apatinib induces endoplasmic reticulum
stress-mediated apoptosis and autophagy and potentiates cell
sensitivity to paclitaxel via the IRE-1α-AKT-mTOR pathway in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Biosci. 11:1242021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Mamik MK and Ghorpade A: Chemokine CXCL8
promotes HIV-1 replication in human monocyte-derived macrophages
and primary microglia via nuclear factor-κB pathway. PLoS One.
9:e921452014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Aarntzen EHJG, Hermsen R, Drenth JPH,
Boerman OC and Oyen WJG: 99mTc-CXCL8 SPECT to monitor disease
activity in inflammatory bowel disease. J Nucl Med. 57:398–403.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Amrouche L, Desbuissons G, Rabant M,
Sauvaget V, Nguyen C, Benon A, Barre P, Rabaté C, Lebreton X,
Gallazzini M, et al: MicroRNA-146a in human and experimental
ischemic AKI: CXCL8-dependent mechanism of action. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 28:479–493. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Barnes PJ: New treatments for chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease. Ann Ist Super Sanita. 39:573–582.
2003.
|
|
52
|
Traves SL, Smith SJ, Barnes PJ and
Donnelly LE: Specific CXC but not CC chemokines cause elevated
monocyte migration in COPD: A role for CXCR2. J Leukoc Biol.
76:441–450. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Long X, Ye Y, Zhang L, Liu P, Yu W, Wei F,
Ren X and Yu J: IL-8, a novel messenger to cross-link inflammation
and tumor EMT via autocrine and paracrine pathways (Review). Int J
Oncol. 48:5–12. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Sheshadri N, Poria DK, Sharan S, Hu Y, Yan
C, Koparde VN, Balamurugan K and Sterneck E: PERK signaling through
C/EBPδ contributes to ER stress-induced expression of
immunomodulatory and tumor promoting chemokines by cancer cells.
Cell Death Dis. 12:10382021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Zhang L, Xu S, Cheng X, Wu J, Wang Y, Gao
W, Bao J and Yu H: Inflammatory tumor microenvironment of thyroid
cancer promotes cellular dedifferentiation and silencing of
iodide-handling genes expression. Pathol Res Pract. 246:1544952023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Püschel F, Favaro F, Redondo-Pedraza J,
Lucendo E, Iurlaro R, Marchetti S, Majem B, Eldering E, Nadal E,
Ricci JE, et al: Starvation and antimetabolic therapy promote
cytokine release and recruitment of immune cells. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 117:9932–9941. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
MacManus CF, Pettigrew J, Seaton A, Wilson
C, Maxwell PJ, Berlingeri S, Purcell C, McGurk M, Johnston PG and
Waugh DJJ: Interleukin-8 signaling promotes translational
regulation of cyclin D in androgen-independent prostate cancer
cells. Mol Cancer Res. 5:737–748. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Matsuo Y, Raimondo M, Woodward TA, Wallace
MB, Gill KR, Tong Z, Burdick MD, Yang Z, Strieter RM, Hoffman RM
and Guha S: CXC-chemokine/CXCR2 biological axis promotes
angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo in pancreatic cancer. Int J
Cancer. 125:1027–1037. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Wang J, Hu W, Wu X, Wang K, Yu J, Luo B,
Luo G, Wang W, Wang H, Li J and Wen J: CXCR1 promotes malignant
behavior of gastric cancer cells in vitro and in vivo in AKT and
ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Int J Oncol. 48:2184–2196. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Urbantat RM, Blank A, Kremenetskaia I,
Vajkoczy P, Acker G and Brandenburg S: The CXCL2/IL8/CXCR2 pathway
is relevant for brain tumor malignancy and endothelial cell
function. Int J Mol Sci. 22:26342021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Knall C, Worthen GS and Johnson GL:
Interleukin 8-stimulated phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase activity
regulates the migration of human neutrophils independent of
extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38 mitogen-activated
protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:3052–3057. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Luppi F, Longo AM, de Boer WI, Rabe KF and
Hiemstra PS: Interleukin-8 stimulates cell proliferation in
non-small cell lung cancer through epidermal growth factor receptor
transactivation. Lung Cancer. 56:25–33. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Brandl M, Seidler B, Haller F, Adamski J,
Schmid RM, Saur D and Schneider G: IKK(α) controls canonical
TGF(ß)-SMAD signaling to regulate genes expressing SNAIL and SLUG
during EMT in panc1 cells. J Cell Sci. 123:4231–4239. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Xiong M, Jiang L, Zhou Y, Qiu W, Fang L,
Tan R, Wen P and Yang J: The miR-200 family regulates
TGF-β1-induced renal tubular epithelial to mesenchymal transition
through Smad pathway by targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2 expression. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 302:F369–F379. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|