|
1
|
Hu D, Sheeja Prabhakaran H, Zhang YY, Luo
G, He W and Liou YC: Mitochondrial dysfunction in sepsis:
Mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives. Crit Care. 28:2922024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, Shackelford
KA, Tsoi D, Kievlan DR, Colombara DV, Ikuta KS, Kissoon N, Finfer
S, et al: Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and
mortality, 1990–2017: Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease
Study. Lancet. 395:200–211. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Borges A and Bento L: Organ crosstalk and
dysfunction in sepsis. Ann Intensive Care. 14:1472024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Slooter AJC, Otte WM, Devlin JW, Arora RC,
Bleck TP, Claassen J, Duprey MS, Ely EW, Kaplan PW, Latronico N, et
al: Updated nomenclature of delirium and acute encephalopathy:
Statement of ten Societies. Intensive Care Med. 46:1020–1022. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mazeraud A, Righy C, Bouchereau E,
Benghanem S, Bozza FA and Sharshar T: Septic-associated
encephalopathy: A comprehensive review. Neurotherapeutics.
17:392–403. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sonneville R, Benghanem S, Jeantin L, de
Montmollin E, Doman M, Gaudemer A, Thy M and Timsit JF: The
spectrum of Sepsis-associated encephalopathy: A clinical
perspective. Crit Care. 27:3862023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Widmann CN and Heneka MT: Long-term
cerebral consequences of sepsis. Lancet Neurol. 13:630–636. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lund-Sorensen H, Benros ME, Madsen T,
Sørensen HJ, Eaton WW, Postolache TT, Nordentoft M and Erlangsen A:
A nationwide cohort study of the association between
hospitalization with infection and risk of death by suicide. JAMA
Psychiatry. 73:912–919. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li D, Zhang X, Lu Y, Jing L, Hu H, Song Y,
Wu S and Zhu W: Post-sepsis psychiatric disorder: Pathophysiology,
prevention, and treatment. Neurol Sci. 45:3093–3105. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhou Y, Bai L, Tang W, Yang W and Sun L:
Research progress in the pathogenesis of sepsis-associated
encephalopathy. Heliyon. 10:e334582024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Denver P and Cunningham C: Microglial
activation and neuroinflammation in acute and chronic cognitive
deficits in sepsis. Neuropharmacology. 267:1102852025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu YX, Yu Y, Liu JP, Liu WJ, Cao Y, Yan
RM and Yao YM: Neuroimmune regulation in Sepsis-associated
encephalopathy: The interaction between the brain and peripheral
immunity. Front Neurol. 13:8924802022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ashrafi G and Schwarz TL: The pathways of
mitophagy for quality control and clearance of mitochondria. Cell
Death Differ. 20:31–42. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ma K, Chen G, Li W, Kepp O, Zhu Y and Chen
Q: Mitophagy, mitochondrial homeostasis, and cell fate. Front Cell
Dev Biol. 8:4672020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Picca A, Faitg J, Auwerx J, Ferrucci L and
D'Amico D: Mitophagy in human health, ageing and disease. Nat
Metab. 5:2047–2061. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu Y, Yang H, Luo N, Fu Y, Qiu F, Pan Z,
Li X, Jian W, Yang X, Xue Q, et al: An Fgr kinase inhibitor
attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy by ameliorating
mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and neuroinflammation
via the SIRT1/PGC-1α signaling pathway. J Transl Med. 21:4862023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pan P, Wang X and Liu D: The potential
mechanism of mitochondrial dysfunction in septic cardiomyopathy. J
Int Med Res. 46:2157–2169. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhu CL, Yao RQ, Li LX, Li P, Xie J, Wang
JF and Deng XM: Mechanism of mitophagy and its role in sepsis
induced organ dysfunction: A review. Front Cell Dev Biol.
9:6648962021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Maximiano TKE, Carneiro JA, Fattori V and
Verri WA: TRPV1: Receptor structure, activation, modulation and
role in neuro-immune interactions and pain. Cell Calcium.
119:1028702024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
In: TRP Ion Channel Function in Sensory
Transduction and Cellular Signaling Cascades. Liedtke WB and Heller
S: CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; Boca Raton, FL: 2007
|
|
21
|
Tyagi S, Shekhar N and Thakur AK:
Protective role of capsaicin in neurological disorders: An
overview. Neurochem Res. 47:1513–1531. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pasierski M and Szulczyk B: Beneficial
effects of capsaicin in disorders of the central nervous system.
Molecules. 27:24842022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ghorbanpour A, Salari S,
Baluchnejadmojarad T and Roghani M: Capsaicin protects against
septic acute liver injury by attenuation of apoptosis and
mitochondrial dysfunction. Heliyon. 9:e142052023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Han J, Wu J, Liu H, Huang Y, Ju W, Xing Y,
Zhang X and Yang J: Inhibition of pyroptosis and apoptosis by
capsaicin protects against LPS-induced acute kidney injury through
TRPV1/UCP2 axis in vitro. Open Life Sci. 18:202206472023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Qiao Y, Wang L, Hu T, Yin D, He H and He
M: Capsaicin protects cardiomyocytes against
lipopolysaccharide-induced damage via 14-3-3gamma-mediated
autophagy augmentation. Front Pharmacol. 12:6590152021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang R, Li Q, Wu P, Ren K, Li Y, Wang Y,
Zhu H and Lv C: Fe-capsaicin nanozymes attenuate Sepsis-induced
acute lung injury via NF-κB signaling. Int J Nanomedicine.
19:73–90. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang Q, Luo P, Xia F, Tang H, Chen J,
Zhang J, Liu D, Zhu Y, Liu Y, Gu L, et al: Capsaicin ameliorates
inflammation in a TRPV1-independent mechanism by inhibiting
PKM2-LDHA-mediated Warburg effect in sepsis. Cell Chem Biol.
29:1248–1259.e6. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yuan J, Liu H, Zhang H, Wang T, Zheng Q
and Li Z: Controlled activation of TRPV1 Channels on microglia to
boost their autophagy for clearance of Alpha-synuclein and enhance
therapy of Parkinson's disease. Adv Mater. 34:e21084352022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lin Y, Huang T, Shen W, Pang Q, Xie Q,
Chen X and Tu F: TRPV1 suppressed NLRP3 through regulating
autophagy in microglia after Ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Mol
Neurosci. 72:792–801. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang C, Huang W, Lu J, Chen H and Yu Z:
TRPV1-mediated microglial autophagy attenuates Alzheimer's
Disease-associated pathology and cognitive decline. Front
Pharmacol. 12:7638662021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Beider K, Rosenberg E, Dimenshtein-Voevoda
V, Sirovsky Y, Vladimirsky J, Magen H, Ostrovsky O, Shimoni A,
Bromberg Z, Weiss L, et al: Blocking of transient receptor
potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) promotes terminal mitophagy in
multiple myeloma, disturbing calcium homeostasis and targeting
ubiquitin pathway and bortezomib-induced unfolded protein response.
J Hematol Oncol. 13:1582020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shibata M, Kayama Y, Takizawa T, Ibata K,
Shimizu T, Yuzaki M, Suzuki N and Nakahara J: Resilience to
capsaicin-induced mitochondrial damage in trigeminal ganglion
neurons. Mol Pain. 16:17448069209608562020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Percie du Sert N, Hurst V, Ahluwalia A,
Alam S, Avey MT, Baker M, Browne WJ, Clark A, Cuthill IC, Dirnagl
U, et al: The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: Updated guidelines for
reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 18:e30004102020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rittirsch D, Huber-Lang MS, Flierl MA and
Ward PA: Immunodesign of experimental sepsis by cecal ligation and
puncture. Nat Protoc. 4:31–36. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wu J, Zhang M, Hao S, Jia M, Ji M, Qiu L,
Sun X, Yang J and Li K: Mitochondria-targeted peptide reverses
mitochondrial dysfunction and cognitive deficits in
Sepsis-Associated encephalopathy. Mol Neurobiol. 52:783–791. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kelliny S, Lin L, Deng I, Xiong J, Zhou F,
Al-Hawwas M, Bobrovskaya L and Zhou XF: A new approach to model
sporadic alzheimer's disease by intracerebroventricular
streptozotocin injection in APP/PS1 mice. Mol Neurobiol.
58:3692–3711. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kawase M, Murakami K, Fujimura M,
Morita-Fujimura Y, Gasche Y, Kondo T, Scott RW and Chan PH:
Exacerbation of delayed cell injury after transient global ischemia
in mutant mice with CuZn superoxide dismutase deficiency. Stroke.
30:1962–1968. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mizushima N, Yoshimori T and Levine B:
Methods in mammalian autophagy research. Cell. 140:313–326. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gofton TE and Young GB: Sepsis-associated
encephalopathy. Nat Rev Neurol. 8:557–566. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sonneville R, de Montmollin E, Poujade J,
Garrouste-Orgeas M, Souweine B, Darmon M, Mariotte E, Argaud L,
Barbier F, Goldgran-Toledano D, et al: Potentially modifiable
factors contributing to sepsis-associated encephalopathy. Intensive
Care Med. 43:1075–1084. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xin Y, Tian M, Pei X, Deng S, Wang Y, Zhao
F, Behnisch T, Gao Y and Gong Y: Optimized mouse model of
Sepsis-associated encephalopathy: A rational standard based on
modified SHIRPA score and neurobehaviors in mice. CNS Neurosci
Ther. 31:e703652025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liao H, Li H, Bao H, Jiang L, Du J, Guo Y
and Si Y: Short chain fatty acids protect the cognitive function of
sepsis associated encephalopathy mice via GPR43. Front Neurol.
13:9094362022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sekino N, Selim M and Shehadah A:
Sepsis-associated brain injury: Underlying mechanisms and potential
therapeutic strategies for acute and long-term cognitive
impairments. J Neuroinflammation. 19:1012022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Xu XE, Liu L, Wang YC, Wang CT, Zheng Q,
Liu QX, Li ZF, Bai XJ and Liu XH: Caspase-1 inhibitor exerts
brain-protective effects against sepsis-associated encephalopathy
and cognitive impairments in a mouse model of sepsis. Brain Behav
Immun. 80:859–870. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tian M, Wang W, Wang K, Jin P, Lenahan C,
Wang Y, Tan J, Wen H, Deng S, Zhao F and Gong Y: Dexmedetomidine
alleviates cognitive impairment by reducing Blood-brain barrier
interruption and neuroinflammation via regulating Th1/Th2/Th17
polarization in an experimental sepsis model of mice. Int
Immunopharmacol. 101:1083322021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bodkin JV and Fernandes ES: TRPV1 and SP:
Key elements for sepsis outcome? Br J Pharmacol. 170:1279–1292.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Bryant P, Shumate M, Yumet G, Lang CH,
Vary TC and Cooney RN: Capsaicin-sensitive nerves regulate the
metabolic response to abdominal sepsis. J Surg Res. 112:152–161.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang Q, Liu J, Shen J, Ou J, Wong YK, Xie
L, Huang J, Zhang C, Fu C, Chen J, et al: Single-cell RNA
sequencing reveals the effects of capsaicin in the treatment of
sepsis-induced liver injury. MedComm (2020). 4:e3952023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chen H, Li N, Zhan X, Zheng T, Huang X,
Chen Q, Song Z, Yang F, Nie H, Zhang Y, et al: Capsaicin protects
against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through the
HMGB1/NF-κB and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways. J Inflamm Res.
14:5291–5304. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Haileselassie B, Joshi AU, Minhas PS,
Mukherjee R, Andreasson KI and Mochly-Rosen D: Mitochondrial
dysfunction mediated through dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1)
propagates impairment in blood brain barrier in septic
encephalopathy. J Neuroinflammation. 17:362020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhang L, Dai L and Li D: Mitophagy in
neurological disorders. J Neuroinflammation. 18:2972021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdel-Aziz AK, Abdelfatah S,
Abdellatif M, Abdoli A, Abe S, Abeliovich H, Abildgaard MH,
Princely Abudu Y, Acevedo-Arozena A, et al: Guidelines for the use
and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (4th
edition)1. Autophagy. 17:1–382. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wang S, Long H, Hou L, Feng B, Ma Z, Wu Y,
Zeng Y, Cai J, Zhang DW and Zhao G: The mitophagy pathway and its
implications in human diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
8:3042023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Cui Y, Liu J, Song Y, Chen C, Shen Y and
Xie K: High Concentration hydrogen protects Sepsis-associated
encephalopathy by enhancing pink1/Parkin-Mediated mitophagy and
inhibiting cGAS-STING-IRF3 pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther.
31:e703052025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Min SY, Yong HJ and Kim D: Sex or gender
differences in treatment outcomes of sepsis and septic shock. Acute
Crit Care. 39:207–213. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Nasa P, Juneja D and Singh O: Severe
sepsis and septic shock in the elderly: An overview. World J Crit
Care Med. 1:23–30. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|















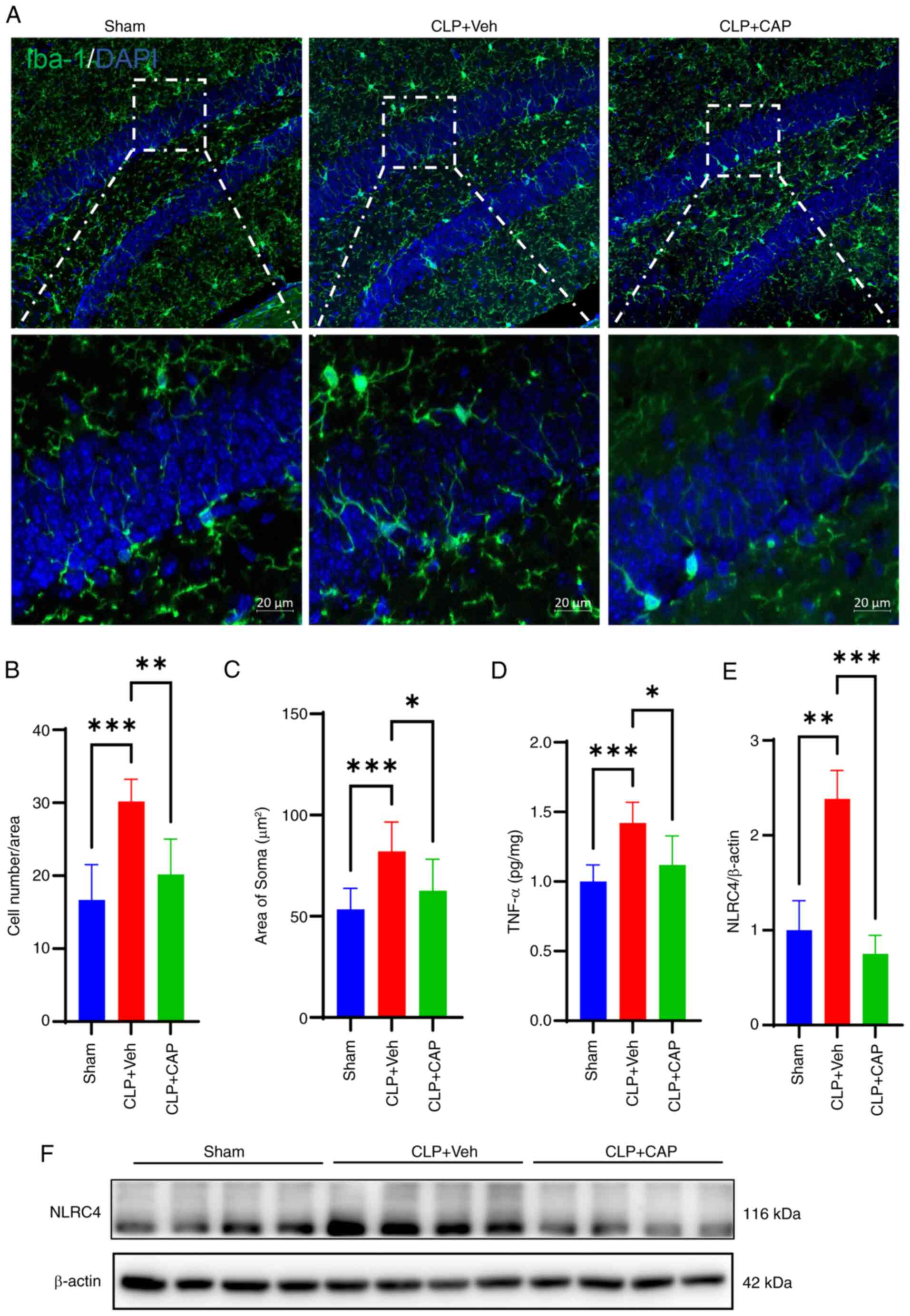
![Effects of subcutaneous CAP
administration on mouse survival rate and cognitive function after
CLP surgery. (A) Western blot analysis and semi-quantitative
analysis of TRPV1 protein expression levels in hippocampal tissues
after CLP surgery (n=6 mice/group; unpaired Student's t-test;
t(10)=3.221;
P<0.01). (B) Survival rate of sham (n=10), CLP + Veh (n=15) and
CLP + 1 mg/kg CAP (n=15) mice were monitored for 7 days. Log-rank
Mantel-Cox test, P=0.035. (C) Recognition index of the novel
objective in the novel object recognition test [Sham (n=8), CLP
(n=6) and CLP + CAP (n=7) mice; one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post
hoc test; F(2,18) =3.670; P=0.046]. (D) Time
spent in the target quadrant in the Morris water maze test phase
[Sham (n=8), CLP (n=10) and CLP + CAP (n=12) mice]. Data are
presented as the mean ± standard deviation. *P<0.05 and
**P<0.01 vs. sham. CAP, capsaicin; CLP, cecal ligation and
puncture; TRPV1, transient receptor potential vanilloid 1; Veh,
vehicle; CAP-1*1, capsaicin 1 mg/kg * 1 application.](/article_images/mmr/32/6/mmr-32-06-13686-g00.jpg)
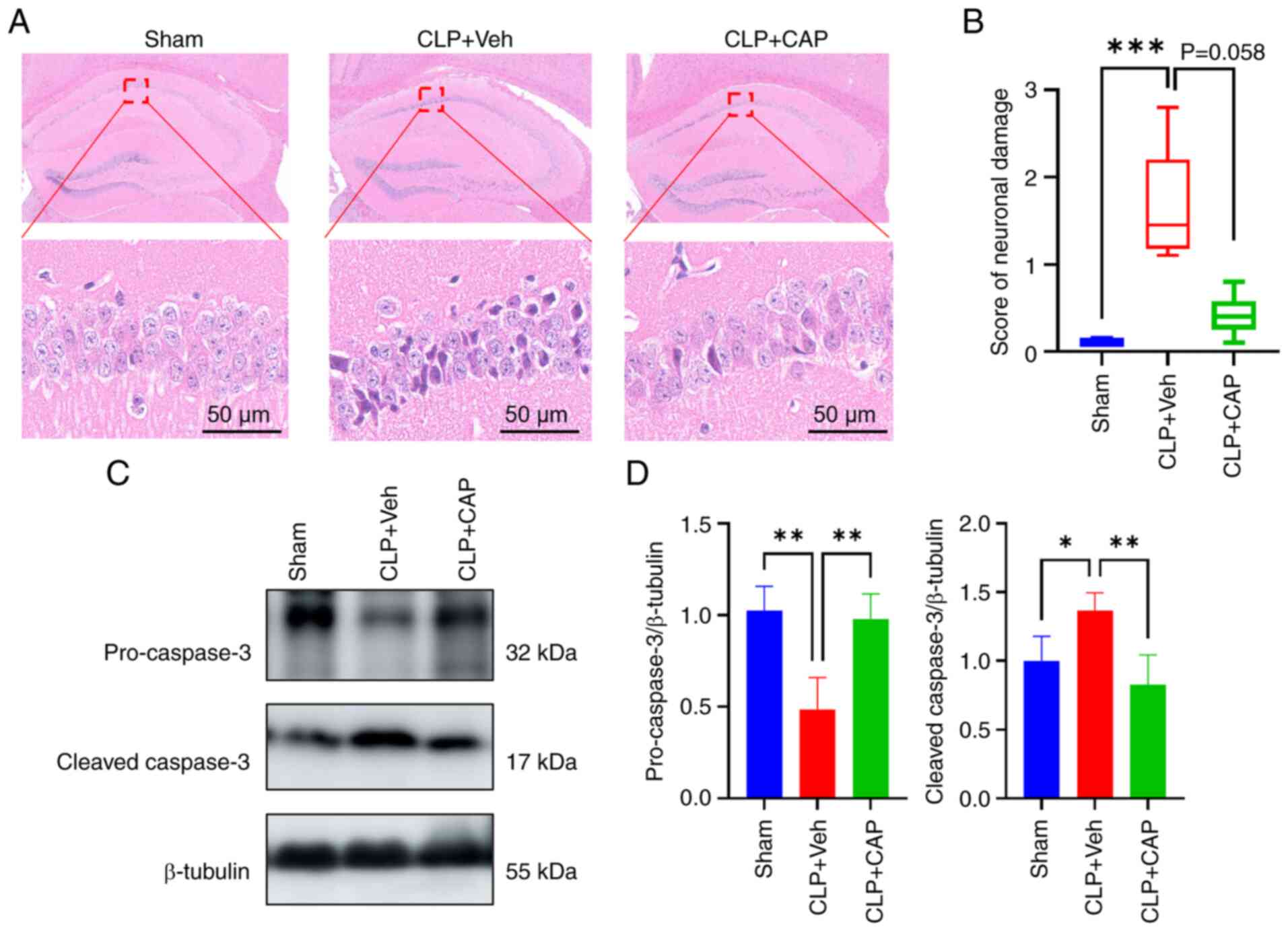
![CAP-induced protection in mice with
sepsis. (A) Recognition index of the novel object in the novel
object recognition test [Sham (n=10), CLP (n=12) and CLP + CAP
(n=11) mice; n=10-12 mice/group; one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post
hoc test; F(2,30)=12.45; P=0.0001]. (B) Escape
latency in the MWM during the training phase [Sham (n=10), CLP
(n=15) and CLP + CAP (n=14) mice]. (C) Time spent in the target
quadrant in the MWM during the test phase (one-way ANOVA with
Bonferroni post hoc test; F(2,35)=8.925; P=0.0007). (D)
Representative swimming traces in the MWM during the learning and
test phase. (E) Average swimming speed in the MWM during the test
phase. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation.
*P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001. CAP, capsaicin; CLP,
cecal ligation and puncture; MWM, Morris water maze; Veh, vehicle;
CAP-1*3, capsaicin 1 mg/kg * 3 application.](/article_images/mmr/32/6/mmr-32-06-13686-g01.jpg)