|
1
|
Czabanski R, Horoba K, Wrobel J, Matonia
A, Martinek R, Kupka T, Jezewski M, Kahankova R, Jezewski J and
Leski JM: Detection of atrial fibrillation episodes in long-term
heart rhythm signals using a support vector machine. Sensors
(Basel). 20:7652020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
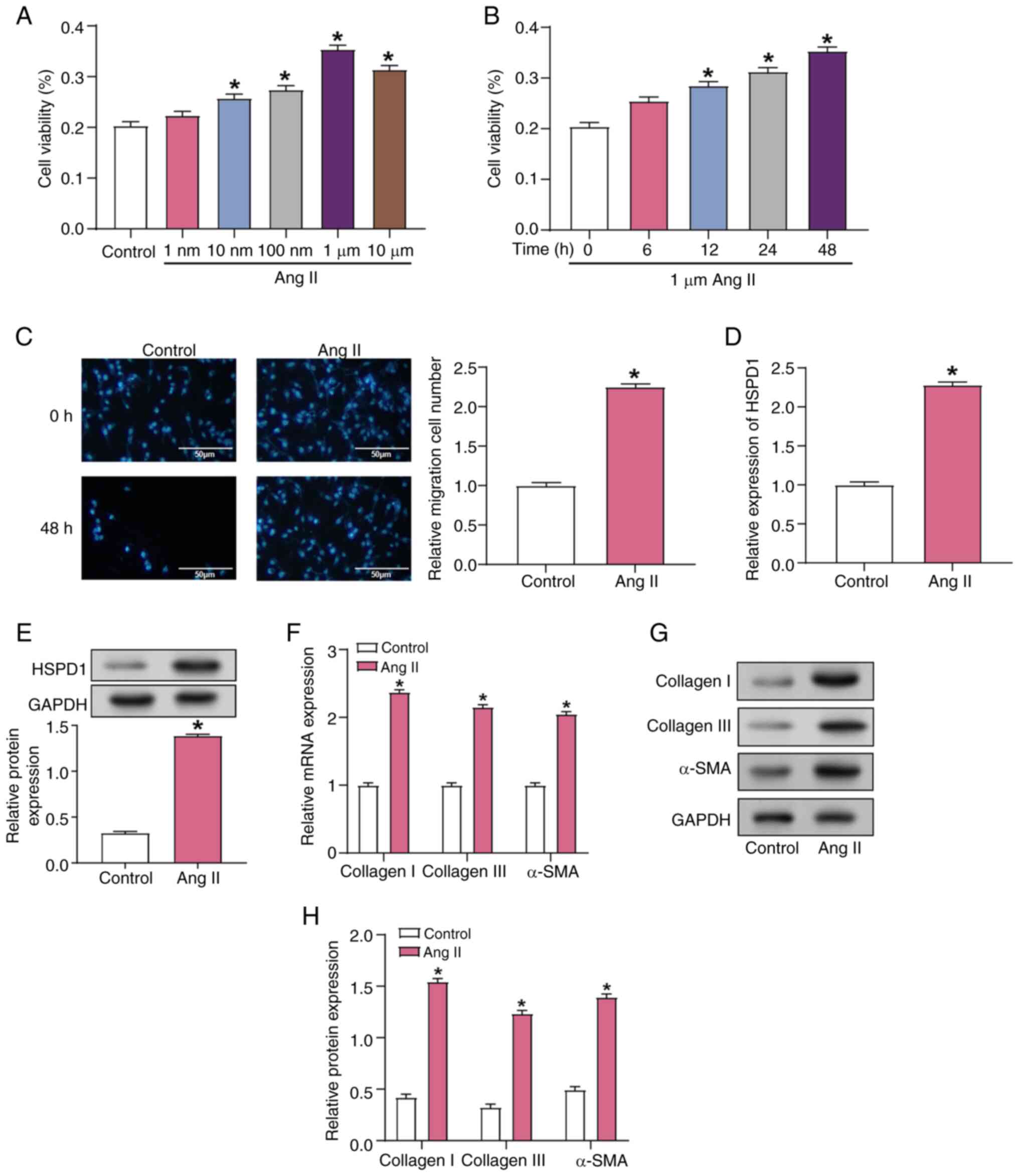
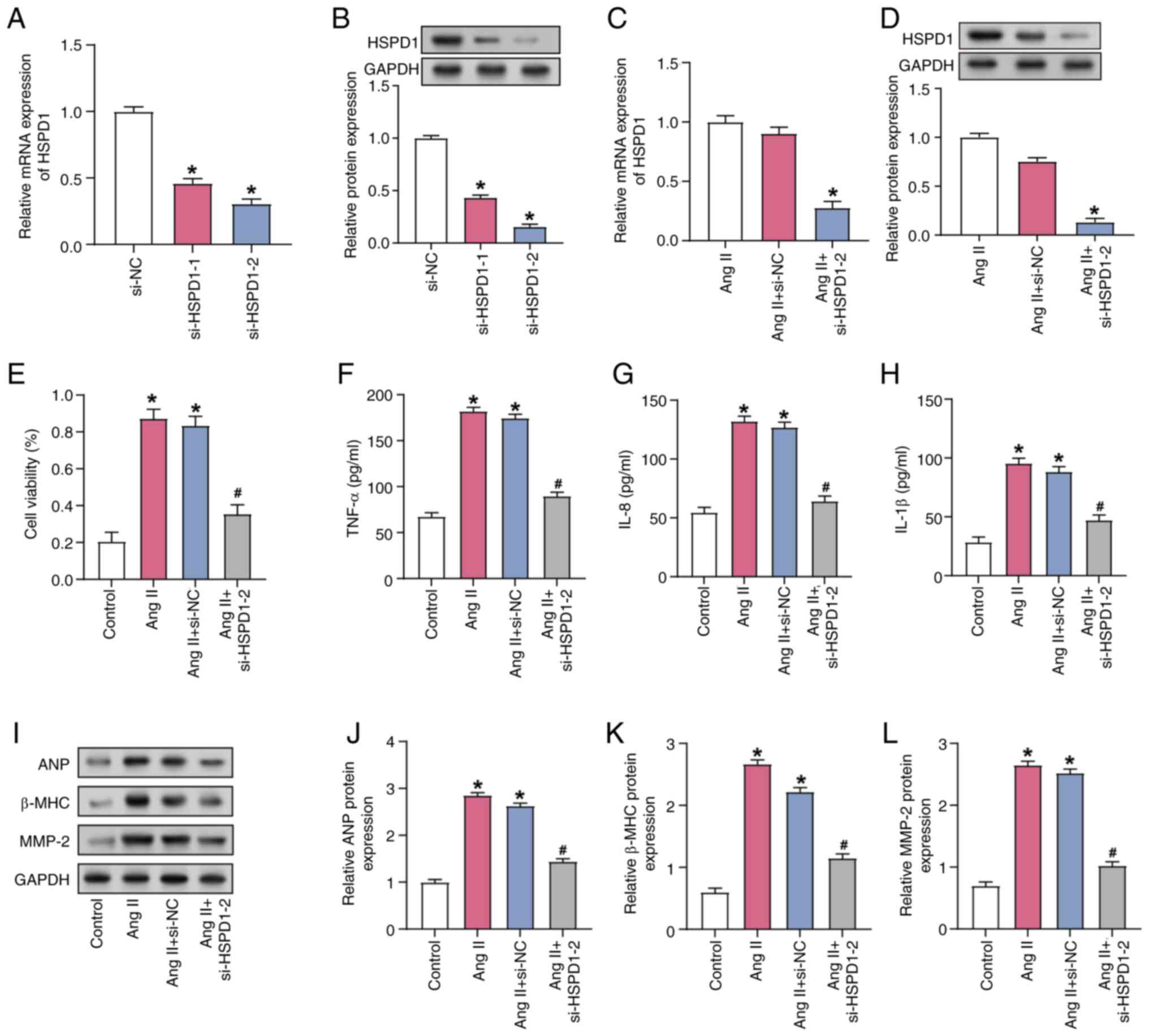
Bavishi A and Patel RB: Addressing
comorbidities in heart failure: Hypertension, atrial fibrillation,
and diabetes. Heart Fail Clin. 16:441–456. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Middeldorp ME, Ariyaratnam J, Lau D and
Sanders P: Lifestyle modifications for treatment of atrial
fibrillation. Heart. 106:325–332. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
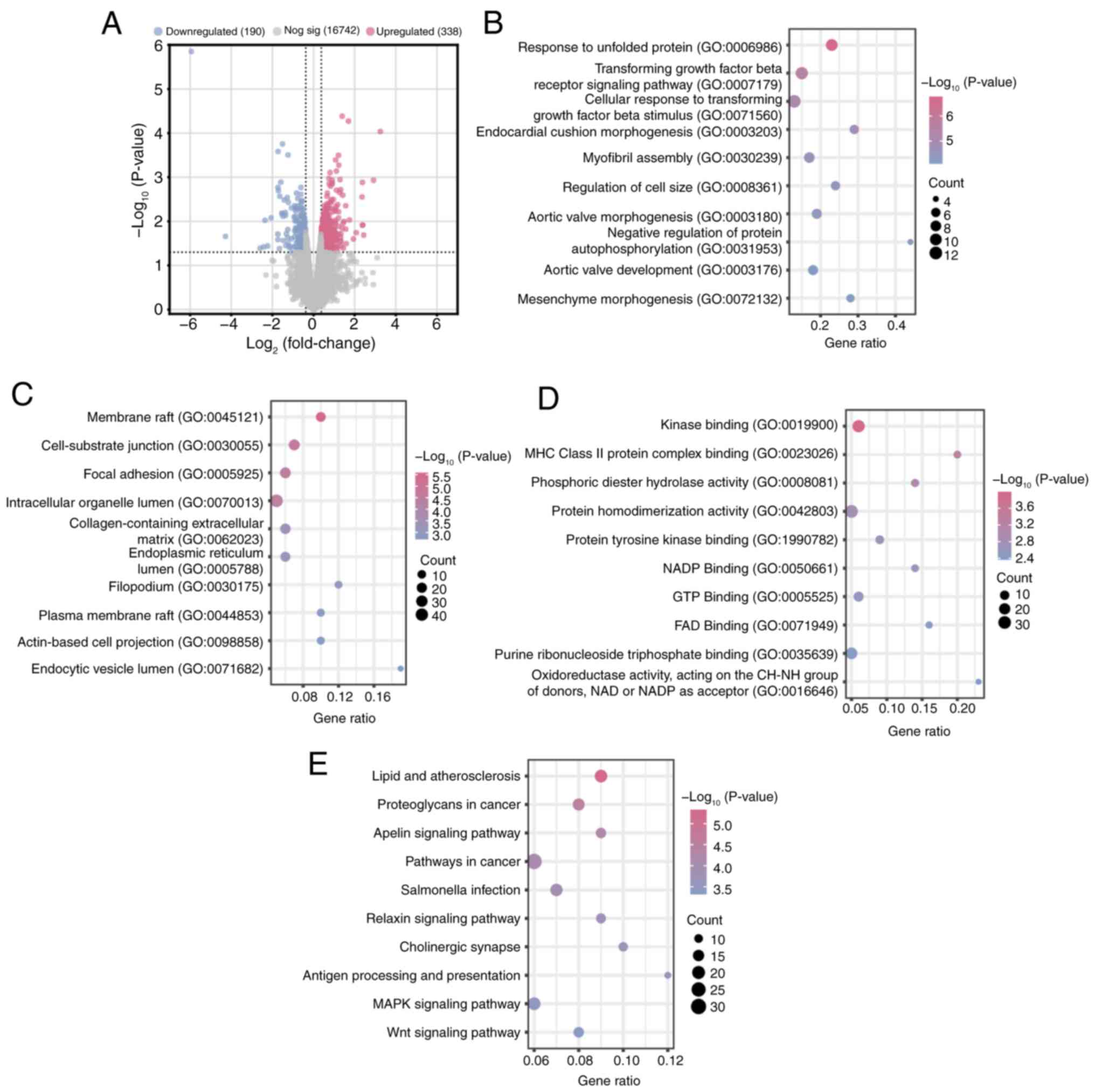
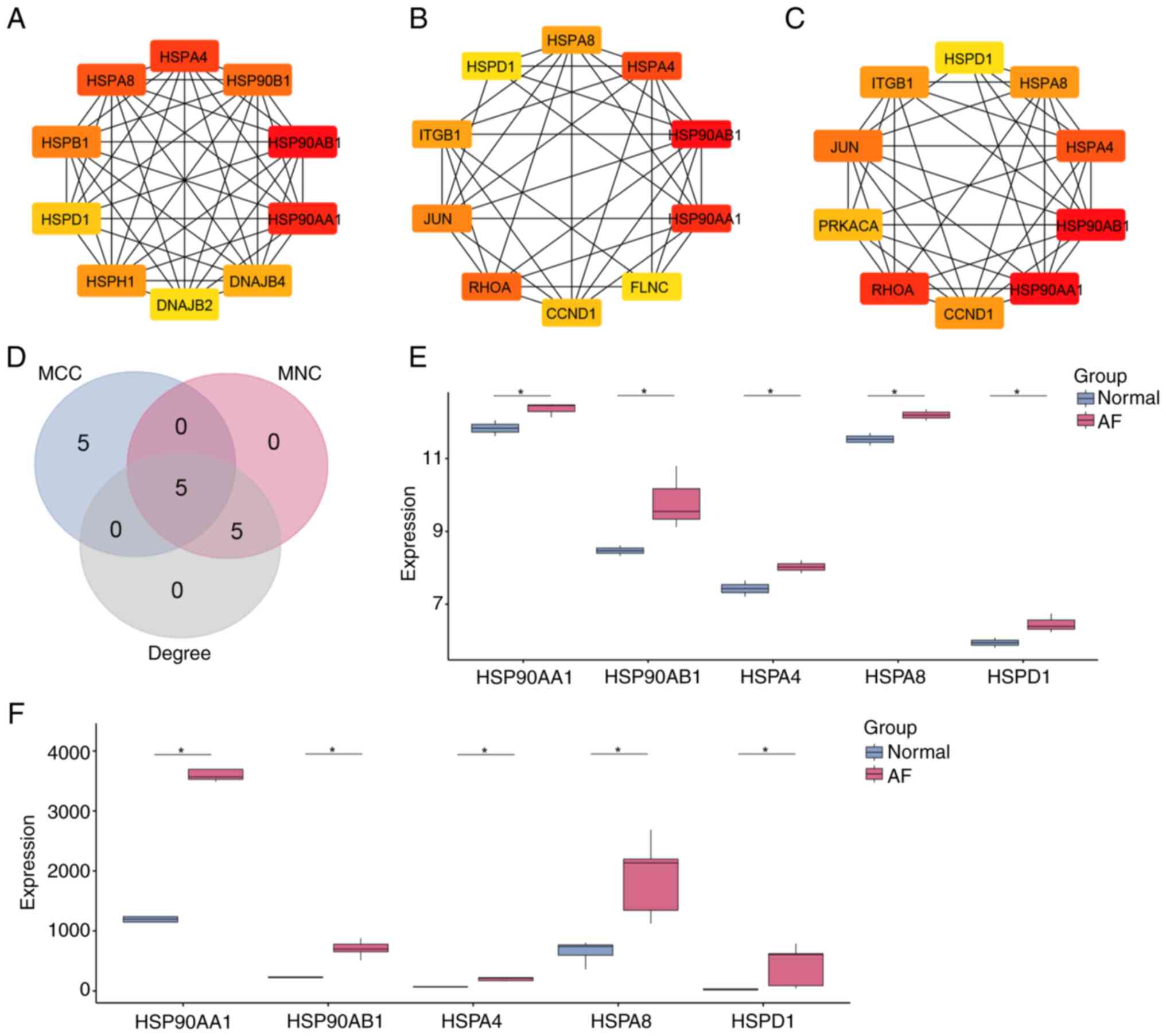
|
4
|
Carlisle MA, Fudim M, DeVore AD and
Piccini JP: Heart failure and atrial fibrillation, like fire and
fury. JACC Heart Fail. 7:447–456. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Karakasis P, Theofilis P, Vlachakis PK,
Korantzopoulos P, Patoulias D, Antoniadis AP and Fragakis N: Atrial
fibrosis in atrial fibrillation: Mechanistic insights, diagnostic
challenges, and emerging therapeutic targets. Int J Mol Sci.
26:2092024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Huang J, Wu B, Qin P, Cheng Y, Zhang Z and
Chen Y: Research on atrial fibrillation mechanisms and prediction
of therapeutic prospects: Focus on the autonomic nervous system
upstream pathways. Front Cardiovasc Med. 10:12704522023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Korbecki J, Bobiński R and Dutka M:
Self-regulation of the inflammatory response by peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors. Inflamm Res. 68:443–458. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Qiu YY, Zhang J, Zeng FY and Zhu YZ: Roles
of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) in the
pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Pharmacol
Res. 192:1067862023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Tahri-Joutey M, Andreoletti P, Surapureddi
S, Nasser B, Cherkaoui-Malki M and Latruffe N: Mechanisms mediating
the regulation of peroxisomal fatty acid beta-oxidation by PPARα.
Int J Mol Sci. 22:89692021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Montaigne D, Butruille L and Staels B:
PPAR control of metabolism and cardiovascular functions. Nat Rev
Cardiol. 18:809–823. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Recinella L, Orlando G, Ferrante C,
Chiavaroli A, Brunetti L and Leone S: Adipokines: New potential
therapeutic target for obesity and metabolic, rheumatic, and
cardiovascular diseases. Front Physiol. 11:5789662020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhu X, Zhang X, Cong X, Zhu L and Ning Z:
ANGPTL4 attenuates Ang II-induced atrial fibrillation and fibrosis
in mice via PPAR pathway. Cardiol Res Pract. 2021:99353102021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zheng P, Zhang W, Wang J, Gong Q, Xu N and
Chen N: Bioinformatics and functional experiments reveal that MRC2
inhibits atrial fibrillation via the PPAR signaling pathway. J
Thorac Dis. 15:5625–5639. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Xu D, Murakoshi N, Igarashi M, Hirayama A,
Ito Y, Seo Y, Tada H and Aonuma K: PPAR-γ activator pioglitazone
prevents age-related atrial fibrillation susceptibility by
improving antioxidant capacity and reducing apoptosis in a rat
model. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 23:209–217. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Enomoto H, Mittal N, Inomata T, Arimura T,
Izumi T, Kimura A, Fukuda K and Makino S: Dilated
cardiomyopathy-linked heat shock protein family D member 1
mutations cause up-regulation of reactive oxygen species and
autophagy through mitochondrial dysfunction. Cardiovasc Res.
117:1118–1131. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wachoski-Dark E, Zhao T, Khan A, Shutt TE
and Greenway SC: Mitochondrial protein homeostasis and
cardiomyopathy. Int J Mol Sci. 23:33532022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Khafaga AF, Noreldin AE and Saadeldin IM:
Role of HSP in the pathogenesis of age-related inflammatory
diseases. Heat Shock Proteins in Inflammatory Diseases. Asea AAA
and Kaur P: Volume 22. Springer; Cham: pp. 341–371. 2020,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
van Marion DMS, Ramos KS, Lanters EAH,
Bulte LB, Bogers AJJC, de Groot NMS and Brundel BJJM: Atrial heat
shock protein levels are associated with early postoperative and
persistence of atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 18:1790–1798.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Oc M, Ucar HI, Pinar A, Akbulut B, Oc B,
Akyon Y, Kanbak M and Dogan R: Heat shock protein70: A new marker
for subsequent atrial fibrillation development? Artif Organs.
32:846–850. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Meijering RAM, Zhang D, Hoogstra-Berends
F, Henning R and Brundel BJJM: Loss of proteostatic control as a
substrate for atrial fibrillation: A novel target for upstream
therapy by heat shock proteins. Front Physiol. 3:362012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Nehme A, Zouein FA, Zayeri ZD and Zibara
K: An update on the tissue renin angiotensin system and its role in
physiology and pathology. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 6:142019.
|
|
22
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang
J, Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for annotation,
visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Boil. 4:P32003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Fang Y, Liu L and Wang H: The four key
genes participated in and maintained atrial fibrillation process
via reprogramming lipid metabolism in AF patients. Front Genet.
13:8217542022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Xiao S, Zhou Y, Liu Q, Zhang T and Pan D:
Identification of pivotal MicroRNAs and target genes associated
with persistent atrial fibrillation based on bioinformatics
analysis. Comput Math Methods Med. 2021:66802112021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Okamoto Y, Nagasawa Y, Obara Y, Ishii K,
Takagi D and Ono K: Molecular identification of HSPA8 as an
accessory protein of a hyperpolarization-activated chloride channel
from rat pulmonary vein cardiomyocytes. J Biol Chem.
294:16049–16061. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Marques Rodrigues D: The role of heat
shock protein A4 (HSPA4) in the heart. eDiss. 2023.
|
|
27
|
Rowin EJ, Link MS, Maron MS and Maron BJ:
Evolving contemporary management of atrial fibrillation in
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Circulation. 148:1797–1811. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Hesselkilde EZ, Carstensen H, Flethøj M,
Fenner M, Kruse DD, Sattler SM, Tfelt-Hansen J, Pehrson S,
Braunstein TH, Carlson J, et al: Longitudinal study of electrical,
functional and structural remodelling in an equine model of atrial
fibrillation. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 19:2282019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Velleca M, Costa G, Goldstein LJ, Bishara
M, Ming Boo L and Sha Q: Management of atrial fibrillation in
Europe: Current care pathways and the clinical impact of
antiarrhythmic drugs and catheter ablation. EMJ Cardiol. 7:98–109.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhou S, Jin X, Chen X, Zhu J, Xu Z, Wang
X, Liu F, Hu W, Zhou L and Su C: Heat shock protein 60 in eggs
specifically induces Tregs and reduces liver immunopathology in
mice with Schistosomiasis japonica. PLoS One. 10:e01391332015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Yang YL, Wang PW, Wang FS, Lin HY and
Huang YH: miR-29a modulates GSK3β/SIRT1-linked mitochondrial
proteostatic stress to ameliorate mouse non-alcoholic
steatohepatitis. Int J Mol Sci. 21:68842020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Fu Y, Zhao D, Zhou Y, Lu J, Kang L, Jiang
X, Xu R, Ding Z and Zou Y: Identification of differential
expression genes between volume and pressure overloaded hearts
based on bioinformatics analysis. Genes (Basel). 13:12762022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zheng J, Zhao S, Yang Q, Wei Y, Li J and
Guo T: Sympathetic activation promotes cardiomyocyte apoptosis in a
rabbit susceptibility model of hyperthyroidism-induced atrial
fibrillation via the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Crit Rev Eukaryot
Gene Expr. 33:17–27. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Wolke C, Antileo E and Lendeckel U: WNT
signaling in atrial fibrillation. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
246:1112–1120. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhao J, Yu L, Xue X, Xu Y, Huang T, Xu D,
Wang Z, Luo L and Wang H: Diminished α7 nicotinic acetylcholine
receptor (α7nAChR) rescues amyloid-β induced atrial remodeling by
oxi-CaMKII/MAPK/AP-1 axis-mediated mitochondrial oxidative stress.
Redox Biol. 59:1025942023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zeng X and Yang Y: Molecular mechanisms
underlying vascular remodeling in hypertension. Rev Cardiovasc Med.
25:722024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Sygitowicz G, Maciejak-Jastrzębska A and
Sitkiewicz D: A review of the molecular mechanisms underlying
cardiac fibrosis and atrial fibrillation. J Clin Med. 10:44302021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Mirabito Colafella KM, Bovée DM and Danser
AHJ: The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and its therapeutic
targets. Exp Eye Res. 186:1076802019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Singh D, Rai V and Agrawal DK: Regulation
of collagen I and collagen III in tissue injury and regeneration.
Cardiol Cardiovasc Med. 7:5–16. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Hinz B, McCulloch CA and Coelho NM:
Mechanical regulation of myofibroblast phenoconversion and collagen
contraction. Exp Cell Res. 379:119–128. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Ma J, Chen Q and Ma S: Left atrial
fibrosis in atrial fibrillation: Mechanisms, clinical evaluation
and management. J Cell Mol Med. 25:2764–2775. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Su H, Su H, Liu CH, Hu HJ, Zhao JB, Zou T
and Tang YX: H2S inhibits atrial fibrillation-induced
atrial fibrosis through miR-133a/CTGF axis. Cytokine.
146:1555572021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Li PF, He RH, Shi SB, Li R, Wang QT, Rao
GT and Yang B: Modulation of miR-10a-mediated TGF-β1/Smads
signaling affects atrial fibrillation-induced cardiac fibrosis and
cardiac fibroblast proliferation. Biosci Rep. 39:BSR201819312019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Nakamura F, Tsukamoto I, Inoue S,
Hashimoto K and Akagi M: Cyclic compressive loading activates
angiotensin II type 1 receptor in articular chondrocytes and
stimulates hypertrophic differentiation through a
G-protein-dependent pathway. FEBS Open Bio. 8:962–973. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Soare AY, Durham ND, Gopal R, Tweel B,
Hoffman KW, Brown JA, O'Brien M, Bhardwaj N, Lim JK, Chen BK and
Swartz TH: P2X antagonists inhibit HIV-1 productive infection and
inflammatory cytokines interleukin-10 (IL-10) and IL-1β in a human
tonsil explant model. J Virol. 93:e01186–18. 2018.
|
|
46
|
Rao S, Pena C, Shurmur S and Nugent K:
Atrial natriuretic peptide: Structure, function, and physiological
effects: A narrative review. Curr Cardiol Rev.
17:e0511211910032021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Bai L, Zhao Y, Zhao L, Zhang M, Cai Z,
Yung KKL, Dong C and Li R: Ambient air PM2.5 exposure
induces heart injury and cardiac hypertrophy in rats through
regulation of miR-208a/b, α/β-MHC, and GATA4. Environ Toxicol
Pharmacol. 85:1036532021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Henriet P and Emonard H: Matrix
metalloproteinase-2: Not (just) a ‘hero’ of the past. Biochimie.
166:223–232. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Thijssen VLJL, van der Velden HMW, van
Ankeren EP, Ausma J, Allessie MA, Borgers M, van Eys GJJM and
Jongsma HJ: Analysis of altered gene expression during sustained
atrial fibrillation in the goat. Cardiovasc Res. 54:427–437. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Yang Q, Qi X, Dang Y, Li Y, Song X and Hao
X: Effects of atorvastatin on atrial remodeling in a rabbit model
of atrial fibrillation produced by rapid atrial pacing. BMC
Cardiovasc Disord. 16:1422016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Xia PP, Li LJ, Qi RD, Shi JJ, Ju WZ and
Chen ML: Electrical and histological remodeling of the pulmonary
vein in 2K1C hypertensive rats: Indication of initiation and
maintenance of atrial fibrillation. Anatol J Cardiol. 19:169–175.
2018.
|
|
52
|
Hauffe R, Rath M, Schell M, Ritter K,
Kappert K, Deubel S, Ott C, Jähnert M, Jonas W, Schürmann A and
Kleinridders A: HSP60 reduction protects against diet-induced
obesity by modulating energy metabolism in adipose tissue. Mol
Metab. 53:1012762021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Kleinridders A, Lauritzen HPMM, Ussar S,
Christensen JH, Mori MA, Bross P and Kahn CR: Leptin regulation of
Hsp60 impacts hypothalamic insulin signaling. J Clin Invest.
123:4667–4680. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Timofeev YS, Kiselev AR, Dzhioeva ON and
Drapkina OM: Heat shock proteins (HSPs) and cardiovascular
complications of obesity: Searching for potential biomarkers. Curr
Issues Mol Biol. 45:9378–9389. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Bougarne N, Weyers B, Desmet SJ, Deckers
J, Ray DW, Staels B and De Bosscher K: Molecular actions of PPARα
in lipid metabolism and inflammation. Endocr Rev. 39:760–802. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Wang X, Zhu XX, Jiao SY, Qi D, Yu BQ, Xie
GM, Liu Y, Song YT, Xu Q, Xu QB, et al: Cardiomyocyte peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor α is essential for energy
metabolism and extracellular matrix homeostasis during pressure
overload-induced cardiac remodeling. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
43:1231–1242. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Song F, Mao YJ, Hu Y, Zhao SS, Wang R, Wu
WY, Li GR, Wang Y and Li G: Acacetin attenuates diabetes-induced
cardiomyopathy by inhibiting oxidative stress and energy metabolism
via PPAR-α/AMPK pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 922:1749162022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Liu X, Xu X, Zhang T, Xu L, Tao H, Liu Y,
Zhang Y and Meng X: Fatty acid metabolism disorders and potential
therapeutic traditional Chinese medicines in cardiovascular
diseases. Phytother Res. 37:4976–4998. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Zhang J, Ren D, Fedorova J, He Z and Li J:
SIRT1/SIRT3 modulates redox homeostasis during ischemia/reperfusion
in the aging heart. Antioxidants (Basel). 9:8582020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Kvandová M, Majzúnová M and Dovinová I:
The role of PPARgamma in cardiovascular diseases. Physiol Res. 65
(Suppl 3):S343–S363. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Metzger JM, Matsoff HN, Zinnen AD,
Fleddermann RA, Bondarenko V, Simmons HA, Mejia A, Moore CF and
Emborg ME: Post mortem evaluation of inflammation, oxidative
stress, and PPARγ activation in a nonhuman primate model of cardiac
sympathetic neurodegeneration. PLoS One. 15:e02269992020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Singh MK, Shin Y, Han S, Ha J, Tiwari PK,
Kim SS and Kang I: Molecular chaperonin HSP60: Current
understanding and future prospects. Int J Mol Sci. 25:54832024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Pokharel MD, Marciano DP, Fu P, Franco MC,
Unwalla H, Tieu K, Fineman JR, Wang T and Black SM: Metabolic
reprogramming, oxidative stress, and pulmonary hypertension. Redox
Biol. 64:1027972023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Navaneethabalakrishnan S, Smith HL, Arenaz
CM, Goodlett BL, McDermott JG and Mitchell BM: Update on immune
mechanisms in hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 35:842–851. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Escobales N, Nuñez RE and Javadov S:
Mitochondrial angiotensin receptors and cardioprotective pathways.
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 316:H1426–H438. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|