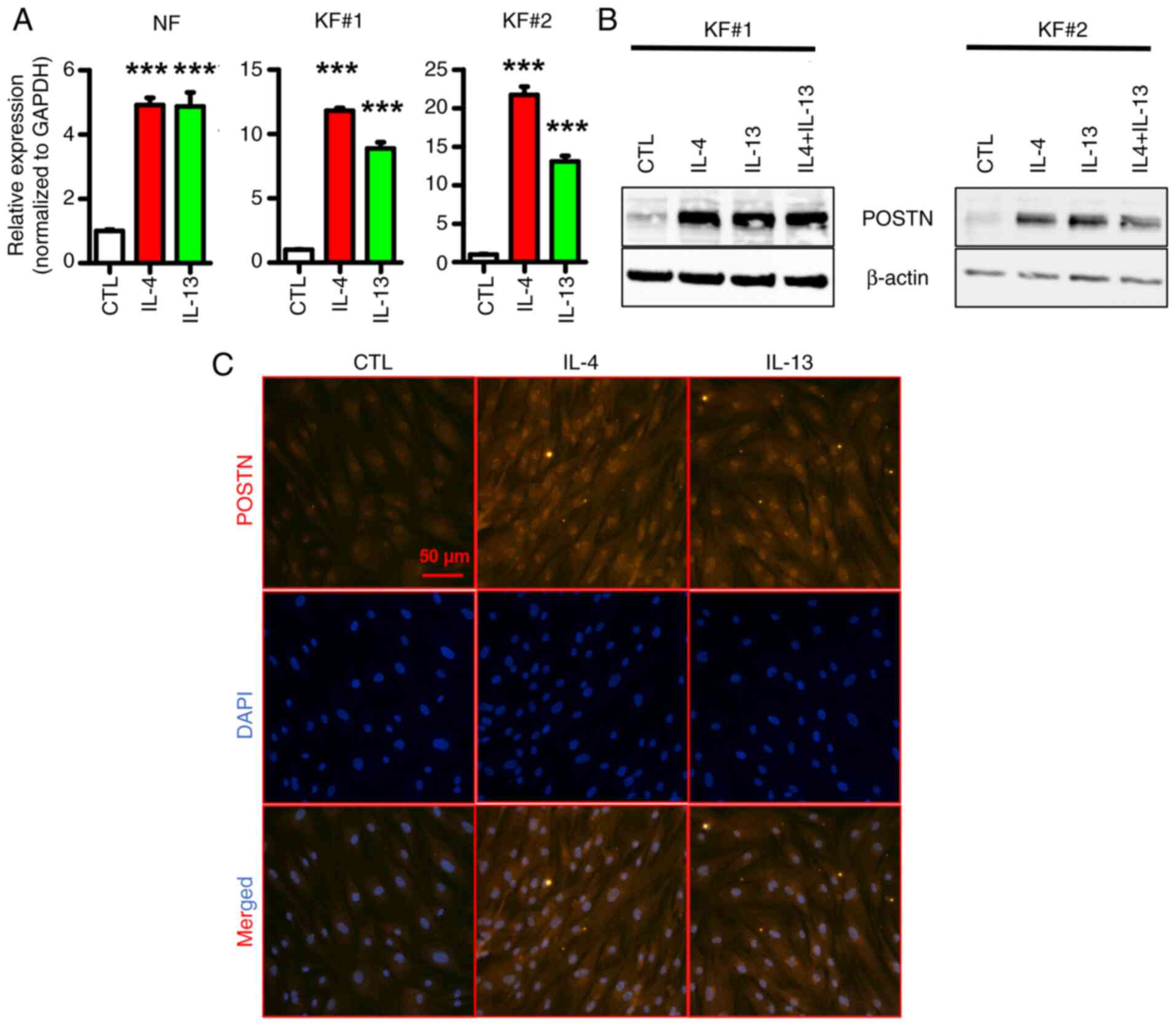
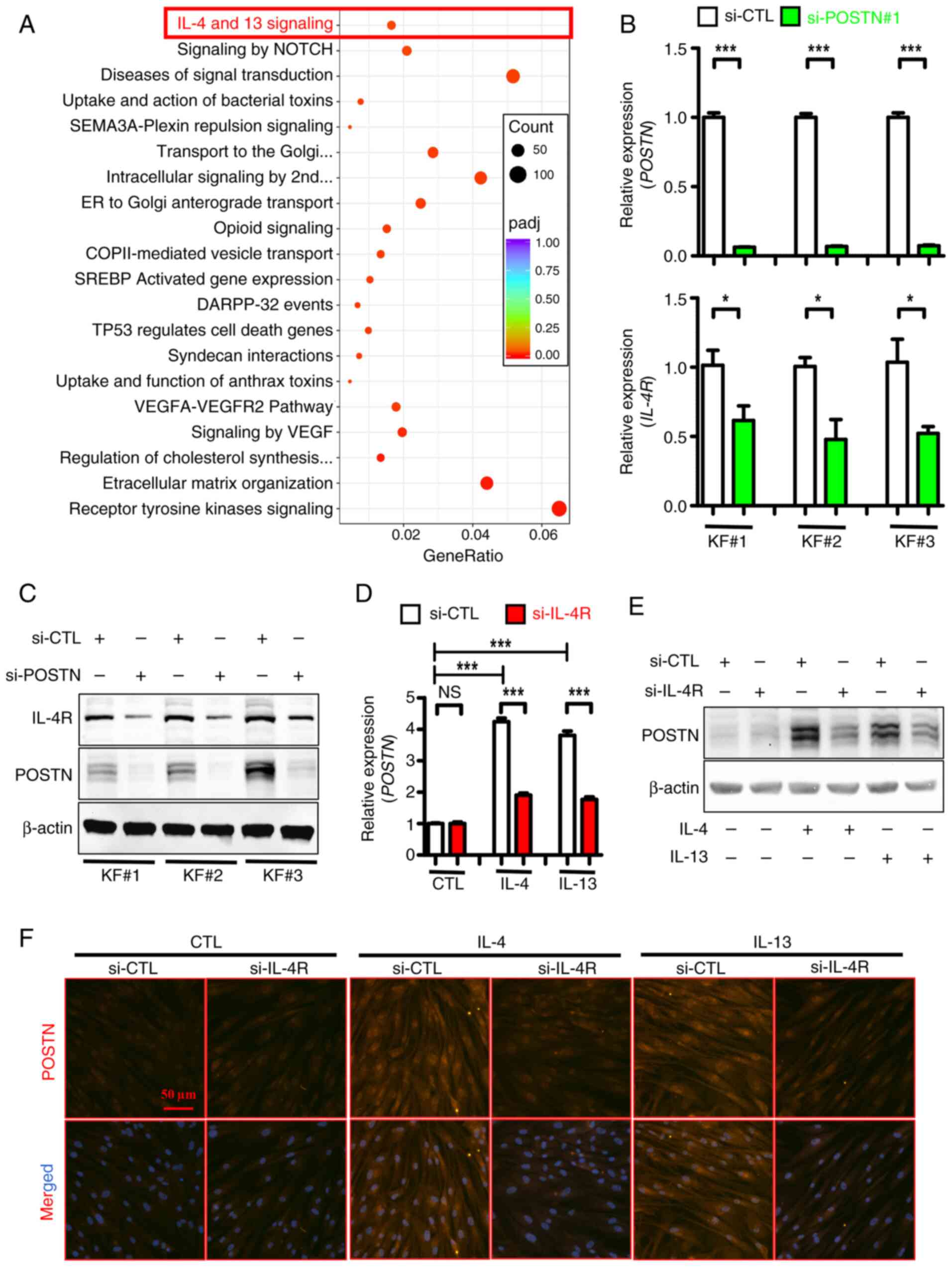
|
1
|
Jiang Z, Chen Z, Xu Y, Li H, Li Y, Peng L,
Shan H, Liu X, Wu H, Wu L, et al: Low-frequency ultrasound
sensitive piezo1 channels regulate Keloid-related characteristics
of fibroblasts. Adv Sci (Weinh). 11:e23054892024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cohen AJ, Nikbakht N and Uitto J: Keloid
disorder: Genetic basis, gene expression profiles, and
immunological modulation of the fibrotic processes in the skin.
Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 15:a0412452023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wang ZC, Zhao WY, Cao Y, Liu YQ, Sun Q,
Shi P, Cai JQ, Shen XZ and Tan WQ: The roles of inflammation in
keloid and hypertrophic scars. Front Immunol. 11:6031872020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zhang M, Chen H, Qian H and Wang C:
Characterization of the skin keloid microenvironment. Cell Commun
Signal. 21:2072023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Delaleu J, Charvet E and Petit A: Keloid
disease: Review with clinical atlas. Part I: Definitions, history,
epidemiology, clinics and diagnosis. Ann Dermatol Venereol.
150:3–15. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hawash AA, Ingrasci G, Nouri K and
Yosipovitch G: Pruritus in keloid scars: Mechanisms and treatments.
Acta Derm Venereol. 101:adv005822021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Walsh LA, Wu E, Pontes D, Kwan KR, Poondru
S, Miller CH and Kundu RV: Keloid treatments: An evidence-based
systematic review of recent advances. Syst Rev. 12:422023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Naik PP: Novel targets and therapies for
keloid. Clin Exp Dermatol. 47:507–515. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ekstein SF, Wyles SP, Moran SL and Meves
A: Keloids: A review of therapeutic management. Int J Dermatol.
60:661–671. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kim J, Kim B, Kim SM, Yang CE, Song SY,
Lee WJ and Lee JH: Hypoxia-induced Epithelial-To-Mesenchymal
transition mediates fibroblast abnormalities via ERK activation in
cutaneous wound healing. Int J Mol Sci. 20:25462019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kang Y, Roh MR, Rajadurai S, Rajadurai A,
Kumar R, Njauw CN, Zheng Z and Tsao H: Hypoxia and HIF-1α regulate
collagen production in keloids. J Invest Dermatol. 140:2157–2165.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Guo C, Liang L, Zheng J, Xie Y, Qiu X, Tan
G, Huang J and Wang L: UCHL1 aggravates skin fibrosis through an
IGF-1-induced Akt/mTOR/HIF-1α pathway in keloid. FASEB J.
37:e230152023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gu JJ, Deng CC, Feng QL, Liu J, Zhu DH,
Cheng Q, Rong Z and Yang B: Relief of extracellular matrix
deposition repression by downregulation of IRF1-mediated TWEAK/Fn14
signaling in keloids. J Invest Dermatol. 143:1208–1219. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wang Y, Chen Y, Wu J and Shi X: BMP1
Promotes keloid by inducing fibroblast inflammation and
fibrogenesis. J Cell Biochem. 125:e306092024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mao J, Chen L, Qian S, Wang Y, Zhao B,
Zhao Q, Lu B, Mao X, Zhai P, Zhang Y, et al: Transcriptome network
analysis of inflammation and fibrosis in keloids. J Dermatol Sci.
113:62–73. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wang X, Wang X, Liu Z, Liu L, Zhang J,
Jiang D and Huang G: Identification of inflammation-related
biomarkers in keloids. Front Immunol. 15:13515132024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lee SY, Lee AR, Choi JW, Lee CR, Cho KH,
Lee JH and Cho ML: IL-17 induces autophagy dysfunction to promote
inflammatory cell death and fibrosis in keloid fibroblasts via the
STAT3 and HIF-1α dependent signaling pathways. Front Immunol.
13:8887192022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lee SY, Kim EK, Seo HB, Choi JW, Yoo JH,
Jung KA, Kim DS, Yang SC, Moon SJ, Lee JH and Cho ML: IL-17 induced
stromal Cell-derived Factor-1 and profibrotic factor in
Keloid-derived skin fibroblasts via the STAT3 pathway.
Inflammation. 43:664–672. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shin JU, Kim SH, Kim H, Noh JY, Jin S,
Park CO, Lee WJ, Lee DW, Lee JH and Lee KH: TSLP Is a potential
initiator of collagen synthesis and an activator of CXCR4/SDF-1
axis in keloid pathogenesis. J Invest Dermatol. 136:507–515. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Chen Z, Gao Z, Xia L, Wang X, Lu L and Wu
X: Dysregulation of DPP4-CXCL12 balance by TGF-β1/SMAD pathway
promotes CXCR4+ inflammatory cell infiltration in keloid scars. J
Inflamm Res. 14:4169–4180. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
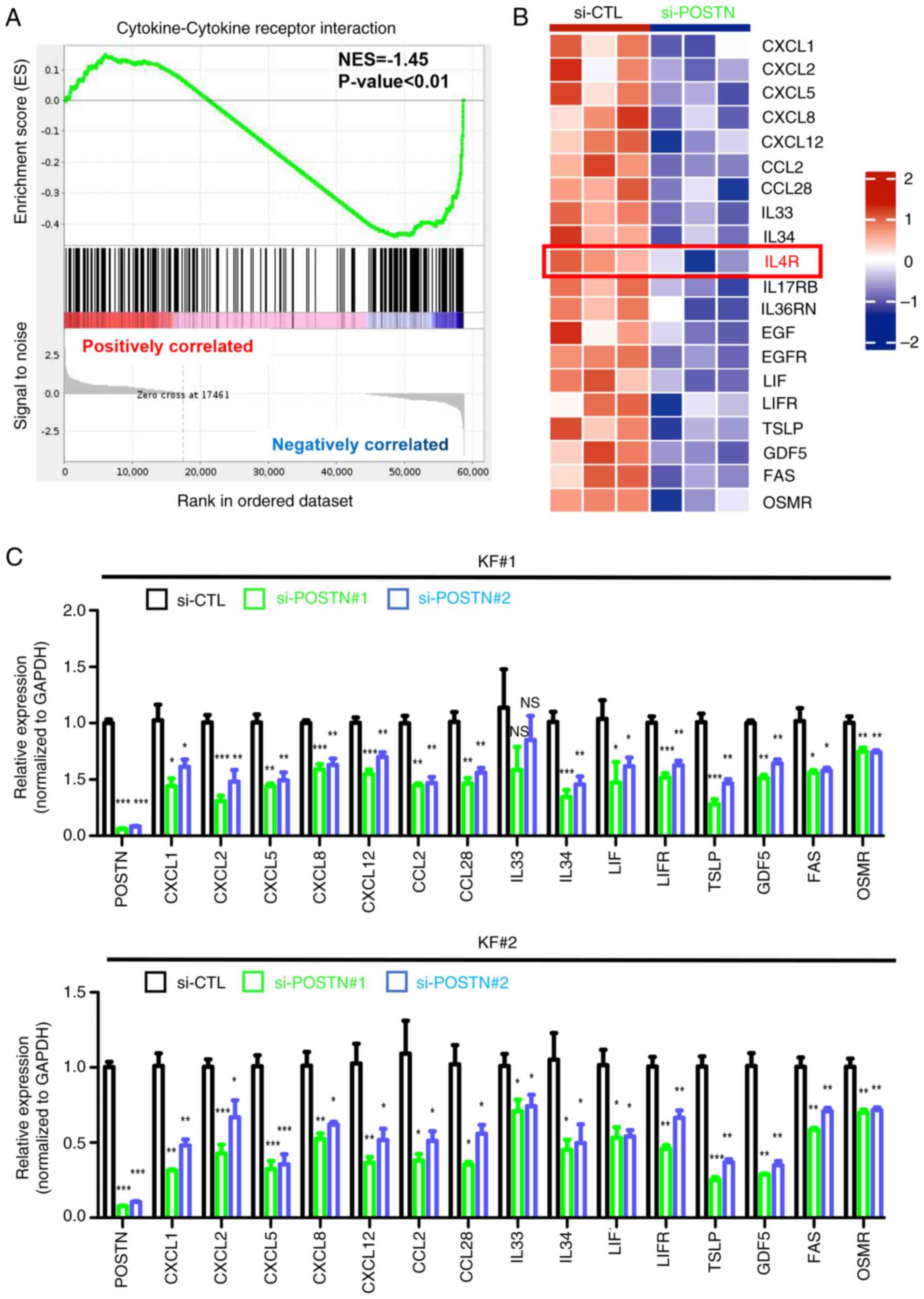
Nguyen JK, Austin E, Huang A, Mamalis A
and Jagdeo J: The IL-4/IL-13 axis in skin fibrosis and scarring:
Mechanistic concepts and therapeutic targets. Arch Dermatol Res.
312:81–92. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Smith JC, Boone BE, Opalenik SR, Williams
SM and Russell SB: Gene profiling of keloid fibroblasts shows
altered expression in multiple fibrosis-associated pathways. J
Invest Dermatol. 128:1298–1310. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Hahn JM, Glaser K, McFarland KL, Aronow
BJ, Boyce ST and Supp DM: Keloid-derived keratinocytes exhibit an
abnormal gene expression profile consistent with a distinct causal
role in keloid pathology. Wound Repair Regen. 21:530–544. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Smyth GK: Limma: Linear models for
microarray data. Bioinformatics and computational biology solutions
using R and Bioconductor. Springer; New York, NY: pp. 397–420.
2005, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: Limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen C, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas HR, Frank
MH, He Y and Xia R: TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for
interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol Plant.
13:1194–1202. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Williams R and Thornton MJ: Isolation of
different dermal fibroblast populations from the skin and the hair
follicle. Methods Mol Biol. 2154:13–22. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Huang C, Zhong W, Ren X, Huang X, Li Z,
Chen C, Jiang B, Chen Z, Jian X, Yang L, et al: MiR-193b-3p-ERBB4
axis regulates psoriasis pathogenesis via modulating cellular
proliferation and inflammatory-mediator production of
keratinocytes. Cell Death Dis. 12:9632021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huang C, Lv X, Chen P, Liu J, He C, Chen
L, Wang H, Moness ML, Dong J, Rueda BR, et al: Human papillomavirus
targets the YAP1-LATS2 feedback loop to drive cervical cancer
development. Oncogene. 41:3761–3777. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Huang C, Li W, Shen C, Jiang B, Zhang K,
Li X, Zhong W, Li Z, Chen Z, Chen C, et al: YAP1 facilitates the
pathogenesis of psoriasis via modulating keratinocyte proliferation
and inflammation. Cell Death Dis. 16:1862025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wu J, Del Duca E, Espino M, Gontzes A,
Cueto I, Zhang N, Estrada YD, Pavel AB, Krueger JG and
Guttman-Yassky E: RNA sequencing keloid transcriptome associates
keloids with Th2, Th1, Th17/Th22, and JAK3-skewing. Front Immunol.
11:5977412020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
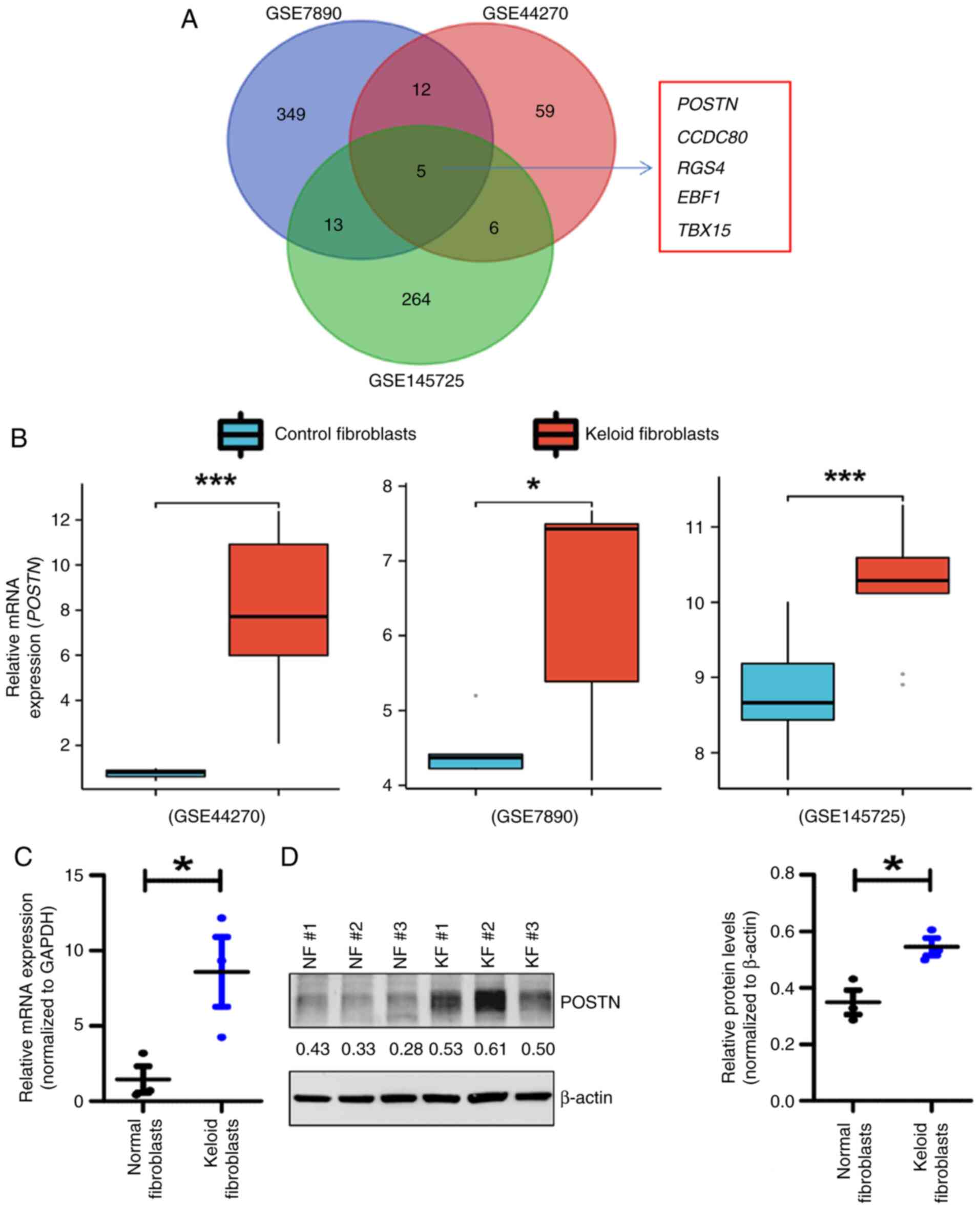
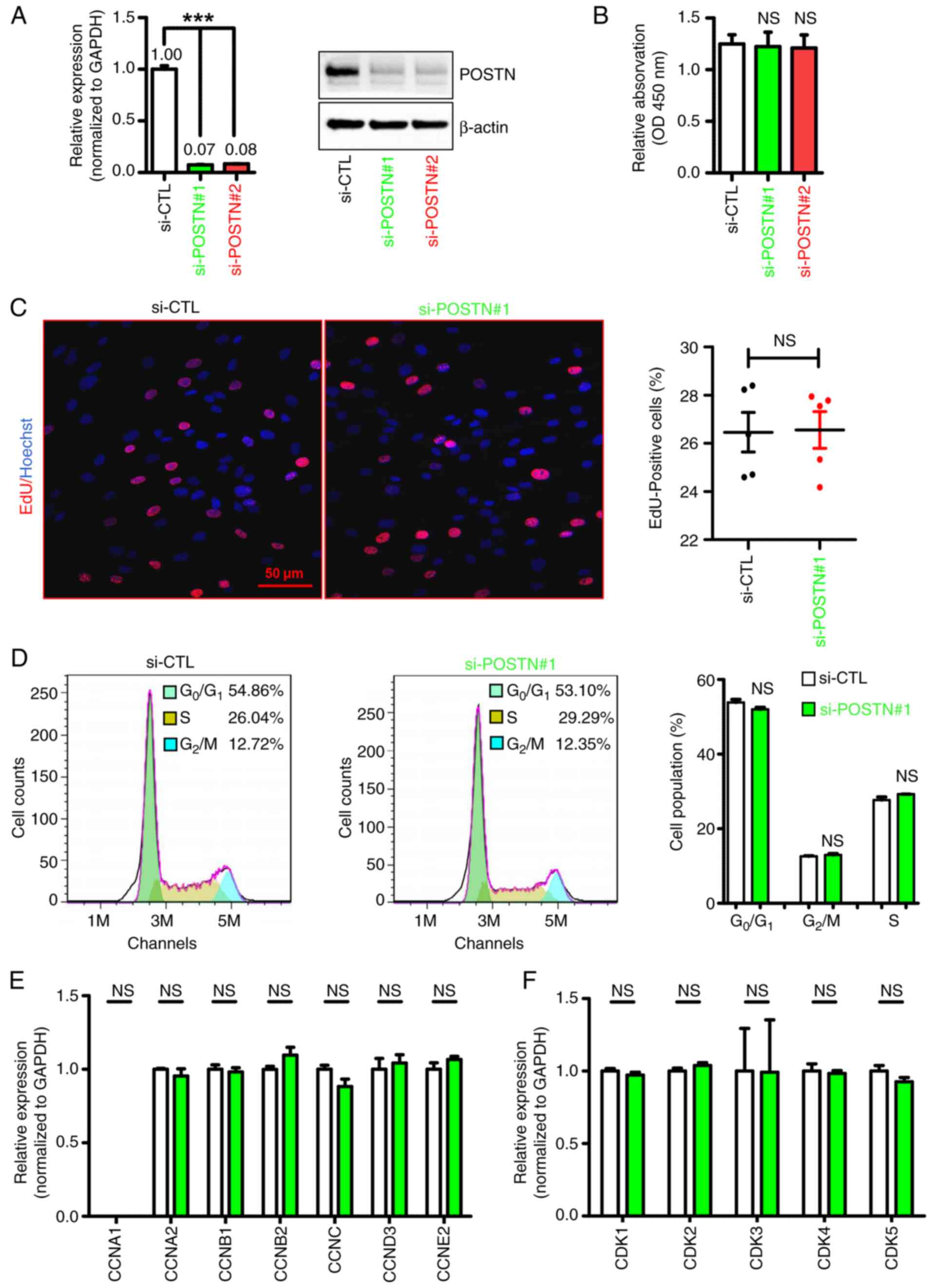
Xu H, Wang Z, Yang H, Zhu J and Hu Z:
Bioinformatics analysis and identification of dysregulated POSTN in
the pathogenesis of keloid. Int Wound J. 20:1700–1711. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nangole FW, Ouyang K, Anzala O, Ogengo J
and Agak GW: Multiple cytokines elevated in patients with keloids:
Is it an indication of Auto-inflammatory disease? J Inflamm Res.
14:2465–2470. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Masuoka M, Shiraishi H, Ohta S, Suzuki S,
Arima K, Aoki S, Toda S, Inagaki N, Kurihara Y, Hayashida S, et al:
Periostin promotes chronic allergic inflammation in response to Th2
cytokines. J Clin Invest. 122:2590–2600. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Arima K, Ohta S, Takagi A, Shiraishi H,
Masuoka M, Ontsuka K, Suto H, Suzuki S, Yamamoto K, Ogawa M, et al:
Periostin contributes to epidermal hyperplasia in psoriasis common
to atopic dermatitis. Allergol Int. 64:41–48. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Mitamura Y, Nunomura S, Nanri Y, Ogawa M,
Yoshihara T, Masuoka M, Tsuji G, Nakahara T, Hashimoto-Hachiya A,
Conway SJ, et al: The IL-13/periostin/IL-24 pathway causes
epidermal barrier dysfunction in allergic skin inflammation.
Allergy. 73:1881–1891. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kou K, Okawa T, Yamaguchi Y, Ono J, Inoue
Y, Kohno M, Matsukura S, Kambara T, Ohta S, Izuhara K and Aihara M:
Periostin levels correlate with disease severity and chronicity in
patients with atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 171:283–291. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Akar-Ghibril N, Casale T, Custovic A and
Phipatanakul W: Allergic endotypes and phenotypes of asthma. J
Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 8:429–440. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Frech FS, Hernandez L, Urbonas R, Zaken
GA, Dreyfuss I and Nouri K: Hypertrophic scars and keloids:
Advances in treatment and review of established therapies. Am J
Clin Dermatol. 24:225–245. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
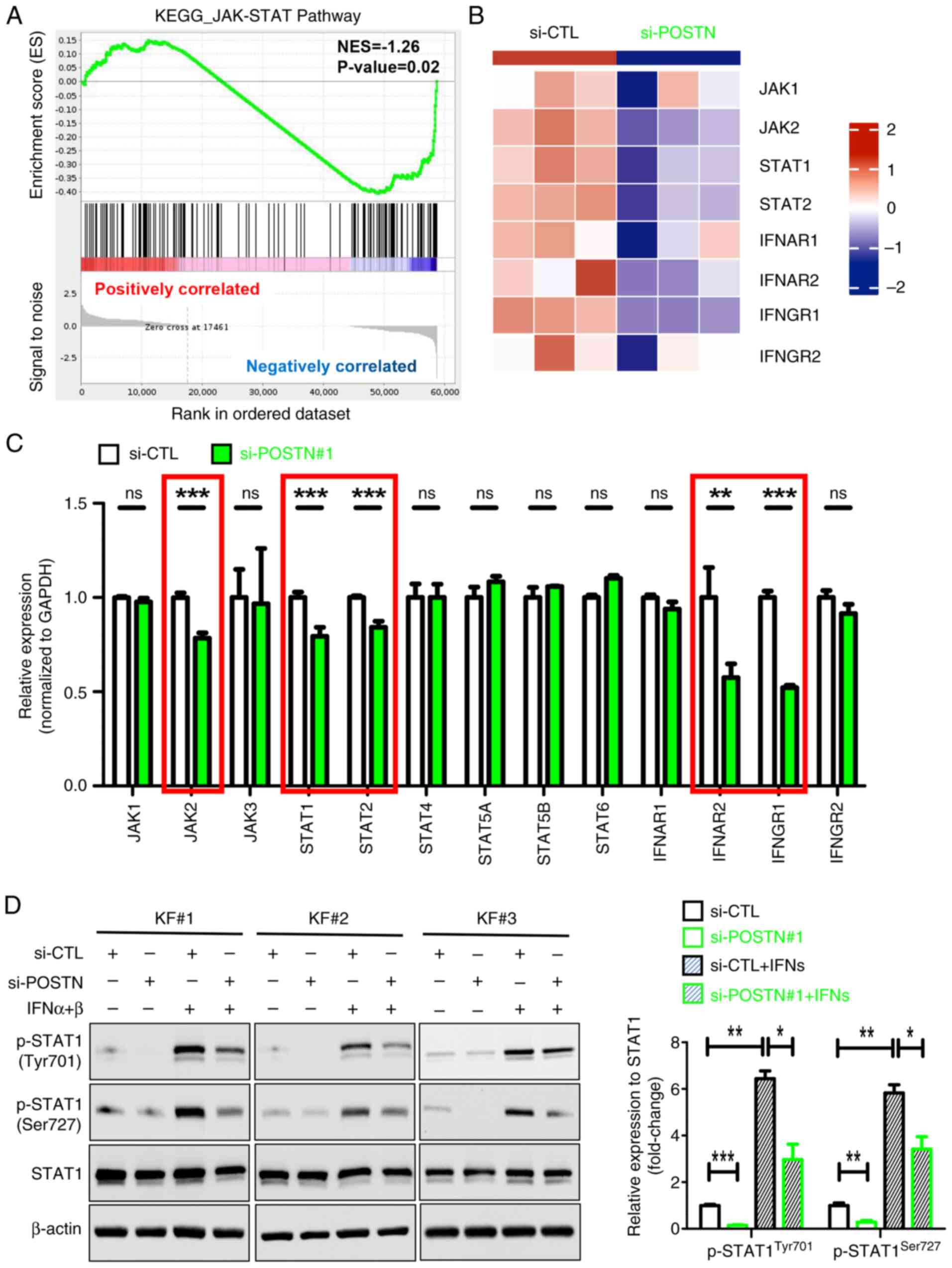
Tian J, Liu X, Zhu D and Li J: Periostin
regulates the activity of keloid fibroblasts by activating the
JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Heliyon. 10:e388212024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yin SL, Qin ZL and Yang X: Role of
periostin in skin wound healing and pathologic scar formation. Chin
Med J (Engl). 133:2236–2238. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sonnenberg-Riethmacher E, Miehe M and
Riethmacher D: Periostin in allergy and inflammation. Front
Immunol. 12:7221702021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Crawford J, Nygard K, Gan BS and O'Gorman
DB: Wound healing and fibrosis: A contrasting role for periostin in
skin and the oral mucosa. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
318:C1065–C1077. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Chen L, Su Y, Yin B, Li S, Cheng X, He Y
and Jia C: LARP6 regulates keloid fibroblast proliferation,
invasion, and ability to synthesize collagen. J Invest Dermatol.
142:2395–2405. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Yin Q, Wolkerstorfer A, Lapid O, Niessen
FB, Van Zuijlen PPM and Gibbs S: The JAK-STAT pathway in keloid
pathogenesis: A systematic review with qualitative synthesis. Exp
Dermatol. 32:588–598. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Limandjaja GC, van den Broek LJ, Waaijman
T, Breetveld M, Monstrey S, Scheper RJ, Niessen FB and Gibbs S:
Reconstructed human keloid models show heterogeneity within keloid
scars. Arch Dermatol Res. 310:815–826. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Tanaka R, Umeyama Y, Hagiwara H,
Ito-Hirano R, Fujimura S, Mizuno H and Ogawa R: Keloid patients
have higher peripheral blood endothelial progenitor cell counts and
CD34+ cells with normal vasculogenic and angiogenic
function that overexpress vascular endothelial growth factor and
interleukin-8. Int J Dermatol. 58:1398–1405. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Liao WT, Yu HS, Arbiser JL, Hong CH,
Govindarajan B, Chai CY, Shan WJ, Lin YF, Chen GS and Lee CH:
Enhanced MCP-1 release by keloid CD14+ cells augments fibroblast
proliferation: Role of MCP-1 and Akt pathway in keloids. Exp
Dermatol. 19:e142–e150. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Diaz A, Tan K, He H, Xu H, Cueto I, Pavel
AB, Krueger JG and Guttman-Yassky E: Keloid lesions show increased
IL-4/IL-13 signaling and respond to Th2-targeting dupilumab
therapy. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 34:e161–e164. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Lee CC, Tsai CH, Chen CH, Yeh YC, Chung WH
and Chen CB: An updated review of the immunological mechanisms of
keloid scars. Front Immunol. 14:11176302023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Junttila IS: Tuning the cytokine
responses: An update on interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 receptor
complexes. Front Immunol. 9:8882018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Zhang D, Li B and Zhao M: Therapeutic
strategies by regulating interleukin family to suppress
inflammation in hypertrophic scar and keloid. Front Pharmacol.
12:6677632021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Nangole FW and Agak GW: Keloid
pathophysiology: Fibroblast or inflammatory disorders? JPRAS Open.
22:44–54. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
He H, Suryawanshi H, Morozov P,
Gay-Mimbrera J, Del Duca E, Kim HJ, Kameyama N, Estrada Y, Der E,
Krueger JG, et al: Single-cell transcriptome analysis of human skin
identifies novel fibroblast subpopulation and enrichment of immune
subsets in atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
145:1615–1628. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Guttman-Yassky E, Bissonnette R, Ungar B,
Suárez-Fariñas M, Ardeleanu M, Esaki H, Suprun M, Estrada Y, Xu H,
Peng X, et al: Dupilumab progressively improves systemic and
cutaneous abnormalities in patients with atopic dermatitis. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 143:155–172. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Lu YY, Lu CC, Yu WW, Zhang L, Wang QR,
Zhang CL and Wu CH: Keloid risk in patients with atopic dermatitis:
A nationwide retrospective cohort study in Taiwan. BMJ Open.
8:e0228652018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Hajdarbegovic E, Bloem A, Balak D, Thio B
and Nijsten T: The association between atopic disorders and
keloids: A Case-control study. Indian J Dermatol. 60:6352015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|