|
1
|
Murayama M, Hirata H, Shiraki M, Iovanna
JL, Yamaza T, Kukita T, Komori T, Moriishi T, Ueno M, Morimoto T,
et al: Nupr1 deficiency downregulates HtrA1, enhances SMAD1
signaling, and suppresses age-related bone loss in male mice. J
Cell Physiol. 238:566–581. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ke HZ, Richards WG, Li X and Ominsky MS:
Sclerostin and Dickkopf-1 as therapeutic targets in bone diseases.
Endocr Rev. 33:747–783. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Creecy A, Brown KL, Rose KL, Voziyan P and
Nyman JS: Post-translational modifications in collagen type I of
bone in a mouse model of aging. Bone. 143:1157632021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang TL, Shen H, Liu A, Dong SS, Zhang L,
Deng FY, Zhao Q and Deng HW: A road map for understanding molecular
and genetic determinants of osteoporosis. Nat Rev Endocrinol.
16:91–103. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rim YA, Nam Y and Ju JH: The role of
chondrocyte hypertrophy and senescence in osteoarthritis initiation
and progression. Int J Mol Sci. 21:23582020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fujii Y, Liu L, Yagasaki L, Inotsume M,
Chiba T and Asahara H: Cartilage homeostasis and osteoarthritis.
Int J Mol Sci. 23:63162022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Verdú E, Ceballos D, Vilches JJ and
Navarro X: Influence of aging on peripheral nerve function and
regeneration. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 5:191–208. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mampay M and Sheridan GK: REST: An
epigenetic regulator of neuronal stress responses in the young and
ageing brain. Front Neuroendocrinol. 53:1007442019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Goto K, Naito K, Nakamura S, Nagura N,
Sugiyama Y, Obata H, Kaneko A and Kaneko K: Protective mechanism
against age-associated changes in the peripheral nerves. Life Sci.
253:1177442020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kaneko A, Naito K, Nakamura S, Miyahara K,
Goto K, Obata H, Nagura N, Sugiyama Y and Kaneko K: Influence of
aging on the peripheral nerve repair process using an artificial
nerve conduit. Exp Ther Med. 21:1682021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rodriguez-Bravo V, Pippa R, Song WM,
Carceles-Cordon M, Dominguez-Andres A, Fujiwara N, Woo J, Koh AP,
Ertel A, Lokareddy RK, et al: Nuclear pores promote lethal prostate
cancer by increasing POM121-driven E2F1, MYC, and AR nuclear
import. Cell. 174:1200–1215.e20. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kawamura M, Sato S, Matsumoto G, Fukuda T,
Shiba-Fukushima K, Noda S, Takanashi M, Mori N and Hattori N: Loss
of nuclear REST/NRSF in aged-dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson's
disease patients. Neurosci Lett. 699:59–63. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lu T, Aron L, Zullo J, Pan Y, Kim H, Chen
Y, Yang TH, Kim HM, Drake D, Liu XS, et al: REST and stress
resistance in ageing and Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 507:448–454.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mir AR and Moinuddin Islam S: Circulating
autoantibodies in cancer patients have high specificity for
glycoxidation modified histone H2A. Clin Chim Acta. 453:48–55.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nagata K, Nakashima-Kamimura N, Mikami T,
Ohsawa I and Ohta S: Consumption of molecular hydrogen prevents the
stress-induced impairments in hippocampus-dependent learning tasks
during chronic physical restraint in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology.
34:501–508. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang J, Zhang XJ, Du YY, Shi G, Zhang CC
and Chen R: Hydrogen-rich saline promotes neuronal recovery in mice
with cerebral ischemia through the AMPK/mTOR signal-mediated
autophagy pathway. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 83:317–330. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Han XC, Ye ZH, Hu HJ, Sun Q and Fan DF:
Hydrogen exerts neuroprotective effects by inhibiting oxidative
stress in experimental diabetic peripheral neuropathy rats. Med Gas
Res. 13:72–77. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2 (−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kose S, Furuta M and Imamoto N: Hikeshi, a
nuclear import carrier for Hsp70s, protects cells from heat
shock-induced nuclear damage. Cell. 149:578–589. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao H, Gong J, Li L, Zhi S, Yang G, Li P,
Li R and Li J: Vitamin E relieves chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease by inhibiting COX2-mediated p-STAT3 nuclear translocation
through the EGFR/MAPK signaling pathway. Lab Invest. 102:272–280.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
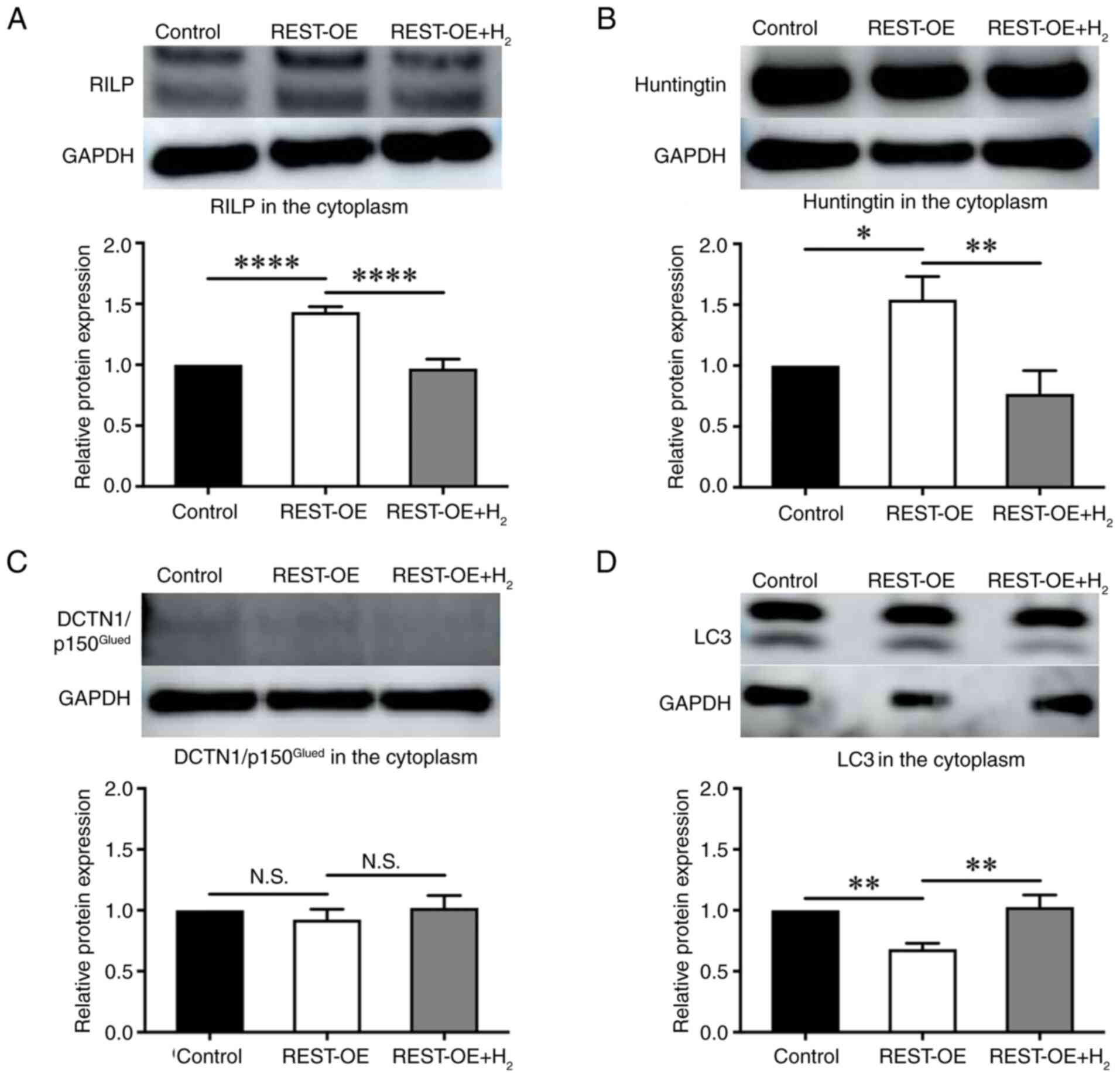
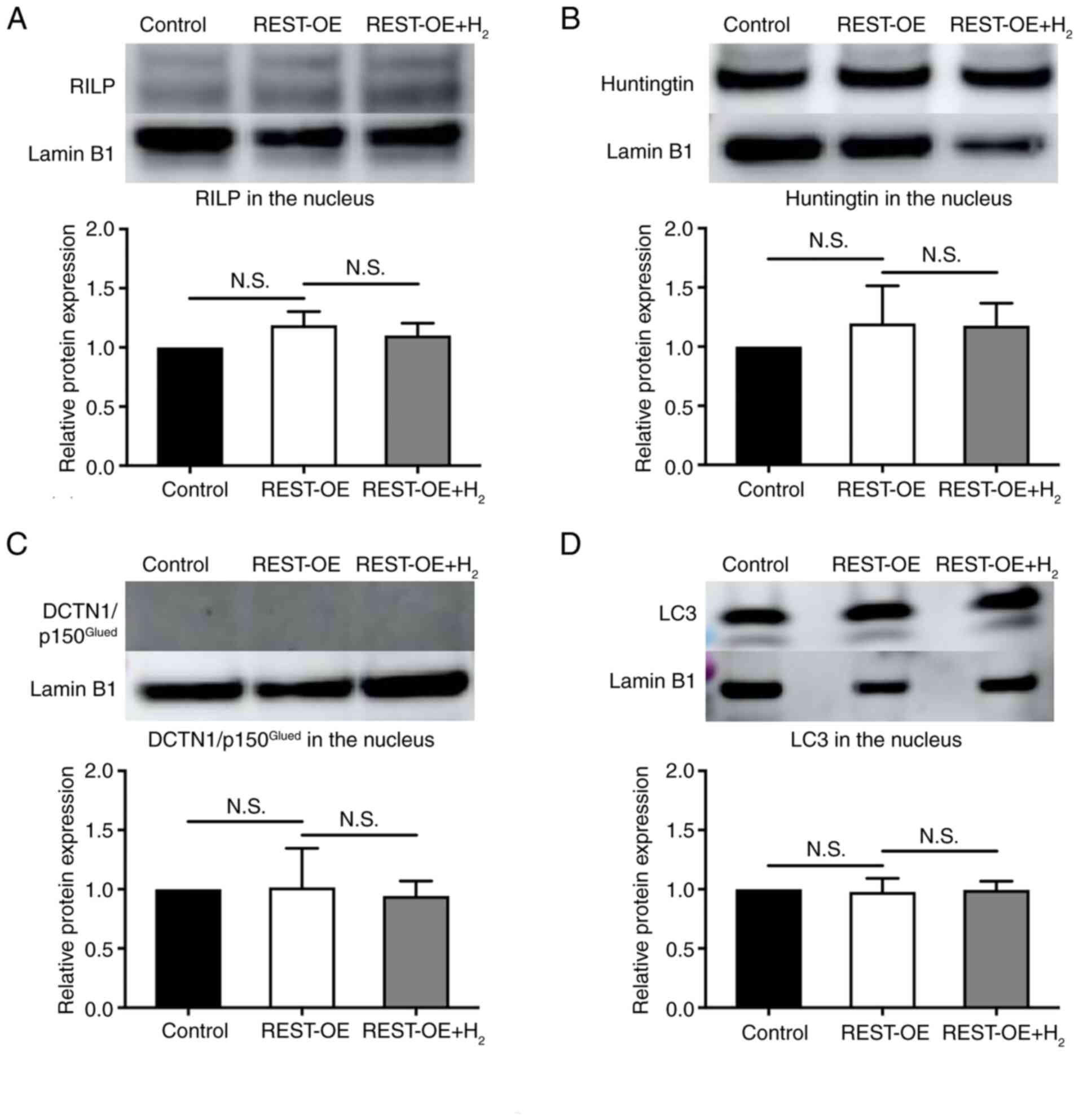
Shimojo M: Huntingtin regulates
RE1-silencing transcription factor/neuron-restrictive silencer
factor (REST/NRSF) nuclear trafficking indirectly through a complex
with REST/NRSF-interacting LIM domain protein (RILP) and dynactin
p150 Glued. J Biol Chem. 283:34880–34886. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Daulat AM, Wagner MS, Audebert S,
Kowalczewska M, Ariey-Bonnet J, Finetti P, Bertucci F, Camoin L and
Borg JP: The serine/threonine kinase MINK1 directly regulates the
function of promigratory proteins. J Cell Sci. 135:jcs2593472022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fu G, Xu Q, Qiu Y, Jin X, Xu T, Dong S,
Wang J, Ke Y, Hu H, Cao X, et al: Suppression of Th17 cell
differentiation by misshapen/NIK-related kinase MINK1. J Exp Med.
214:1453–1469. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim J, Li W, Wang J, Baranov SV, Heath BE,
Jia J, Suofu Y, Baranova OV, Wang X, Larkin TM, et al: Biosynthesis
of neuroprotective melatonin is dysregulated in Huntington's
disease. J Pineal Res. 75:e129092023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Moughamian AJ and Holzbaur EL: Dynactin is
required for transport initiation from the distal axon. Neuron.
74:331–343. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lazarus JE, Moughamian AJ, Tokito MK and
Holzbaur EL: Dynactin subunit p150(Glued) is a neuron-specific
anti-catastrophe factor. PLoS Biol. 11:e10016112013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mizushima N and Komatsu M: Autophagy:
Renovation of cells and tissues. Cell. 147:728–741. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Aman Y, Schmauck-Medina T, Hansen M,
Morimoto RI, Simon AK, Bjedov I, Palikaras K, Simonsen A, Johansen
T, Tavernarakis N, et al: Autophagy in healthy aging and disease.
Nat Aging. 1:634–650. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kaushik S, Tasset I, Arias E, Pampliega O,
Wong E, Martinez-Vicente M and Cuervo AM: Autophagy and the
hallmarks of aging. Ageing Res Rev. 72:1014682021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xue WJ, He CF, Zhou RY, Xu XD, Xiang LX,
Wang JT, Wang XR, Zhou HG and Guo JC: High glucose and palmitic
acid induces neuronal senescence by NRSF/REST elevation and the
subsequent mTOR-related autophagy suppression. Mol Brain.
15:612022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cui Y, Li Y, Meng S, Song Y and Xie K:
Molecular hydrogen attenuates sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy in mice
by promoting autophagy. BMC Anesthesiol. 24:722024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Iketani M and Ohsawa I: Molecular hydrogen
as a neuroprotective agent. Curr Neuropharmacol. 15:324–331. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang H, Huo X, Chen H, Li B, Liu J, Ma W,
Wang X, Xie K, Yu Y and Shi K: Hydrogen-rich saline activated
autophagy via HIF-1α pathways in neuropathic pain model. Biomed Res
Int. 2018:46708342018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Song D, Liu X, Diao Y, Sun Y, Gao G, Zhang
T, Chen K and Pei L: Hydrogen-rich solution against myocardial
injury and aquaporin expression via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
during cardiopulmonary bypass in rats. Mol Med Rep. 18:1925–1938.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Palomino SM, Gabriel KA, Mwirigi JM,
Cervantes A, Horton P, Funk G, Moutal A, Martin LF, Khanna R, Price
TJ and Patwardhan A: Genetic editing of primary human dorsal root
ganglion neurons using CRISPR-Cas9. Sci Rep. 15:111162025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tanaka H, Yamashita T, Asada M, Mizutani
S, Yoshikawa H and Tohyama M: Cytoplasmic p21(Cip1/WAF1) regulates
neurite remodeling by inhibiting Rho-kinase activity. J Cell Biol.
158:321–329. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rajakylä EK, Viita T, Kyheröinen S, Huet
G, Treisman R and Vartiainen MK: RNA export factor Ddx19 is
required for nuclear import of the SRF coactivator MKL1. Nat
Commun. 6:59782015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Vierbuchen T, Ostermeier A, Pang ZP,
Kokubu Y, Südhof TC and Wernig M: Direct conversion of fibroblasts
to functional neurons by defined factors. Nature. 463:1035–1041.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|