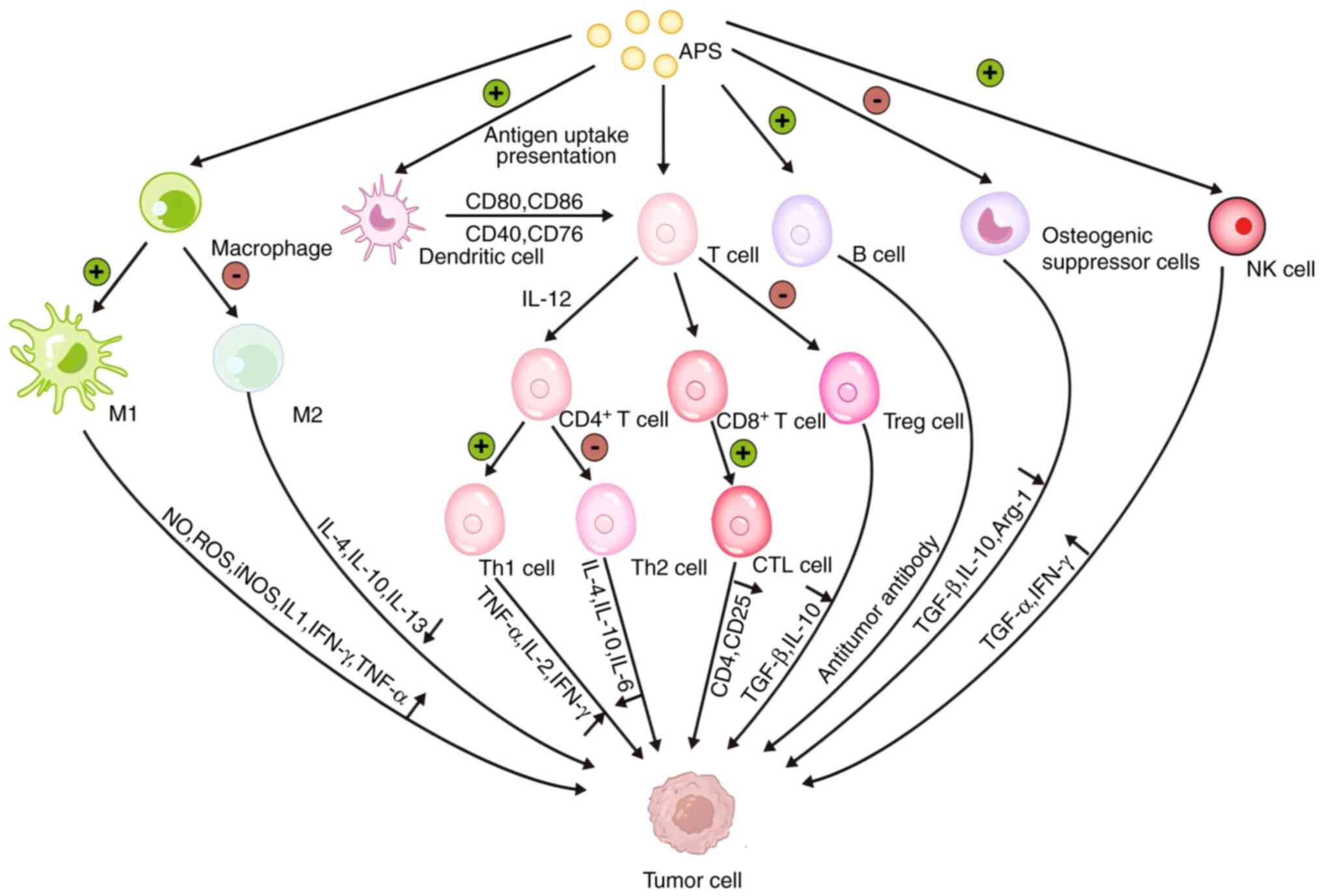
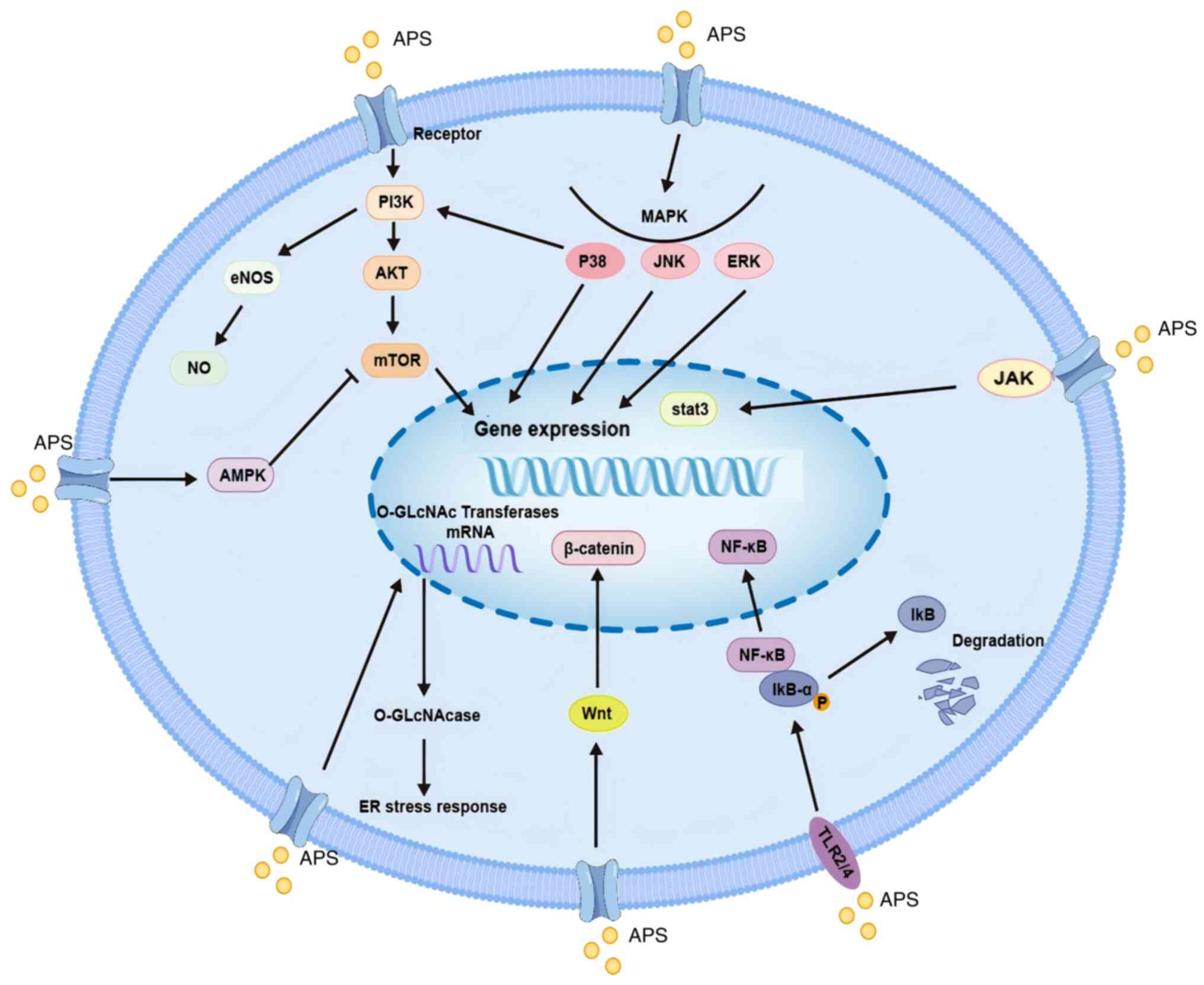
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 73:17–48.
2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu Y, Zhao Y, Song H, Li Y, Liu Z, Ye Z,
Zhao J, Wu Y, Tang J and Yao M: Metabolic reprogramming in tumor
immune microenvironment: Impact on immune cell function and
therapeutic implications. Cancer Lett. 597:2170762024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xie D, Wang N, Chen Z, Liu Z, Zhou Z, Zeng
J, Zhong Y and Wang Z: Medication Rules and Core Formula Analysis
of Famous National Traditional. Chinese Medicine Masters for Cancer
Treatment Based on Data Mining World Chin Med. 15:2726–2734.
2020.(In Chinese).
|
|
4
|
He Z, Liu X, Qin S, Yang Q, Na J, Xue Z
and Zhong L: Anticancer mechanism of Astragalus
polysaccharide and its application in cancer immunotherapy.
Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 17:6362024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
National Pharmacopoeia Commission:
Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China (Part 1).
Pharmaceutical Science and Technology Press. (Beijing, China).
3632020.(In Chinese).
|
|
6
|
Su HF, Shaker S, Kuang Y, Zhang M, Ye M
and Qiao X: Phytochemistry and cardiovascular protective effects of
Huang-Qi (Astragali Radix). Med Res Rev. 41:1999–2038. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tong X: The Pharmacology Study of Active
Constituents from Astragalus. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia
Medica Research. 22:1246–1249. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
8
|
Xiao M, Chen H, Shi Z and Rui W: Rapid and
reliable method for analysis of raw and honey-processed
Astragalus by UPLC/ESI-Q-TOF-MS using HSS T3 columns. Anal
Methods. 6:8045–8054. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Liao J, Huang J, Liu W, Liao S, Chen H and
Rui W: Effects of total flavonoids and astragalosides of
honey-processed Astragalus on NO secretion levels. J
Guangdong Pharm Univ. 33:162–166. 2017.(In Chinese).
|
|
10
|
Huang J, Liao J, Liu W, Liao S, Feng Y,
Chen H and Rui W: Establishment of determination method for three
main active ingredients of honey-processed Astragalus in rat urine
based on UPLC/Q-TOF-MS. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res. 28:2564–2567.
2017.(In Chinese).
|
|
11
|
Zhong RZ, Yu M, Liu HW, Sun HX, Cao Y and
Zhou DW: Effects of dietary Astragalus polysaccharide and
Astragalus membranaceus root supplementation on growth
performance, rumen fermentation, immune responses, and antioxidant
status of lambs. Animal Feed Sci Technol. 174:60–67. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zeng P, Li J, Chen Y and Zhang L: The
structures and biological functions of polysaccharides from
traditional Chinese herbs. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 163:423–444.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fan X, Li K, Yang Y, Li H, Li X and Qin X:
Research Progress on structural characterization of astragalus
polysaccharides. J Shanxi Coll Tradit Chin Med. 23:260–267.
2022.(In Chinese).
|
|
14
|
Synytsya A and Novák M: Structural
diversity of fungal glucans. Carbohydr Polym. 92:792–809. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lin MG, Yang YF and Xu HY: Chemical
structure of Astragalus polysaccharide MAPS-5 and its in
vitro lymphocyte proliferative activity. Chin Tradit Herbal Drugs.
40:1865–1868. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
16
|
Fang SD, Chen Y, Xu XY and Ye C: Studies
on the Active Principles of Astragalus Mongholicus Bunge I.
Isolation, Characterization and Biological Effect of its
Polysaccharaides. Chin J Org Chem. 2:26–31. 1982.(In Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Huang Q, Lu G, Li Y, Guo J and Wang R:
Studies on the polysaccharides of “Huang Qi” (Astragalus
Mongholicus Bunge.). Acta Pharm Sin. 17:200–206. 1982.(In
Chinese).
|
|
18
|
Tang Y, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Zhao H and Shen
Y: Isolation and Structural Feature Analysis of Astragalus
Polysaccharides. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res. 25:1097–1100.
2014.(In Chinese).
|
|
19
|
Cao Y, Li K, Qin X, Jiao S, Du Y, Li S and
Li X: Quality evaluation of different areas of Astragali Radix
based on carbohydrate specific chromatograms and immune cell
activities. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica. 54:1277–1287. 2019.(In
Chinese).
|
|
20
|
Liu W, Yu X, Xu J, et al: Isolation,
structural characterization and prebiotic activity of
polysaccharides from Astragalus membranaceus. Food Ferment
Ind. 46:50–56. 2020.(In Chinese).
|
|
21
|
Bergman PJ: Cancer immunotherapies. Vet
Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 49:881–902. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rui R, Zhou L and He S: Cancer
immunotherapies: Advances and bottlenecks. Front Immunol.
14:12124762023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Helmy KY, Patel SA, Nahas GR and Rameshwar
P: Cancer immunotherapy: Accomplishments to date and future
promise. Ther Deliv. 4:1307–1320. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ganesh K, Stadler ZK, Cercek A, Mendelsohn
RB, Shia J, Segal NH and Diaz LA Jr: Immunotherapy in colorectal
cancer: Rationale, challenges and potential. Nat Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 16:361–375. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lei X, Lei Y, Li JK, Du WX, Li RG, Yang J,
Li J, Li F and Tan HB: Immune cells within the tumor
microenvironment: Biological functions and roles in cancer
immunotherapy. Cancer Lett. 470:126–133. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Katz JB, Muller AJ and Prendergast GC:
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in T-cell tolerance and tumoral immune
escape. Immunol Rev. 222:206–221. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Velcheti V and Schalper K: Basic overview
of current immunotherapy approaches in cancer. Am Soc Clin Oncol
Educ Book. 35:298–308. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang Z, Li M, Bi L, Hu X and Wang Y:
Traditional Chinese medicine in regulating tumor microenvironment.
Onco Targets Ther. 17:313–325. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kong F, Chen T, Li X and Jia Y: The
current application and future prospects of Astragalus
polysaccharide combined with cancer immunotherapy: A review. Front
Pharmacol. 12:7376742021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhou L, Liu Z, Wang Z, Yu S, Long T, Zhou
X and Bao Y: Astragalus polysaccharides exerts
immunomodulatory effects via TLR4-mediated MyD88-dependent
signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo. Sci Rep. 7:448222017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Huang WC, Kuo KT, Bamodu OA, Lin YK, Wang
CH, Lee KY, Wang LS, Yeh CT and Tsai JT: Astragalus
polysaccharide (PG2) ameliorates cancer symptom clusters, as well
as improves quality of life in patients with metastatic disease,
through modulation of the inflammatory cascade. Cancers (Basel).
11:10542019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bonnardel J and Guilliams M: Developmental
control of macrophage function. Curr Opin Immunol. 50:64–74. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li M, Yang Y, Xiong L, Jiang P, Wang J and
Li C: Metabolism, metabolites, and macrophages in cancer. J Hematol
Oncol. 16:802023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mantovani A, Marchesi F, Malesci A, Laghi
L and Allavena P: Tumour-associated macrophages as treatment
targets in oncology. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 14:399–416. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mantovani A and Allavena P: The
interaction of anticancer therapies with tumor-associated
macrophages. J Exp Med. 212:435–445. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wei W, Li ZP, Bian ZX and Han QB:
Astragalus polysaccharide RAP induces macrophage phenotype
polarization to M1 via the notch signaling pathway. Molecules.
24:20162019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen R, Li Y, Zuo L, Xiong H, Sun R, Song
X and Liu H: Astragalus polysaccharides inhibits tumor
proliferation and enhances cisplatin sensitivity in bladder cancer
by regulating the PI3K/AKT/FoxO1 axis. Int J Biological
Macromolecules. 311:1437392025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li C, Pan XY, Ma M, Zhao J, Zhao F and Lv
YP: Astragalus polysacharin inhibits hepatocellular
carcinoma-like phenotypes in a murine HCC model through repression
of M2 polarization of tumour-associated macrophages. Pharm Biol.
59:1531–1537. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Li SY, Li K, Qin XM, Li XR and Du YG:
Study on active constituents of Astragalus polysaccharides
for injection to regulate metabolism of macrophages based on LC-MS
metabolomics. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs. 51:1575–1585. 2020.(In
Chinese).
|
|
40
|
Feng S, Ding H, Liu L, Peng C, Huang Y,
Zhong F, Li W, Meng T, Li J, Wang X, et al: Astragalus
polysaccharide enhances the immune function of RAW264.7 macrophages
via the NF-κB p65/MAPK signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 21:202021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shao BM, Xu W, Dai H, Tu P, Li Z and Gao
XM: A study on the immune receptors for polysaccharides from the
roots of Astragalus membranaceus, a Chinese medicinal herb.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 320:1103–1111. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wei W, Xiao HT, Bao WR, Ma DL, Leung CH,
Han XQ, Ko CH, Lau CB, Wong CK, Fung KP, et al: TLR-4 may mediate
signaling pathways of Astragalus polysaccharide RAP induced
cytokine expression of RAW264.7 cells. J Ethnopharmacol.
179:243–252. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li W, Hu X, Wang S, Jiao Z, Sun T, Liu T
and Song K: Characterization and anti-tumor bioactivity of
Astragalus polysaccharides by immunomodulation. Int J Biol
Macromol. 145:985–997. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lin W, Liu T, Wang B and Bi H: The role of
ocular dendritic cells in uveitis. Immunol Lett. 209:4–10. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Villar J and Segura E: Decoding the
heterogeneity of human dendritic cell subsets. Trends Immunol.
41:1062–1071. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chudnovskiy A, Pasqual G and Victora GD:
Studying interactions between Dendritic Cells and T cells in vivo.
Curr Opin Immunol. 58:24–30. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Bamodu OA, Kuo KT, Wang CH, Huang WC, Wu
ATH, Tsai JT, Lee KY, Yeh CT and Wang LS: Astragalus
polysaccharides (PG2) enhances the M1 polarization of macrophages,
functional maturation of dendritic cells, and T cell-mediated
anticancer immune responses inpatients with lung cancer. Nutrients.
11:22642019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jing XN, Qiu B, Wang JF, Wu YG, Wu JB and
Chen DD: In vitro anti-tumor effect of human dendritic cells
vaccine induced by Astragalus polysacharin: An experimental
study. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 34:1103–1107. 2014.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Gu Y, Pu X, Yin N and Wan C: The study on
mechanism of the anti-tumor effect of Fufang Huangqi Oral Solution
combined chemotherapy. J Tianjin Univ Tradit Chin Med. 41:85–89.
2022.(In Chinese).
|
|
50
|
Bian Y, Zhang J, Wang L, Wang X, Zhang K,
Wang X, Meng J and Li J: Progress of research on the effect of
Astragalus polysaccharide on the morphology and function of
dendritic cells. Prog Vet Med. 37:86–89. 2016.(In Chinese).
|
|
51
|
Pang G, Chen C, Liu Y, Jiang T, Yu H, Wu
Y, Wang Y, Wang FJ, Liu Z and Zhang LW: Bioactive polysaccharide
nanoparticles improve radiation-induced abscopal effect through
manipulation of dendritic cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.
11:42661–42670. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Chang WT, Lai TH, Chyan YJ, Yin SY, Chen
YH, Wei WC and Yang NS: Specific medicinal plant polysaccharides
effectively enhance the potency of a DC-based vaccine against mouse
mammary tumor metastasis. PLoS One. 10:e01223742015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
An EK, Zhang W, Kwak M, Lee PC and Jin JO:
Polysaccharides from Astragalus membranaceus elicit T cell
immunity by activation of human peripheral blood dendritic cells.
Int J Biol Macromol. 223:370–377. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lasser SA, Ozbay Kurt FG, Arkhypov I,
Utikal J and Umansky V: Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in cancer
and cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 21:147–164. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Xia L, Zhao S, Wei Q and Xu X: Study on
changes of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in tumor tissues of
tumor-bearing mice and its significance. Curr Immunol. 34:232–236.
2014.(In Chinese).
|
|
56
|
Hao WB, Xiang FF, Liu QL, Yue HK and Kang
XD: Research adances of myeloid inhibitory cells in tumor
microenvironment. Immunol J. 33:729–732. 2017.(In Chinese).
|
|
57
|
Chai W, He X, Zhu J, Lv C, Zhao H, Lv A
and Yv C: Immunoregulatory effects of astragalus polysaccharides on
myeloid derived suppressor cells in B16-F10 tumor bearing mice.
Chin J Basic Med Tradit Chin Med. 18:63–65. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
58
|
Ding G, Gong Q, Ma J, Liu X, Wang Y and
Cheng X: Immunosuppressive activity is attenuated by
Astragalus polysaccharides through remodeling the gut
microenvironment in melanoma mice. Cancer Sci. 112:4050–4063. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Mei Q, Zhang W, Ran R and Wang J: Effect
of astragalus polysaccharide on peripheral circulation MDSC in lung
cancer and its clinical effect. Modern Doctor. 55:10–13. 2017.(In
Chinese).
|
|
60
|
Li Y, Yan B and He S: Advances and
challenges in the treatment of lung cancer. Biomed Pharmacother.
169:1158912023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Shen M, Wang YJ, Liu ZH, Chen YW, Liang
QK, Li Y and Ming HX: Inhibitory effect of Astragalus
polysaccharide on premetastatic niche of lung cancer through the
S1PR1-STAT3 signaling pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2023:40107972023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Liu Y, Yuan J, Guo M, Zhang Y, Lu J and
Cao W: Effect of astragalus polysaccharides based on
TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway on immune function of lung
cancer mice and its regulatory effect on Th1/ Th2. Chin J Immunol.
37:676–682. 2021.(In Chinese).
|
|
63
|
Li K, Li S, Wang D, Li X, Wu X, Liu X, Du
G, Li X, Qin X and Du Y: Extraction, characterization, antitumor
and immunological activities of hemicellulose polysaccharide from
Astragalus radix herb residue. Molecules. 24:36442019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhou X, Liu Z, Long T, Zhou L and Bao Y:
Immunomodulatory effects of herbal formula of Astragalus
polysaccharide (APS) and polysaccharopeptide (PSP) in mice with
lung cancer. Int J Biol Macromol. 106:596–601. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Yu J, Dong XD, Jiao JS, Ji HY and Liu AJ:
Antitumor and immunoregulatory activities of a novel polysaccharide
from Astragalus membranaceus on S180 tumor-bearing mice. Int
J Biol Macromol. 189:930–938. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Deng M, Chen Z, Dou X, Shi Y and Wo X: The
Anti - leukemia Effect Mediated by DCs Derived from the Human Cord
Blood Monocyte Induced by the Astragalus Polysaccharides (APS) in
Vitro. Chin Arch Tradit Chin Med. 27:2360–2365. 2009.(In
Chinese).
|
|
67
|
Jang JE, Hajdu CH, Liot C, Miller G,
Dustin ML and Bar-Sagi D: Crosstalk between regulatory T cells and
tumor-associated dendritic cells negates anti-tumor immunity in
pancreatic cancer. Cell Rep. 20:558–571. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Mentucci FM, Ferrara MG, Ercole A, Rumie
Vittar NB and Lamberti MJ: Interplay between cancer-associated
fibroblasts and dendritic cells: implications for tumor immunity.
Front Immunol. 16:15153902025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Sun S, He X, Chai W, Lv C, Wang P, Lv A
and Yu C: Effects of Astragalus Polysaccharide on Treg Cells
in Tumor-bearing Mice. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formulae. 19:176–178.
2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
70
|
Li Q, Bao JM, Li XL, Zhang T and Shen XH:
Inhibiting effect of Astragalus polysaccharides on the
functions of CD4+CD25 highTreg cells in the tumor microenvironment
of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Chin Med J (Engl). 125:786–793.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Du X, Chen X, Zhao B, Lv Y, Zhang H, Liu
H, Chen Z, Chen Y and Zeng X: Astragalus polysaccharides
enhance the humoral and cellular immune responses of hepatitis B
surface antigen vaccination through inhibiting the expression of
transforming growth factor β and the frequency of regulatory T
cells. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 63:228–235. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Shokati E, Safari E and Motalebnezhad M:
Astragalus Polysaccharide Mediates Immunomodulatory Effects on
Crosstalk between Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells and
Ovarian Cancer Cell Line. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol.
22:172–182. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Guillerey C and Smyth MJ: NK cells and
cancer immunoediting. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 395:115–145.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zhou J, Peng H and Tian ZG: Research
progress on negative regulation of adaptive immune response by NK
cells. Chin J Immunol. 32:769–776. 2016.(In Chinese).
|
|
75
|
Wang W, Xi J, Zhao Y, He L, Zhou J, Fan Z,
Zhang B, Wang H, Zeng Q, et al: Specific cytotoxicity of natural
killer cells against hepatocellular carcinoma and potential
mechanism. Mil Med Sci. 41:775–783. 2017.(In Chinese).
|
|
76
|
Yang Y, Li H, Guo S, Li X, Yin J, Zhao P,
Gao L and Wu S: Killing effect of NK cells on non-small cell lung
cancer cells NCI-H292 and the effect on their β-catenin protein
expression. Shandong Med J. 57:33–35. 2017.(In Chinese).
|
|
77
|
Liu C, Zhang Y and Lu H: Efficient
amplification of NK cells and their anti-tumor cytotoxic activity
in vitro. Chin J Immunol. 33:1186–1190+1196. 2017.(In Chinese).
|
|
78
|
Zeng PY, Deng LL, Yue LL and Zhang L:
Effect of Astragalus Polysaccharide on Sensitivity of Leukemic Cell
Line HL- 60 to NK Cell Cytotoxicity and Its Mechanism. J Exp
Hematol. 20:880–883. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
79
|
Li H: Effects of Astragalus Polysaccharide
on Quality of Life and Cellular Immune Function in Elderly Patients
with Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Chinese Journal of Traditional
Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy. 17:243–244. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
80
|
Li R, Chen WC, Wang WP, Tian WY and Zhang
XG: Extraction, characterization of Astragalus
polysaccharides and its immune modulating activities in rats with
gastric cancer. Carbohydr Polym. 78:738–742. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Guo Y, Zhang Z, Wang Z, Liu G, Liu Y and
Wang H: Astragalus polysaccharides inhibit ovarian cancer
cell growth via microRNA-27a/FBXW7 signaling pathway. Biosci Rep.
40:BSR201933962020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Miao D, Zhao J, Han Y, Zhou J, Li X, Zhang
T, Li W and Xia Y: Management of locally advanced non-small cell
lung cancer: State of the art and future directions. Cancer Commun
(Lond). 44:23–46. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Tao X, Zhang X and Feng F:
Astragalus polysaccharide suppresses cell proliferation and
invasion by up-regulation of miR-195-5p in non-small cell lung
cancer. Biol Pharm Bull. 45:553–560. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Zhang YM, Liu YQ, Liu D, Zhang L, Qin J,
Zhang Z, Su Y, Yan C, Luo YL, Li J, et al: The effects of
Astragalus polysaccharide on bone marrow-derived mesenchymal
stem cell proliferation and morphology induced by A549 lung cancer
cells. Med Sci Monit. 25:4110–4121. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Zhang Y, Wang CH, Yu D, Gao Y, Jing H,
Wang Y and Liu C: Effect of Astragalus Polysaccharide on EMT of
A549/DDP Lung Adenocarcinoma Xenograft: An Exploration Based on
PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formulae.
27:51–58. 2021.(In Chinese).
|
|
86
|
Yang YL, Lin ZW, He PT, Nie H, Yao QY and
Zhang SY: Inhibitory effect of Astragalus polysaccharide
combined with cisplatin on cell cycle and migration of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines. Biol Pharm Bull. 44:926–931.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Yan L, Hong T, Luo J, Cao X, Liu W, Gao Y,
Cui W and Wang F: Effect of Astragali Radix Polysaccharides on
Proliferation and Apoptosis of Human Colon Cancer Cell Line SW620.
Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formulae. 23:97–101. 2017.(In Chinese).
|
|
88
|
Guo S, Ma B, Jiang X, Li X and Jia Y:
Astragalus polysaccharides inhibits tumorigenesis and lipid
metabolism through miR-138-5p/SIRT1/SREBP1 pathway in prostate
cancer. Front Pharmacol. 11:5982020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Chu Y, Fang Y, Chi J, Li J, Zhang D, Zou Y
and Wang Z: Astragalus polysaccharides decrease
proliferation, migration, and invasion but increase apoptosis of
human osteosarcoma cells by up-regulation of microRNA-133a. Braz J
Med Biol Res. 51:e76652018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Mocan L, Matea C, Tabaran FA, Mosteanu O,
Pop T, Mocan T and Iancu C: Photothermal treatment of liver cancer
with albumin-conjugated gold nanoparticles initiates Golgi
Apparatus-ER dysfunction and caspase-3 apoptotic pathway activation
by selective targeting of Gp60 receptor. Int J Nanomedicine.
10:5435–5445. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Moyer A, Tanaka K and Cheng EH: Apoptosis
in cancer biology and therapy. Annu Rev Pathol. 20:303–328. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: A review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Ouyang L, Shi Z, Zhao S, Wang FT, Zhou TT,
Liu B and Bao JK: Programmed cell death pathways in cancer: A
review of apoptosis, autophagy and programmed necrosis. Cell
Prolif. 45:487–498. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Zhou Z, Meng M and Ni H: Chemosensitizing
effect of Astragalus polysaccharides on nasopharyngeal
carcinoma cells by inducing apoptosis and modulating expression of
Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and caspases. Med Sci Monit. 23:462–469. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Song J, Chen Y, He D, Tan W, Lv F, Liang
B, Xia T and Li J: Astragalus polysaccharide promotes
adriamycin-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells. Cancer Manag
Res. 12:2405–2414. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Yu J, Ji H, Dong X, Feng Y and Liu A:
Apoptosis of human gastric carcinoma MGC-803 cells induced by a
novel Astragalus membranaceus polysaccharide via intrinsic
mitochondrial pathways. Int J Biol Macromol. 126:811–819. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Ohnuki H, Jiang K, Wang D, Salvucci O,
Kwak H, Sánchez-Martín D, Maric D and Tosato G: Tumor-infiltrating
myeloid cells activate Dll4/Notch/TGF-β signaling to drive
malignant progression. Cancer Res. 74:2038–2049. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Li C, Zhang S, Lu Y, Zhang Y, Wang E and
Cui Z: The roles of Notch3 on the cell proliferation and apoptosis
induced by CHIR99021 in NSCLC cell lines: A functional link between
Wnt and Notch signaling pathways. PLoS One. 8:e846592013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Haruki N, Kawaguchi KS, Eichenberger S,
Massion PP, Olson S, Gonzalez A, Carbone DP and Dang TP:
Dominant-negative Notch3 receptor inhibits mitogen-activated
protein kinase pathway and the growth of human lung cancers. Cancer
Res. 65:3555–3561. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Konishi J, Kawaguchi KS, Vo H, Haruki N,
Gonzalez A, Carbone DP and Dang TP: Gamma-secretase inhibitor
prevents Notch3 activation and reduces proliferation in human lung
cancers. Cancer Res. 67:8051–8057. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Zhang JX, Han YP, Bai C and Li Q: Notch1/3
and p53/p21 are a potential therapeutic target for APS-induced
apoptosis in non-small cell lung carcinoma cell lines. Int J Clin
Exp Med. 8:12539–12547. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Sha X, Xu X, Liao S, Chen H and Rui W:
Evidence of immunogenic cancer cell death induced by
honey-processed Astragalus polysaccharides in vitro and in
vivo. Exp Cell Res. 410:1129482022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Feng T and Zhang BG: Inhibitory effect of
Astragalus polysaccharide on hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2
cells and its mechanism. Prac Geriatr. 6:486–488. 4952010.(In
Chinese).
|
|
104
|
Jiao J, Yu J, Ji H and Liu A: Synthesis of
macromolecular Astragalus polysaccharide-nano selenium
complex and the inhibitory effects on HepG2 cells. Int J Biol
Macromol. 211:481–489. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Wang HY: The Role of ERK1 /2 in Astragalus
Polysaccharide-induced Apoptosis in HepG2 Cell Line. Chin J Exp
Tradit Med Formulae. 7:235–238. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
106
|
Hart GW, Housley MP and Slawson C: Cycling
of O-linked beta-N-acetylglucosamine on nucleocytoplasmic proteins.
Nature. 446:1017–1022. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Dong DL and Hart GW: Purification and
characterization of an O-GlcNAc selective
N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase from rat spleen cytosol. J Biol
Chem. 269:19321–19330. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Kreppel LK, Blomberg MA and Hart GW:
Dynamic glycosylation of nuclear and cytosolic proteins. Cloning
and characterization of a unique O-GlcNAc transferase with multiple
tetratricopeptide repeats. J Biol Chem. 272:9308–9315. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Haltiwanger RS, Holt GD and Hart GW:
Enzymatic addition of O-GlcNAc to nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins.
Identification of a uridine diphospho-N-acetylglucosamine: Peptide
beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 265:2563–2568.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Hart GW, Slawson C, Ramirez-Correa G and
Lagerlof O: Cross talk between O-GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation:
Roles in signaling, transcription, and chronic disease. Annu Rev
Biochem. 80:825–858. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Lee SJ, Lee DE, Choi SY and Kwon OS:
OSMI-1 enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis through ER stress and NF-κB
signaling in colon cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 22:110732021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Lee SJ and Kwon OS: O-GlcNAc transferase
inhibitor synergistically enhances doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in
HepG2 cells. Cancers (Basel). 12:31542020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Ferrer CM, Lynch TP, Sodi VL, Falcone JN,
Schwab LP, Peacock DL, Vocadlo DJ, Seagroves TN and Reginato MJ:
O-GlcNAcylation regulates cancer metabolism and survival stress
signaling via regulation of the HIF-1 pathway. Mol Cell.
54:820–831. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Li M, Duan F, Pan Z, Liu X, Lu W, Liang C,
Fang Z, Peng P and Jia D: Astragalus polysaccharide promotes
doxorubicin-induced apoptosis by reducing O-GlcNAcylation in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cells. 12:8662023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Kemse NG, Kale A and Joshi SR:
Supplementation of maternal omega-3 fatty acids to pregnancy
induced hypertension Wistar rats improves IL-10 and VEGF levels.
PLEFA. 43:276–279. 2015.
|
|
116
|
Zhao L, Zhong Y, Liang J, Gao H and Tang
N: Effect of Astragalus polysaccharide on the expression of
VEGF and EGFR in mice with lewis transplantable lung cancer. J Coll
Physicians Surg Pak. 29:392–394. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Chen W, Li Z, Bai L and Lin Y: NF-kappaB
in lung cancer, a carcinogenesis mediator and a prevention and
therapy target. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 16:1172–1185. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Wu CY, Ke Y, Zeng YF, Zhang YW and Yu HJ:
Anticancer activity of Astragalus polysaccharide in human
non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 17:1152017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Auyeung KK, Law PC and Ko JK: Novel
anti-angiogenic effects of formononetin in human colon cancer cells
and tumor xenograft. Oncol Rep. 28:2188–2194. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Li M, Zhao W, Geng L, Jiang J, Yang N, Gu
L, Wang L and Wang Y: Astragalus Polysaccharides Inhibiting Gastric
Cancer Cell Proliferation and Invasion via miR-25/FBXW7 Signaling
Pathway. New Chinese Medicine. 57:150–155. 2025.(In Chinese).
|
|
121
|
Ji F, Zhang H, Wang Y, Li M, Xu W, Kang Y,
Wang Z, Wang Z, Cheng P, Tong D, et al: MicroRNA-133a,
downregulated in osteosarcoma, suppresses proliferation and
promotes apoptosis by targeting Bcl-xL and Mcl-1. Bone. 56:220–226.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Medici D, Shore EM, Lounev VY, Kaplan FS,
Kalluri R and Olsen BR: Conversion of vascular endothelial cells
into multipotent stem-like cells. Nat Med. 16:1400–1406. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Yang S, Sun S, Xu W, Yu B, Wang G and Wang
H: Astragalus polysaccharide inhibits breast cancer cell
migration and invasion by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal
transition via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep.
21:1819–1832. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
He L, Xu K, Niu L and Lin L:
Astragalus polysaccharide (APS) attenuated PD-L1-mediated
immunosuppression via the miR-133a-3p/MSN axis in HCC. Pharm Biol.
60:1710–1720. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Yang N, Jia X, Zhang Z, Sun E and Yan H:
Advance in studies on anti-cancer activity and mechanism of
flavonoids. China J Chin Mater Med. 40:373–381. 2015.(In
Chinese).
|
|
126
|
Glorieux C, Liu S, Trachootham D and Huang
P: Targeting ROS in cancer: Rationale and strategies. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 23:583–606. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Pu X, Fan W, Yu S, Li Y, Ma X, Liu L, Ren
J and Zhang W: Polysaccharides from angelica and Astragalus
exert hepatoprotective effects against carbon-tetrachloride-induced
intoxication in mice. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 93:39–43. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Bukowski K, Kciuk M and Kontek R:
Mechanisms of multidrug resistance in cancer chemotherapy. IntJ Mol
Sci. 21:32332020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Li YJ, Lei YH, Yao N, Wang CR, Hu N, Ye
WC, Zhang DM and Chen ZS: Autophagy and multidrug resistance in
cancer. Chin J Cancer. 36:522017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Cao Y, Ruan Y, Shen T, Huang X, Li M, Yu
W, Zhu Y, Man Y, Wang S and Li J: Astragalus polysaccharide
suppresses doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by regulating the
PI3k/Akt and p38MAPK pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2014:6742192014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Zhang Y, Wang CH, Yu D, Gao Y, Jing H,
Tang Y and Liu C: Astragalus Polysaccharides Improve Cisplatin
Resistance by Inhibiting EMT of Lung Adenocarcinoma A549/DDP Cells
Transplanted into Nude Mice. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formulae.
28:79–85. 2022.(In Chinese).
|
|
132
|
Peng H, Zhang X and Li F: Mechanisms of
Astragalus Polysaccharids Synergized with Doxorubicin against Drug
Resistance in HL-60/A Cells. J Exp Hemat. 25:743–748. 2017.(In
Chinese).
|
|
133
|
Zhai QL, Hu XD, Xiao J and Yu DQ:
Astragalus polysaccharide may increase sensitivity of
cervical cancer HeLa cells to cisplatin by regulating cell
autophagy. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 43:805–812. 2018.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Tian Q: The study on the adjunct
anticancer mechanism of astragalus polysaccharide in vivo and in
vitro. PhD Thesis. Central South University. 26–49. 2013.(In
Chinese).
|
|
135
|
Li C, Hong L, Liu C, Min J, Hu M and Guo
W: Astragalus polysaccharides increase the sensitivity of
SKOV3 cells to cisplatin. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 297:381–386. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Wei J, Li Y, Xu B and Yu J:
Astragalus polysaccharides reverse gefitinib resistance by
inhibiting mesenchymal transformation in lung adenocarcinoma cells.
Am J Transl Res. 12:1640–1657. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Zhang Y, Chen Z, Chen L, Dong Q, Yang DH,
Zhang Q, Zeng J, Wang Y, Liu X, Cui Y, et al: Astragali radix
(Huangqi): A time-honored nourishing herbal medicine. Chin Med.
19:1192024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|