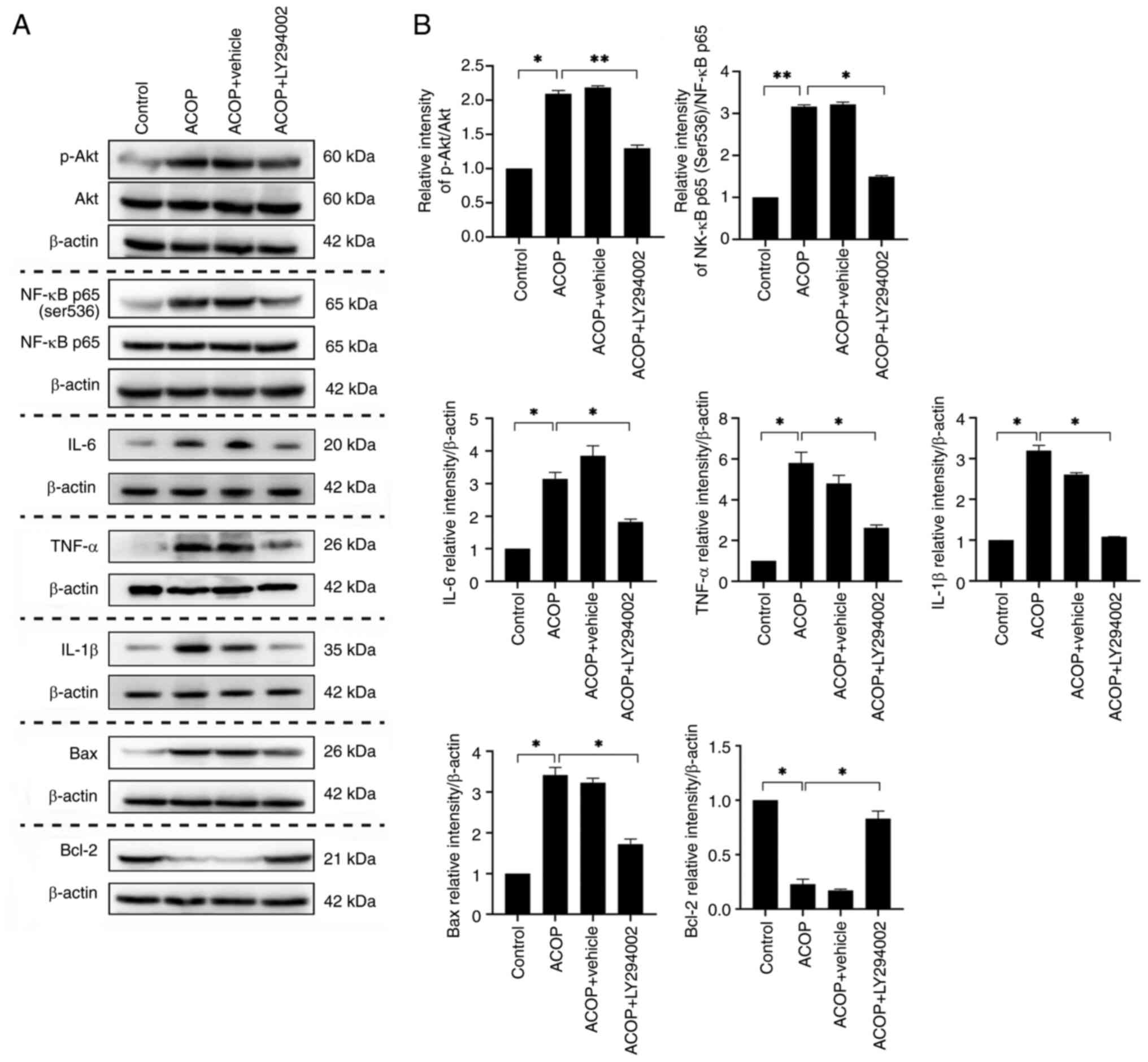
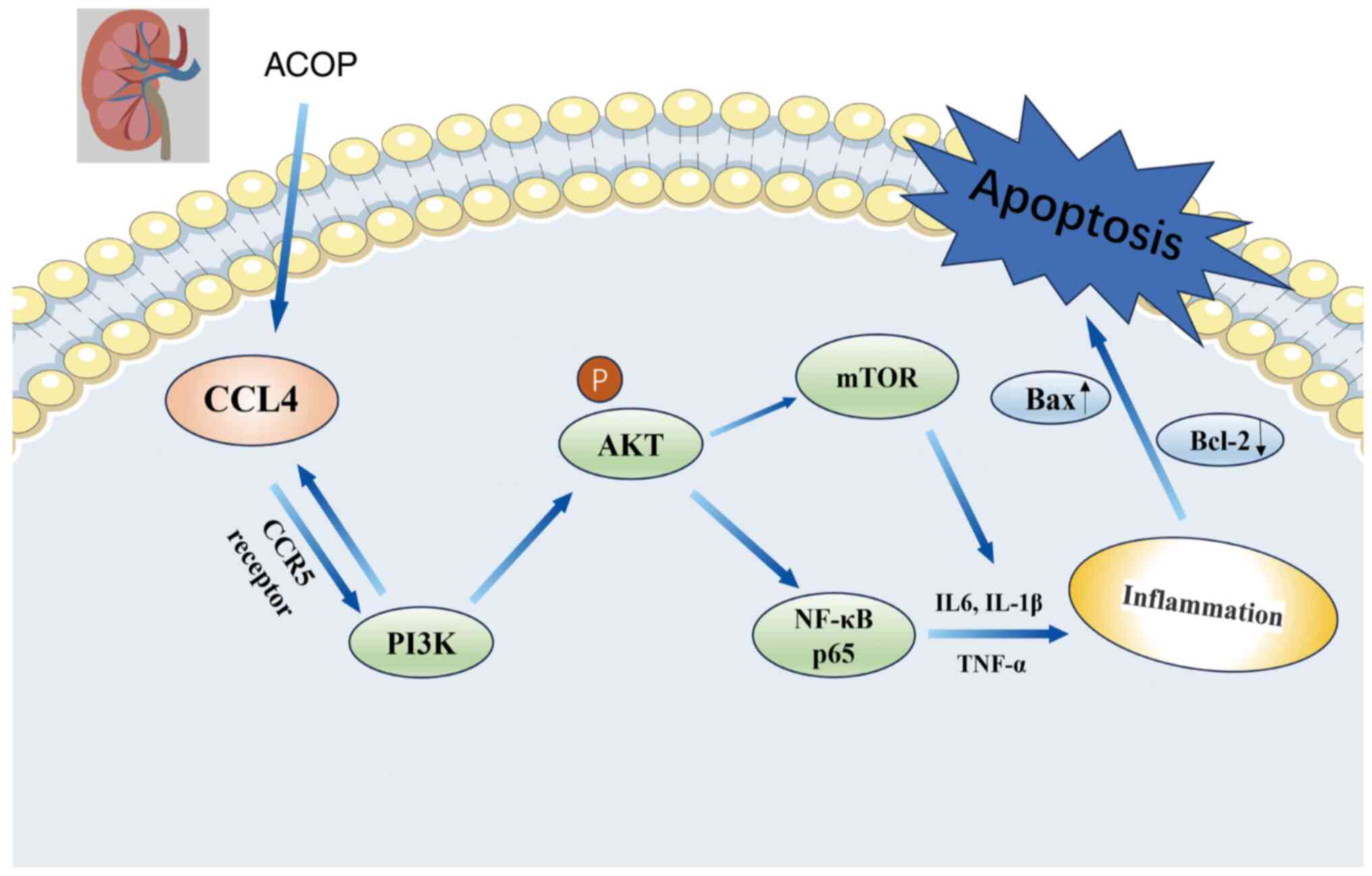
|
1
|
Rose JJ, Wang L, Xu Q, McTiernan CF, Shiva
S, Tejero J and Gladwin MT: Carbon monoxide poisoning:
Pathogenesis, management, and future directions of therapy. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 195:596–606. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Huang TL, Tung MC, Lin CL and Chang KH:
Risk of acute kidney injury among patients with carbon monoxide
poisoning. Medicine (Baltimore). 100:e272392021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kim YJ, Sohn CH, Seo DW, Oh BJ, Lim KS,
Chang JW and Kim WY: Analysis of the development and progression of
carbon monoxide poisoning-related acute kidney injury according to
the kidney disease improving global outcomes (KDIGO) criteria. Clin
Toxicol (Phila). 56:759–764. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Garrabou G, Inoriza JM, Morén C, Oliu G,
Miró Ò, Martí MJ and Cardellach F: Mitochondrial injury in human
acute carbon monoxide poisoning: The effect of oxygen treatment. J
Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev. 29:32–51.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rose JJ, Bocian KA, Xu Q, Wang L,
DeMartino AW, Chen X, Corey CG, Guimarães DA, Azarov I, Huang XN,
et al: A neuroglobin-based high-affinity ligand trap reverses
carbon monoxide-induced mitochondrial poisoning. J Biol Chem.
295:6357–6371. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Teksam O, Sabuncuoğlu S, Girgin G and
Özgüneş H: Evaluation of oxidative stress and antioxidant
parameters in children with carbon monoxide poisoning. Hum Exp
Toxicol. 38:1235–1243. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Thom SR, Fisher D and Manevich Y: Roles
for platelet-activating factor and *NO-derived oxidants causing
neutrophil adherence after CO poisoning. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 281:H923–H930. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee SJ, Ryter SW, Xu JF, Nakahira K, Kim
HP, Choi AM and Kim YS: Carbon monoxide activates autophagy via
mitochondrial reactive oxygen species formation. Am J Respir Cell
Mol Biol. 45:867–873. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Z, Gerstein M and Snyder M: RNA-Seq:
A revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat Rev Genet. 10:57–63.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ozsolak F and Milos PM: RNA sequencing:
Advances, challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Genet. 12:87–98.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Stark R, Grzelak M and Hadfield J: RNA
sequencing: The teenage years. Nat Rev Genet. 20:631–656. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Conesa A, Madrigal P, Tarazona S,
Gomez-Cabrero D, Cervera A, McPherson A, Szcześniak MW, Gaffney DJ,
Elo LL, Zhang X and Mortazavi A: A survey of best practices for
RNA-seq data analysis. Genome Biol. 17:132016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang S, Xiong B, Tian Y, Hu Q, Jiang X,
Zhang J, Chen L, Wang R, Li M, Zhou X, et al: Targeting ferroptosis
promotes functional recovery by mitigating white matter injury
following acute carbon monoxide poisoning. Mol Neurobiol.
61:1157–1174. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang P, Guan P, Ye X, Lu Y, Hang Y, Su Y
and Hu W: SOCS6 promotes mitochondrial fission and cardiomyocyte
apoptosis and is negatively regulated by quaking-mediated miR-19b.
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022:11213232022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nishio T, Koyama Y, Liu X, Rosenthal SB,
Yamamoto G, Fuji H, Baglieri J, Li N, Brenner LN, Iwaisako K, et
al: Immunotherapy-based targeting of MSLN+ activated
portal fibroblasts is a strategy for treatment of cholestatic liver
fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 118:e21012701182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sun J, Ren H, Wang J, Xiao X, Zhu L, Wang
Y and Yang L: CHAC1: A master regulator of oxidative stress and
ferroptosis in human diseases and cancers. Front Cell Dev Biol.
12:14587162024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chang TT, Lin LY, Chen C and Chen JW: CCL4
contributes to aging related angiogenic insufficiency through
activating oxidative stress and endothelial inflammation.
Angiogenesis. 27:475–499. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim MG, Yun D, Kang CL, Hong M, Hwang J,
Moon KC, Jeong CW, Kwak C, Kim DK, Oh KH, et al: Kidney VISTA
prevents IFN-γ/IL-9 axis-mediated tubulointerstitial fibrosis after
acute glomerular injury. J Clin Invest. 132:e1511892022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mattiuzzi C and Lippi G: Worldwide
epidemiology of carbon monoxide poisoning. Hum Exp Toxicol.
39:387–392. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wei KY, Liao CY, Chung CH, Lin FH, Tsao
CH, Sun CA, Lu KC, Chien WC and Wu CC: Carbon monoxide poisoning
and chronic kidney disease risk: A nationwide, population-based
study. Am J Nephrol. 52:292–303. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ostermann M, Bellomo R, Burdmann EA, Doi
K, Endre ZH, Goldstein SL, Kane-Gill SL, Liu KD, Prowle JR, Shaw
AD, et al: Controversies in acute kidney injury: Conclusions from a
kidney disease: Improving global outcomes (KDIGO) conference.
Kidney Int. 98:294–309. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dent MR, Rose JJ, Tejero J and Gladwin MT:
Carbon monoxide poisoning: From microbes to therapeutics. Annu Rev
Med. 75:337–351. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Scholz H, Boivin FJ, Schmidt-Ott KM,
Bachmann S, Eckardt KU, Scholl UI and Persson PB: Kidney physiology
and susceptibility to acute kidney injury: Implications for
renoprotection. Nat Rev Nephrol. 17:335–349. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhao ZB, Marschner JA, Iwakura T, Li C,
Motrapu M, Kuang M, Popper B, Linkermann A, Klocke J, Enghard P, et
al: Tubular epithelial cell HMGB1 promotes AKI-CKD transition by
sensitizing cycling tubular cells to oxidative stress: A rationale
for targeting HMGB1 during AKI recovery. J Am Soc Nephrol.
34:394–411. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Weaver LK: Carbon monoxide poisoning.
Undersea Hyperb Med. 47:151–169. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ozga AJ, Chow MT and Luster AD: Chemokines
and the immune response to cancer. Immunity. 54:859–874. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Glaviano A, Foo ASC, Lam HY, Yap KCH,
Jacot W, Jones RH, Eng H, Nair MG, Makvandi P, Geoerger B, et al:
PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling transduction pathway and targeted therapies
in cancer. Mol Cancer. 22:1382023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Vanhaesebroeck B, Perry MWD, Brown JR,
André F and Okkenhaug K: PI3K inhibitors are finally coming of age.
Nat Rev Drug Discov. 20:741–769. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Castel P, Toska E, Engelman JA and
Scaltriti M: The present and future of PI3K inhibitors for cancer
therapy. Nat Cancer. 2:587–597. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhao J, Yan Y, Zhen S, Yu L, Ding J, Tang
Q, Liu L, Zhu H and Xie M: LY294002 alleviates bone cancer pain by
reducing mitochondrial dysfunction and the inflammatory response.
Int J Mol Med. 51:422023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang H and Sun SC: NF-κB in inflammation
and renal diseases. Cell Biosci. 5:632015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dai C, Liu D, Qin C, Fang J, Cheng G, Xu
C, Wang Q, Lu T, Guo Z, Wang J, et al: Guben Kechuan granule
attenuates bronchial asthma by inhibiting NF-κB/STAT3 signaling
pathway-mediated apoptosis. J Ethnopharmacol. 340:1191242025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Arya AK, Sethuraman K, Waddell J, Cha YS,
Liang Y, Bhopale VM, Bhat AR, Imtiyaz Z, Dakessian A, Lee Y and
Thom SR: Inflammatory responses to acute carbon monoxide poisoning
and the role of plasma gelsolin. Sci Adv. 11:eado97512025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Festa BP, Siddiqi FH, Jimenez-Sanchez M
and Rubinsztein DC: Microglial cytokines poison neuronal autophagy
via CCR5, a druggable target. Autophagy. 20:949–951. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Deng H, Xue P, Zhou X, Wang Y and Liu W:
CCL4/CCR5 regulates chondrocyte biology and OA progression.
Cytokine. 183:1567462024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|