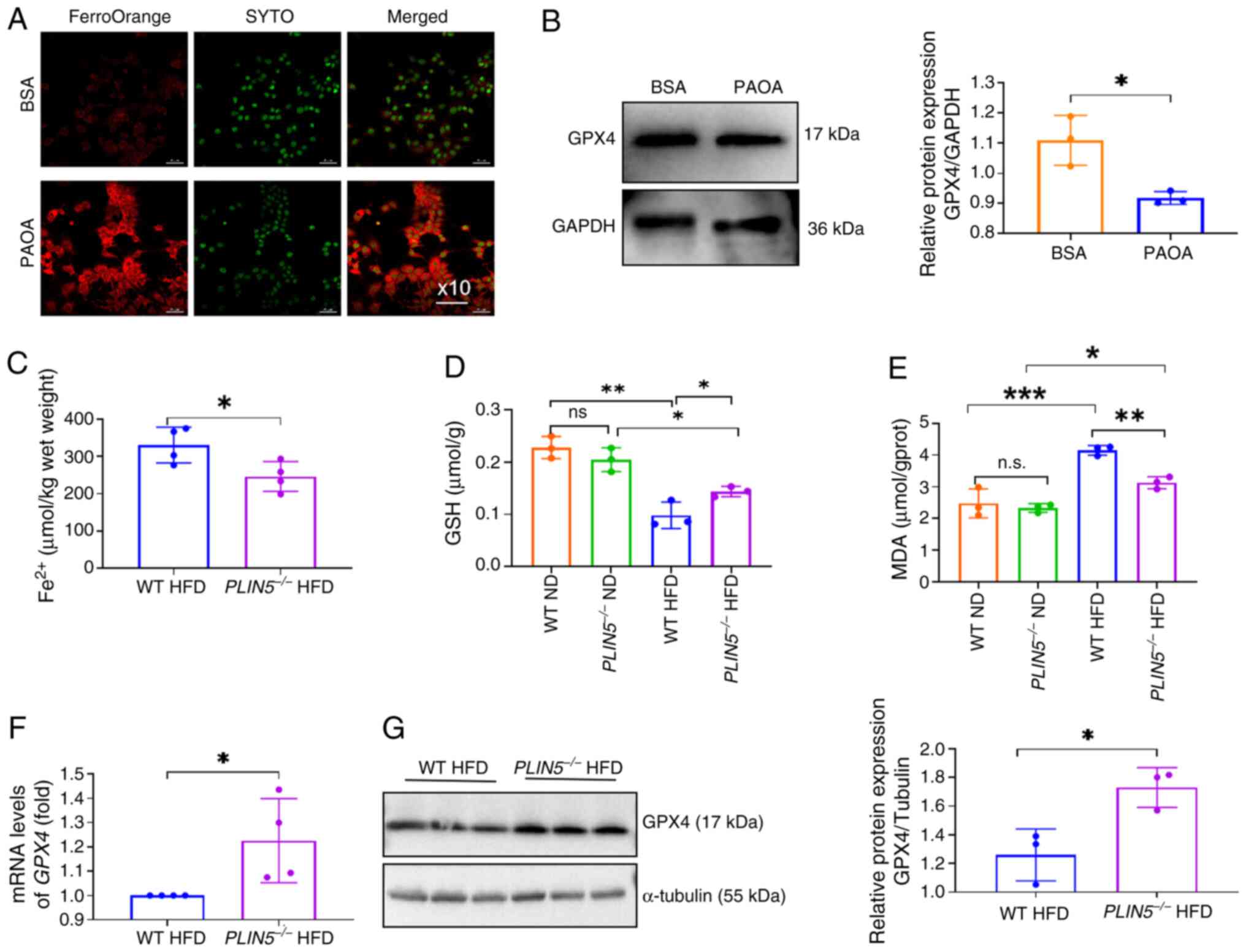
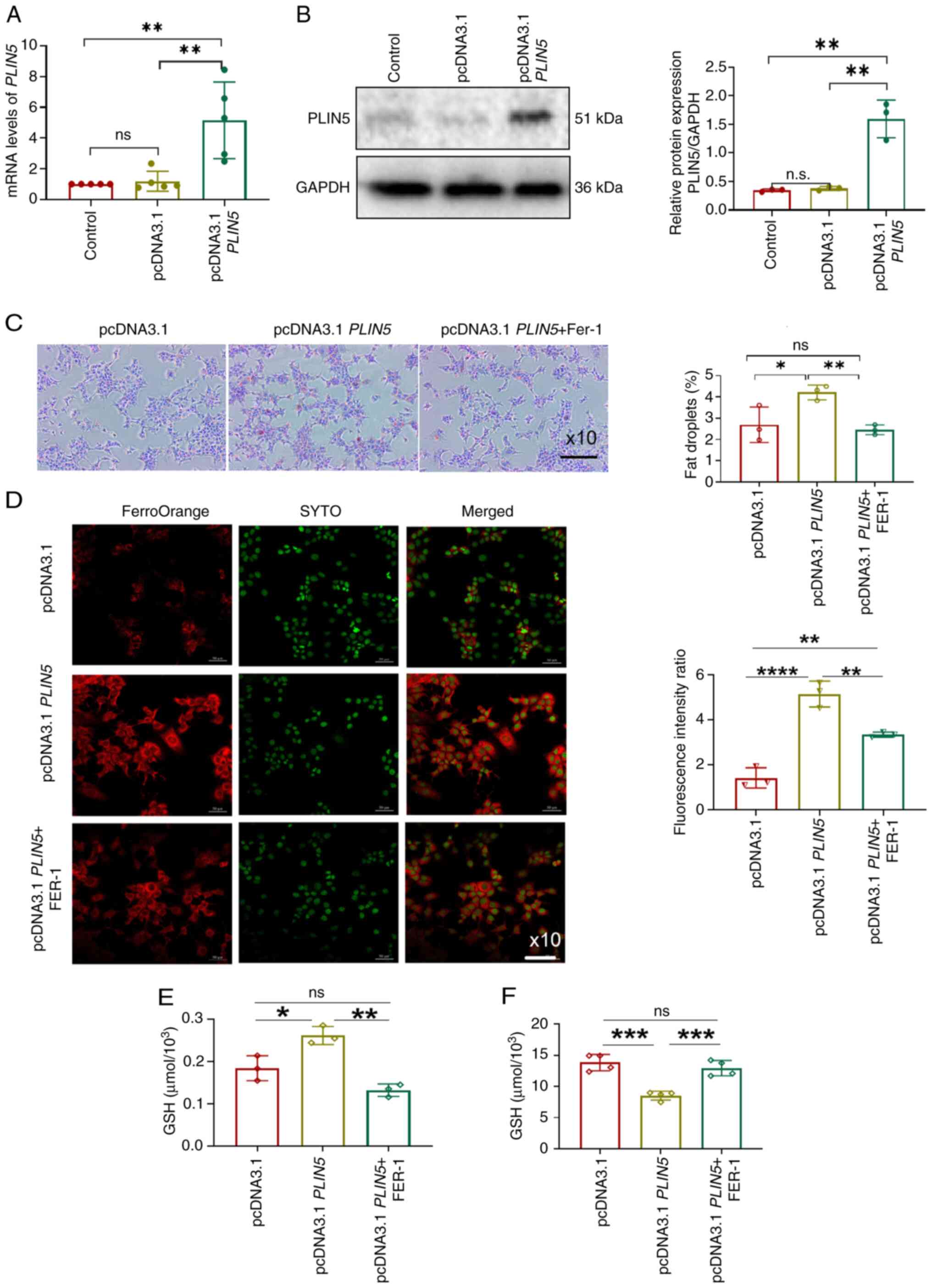
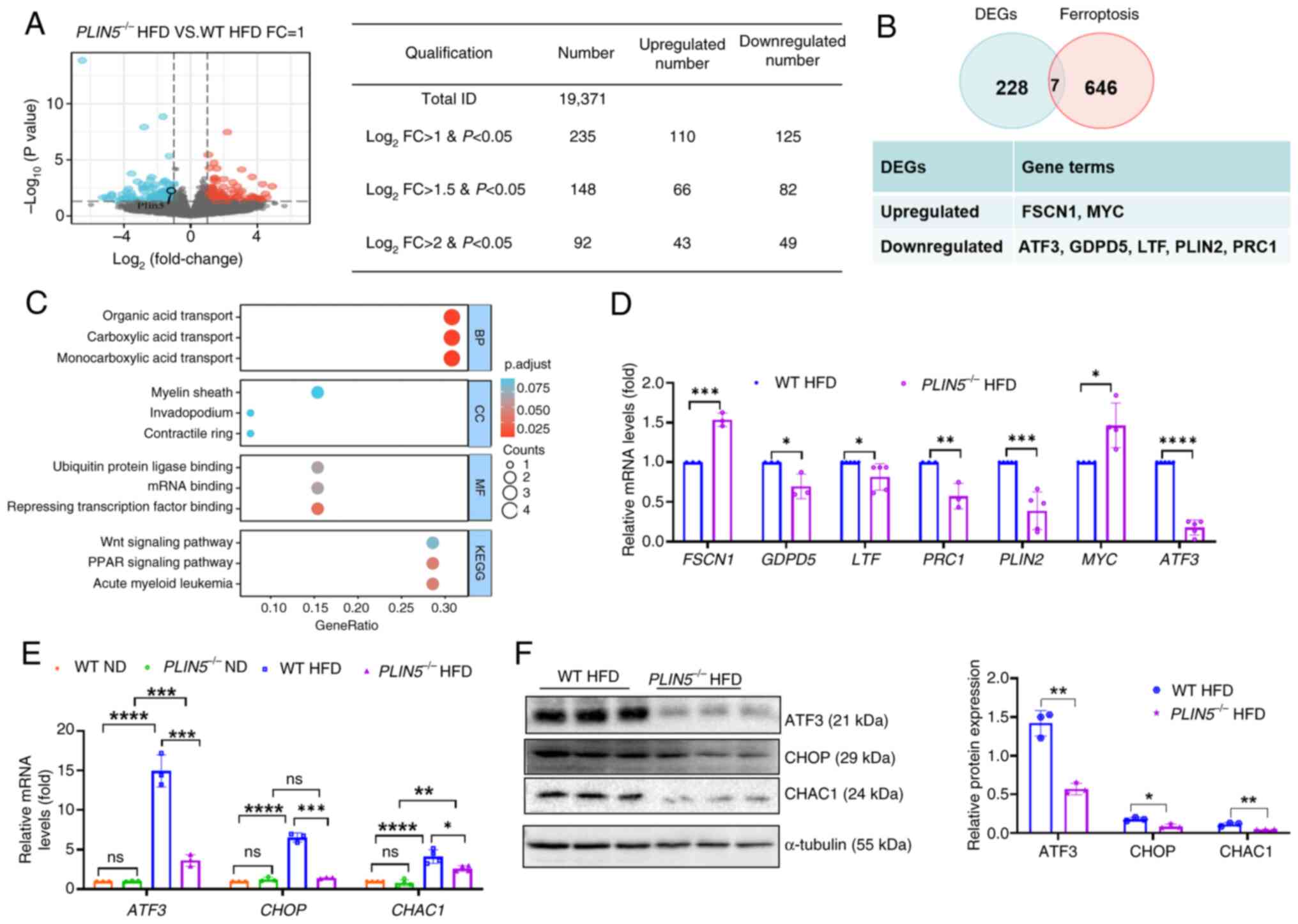
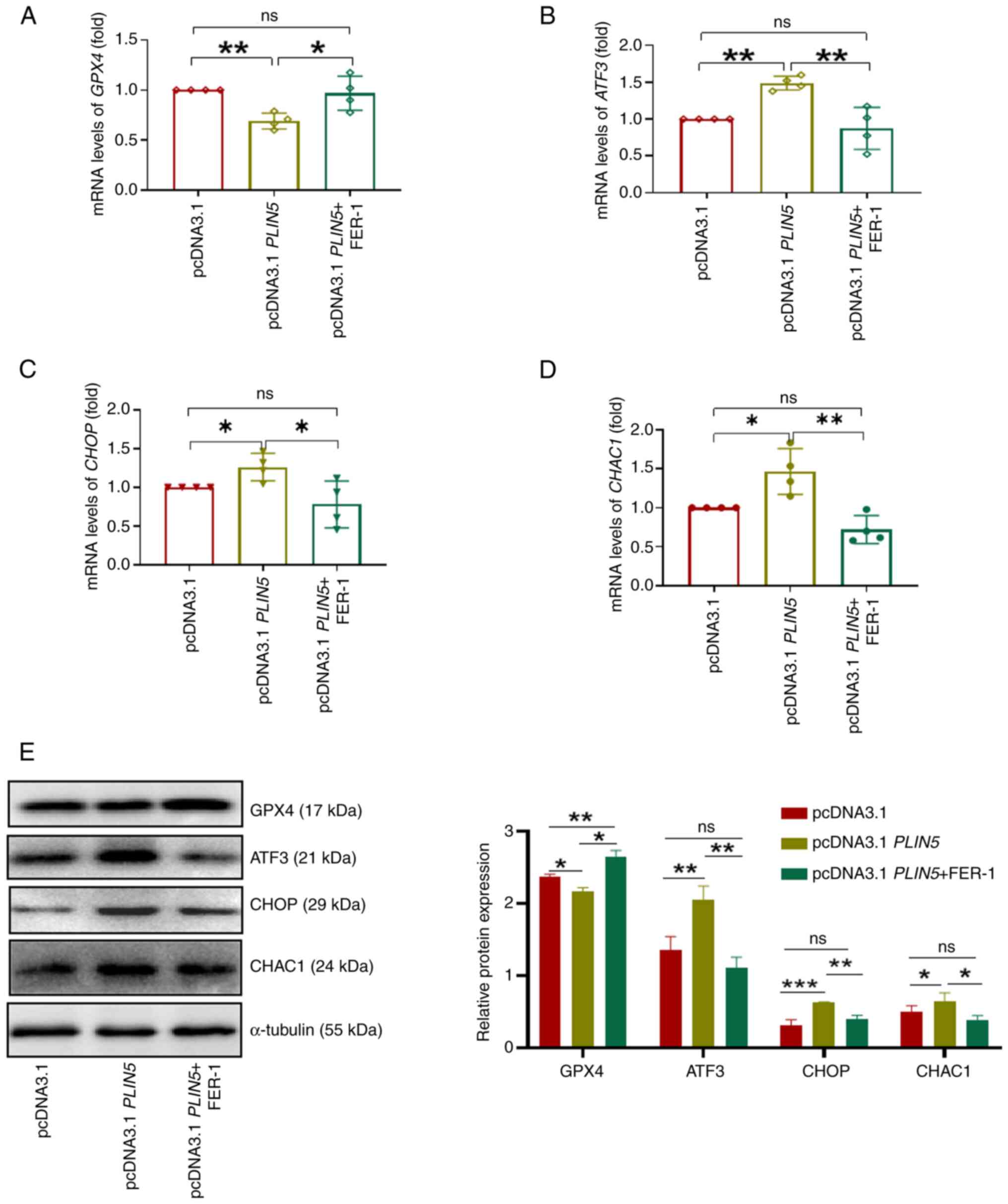
|
1
|
Rinella ME, Neuschwander-Tetri BA,
Siddiqui MS, Abdelmalek MF, Caldwell S, Barb D, Kleiner DE and
Loomba R: AASLD Practice Guidance on the clinical assessment and
management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology.
77:1797–1835. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yip TCF, Vilar-Gomez E, Petta S, Yilmaz Y,
Wong GL, Adams LA, de Lédinghen V, Sookoian S and Wong VW:
Geographical similarity and differences in the burden and genetic
predisposition of NAFLD. Hepatology. 77:1404–1427. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Syed-Abdul MM: Lipid metabolism in
Metabolic-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). Metabolites.
14:122024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Guo X, Yin X, Liu Z and Wang J:
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) pathogenesis and natural
products for prevention and treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 23:154892022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Petta S, Targher G, Romeo S, Pajvani UB,
Zheng MH, Aghemo A and Valenti LVC: The first MASH drug therapy on
the horizon: Current perspectives of resmetirom. Liver Int.
44:1526–1536. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Herker E, Vieyres G, Beller M, Krahmer N
and Bohnert M: Lipid droplet contact sites in health and disease.
Trends Cell Biol. 31:345–358. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gluchowski NL, Becuwe M, Walther TC and
Farese RV Jr: Lipid droplets and liver disease: From basic biology
to clinical implications. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
14:343–355. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Najt CP, Khan SA, Heden TD, Witthuhn BA,
Perez M, Heier JL, Mead LE, Franklin MP, Karanja KK, Graham MJ, et
al: Lipid Droplet-derived monounsaturated fatty acids traffic via
PLIN5 to allosterically activate SIRT1. Mol Cell. 77:810–824.e8.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mason RR and Watt MJ: Unraveling the roles
of PLIN5: Linking cell biology to physiology. Trends Endocrinol
Metab. 26:144–152. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Asimakopoulou A, Engel KM, Gassler N,
Bracht T, Sitek B, Buhl EM, Kalampoka S, Pinoé-Schmidt M, van
Helden J, Schiller J and Weiskirchen R: Deletion of perilipin 5
protects against hepatic injury in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
via missing inflammasome activation. Cells. 9:13462020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ma Y, Yin X, Qin Z, Ke X, Mi Y, Zheng P
and Tang Y: Role of Plin5 deficiency in progression of
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease induced by a High-fat diet in
mice. J Comp Pathol. 189:88–97. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yin X, Dong L, Wang X, Qin Z, Ma Y, Ke X,
Li Y, Wang Q, Mi Y, Lyu Q, et al: Perilipin 5 regulates hepatic
stellate cell activation and high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic
fatty liver disease. Animal Model Exp Med. 7:166–178. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jiang X, Stockwell BR and Conrad M:
Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 22:266–282. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu J, Wang Y, Jiang R, Xue R, Yin X, Wu M
and Meng Q: Ferroptosis in liver disease: New insights into disease
mechanisms. Cell Death Discov. 7:2762021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhou X, Fu Y, Liu W, Mu Y, Zhang H, Chen J
and Liu P: Ferroptosis in chronic liver diseases: Opportunities and
challenges. Front Mol Biosci. 9:9283212022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang S, Liu Z, Geng J, Li L and Feng X: An
overview of ferroptosis in Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Biomed Pharmacother. 153:1133742022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang H, Axinbai M, Zhao Y, Wei J, Qu T,
Kong J, He Y and Zhang L: Bioinformatics analysis of
Ferroptosis-related genes and immune cell infiltration in
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Eur J Med Res. 28:6052023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yin X, Mi Y, Wang X, Li Y, Zhu X, Bukhari
I, Wang Q, Zheng P, Xue X and Tang Y: Exploration and validation of
Ferroptosis-associated genes in ADAR1 Deletion-induced NAFLD
through RNA-seq analysis. Int Immunopharmacol. 134:1121772024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fu D, Wang C, Yu L and Yu R: Induction of
ferroptosis by ATF3 elevation alleviates cisplatin resistance in
gastric cancer by restraining Nrf2/Keap1/xCT signaling. Cell Mol
Biol Lett. 26:262021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao X, Wang Z, Wu G, Yin L, Xu L, Wang N
and Peng J: Apigenin-7-glucoside-loaded nanoparticle alleviates
intestinal ischemia-reperfusion by ATF3/SLC7A11-mediated
ferroptosis. J Control Release. 366:182–193. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Inaba Y, Hashiuchi E, Watanabe H, Kimura
K, Oshima Y, Tsuchiya K, Murai S, Takahashi C, Matsumoto M,
Kitajima S, et al: The transcription factor ATF3 switches cell
death from apoptosis to necroptosis in hepatic steatosis in male
mice. Nat Commun. 14:1672023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
National Research Council (US) Institute
for Laboratory Animal Research, . The Development of Science-based
Guidelines for Laboratory Animal Care: Proceedings of the November
2003 International Workshop. National Academies Press; Washington
DC: 2004
|
|
23
|
Hu Y, He W, Huang Y, Xiang H, Guo J, Che
Y, Cheng X, Hu F, Hu M, Ma T, et al: Fatty acid synthase-suppressor
screening identifies sorting Nexin 8 as a therapeutic target for
NAFLD. Hepatology. 74:2508–2525. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ren Y, Mao X, Xu H, Dang Q, Weng S, Zhang
Y, Chen S, Liu S, Ba Y, Zhou Z, et al: Ferroptosis and EMT: Key
targets for combating cancer progression and therapy resistance.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 80:2632023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen GH, Song CC, Pantopoulos K, Wei XL,
Zheng H and Luo Z: Mitochondrial oxidative stress mediated
Fe-induced ferroptosis via the NRF2-ARE pathway. Free Radic Biol
Med. 180:95–107. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Asghari S, Hamedi-Shahraki S and Amirkhizi
F: Systemic redox imbalance in patients with nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease. Eur J Clin Invest. 50:e132112020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bathish B, Robertson H, Dillon JF,
Dinkova-Kostova AT and Hayes JD: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and
mechanisms by which it is ameliorated by activation of the CNC-bZIP
transcription factor Nrf2. Free Radic Biol Med. 188:221–261. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hong SH, Lee DH, Lee YS, Jo MJ, Jeong YA,
Kwon WT, Choudry HA, Bartlett DL and Lee YJ: Molecular crosstalk
between ferroptosis and apoptosis: Emerging role of ER
stress-induced p53-independent PUMA expression. Oncotarget.
8:115164–115178. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mungrue IN, Pagnon J, Kohannim O,
Gargalovic PS and Lusis AJ: CHAC1/MGC4504 is a novel proapoptotic
component of the unfolded protein response, downstream of the
ATF4-ATF3-CHOP cascade. J Immunol. 182:466–476. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Stockwell BR: Ferroptosis turns 10:
Emerging mechanisms, physiological functions, and therapeutic
applications. Cell. 185:2401–2421. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Golabi P, Paik JM, AlQahtani S, Younossi
Y, Tuncer G and Younossi ZM: Burden of non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease in Asia, the Middle East and North Africa: Data from global
burden of disease 2009–2019. J Hepatol. 75:795–809. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li J, Wang T, Liu P, Yang F, Wang X, Zheng
W and Sun W: Hesperetin ameliorates hepatic oxidative stress and
inflammation via the PI3K/AKT-Nrf2-ARE pathway in oleic
acid-induced HepG2 cells and a rat model of high-fat diet-induced
NAFLD. Food Funct. 12:3898–3918. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tong J, Lan X, Zhang Z, Liu Y, Sun D, Wang
X, Ou-Yang SX, Zhuang CL, Shen FM, Wang P and Li DJ: Ferroptosis
inhibitor liproxstatin-1 alleviates metabolic
dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in mice: Potential
involvement of PANoptosis. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 44:1014–1028. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen X, Li J, Kang R, Klionsky DJ and Tang
D: Ferroptosis: Machinery and regulation. Autophagy. 17:2054–2081.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tsurusaki S, Tsuchiya Y, Koumura T,
Nakasone M, Sakamoto T, Matsuoka M, Imai H, Yuet-Yin Kok C, Okochi
H, Nakano H, et al: Hepatic ferroptosis plays an important role as
the trigger for initiating inflammation in nonalcoholic
steatohepatitis. Cell Death Dis. 10:4492019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Guan Q, Wang Z, Hu K, Cao J, Dong Y and
Chen Y: Melatonin ameliorates hepatic ferroptosis in NAFLD by
inhibiting ER stress via the MT2/cAMP/PKA/IRE1 signaling pathway.
Int J Biol Sci. 19:3937–3950. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tan Y, Jin Y, Wang Q, Huang J, Wu X and
Ren Z: Perilipin 5 Protects against cellular oxidative stress by
enhancing mitochondrial function in HepG2 cells. Cells. 8:12412019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gallardo-Montejano VI, Saxena G, Kusminski
CM, Yang C, McAfee JL, Hahner L, Hoch K, Dubinsky W, Narkar VA and
Bickel PE: Nuclear Perilipin 5 integrates lipid droplet lipolysis
with PGC-1α/SIRT1-dependent transcriptional regulation of
mitochondrial function. Nat Commun. 7:127232016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fang Z, Xu H, Duan J, Ruan B, Liu J, Song
P, Ding J, Xu C, Li Z, Dou K and Wang L: Short-term tamoxifen
administration improves hepatic steatosis and glucose intolerance
through JNK/MAPK in mice. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 8:942023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jin L, Wang M, Yang B, Ye L, Zhu W, Zhang
Q, Lou S, Zhang Y, Luo W and Liang G: A small-molecule JNK
inhibitor JM-2 attenuates high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 115:1095872023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mass-Sanchez PB, Krizanac M, Štancl P,
Leopold M, Engel KM, Buhl EM, van Helden J, Gassler N, Schiller J,
Karlić R, et al: Perilipin 5 deletion protects against nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma by modulating
lipid metabolism and inflammatory responses. Cell Death Discov.
10:942024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xu X, Qiu J, Li X, Chen J, Li Y, Huang X,
Zang S, Ma X and Liu J: Perilipin5 protects against Non-alcoholic
steatohepatitis by increasing 11-Dodecenoic acid and inhibiting the
occurrence of ferroptosis. Nutr Metab (Lond). 20:292023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mass Sanchez PB, Krizanac M, Weiskirchen R
and Asimakopoulos A: Understanding the role of perilipin 5 in
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its role in hepatocellular
carcinoma: A review of novel insights. Int J Mol Sci. 22:52842021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Shen X, Zhang J, Zhou Z and Yu R: PLIN5
suppresses lipotoxicity and ferroptosis in cardiomyocyte via
modulating PIR/NF-κB Axis. Int Heart J. 65:537–547. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Mason RR, Mokhtar R, Matzaris M,
Selathurai A, Kowalski GM, Mokbel N, Meikle PJ, Bruce CR and Watt
MJ: PLIN5 deletion remodels intracellular lipid composition and
causes insulin resistance in muscle. Mol Metab. 3:652–663. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gallardo-Montejano VI, Yang C, Hahner L,
McAfee JL, Johnson JA, Holland WL, Fernandez-Valdivia R and Bickel
PE: Perilipin 5 links mitochondrial uncoupled respiration in brown
fat to healthy white fat remodeling and systemic glucose tolerance.
Nat Commun. 12:33202021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Navik U, Singh SK, Khurana A and
Weiskirchen R: Revolutionizing liver fibrosis research: The promise
of 3D organoid models in understanding and treating chronic liver
disease. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 19:105–110. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Liu Y, Gilchrist AE, Johansson PK, Guan Y,
Deras JD, Liu YC, Ceva S, Huang MS, Navarro RS, Enejder A, et al:
Engineered hydrogels for organoid models of human nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease. Adv Sci (Weinh). 12:e173322025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hu S, Li R, Gong D, Hu P, Xu J, Ai Y, Zhao
X, Hu C, Xu M, Liu C, et al: Atf3-mediated metabolic reprogramming
in hepatic macrophage orchestrates metabolic dysfunction-associated
steatohepatitis. Sci Adv. 10:eado31412024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Basak M, Das K, Mahata T, Sengar AS, Verma
SK, Biswas S, Bhadra K, Stewart A and Maity B: RGS7-ATF3-Tip60
complex promotes hepatic steatosis and fibrosis by directly
inducing TNFα. Antioxid Redox Signal. 38:137–159. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kang Y, Li Q, Zhu R, Li S, Xu X, Shi X and
Yin Z: Identification of Ferroptotic genes in spinal cord injury at
different time points: Bioinformatics and experimental validation.
Mol Neurobiol. 59:5766–5784. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Tian K, Wei J, Wang R, Wei M, Hou F and Wu
L: Sophoridine derivative 6j inhibits liver cancer cell
proliferation via ATF3 mediated ferroptosis. Cell Death Discov.
9:2962023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wang L, Liu Y, Du T, Yang H, Lei L, Guo M,
Ding HF, Zhang J, Wang H, Chen X and Yan C: ATF3 promotes
erastin-induced ferroptosis by suppressing system Xc. Cell Death
Differ. 27:662–675. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Alosaimi M, Abd-Elhakim YM, Mohamed AA,
Metwally MMM, Khamis T, Alansari WS, Eskandrani AA, Essawi WM, Awad
MM, El-Shaer RAA, et al: Green synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles
attenuate acrylamide-induced cardiac injury via controlling
endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated apoptosis through
ATF3/CHOP/BCL2 signaling in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res.
202:2657–2671. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Crawford RR, Prescott ET, Sylvester CF,
Higdon AN, Shan J, Kilberg MS and Mungrue IN: Human CHAC1 protein
degrades glutathione, and mRNA induction is regulated by the
transcription factors ATF4 and ATF3 and a bipartite ATF/CRE
regulatory element. J Biol Chem. 290:15878–15891. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wang X, He MJ, Chen XJ, Bai YT and Zhou G:
Glaucocalyxin A impairs tumor growth via amplification of the
ATF4/CHOP/CHAC1 cascade in human oral squamous cell carcinoma. J
Ethnopharmacol. 290:1151002022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Drummer C IVth, Saaoud F, Jhala NC, Cueto
R, Sun Y, Xu K, Shao Y, Lu Y, Shen H, Yang L, et al: Caspase-11
promotes high-fat diet-induced NAFLD by increasing glycolysis,
OXPHOS, and pyroptosis in macrophages. Front Immunol.
14:11138832023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ma SY, Sun KS, Zhang M, Zhou X, Zheng XH,
Tian SY, Liu YS, Chen L, Gao X, Ye J, et al: Disruption of Plin5
degradation by CMA causes lipid homeostasis imbalance in NAFLD.
Liver Int. 40:2427–2438. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kim JY, Park KJ, Hwang JY, Kim GH, Lee D,
Lee YJ, Song EH, Yoo MG, Kim BJ, Suh YH, et al: Activating
transcription factor 3 is a target molecule linking hepatic
steatosis to impaired glucose homeostasis. J Hepatol. 67:349–359.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Cusi K, Isaacs S, Barb D, Basu R, Caprio
S, Garvey WT, Kashyap S, Mechanick JI, Mouzaki M, Nadolsky K, et
al: American association of clinical endocrinology clinical
practice guideline for the diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease in primary care and endocrinology clinical
settings: Co-sponsored by the American association for the study of
liver diseases (AASLD). Endocr Pract. 28:528–562. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Paternostro R and Trauner M: Current
treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Intern Med.
292:190–204. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Langhi C, Marquart TJ, Allen RM and Baldán
A: Perilipin-5 is regulated by statins and controls triglyceride
contents in the hepatocyte. J Hepatol. 61:358–365. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Gao X, Nan Y, Zhao Y, Yuan Y, Ren B and
Sun C: Atorvastatin reduces lipid accumulation in the liver by
activating protein kinase A-mediated phosphorylation of perilipin
5. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 1862:1512–1519. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Yu M, Tang TMS, Ghamsari L, Yuen G,
Scuoppo C, Rotolo JA, Kappel BJ and Mason JM: Exponential
Combination of a and e/g intracellular peptide libraries identifies
a selective ATF3 inhibitor. ACS Chem Biol. 19:753–762. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|