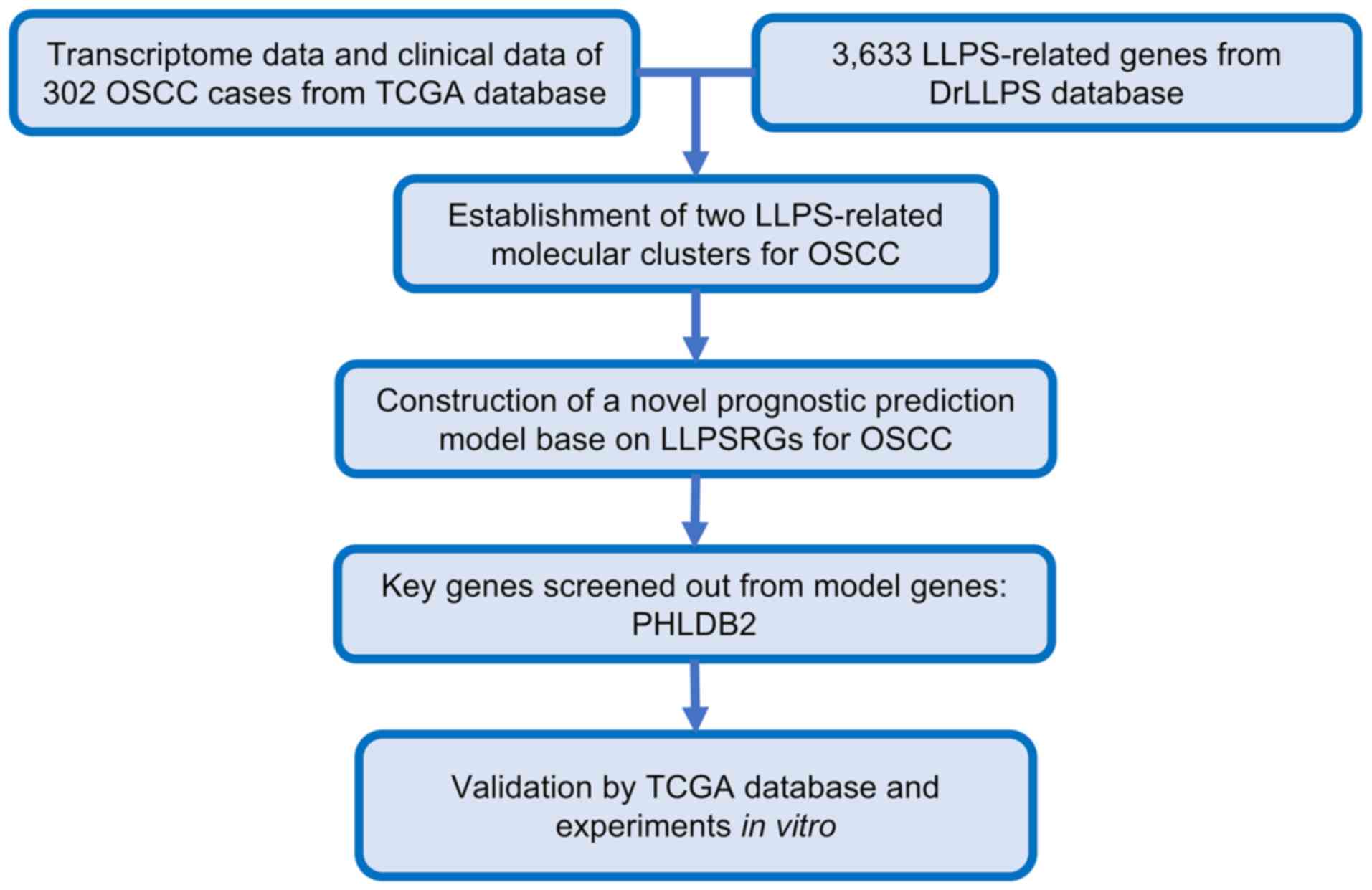
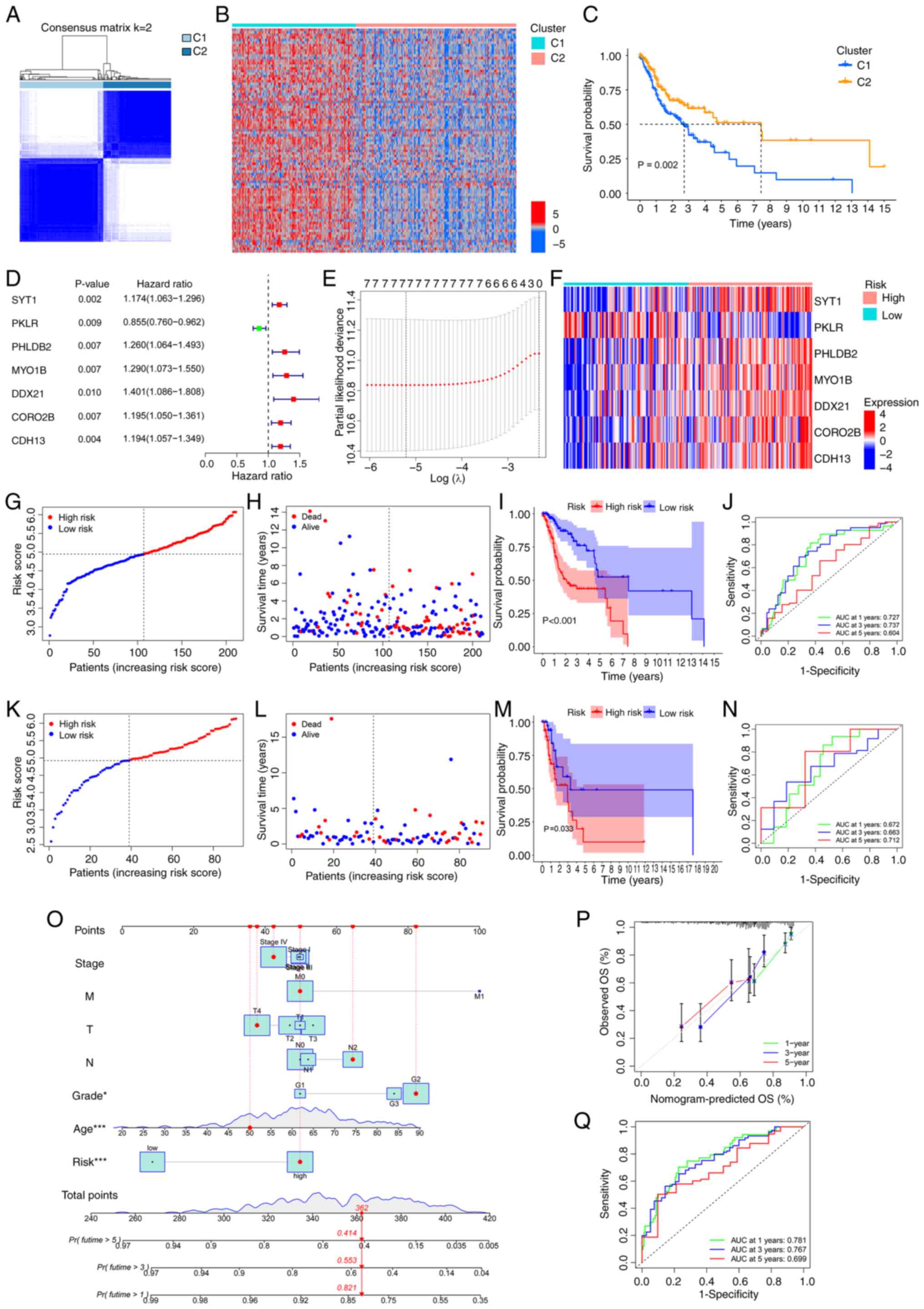
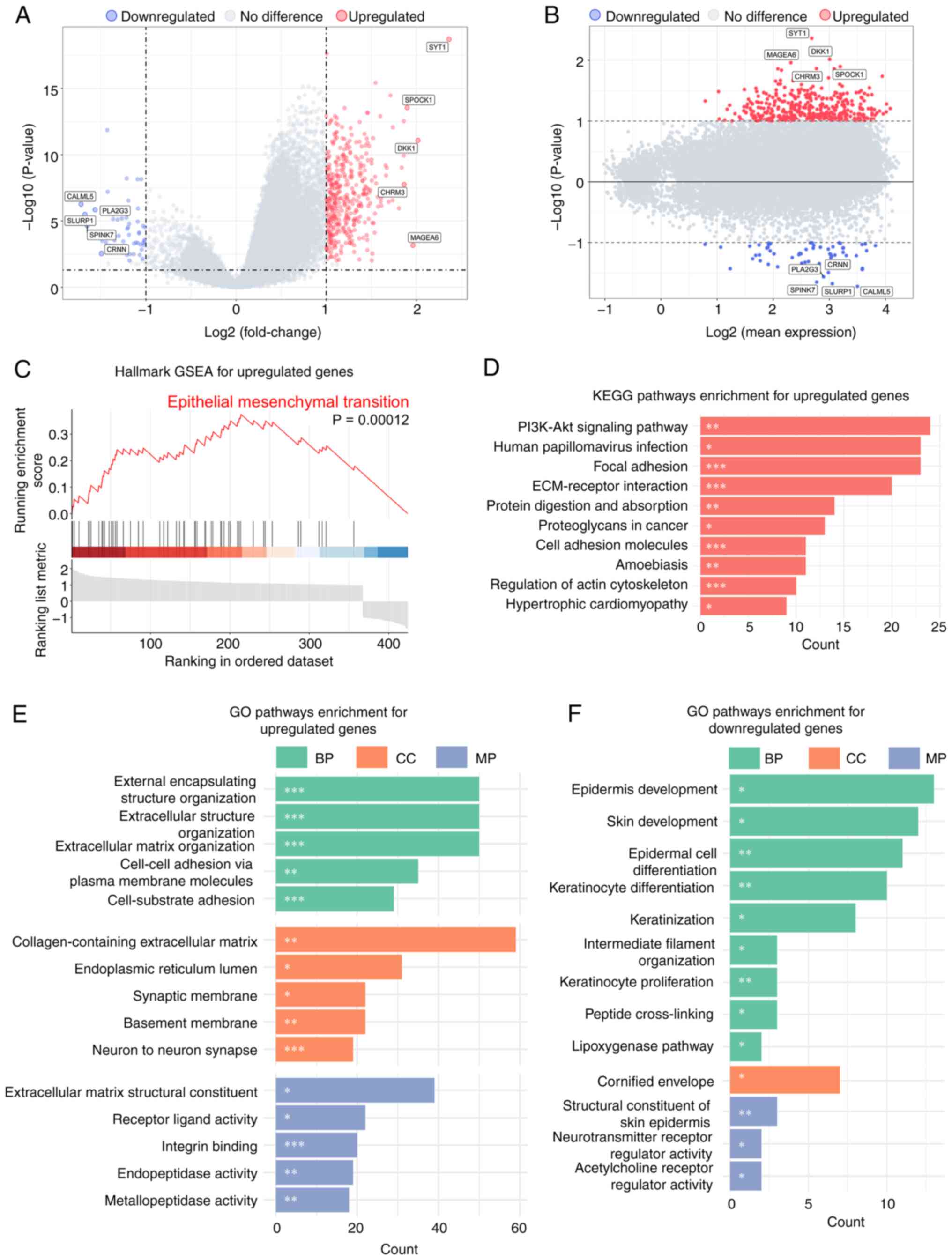
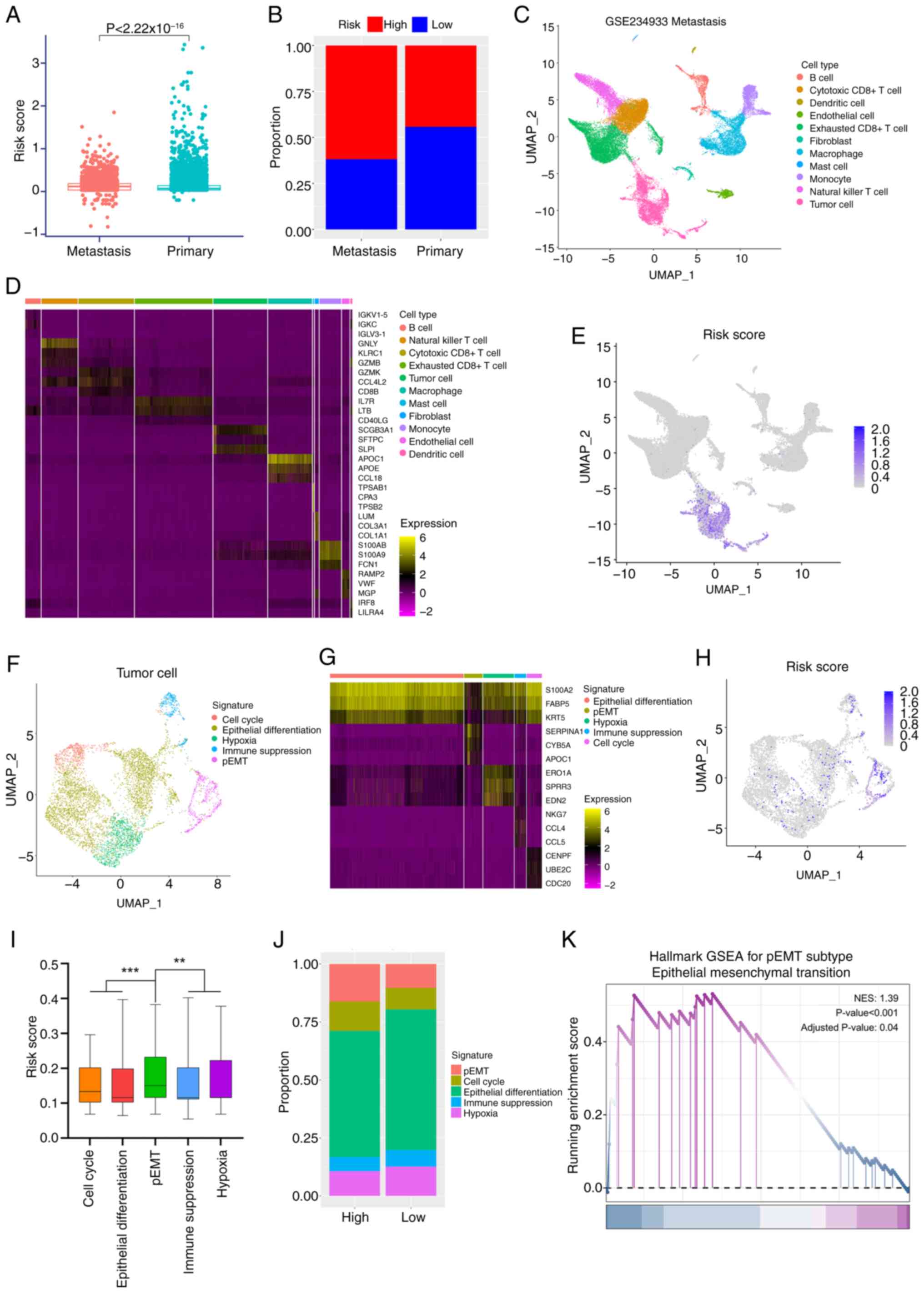
|
1
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263.
2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cramer JD, Burtness B, Le QT and Ferris
RL: The changing therapeutic landscape of head and neck cancer. Nat
Rev Clin Oncol. 16:669–683. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Alberti S, Gladfelter A and Mittag T:
Considerations and challenges in studying liquid-liquid phase
separation and biomolecular condensates. Cell. 176:419–434. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tong X, Tang R, Xu J, Wang W, Zhao Y, Yu X
and Shi S: Liquid-liquid phase separation in tumor biology. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 7:2212022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mehta S and Zhang J: Liquid-liquid phase
separation drives cellular function and dysfunction in cancer. Nat
Rev Cancer. 22:239–252. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zheng LW, Liu CC and Yu KD: Phase
separations in oncogenesis, tumor progressions and metastasis: A
glance from hallmarks of cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 16:1232023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Blackburn EH: Structure and function of
telomeres. Nature. 350:569–573. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang H, Zhao R, Tones J, Liu M, Dilley
RL, Chenoweth DM, Greenberg RA and Lampson MA: Nuclear body phase
separation drives telomere clustering in ALT cancer cells. Mol Biol
Cell. 31:2048–2056. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lu Y, Wu T, Gutman O, Lu H, Zhou Q, Henis
YI and Luo K: Phase separation of TAZ compartmentalizes the
transcription machinery to promote gene expression. Nat Cell Biol.
22:453–464. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cheng Y, Xie W, Pickering BF, Chu KL,
Savino AM, Yang X, Luo H, Nguyen DT, Mo S, Barin E, et al:
N6-methyladenosine on mRNA facilitates a phase-separated
nuclear body that suppresses myeloid leukemic differentiation.
Cancer Cell. 39:958–972.e8. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tulpule A, Guan J, Neel DS, Allegakoen HR,
Lin YP, Brown D, Chou YT, Heslin A, Chatterjee N, Perati S, et al:
Kinase-mediated RAS signaling via membraneless cytoplasmic protein
granules. Cell. 184:2649–2664.e18. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Qiu Y, Pan M and Chen X: A liquid-liquid
phase separation-related gene signature as prognostic biomarker for
epithelial ovarian cancer. Front Oncol. 11:6718922021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yu-Qing H, Peng-Ping L, Ke S, Ke-Xing Y,
Wei-Jun Z and Zhen-Yu W: Comprehensive analysis of liquid-liquid
phase separation-related genes in prediction of breast cancer
prognosis. Front Genet. 13:8344712022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sun L, Liu XP, Yan X, Wu S, Tang X, Chen
C, Li G, Hu H, Wang D and Li S: Identification of molecular
subtypes based on liquid-liquid phase separation and cross-talk
with immunological phenotype in bladder cancer. Front Immunol.
13:10595682022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chatterjee A, Chaudhary A, Ghosh A, Arun
P, Mukherjee G, Arun I, Maitra A, Biswas N and Majumder PP:
Overexpression of CD73 is associated with recurrence and poor
prognosis of gingivobuccal oral cancer as revealed by transcriptome
and deep immune profiling of paired tumor and margin tissues.
Cancer Med. 12:16774–16787. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wilkerson MD and Hayes DN:
ConsensusClusterPlus: A class discovery tool with confidence
assessments and item tracking. Bioinformatics. 26:1572–1573. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Love MI, Huber W and Anders S: Moderated
estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with
DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15:5502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bill R, Wirapati P, Messemaker M, Roh W,
Zitti B, Duval F, Kiss M, Park JC, Saal TM, Hoelzl J, et al:
CXCL9:SPP1 macrophage polarity identifies a network of cellular
programs that control human cancers. Science. 381:515–524. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tang Z, Kang B, Li C, Chen T and Zhang Z:
GEPIA2: An enhanced web server for large-scale expression profiling
and interactive analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 47:W556–W560. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mészáros B, Erdos G and Dosztányi Z:
IUPred2A: context-dependent prediction of protein disorder as a
function of redox state and protein binding. Nucleic Acids Res.
46:W329–W337. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hou C, Wang X, Xie H, Chen T, Zhu P, Xu X,
You K and Li T: PhaSepDB in 2022: Annotating phase
separation-related proteins with droplet states, co-phase
separation partners and other experimental information. Nucleic
Acids Res. 51:D460–D465. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lydiatt WM, Patel SG, O'Sullivan B,
Brandwein MS, Ridge JA, Migliacci JC, Loomis AM and Shah JP: Head
and Neck cancers-major changes in the American Joint Committee on
cancer eighth edition cancer staging manual. CA Cancer J Clin.
67:122–137. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Coussy F, El Botty R, Lavigne M, Gu C,
Fuhrmann L, Briaux A, de Koning L, Dahmani A, Montaudon E, Morisset
L, et al: Combination of PI3K and MEK inhibitors yields durable
remission in PDX models of PIK3CA-mutated metaplastic breast
cancers. J Hematol Oncol. 13:132020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jeong YG, Katuwal NB, Kang MS, Ghosh M,
Hong SD, Park SM, Kim SG, Kim TH and Moon YW: Combined PI3K
inhibitor and eribulin enhances anti-tumor activity in preclinical
models of paclitaxel-resistant, PIK3CA-mutated endometrial cancer.
Cancers (Basel). 15:48872023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang J, Ni Z, Zhang Y, Guo Y, Zhai R,
Wang M, Gong Z, Wang M, Zeng F, Gu Z, et al: DAZAP1 phase
separation regulates mitochondrial metabolism to facilitate
invasion and metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer
Res. 84:3818–3833. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang W, Yun B, Hoyle RG, Ma Z, Zaman SU,
Xiong G, Yi C, Xie N, Zhang M, Liu X, et al: CYTOR facilitates
formation of FOSL1 phase separation and super enhancers to drive
metastasis of tumor budding cells in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Adv Sci (Weinh). 11:e23050022024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ning W, Guo Y, Lin S, Mei B, Wu Y, Jiang
P, Tan X, Zhang W, Chen G, Peng D, et al: DrLLPS: A data resource
of liquid-liquid phase separation in eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res.
48(D1): D288–D295. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shi J, Li W, Jia Z, Peng Y, Hou J, Li N,
Meng R, Fu W, Feng Y, Wu L, et al: Synaptotagmin 1 suppresses
colorectal cancer metastasis by inhibiting ERK/MAPK
signaling-mediated tumor cell pseudopodial formation and migration.
Cancers (Basel). 15:52822023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Balood M, Ahmadi M, Eichwald T, Ahmadi A,
Majdoubi A, Roversi K, Roversi K, Lucido CT, Restaino AC, Huang S,
et al: Nociceptor neurons affect cancer immunosurveillance. Nature.
611:405–412. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang Y, Lin C, Liu Z, Sun Y, Chen M, Guo
Y, Liu W, Zhang C, Chen W, Sun J, et al: Cancer cells co-opt
nociceptive nerves to thrive in nutrient-poor environments and upon
nutrient-starvation therapies. Cell Metab. 34:1999–2017.e10. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Qiao N, Dai X, Chen J, Cao H, Hu G, Guo X,
Liu P, Xing C and Yang F: Single nucleus RNA sequencing reveals
cellular and molecular responses to vanadium exposure in duck
kidneys. J Hazard Mater. 480:1364922024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yamada Y, Koshizuka K, Hanazawa T, Kikkawa
N, Okato A, Idichi T, Arai T, Sugawara S, Katada K, Okamoto Y and
Seki N: Passenger strand of miR-145-3p acts as a tumor-suppressor
by targeting MYO1B in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J
Oncol. 52:166–178. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhou X, Wang R, Li X, Yu L, Hua D, Sun C,
Shi C, Luo W, Rao C, Jiang Z, et al: Splicing factor SRSF1 promotes
gliomagenesis via oncogenic splice-switching of MYO1B. J Clin
Invest. 129:676–693. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen YH, Xu NZ, Hong C, Li WQ, Zhang YQ,
Yu XY, Huang YL and Zhou JY: Myo1b promotes tumor progression and
angiogenesis by inhibiting autophagic degradation of HIF-1α in
colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 13:9392022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang H, Yang F, Ye J, Dai X, Liao H, Xing
C, Jiang Z, Peng C, Gao F and Cao H: Ginkgo biloba extract
alleviates deltamethrin-induced testicular injury by upregulating
SKP2 and inhibiting Beclin1-independent autophagy. Phytomedicine.
135:1562452024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang D, Qian C, Wei H and Qian X:
Identification of the prognostic value of tumor
microenvironment-related genes in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Front Mol Biosci. 7:5994752020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shao Y, Li W, Zhang L, Xue B, Chen Y,
Zhang Z, Wang D and Wu B: CDH13 is a prognostic biomarker and a
potential therapeutic target for patients with clear cell renal
cell carcinoma. Am J Cancer Res. 12:4520–4544. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gao H, Wei H, Yang Y, Li H, Liang J, Ye J,
Zhang F, Wang L, Shi H, Wang J and Han A: Phase separation of DDX21
promotes colorectal cancer metastasis via MCM5-dependent EMT
pathway. Oncogene. 42:1704–1715. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang S, Zhang Y, Cai Q, Ma M, Jin LY, Weng
M, Zhou D, Tang Z, Wang JD and Quan Z: Circular RNA FOXP1 promotes
tumor progression and Warburg effect in gallbladder cancer by
regulating PKLR expression. Mol Cancer. 18:1452019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen WY, Thuy Dung PV, Yeh HL, Chen WH,
Jiang KC, Li HR, Chen ZQ, Hsiao M, Huang J, Wen YC and Liu YN:
Targeting PKLR/MYCN/ROMO1 signaling suppresses neuroendocrine
differentiation of castration-resistant prostate cancer. Redox
Biol. 62:1026862023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Peng J, Dai X, Zhang T, Hu G, Cao H, Guo
X, Fan H, Chen J, Tang W and Yang F: Copper as the driver of the
lncRNA-TCONS-6251/miR-novel-100/TC2N axis: Unraveling ferroptosis
in duck kidney. Int J Biol Macromol. 282:1367972024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li H, Wang Z, Liang H, Liu X, Liu H,
Zhuang Z and Hou J: Depletion of PHLDB2 suppresses
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and enhances anti-tumor immunity
in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Biomolecules. 14:2322024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chen J, Dai X, Xing C, Zhang Y, Cao H, Hu
G, Guo X, Gao X, Liu P and Yang F: Cooperative application of
transcriptomics and ceRNA hypothesis: lncRNA-00742/miR-116 targets
CD74 to mediate vanadium-induced mitochondrial apoptosis in duck
liver. J Hazard Mater. 480:1359042024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chen G, Zhou T, Ma T, Cao T and Yu Z:
Oncogenic effect of PHLDB2 is associated with
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and E-cadherin regulation in
colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 19:1842019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kang W, Zhang J, Huang T, Zhou Y, Wong CC,
Chan RCK, Dong Y, Wu F, Zhang B, Wu WKK, et al: NOTCH3, a crucial
target of miR-491-5p/miR-875-5p, promotes gastric carcinogenesis by
upregulating PHLDB2 expression and activating Akt pathway.
Oncogene. 40:1578–1594. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|