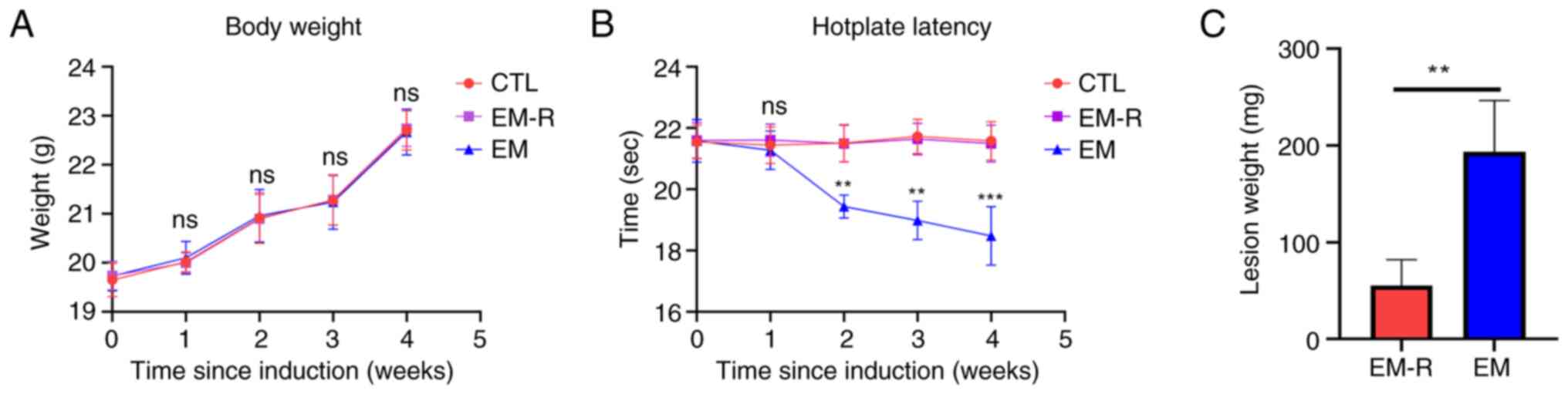
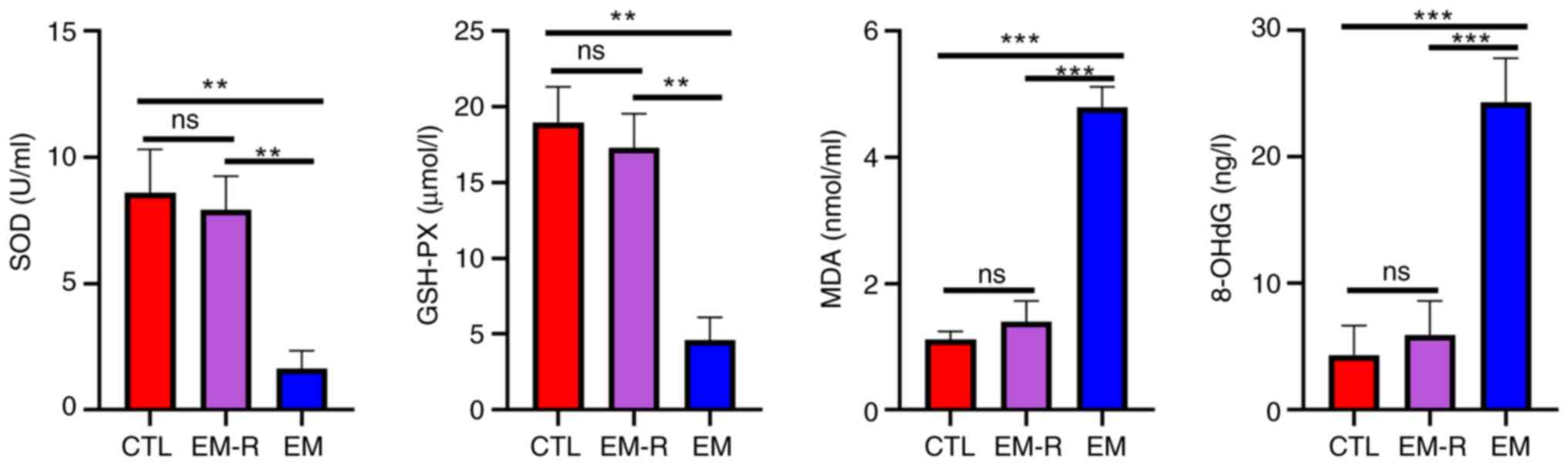
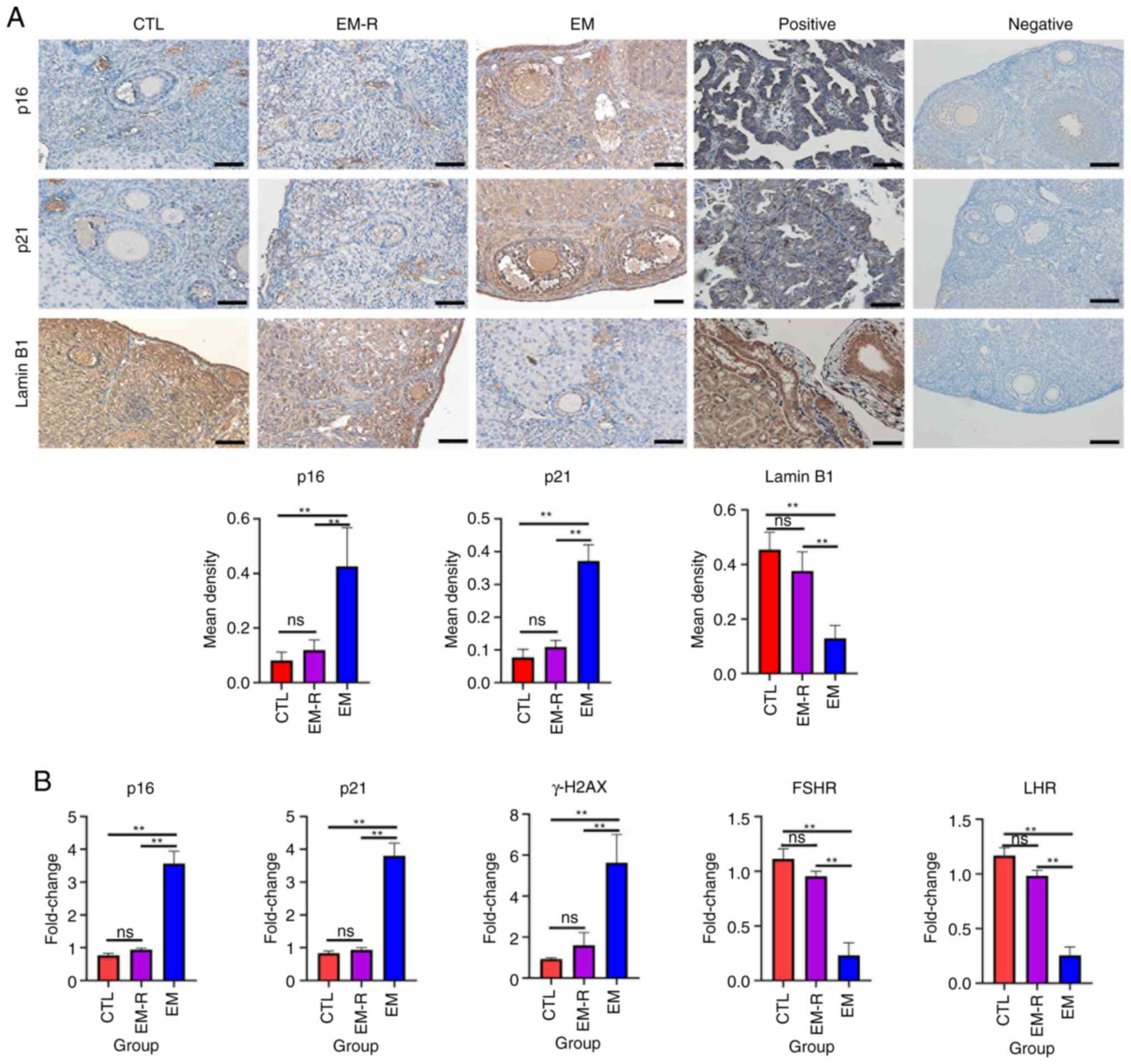
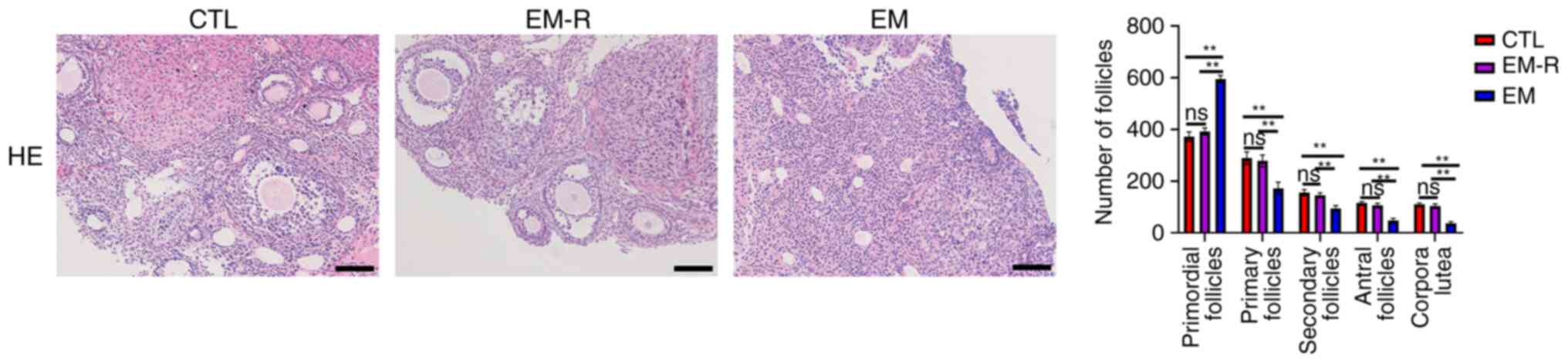
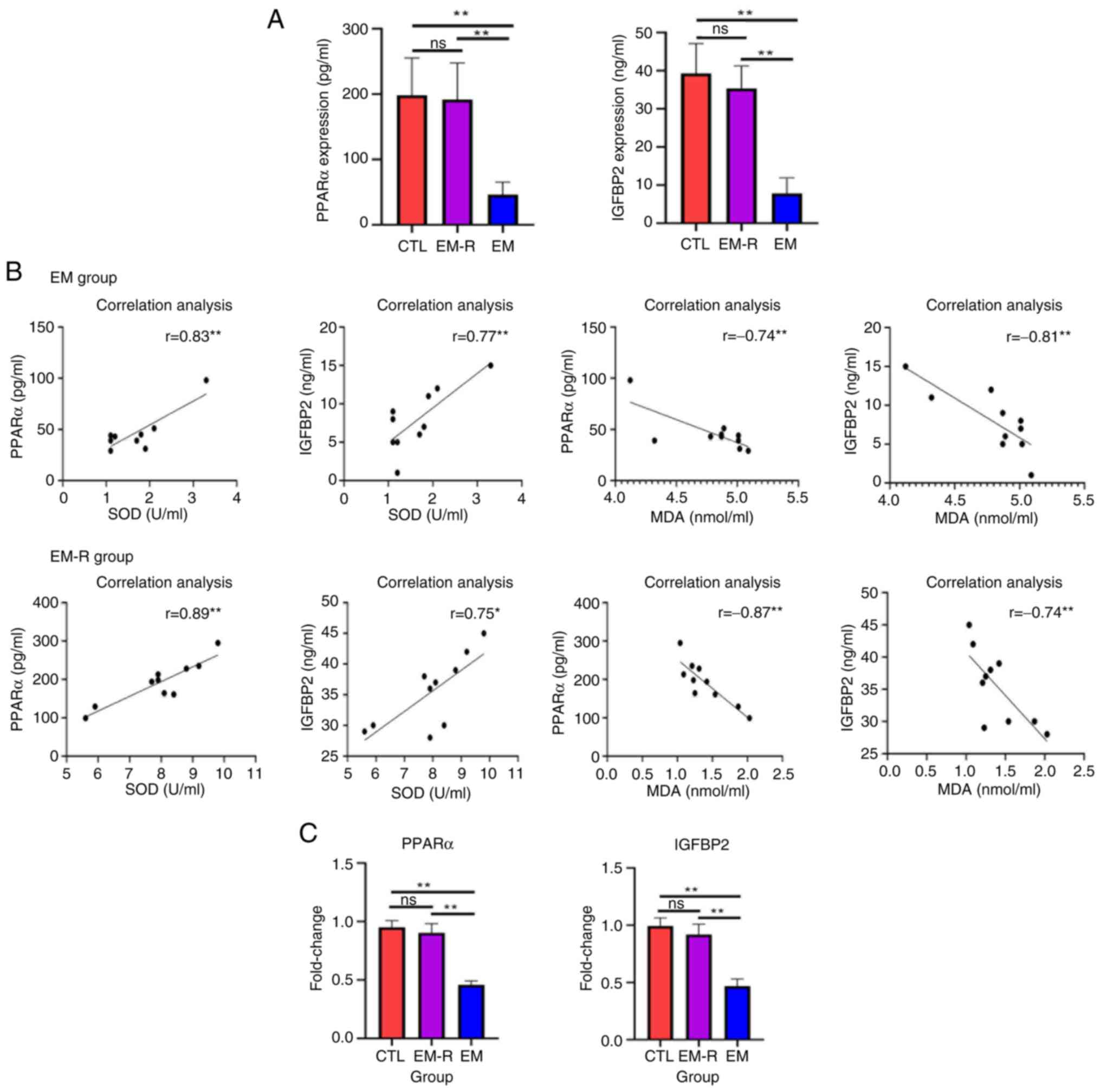
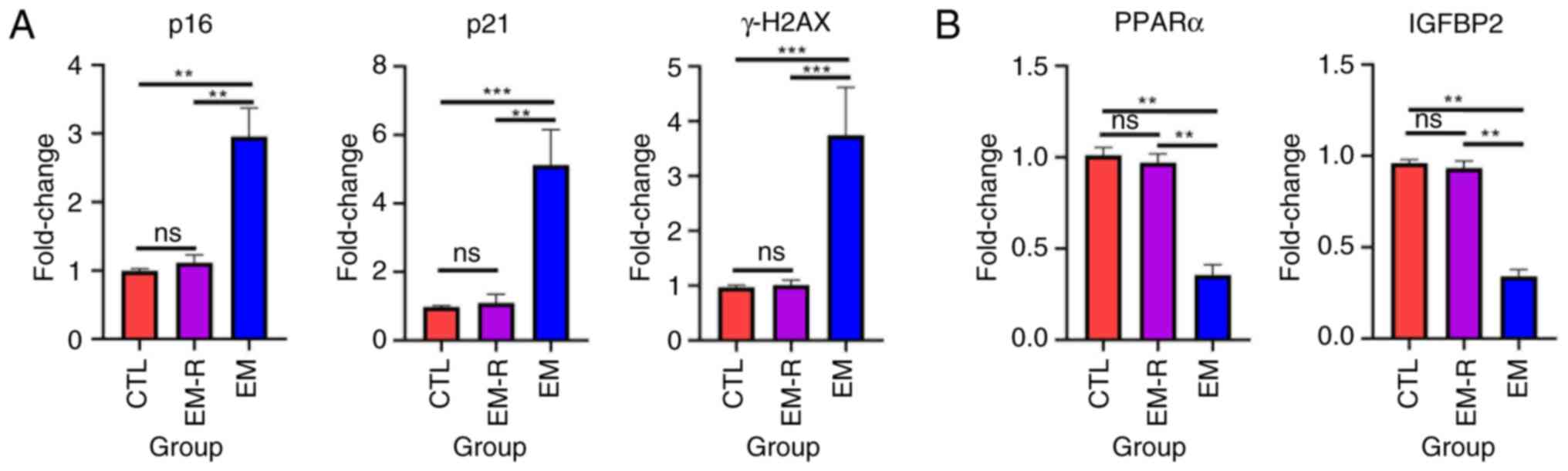
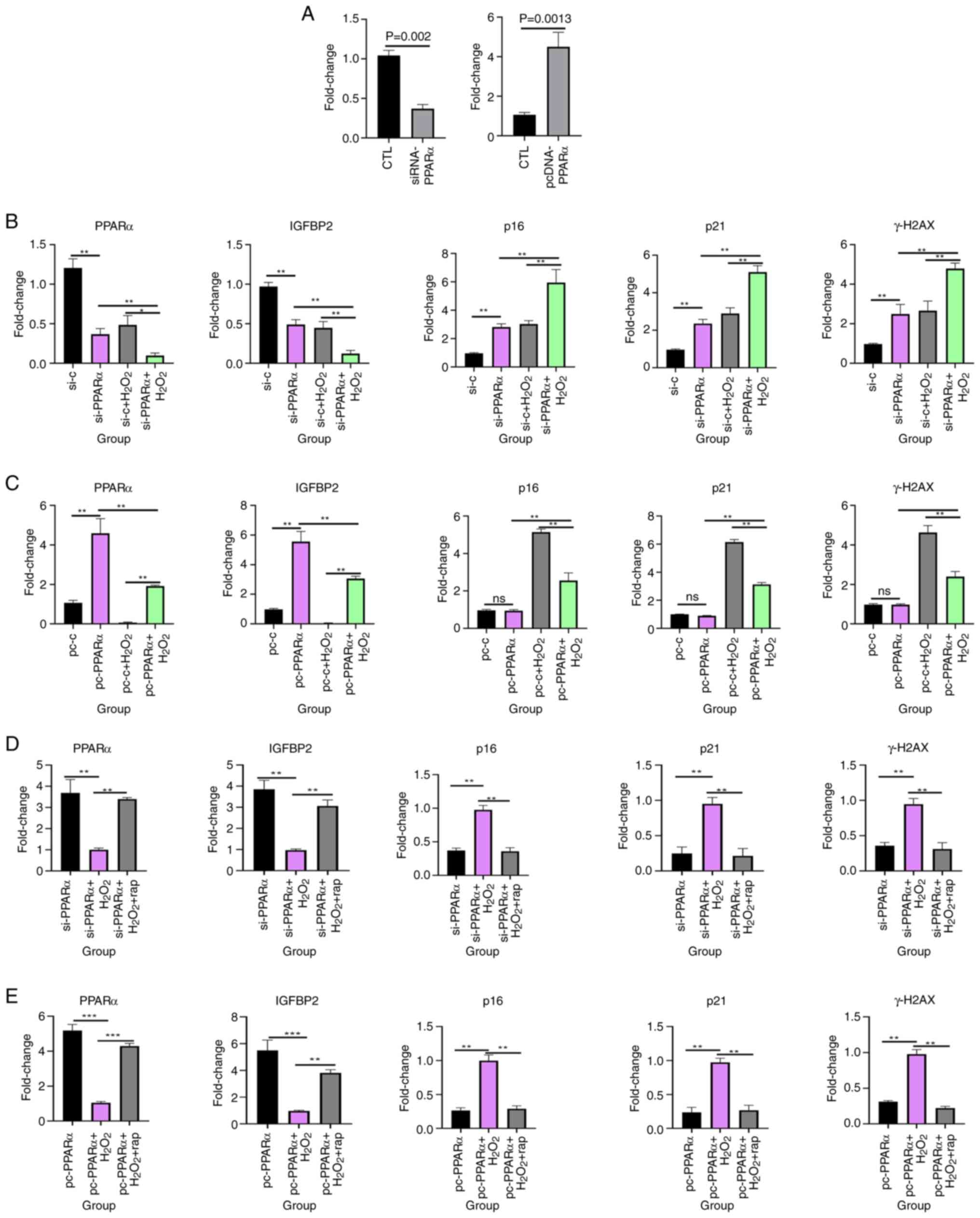
|
1
|
Bulun SE, Yilmaz BD, Sison C, Miyazaki K,
Bernardi L, Liu S, Kohlmeier A, Yin P, Milad M and Wei J:
Endometriosis. Endocr Rev. 40:1048–1079. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Harb HM, Gallos ID, Chu J, Harb M and
Coomarasamy A: The effect of endometriosis on in vitro
fertilisation outcome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BJOG.
120:1308–1320. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sanchez AM, Vanni VS, Bartiromo L, Papaleo
E, Zilberberg E, Candiani M, Orvieto R and Viganò P: Is the oocyte
quality affected by endometriosis? A review of the literature. J
Ovarian Res. 10:432017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
De Hondt A, Peeraer K, Meuleman C, Meeuwis
L, De Loecker P and D'Hooghe TM: Endometriosis and subfertility
treatment: A review. Minerva Ginecol. 57:257–267. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Barnhart K, Dunsmoor-Su R and Coutifaris
C: Effect of endometriosis on in vitro fertilization. Fertil
Steril. 77:1148–1155. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Burney RO and Giudice LC: Pathogenesis and
pathophysiology of endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 98:511–519. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ansariniya H, Yavari A, Javaheri A and
Zare F: Oxidative stress-related effects on various aspects of
endometriosis. Am J Reprod Immunol. 88:e135932022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schieber M and Chandel NS: ROS function in
redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr Biol. 24:R453–R462.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Malvezzi H, Dobo C, Filippi RZ, Mendes do
Nascimento H, Palmieri da Silva E Sousa L, Meola J, Piccinato CA
and Podgaec S: Altered p16Ink4a, IL-1β, and lamin b1
protein expression suggest cellular senescence in deep
endometriotic lesions. Int J Mol Sci. 23:24762022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lin X, Dai Y, Tong X, Xu W, Huang Q, Jin
X, Li C, Zhou F, Zhou H, Lin X, et al: Excessive oxidative stress
in cumulus granulosa cells induced cell senescence contributes to
endometriosis-associated infertility. Redox Biol. 30:1014312020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Duval C, Wyse BA, Tsang BK and Librach CL:
Extracellular vesicles and their content in the context of
polycystic ovarian syndrome and endometriosis: A review. J Ovarian
Res. 17:1602024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Blagosklonny MV: Cell senescence,
rapamycin and hyperfunction theory of aging. Cell Cycle.
21:1456–1467. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Selvarani R, Mohammed S and Richardson A:
Effect of rapamycin on aging and age-related diseases-past and
future. Geroscience. 43:1135–1158. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fan J, Chen C and Zhong Y: A cohort study
on IVF outcomes in infertile endometriosis patients: The effects of
rapamycin treatment. Reprod Biomed Online. 48:1033192024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sung B, Park S, Yu BP and Chung HY:
Modulation of PPAR in aging, inflammation, and calorie restriction.
J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 59:997–1006. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Iemitsu M, Miyauchi T, Maeda S, Tanabe T,
Takanashi M, Irukayama-Tomobe Y, Sakai S, Ohmori H, Matsuda M and
Yamaguchi I: Aging-induced decrease in the PPAR-alpha level in
hearts is improved by exercise training. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 283:H1750–H1760. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sanguino E, Roglans N, Alegret M, Sánchez
RM, Vázquez-Carrera M and Laguna JC: Atorvastatin reverses
age-related reduction in rat hepatic PPARalpha and HNF-4. Br J
Pharmacol. 145:853–861. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kang HS, Cho HC, Lee JH, Oh GT, Koo SH,
Park BH, Lee IK, Choi HS, Song DK and Im SS: Metformin stimulates
IGFBP-2 gene expression through PPARalpha in diabetic states. Sci
Rep. 6:236652016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shin M, Kang HS, Park JH, Bae JH, Song DK
and Im SS: Recent insights into insulin-like growth factor binding
protein 2 transcriptional regulation. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul).
32:11–17. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Spitschak M and Hoeflich A: Potential
functions of IGFBP-2 for ovarian folliculogenesis and
steroidogenesis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 9:1192018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Haouzi D, Assou S, Monzo C, Vincens C,
Dechaud H and Hamamah S: Altered gene expression profile in cumulus
cells of mature MII oocytes from patients with polycystic ovary
syndrome. Hum Reprod. 27:3523–3530. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kamangar BB, Gabillard JC and Bobe J:
Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP)-1, −2, −3, −4,
−5, and −6 and IGFBP-related protein 1 during rainbow trout
postvitellogenesis and oocyte maturation: molecular
characterization, expression profiles, and hormonal regulation.
Endocrinology. 147:2399–2410. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Somigliana E, Viganò P, Rossi G, Carinelli
S, Vignali M and Panina-Bordignon P: Endometrial ability to implant
in ectopic sites can be prevented by interleukin-12 in a murine
model of endometriosis. Hum Reprod. 14:2944–2950. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ren XU, Wang Y, Xu G and Dai L: Effect of
rapamycin on endometriosis in mice. Exp Ther Med. 12:101–106. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lu Y, Nie J, Liu X, Zheng Y and Guo SW:
Trichostatin A, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, reduces lesion
growth and hyperalgesia in experimentally induced endometriosis in
mice. Hum Reprod. 25:1014–1025. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tilly JL: Ovarian follicle counts-not as
simple as 1, 2, 3. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 1:112003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Luo LL, Huang J, Fu YC, Xu JJ and Qian YS:
Effects of tea polyphenols on ovarian development in rats. J
Endocrinol Invest. 31:1110–1118. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tian Y, Shen W, Lai Z, Shi L, Yang S, Ding
T, Wang S and Luo A: Isolation and identification of ovarian
theca-interstitial cells and granulose cells of immature female
mice. Cell Biol Int. 39:584–590. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hernandez-Segura A, Nehme J and Demaria M:
Hallmarks of cellular senescence. Trends Cell Biol. 28:436–453.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fragouli E, Lalioti MD and Wells D: The
transcriptome of follicular cells: biological insights and clinical
implications for the treatment of infertility. Hum Reprod Update.
20:1–11. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Laschke MW, Elitzsch A, Scheuer C,
Holstein JH, Vollmar B and Menger MD: Rapamycin induces regression
of endometriotic lesions by inhibiting neovascularization and cell
proliferation. Br J Pharmacol. 149:137–144. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Augoulea A, Mastorakos G, Lambrinoudaki I,
Christodoulakos G and Creatsas G: The role of the oxidative-stress
in the endometriosis-related infertility. Gynecol Endocrinol.
25:75–81. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mansour G, Sharma RK, Agarwal A and
Falcone T: Endometriosis-induced alterations in mouse metaphase II
oocyte microtubules and chromosomal alignment: A possible cause of
infertility. Fertil Steril. 94:1894–1899. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ding GL, Chen XJ, Luo Q, Dong MY, Wang N
and Huang HF: Attenuated oocyte fertilization and embryo
development associated with altered growth factor/signal
transduction induced by endometriotic peritoneal fluid. Fertil
Steril. 93:2538–2544. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Papaconstantinou J: The role of signaling
pathways of inflammation and oxidative stress in development of
senescence and aging phenotypes in cardiovascular disease. Cells.
8:13832019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kishi H, Kitahara Y, Imai F, Nakao K and
Suwa H: Expression of the gonadotropin receptors during follicular
development. Reprod Med Biol. 17:11–19. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Harrison DE, Strong R, Sharp ZD, Nelson
JF, Astle CM, Flurkey K, Nadon NL, Wilkinson JE, Frenkel K, Carter
CS, et al: Rapamycin fed late in life extends lifespan in
genetically heterogeneous mice. Nature. 460:392–395. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Weichhart T: mTOR as regulator of
lifespan, aging, and cellular senescence: A mini-review.
Gerontology. 64:127–134. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shen B, Wang Y, Cheng J, Peng Y, Zhang Q,
Li Z, Zhao L, Deng X and Feng H: Pterostilbene alleviated NAFLD via
AMPK/mTOR signaling pathways and autophagy by promoting Nrf2.
Phytomedicine. 109:1545612023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chung KW, Lee EK, Lee MK, Oh GT, Yu BP and
Chung HY: Impairment of PPARα and the fatty Acid oxidation pathway
aggravates renal fibrosis during aging. J Am Soc Nephrol.
29:1223–1237. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chin C, Ravichandran R, Sanborn K, Fleming
T, Wheatcroft SB, Kearney MT, Tokman S, Walia R, Smith MA, Flint
DJ, et al: Loss of IGFBP2 mediates alveolar type 2 cell senescence
and promotes lung fibrosis. Cell Rep Med. 4:1009452023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|