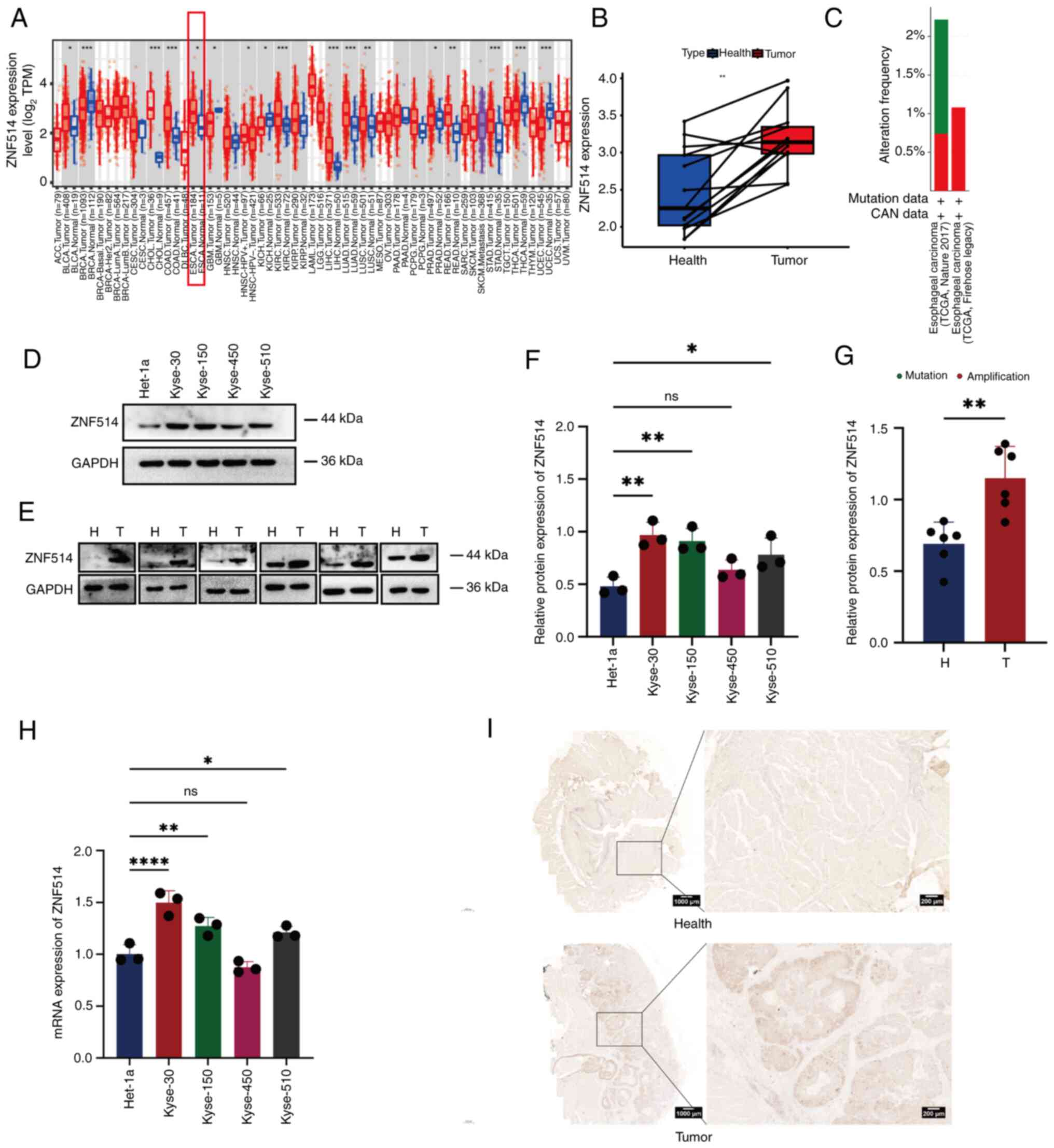
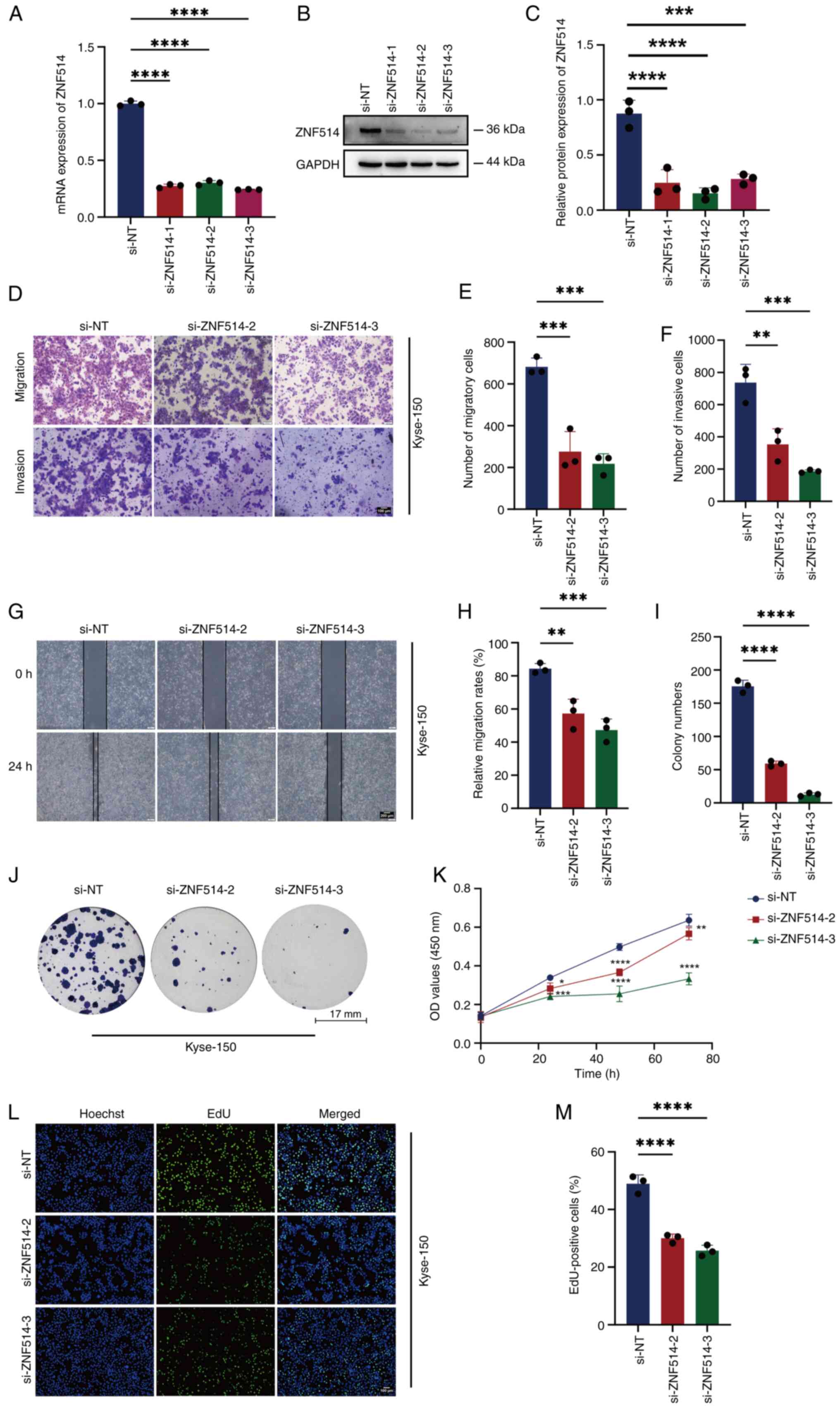
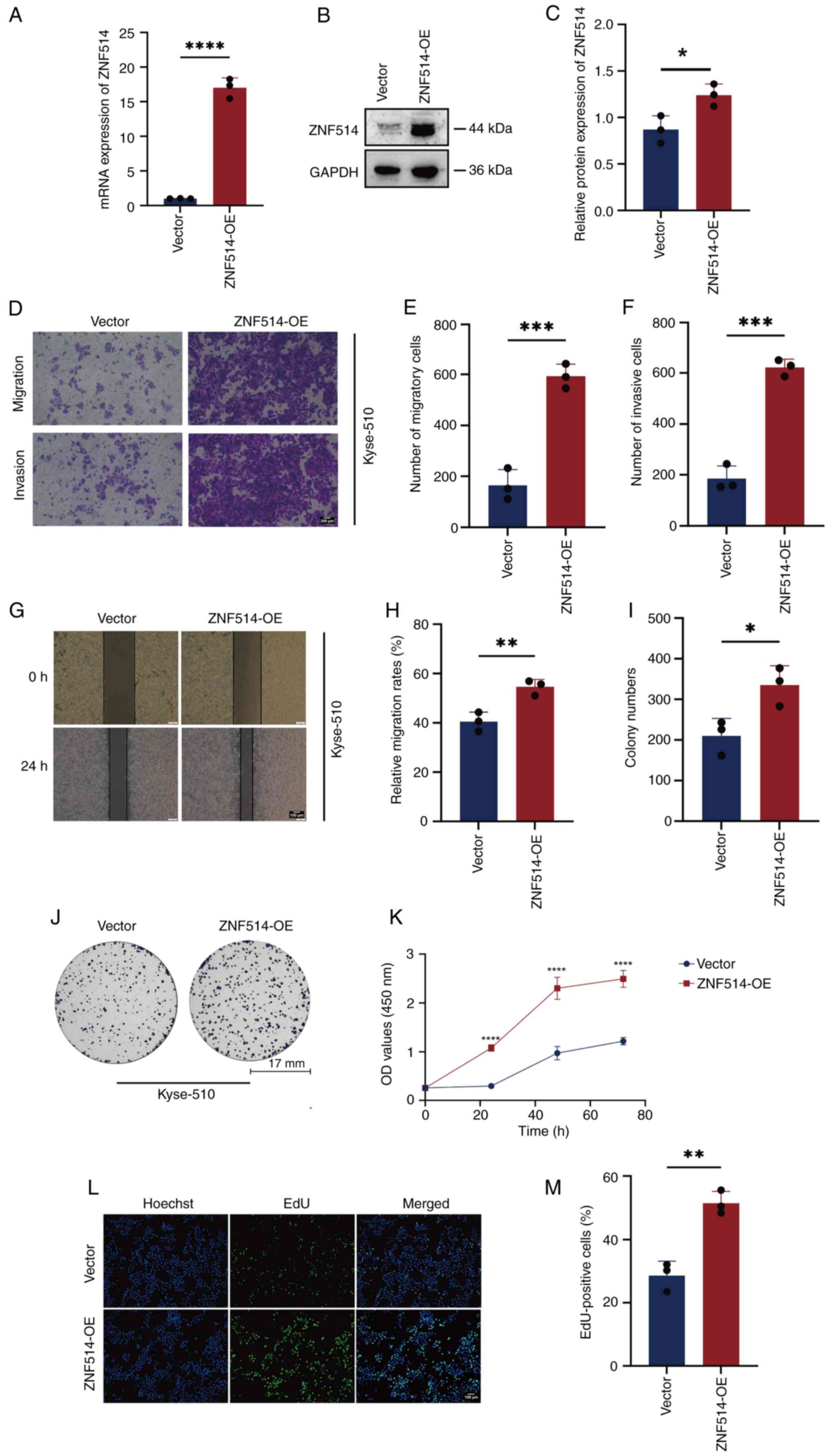
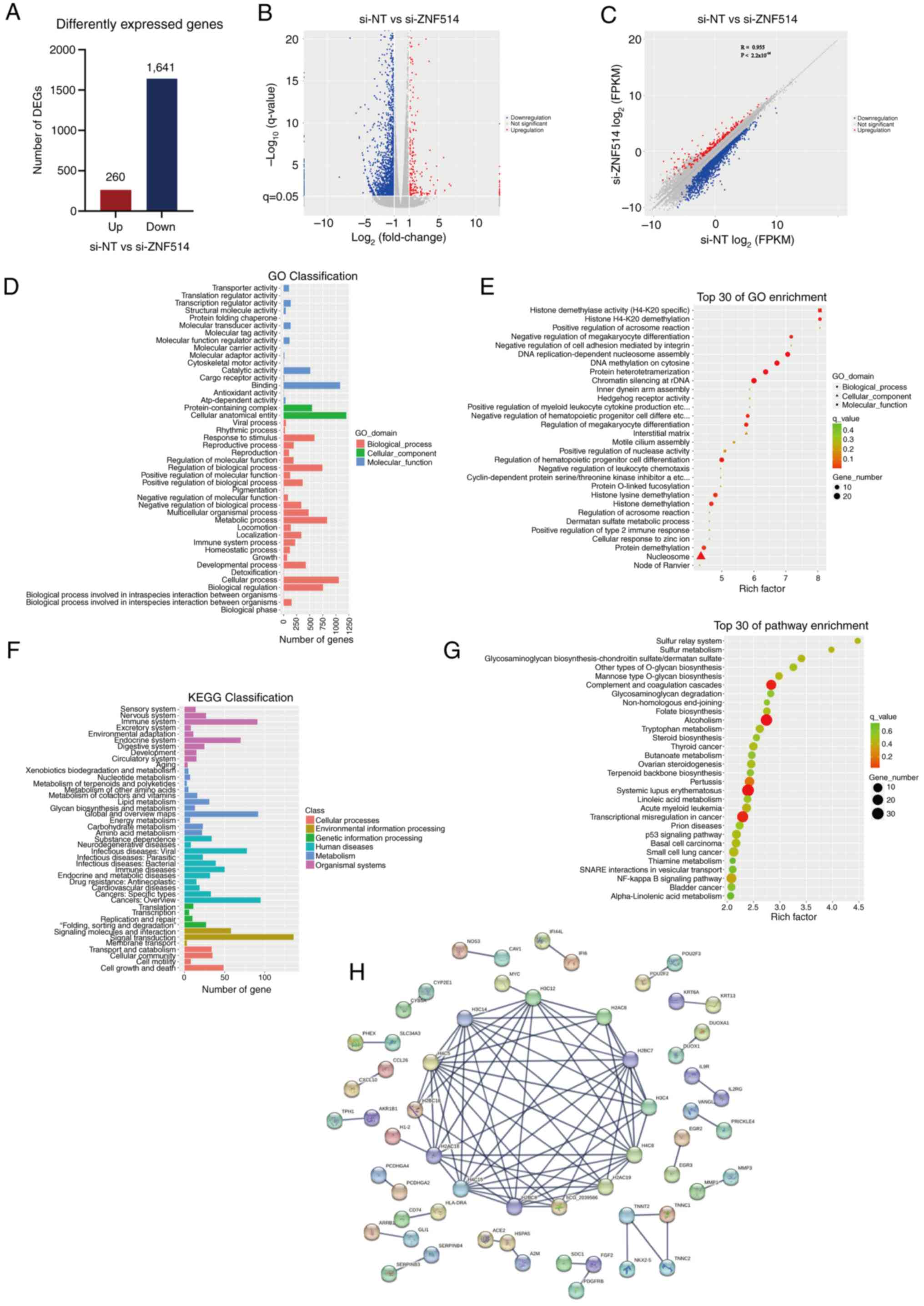
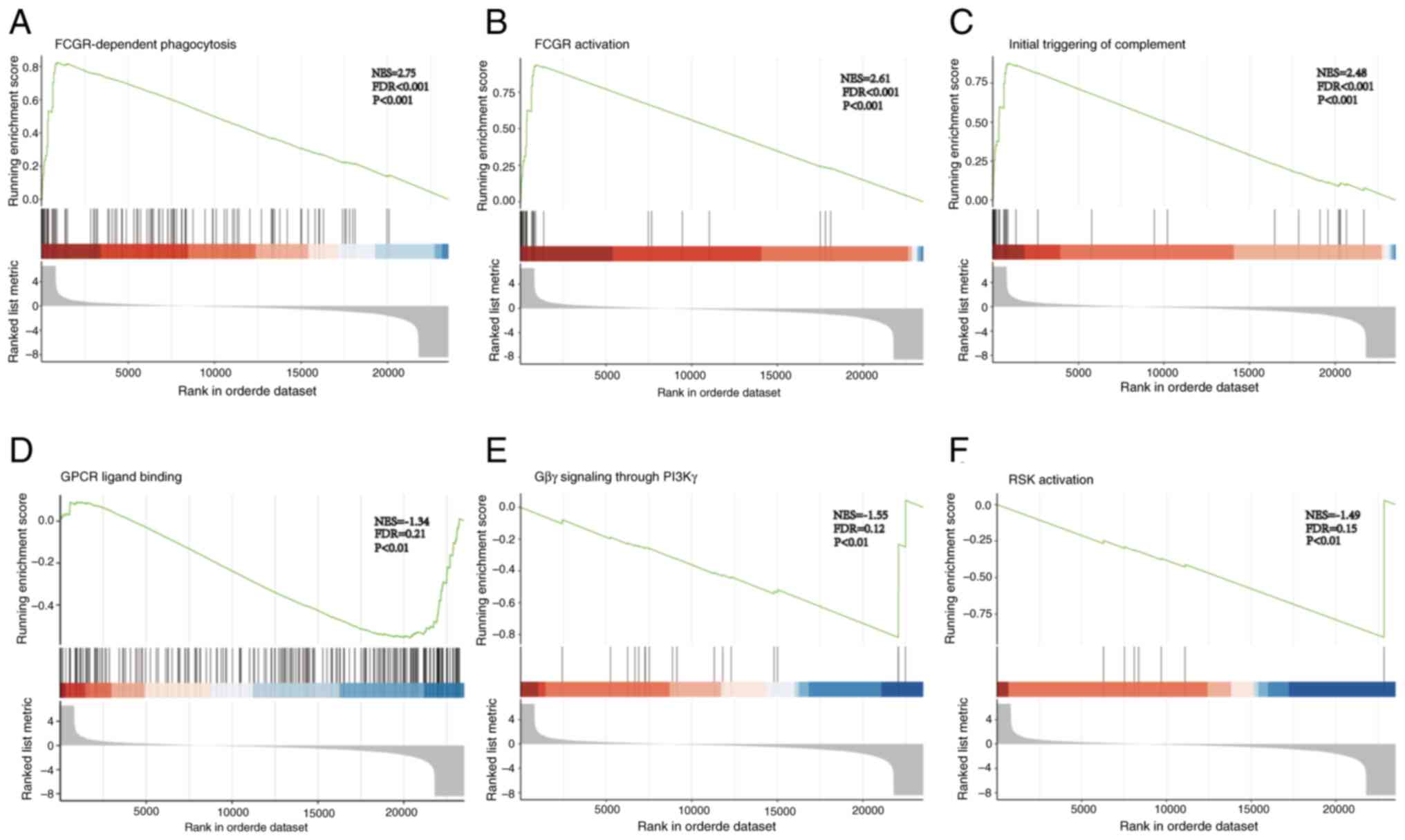
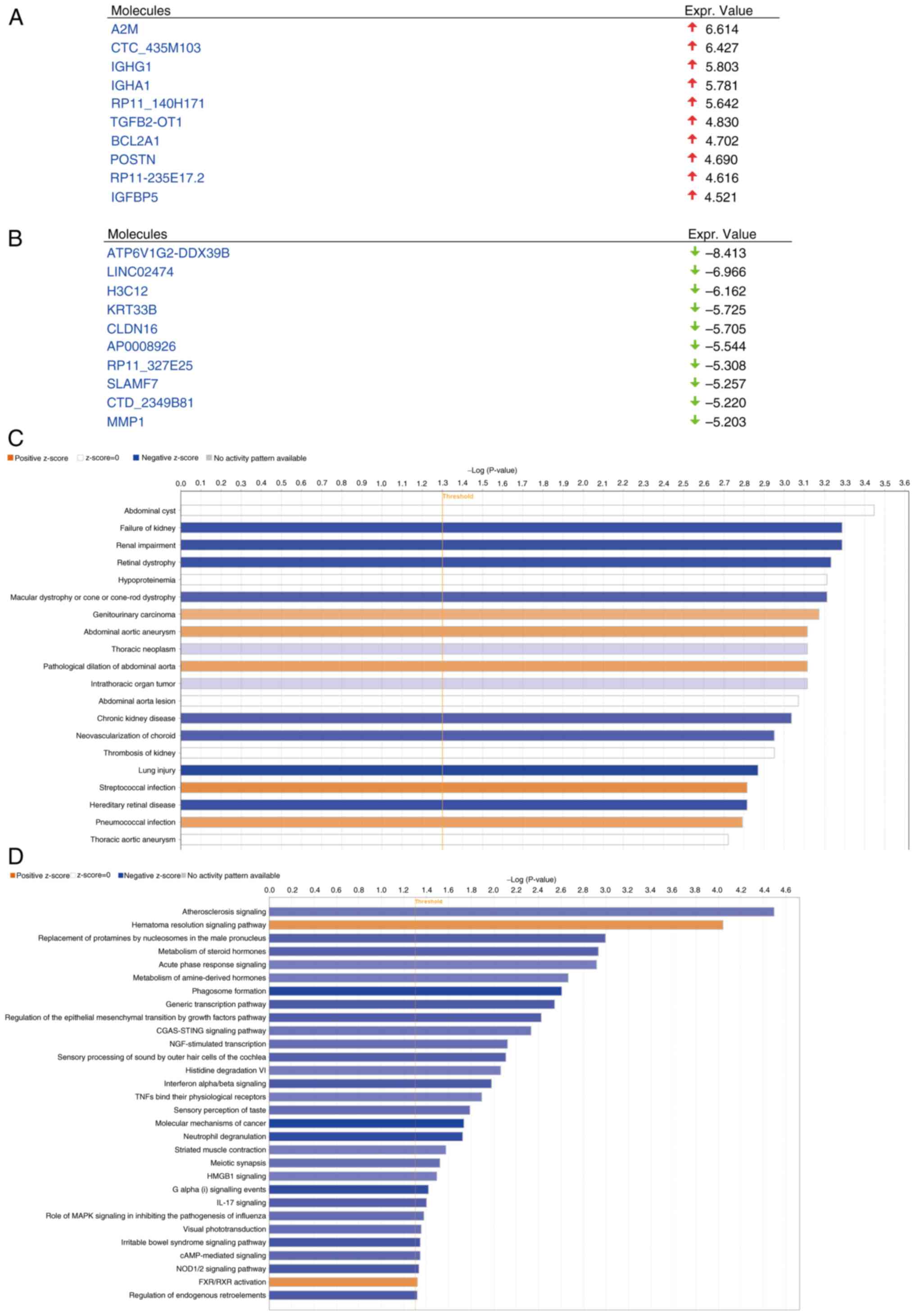
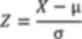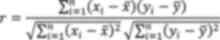|
1
|
Deboever N, Jones CM, Yamashita K, Ajani
JA and Hofstetter WL: Advances in diagnosis and management of
cancer of the esophagus. BMJ. 385:e0749622024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Smyth EC, Lagergren J, Fitzgerald RC,
Lordick F, Shah MA, Lagergren P and Cunningham D: Oesophageal
cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 3:170482017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Huang FL and Yu SJ: Esophageal cancer:
Risk factors, genetic association, and treatment. Asian J Surg.
41:210–215. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lin L and Lin DC: Biological significance
of tumor heterogeneity in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Cancers (Basel). 11:11562019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jen J and Wang YC: Zinc finger proteins in
cancer progression. J Biomed Sci. 23:532016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hong K, Yang Q, Yin H, Wei N, Wang W and
Yu B: Comprehensive analysis of ZNF family genes in prognosis,
immunity, and treatment of esophageal cancer. BMC Cancer.
23:3012023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jen J, Lin LL, Lo FY, Chen HT, Liao SY,
Tang YA, Su WC, Salgia R, Hsu CL, Huang HC, et al: Oncoprotein
ZNF322A transcriptionally deregulates alpha-adducin, cyclin D1 and
p53 to promote tumor growth and metastasis in lung cancer.
Oncogene. 36:52192017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yao J, Qian K, Chen C, Liu X, Yu D, Yan X,
Liu T and Li S: Correction for: ZNF139/circZNF139 promotes
cell proliferation, migration and invasion via activation of
PI3K/AKT pathway in bladder cancer. Aging (Albany NY).
14:4927–4928. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Y, Gong Y, Li X, Long W, Zhang J, Wu
J and Dong Y: Targeting the ZNF-148/miR-335/SOD2 signaling cascade
triggers oxidative stress-mediated pyroptosis and suppresses breast
cancer progression. Cancer Med. 12:21308–21320. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network;
Analysis Working Group; Asan University; BC Cancer Agency; Brigham
and Women's Hospital; Broad Institute; Brown University; Case
Western Reserve University; Dana-Farber Cancer Institute; Duke
University; Greater Poland Cancer Centre, et al, . Integrated
genomic characterization of oesophageal carcinoma. Nature.
541:169–175. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ and Smyth GK:
edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis
of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 26:139–140. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Korthauer K, Kimes PK, Duvallet C, Reyes
A, Subramanian A, Teng M, Shukla C, Alm EJ and Hicks SC: A
practical guide to methods controlling false discoveries in
computational biology. Genome Biol. 20:1182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ye Q, Liu J and Xie K: Zinc finger
proteins and regulation of the hallmarks of cancer. Histol
Histopathol. 34:1097–1109. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang J, Chitsaz F, Derbyshire MK, Gonzales
NR, Gwadz M, Lu S, Marchler GH, Song JS, Thanki N, Yamashita RA, et
al: The conserved domain database in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res.
51:D384–D388. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lu S, Wang J, Chitsaz F, Derbyshire MK,
Geer RC, Gonzales NR, Gwadz M, Hurwitz DI, Marchler GH, Song JS, et
al: CDD/SPARCLE: The conserved domain database in 2020. Nucleic
Acids Res. 48:D265–D268. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Marchler-Bauer A, Bo Y, Han L, He J,
Lanczycki CJ, Lu S, Chitsaz F, Derbyshire MK, Geer RC, Gonzales NR,
et al: CDD/SPARCLE: Functional classification of proteins via
subfamily domain architectures. Nucleic Acids Res. 45:D200–D203.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lehmann W, Mossmann D, Kleemann J, Mock K,
Meisinger C, Brummer T, Herr R, Brabletz S, Stemmler MP and
Brabletz T: ZEB1 turns into a transcriptional activator by
interacting with YAP1 in aggressive cancer types. Nat Commun.
7:104982016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Qin X, Zhou K, Dong L, Yang L, Li W, Chen
Z, Shen C, Han L, Li Y, Chan AKN, et al: CRISPR screening reveals
ZNF217 as a vulnerability in high-risk B-cell acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. Theranostics. 15:3234–3256. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Enesa K and Evans P: The biology of
A20-like molecules. Adv Exp Med Biol. 809:33–48. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee JH, Jung SM, Yang KM, Bae E, Ahn SG,
Park JS, Seo D, Kim M, Ha J, Lee J, et al: A20 promotes metastasis
of aggressive basal-like breast cancers through
multi-monoubiquitylation of Snail1. Nat Cell Biol. 19:1260–1273.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li J, Zhou Q, Zhang C, Zhu H, Yao J and
Zhang M: Development and validation of novel prognostic models for
zinc finger proteins-related genes in soft tissue sarcoma. Aging
(Albany NY). 15:3171–3190. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu P, Lin Y, Dai F, Wang H, Wen H, Xu Z,
Sun G and Lyu Z: Pan-cancer analysis and experimental validation
revealed the prognostic role of ZNF83 in renal and lung cancer
cohorts. Discov Oncol. 16:13352025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kou H, Jiang S, Wu X, Jing C, Xu X, Wang
J, Zhang C, Liu W, Gao Y, Men Q, et al: ZNF655 involved in the
progression of multiple myeloma via the activation of AKT. Cell
Biol Int. 49:177–187. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gan SY, Tye GJ, Chew AL and Lai NS:
Current development of Fc gamma receptors (FcγRs) in diagnostics: A
review. Mol Biol Rep. 51:9372024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rajasekaran N, Chester C, Yonezawa A, Zhao
X and Kohrt HE: Enhancement of antibody-dependent cell mediated
cytotoxicity: A new era in cancer treatment. Immunotargets Ther.
4:91–100. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Omori T, Machida T, Ishida Y, Sekiryu T
and Sekine H: Roles of MASP-1 and MASP-3 in the development of
retinal degeneration in a murine model of dry age-related macular
degeneration. Front Immunol. 16:15660182025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Roumenina LT, Daugan MV, Petitprez F,
Sautès-Fridman C and Fridman WH: Context-dependent roles of
complement in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 19:698–715. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Merle NS and Roumenina LT: The complement
system as a target in cancer immunotherapy. Eur J Immunol.
54:e23508202024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wess J: Designer GPCRs as novel tools to
identify metabolically important signaling pathways. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 12:7069572021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Inverso D, Tacconi C, Ranucci S and De
Giovanni M: The power of many: Multilevel targeting of
representative chemokine and metabolite GPCRs in personalized
cancer therapy. Eur J Immunol. 54:e23508702024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen CL, Syahirah R, Ravala SK, Yen YC,
Klose T, Deng Q and Tesmer JJG: Molecular basis for Gβγ-mediated
activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase γ. Nat Struct Mol Biol.
31:1198–1207. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Romeo Y and Roux PP: Paving the way for
targeting RSK in cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 15:5–9. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chatterjee P, Ghosh D, Chowdhury SR and
Roy SS: ETS1 drives EGF-induced glycolytic shift and metastasis of
epithelial ovarian cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res.
1871:1198052024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nussinov R, Yavuz BR and Jang H: Molecular
principles underlying aggressive cancers. Signal Transduct Target
Ther. 10:422025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Du R, Shen W, Liu Y, Gao W, Zhou W, Li J,
Zhao S, Chen C, Chen Y, Liu Y, et al: TGIF2 promotes the
progression of lung adenocarcinoma by bridging EGFR/RAS/ERK
signaling to cancer cell stemness. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
4:602019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Asghar J, Latif L, Alexander SPH and
Kendall DA: Development of a novel cell-based, In-Cell Western/ERK
assay system for the high-throughput screening of agonists acting
on the delta-opioid receptor. Front Pharmacol. 13:9333562022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Caunt CJ, Sale MJ, Smith PD and Cook SJ:
MEK1 and MEK2 inhibitors and cancer therapy: The long and winding
road. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:577–592. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tian T, Li X and Zhang J: mTOR signaling
in cancer and mTOR inhibitors in solid tumor targeting therapy. Int
J Mol Sci. 20:7552019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mangé A, Coyaud E, Desmetz C, Laurent E,
Béganton B, Coopman P, Raught B and Solassol J: FKBP4 connects
mTORC2 and PI3K to activate the PDK1/Akt-dependent cell
proliferation signaling in breast cancer. Theranostics.
9:7003–7015. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Al-Bari MAA and Xu P: Molecular regulation
of autophagy machinery by mTOR-dependent and -independent pathways.
Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1467:3–20. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Nowosad A, Jeannot P, Callot C, Creff J,
Perchey RT, Joffre C, Codogno P, Manenti S and Besson A: Publisher
correction: p27 controls ragulator and mTOR activity in amino
acid-deprived cells to regulate the autophagy-lysosomal pathway and
coordinate cell cycle and cell growth. Nat Cell Biol. 23:10482021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
He K, Zheng X, Li M, Zhang L and Yu J:
mTOR inhibitors induce apoptosis in colon cancer cells via
CHOP-dependent DR5 induction on 4E-BP1 dephosphorylation. Oncogene.
35:148–157. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Karar J and Maity A: PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway
in angiogenesis. Front Mol Neurosci. 4:512011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kim K, Kim IK, Yang JM, Lee E, Koh BI,
Song S, Park J, Lee S, Choi C, Kim JW, et al: SoxF transcription
factors are positive feedback regulators of VEGF signaling. Circ
Res. 119:839–852. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Herrerias MM and Budinger GRS: Revisiting
mTOR and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Am J Respir Cell Mol
Biol. 62:669–670. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Karimi Roshan M, Soltani A, Soleimani A,
Rezaie Kahkhaie K, Afshari AR and Soukhtanloo M: Role of AKT and
mTOR signaling pathways in the induction of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition (EMT) process. Biochimie. 165:229–234. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Tian F, Yang X, Liu Y, Yuan X, Fan T,
Zhang F, Zhao J, Lu J, Jiang Y, Dong Z and Yang Y: Constitutive
activated STAT3 is an essential regulator and therapeutic target in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 8:88719–88729.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
D'Amico S, Shi J, Martin BL, Crawford HC,
Petrenko O and Reich NC: STAT3 is a master regulator of epithelial
identity and KRAS-driven tumorigenesis. Genes Dev. 32:1175–1187.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Andersson EI, Brück O, Braun T, Mannisto
S, Saikko L, Lagström S, Ellonen P, Leppä S, Herling M, Kovanen PE
and Mustjoki S: STAT3 mutation is associated with STAT3
activation in CD30+ ALK− ALCL. Cancers
(Basel). 12:7022020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Groner B and von Manstein V: Jak Stat
signaling and cancer: Opportunities, benefits and side effects of
targeted inhibition. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 451:1–14. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Sadrkhanloo M, Entezari M, Orouei S,
Ghollasi M, Fathi N, Rezaei S, Hejazi ES, Kakavand A, Saebfar H,
Hashemi M, et al: STAT3-EMT axis in tumors: Modulation of cancer
metastasis, stemness and therapy response. Pharmacol Res.
182:1063112022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Moreno L and Gatheral T: Therapeutic
targeting of NOD1 receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 170:475–485. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhang W and Wang Y: Activation of
RIPK2-mediated NOD1 signaling promotes proliferation and invasion
of ovarian cancer cells via NF-κB pathway. Histochem Cell Biol.
157:173–182. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Taniguchi K and Karin M: NF-κB,
inflammation, immunity and cancer: Coming of age. Nat Rev Immunol.
18:309–324. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|