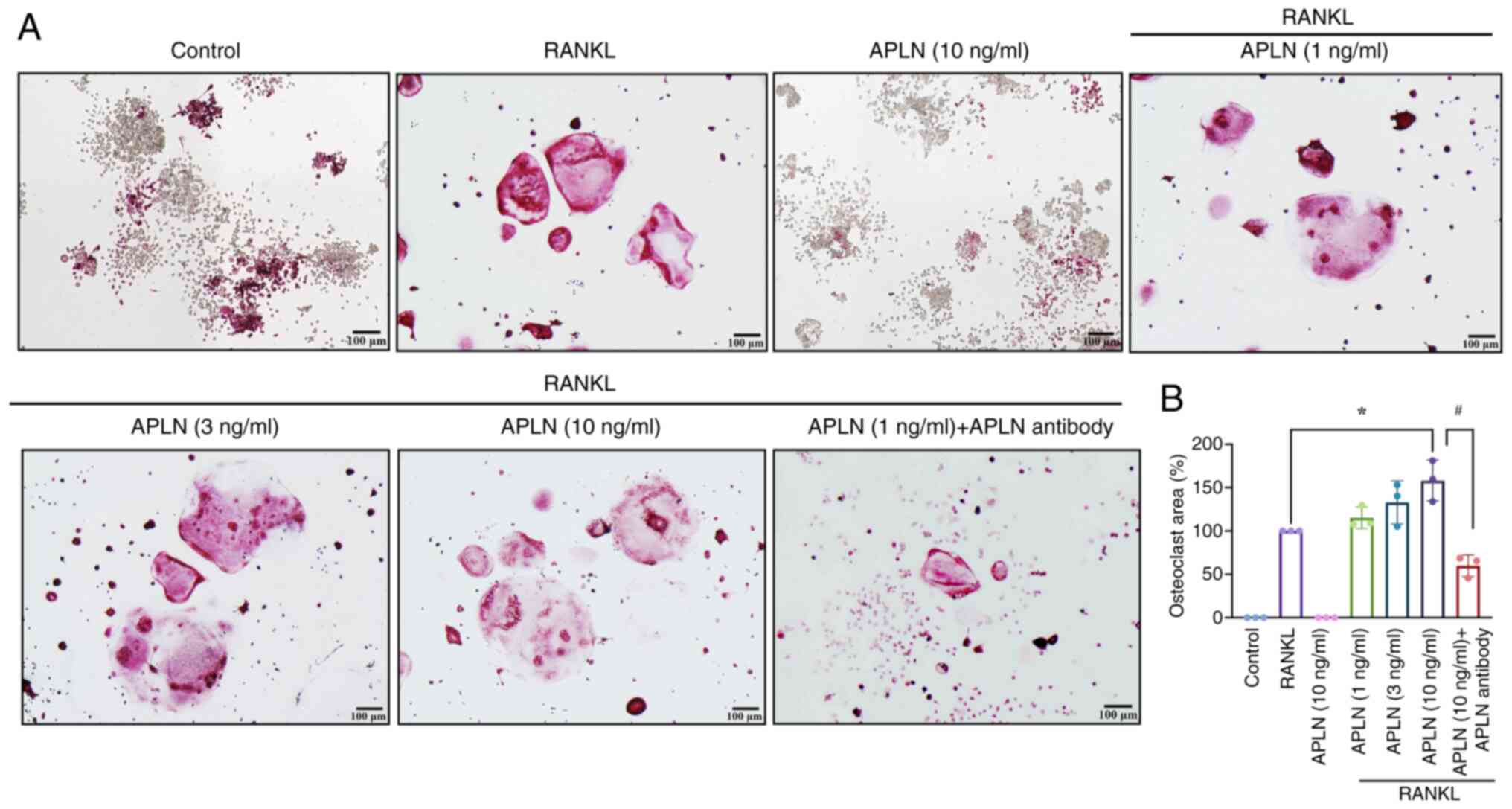
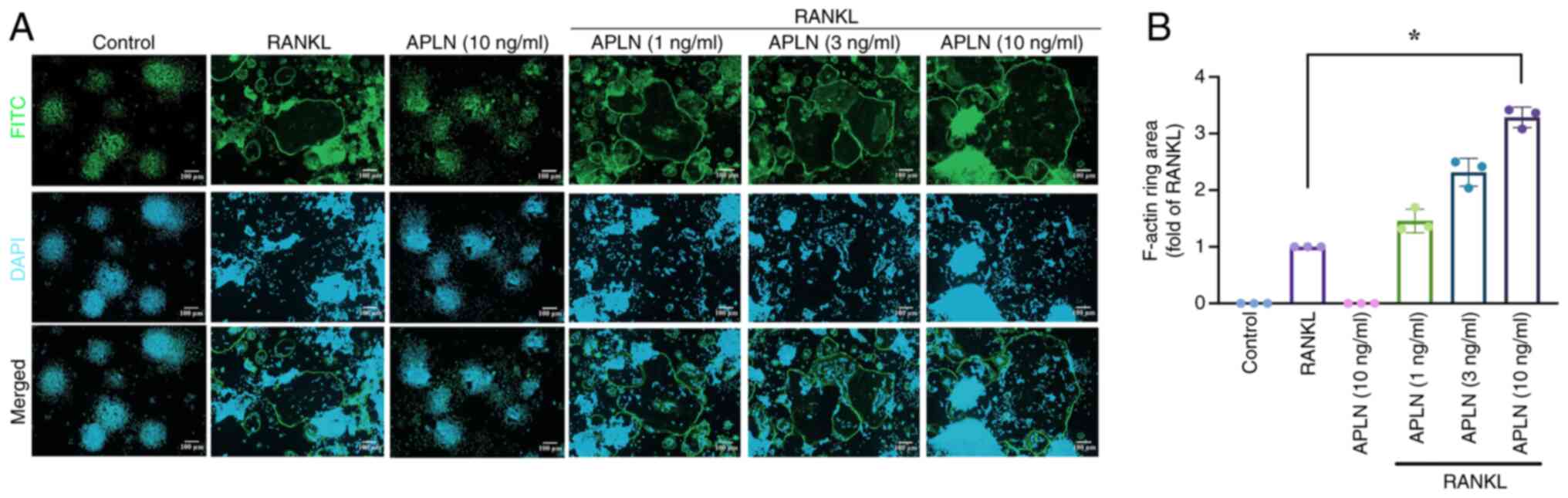
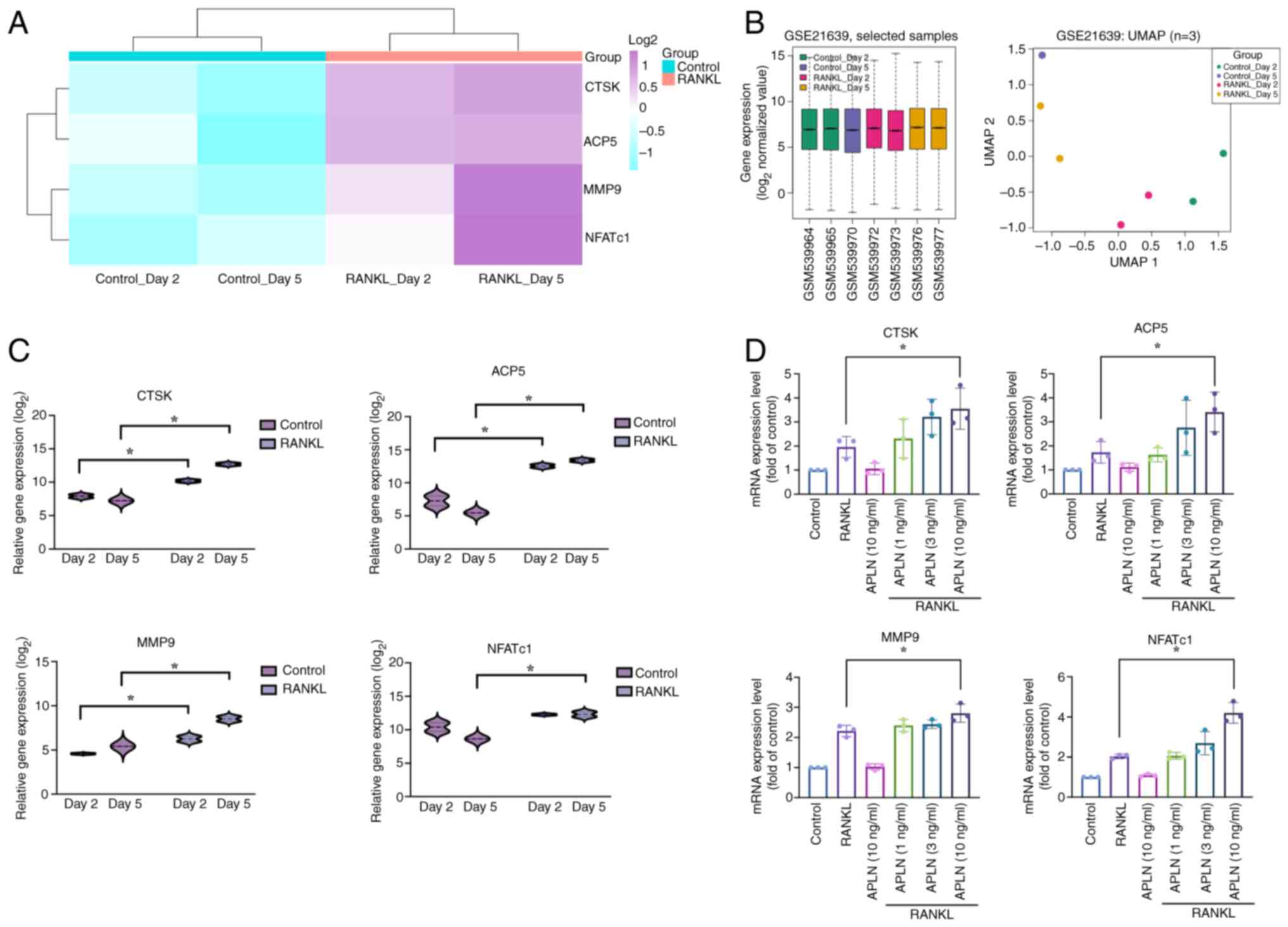
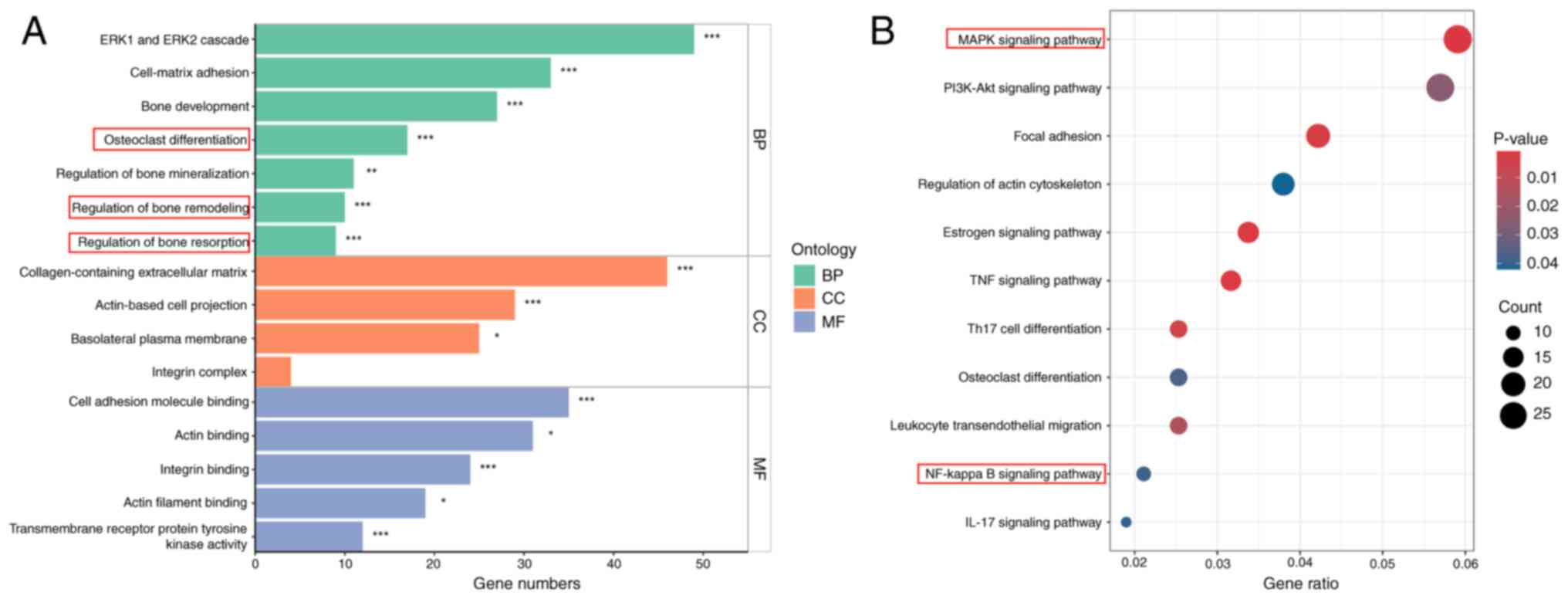
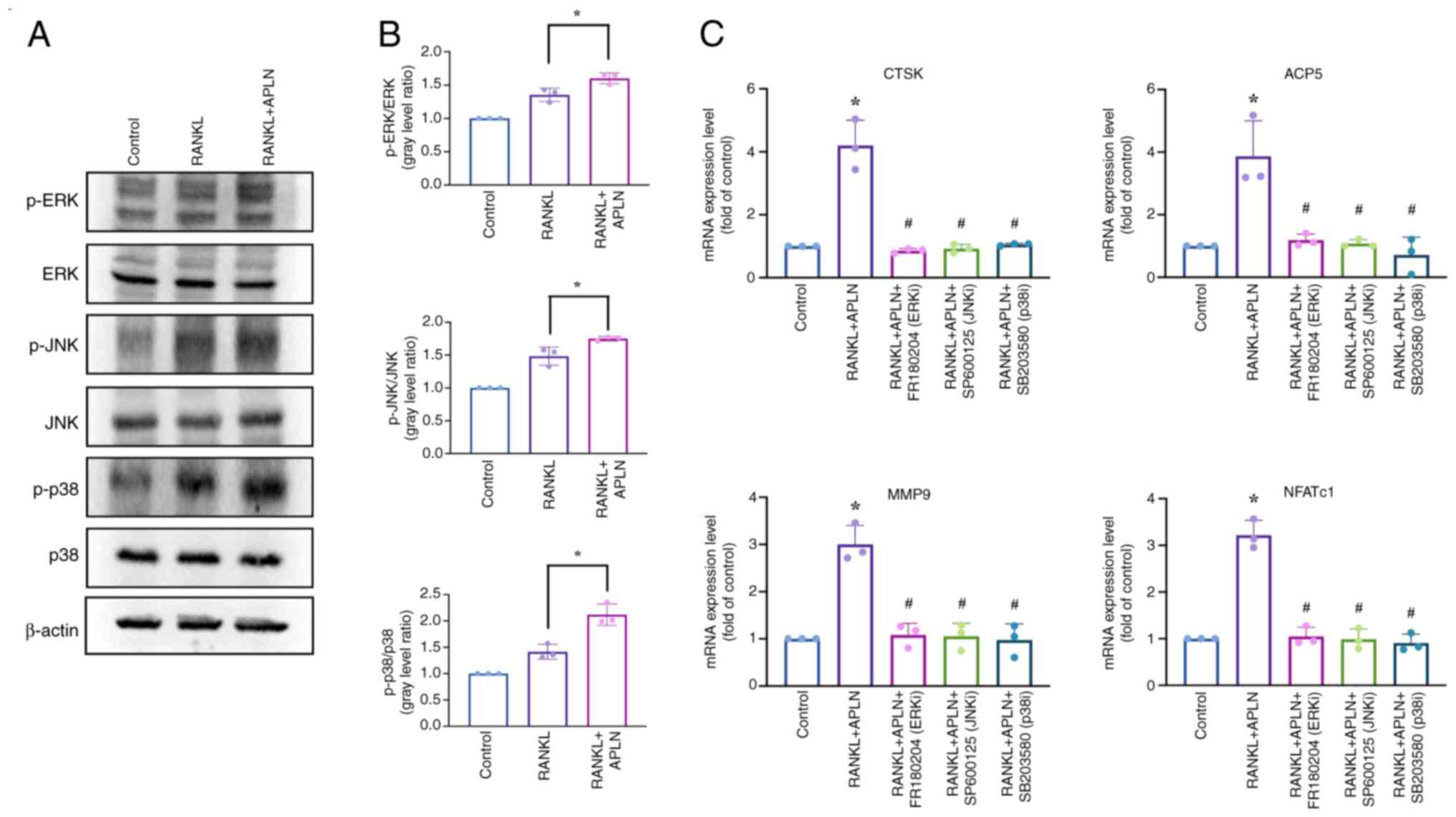
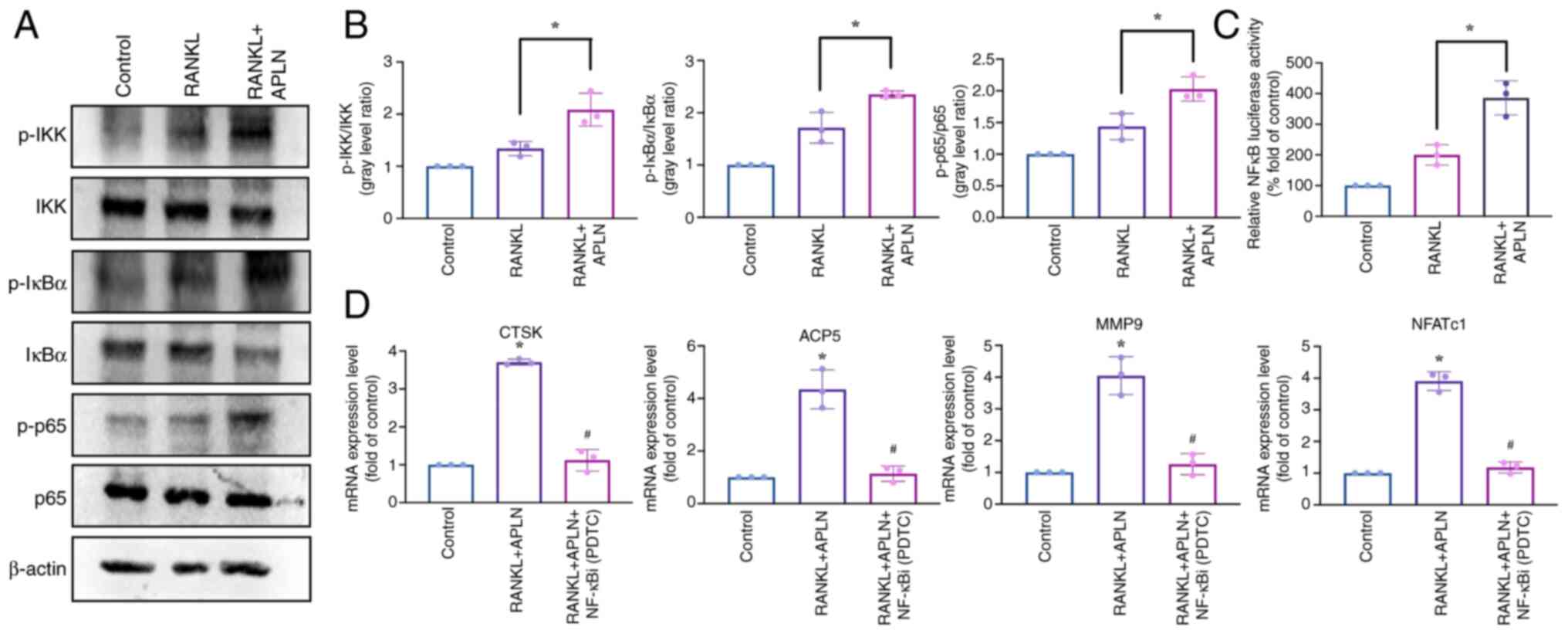
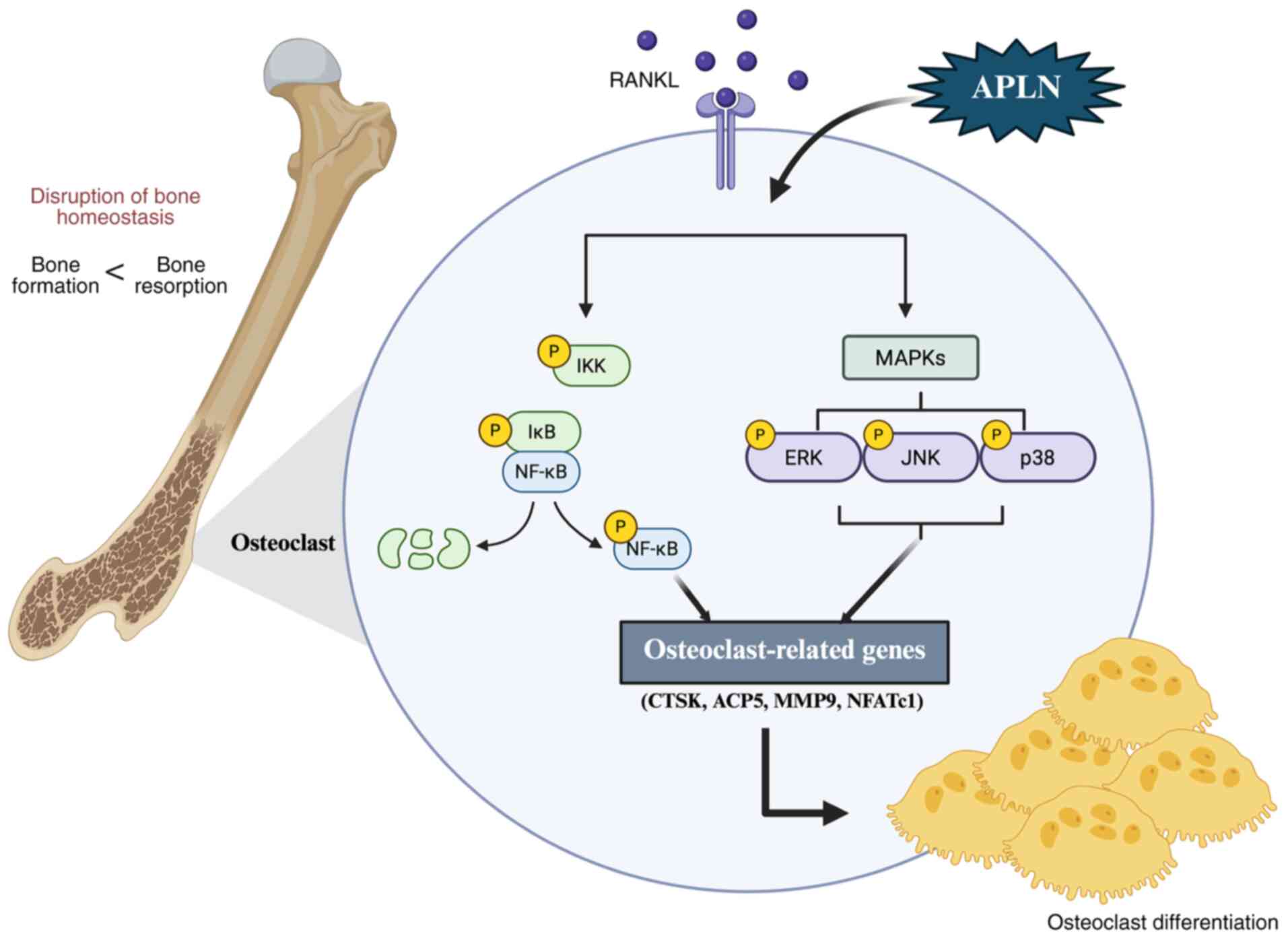
|
1
|
Bolamperti S, Villa I and Rubinacci A:
Bone remodeling: An operational process ensuring survival and bone
mechanical competence. Bone Res. 10:482022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhu L, Zhou C, Chen S, Huang D, Jiang Y,
Lan Y, Zou S and Li Y: Osteoporosis and alveolar bone health in
periodontitis niche: A predisposing factors-centered review. Cells.
11:33802022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ashai S and Harvey NC: Rheumatoid
arthritis and bone health. Clin Med (Lond). 20:565–567. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Park JJ and Wong C: Pharmacological
prevention and management of skeletal-related events and bone loss
in individuals with cancer. Semin Oncol Nurs. 38:1512762022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Salari N, Ghasemi H, Mohammadi L, Behzadi
MH, Rabieenia E, Shohaimi S and Mohammadi M: The global prevalence
of osteoporosis in the world: A comprehensive systematic review and
meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 16:6092021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Elahmer NR, Wong SK, Mohamed N, Alias E,
Chin KY and Muhammad N: Mechanistic insights and therapeutic
strategies in osteoporosis: A comprehensive review. Biomedicines.
12:16352024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ayers C, Kansagara D, Lazur B, Fu R, Kwon
A and Harrod C: Effectiveness and safety of treatments to prevent
fractures in people with low bone mass or primary osteoporosis: A
living systematic review and network meta-analysis for the American
College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 176:182–195. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Weivoda MM and Bradley EW: Macrophages and
bone remodeling. J Bone Miner Res. 38:359–369. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Campbell MJ, Bustamante-Gomez C, Fu Q,
Beenken KE, Reyes-Pardo H, Smeltzer MS and O'Brien CA:
RANKL-mediated osteoclast formation is required for bone loss in a
murine model of Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis. Bone.
187:1171812024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Park JH, Lee NK and Lee SY: Current
understanding of RANK signaling in osteoclast differentiation and
maturation. Mol Cells. 40:706–713. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yan J, Wang A, Cao J and Chen L:
Apelin/APJ system: An emerging therapeutic target for respiratory
diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci. 77:2919–2930. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang YH, Kuo SJ, Liu SC, Wang SW, Tsai CH,
Fong YC and Tang CH: Apelin affects the progression of
osteoarthritis by regulating VEGF-dependent angiogenesis and
miR-150-5p expression in human synovial fibroblasts. Cells.
9:5942020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hu G, Wang Z, Zhang R, Sun W and Chen X:
The role of apelin/apelin receptor in energy metabolism and water
homeostasis: A comprehensive narrative review. Front Physiol.
12:6328862021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chapman FA, Melville V, Godden E, Morrison
B, Bruce L, Maguire JJ, Davenport AP, Newby DE and Dhaun N:
Cardiovascular and renal effects of apelin in chronic kidney
disease: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover
study. Nat Commun. 15:83872024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wysocka MB, Pietraszek-Gremplewicz K and
Nowak D: The role of apelin in cardiovascular diseases, obesity and
cancer. Front Physiol. 9:5572018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chang TK, Wang YH, Kuo SJ, Wang SW, Tsai
CH, Fong YC, Wu NL, Liu SC and Tang CH: Apelin enhances IL-1beta
expression in human synovial fibroblasts by inhibiting miR-144-3p
through the PI3K and ERK pathways. Aging (Albany NY). 12:9224–9239.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ducy P, Amling M, Takeda S, Priemel M,
Schilling AF, Beil FT, Shen J, Vinson C, Rueger JM and Karsenty G:
Leptin inhibits bone formation through a hypothalamic relay: A
central control of bone mass. Cell. 100:197–207. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tu Q, Zhang J, Dong LQ, Saunders E, Luo E,
Tang J and Chen J: Adiponectin inhibits osteoclastogenesis and bone
resorption via APPL1-mediated suppression of Akt1. J Biol Chem.
286:12542–12553. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wattanachanya L, Lu WD, Kundu RK, Wang L,
Abbott MJ, O'Carroll D, Quertermous T and Nissenson RA: Increased
bone mass in mice lacking the adipokine apelin. Endocrinology.
154:2069–2080. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Izgut-Uysal VN, Gemici B, Birsen I, Acar N
and Ustunel I: The effect of apelin on the functions of peritoneal
macrophages. Physiol Res. 66:489–496. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sharma P, Patntirapong S, Hann S and
Hauschka PV: RANKL-RANK signaling regulates expression of
xenotropic and polytropic virus receptor (XPR1) in osteoclasts.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 399:129–132. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Love MI, Huber W and Anders S: Moderated
estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with
DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15:5502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang
J, Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for annotation,
visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 4:P32003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lampiasi N, Russo R, Kireev I, Strelkova
O, Zhironkina O and Zito F: Osteoclasts differentiation from murine
RAW 264.7 cells stimulated by RANKL: Timing and behavior. Biology
(Basel). 10:1172021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sun W, Li Y, Li J, Tan Y, Yuan X, Meng H,
Ye J, Zhong G, Jin X, Liu Z, et al: Mechanical stimulation controls
osteoclast function through the regulation of Ca(2+)-activated
Cl(−) channel Anoctamin 1. Commun Biol. 6:4072023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Greco EA, Lenzi A and Migliaccio S: The
obesity of bone. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 6:273–286. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Armutcu F, McCloskey E and Ince M: Obesity
significantly modifies signaling pathways associated with bone
remodeling and metabolism. J Cell Signal. 5:183–194. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yang WH, Tsai CH, Fong YC, Huang YL, Wang
SJ, Chang YS and Tang CH: Leptin induces oncostatin M production in
osteoblasts by downregulating miR-93 through the Akt signaling
pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 15:15778–15790. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Park KH, Kim DK, Huh YH, Lee G, Lee SH,
Hong Y, Kim SH, Kook MS, Koh JT, Chun JS, et al: NAMPT enzyme
activity regulates catabolic gene expression in gingival
fibroblasts during periodontitis. Exp Mol Med. 49:e3682017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
de Oliveira AA, Vergara A, Wang X, Vederas
JC and Oudit GY: Apelin pathway in cardiovascular, kidney, and
metabolic diseases: Therapeutic role of apelin analogs and apelin
receptor agonists. Peptides. 147:1706972022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang Q, Wang B, Zhang W, Zhang T, Liu Q,
Jiao X, Ye J, Hao Y, Gao Q, Ma G, et al: APLN promotes the
proliferation, migration, and glycolysis of cervical cancer through
the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys. 755:1099832024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen L, Tao Y and Jiang Y: Apelin
activates the expression of inflammatory cytokines in microglial
BV2 cells via PI-3K/Akt and MEK/Erk pathways. Sci China Life Sci.
58:531–540. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tilotta F, Gosset M, Herrou J, Briot K and
Roux C: Association between osteoporosis and periodontitis. Joint
Bone Spine. 92:1058832025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Llorente I, Garcia-Castaneda N, Valero C,
Gonzalez-Alvaro I and Castaneda S: Osteoporosis in rheumatoid
arthritis: Dangerous liaisons. Front Med (Lausanne). 7:6016182020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sarhan RS, El-Hammady AM, Marei YM, Elwia
SK, Ismail DM and Ahmed EAS: Plasma levels of miR-21b and miR-146a
can discriminate rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis and severity.
Biomedicine (Taipei). 15:30–41. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Takegahara N, Kim H and Choi Y: Unraveling
the intricacies of osteoclast differentiation and maturation:
Insight into novel therapeutic strategies for bone-destructive
diseases. Exp Mol Med. 56:264–272. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lee NK: RANK signaling pathways and key
molecules inducing osteoclast differentiation. Biomed Sci Lett.
23:295–302. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Castan-Laurell I, Dray C and Valet P: The
therapeutic potentials of apelin in obesity-associated diseases.
Mol Cell Endocrinol. 529:1112782021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yasir M, Senthilkumar GP, Jayashree K,
Ramesh Babu K, Vadivelan M and Palanivel C: Association of serum
omentin-1, apelin and chemerin concentrations with the presence and
severity of diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus
patients. Arch Physiol Biochem. 128:313–320. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gao S and Chen H: Therapeutic potential of
apelin and Elabela in cardiovascular disease. Biomed Pharmacother.
166:1152682023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Couvineau P and Llorens-Cortes C:
Metabolically stable apelin analogs: Development and functional
role in water balance and cardiovascular function. Clin Sci (Lond).
139:131–149. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liang B, Burley G, Lin S and Shi YC:
Osteoporosis pathogenesis and treatment: Existing and emerging
avenues. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 27:722022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mbese Z and Aderibigbe BA:
Bisphosphonate-based conjugates and derivatives as potential
therapeutic agents in osteoporosis, bone cancer and metastatic bone
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 22:68692021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hussain MA, Joseph A, Cherian VM,
Srivastava A, Cherian KE, Kapoor N and Paul TV:
Bisphosphonate-induced atypical femoral fracture in tandem:
long-term follow-up is warranted. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case
Rep. 2022:2022:22–0249. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tsourdi E, Zillikens MC, Meier C, Body JJ,
Rodriguez EG, Anastasilakis AD, Abrahamsen B, McCloskey E, Hofbauer
LC, Guañabens N, et al: Fracture risk and management of
discontinuation of denosumab therapy: A systematic review and
position statement by ECTS. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
26:dgaa7562020.
|
|
47
|
Okamoto H, Shibazaki N, Yoshimura T, Uzawa
T and Sugimoto T: Association between elcatonin use and cancer risk
in Japan: A follow-up study after a randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled study of once-weekly elcatonin in primary
postmenopausal osteoporosis. Osteoporos Sarcopenia. 6:15–19. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Vinogradova Y, Coupland C and
Hippisley-Cox J: Use of hormone replacement therapy and risk of
breast cancer: Nested case-control studies using the QResearch and
CPRD databases. BMJ. 371:m38732020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Nordstrom BL, Cai B, De Gregorio F, Ban L,
Fraeman KH, Yoshida Y and Gibbs T: Risk of venous thromboembolism
among women receiving ospemifene: A comparative observational
study. Ther Adv Drug Saf. Nov 19–2022.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|