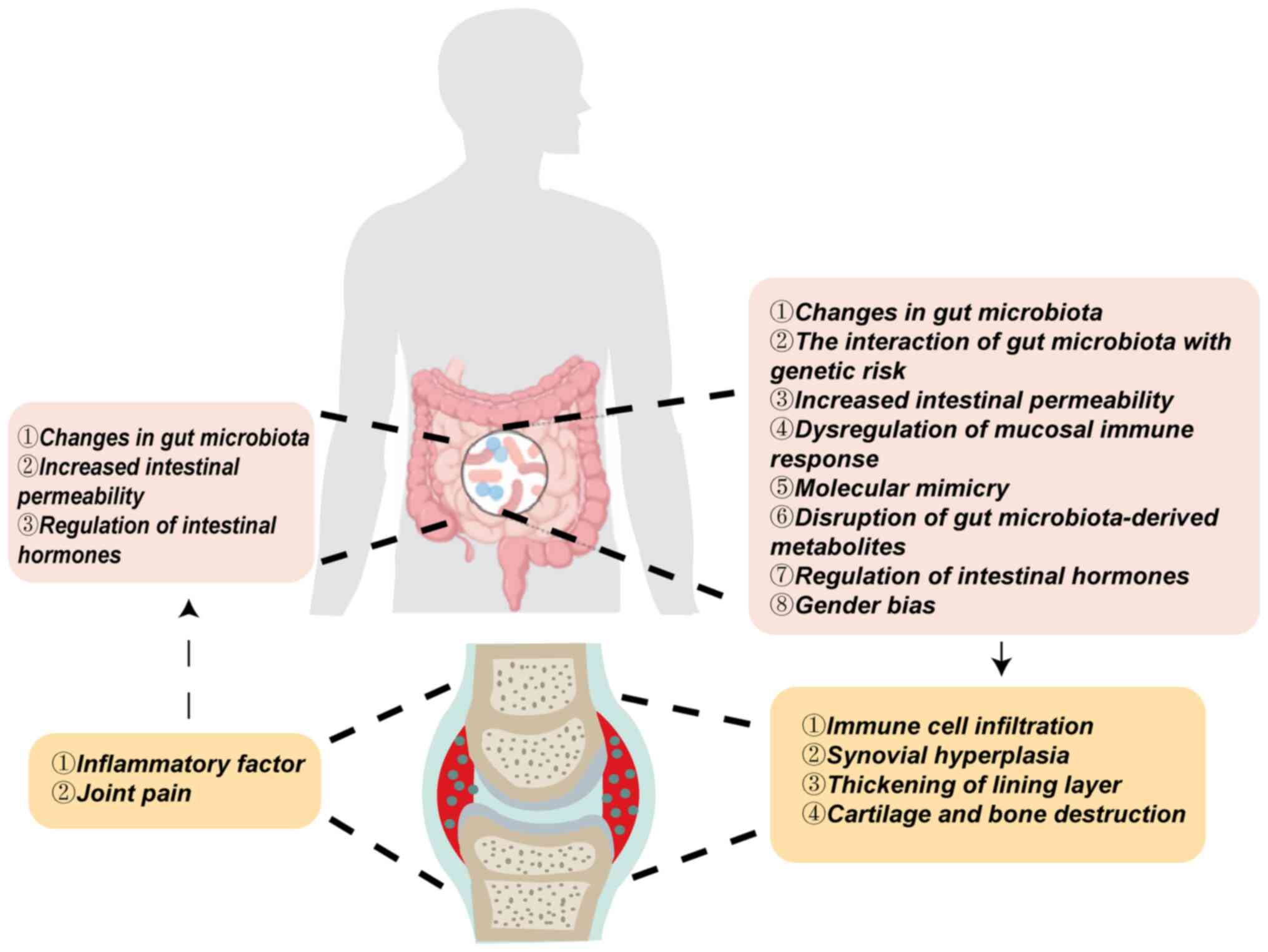
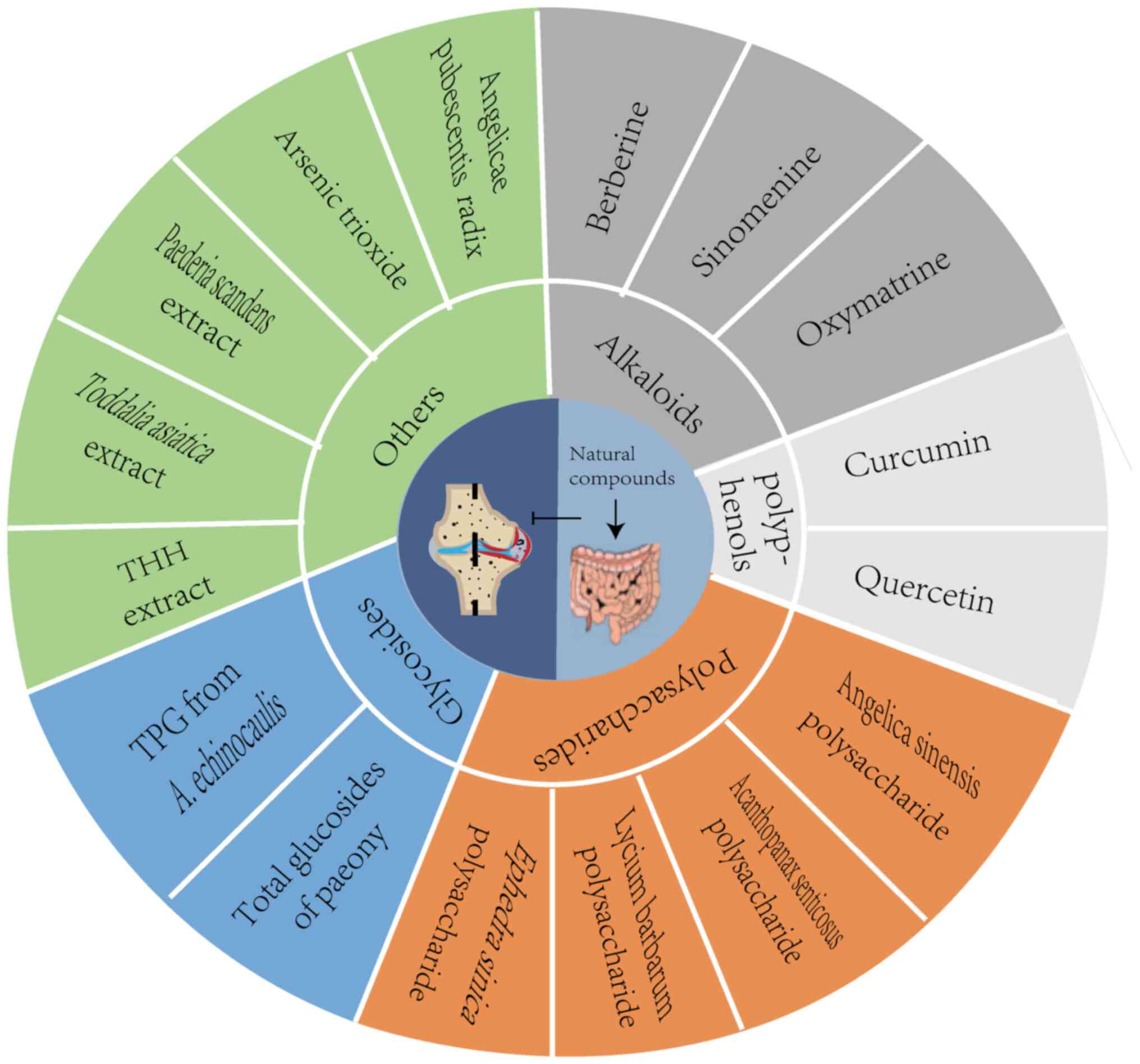
|
1
|
Di Matteo A, Bathon JM and Emery P:
Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 402:2019–2033. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
GBD 2021 Rheumatoid Arthritis
Collaborators, . Global, regional, and national burden of
rheumatoid arthritis, 1990–2020, and projections to 2050: A
systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021.
Lancet Rheumatol. 5:e594–e610. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Aletaha D and Smolen JS: Diagnosis and
management of rheumatoid arthritis: A Review. JAMA. 320:1360–1372.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Brewer RC, Lanz TV, Hale CR, Sepich-Poore
GD, Martino C, Swafford AD, Carroll TS, Kongpachith S, Blum LK,
Elliott SE, et al: Oral mucosal breaks trigger anti-citrullinated
bacterial and human protein antibody responses in rheumatoid
arthritis. Sci Transl Med. 15:eabq84762023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Luo Y, Tong Y, Wu L, Niu H, Li Y, Su LC,
Wu Y, Bozec A, Zaiss MM, Qing P, et al: Alteration of gut
microbiota in individuals at High-Risk for rheumatoid arthritis
associated with disturbed metabolome and the initiation of
arthritis through the triggering of mucosal immunity imbalance.
Arthritis Rheumatol. 75:1736–1748. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
de Jesus VC, Singh M, Schroth RJ,
Chelikani P and Hitchon CA: Association of bitter taste receptor
T2R38 polymorphisms, oral microbiota, and rheumatoid arthritis.
Curr Issues Mol Biol. 43:1460–1472. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
van Delft MAM and Huizinga TWJ: An
overview of autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. J Autoimmun.
110:1023922020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kronzer VL and Sparks JA: Occupational
inhalants, genetics and the respiratory mucosal paradigm for
ACPA-positive rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 82:303–305.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Holers VM, Demoruelle KM, Buckner JH,
James EA, Firestein GS, Robinson WH, Steere AC, Zhang F, Norris JM,
Kuhn KA and Deane KD: Distinct mucosal endotypes as initiators and
drivers of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 20:601–613.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhao T, Wei Y, Zhu Y, Xie Z, Hai Q, Li Z
and Qin D: Gut microbiota and rheumatoid arthritis: From
pathogenesis to novel therapeutic opportunities. Front Immunol.
13:10071652022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jiao Y, Wu L, Huntington ND and Zhang X:
Crosstalk between gut microbiota and innate immunity and its
implication in autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol. 11:2822020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wells PM, Adebayo AS, Bowyer RCE, Freidin
MB, Finckh A, Strowig T, Lesker TR, Alpizar-Rodriguez D, Gilbert B,
Kirkham B, et al: Associations between gut microbiota and genetic
risk for rheumatoid arthritis in the absence of disease: A
cross-sectional study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2:e418–e427. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang X, Zhang D, Jia H, Feng Q, Wang D,
Liang D, Wu X, Li J, Tang L, Li Y, et al: The oral and gut
microbiomes are perturbed in rheumatoid arthritis and partly
normalized after treatment. Nat Med. 21:895–905. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen J, Wright K, Davis JM, Jeraldo P,
Marietta EV, Murray J, Nelson H, Matteson EL and Taneja V: An
expansion of rare lineage intestinal microbes characterizes
rheumatoid arthritis. Genome Med. 8:432016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Inamo J: Non-causal association of gut
microbiome on the risk of rheumatoid arthritis: A Mendelian
randomisation study. Ann Rheum Dis. 80:e1032021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jeong Y, Kim JW, You HJ, Park SJ, Lee J,
Ju JH, Park MS, Jin H, Cho ML, Kwon B, et al: Gut microbial
composition and function are altered in patients with early
rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Med. 8:6932019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cheng M, Zhao Y, Cui Y, Zhong C, Zha Y, Li
S, Cao G, Li M, Zhang L, Ning K and Han J: Stage-specific roles of
microbial dysbiosis and metabolic disorders in rheumatoid
arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 81:1669–1677. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sun H, Guo Y, Wang H, Yin A, Hu J, Yuan T,
Zhou S, Xu W, Wei P, Yin S, et al: Gut commensal Parabacteroides
distasonis alleviates inflammatory arthritis. Gut. 72:1664–1677.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xu X, Zhan G, Chen R, Wang D, Guan S and
Xu H: Gut microbiota and its role in stress-induced hyperalgesia:
Gender-specific responses linked to different changes in serum
metabolites. Pharmacol Res. 177:1061292022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Barton JR, Londregan AK, Alexander TD,
Entezari AA, Covarrubias M and Waldman SA: Enteroendocrine cell
regulation of the gut-brain axis. Front Neurosci. 17:12729552023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fan L, Xia Y, Wang Y, Han D, Liu Y, Li J,
Fu J, Wang L, Gan Z, Liu B, et al: Gut microbiota bridges dietary
nutrients and host immunity. Sci China Life Sci. 66:2466–2514.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen S, Dan L, Xiang L, He Q, Hu D and Gao
Y: The role of gut flora-driven Th cell responses in preclinical
rheumatoid arthritis. J Autoimmun. 154:1034262025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Alpizar-Rodriguez D, Lesker TR, Gronow A,
Gilbert B, Raemy E, Lamacchia C, Gabay C, Finckh A and Strowig T:
Prevotella copri in individuals at risk for rheumatoid
arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 78:590–593. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Scher JU, Sczesnak A, Longman RS, Segata
N, Ubeda C, Bielski C, Rostron T, Cerundolo V, Pamer EG, Abramson
SB, et al: Expansion of intestinal Prevotella copri
correlates with enhanced susceptibility to arthritis. Elife.
2:e012022013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Picchianti-Diamanti A, Panebianco C,
Salemi S, Sorgi ML, Di Rosa R, Tropea A, Sgrulletti M, Salerno G,
Terracciano F, D'Amelio R, et al: Analysis of gut microbiota in
rheumatoid arthritis patients: Disease-related dysbiosis and
modifications induced by etanercept. Int J Mol Sci. 19:29382018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu X, Zeng B, Zhang J, Li W, Mou F, Wang
H, Zou Q, Zhong B, Wu L, Wei H and Fang Y: Role of the gut
microbiome in modulating arthritis progression in mice. Sci Rep.
6:305942016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hu Q, Wu C, Yu J, Luo J and Peng X:
Angelica sinensis polysaccharide improves rheumatoid
arthritis by modifying the expression of intestinal Cldn5, Slit3
and Rgs18 through gut microbiota. Int J Biol Macromol. 209:153–161.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pianta A, Arvikar S, Strle K, Drouin EE,
Wang Q, Costello CE and Steere AC: Evidence of the immune relevance
of Prevotella copri, a gut microbe, in patients with
rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 69:964–975. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pianta A, Chiumento G, Ramsden K, Wang Q,
Strle K, Arvikar S, Costello CE and Steere AC: Identification of
novel, immunogenic HLA-DR-Presented Prevotella copri
peptides in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis
Rheumatol. 73:2200–2205. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhao Y, Chen B, Li S, Yang L, Zhu D, Wang
Y, Wang H, Wang T, Shi B, Gai Z, et al: Detection and
characterization of bacterial nucleic acids in culture-negative
synovial tissue and fluid samples from rheumatoid arthritis or
osteoarthritis patients. Sci Rep. 8:143052018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Peng Y, Huang Y, Li H, Li C, Wu Y, Wang X,
Wang Q, He J and Miao C: Associations between rheumatoid arthritis
and intestinal flora, with special emphasis on RA pathologic
mechanisms to treatment strategies. Microb Pathog. 188:1065632024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu Z, Wu Y, Luo Y, Wei S, Lu C, Zhou Y,
Wang J, Miao T, Lin H, Zhao Y, et al: Self-Balance of intestinal
flora in spouses of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Front Med
(Lausanne). 7:5382020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Padyukov L: Genetics of rheumatoid
arthritis. Semin Immunopathol. 44:47–62. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Saevarsdottir S, Stefansdottir L, Sulem P,
Thorleifsson G, Ferkingstad E, Rutsdottir G, Glintborg B,
Westerlind H, Grondal G, Loft IC, et al: Multiomics analysis of
rheumatoid arthritis yields sequence variants that have large
effects on risk of the seropositive subset. Ann Rheum Dis.
81:1085–1095. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Larid G, Pancarte M, Offer G, Clavel C,
Martin M, Pradel V, Auger I, Lafforgue P, Roudier J, Serre G and
Balandraud N: In rheumatoid arthritis patients, HLA-DRB1*04:01 and
rheumatoid nodules are associated with ACPA to a particular fibrin
epitope. Front Immunol. 12:6920412021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Asquith M, Sternes PR, Costello ME,
Karstens L, Diamond S, Martin TM, Li Z, Marshall MS, Spector TD, le
Cao KA, et al: HLA alleles associated with risk of ankylosing
spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis influence the gut microbiome.
Arthritis Rheumatol. 71:1642–1650. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Paray BA, Albeshr MF, Jan AT and Rather
IA: Leaky gut and autoimmunity: An Intricate balance in individuals
health and the diseased State. Int J Mol Sci. 21:97702020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Marietta EV, Murray JA, Luckey DH, Jeraldo
PR, Lamba A, Patel R, Luthra HS, Mangalam A and Taneja V:
Suppression of inflammatory arthritis by human Gut-derived
prevotella histicola in humanized mice. Arthritis Rheumatol.
68:2878–2888. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tajik N, Frech M, Schulz O, Schälter F,
Lucas S, Azizov V, Dürholz K, Steffen F, Omata Y, Rings A, et al:
Targeting zonulin and intestinal epithelial barrier function to
prevent onset of arthritis. Nat Commun. 11:19952020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Audo R, Sanchez P, Riviere B, Mielle J,
Tan J, Lukas C, Macia L, Morel J and Immediato Daien C: Rheumatoid
arthritis is associated with increased gut permeability and
bacterial translocation which are reversed by inflammation control.
Rheumatology (Oxford). Aug 10–2022.(Epub ahead of print). doi:
10.1093/rheumatology/keac454.
|
|
41
|
Heidt C, Kammerer U, Fobker M, Ruffer A,
Marquardt T and Reuss-Borst M: Assessment of intestinal
permeability and inflammation Bio-markers in patients with
rheumatoid arthritis. Nutrients. 15:23862023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wen J, Lyu P, Stolzer I, Xu J, Gießl A,
Lin Z, Andreev D, Kachler K, Song R, Meng X, et al: Epithelial
HIF2α expression induces intestinal barrier dysfunction and
exacerbation of arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 81:1119–1130. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ruiz-Limón P, Mena-Vázquez N,
Moreno-Indias I, Manrique-Arija S, Lisbona-Montañez JM, Cano-García
L, Tinahones FJ and Fernández-Nebro A: Collinsella is associated
with cumulative inflammatory burden in an established rheumatoid
arthritis cohort. Biomed Pharmacother. 153:1135182022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Schwartz AJ, Das NK, Ramakrishnan SK, Jain
C, Jurkovic MT, Wu J, Nemeth E, Lakhal-Littleton S, Colacino JA and
Shah YM: Hepatic hepcidin/intestinal HIF-2α axis maintains iron
absorption during iron deficiency and overload. J Clin Invest.
129:336–348. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Saeedi BJ, Kao DJ, Kitzenberg DA,
Dobrinskikh E, Schwisow KD, Masterson JC, Kendrick AA, Kelly CJ,
Bayless AJ, Kominsky DJ, et al: HIF-dependent regulation of
claudin-1 is central to intestinal epithelial tight junction
integrity. Mol Biol Cell. 26:2252–2262. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Das NK, Schwartz AJ, Barthel G, Inohara N,
Liu Q, Sankar A, Hill DR, Ma X, Lamberg O, Schnizlein MK, et al:
Microbial metabolite signaling is required for systemic Iron
homeostasis. Cell Metab. 31:115–130.e6. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Rogier R, Evans-Marin H, Manasson J, van
der Kraan PM, Walgreen B, Helsen MM, van den Bersselaar LA, van de
Loo FA, van Lent PL, Abramson SB, et al: Alteration of the
intestinal microbiome characterizes preclinical inflammatory
arthritis in mice and its modulation attenuates established
arthritis. Sci Rep. 7:156132017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chriswell ME, Lefferts AR, Clay MR, Hsu
AR, Seifert J, Feser ML, Rims C, Bloom MS, Bemis EA, Liu S, et al:
Clonal IgA and IgG autoantibodies from individuals at risk for
rheumatoid arthritis identify an arthritogenic strain of
Subdoligranulum. Sci Transl Med. 14:eabn51662022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Takahashi D, Hoshina N, Kabumoto Y, Maeda
Y, Suzuki A, Tanabe H, Isobe J, Yamada T, Muroi K, Yanagisawa Y, et
al: Microbiota-derived butyrate limits the autoimmune response by
promoting the differentiation of follicular regulatory T cells.
EBioMedicine. 58:1029132020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ivanov II, Atarashi K, Manel N, Brodie EL,
Shima T, Karaoz U, Wei D, Goldfarb KC, Santee CA, Lynch SV, et al:
Induction of intestinal Th17 cells by segmented filamentous
bacteria. Cell. 139:485–498. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Tan TG, Sefik E, Geva-Zatorsky N, Kua L,
Naskar D, Teng F, Pasman L, Ortiz-Lopez A, Jupp R, Wu HJ, et al:
Identifying species of symbiont bacteria from the human gut that,
alone, can induce intestinal Th17 cells in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 113:E8141–E8150. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wu HJ, Ivanov II, Darce J, Hattori K,
Shima T, Umesaki Y, Littman DR, Benoist C and Mathis D:
Gut-residing segmented filamentous bacteria drive autoimmune
arthritis via T helper 17 cells. Immunity. 32:815–827. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Rojas M, Restrepo-Jimenez P, Monsalve DM,
Pacheco Y, Acosta-Ampudia Y, Ramírez-Santana C, Leung PSC, Ansari
AA, Gershwin ME and Anaya JM: Molecular mimicry and autoimmunity. J
Autoimmun. 95:100–123. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Albani S, Keystone EC, Nelson JL, Ollier
WE, La Cava A, Montemayor AC, Weber DA, Montecucco C, Martini A and
Carson DA: Positive selection in autoimmunity: Abnormal immune
responses to a bacterial dnaJ antigenic determinant in patients
with early rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Med. 1:448–452. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Alcaide-Ruggiero L, Molina-Hernandez V,
Granados MM and Dominguez JM: Main and minor types of collagens in
the articular cartilage: The role of collagens in repair tissue
evaluation in chondral defects. Int J Mol Sci. 22:133292021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Gomez A, Luckey D, Yeoman CJ, Marietta EV,
Berg Miller ME, Murray JA, White BA and Taneja V: Loss of sex and
age driven differences in the gut microbiome characterize
arthritis-susceptible 0401 mice but not arthritis-resistant 0402
mice. PLoS One. 7:e360952012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhou C, Zhao H, Xiao XY, Chen BD, Guo RJ,
Wang Q, Chen H, Zhao LD, Zhang CC, Jiao YH, et al: Metagenomic
profiling of the pro-inflammatory gut microbiota in ankylosing
spondylitis. J Autoimmun. 107:1023602020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Miyoshi M and Liu S: Collagen-induced
arthritis models. Methods Mol Biol. 2766:3–7. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Liang B, Ge C, Lönnblom E, Lin X, Feng H,
Xiao L, Bai J, Ayoglu B, Nilsson P, Nandakumar KS, et al: The
autoantibody response to cyclic citrullinated collagen type II
peptides in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford).
58:1623–1633. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Pianta A, Arvikar SL, Strle K, Drouin EE,
Wang Q, Costello CE and Steere AC: Two rheumatoid
arthritis-specific autoantigens correlate microbial immunity with
autoimmune responses in joints. J Clin Invest. 127:2946–2956. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wang JY and Roehrl MH: Glycosaminoglycans
are a potential cause of rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 99:14362–14367. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Hua R, Ni Q, Eliason TD, Han Y, Gu S,
Nicolella DP, Wang X and Jiang JX: Biglycan and chondroitin sulfate
play pivotal roles in bone toughness via retaining bound water in
bone mineral matrix. Matrix Biol. 94:95–109. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Rosser EC, Piper CJM, Matei DE, Blair PA,
Rendeiro AF, Orford M, Alber DG, Krausgruber T, Catalan D, Klein N,
et al: Microbiota-derived metabolites suppress arthritis by
amplifying Aryl-hydrocarbon receptor activation in regulatory B
cells. Cell Metab. 31:837–851.e10. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Correa-Oliveira R, Fachi JL, Vieira A,
Sato FT and Vinolo MA: Regulation of immune cell function by
short-chain fatty acids. Clin Transl Immunol. 5:e732016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Yao Y, Cai X, Zheng Y, Zhang M, Fei W, Sun
D, Zhao M, Ye Y and Zheng C: Short-chain fatty acids regulate B
cells differentiation via the FFA2 receptor to alleviate rheumatoid
arthritis. Br J Pharmacol. 179:4315–4329. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wang Y, Wei J, Zhang W, Doherty M, Zhang
Y, Xie H, Li W, Wang N, Lei G and Zeng C: Gut dysbiosis in
rheumatic diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 92
observational studies. EBioMedicine. 80:1040552022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
He J, Chu Y, Li J, Meng Q, Liu Y, Jin J,
Wang Y, Wang J, Huang B, Shi L, et al: Intestinal
butyrate-metabolizing species contribute to autoantibody production
and bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Adv. 8:eabm15112022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Kim DS, Kwon JE, Lee SH, Kim EK, Ryu JG,
Jung KA, Choi JW, Park MJ, Moon YM, Park SH, et al: Attenuation of
rheumatoid inflammation by sodium butyrate through reciprocal
targeting of HDAC2 in osteoclasts and HDAC8 in T cells. Front
Immunol. 9:15252018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Wang M, Huang J, Fan H, He D, Zhao S, Shu
Y, Li H, Liu L, Lu S, Xiao C and Liu Y: Treatment of rheumatoid
arthritis using combination of methotrexate and tripterygium
glycosides Tablets-A quantitative plasma pharmacochemical and
pseudotargeted metabolomic approach. Front Pharmacol. 9:10512018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Surowiec I, Arlestig L, Rantapaa-Dahlqvist
S and Trygg J: Metabolite and lipid profiling of biobank plasma
samples collected prior to onset of rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS One.
11:e01641962016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Seymour BJ, Trent B, Allen BE, Berlinberg
AJ, Tangchittsumran J, Jubair WK, Chriswell ME, Liu S, Ornelas A,
Stahly A, et al: Microbiota-dependent indole production stimulates
the development of collagen-induced arthritis in mice. J Clin
Invest. 134:e1676712023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Cao S, Meng X, Li Y, Sun L, Jiang L, Xuan
H and Chen X: Bile acids elevated in chronic periaortitis could
activate Farnesoid-X-receptor to suppress IL-6 production by
macrophages. Front Immunol. 12:6328642021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Fiorucci S, Biagioli M, Zampella A and
Distrutti E: Bile acids activated receptors regulate innate
immunity. Front Immunol. 9:18532018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Hu J, Wang C, Huang X, Yi S, Pan S, Zhang
Y, Yuan G, Cao Q, Ye X and Li H: Gut microbiota-mediated secondary
bile acids regulate dendritic cells to attenuate autoimmune uveitis
through TGR5 signaling. Cell Rep. 36:1097262021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Zou F, Qiu Y, Huang Y, Zou H, Cheng X, Niu
Q, Luo A and Sun J: Effects of short-chain fatty acids in
inhibiting HDAC and activating p38 MAPK are critical for promoting
B10 cell generation and function. Cell Death Dis. 12:5822021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Ignacio Barrasa J, Olmo N, Perez-Ramos P,
Santiago-Gómez A, Lecona E, Turnay J and Antonia Lizarbe M:
Deoxycholic and chenodeoxycholic bile acids induce apoptosis via
oxidative stress in human colon adenocarcinoma cells. Apoptosis.
16:1054–1067. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Cheng X, Pi Z, Zheng Z, Liu S, Song F and
Liu Z: Combined 16S rRNA gene sequencing and metabolomics to
investigate the protective effects of Wu-tou decoction on
rheumatoid arthritis in rats. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed
Life Sci. 1199:1232492022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Liu M, Li S, Cao N, Wang Q, Liu Y, Xu Q,
Zhang L, Sun C, Xiao X and Yao J: Intestinal flora, intestinal
metabolism, and intestinal immunity changes in complete Freud's
adjuvant-rheumatoid arthritis C57BL/6 mice. Int Immunopharmacol.
125:1110902023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Wang Z, Yu Y, Liao J, Hu W, Bian X, Wu J
and Zhu YZ: S-Propargyl-Cysteine remodels the gut microbiota to
alleviate rheumatoid arthritis by regulating bile acid metabolism.
Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 11:6705932021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Liu J, Peng F, Cheng H, Zhang D, Zhang Y,
Wang L, Tang F, Wang J, Wan Y, Wu J, et al: Chronic cold
environment regulates rheumatoid arthritis through modulation of
gut microbiota-derived bile acids. Sci Total Environ.
903:1668372023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Gonzalez-Rey E, Delgado-Maroto V, Souza
Moreira L and Delgado M: Neuropeptides as therapeutic approach to
autoimmune diseases. Curr Pharm Des. 16:3158–3172. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Delgado M, Pozo D and Ganea D: The
significance of vasoactive intestinal peptide in immunomodulation.
Pharmacol Rev. 56:249–290. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Imhof AK, Gluck L, Gajda M, Lupp A, Bräuer
R, Schaible HG and Schulz S: Differential antiinflammatory and
antinociceptive effects of the somatostatin analogs octreotide and
pasireotide in a mouse model of immune-mediated arthritis.
Arthritis Rheum. 63:2352–2362. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Jimeno R, Leceta J, Martínez C,
Gutiérrez-Cañas I, Pérez-García S, Carrión M, Gomariz RP and
Juarranz Y: Effect of VIP on the balance between cytokines and
master regulators of activated helper T cells. Immunol Cell Biol.
90:178–186. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Jimeno R, Gomariz RP, Gutierrez-Canas I,
Martinez C, Juarranz Y and Leceta J: New insights into the role of
VIP on the ratio of T-cell subsets during the development of
autoimmune diabetes. Immunol Cell Biol. 88:734–745. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Leceta J, Garin MI and Conde C: Mechanism
of immunoregulatory properties of vasoactive intestinal peptide in
the K/BxN mice model of autoimmune arthritis. Front Immunol.
12:7018622021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
O'Connor TM, O'Connell J, O'Brien DI,
Goode T, Bredin CP and Shanahan F: The role of substance P in
inflammatory disease. J Cell Physiol. 201:167–180. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Raap T, Justen HP, Miller LE, Cutolo M,
Scholmerich J and Straub RH: Neurotransmitter modulation of
interleukin 6 (IL-6) and IL-8 secretion of synovial fibroblasts in
patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared to osteoarthritis. J
Rheumatol. 27:2558–2565. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Barbosa-Cobos RE, Lugo-Zamudio G,
Flores-Estrada J, Becerril-Mendoza LT, Rodríguez-Henríquez P,
Torres-González R, Moreno-Eutimio MA, Ramirez-Bello J and Moreno J:
Serum substance P: An indicator of disease activity and subclinical
inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 37:901–908.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Jiang MH, Chung E, Chi GF, Ahn W, Lim JE,
Hong HS, Kim DW, Choi H, Kim J and Son Y: Substance P induces
M2-type macrophages after spinal cord injury. Neuroreport.
23:786–792. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Hong HS and Son Y: Substance P ameliorates
collagen II-induced arthritis in mice via suppression of the
inflammatory response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 453:179–184.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Galarza-Delgado DA, Azpiri-Lopez JR,
Colunga-Pedraza IJ, Cárdenas-de la Garza JA, Vera-Pineda R,
Wah-Suárez M, Arvizu-Rivera RI, Martínez-Moreno A, Ramos-Cázares
RE, Torres-Quintanilla FJ, et al: Prevalence of comorbidities in
Mexican mestizo patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int.
37:1507–1511. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Castillo-Canon JC, Trujillo-Caceres SJ,
Bautista-Molano W, Valbuena-Garcia AM, Fernandez-Avila DG and
Acuna-Merchan L: Rheumatoid arthritis in Colombia: A clinical
profile and prevalence from a national registry. Clin Rheumatol.
40:3565–3573. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Niu Q, Hao J, Li Z and Zhang H: Helper T
cells: A potential target for sex hormones to ameliorate rheumatoid
arthritis? (Review). Mol Med Rep. 30:2152024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Li JY, Chassaing B, Tyagi AM, Vaccaro C,
Luo T, Adams J, Darby TM, Weitzmann MN, Mulle JG, Gewirtz AT, et
al: Sex steroid deficiency-associated bone loss is microbiota
dependent and prevented by probiotics. J Clin Invest.
126:2049–2063. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Porwal K, Pal S, Kulkarni C, Singh P,
Sharma S, Singh P, Prajapati G, Gayen JR, Ampapathi RS, Mullick A
and Chattopadhyay N: A prebiotic, short-chain
fructo-oligosaccharides promotes peak bone mass and maintains bone
mass in ovariectomized rats by an osteogenic mechanism. Biomed
Pharmacother. 129:1104482020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Dominianni C, Sinha R, Goedert JJ, Pei Z,
Yang L, Hayes RB and Ahn J: Sex, body mass index, and dietary fiber
intake influence the human gut microbiome. PLoS One.
10:e01245992015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Balakrishnan B, Luckey D, Wright K, Davis
JM, Chen J and Taneja V: Eggerthella lenta augments
preclinical autoantibody production and metabolic shift mimicking
senescence in arthritis. Sci Adv. 9:eadg11292023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Bhambhani S, Kondhare KR and Giri AP:
Diversity in chemical structures and biological properties of plant
alkaloids. Molecules. 26:33742021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Ettefagh KA, Burns JT, Junio HA, Kaatz GW
and Cech NB: Goldenseal (Hydrastis canadensis L.) extracts
synergistically enhance the antibacterial activity of berberine via
efflux pump inhibition. Planta Med. 77:835–840. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Zhu M, Wang H, Chen J and Zhu H:
Sinomenine improve diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting fibrosis and
regulating the JAK2/STAT3/SOCS1 pathway in streptozotocin-induced
diabetic rats. Life Sci. 265:1188552021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Samra YA, Said HS, Elsherbiny NM, Liou GI,
El-Shishtawy MM and Eissa LA: Cepharanthine and Piperine ameliorate
diabetic nephropathy in rats: Role of NF-kappaB and NLRP3
inflammasome. Life Sci. 157:187–199. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Naz I, Masoud MS, Chauhdary Z, Shah MA and
Panichayupakaranant P: Anti-inflammatory potential of
berberine-rich extract via modulation of inflammation biomarkers. J
Food Biochem. 46:e143892022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Alorabi M, Cavalu S, Al-Kuraishy HM,
Al-Gareeb AI, Mostafa-Hedeab G, Negm WA, Youssef A, El-Kadem AH,
Saad HM and Batiha GE: Pentoxifylline and berberine mitigate
diclofenac-induced acute nephrotoxicity in male rats via modulation
of inflammation and oxidative stress. Biomed Pharmacother.
152:1132252022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Luo R, Liao Z, Song Y, Yin H, Zhan S, Li
G, Ma L, Lu S, Wang K, Li S, et al: Berberine ameliorates oxidative
stress-induced apoptosis by modulating ER stress and autophagy in
human nucleus pulposus cells. Life Sci. 228:85–97. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Samadi P, Sarvarian P, Gholipour E,
Asenjan KS, Aghebati-Maleki L, Motavalli R, Hojjat-Farsangi M and
Yousefi M: Berberine: A novel therapeutic strategy for cancer.
IUBMB Life. 72:2065–2079. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Pirillo A and Catapano AL: Berberine, a
plant alkaloid with lipid- and glucose-lowering properties: From in
vitro evidence to clinical studies. Atherosclerosis. 243:449–461.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Song D, Hao J and Fan D: Biological
properties and clinical applications of berberine. Front Med.
14:564–582. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Liu YT, Hao HP, Xie HG, Lai L, Wang Q, Liu
CX and Wang GJ: Extensive intestinal first-pass elimination and
predominant hepatic distribution of berberine explain its low
plasma levels in rats. Drug Metab Dispos. 38:1779–1784. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Yue M, Xia Y, Shi C, Guan C, Li Y, Liu R,
Wei Z and Dai Y: Berberine ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis
in rats by suppressing Th17 cell responses via inducing cortistatin
in the gut. FEBS J. 284:2786–2801. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Tan XS, Ma JY, Feng R, Ma C, Chen WJ, Sun
YP, Fu J, Huang M, He CY, Shou JW, et al: Tissue distribution of
berberine and its metabolites after oral administration in rats.
PLoS One. 8:e779692013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Yue M, Tao Y, Fang Y, Lian X, Zhang Q, Xia
Y, Wei Z and Dai Y: The gut microbiota modulator berberine
ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis in rats by facilitating the
generation of butyrate and adjusting the intestinal hypoxia and
nitrate supply. FASEB J. 33:12311–12323. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Sun Y, Yao Y and Ding CZ: A combination of
sinomenine and methotrexate reduces joint damage of collagen
induced arthritis in rats by modulating osteoclast-related
cytokines. Int Immunopharmacol. 18:135–141. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Liu W, Zhang Y, Zhu W, Ma C, Ruan J, Long
H and Wang Y: Sinomenine inhibits the progression of rheumatoid
arthritis by regulating the secretion of inflammatory cytokines and
Monocyte/macrophage subsets. Front Immunol. 9:22282018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Huang RY, Pan HD, Wu JQ, Zhou H, Li ZG,
Qiu P, Zhou YY, Chen XM, Xie ZX, Xiao Y, et al: Comparison of
combination therapy with methotrexate and sinomenine or leflunomide
for active rheumatoid arthritis: A randomized controlled clinical
trial. Phytomedicine. 57:403–410. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Chen JJ, Sun Y and Huang CB: Clinical
observation of sinomenine hydrochloride in the treat-to-target
therapy of rheumatoid arthritis and patient-reported outcomes. J
Chin Med Materials. 228–231. 2025.
|
|
117
|
Xiang G, Gao M, Qin H, Shen X, Huang H,
Hou X and Feng Z: Benefit-risk assessment of traditional Chinese
medicine preparations of sinomenine using multicriteria decision
analysis (MCDA) for patients with rheumatoid arthritis. BMC
Complement Med Ther. 23:372023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Li X, He L, Hu Y, Duan H, Li X, Tan S, Zou
M, Gu C, Zeng X, Yu L, et al: Sinomenine suppresses osteoclast
formation and Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Ra-induced bone loss by
modulating RANKL signaling pathways. PLoS One. 8:e742742013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Chen DP, Wong CK, Leung PC, Fung KP, Lau
CB, Lau CP, Li EK, Tam LS and Lam CW: Anti-inflammatory activities
of Chinese herbal medicine sinomenine and Liang Miao San on tumor
necrosis factor-α-activated human fibroblast-like synoviocytes in
rheumatoid arthritis. J Ethnopharmacol. 137:457–468. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Tong B, Yu J, Wang T, Dou Y, Wu X, Kong L,
Dai Y and Xia Y: Sinomenine suppresses collagen-induced arthritis
by reciprocal modulation of regulatory T cells and Th17 cells in
gut-associated lymphoid tissues. Mol Immunol. 65:94–103. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Wang H, Liao H, Ochani M, Justiniani M,
Lin X, Yang L, Al-Abed Y, Wang H, Metz C, Miller EJ, et al:
Cholinergic agonists inhibit HMGB1 release and improve survival in
experimental sepsis. Nat Med. 10:1216–1221. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Yi L, Luo JF, Xie BB, Liu JX, Wang JY, Liu
L, Wang PX, Zhou H and Dong Y: α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
is a novel mediator of sinomenine Anti-Inflammation effect in
macrophages stimulated by lipopolysaccharide. Shock. 44:188–195.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Hayashi S, Hamada T, Zaidi SF, Oshiro M,
Lee J, Yamamoto T, Ishii Y, Sasahara M and Kadowaki M: Nicotine
suppresses acute colitis and colonic tumorigenesis associated with
chronic colitis in mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
307:G968–G978. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Yue M, Zhang X, Dou Y, Wei Z, Tao Y, Xia Y
and Dai Y: Gut-sourced vasoactive intestinal polypeptide induced by
the activation of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor substantially
contributes to the anti-inflammatory effect of sinomenine in
collagen-induced arthritis. Front Pharmacol. 9:6752018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Zhang H, Chen L, Sun X, Yang Q, Wan L and
Guo C: Matrine: A promising natural product with various
pharmacological activities. Front Pharmacol. 11:5882020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Ao L, Gao H, Jia L, Liu S, Guo J, Liu B
and Dong Q: Matrine inhibits synovial angiogenesis in
collagen-induced arthritis rats by regulating HIF-VEGF-Ang and
inhibiting the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Mol Immunol. 141:13–20.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Niu Y, Dong Q and Li R: Matrine regulates
Th1/Th2 cytokine responses in rheumatoid arthritis by attenuating
the NF-κB signaling. Cell Biol Int. 41:611–621. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Zou Y, Li Q, Liu D, Li J, Cai Q, Li C,
Zhao Q and Xu W: Therapeutic effects of matrine derivate MASM in
mice with collagen-induced arthritis and on fibroblast-like
synoviocytes. Sci Rep. 7:24542017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Cao G, Mao Z, Niu T, Wang P, Yue X, Wang
X, Ma A and Zhang Y: Oxymatrine ameliorates rheumatoid arthritis by
regulation of Tfr/Tfh cell balance via the TLR9-MyD88-STAT3
signaling pathway. J Sci Food Agric. 103:6017–6024. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Zhang G, Liu B, Zeng Z, Chen Q, Feng Y and
Ning X: Oxymatrine hydrazone (OMTH) synthesis and its protective
effect for rheumatoid arthritis through downregulation of MEK/NF-κB
pathway. Environ Toxicol. 36:2448–2453. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Cao G, Li J, Mao Z and Zhang Y: Oxymatrine
alleviates Collagen-induced arthritis in mice by regulating the
immune balance of T cells. Molecules. 28:58792023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Shi F, Li S and Shi H: Oxymatrine
modulates immune balance in rheumatoid arthritis and its effect on
patients' inflammatory profile. Hainan Med J. 29:2997–3000.
2018.
|
|
133
|
Li W and Zhang SN: Effect of oxymatrine on
immune balance and its influence on the inflammatory status in
patients with rheumatoid arthritis. China Modern Med. 26:18–21.
2019.
|
|
134
|
Kacena C: Effects of the curcuminoid and
Non-curcuminoid compounds of turmeric on the gut microbiome and
inflammation: Potential use in the treatment and prevention of
disease. Nutr Rev. 83:1771–1783. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Hasanzadeh S, Read MI, Bland AR, Majeed M,
Jamialahmadi T and Sahebkar A: Curcumin: An inflammasome silencer.
Pharmacol Res. 159:1049212020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Kou H, Huang L, Jin M, He Q, Zhang R and
Ma J: Effect of curcumin on rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Front Immunol. 14:11216552023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Chandran B and Goel A: A randomized, pilot
study to assess the efficacy and safety of curcumin in patients
with active rheumatoid arthritis. Phytother Res. 26:1719–1725.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Pourhabibi-Zarandi F, Rafraf M, Zayeni H,
Asghari-Jafarabadi M and Ebrahimi AA: The efficacy of curcumin
supplementation on serum total antioxidant capacity,
malondialdehyde, and disease activity in women with rheumatoid
arthritis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical
trial. Phytother Res. 38:3552–3563. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Pourhabibi-Zarandi F, Rafraf M, Zayeni H,
Asghari-Jafarabadi M and Ebrahimi AA: Effects of curcumin
supplementation on metabolic parameters, inflammatory factors and
obesity values in women with rheumatoid arthritis: A randomized,
double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Phytother Res.
36:1797–1806. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Amalraj A, Varma K, Jacob J, Divya C,
Kunnumakkara AB, Stohs SJ and Gopi S: A novel highly bioavailable
curcumin formulation improves symptoms and diagnostic indicators in
rheumatoid arthritis patients: A randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled, two-dose, three-arm, and parallel-group study.
J Med Food. 20:1022–1030. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Yang KY, Lin LC, Tseng TY, Wang SC and
Tsai TH: Oral bioavailability of curcumin in rat and the herbal
analysis from Curcuma longa by LC-MS/MS. J Chromatogr B Analyt
Technol Biomed Life Sci. 853:183–189. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Jang DJ, Kim ST, Oh E and Lee K: Enhanced
oral bioavailability and antiasthmatic efficacy of curcumin using
redispersible dry emulsion. Biomed Mater Eng. 24:917–930.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Kloesch B, Becker T, Dietersdorfer E,
Kiener H and Steiner G: Anti-inflammatory and apoptotic effects of
the polyphenol curcumin on human fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Int
Immunopharmacol. 15:400–405. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Huang G, Xu Z, Huang Y, Duan X, Gong W,
Zhang Y, Fan J and He F: Curcumin protects against collagen-induced
arthritis via suppression of BAFF production. J Clin Immunol.
33:550–557. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Yang Y, Wu X, Wei Z, Dou Y, Zhao D, Wang
T, Bian D, Tong B, Xia Y, Xia Y and Dai Y: Oral curcumin has
anti-arthritic efficacy through somatostatin generation via
cAMP/PKA and Ca(2+)/CaMKII signaling pathways in the small
intestine. Pharmacol Res. 95-96:71–81. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Javadi F, Ahmadzadeh A, Eghtesadi S,
Aryaeian N, Zabihiyeganeh M, Rahimi Foroushani A and Jazayeri S:
The effect of quercetin on inflammatory factors and clinical
symptoms in women with rheumatoid arthritis: A Double-blind,
randomized controlled trial. J Am Coll Nutr. 36:9–15. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Javadi F, Eghtesadi S, Ahmadzadeh A,
Aryaeian N, Zabihiyeganeh M, Foroushani AR and Jazayeri S: The
effect of quercetin on plasma oxidative status, C-reactive protein
and blood pressure in women with rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Prev
Med. 5:293–301. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Tang M, Zeng Y, Peng W, Xie X, Yang Y, Ji
B and Li F: Pharmacological aspects of natural quercetin in
rheumatoid arthritis. Drug Des Devel Ther. 16:2043–2053. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Liu X, Tao T, Yao H, Zheng H, Wang F and
Gao Y: Mechanism of action of quercetin in rheumatoid arthritis
models: Meta-analysis and systematic review of animal studies.
Inflammopharmacology. 31:1629–1645. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Cojocaru M, Cojocaru IM, Silosi I and
Vrabie CD: Gastrointestinal manifestations in systemic autoimmune
diseases. Maedica (Bucur). 6:45–51. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Souza ID, Ribeiro JS, Bersani-Amado CA and
Zanoni JN: Analysis of myosin-V immunoreactive myenteric neurons
from arthritic rats. Arq Gastroenterol. 48:205–210. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Piovezana Bossolani GD, Silva BT, Colombo
Martins Perles JV, Lima MM, Vieira Frez FC, Garcia de Souza SR,
Sehaber-Sierakowski CC, Bersani-Amado CA and Zanoni JN: Rheumatoid
arthritis induces enteric neurodegeneration and jejunal
inflammation, and quercetin promotes neuroprotective and
anti-inflammatory actions. Life Sci. 238:1169562019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Silva BTD, Martins-Perles JVC, Bossolani
GDP, Lima MM, Sehaber-Sierakowski CC, Gremaschi LB, Cunha JPSE,
Bersani-Amado CA and Zanoni JN: Quercetin and ibuprofen combination
displayed anti-inflammatory effects and also extenuates the enteric
neurons damage of arthritic rats. An Acad Bras Cienc. 96 (Suppl
1):e202302442024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Zhao Y, Yan B, Wang Z, Li M and Zhao W:
Natural polysaccharides with immunomodulatory activities. Mini Rev
Med Chem. 20:96–106. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Ho Do M, Seo YS and Park HY:
Polysaccharides: Bowel health and gut microbiota. Crit Rev Food Sci
Nutr. 61:1212–1224. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Luo J, Yang Q, Jiang W, Liu Y, Hu Q and
Peng X: The interaction between Angelica sinensis
polysaccharide ASP-2pb and specific gut bacteria alleviates
rheumatoid arthritis in rats. Int J Biol Macromol. 301:1404732025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Lim H, Min DS, Yun HE, Kim KT, Sun YN, Dat
LD, Kim YH and Kim HP: Impressic acid from Acanthopanax koreanum,
possesses matrix metalloproteinase-13 down-regulating capacity and
protects cartilage destruction. J Ethnopharmacol. 209:73–81. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Takahashi Y, Tanaka M, Murai R,
Kuribayashi K, Kobayashi D, Yanagihara N and Watanabe N:
Prophylactic and therapeutic effects of Acanthopanax
senticosus Harms extract on murine collagen-induced arthritis.
Phytother Res. 28:1513–1519. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Kang MC, Kim SY, Kim EA, Lee JH, Kim YS,
Yu SK, Chae JB, Choe IH, Cho JH and Jeon YJ: Antioxidant activity
of polysaccharide purified from Acanthopanax koreanum Nakai stems
in vitro and in vivo zebrafish model. Carbohydr Polym. 127:38–46.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Fu J, Fu J, Yuan J, Zhang N, Gao B, Fu G,
Tu Y and Zhang Y: Anti-diabetic activities of Acanthopanax
senticosus polysaccharide (ASP) in combination with metformin.
Int J Biol Macromol. 50:619–623. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Lee JB, Tanikawa T, Hayashi K, Asagi M,
Kasahara Y and Hayashi T: Characterization and biological effects
of two polysaccharides isolated from Acanthopanax sciadophylloides.
Carbohydr Polym. 116:159–166. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Liu A, Zhang M, Wu Y, Zhang C, Zhang Q, Su
X, Zhu X, Shi W, Liu J, Zhang Y, et al: ASPS exhibits
Anti-rheumatic effects by reprogramming gut microbiota and
increasing serum γ-Glutamylcysteine Level. Adv Sci (Weinh).
10:e22056452023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Liu L, Sha XY, Wu YN, Chen MT and Zhong
JX: Lycium barbarum polysaccharides protects retinal
ganglion cells against oxidative stress injury. Neural Regen Res.
15:1526–1531. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Ran L, Chen F, Zhang J, Mi J, Lu L, Yan Y
and Cao Y: Antitumor effects of pollen polysaccharides from Chinese
wolfberry on DU145 cells via the PI3K/AKT pathway in vitro and in
vivo. Int J Biol Macromol. 152:1164–1173. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Li W, Gao M and Han T: Lycium
barbarum polysaccharides ameliorate intestinal barrier
dysfunction and inflammation through the MLCK-MLC signaling pathway
in Caco-2 cells. Food Funct. 11:3741–3748. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Fu YW, Peng YF, Huang XD, Yang Y, Huang L,
Xi Y, Hu ZF, Lin S, So KF and Ren CR: Lycium barbarum
polysaccharide-glycoprotein preventative treatment ameliorates
aversive. Neural Regen Res. 16:543–549. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Kalinkovich A and Livshits G: A cross talk
between dysbiosis and Gut-associated immune system governs the
development of inflammatory arthropathies. Semin Arthritis Rheum.
49:474–484. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Liu Y, Lv J, Yang B, Liu F, Tian Z, Cai Y,
Yang D, Ouyang J, Sun F, Shi Y and Xia P: Lycium barbarum
polysaccharide attenuates type II collagen-induced arthritis in
mice. Int J Biol Macromol. 78:318–323. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Cai S, Sun J and Wei X: Lycium
barbarum polysaccharide inhibits NF-κB pathway to reduce the
level of inflammatory cytokines in osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Xi
Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 34:989–993. 2018.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Lai W, Wang C, Lai R, Peng X and Luo J:
Lycium barbarum polysaccharide modulates gut microbiota to
alleviate rheumatoid arthritis in a rat model. NPJ Sci Food.
6:342022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Liu Y, Liu L, Luo J and Peng X:
Metabolites from specific intestinal bacteria in vivo fermenting
Lycium barbarum polysaccharide improve collagenous arthritis
in rats. Int J Biol Macromol. 226:1455–1467. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Cao W, Liu J, Dai Y, Zhou Y, Li R and Yu
P: Bibliometric analysis of marine traditional chinese medicine in
pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China: Development,
differences, and trends directions. Evid Based Complement Alternat
Med. 2022:39719672022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Zheng Q, Mu X, Pan S, Luan R and Zhao P:
Ephedrae herba: A comprehensive review of its traditional uses,
phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology. J Ethnopharmacol.
307:1161532023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Ma Y, Wei X, Peng J, Wei F, Wen Y, Liu M,
Song B, Wang Y, Zhang Y and Peng T: Ephedra sinica polysaccharide
regulate the anti-inflammatory immunity of intestinal microecology
and bacterial metabolites in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Pharmacol.
15:14146752024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Chen Z, Li XP, Li ZJ, Xu L and Li XM:
Reduced hepatotoxicity by total glucosides of paeony in combination
treatment with leflunomide and methotrexate for patients with
active rheumatoid arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. 15:474–477. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Xiang N, Li XM, Zhang MJ, Zhao DB, Zhu P,
Zuo XX, Yang M, Su Y, Li ZG, Chen Z and Li XP: Total glucosides of
paeony can reduce the hepatotoxicity caused by Methotrexate and
Leflunomide combination treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis.
Int Immunopharmacol. 28:802–807. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Wang Y and Xing HY: Clinical observation
on effect of total glucosides of paeony combined with methotrexate
on rheumatoid arthritis. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi.
27:839–840. 2007.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Luo J, Jin DE, Yang GY, Zhang YZ, Wang JM,
Kong WP and Tao QW: Total glucosides of paeony for rheumatoid
arthritis: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials.
Complement Ther Med. 34:46–56. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Fei F, Yang H, Peng Y, Wang P, Wang S,
Zhao Y, Huang J, Yu X, Feng S, Sun R, et al: Sensitive analysis and
pharmacokinetic study of the isomers paeoniflorin and albiflorin
after oral administration of total glucosides of white paeony
capsule in rats. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci.
1022:30–37. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Xia SM, Shen R, Sun XY, Shen LL, Yang YM,
Ke Y, Wang Y, Chen DY and Han XM: Development and validation of a
sensitive liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for
the determination of paeoniflorin in rat brain and its application
to pharmacokinetic study. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life
Sci. 857:32–39. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Zhang W and Dai SM: Mechanisms involved in
the therapeutic effects of Paeonia lactiflora Pallas in rheumatoid
arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. 14:27–31. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Sun B, Dai G, Bai Y, Zhang W, Zhu L, Chu
J, Pan R and Ju W: Determination of paeoniflorin in rat plasma by
Ultra-high performance liquid Chromatography-tandem mass
spectrometry and its application to a pharmacokinetic study. J
Chromatogr Sci. 55:1006–1012. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Tong L, Wan M, Zhou D, Gao J, Zhu Y and Bi
K: LC-MS/MS determination and pharmacokinetic study of albiflorin
and paeoniflorin in rat plasma after oral administration of Radix
Paeoniae Alba extract and Tang-Min-Ling-Wan. Biomed Chromatogr.
24:1324–1331. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Peng J, Lu X, Xie K, Xu Y, He R, Guo L,
Han Y, Wu S, Dong X, Lu Y, et al: Dynamic alterations in the gut
microbiota of Collagen-induced arthritis rats following the
prolonged administration of total glucosides of paeony. Front Cell
Infect Microbiol. 9:2042019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Bao BL and Wang ZZ: Resource and
pharmacognostical study on Aralia echinocaulis. Zhongguo
Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 29:508–510. 2004.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Li Y, Dai M, Wang L and Wang G:
Polysaccharides and glycosides from Aralia echinocaulis
protect rats from arthritis by modulating the gut microbiota
composition. J Ethnopharmacol. 269:1137492021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Zhao J, Zhang F, Xiao X, Wu Z, Hu Q, Jiang
Y, Zhang W, Wei S, Ma X and Zhang X: Tripterygium hypoglaucum
(Levl.) hutch and its main bioactive components: recent advances in
pharmacological activity, pharmacokinetics and potential toxicity.
Front Pharmacol. 12:7153592021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Zhou X, Liu Q, Zhou X, Zhang J, Liu W,
Zhao X and Luo N: THH Relieves CIA inflammation by reducing
inflammatory-related cytokines. Cell Biochem Biophys. 78:367–374.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Long C, Yang Y, Wang Y, Zhang X, Zhang L,
Huang S, Yang D, Qiao X, Yang Y and Guo Y: Role of
Glutamine-glutamate/GABA cycle and potential target GLUD2 in
alleviation of rheumatoid arthritis by Tripterygium hypoglaucum
(levl.) Hutch based on metabolomics and molecular pharmacology. J
Ethnopharmacol. 281:1145612021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Hu J, Ni J, Zheng J, Guo Y, Yang Y, Ye C,
Sun X, Xia H, Liu Y and Liu H: Tripterygium hypoglaucum extract
ameliorates adjuvant-induced arthritis in mice through the gut
microbiota. Chin J Nat Med. 21:730–744. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Zheng J, Hu J, Yang Y, Xiong L, Yang H,
Zhang Z, Jiang N and Liu H: Suppressive effect of Tripterygium
hypoglaucum (Levl.) Hutch extract on rheumatoid arthritis in mice
by modulating inflammasome and bile acid metabolism. Biomed
Pharmacother. 167:1154942023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Orwa JA, Jondiko IJ, Minja RJ and Bekunda
M: The use of Toddalia asiatica (L) Lam. (Rutaceae) in
traditional medicine practice in East Africa. J Ethnopharmacol.
115:257–262. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Sukieum S, Sang-Aroon W and Yenjai C:
Coumarins and alkaloids from the roots of Toddalia asiatica. Nat
Prod Res. 32:944–952. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Yang K, Tong L, Chen C, Zhang P, Pi H,
Ruan H and Wu J: Therapeutic effects of extracts from Radix
Toddaliae Asiaticae on collagen-induced arthritis in Balb/c mice. J
Ethnopharmacol. 146:355–362. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Tong L, Chen T, Chen Z, Zhang P, Pi H,
Ruan H and Wu J: Anti-inflammatory activity of omphalocarpin
isolated from radix toddaliae asiaticae. J Ethnopharmacol.
155:1553–1560. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Yan C and Wu J: Effect of Toddalia
asiatica extract combined with miR-483 on proliferation, apoptosis
and inflammatory factors expression of osteoarthritis chondrocyte.
Pak J Pharm Sci. 33:1333–1340. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Qin H, Fu Y, Zhou K, Song H, Fang G, Chen
Q and Pang Y: Toddalia asiatica extract attenuates adjuvant-induced
arthritis by modulating colon Th17/Treg balance and colony
homeostasis. J Ethnopharmacol. 313:1165422023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Chen BC, He HY, Niu K, Rui K, Huang JG,
Xie YQ and Xiao M: Network pharmacology-based approach uncovers the
JAK/STAT signaling mechanism underlying Paederia scandens
extract treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Transl Res.
14:5295–5307. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Xiao M, Fu X, Ni Y, Chen J, Jian S, Wang
L, Li L and Du G: Protective effects of Paederia scandens
extract on rheumatoid arthritis mouse model by modulating gut
microbiota. J Ethnopharmacol. 226:97–104. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Swindell EP, Hankins PL, Chen H,
Miodragovic DU and O'Halloran TV: Anticancer activity of
small-molecule and nanoparticulate arsenic(III) complexes. Inorg
Chem. 52:12292–12304. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
201
|
Zhang J, Li C, Zheng Y, Lin Z, Zhang Y and
Zhang Z: Inhibition of angiogenesis by arsenic trioxide via
TSP-1-TGF-β1-CTGF-VEGF functional module in rheumatoid arthritis.
Oncotarget. 8:73529–73546. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Zhang J, Ma Y, Zhang Y, Niu S, Chu M and
Zhang Z: Angiogenesis is inhibited by arsenic trioxide through
downregulation of the CircHIPK3/miR-149-5p/FOXO1/VEGF functional
module in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Pharmacol. 12:7516672021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
203
|
Li C, Zhang J, Wang W, Wang H, Zhang Y and
Zhang Z: Arsenic trioxide improves Treg and Th17 balance by
modulating STAT3 in treatment-naive rheumatoid arthritis patients.
Int Immunopharmacol. 73:539–551. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Niu S, Zhu X, Zhang J, Ma Y, Lang X, Luo
L, Li W, Zhao Y and Zhang Z: Arsenic trioxide modulates the
composition and metabolic function of the gut microbiota in a mouse
model of rheumatoid arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. 111:1091592022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
205
|
Kang JI, Hong JY, Choi JS and Lee SK:
Columbianadin inhibits cell proliferation by inducing apoptosis and
necroptosis in HCT116 colon cancer cells. Biomol Ther (Seoul).
24:320–327. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Lim HJ, Lee JH, Choi JS, Lee SK, Kim YS
and Kim HP: Inhibition of airway inflammation by the roots of
Angelica decursiva and its constituent, columbianadin. J
Ethnopharmacol. 155:1353–1361. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Li R, Zhao C, Yao M, Song Y, Wu Y and Wen
A: Analgesic effect of coumarins from Radix angelicae pubescentis
is mediated by inflammatory factors and TRPV1 in a spared nerve
injury model of neuropathic pain. J Ethnopharmacol. 195:81–88.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
Su X, Wu B, Zhang W, Ji YH, Wang Q and Tan
ZY: Inhibitory effects of columbianadin on nociceptive behaviors in
a neuropathic pain model, and on Voltage-gated calcium currents in
dorsal root ganglion neurons in mice. Front Pharmacol. 10:15222019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Chen S, Wang Y, Zhang L, Han Y, Liang C,
Wang S, Qi L, Pang X, Li J and Chang Y: Therapeutic effects of
columbianadin from Angelicae Pubescentis radix on the progression
of collagen-induced rheumatoid arthritis by regulating inflammation
and oxidative stress. J Ethnopharmacol. 316:1167272023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Gracey E, Vereecke L, McGovern D, Fröhling
M, Schett G, Danese S, De Vos M, Van den Bosch F and Elewaut D:
Revisiting the Gut-joint axis: Links between gut inflammation and
spondyloarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 16:415–433. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
de Winter JJ, van Mens LJ, van der Heijde
D, Landewe R and Baeten DL: Prevalence of peripheral and
extra-articular disease in ankylosing spondylitis versus
non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: A meta-analysis.
Arthritis Res Ther. 18:1962016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Guggino G, Mauro D, Rizzo A, Alessandro R,
Raimondo S, Bergot AS, Rahman MA, Ellis JJ, Milling S, Lories R, et
al: Inflammasome activation in ankylosing spondylitis is associated
with gut dysbiosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 73:1189–1199. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
Mauro D, Nakamura A, Haroon N and Ciccia
F: The gut-enthesis axis and the pathogenesis of Spondyloarthritis.
Semin Immunol. 58:1016072021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
Fan J, Jiang T and He D: Advances in the
implications of the gut microbiota on the treatment efficacy of
disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis.
Front Immunol. 14:11890362023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Qiao J, Zhang SX, Chang MJ, Cheng T, Zhang
JQ, Zhao R, Song S, Liu GY, Chang JS and Li XF: Specific enterotype
of gut microbiota predicted clinical effect of methotrexate in
patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford).
62:1087–1096. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Liu X, Wang Z, Qian H, Tao W, Zhang Y, Hu
C, Mao W and Guo Q: Natural medicines of targeted rheumatoid
arthritis and its action mechanism. Front Immunol. 13:9451292022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Han Y, Chen S, Liu C, Sun H, Jia Z, Shi J,
Li J and Chang Y: A comprehensive review of natural products in
rheumatoid arthritis: Therapeutic potential and mechanisms. Front
Immunol. 16:15010192025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
218
|
Guo W, Lv G, Yang D, Zhang W, Li N, Hu J,
Wu Y, Pi Z and Lin Z: Advances in the effect of gut-joint axis
dysfunction on rheumatoid arthritis and the intervention of natural
products. Chin J Analytical Chemistry. 52:1003542024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
219
|
Liang Y, Liu M, Cheng Y, Wang X and Wang
W: Prevention and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis through
traditional Chinese medicine: Role of the gut microbiota. Front
Immunol. 14:12339942023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|