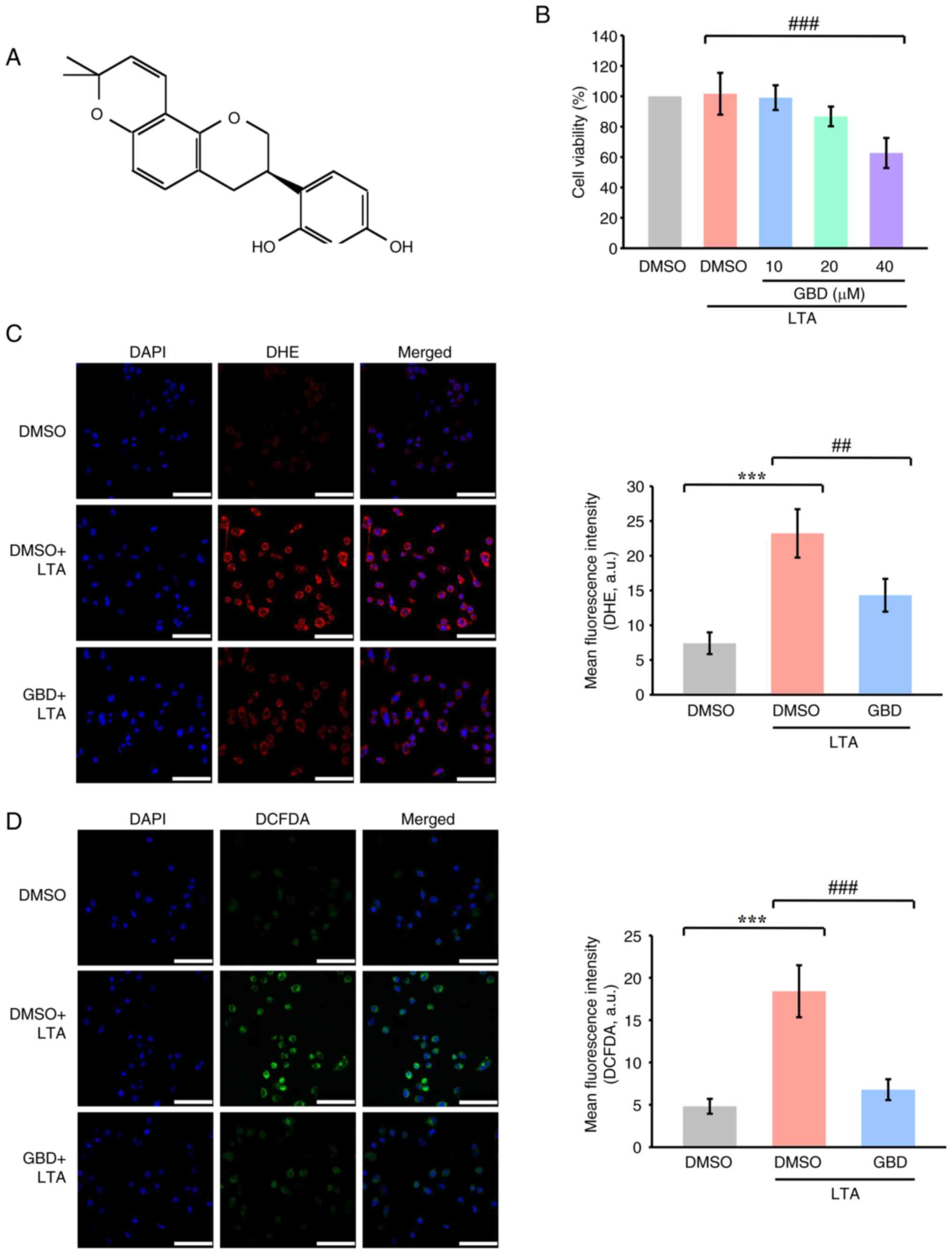
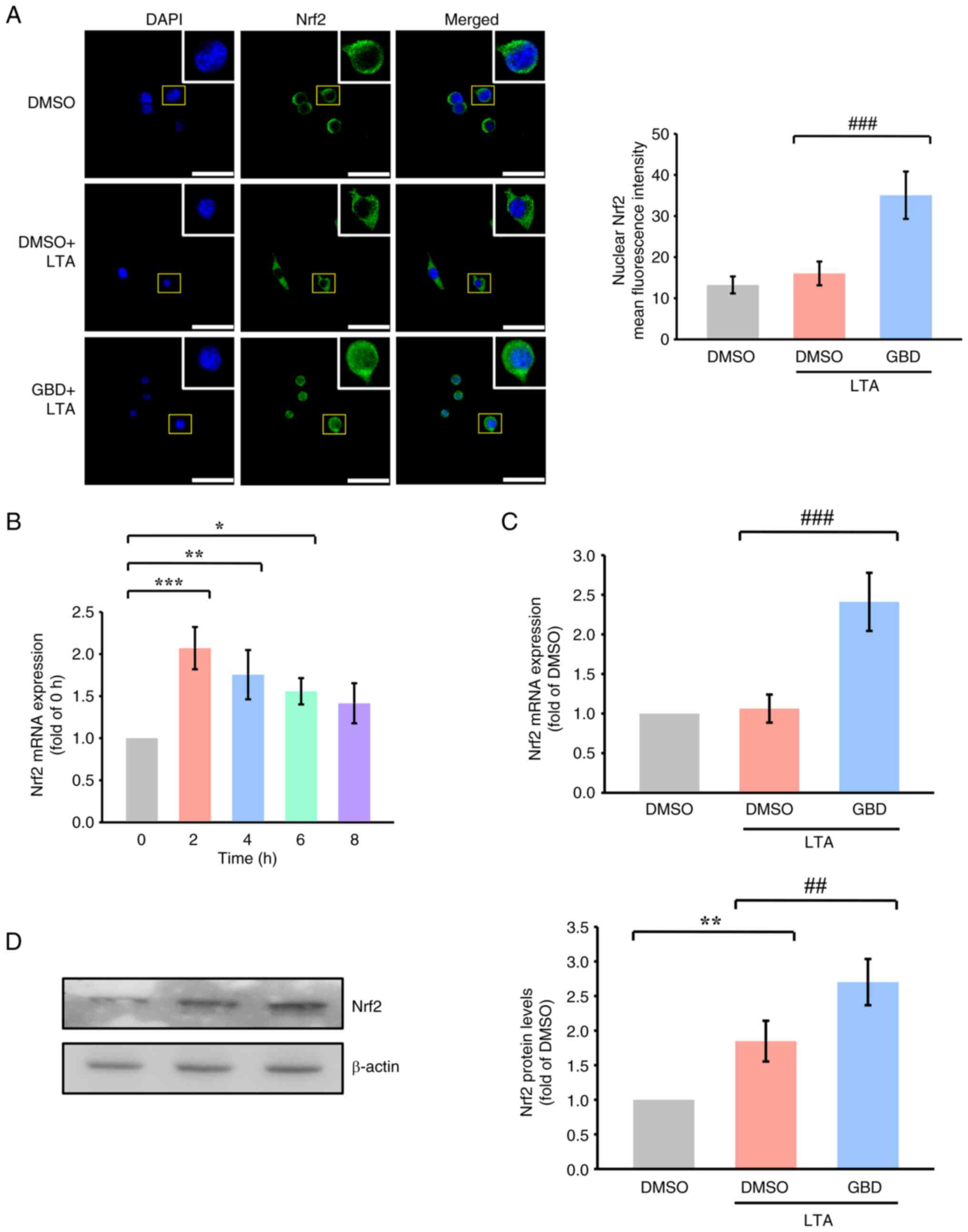
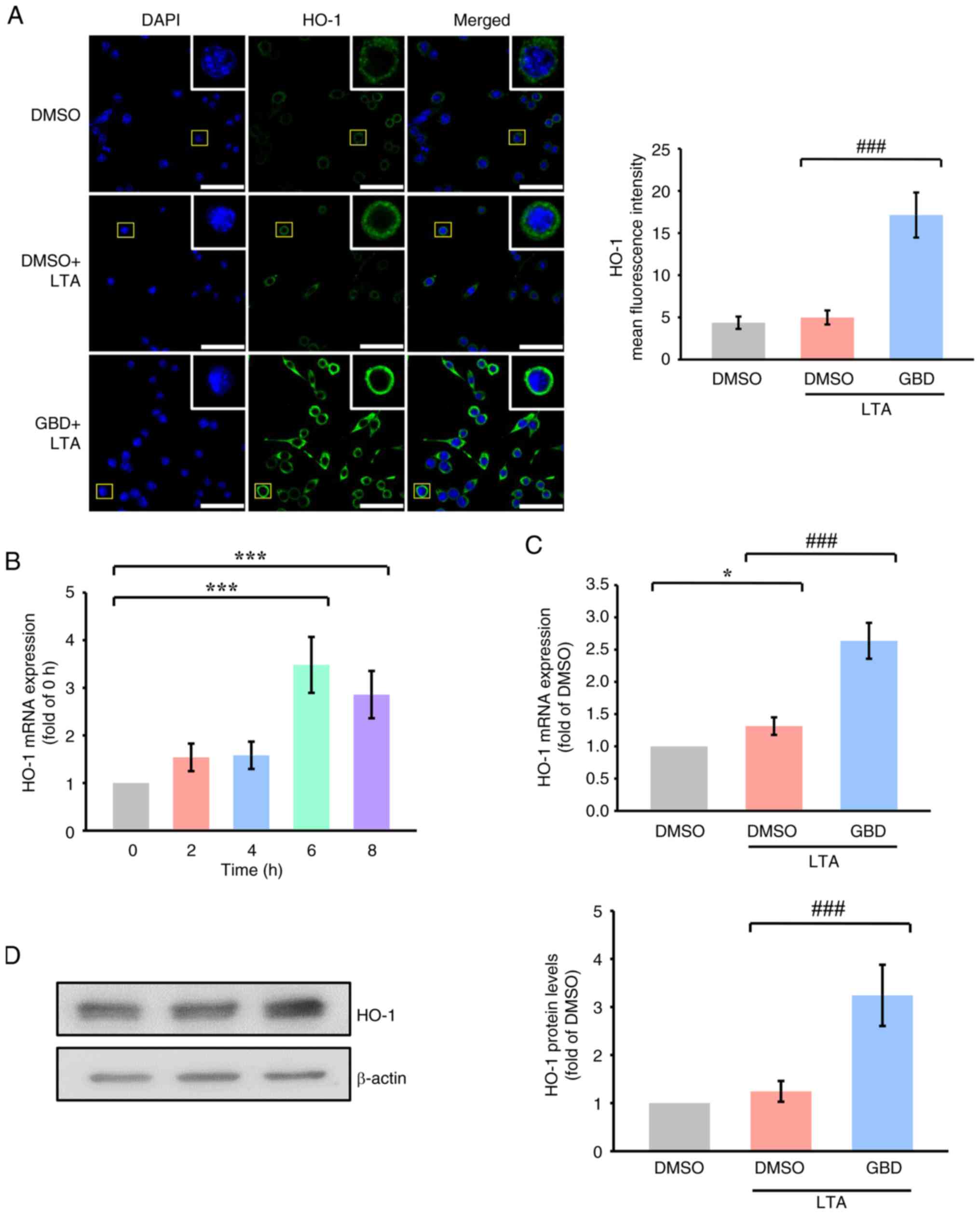
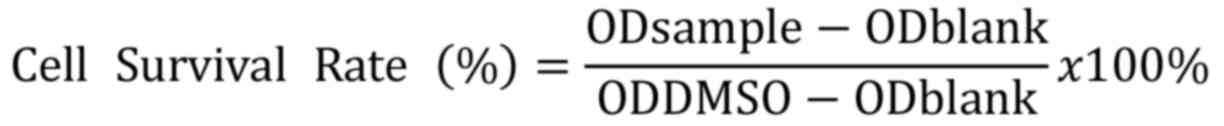|
1
|
Takeuchi O, Hoshino K, Kawai T, Sanjo H,
Takada H, Ogawa T, Takeda K and Akira S: Differential roles of TLR2
and TLR4 in recognition of gram-negative and gram-positive
bacterial cell wall components. Immunity. 11:443–451. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pai AB, Patel H, Prokopienko AJ, Alsaffar
H, Gertzberg N, Neumann P, Punjabi A and Johnson A: Lipoteichoic
acid from staphylococcus aureus induces lung endothelial cell
barrier dysfunction: Role of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species.
PLoS One. 7:e492092012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Percy MG and Gründling A: Lipoteichoic
acid synthesis and function in gram-positive bacteria. Annu Rev
Microbiol. 68:81–100. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hussell T and Bell TJ: Alveolar
macrophages: Plasticity in a tissue-specific context. Nat Rev
Immunol. 14:81–93. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Boyd AR, Shivshankar P, Jiang S, Berton MT
and Orihuela CJ: Age-related defects in TLR2 signaling diminish the
cytokine response by alveolar macrophages during murine
pneumococcal pneumonia. Exp Gerontol. 47:507–518. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu CF, Drocourt D, Puzo G, Wang JY and
Riviere M: Innate immune response of alveolar macrophage to house
dust mite allergen is mediated through TLR2/-4 co-activation. PLoS
One. 8:e759832013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Aggarwal S, Dimitropoulou C, Lu Q, Black
SM and Sharma S: Glutathione supplementation attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis
in a mouse model of acute lung injury. Front Physiol. 3:1612012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Birben E, Sahiner UM, Sackesen C, Erzurum
S and Kalayci O: Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense. World
Allergy Organ J. 5:9–19. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Malainou C, Abdin SM, Lachmann N, Matt U
and Herold S: Alveolar macrophages in tissue homeostasis,
inflammation, and infection: Evolving concepts of therapeutic
targeting. J Clin Invest. 133:e1705012023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Harvey CJ, Thimmulappa RK, Sethi S, Kong
X, Yarmus L, Brown RH, Feller-Kopman D, Wise R and Biswal S:
Targeting Nrf2 signaling improves bacterial clearance by alveolar
macrophages in patients with COPD and in a mouse model. Sci Transl
Med. 3:78ra322011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Itoh K, Chiba T, Takahashi S, Ishii T,
Igarashi K, Katoh Y, Oyake T, Hayashi N, Satoh K, Hatayama I, et
al: An Nrf2/small Maf heterodimer mediates the induction of phase
II detoxifying enzyme genes through antioxidant response elements.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 236:313–322. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ma Q: Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and
toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 53:401–426. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Itoh K, Wakabayashi N, Katoh Y, Ishii T,
Igarashi K, Engel JD and Yamamoto M: Keap1 represses nuclear
activation of antioxidant responsive elements by Nrf2 through
binding to the amino-terminal Neh2 domain. Genes Dev. 13:76–86.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ryter SW, Alam J and Choi AM: Heme
oxygenase-1/carbon monoxide: From basic science to therapeutic
applications. Physiol Rev. 86:583–650. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Meng X, Hu L and Li W: Baicalin
ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice by
suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation via the activation of
the Nrf2-mediated HO-1 signaling pathway. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch
Pharmacol. 392:1421–1433. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Luan R, Ding D and Yang J: The protective
effect of natural medicines against excessive inflammation and
oxidative stress in acute lung injury by regulating the Nrf2
signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol. 13:10390222022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shin J, Choi LS, Jeon HJ, Lee HM, Kim SH,
Kim KW, Ko W, Oh H and Park HS: Synthetic glabridin derivatives
inhibit LPS-induced inflammation via MAPKs and NF-κB Pathways in
RAW264.7 macrophages. Molecules. 28:21352023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shu L, Zhang Z, Wang N, Yin Q, Chao Y and
Ge X: Glabridin ameliorates hemorrhagic shock induced acute kidney
injury by activating Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol
Basis Dis. 1871:1678102025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Murrey MW, Ng IT and Pixley FJ: The role
of macrophage migratory behavior in development, homeostasis and
tumor invasion. Front Immunol. 15:14800842024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rodriguez-Morales P and Franklin RA:
Macrophage phenotypes and functions: Resolving inflammation and
restoring homeostasis. Trends Immunol. 44:986–998. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tran N and Mills EL: Redox regulation of
macrophages. Redox Biol. 72:1031232024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Breßer M, Siemens KD, Schneider L,
Lunnebach JE, Leven P, Glowka TR, Oberländer K, De Domenico E,
Schultze JL, Schmidt J, et al: Macrophage-induced enteric
neurodegeneration leads to motility impairment during gut
inflammation. EMBO Mol Med. 17:301–335. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gatica S, Fuentes B, Rivera-Asin E,
Ramírez-Céspedes P, Sepúlveda-Alfaro J, Catalán EA, Bueno SM,
Kalergis AM, Simon F, Riedel CA and Melo-Gonzalez F: Novel evidence
on sepsis-inducing pathogens: From laboratory to bedside. Front
Microbiol. 14:11982002023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
He J, Zhao Y, Fu Z, Chen L, Hu K, Lin X,
Wang N, Huang W, Xu Q, He S, et al: A novel tree shrew model of
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. J
Adv Res. 56:157–165. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang Y, Han Z, Jiang A, Wu D, Li S, Liu
Z, Wei Z, Yang Z and Guo C: Protective effects of pterostilbene on
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice by inhibiting
NF-κB and activating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways. Front Pharmacol.
11:5918362021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Knapp S, von Aulock S, Leendertse M,
Haslinger I, Draing C, Golenbock DT and van der Poll T:
Lipoteichoic acid-induced lung inflammation depends on TLR2 and the
concerted action of TLR4 and the platelet-activating factor
receptor. J Immunol. 180:3478–3484. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hoogerwerf JJ, de Vos AF, Bresser P, van
der Zee JS, Pater JM, de Boer A, Tanck M, Lundell DL, Her-Jenh C,
Draing C, et al: Lung inflammation induced by lipoteichoic acid or
lipopolysaccharide in humans. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 178:34–41.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hou F, Xiao K, Tang L and Xie L: Diversity
of macrophages in lung homeostasis and diseases. Front Immunol.
12:7539402021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Guilliams M, De Kleer I, Henri S, Post S,
Vanhoutte L, De Prijck S, Deswarte K, Malissen B, Hammad H and
Lambrecht BN: Alveolar macrophages develop from fetal monocytes
that differentiate into long-lived cells in the first week of life
via GM-CSF. J Exp Med. 210:1977–1992. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Röszer T: Understanding the biology of
self-renewing macrophages. Cells. 7:1032018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Guan F, Wang R, Yi Z, Luo P, Liu W, Xie Y,
Liu Z, Xia Z, Zhang H and Cheng Q: Tissue macrophages: Origin,
heterogenity, biological functions, diseases and therapeutic
targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 10:932025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ahmad S, Nasser W and Ahmad A: Epigenetic
mechanisms of alveolar macrophage activation in chemical-induced
acute lung injury. Front Immunol. 15:14889132024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mbawuike IN and Herscowitz HB: MH-S, a
murine alveolar macrophage cell line: Morphological, cytochemical,
and functional characteristics. J Leukoc Biol. 46:119–127. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Loboda A, Damulewicz M, Pyza E, Jozkowicz
A and Dulak J: Role of Nrf2/HO-1 system in development, oxidative
stress response and diseases: An evolutionarily conserved
mechanism. Cell Mol Life Sci. 73:3221–3247. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li N, Hao L, Li S, Deng J, Yu F, Zhang J,
Nie A and Hu X: The NRF-2/HO-1 signaling pathway: A promising
therapeutic target for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic
liver disease. J Inflamm Res. 17:8061–8083. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Su H, Wang Z, Zhou L, Liu D and Zhang N:
Regulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 axis by mesenchymal stem cells-derived
extracellular vesicles: Implications for disease treatment. Front
Cell Dev Biol. 12:13979542024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
O'Rourke SA, Shanley LC and Dunne A: The
Nrf2-HO-1 system and inflammaging. Front Immunol. 15:14570102024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Alam J and Cook JL: How many transcription
factors does it take to turn on the heme oxygenase-1 gene? Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 36:166–174. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Vijayan V, Wagener FADTG and Immenschuh S:
The macrophage heme-heme oxygenase-1 system and its role in
inflammation. Biochem Pharmacol. 153:159–167. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang L and He C: Nrf2-mediated
anti-inflammatory polarization of macrophages as therapeutic
targets for osteoarthritis. Front Immunol. 13:9671932022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Feng R, Morine Y, Ikemoto T, Imura S,
Iwahashi S, Saito Y and Shimada M: Nrf2 activation drive
macrophages polarization and cancer cell epithelial-mesenchymal
transition during interaction. Cell Commun Signal. 16:542018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Han H, Gao Y, Chen B, Xu H, Shi C, Wang X,
Liang Y, Wu Z, Wang Z, Bai Y and Wu C: Nrf2 inhibits M1 macrophage
polarization to ameliorate renal ischemia-reperfusion injury
through antagonizing NF-κB signaling. Int Immunopharmacol.
143:1133102024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jagadeesh ASV, Fang X, Kim SH,
Guillen-Quispe YN, Zheng J, Surh YJ and Kim SJ: Non-canonical vs.
canonical functions of heme oxygenase-1 in cancer. J Cancer Prev.
27:7–15. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Freitas A, Alves-Filho JC, Secco DD, Neto
AF, Ferreira SH, Barja-Fidalgo C and Cunha FQ: Heme
oxygenase/carbon monoxide-biliverdin pathway down regulates
neutrophil rolling, adhesion and migration in acute inflammation.
Br J Pharmacol. 149:345–354. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cheng P, Li S and Chen H: Macrophages in
lung injury, repair, and fibrosis. Cells. 10:4362021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chen S, Saeed AFUH, Liu Q, Jiang Q, Xu H,
Xiao GG, Rao L and Duo Y: Macrophages in immunoregulation and
therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 8:2072023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ngo V and Duennwald ML: Nrf2 and oxidative
stress: A general overview of mechanisms and implications in human
disease. Antioxidants (Basel). 11:23452022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Matthay MA and Zemans RL: The acute
respiratory distress syndrome: Pathogenesis and treatment. Annu Rev
Pathol. 6:147–163. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Barnes PJ: Inflammatory mechanisms in
patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 138:16–27. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gordon S and Plüddemann A: Macrophage
clearance of apoptotic cells: A critical assessment. Front Immunol.
9:1272018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wynn TA and Vannella KM: Macrophages in
tissue repair, regeneration, and fibrosis. Immunity. 44:450–462.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Gordon S, Plüddemann A and Martinez
Estrada F: Macrophage heterogeneity in tissues: Phenotypic
diversity and functions. Immunol Rev. 262:36–55. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Mantovani A, Biswas SK, Galdiero MR, Sica
A and Locati M: Macrophage plasticity and polarization in tissue
repair and remodelling. J Pathol. 229:176–185. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Murray PJ, Allen JE, Biswas SK, Fisher EA,
Gilroy DW, Goerdt S, Gordon S, Hamilton JA, Ivashkiv LB, Lawrence
T, et al: Macrophage activation and polarization: Nomenclature and
experimental guidelines. Immunity. 41:14–20. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Auffray C, Fogg D, Garfa M, Elain G,
Join-Lambert O, Kayal S, Sarnacki S, Cumano A, Lauvau G and
Geissmann F: Monitoring of blood vessels and tissues by a
population of monocytes with patrolling behavior. Science.
317:666–670. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Lawrence T and Natoli G: Transcriptional
regulation of macrophage polarization: Enabling diversity with
identity. Nat Rev Immunol. 11:750–761. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Xie L, Diao Z, Xia J, Zhang J, Xu Y, Wu Y,
Liu Z, Jiang C, Peng Y, Song Z, et al: Comprehensive evaluation of
metabolism and the contribution of the hepatic first-pass effect in
the bioavailability of glabridin in rats. J Agric Food Chem.
71:1944–1956. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|