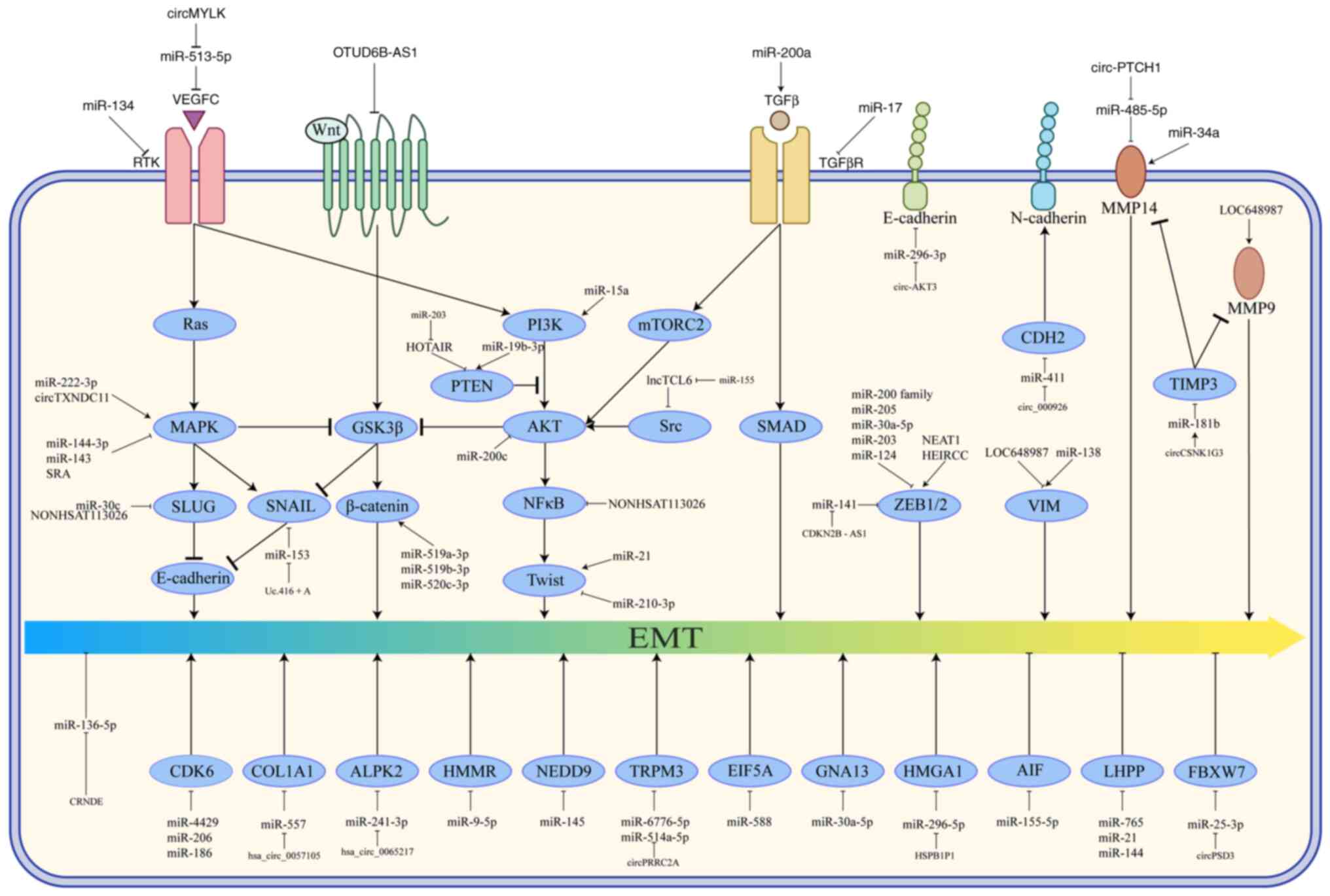
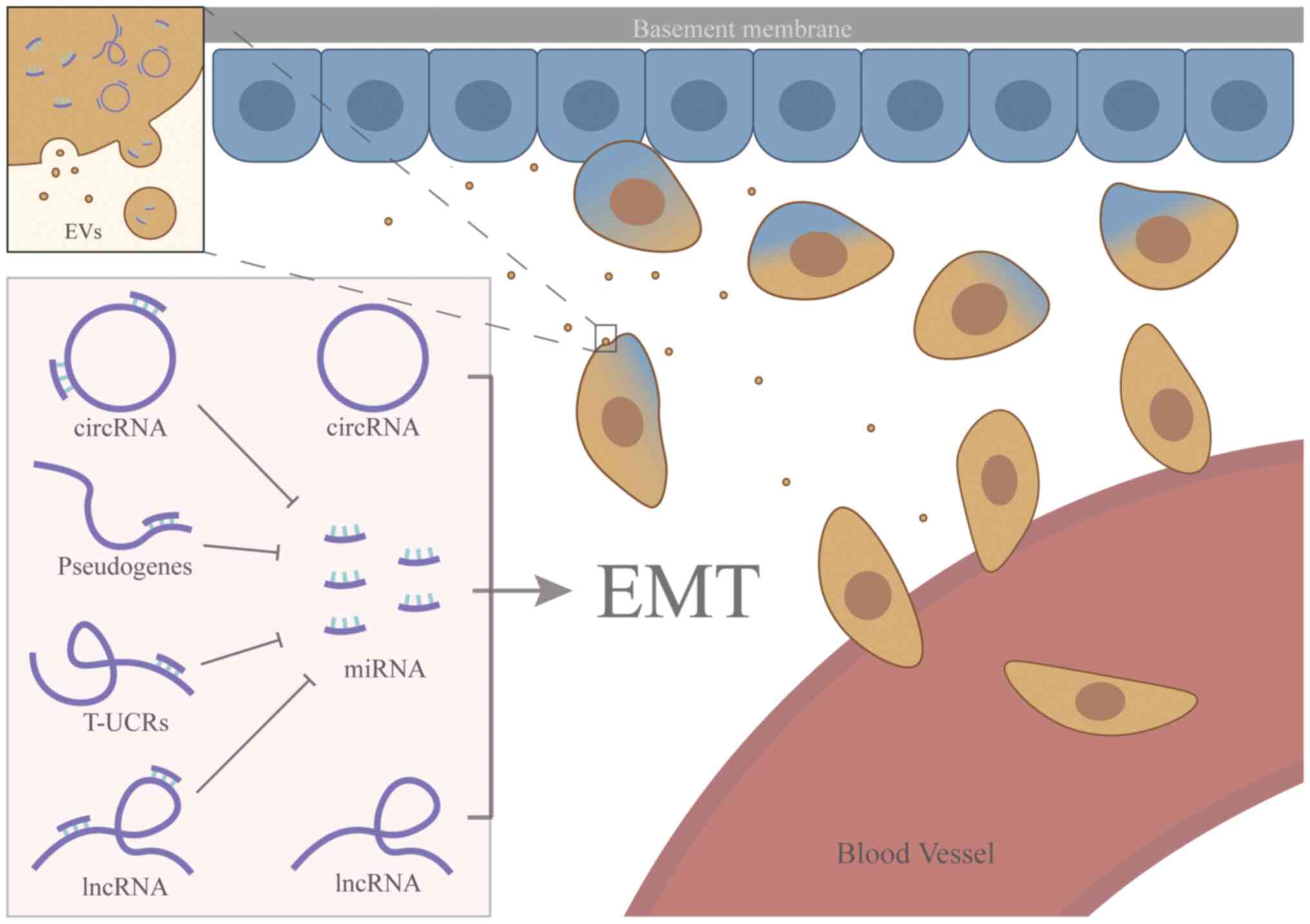
|
1
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263.
2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rouprêt M, Seisen T, Birtle AJ, Capoun O,
Compérat EM, Dominguez-Escrig JL, Gürses Andersson I, Liedberg F,
Mariappan P, Hugh Mostafid A, et al: European association of
urology guidelines on upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma:
2023 Update. Eur Urol. 84:49–64. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Motzer RJ, Jonasch E, Agarwal N, Alva A,
Baine M, Beckermann K, Carlo MI, Choueiri TK, Costello BA, Derweesh
IH, et al: Kidney cancer, version 3.2022, NCCN clinical practice
guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw. 20:71–90. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Young M, Jackson-Spence F, Beltran L, Day
E, Suarez C, Bex A, Powles T and Szabados B: Renal cell carcinoma.
Lancet. 404:476–491. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zheng X, Carstens JL, Kim J, Scheible M,
Kaye J, Sugimoto H, Wu CC, LeBleu VS and Kalluri R:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is dispensable for metastasis
but induces chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. Nature.
527:525–530. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Berkers J, Govaere O, Wolter P, Beuselinck
B, Schöffski P, van Kempen LC, Albersen M, Van den Oord J, Roskams
T, Swinnen J, et al: A possible role for microRNA-141
down-regulation in sunitinib resistant metastatic clear cell renal
cell carcinoma through induction of epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition and hypoxia resistance. J Urol. 189:1930–1938. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Galichon P, Finianos S and Hertig A:
EMT-MET in renal disease: Should we curb our enthusiasm? Cancer
Lett. 341:24–29. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fu XD: Non-coding RNA: A new frontier in
regulatory biology. Natl Sci Rev. 1:190–204. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xiao Y, Ren Y, Hu W, Paliouras AR, Zhang
W, Zhong L, Yang K, Su L, Wang P, Li Y, et al: Long non-coding
RNA-encoded micropeptides: Functions, mechanisms and implications.
Cell Death Discov. 10:4502024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Esteller M: Non-coding RNAs in human
disease. Nat Rev Genet. 12:861–874. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Slack FJ and Chinnaiyan AM: The role of
non-coding RNAs in oncology. Cell. 179:1033–1055. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Niu X, Lu D, Zhan W, Sun J, Li Y, Shi Y,
Yu K, Huang S, Ma X, Liu X and Liu B: miR-9-5p/HMMR regulates the
tumorigenesis and progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma
through EMT and JAK1/STAT1 signaling pathway. J Transl Med.
23:362025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen J, Zhong Y and Li L: miR-124 and
miR-203 synergistically inactivate EMT pathway via coregulation of
ZEB2 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). J Transl Med.
18:692020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang L, Yang G, Zhao D, Wang J, Bai Y,
Peng Q, Wang H, Fang R, Chen G, Wang Z, et al: CD103-positive CSC
exosome promotes EMT of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Role of
remote MiR-19b-3p. Mol Cancer. 18:862019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kulkarni P, Dasgupta P, Hashimoto Y,
Shiina M, Shahryari V, Tabatabai ZL, Yamamura S, Tanaka Y, Saini S,
Dahiya R and Majid S: A lncRNA TCL6-miR-155 interaction regulates
the Src-Akt-EMT network to mediate kidney cancer progression and
metastasis. Cancer Res. 81:1500–1512. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Saleeb R, Kim SS, Ding Q, Scorilas A, Lin
S, Khella HW, Boulos C, Ibrahim G and Yousef GM: The miR-200 family
as prognostic markers in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Urol
Oncol. 37:955–963. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang ZH, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Zheng SF, Feng
T, Tian X, Abudurexiti M, Wang ZD, Zhu WK, Su JQ, et al: The
function and mechanisms of action of circular RNAs in urologic
cancer. Mol Cancer. 22:612023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Javdani H, Mollaei H, Karimi F, Mahmoudi
S, Farahi A, Mirzaei-Parsa MJ and Shahabi A: Review article
epithelial to mesenchymal transition-associated microRNAs in breast
cancer. Mol Biol Rep. 49:9963–9973. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen RX, Chen X, Xia LP, Zhang JX, Pan ZZ,
Ma XD, Han K, Chen JW, Judde JG, Deas O, et al:
N6-methyladenosine modification of circNSUN2 facilitates
cytoplasmic export and stabilizes HMGA2 to promote colorectal liver
metastasis. Nat Commun. 10:46952019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Entezari M, Taheriazam A, Orouei S, Fallah
S, Sanaei A, Hejazi ES, Kakavand A, Rezaei S, Heidari H,
Behroozaghdam M, et al: LncRNA-miRNA axis in tumor progression and
therapy response: An emphasis on molecular interactions and
therapeutic interventions. Biomed Pharmacother. 154:1136092022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen B, Dragomir MP, Yang C, Li Q, Horst D
and Calin GA: Targeting non-coding RNAs to overcome cancer therapy
resistance. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 7:1212022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen L and Shan G: CircRNA in cancer:
Fundamental mechanism and clinical potential. Cancer Lett.
505:49–57. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xu Y, Liu H, Zhang Y, Luo J, Li H, Lai C,
Shi L and Heng B: piRNAs and circRNAs acting as diagnostic
biomarkers in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Sci Rep.
15:77742025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nieto MA: Epithelial plasticity: A common
theme in embryonic and cancer cells. Science. 342:12348502013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Glauert AM, Daniel MR, Lucy JA and Dingle
JT: Studies on the mode of action of excess of vitamin A. VII.
Changes in the fine structure of erythrocytes during haemolysis by
vitamin A. J Cell Biol. 17:111–121. 1963. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Royer C and Lu X: Epithelial cell
polarity: A major gatekeeper against cancer? Cell Death Differ.
18:1470–1477. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Han L, Luo H, Huang W, Zhang J, Wu D, Wang
J, Pi J, Liu C, Qu X, Liu H, et al: Modulation of the EMT/MET
process by E-cadherin in airway epithelia stress injury.
Biomolecules. 11:6692021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang SS, Jiang J, Liang XH and Tang YL:
Links between cancer stem cells and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. OncoTargets Ther. 8:2973–2980. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Banales JM, Marin JJG, Lamarca A,
Rodrigues PM, Khan SA, Roberts LR, Cardinale V, Carpino G, Andersen
JB, Braconi C, et al: Cholangiocarcinoma 2020: The next horizon in
mechanisms and management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
17:557–588. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan
A, Zhou AY, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, et al: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties
of stem cells. Cell. 133:704–715. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lan T, Luo M and Wei X: Mesenchymal
stem/stromal cells in cancer therapy. J Hematol Oncol. 14:1952021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Polyak K and Weinberg RA: Transitions
between epithelial and mesenchymal states: Acquisition of malignant
and stem cell traits. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:265–273. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Galassi C, Manic G, Esteller M, Galluzzi L
and Vitale I: Epigenetic regulation of cancer stemness. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 10:2432025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dongre A and Weinberg RA: New insights
into the mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
implications for cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 20:69–84. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fischer KR, Durrans A, Lee S, Sheng J, Li
F, Wong STC, Choi H, El Rayes T, Ryu S, Troeger J, et al:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is not required for lung
metastasis but contributes to chemoresistance. Nature. 527:472–476.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
De Las Rivas J, Brozovic A, Izraely S,
Casas-Pais A, Witz IP and Figueroa A: Cancer drug resistance
induced by EMT: Novel therapeutic strategies. Arch Toxicol.
95:2279–2297. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Spranger S, Koblish HK, Horton B, Scherle
PA, Newton R and Gajewski TF: Mechanism of tumor rejection with
doublets of CTLA-4, PD-1/PD-L1, or IDO blockade involves restored
IL-2 production and proliferation of CD8(+) T cells directly within
the tumor microenvironment. J Immunother Cancer. 2:32014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fridlender ZG, Sun J, Kim S, Kapoor V,
Cheng G, Ling L, Worthen GS and Albelda SM: Polarization of
tumor-associated neutrophil phenotype by TGF-beta: ‘N1’ versus ‘N2’
TAN. Cancer Cell. 16:183–194. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhai L, Spranger S, Binder DC, Gritsina G,
Lauing KL, Giles FJ and Wainwright DA: Molecular pathways:
Targeting IDO1 and other tryptophan dioxygenases for cancer
immunotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 21:5427–5433. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Taki M, Abiko K, Ukita M, Murakami R,
Yamanoi K, Yamaguchi K, Hamanishi J, Baba T, Matsumura N and Mandai
M: Tumor immune microenvironment during epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Clin Cancer Res. 27:4669–4679. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhang F, Wang H, Wang X, Jiang G, Liu H,
Zhang G, Wang H, Fang R, Bu X, Cai S and Du J: TGF-β induces
M2-like macrophage polarization via SNAIL-mediated suppression of a
pro-inflammatory phenotype. Oncotarget. 7:52294–52306. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mittal V: Epithelial mesenchymal
transition in tumor metastasis. Annu Rev Pathol. 13:395–412. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Aparicio LA, Blanco M, Castosa R, Concha
Á, Valladares M, Calvo L and Figueroa A: Clinical implications of
epithelial cell plasticity in cancer progression. Cancer Lett.
366:1–10. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lin S, Sun JG, Wu JB, Long HX, Zhu CH,
Xiang T, Ma H, Zhao ZQ, Yao Q, Zhang AM, et al: Aberrant microRNAs
expression in CD133+/CD326+ human lung
adenocarcinoma initiating cells from A549. Mol Cells. 33:277–283.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yuan J, Dong R, Liu F, Zhan L, Liu Y, Wei
J and Wang N: The miR-183/182/96 cluster functions as a potential
carcinogenic factor and prognostic factor in kidney renal clear
cell carcinoma. Exp Ther Med. 17:2457–2464. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bartel DP: Metazoan MicroRNAs. Cell.
173:20–51. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Seyhan AA: Trials and tribulations of
MicroRNA therapeutics. Int J Mol Sci. 25:14692024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hill M and Tran N: miRNA interplay:
Mechanisms and consequences in cancer. Dis Model Mech.
14:dmm0476622021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ransohoff JD, Wei Y and Khavari PA: The
functions and unique features of long intergenic non-coding RNA.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 19:143–157. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
McCabe EM and Rasmussen TP: lncRNA
involvement in cancer stem cell function and epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions. Semin Cancer Biol. 75:38–48. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yoon JH, Abdelmohsen K and Gorospe M:
Post-transcriptional gene regulation by long noncoding RNA. J Mol
Biol. 425:3723–3730. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wang KC and Chang HY: Molecular mechanisms
of long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell. 43:904–914. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kristensen LS, Andersen MS, Stagsted LVW,
Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB and Kjems J: The biogenesis, biology and
characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 20:675–691. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Mauer C, Paz S and Caputi M: Backsplicing
of the HIV-1 transcript generates multiple circRNAs to promote
viral replication. Npj Viruses. 3:212025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ma Y, Wang T, Zhang X, Wang P and Long F:
The role of circular RNAs in regulating resistance to cancer
immunotherapy: Mechanisms and implications. Cell Death Dis.
15:3122024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen
JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK and Kjems J: Natural RNA circles function
as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 495:384–388. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F,
Krueger J, Rybak A, Maier L, Mackowiak SD, Gregersen LH, Munschauer
M, et al: Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with
regulatory potency. Nature. 495:333–338. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Thamjamrassri P and Ariyachet C: Circular
RNAs in cell cycle regulation of cancers. Int J Mol Sci.
25:60942024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Hu X, Wu D, He X, Zhao H, He Z, Lin J,
Wang K, Wang W, Pan Z, Lin H and Wang M: circGSK3β promotes
metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by augmenting
β-catenin signaling. Mol Cancer. 18:1602019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Fang L, Du WW, Awan FM, Dong J and Yang
BB: The circular RNA circ-Ccnb1 dissociates Ccnb1/Cdk1 complex
suppressing cell invasion and tumorigenesis. Cancer Lett.
459:216–226. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Fei T, Chen Y, Xiao T, Li W, Cato L, Zhang
P, Cotter MB, Bowden M, Lis RT, Zhao SG, et al: Genome-wide CRISPR
screen identifies HNRNPL as a prostate cancer dependency regulating
RNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:E5207–E5215. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Yang Y, Fan X, Mao M, Song X, Wu P, Zhang
Y, Jin Y, Yang Y, Chen LL, Wang Y, et al: Extensive translation of
circular RNAs driven by N6-methyladenosine. Cell Res.
27:626–641. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry
SC, Tsykin A, Farshid G, Vadas MA, Khew-Goodall Y and Goodall GJ:
The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal
transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol. 10:593–601.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Lu R, Ji Z, Li X, Qin J, Cui G, Chen J,
Zhai Q, Zhao C, Zhang W and Yu Z: Tumor suppressive microRNA-200a
inhibits renal cell carcinoma development by directly targeting
TGFB2. Tumour Biol. 36:6691–6700. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wang X, Chen X, Wang R, Xiao P, Xu Z, Chen
L, Hang W, Ruan A, Yang H and Zhang X: microRNA-200c modulates the
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human renal cell carcinoma
metastasis. Oncol Rep. 30:643–650. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Xu XW, Li S, Yin F and Qin LL: Expression
of miR-205 in renal cell carcinoma and its association with
clinicopathological features and prognosis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol
Sci. 22:662–670. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Qiu M, Liang Z, Chen L, Tan G, Wang K, Liu
L, Liu J and Chen H: MicroRNA-429 suppresses cell proliferation,
epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and metastasis by direct
targeting of BMI1 and E2F3 in renal cell carcinoma. Urol Oncol.
33:332.e9–e18. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Machackova T, Mlcochova H, Stanik M,
Dolezel J, Fedorko M, Pacik D, Poprach A, Svoboda M and Slaby O:
MiR-429 is linked to metastasis and poor prognosis in renal cell
carcinoma by affecting epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Tumour
Biol. 37:14653–14658. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Chen Z, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Feng Z, Wei J,
Lu J, Fang Y, Liang Y, Cen J, Pan Y, et al: The putative tumor
suppressor microRNA-30a-5p modulates clear cell renal cell
carcinoma aggressiveness through repression of ZEB2. Cell Death
Dis. 8:e28592017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Liu W, Li H, Wang Y, Zhao X, Guo Y, Jin J
and Chi R: MiR-30b-5p functions as a tumor suppressor in cell
proliferation, metastasis and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
by targeting G-protein subunit α-13 in renal cell carcinoma. Gene.
626:275–281. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Han N, Li H and Wang H: MicroRNA-203
inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration, and invasion
of renal cell carcinoma cells via the inactivation of the PI3K/AKT
signaling pathway by inhibiting CAV1. Cell Adhes Migr. 14:227–241.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Yamasaki T, Seki N, Yamada Y, Yoshino H,
Hidaka H, Chiyomaru T, Nohata N, Kinoshita T, Nakagawa M and
Enokida H: Tumor suppressive microRNA-138 contributes to cell
migration and invasion through its targeting of vimentin in renal
cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 41:805–817. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Dasgupta P, Kulkarni P, Majid S, Hashimoto
Y, Shiina M, Shahryari V, Bhat NS, Tabatabai L, Yamamura S, Saini
S, et al: LncRNA CDKN2B-AS1/miR-141/cyclin D network regulates
tumor progression and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma. Cell
Death Dis. 11:6602020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Lu R, Ji Z, Li X, Zhai Q, Zhao C, Jiang Z,
Zhang S, Nie L and Yu Z: miR-145 functions as tumor suppressor and
targets two oncogenes, ANGPT2 and NEDD9, in renal cell carcinoma. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 140:387–397. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Lichner Z, Saleh C, Subramaniam V,
Seivwright A, Prud'homme GJ and Yousef GM: miR-17 inhibition
enhances the formation of kidney cancer spheres with stem
cell/tumor initiating cell properties. Oncotarget. 6:5567–5581.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Liu Y, Zhang M, Qian J, Bao M, Meng X,
Zhang S, Zhang L, Zhao R, Li S, Cao Q, et al: miR-134 functions as
a tumor suppressor in cell proliferation and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by targeting KRAS in renal
cell carcinoma cells. DNA Cell Biol. 34:429–436. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Liu F, Chen N, Xiao R, Wang W and Pan Z:
miR-144-3p serves as a tumor suppressor for renal cell carcinoma
and inhibits its invasion and metastasis by targeting MAP3K8.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 480:87–93. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Dasgupta P, Kulkarni P, Majid S, Shahryari
V, Hashimoto Y, Bhat NS, Shiina M, Deng G, Saini S, Tabatabai ZL,
et al: MicroRNA-203 inhibits long noncoding RNA HOTAIR and
regulates tumorigenesis through epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition pathway in renal cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther.
17:1061–1069. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Dong JS, Wu B and Zha ZL: MicroRNA-588
regulates migration capacity and invasiveness of renal cancer cells
by targeting EIF5A2. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:10248–10256.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Pan H, Hong Y, Yu B, Li L and Zhang X:
miR-4429 inhibits tumor progression and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition via targeting CDK6 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 34:334–341. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Guo Z, Jia H and Ge J: MiR-206 suppresses
proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of renal cell
carcinoma by inhibiting CDK6 expression. Hum Cell. 33:750–758.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Guo Z, Lv X and Jia H: MiR-186 represses
progression of renal cell cancer by directly targeting CDK6. Hum
Cell. 33:759–767. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Xu B, Wang C, Wang YL, Chen SQ, Wu JP, Zhu
WD, Wang CY, Guan H, Guan C, You ZH and Chen M: miR-143 inhibits
renal cell carcinoma cells metastatic potential by suppressing
ABL2. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 36:592–598. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Sekino Y, Sakamoto N, Goto K, Honma R,
Shigematsu Y, Quoc TP, Sentani K, Oue N, Teishima J, Kawakami F, et
al: Uc.416 + A promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
through miR-153 in renal cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 18:9522018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Xue D, Wang H, Chen Y, Shen D, Lu J, Wang
M, Zebibula A, Xu L, Wu H, Li G and Xia L: Circ-AKT3 inhibits clear
cell renal cell carcinoma metastasis via altering
miR-296-3p/E-cadherin signals. Mol Cancer. 18:1512019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Chen Z, Wang Z, Chen Z, Fu F, Huang X and
Huang Z: Pseudogene HSPB1P1 contributes to renal cell carcinoma
proliferation and metastasis by targeting miR-296-5p to regulate
HMGA1 expression. Cell Biol Int. 45:2479–2489. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Wang YB, Zhang ZL, Shao JK and Li RS:
Effect of miR-186 targeting E-cadherin on proliferation and
metastasis of renal cell carcinoma. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi.
101:1020–1025. 2021.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Sharma A, Singh P, Jha R, Almatroodi SA,
Alrumaihi F, Rahmani AH, Alharbi HO, Dohare R and Syed MA:
Exploring the role of miR-200 family in regulating CX3CR1 and CXCR1
in lung adenocarcinoma tumor microenvironment: Implications for
therapeutic intervention. Sci Rep. 13:163332023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
He L, Jiang Z, Wang J and Han Z: Mechanism
of miR-200b-3p-induced FOSL2 inhibition of endometrial cancer cell
proliferation and metastasis. Sci Rep. 15:157422025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Jo H, Shim K and Jeoung D: Potential of
the miR-200 family as a target for developing anti-cancer
therapeutics. Int J Mol Sci. 23:58812022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Castro-Vega LJ, Jouravleva K, Liu WY,
Martinez C, Gestraud P, Hupé P, Servant N, Albaud B, Gentien D, Gad
S, et al: Telomere crisis in kidney epithelial cells promotes the
acquisition of a microRNA signature retrieved in aggressive renal
cell carcinomas. Carcinogenesis. 34:1173–1180. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Richardsen E, Andersen S, Melbø-Jørgensen
C, Rakaee M, Ness N, Al-Saad S, Nordby Y, Pedersen MI, Dønnem T,
Bremnes RM and Busund LT: MicroRNA 141 is associated to outcome and
aggressive tumor characteristics in prostate cancer. Sci Rep.
9:3862019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Yang C, Dou R, Yin T and Ding J:
MiRNA-106b-5p in human cancers: Diverse functions and promising
biomarker. Biomed Pharmacother. 127:1102112020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Mlcochova H, Machackova T, Rabien A,
Radova L, Fabian P, Iliev R, Slaba K, Poprach A, Kilic E, Stanik M,
et al: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition-associated microRNA/mRNA
signature is linked to metastasis and prognosis in clear-cell renal
cell carcinoma. Sci Rep. 6:318522016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Han W, Cui H, Liang J and Su X: Role of
MicroRNA-30c in cancer progression. J Cancer. 11:2593–2601. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Huang J, Yao X, Zhang J, Dong B, Chen Q,
Xue W, Xue W, Liu D and Huang Y: Hypoxia-induced downregulation of
miR-30c promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human renal
cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 104:1609–1617. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Butz H, Szabó PM, Khella HWZ, Nofech-Mozes
R, Patocs A and Yousef GM: miRNA-target network reveals miR-124as a
key miRNA contributing to clear cell renal cell carcinoma
aggressive behaviour by targeting CAV1 and FLOT1. Oncotarget.
6:12543–12557. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
He S, Zhang G, Dong H, Ma M and Sun Q:
miR-203 facilitates tumor growth and metastasis by targeting
fibroblast growth factor 2 in breast cancer. OncoTargets Ther.
9:6203–6210. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Grange C, Tapparo M, Collino F, Vitillo L,
Damasco C, Deregibus MC, Tetta C, Bussolati B and Camussi G:
Microvesicles released from human renal cancer stem cells stimulate
angiogenesis and formation of lung premetastatic niche. Cancer Res.
71:5346–5356. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Li DY, Lin FF, Li GP and Zeng FC: Exosomal
microRNA-15a from ACHN cells aggravates clear cell renal cell
carcinoma via the BTG2/PI3K/AKT axis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci.
37:973–982. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Cao J, Liu J, Xu R, Zhu X, Liu L and Zhao
X: MicroRNA-21 stimulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and
tumorigenesis in clear cell renal cells. Mol Med Rep. 13:75–82.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Wu TK, Wei CW, Pan YR, Hsu RJ, Wu CY and
Yu YL: The uremic toxin p-cresyl sulfate induces proliferation and
migration of clear cell renal cell carcinoma via microRNA-21/
HIF-1α axis signals. Sci Rep. 9:32072019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Lyu J, Zhu Y and Zhang Q: An increased
level of MiR-222-3p is associated with TMP2 suppression, ERK
activation and is associated with metastasis and a poor prognosis
in renal clear cell carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 28:141–149. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Gorka J, Marona P, Kwapisz O, Waligórska
A, Pospiech E, Dobrucki JW, Rys J, Jura J and Miekus K: MCPIP1
inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway activity and modulates
epithelial-mesenchymal transition during clear cell renal cell
carcinoma progression by targeting miRNAs. Oncogene. 40:6720–6735.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Lei QQ, Huang Y, Li B, Han L and Lv C:
MiR-155-5p promotes metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition of renal cell carcinoma by targeting apoptosis-inducing
factor. Int J Biol Markers. 36:20–27. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Meng K, Li Z and Cui X: Three LHPP
gene-targeting co-expressed microRNAs (microRNA-765, microRNA-21,
and microRNA-144) promote proliferation, epithelial-mesenchymal
transition, invasion, and are independent prognostic biomarkers in
renal cell carcinomas patients. J Clin Lab Anal. 35:e240772021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Landolt L, Eikrem Ø, Strauss P, Scherer A,
Lovett DH, Beisland C, Finne K, Osman T, Ibrahim MM, Gausdal G, et
al: Clear cell renal cell carcinoma is linked to
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and to fibrosis. Physiol Rep.
5:e133052017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Yoshino H, Yonemori M, Miyamoto K,
Tatarano S, Kofuji S, Nohata N, Nakagawa M and Enokida H:
microRNA-210-3p depletion by CRISPR/Cas9 promoted tumorigenesis
through revival of TWIST1 in renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget.
8:20881–20894. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Xiong J, Liu Y, Jiang L, Zeng Y and Tang
W: High expression of long non-coding RNA lncRNA-ATB is correlated
with metastases and promotes cell migration and invasion in renal
cell carcinoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 46:378–384. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
He X, Liu H, Guo F, Feng Y, Gao Y, Sun F,
Song B, Lu H and Li Y: Long non-coding RNA Z38 promotes cell
proliferation and metastasis in human renal cell carcinoma. Mol Med
Rep. 16:5489–5494. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Ning L, Li Z, Wei D, Chen H and Yang C:
LncRNA, NEAT1 is a prognosis biomarker and regulates cancer
progression via epithelial-mesenchymal transition in clear cell
renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 19:75–83. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Xiong J, Liu Y, Luo S, Jiang L, Zeng Y,
Chen Z, Shi X, Lv B and Tang W: High expression of the long
non-coding RNA HEIRCC promotes renal cell carcinoma metastasis by
inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget.
8:6555–6563. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Du Y, Kong C, Zhu Y, Yu M, Li Z, Bi J, Li
Z, Liu X, Zhang Z and Yu X: Knockdown of SNHG15 suppresses renal
cell carcinoma proliferation and EMT by regulating the NF-κB
signaling pathway. Int J Oncol. 53:384–394. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Su Y, Zhou L, Yu Q, Lu J and Liu W: Long
non-coding RNA LOC648987 promotes proliferation and metastasis of
renal cell carcinoma by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 20:15330338219978342021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Yu H, Liu J, Zhang Z, Zhu Y, Bi J and Kong
C: SNHG12 promotes carcinogenesis of human renal cell cancer via
functioning as a competing endogenous RNA and sponging miR-30a-3p.
J Cell Mol Med. 25:4696–4708. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Zhang Y, Lan X, Wang Y, Liu C and Cui T:
CRNDE mediates the viability and epithelial-mesenchymal transition
of renal cell carcinoma via miR-136-5p. J Recept Signal Transduct
Res. 41:234–244. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Shao IH, Peng PH, Wu HH, Chen JL, Lai JCY,
Chang JS, Wu HT, Wu KJ, Pang ST and Hsu KW: RP11-367G18.1 V2
enhances clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression via induction
of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Med. 12:9788–9801.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, Kim J, Horlings
HM, Wong DJ, Tsai MC, Hung T, Argani P, Rinn JL, et al: Long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer
metastasis. Nature. 464:1071–1076. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Zhang A, Zhao JC, Kim J, Fong KW, Yang YA,
Chakravarti D, Mo YY and Yu J: LncRNA HOTAIR enhances the
androgen-receptor-mediated transcriptional program and drives
castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cell Rep. 13:209–221. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Pu Y, Dong Z, Xia Y, Zhang M, Song J, Han
J and Liu H: LncRNA NONHSAT113026 represses renal cell carcinoma
tumorigenesis through interacting with NF-κB/p50 and SLUG. Biomed
Pharmacother. 118:1093822019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Wang G, Zhang ZJ, Jian WG, Liu PH, Xue W,
Wang TD, Meng YY, Yuan C, Li HM, Yu YP, et al: Novel long noncoding
RNA OTUD6B-AS1 indicates poor prognosis and inhibits clear cell
renal cell carcinoma proliferation via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway. Mol Cancer. 18:152019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Zhang C, Zhu N, Liu C, Wu H, Yin Y, Shi Y,
Liao D and Qin L: Steroid receptor RNA activator inhibits the
migration, invasion and stemness characteristics of renal cell
carcinoma cells. Int J Mol Med. 46:1765–1776. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Singh D, Kesharwani P, Alhakamy NA and
Siddique HR: Accentuating CircRNA-miRNA-transcription factors axis:
A conundrum in cancer research. Front Pharmacol. 12:7848012022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Rong D, Sun H, Li Z, Liu S, Dong C, Fu K,
Tang W and Cao H: An emerging function of circRNA-miRNAs-mRNA axis
in human diseases. Oncotarget. 8:73271–73281. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Zhang D, Yang XJ, Luo QD, Fu DL, Li ZL,
Zhang P and Chong T: Down-regulation of circular RNA_000926
attenuates renal cell carcinoma progression through
miRNA-411-dependent CDH2 inhibition. Am J Pathol. 189:2469–8246.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Li J, Huang C, Zou Y, Yu J and Gui Y:
Circular RNA MYLK promotes tumour growth and metastasis via
modulating miR-513a-5p/VEGFC signalling in renal cell carcinoma. J
Cell Mol Med. 24:6609–6621. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Li W, Yang FQ, Sun CM, Huang JH, Zhang HM,
Li X, Wang GC, Zhang N, Che JP, Zhang WT, et al: circPRRC2A
promotes angiogenesis and metastasis through epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and upregulates TRPM3 in renal cell carcinoma.
Theranostics. 10:4395–4409. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Liu H, Hu G, Wang Z, Liu Q, Zhang J, Chen
Y, Huang Y, Xue W, Xu Y and Zhai W: circPTCH1 promotes invasion and
metastasis in renal cell carcinoma via regulating miR-485-5p/MMP14
axis. Theranostics. 10:10791–10807. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Yan JS, Chen Q, Li YL and Gao YQ:
Hsa_circ_0065217 promotes growth and metastasis of renal cancer
through regulating the miR-214-3p-ALPK2 axis. Cell Cycle.
20:2519–2530. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Li W, Song YYY, Rao T, Yu WM, Ruan Y, Ning
JZ, Yao XB, Yang SY and Cheng F: CircCSNK1G3 up-regulates miR-181b
to promote growth and metastasis via TIMP3-mediated epithelial to
mesenchymal transitions in renal cell carcinoma. J Cell Mol Med.
26:1729–1741. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Cen J, Liang Y, Feng Z, Chen X, Chen J,
Wang Y, Zhu J, Xu Q, Shu G, Zheng W, et al: Hsa_circ_0057105
modulates a balance of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
ferroptosis vulnerability in renal cell carcinoma. Clin Transl Med.
13:e13392023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Xie X, Li H, Gao C, Lai Y, Liang J, Chen
Z, Chen Z, Heng B, Yao N and Lai C: Downregulation of circular RNA
circPSD3 promotes metastasis by modulating FBXW7 expression in
clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J Oncol. 2022:50846312022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Yang CY, Wang J, Zhang JQ and Cai HM:
Human circular RNA hsa_circRNA_101705 (circTXNDC11) regulates renal
cancer progression by regulating MAPK/ERK pathway. Bioengineered.
12:4432–4441. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Mighell AJ, Smith NR, Robinson PA and
Markham AF: Vertebrate pseudogenes. FEBS Lett. 468:109–914. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Ayubi E, Shahbazi F and Khazaei S:
Decomposing difference in the kidney cancer burden measures between
1990 and 2019 based on the global burden of disease study. Sci Rep.
14:103902024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Choi J, Bang S, Suh J, Choi CI, Song W,
Yuk HD, Lee CH, Kang M, Choo SH, Kim JK, et al: Survival pattern of
metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients according to WHO/ISUP
grade: A long-term multi-institutional study. Sci Rep. 14:47402024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Logan JE, Rampersaud EN, Sonn GA, Chamie
K, Belldegrun AS, Pantuck AJ, Slamon DJ and Kabbinavar FF: Systemic
therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A review and update.
Rev Urol. 14:65–78. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Yang J, Antin P, Berx G, Blanpain C,
Brabletz T, Bronner M, Campbell K, Cano A, Casanova J, Christofori
G, et al: Guidelines and definitions for research on
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
21:341–352. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Zhang L, Lin H, Liang J, Liu X, Zhang C,
Man Q, Li R, Zhao Y and Liu B: Programmed death-ligand 1 regulates
ameloblastoma growth and recurrence. Int J Oral Sci. 17:292025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Zhong W and Sun T: Editorial:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) as a therapeutic target in
cancer, volume II. Front Oncol. 13:12188552023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Mao W, Wang K, Xu B, Zhang H, Sun S, Hu Q,
Zhang L, Liu C, Chen S, Wu J, et al: ciRS-7 is a prognostic
biomarker and potential gene therapy target for renal cell
carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 20:1422021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Silva-Santos RM, Costa-Pinheiro P, Luis A,
Antunes L, Lobo F, Oliveira J, Henrique R and Jerónimo C: MicroRNA
profile: A promising ancillary tool for accurate renal cell tumour
diagnosis. Br J Cancer. 109:2646–2653. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Zhang YP, Cheng YB, Li S, Zhao N and Zhu
ZH: An epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related long non-coding
RNA signature to predict overall survival and immune
microenvironment in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma.
Bioengineered. 12:555–564. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Jin J, Xie Y, Zhang JS, Wang JQ, Dai SJ,
He WF, Li SY, Ashby CR Jr, Chen ZS and He Q: Sunitinib resistance
in renal cell carcinoma: From molecular mechanisms to predictive
biomarkers. Drug Resist Updat. 67:1009292023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Enuka Y, Lauriola M, Feldman ME, Sas-Chen
A, Ulitsky I and Yarden Y: Circular RNAs are long-lived and display
only minimal early alterations in response to a growth factor.
Nucleic Acids Res. 44:1370–1383. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Chen YG, Chen R, Ahmad S, Verma R, Kasturi
SP, Amaya L, Broughton JP, Kim J, Cadena C, Pulendran B, et al:
N6-methyladenosine modification controls circular RNA immunity. Mol
Cell. 76:96–109.e9. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Wesselhoeft RA, Kowalski PS, Parker-Hale
FC, Huang Y, Bisaria N and Anderson DG: RNA circularization
diminishes immunogenicity and can extend translation duration in
vivo. Mol Cell. 74:508–520.e4. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Li H, Peng K, Yang K, Ma W, Qi S, Yu X, He
J, Lin X and Yu G: Circular RNA cancer vaccines drive immunity in
hard-to-treat malignancies. Theranostics. 12:6422–6436. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Liu Y, Wu W, Cai C, Zhang H, Shen H and
Han Y: Patient-derived xenograft models in cancer therapy:
Technologies and applications. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
8:1602023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Zhu J, Ding Y and Xu Q: Exosomal noncoding
RNAs in renal cell carcinoma: Mechanisms, roles, and therapeutic
potential. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 213:1048292025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Yu X, Du Z, Zhu P and Liao B: Diagnostic,
prognostic, and therapeutic potential of exosomal microRNAs in
renal cancer. Pharmacol Rep. 76:273–286. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|