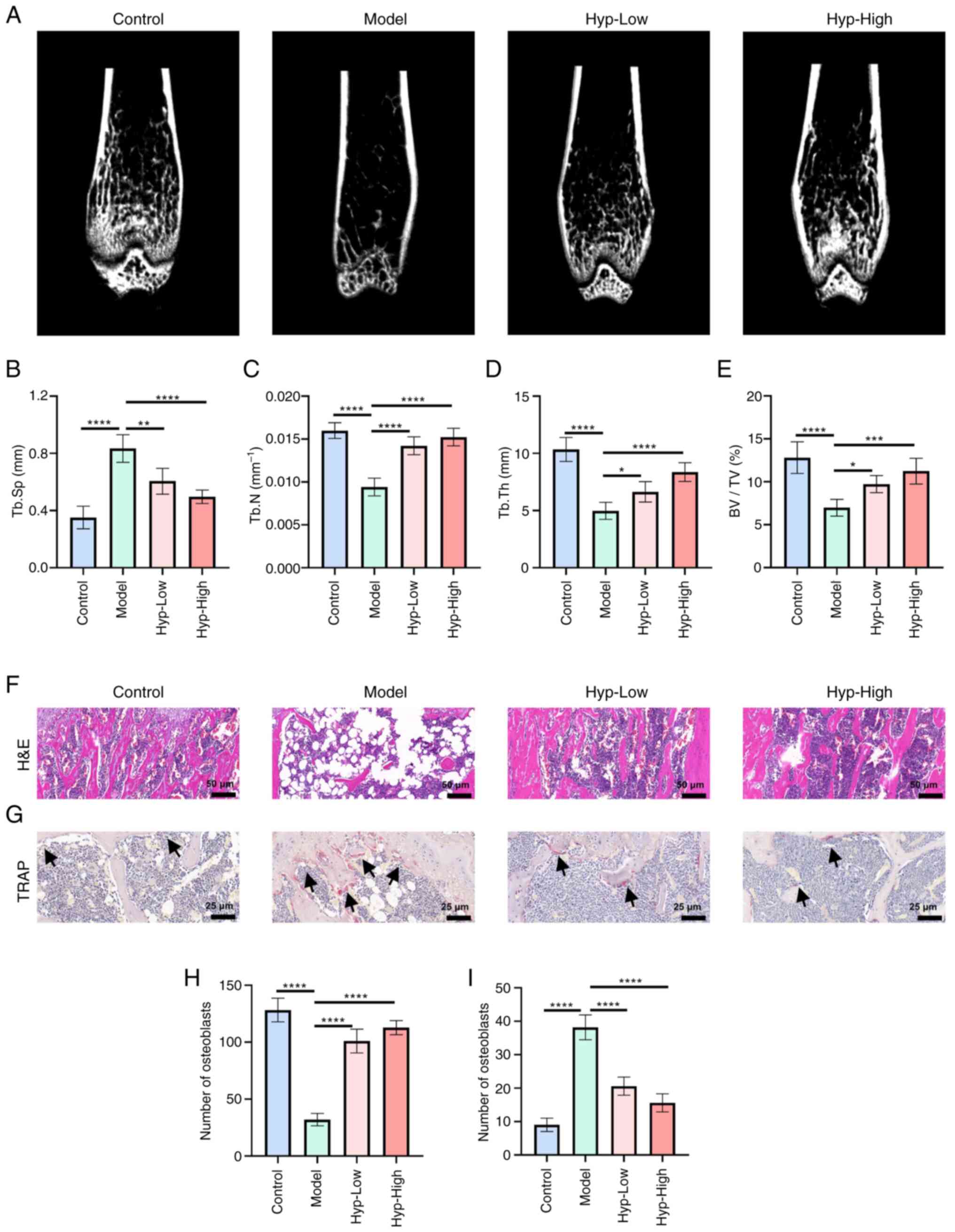
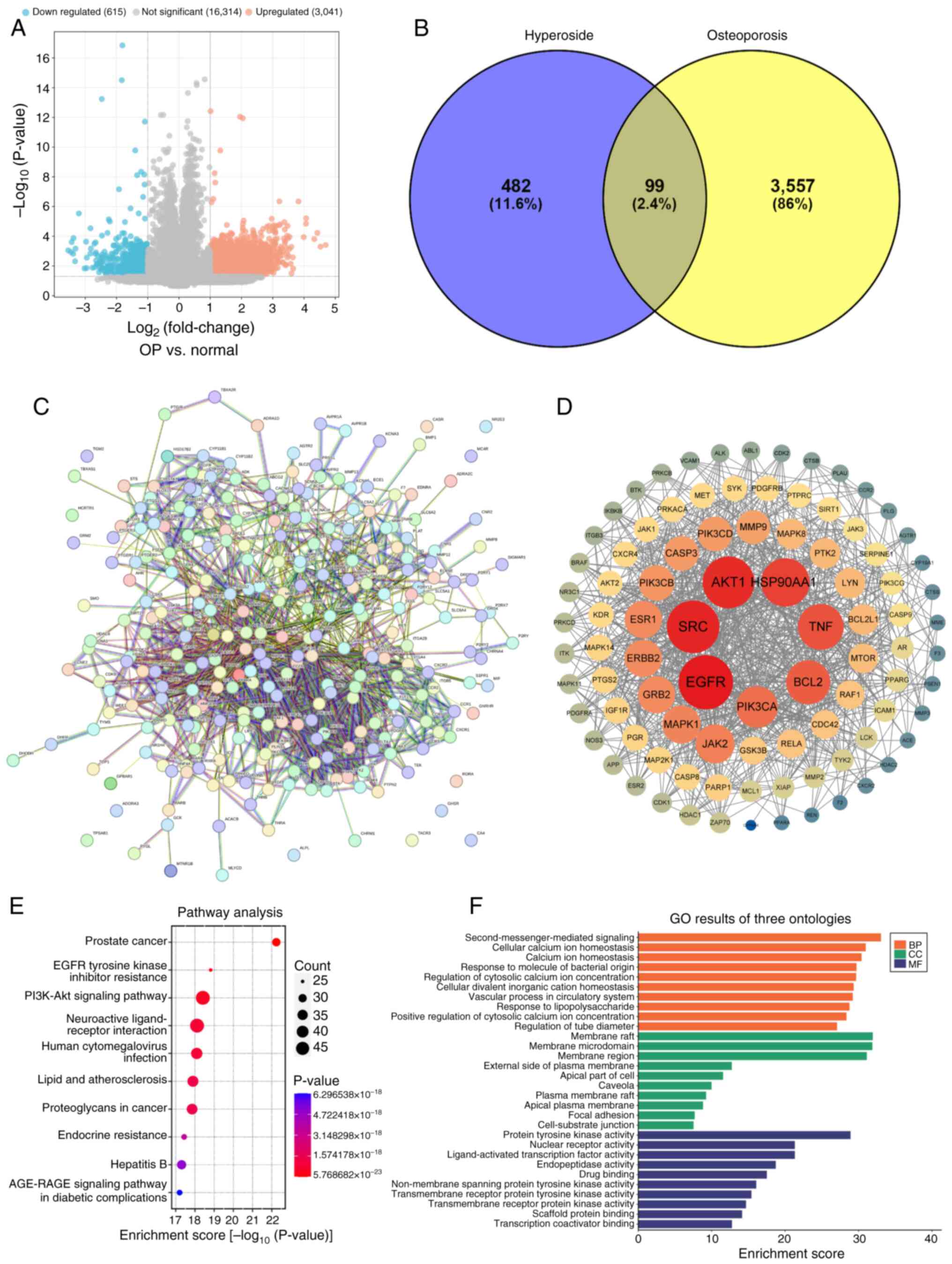
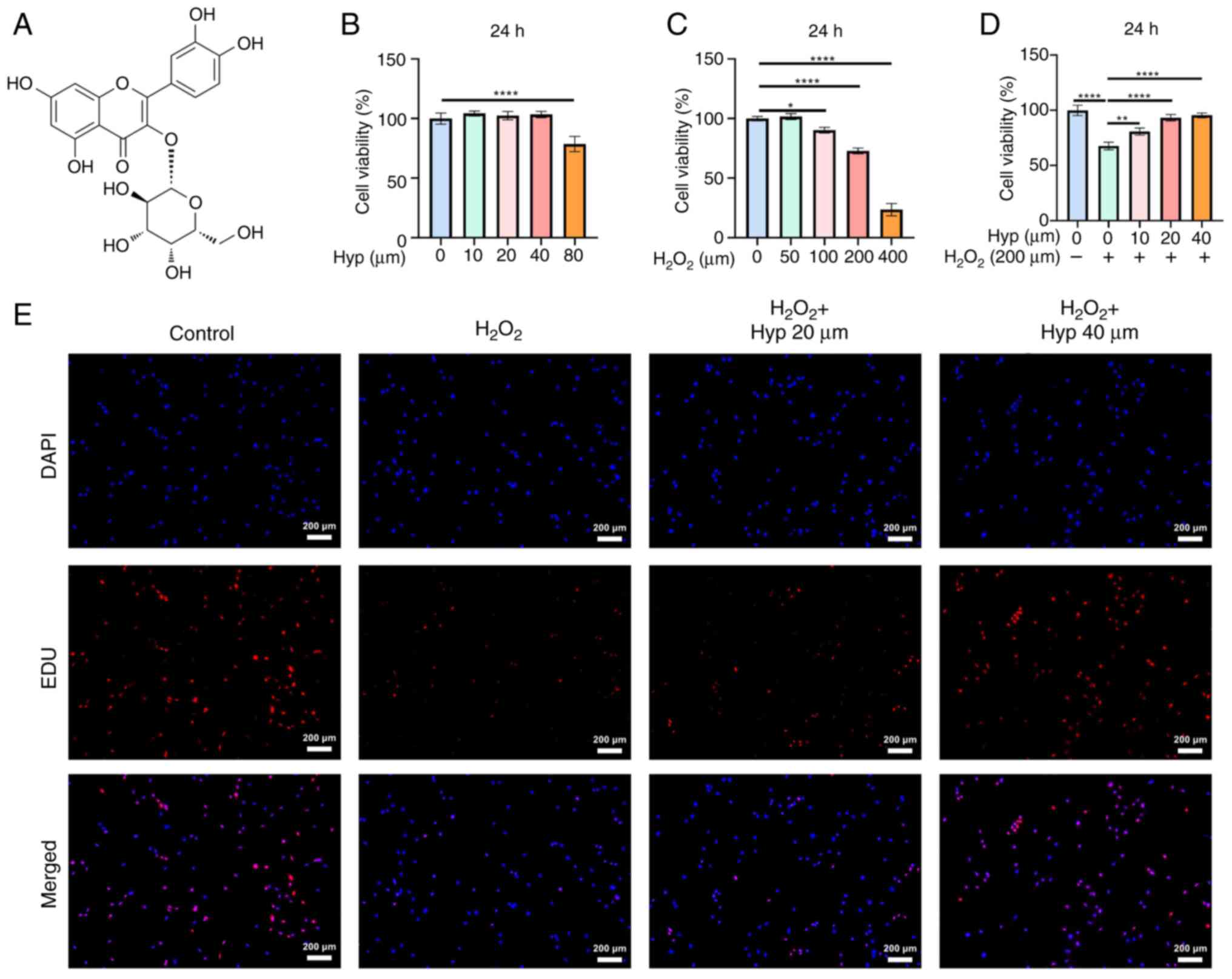
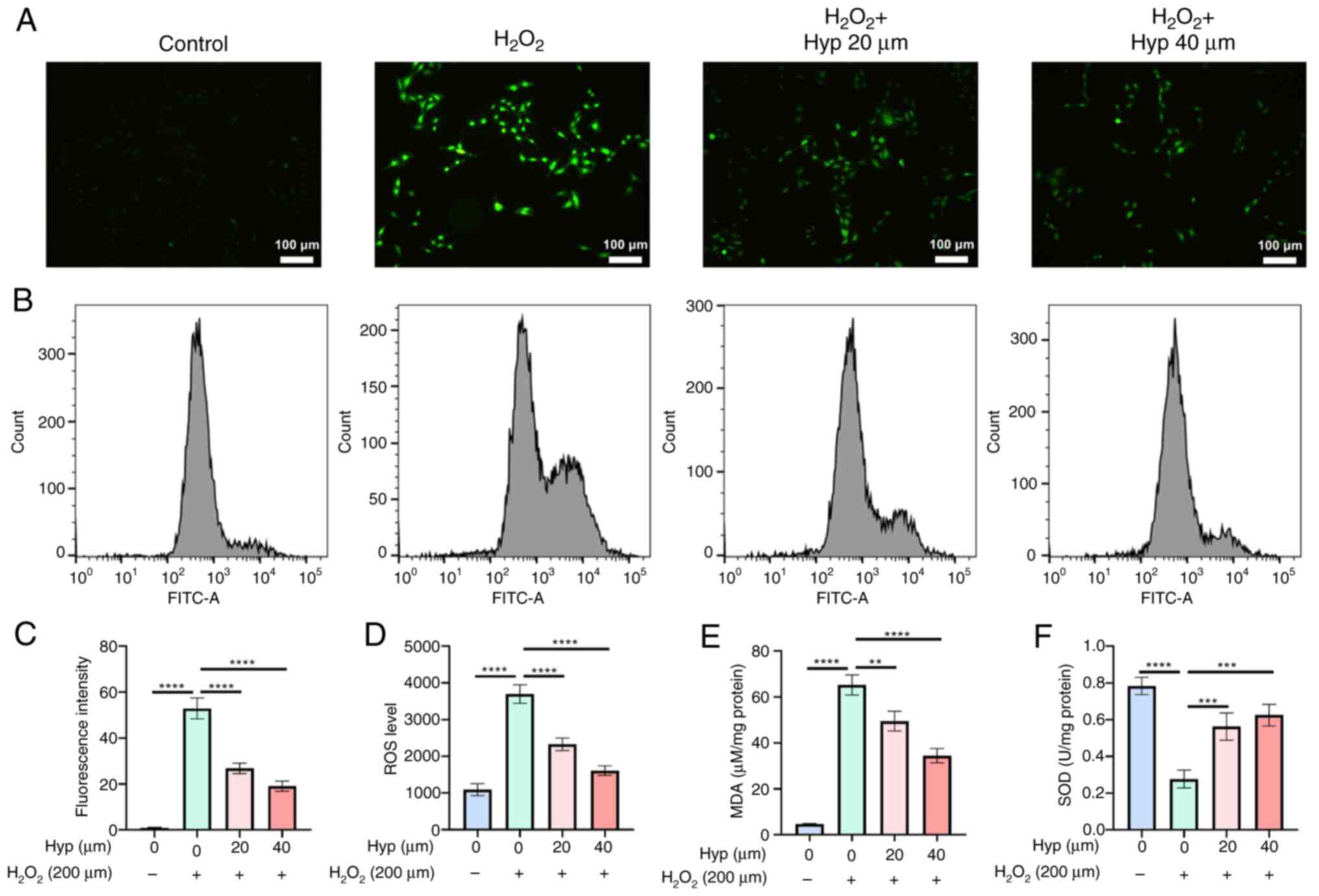
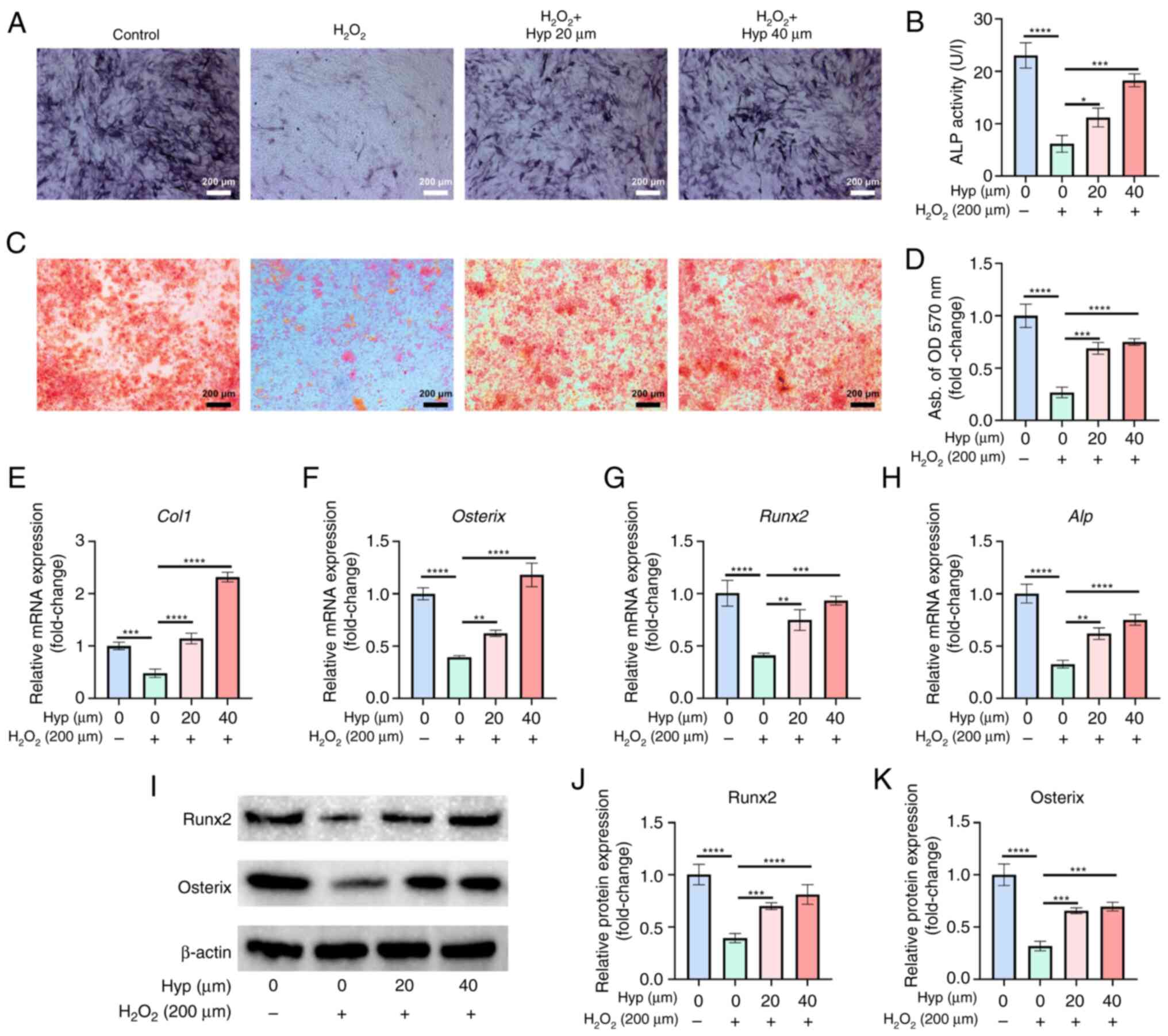
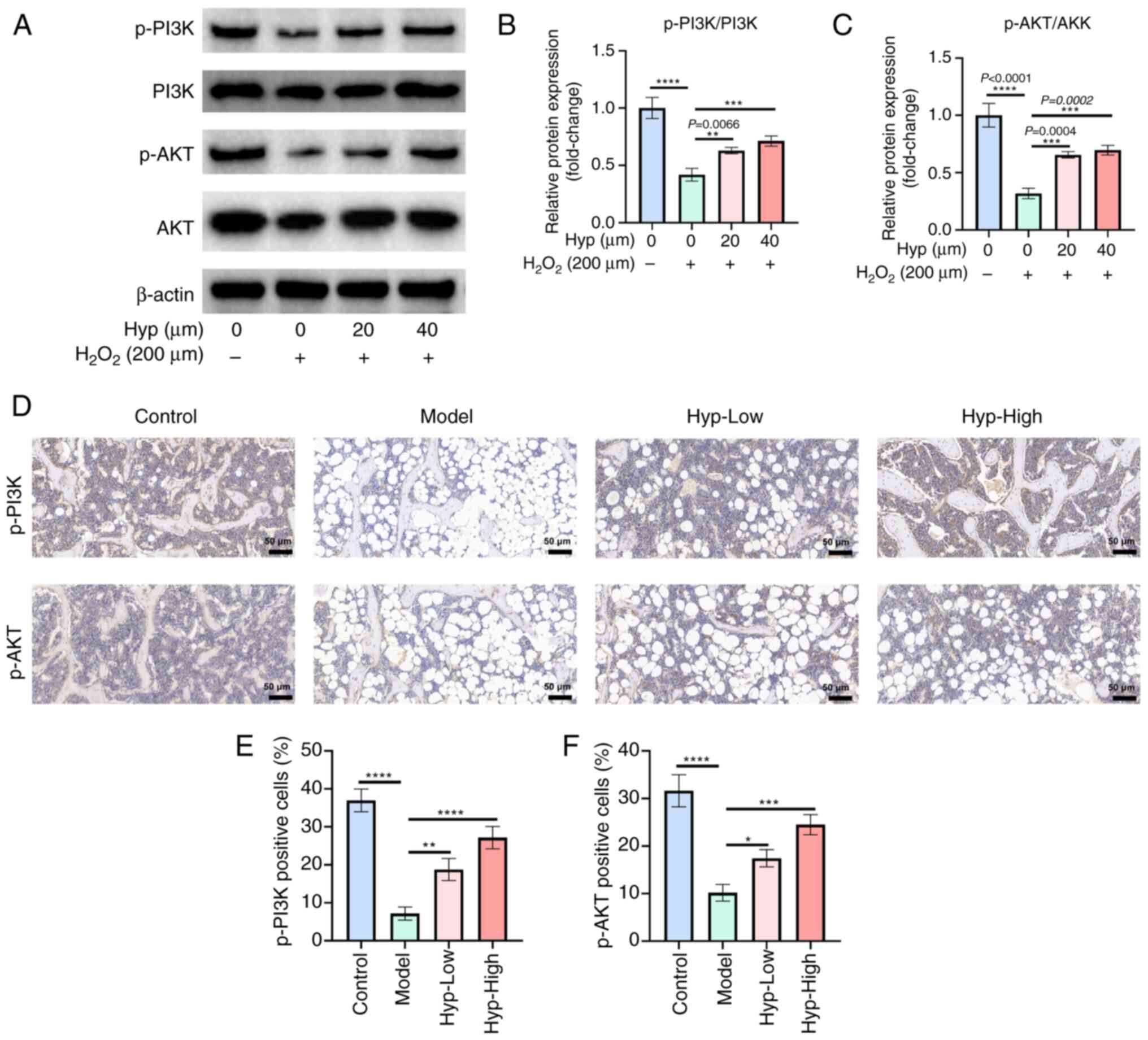
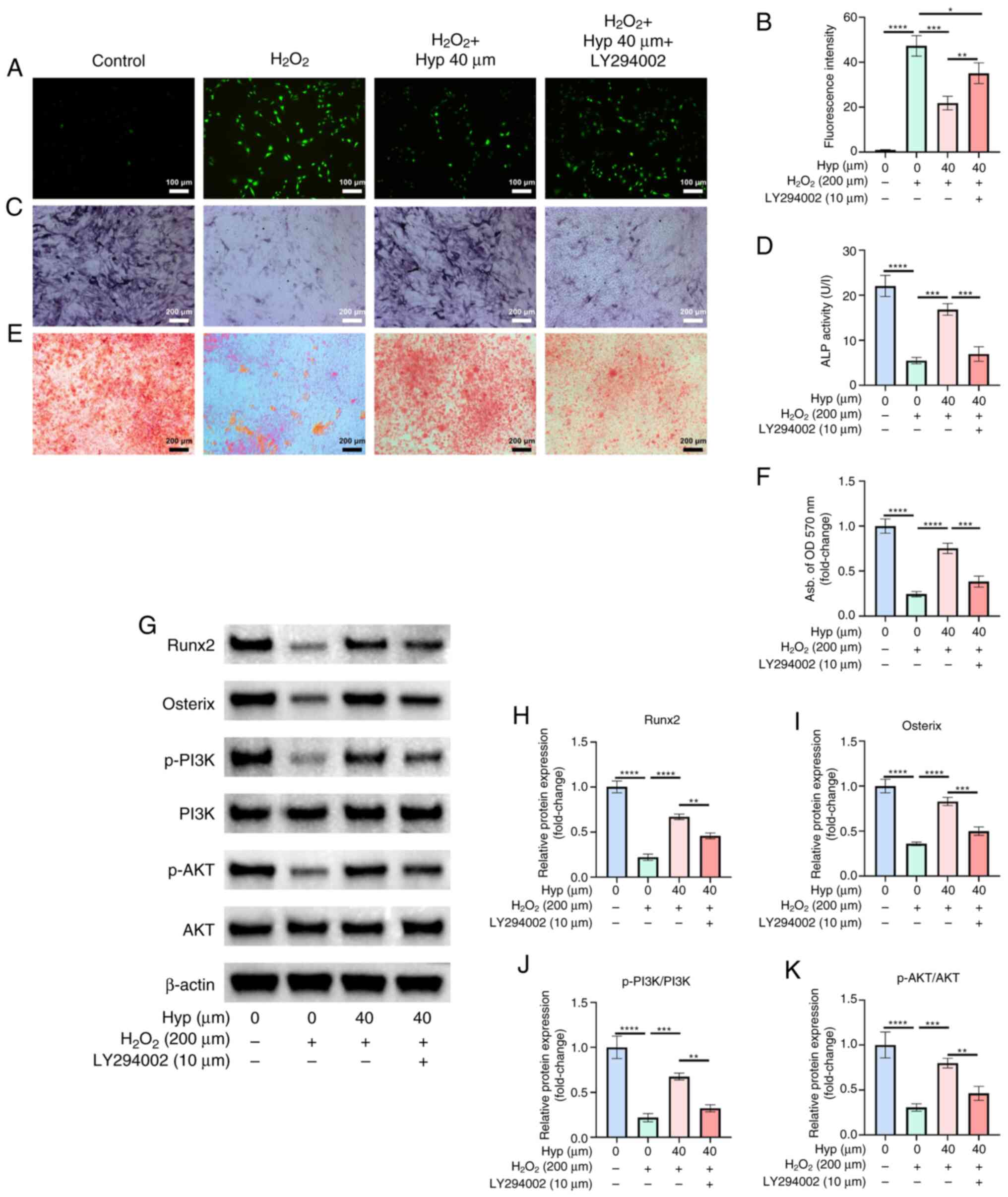
|
1
|
Walker MD and Shane E: Postmenopausal
osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 389:1979–1991. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tang SS, Yin XJ, Yu W, Cui L, Li ZX, Cui
LJ, Wang LH and Xia W: Prevalence of osteoporosis and related
factors in postmenopausal women aged 40 and above in China.
Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 43:509–516. 2022.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
LeBoff MS, Greenspan SL, Insogna KL,
Lewiecki EM, Saag KG, Singer AJ and Siris ES: The clinician's guide
to prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int.
33:2049–2102. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cosman F, Langdahl B and Leder BZ:
Treatment sequence for osteoporosis. Endocr Pract. 30:490–496.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Eid A and Atlas J: The role of
bisphosphonates in medical oncology and their association with jaw
bone necrosis. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 26:231–237.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chlebowski RT and Manson JE: Menopausal
hormone therapy and breast cancer. Cancer J. 28:169–175. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cho L, Kaunitz AM, Faubion SS, Hayes SN,
Lau ES, Pristera N, Scott N, Shifren JL, Shufelt CL, Stuenkel CA,
et al: Rethinking menopausal hormone therapy: For whom, what, when,
and how long? Circulation. 147:597–610. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Luo J, Mills K, le Cessie S, Noordam R and
van Heemst D: Ageing, age-related diseases and oxidative stress:
What to do next? Ageing Res Rev. 57:1009822020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Iantomasi T, Romagnoli C, Palmini G,
Donati S, Falsetti I, Miglietta F, Aurilia C, Marini F, Giusti F
and Brandi ML: Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoporosis:
Molecular mechanisms involved and the relationship with microRNAs.
Int J Mol Sci. 24:37722023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Marcucci G, Domazetovic V, Nediani C,
Ruzzolini J, Favre C and Brandi ML: Oxidative stress and natural
antioxidants in osteoporosis: Novel preventive and therapeutic
approaches. Antioxidants (Basel). 12:3732023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kimball JS, Johnson JP and Carlson DA:
Oxidative stress and osteoporosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am.
103:1451–1461. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen Y, Cai Y, Chen C, Li M, Lu L, Yu Z,
Wang S, Fang L and Xu S: Aroclor 1254 induced inhibitory effects on
osteoblast differentiation in murine MC3T3-E1 cells through
oxidative stress. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 13:9406242022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tanaka M, Inoue H, Takahashi N and Uehara
M: AMPK negatively regulates RANKL-induced osteoclast
differentiation by controlling oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol
Med. 205:107–115. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhu C, Shen S, Zhang S, Huang M, Zhang L
and Chen X: Autophagy in bone remodeling: A regulator of oxidative
stress. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 13:8986342022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhao Q, Feng J, Liu F, Liang Q, Xie M,
Dong J, Zou Y, Ye J, Liu G, Cao Y, et al: Rhizoma Drynariae-derived
nanovesicles reverse osteoporosis by potentiating osteogenic
differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via
targeting ERα signaling. Acta Pharm Sin B. 14:2210–2227. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li B, Wang Y, Gong S, Yao W, Gao H, Liu M
and Wei M: Puerarin improves OVX-induced osteoporosis by regulating
phospholipid metabolism and biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids
based on serum metabolomics. Phytomedicine. 102:1541982022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rao T, Tong H, Li J, Huang J, Yin Y and
Zhang J: Exploring the role and mechanism of hyperoside against
cardiomyocyte injury in mice with myocardial infarction based on
JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Phytomedicine. 128:1553192024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhao K, Zhou F, Lu Y, Gao T, Wang R, Xie M
and Wang H: Hyperoside alleviates depressive-like behavior in
social defeat mice by mediating microglial polarization and
neuroinflammation via TRX1/NLRP1/Caspase-1 signal pathway. Int
Immunopharmacol. 145:1137312025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen Y, Dai F, He Y, Chen Q, Xia Q, Cheng
G, Lu Y and Zhang Q: Beneficial effects of hyperoside on bone
metabolism in ovariectomized mice. Biomed Pharmacother.
107:1175–1182. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yan K, Zhang RK, Wang JX, Chen HF, Zhang
Y, Cheng F, Jiang Y, Wang M, Wu Z, Chen XG, et al: Using network
pharmacology and molecular docking technology, proteomics and
experiments were used to verify the effect of Yigu decoction (YGD)
on the expression of key genes in osteoporotic mice. Ann Med.
57:24492252025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang PH, Wei YN, Xiao BJ, Li SY, Li XL,
Yang LJ, Pan HF and Chen GX: Curcumin for gastric cancer: Mechanism
prediction via network pharmacology, docking, and in vitro
experiments. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 16:3635–3650. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Benisch P, Schilling T, Klein-Hitpass L,
Frey SP, Seefried L, Raaijmakers N, Krug M, Regensburger M, Zeck S,
Schinke T, et al: The transcriptional profile of mesenchymal stem
cell populations in primary osteoporosis is distinct and shows
overexpression of osteogenic inhibitors. PLoS One. 7:e451422012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
van de Peppel J, Strini T, Tilburg J,
Westerhoff H, van Wijnen AJ and van Leeuwen JP: Identification of
three early phases of cell-fate determination during osteogenic and
adipogenic differentiation by transcription factor dynamics. Stem
Cell Reports. 8:947–960. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang C, Li H, Li J, Hu J, Yang K and Tao
L: Oxidative stress: A common pathological state in a high-risk
population for osteoporosis. Biomed Pharmacother. 163:1148342023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Karthik V and Guntur AR: Energy metabolism
of osteocytes. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 19:444–451. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shinohara I, Morita M, Chow SK, Murayama
M, Sususki Y, Gao Q and Goodman SB: Pathophysiology of the effects
of oxidative stress on the skeletal system. J Orthop Res.
43:1059–1072. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li D, Zhao Z, Zhu L, Feng H, Song J, Fu J,
Li J, Chen Z and Fu H: 7,8-DHF inhibits BMSC oxidative stress via
the TRKB/PI3K/AKT/NRF2 pathway to improve symptoms of
postmenopausal osteoporosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 223:413–429.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chai S, Yang Y, Wei L, Cao Y, Ma J, Zheng
X, Teng J and Qin N: Luteolin rescues postmenopausal osteoporosis
elicited by OVX through alleviating osteoblast pyroptosis via
activating PI3K-AKT signaling. Phytomedicine. 128:1555162024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jang E: Hyperoside as a potential natural
product targeting oxidative stress in liver diseases. Antioxidants
(Basel). 11:14372022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ku SK, Zhou W, Lee W, Han MS, Na M and Bae
JS: Anti-inflammatory effects of hyperoside in human endothelial
cells and in mice. Inflammation. 38:784–799. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wu L, Li Q, Liu S, An X, Huang Z, Zhang B,
Yuan Y and Xing C: Protective effect of hyperoside against renal
ischemia-reperfusion injury via modulating mitochondrial fission,
oxidative stress, and apoptosis. Free Radic Res. 53:727–736. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lennicke C and Cocheme HM: Redox
metabolism: ROS as specific molecular regulators of cell signaling
and function. Mol Cell. 81:3691–3707. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gebicki JM: Oxidative stress, free
radicals and protein peroxides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 595:33–39.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jomova K, Raptova R, Alomar SY, Alwasel
SH, Nepovimova E, Kuca K and Valko M: Reactive oxygen species,
toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: chronic diseases and
aging. Arch Toxicol. 97:2499–2574. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ren BC, Zhang YF, Liu SS, Cheng XJ, Yang
X, Cui XG, Zhao XR, Zhao H, Hao MF, Li MD, et al: Curcumin
alleviates oxidative stress and inhibits apoptosis in diabetic
cardiomyopathy via Sirt1-Foxo1 and PI3K-Akt signalling pathways. J
Cell Mol Med. 24:12355–12367. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Deng S, Dai G, Chen S, Nie Z, Zhou J, Fang
H and Peng H: Dexamethasone induces osteoblast apoptosis through
ROS-PI3K/AKT/GSK3β signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother.
110:602–608. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wei L, Chen W, Huang L, Wang H, Su Y,
Liang J, Lian H, Xu J, Zhao J and Liu Q: Alpinetin ameliorates bone
loss in LPS-induced inflammation osteolysis via ROS mediated
P38/PI3K signaling pathway. Pharmacol Res. 184:1064002022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xin L, Feng HC and Zhang Q, Cen XL, Huang
RR, Tan GY and Zhang Q: Exploring the osteogenic effects of simiao
wan through activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway in osteoblasts. J
Ethnopharmacol. 338:1190232025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang D, Liu Y, Tang D, Wei S, Sun J, Ruan
L, He L, Li R, Ren Q, Tian X and Chen Y: Induction of
PI3K/Akt-mediated apoptosis in osteoclasts is a key approach for
buxue tongluo pills to treat osteonecrosis of the femoral head.
Front Pharmacol. 12:7299092021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wu CH, Hung TH, Chen CC, Ke CH, Lee CY,
Wang PY and Chen SF: Post-injury treatment with
7,8-dihydroxyflavone, a TrkB receptor agonist, protects against
experimental traumatic brain injury via PI3K/Akt signaling. PLoS
One. 9:e1133972014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liang G, Zhao J, Dou Y, Yang Y, Zhao D,
Zhou Z, Zhang R, Yang W and Zeng L: Mechanism and experimental
verification of luteolin for the treatment of osteoporosis based on
network pharmacology. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 13:8666412022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Xiong Y, Zhao B, Zhang W, Jia L, Zhang Y
and Xu X: Curcumin promotes osteogenic differentiation of
periodontal ligament stem cells through the PI3K/AKT/Nrf2 signaling
pathway. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 23:954–960. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lu J, Shi X, Fu Q, Han Y, Zhu L, Zhou Z,
Li Y and Lu N: New mechanistic understanding of osteoclast
differentiation and bone resorption mediated by P2X7 receptors and
PI3K-Akt-GSK3beta signaling. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 29:1002024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Jiang Z, Deng L, Li M, Alonge E and Wang Y
and Wang Y: Ginsenoside Rg1 modulates PI3K/AKT pathway for enhanced
osteogenesis via GPER. Phytomedicine. 124:1552842024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|