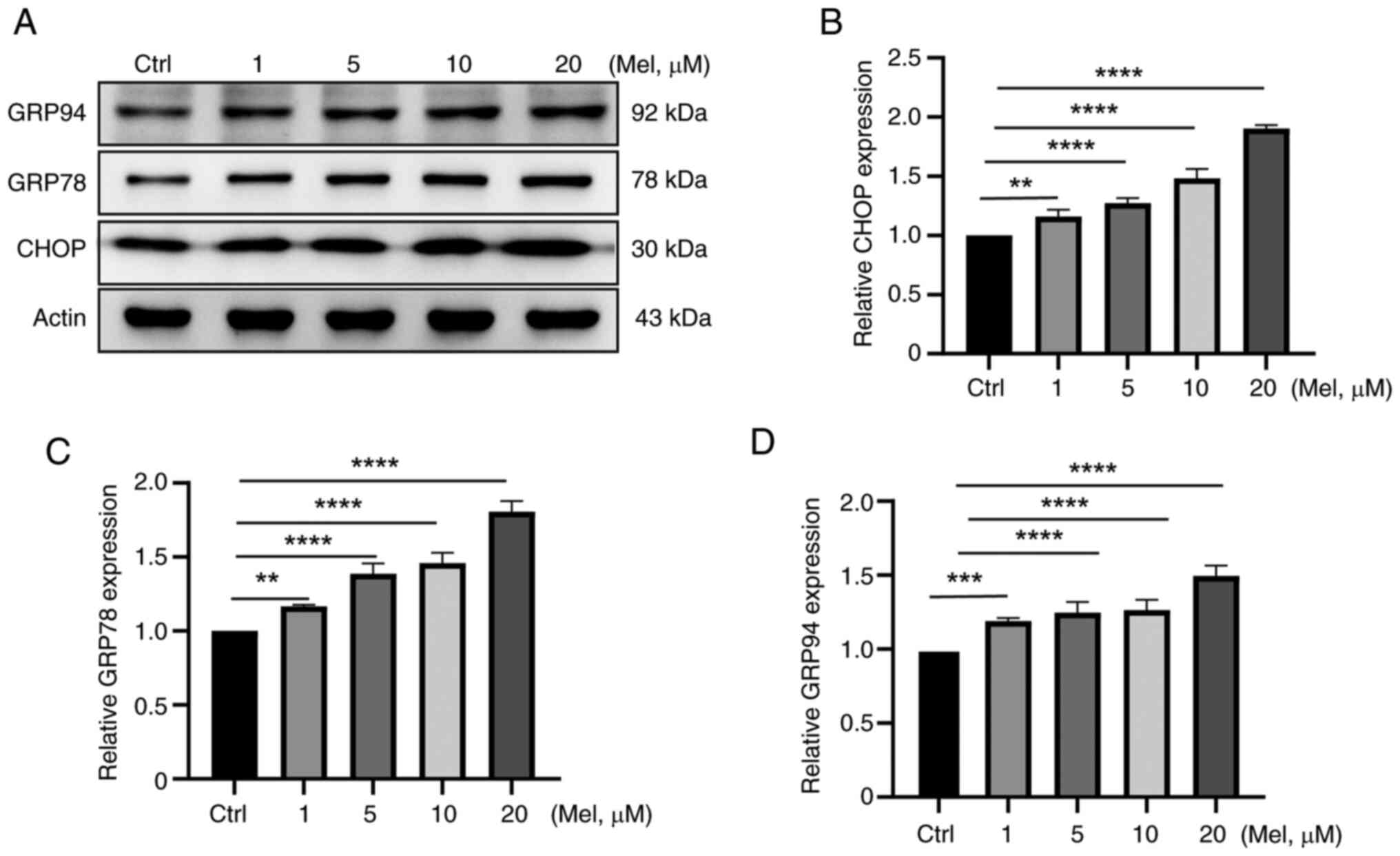
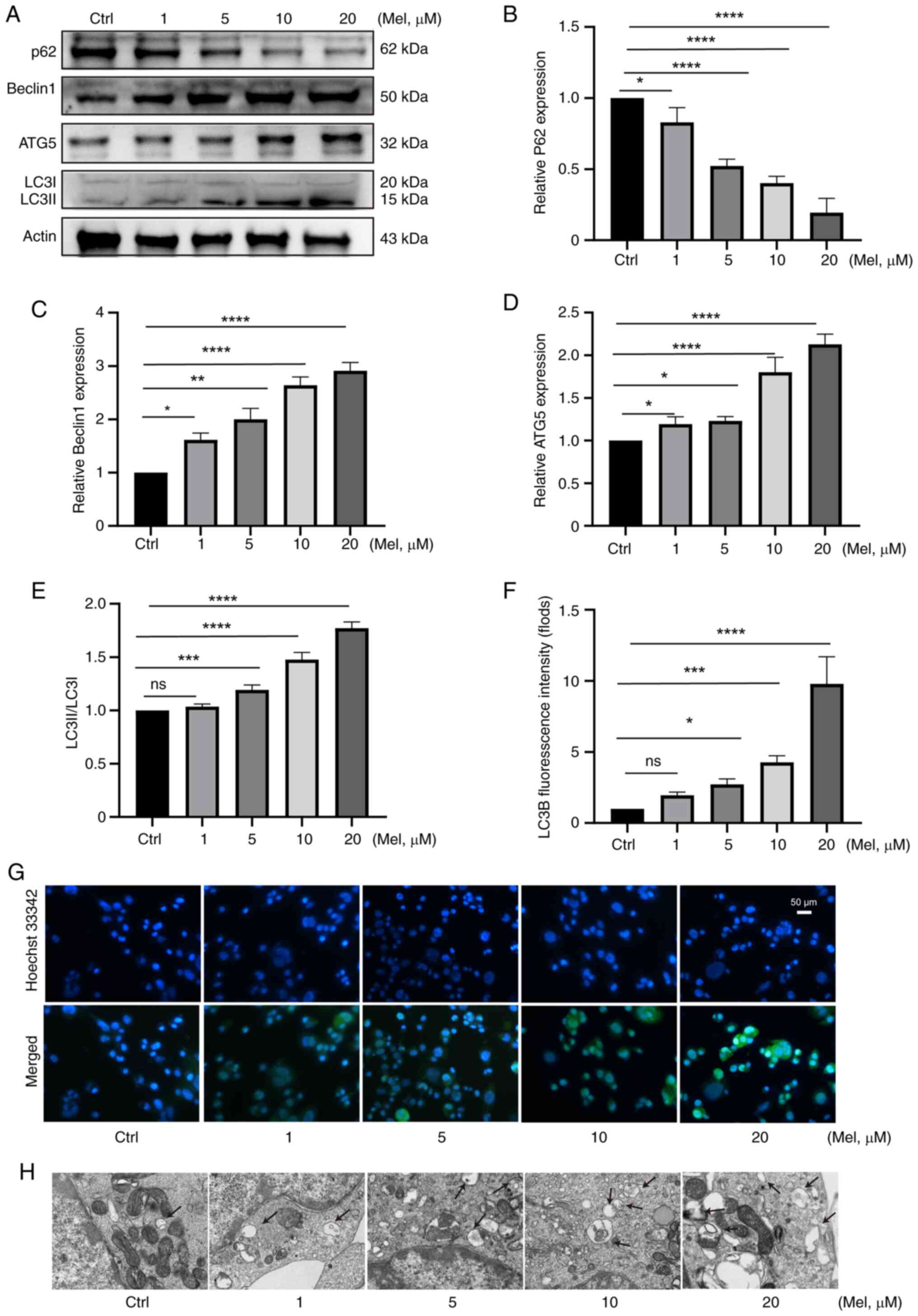
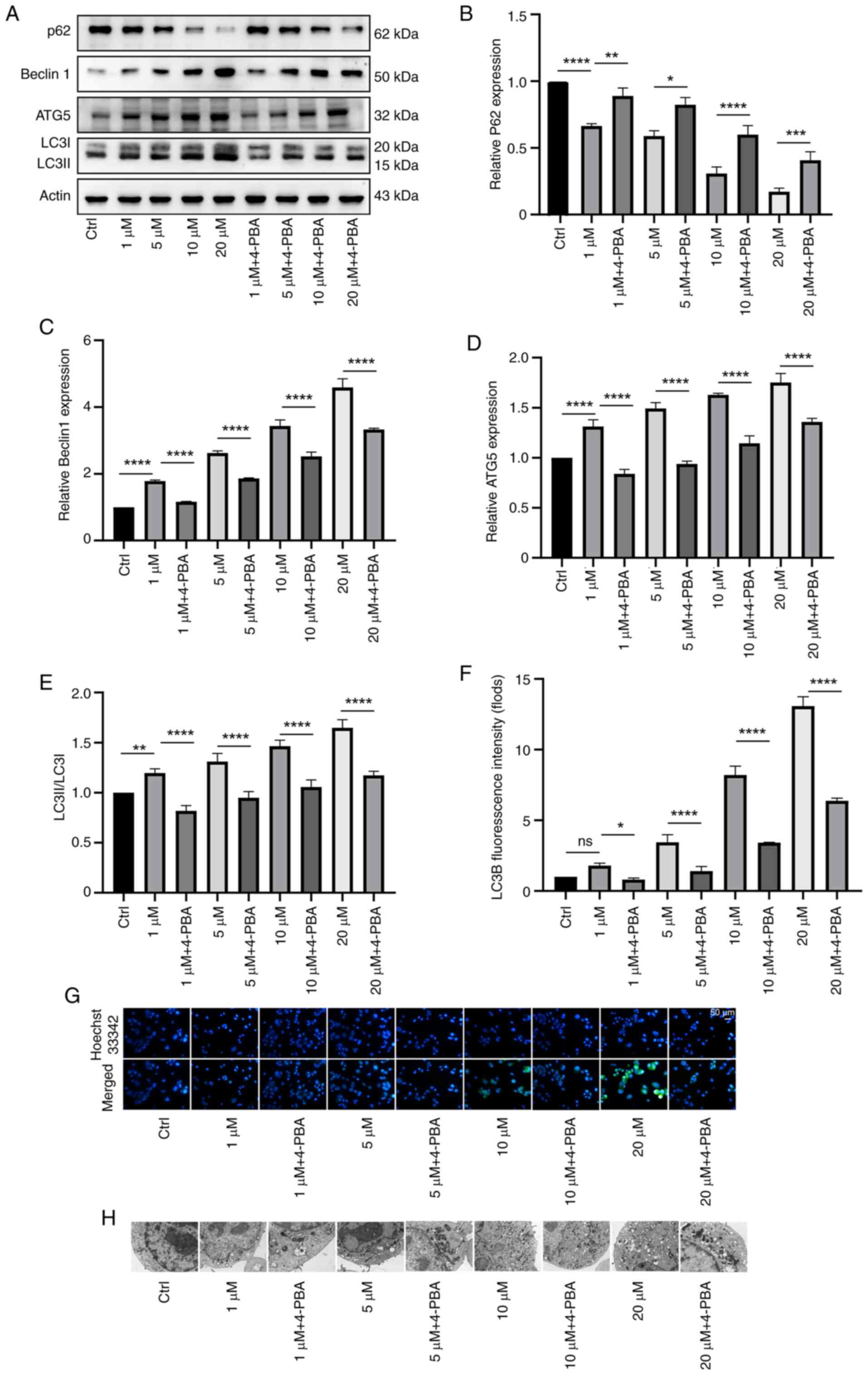
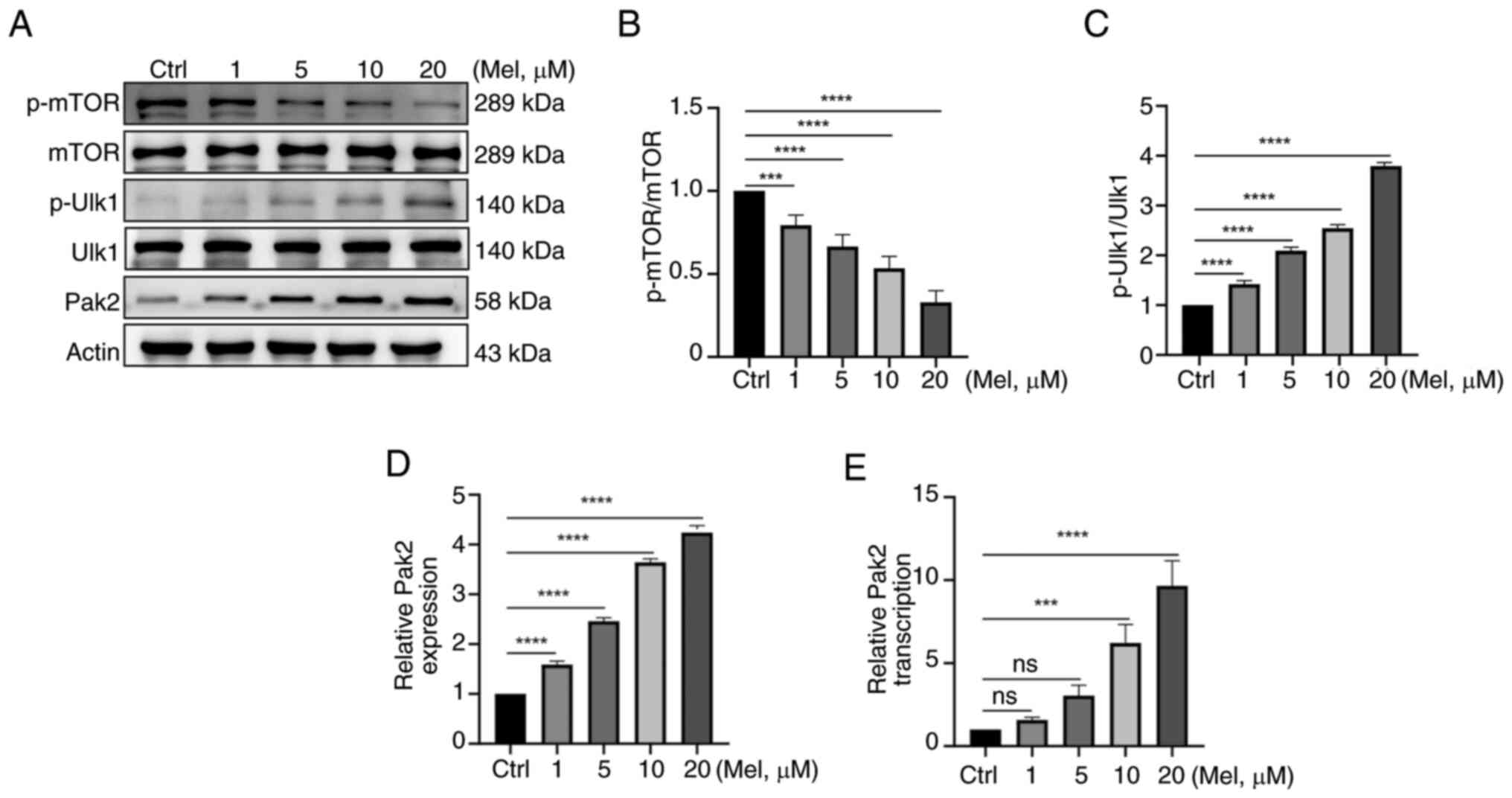
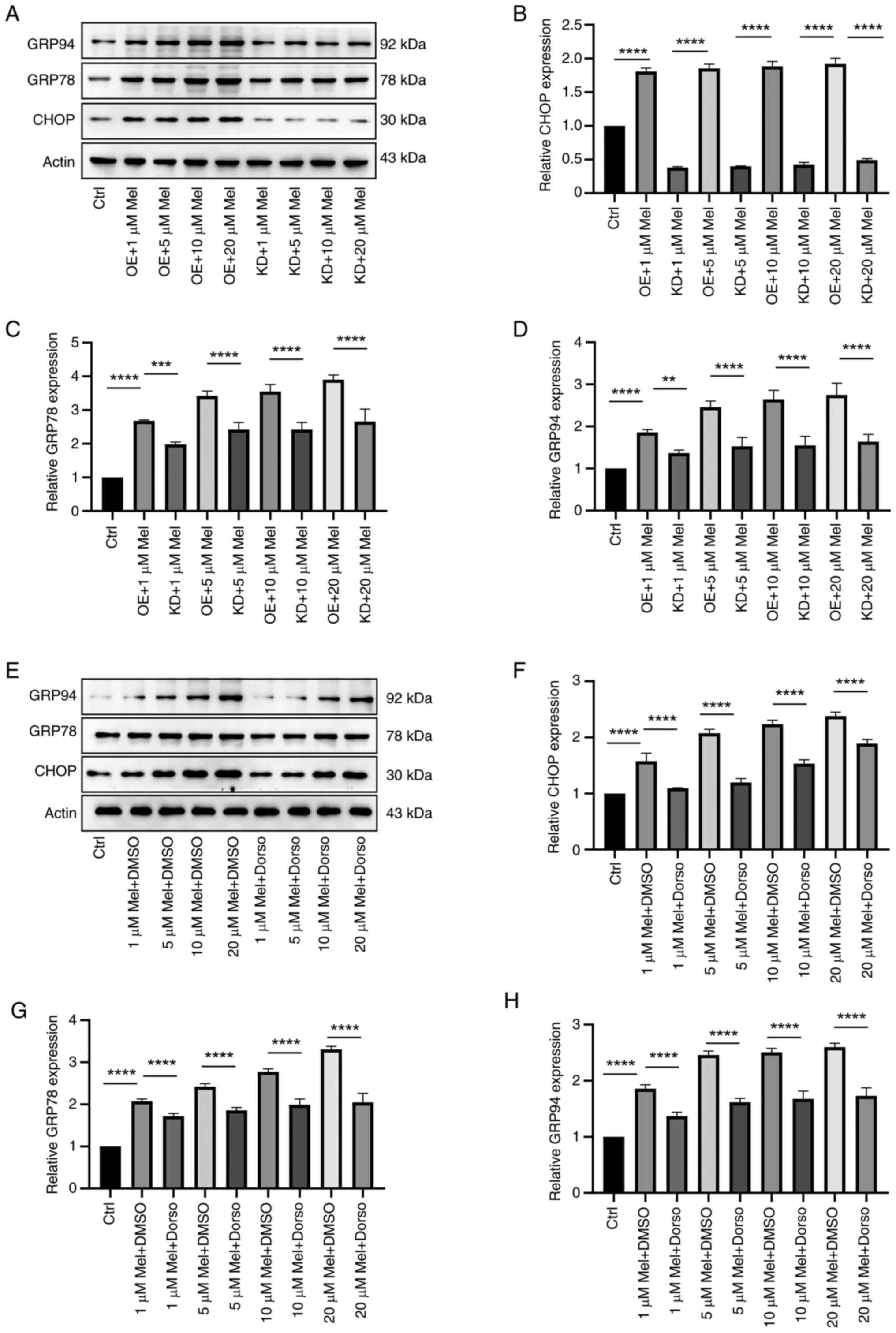
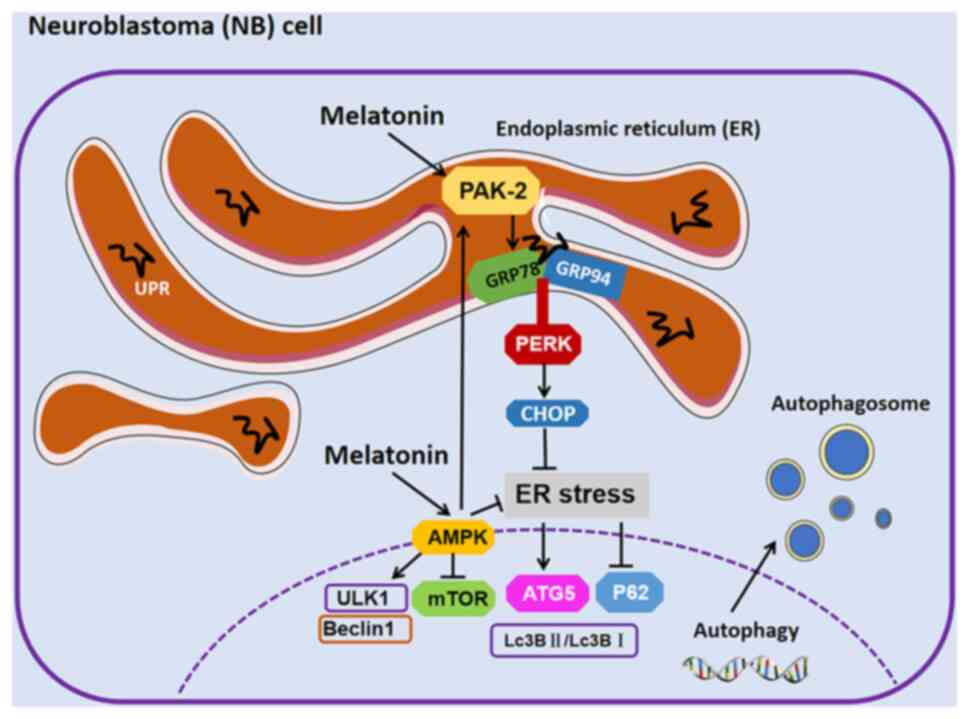
|
1
|
Del Bufalo F, De Angelis B, Caruana I, Del
Baldo G, De Ioris MA, Serra A, Mastronuzzi A, Cefalo MG, Pagliara
D, Amicucci M, et al: GD2-CART01 for relapsed or refractory
High-risk neuroblastoma. N Engl J Med. 388:1284–1295. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Qiu B and Matthay KK: Advancing therapy
for neuroblastoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 19:515–533. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Abbasi J: Mixed findings in pediatric
neuroblastoma CAR-T therapy trial. JAMA. 325:1212021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Debnath J, Gammoh N and Ryan KM: Autophagy
and autophagy-related pathways in cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
24:560–575. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xia H, Green DR and Zou W: Autophagy in
tumour immunity and therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 21:281–297. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bian Y, Li W, Kremer DM, Sajjakulnukit P,
Li S, Crespo J, Nwosu ZC, Zhang L, Czerwonka A, Pawłowska A, et al:
Cancer SLC43A2 alters T cell methionine metabolism and histone
methylation. Nature. 585:277–282. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim J, Kundu M, Viollet B and Guan KL:
AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of
Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol. 13:132–141. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Egan DF, Shackelford DB, Mihaylova MM,
Gelino S, Kohnz RA, Mair W, Vasquez DS, Joshi A, Gwinn DM, Taylor
R, et al: Phosphorylation of ULK1 (hATG1) by AMP-activated protein
kinase connects energy sensing to mitophagy. Science. 331:456–461.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim J, Kim YC, Fang C, Russell RC, Kim JH,
Fan W, Liu R, Zhong Q and Guan KL: Differential regulation of
distinct Vps34 complexes by AMPK in nutrient stress and autophagy.
Cell. 152:290–303. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang Y, Zhao W, Xiao Z, Guan G, Liu X and
Zhuang M: A risk signature with four autophagy-related genes for
predicting survival of glioblastoma multiforme. J Cell Mol Med.
24:3807–3821. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bishayee K, Habib K, Nazim UM, Kang J,
Szabo A, Huh SO, Sadra A, et al: RNA binding protein HuD promotes
autophagy and tumor stress survival by suppressing mTORC1 activity
and augmenting ARL6IP1 levels. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 41:182022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ugun-Klusek A, Theodosi TS, Fitzgerald JC,
Burté F, Ufer C, Boocock DJ, Yu-Wai-Man P, Bedford L and Billett
EE: Monoamine oxidase-A promotes protective autophagy in human
SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells through Bcl-2 phosphorylation. Redox
Biol. 20:167–181. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Marciniak SJ, Chambers JE and Ron D:
Pharmacological targeting of endoplasmic reticulum stress in
disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 21:115–140. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Clarke HJ, Chambers JE, Liniker E and
Marciniak SJ: Endoplasmic reticulum stress in malignancy. Cancer
Cell. 25:563–573. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang R, Ma S, Zhuo R, Xu L, Jia S, Yang P,
Yao Y, Cao H, Ma L, Pan J and Wang J: Suppression of endoplasmic
reticulum stress-dependent autophagy enhances cynaropicrin-induced
apoptosis via attenuation of the P62/Keap1/Nrf2 pathways in
neuroblastoma. Front Pharmacol. 13:9776222022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Celesia A, Morana O, Fiore T, Pellerito C,
D'Anneo A, Lauricella M, Carlisi D, De Blasio A, Calvaruso G,
Giuliano M and Emanuele S: ROS-Dependent ER stress and autophagy
mediate the anti-tumor effects of tributyltin (IV) ferulate in
colon cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 21:81352020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
París-Coderch L, Soriano A, Jiménez C,
Erazo T, Muñoz-Guardiola P, Masanas M, Antonelli R, Boloix A, Alfón
J, Pérez-Montoyo H, et al: The antitumour drug ABTL0812 impairs
neuroblastoma growth through endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated
autophagy and apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 11:7732020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ge W, Yan ZH, Wang L, Tan SJ, Liu J,
Reiter RJ, Luo SM, Sun QY and Shen W: A hypothetical role for
autophagy during the day/night rhythm-regulated melatonin synthesis
in the rat pineal gland. J Pineal Res. 71:e127422021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Boga JA, Caballero B, Potes Y,
Perez-Martinez Z, Reiter RJ, Vega-Naredo I and Coto-Montes A:
Therapeutic potential of melatonin related to its role as an
autophagy regulator: A review. J Pineal Res. 66:e125342029.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fernández A, Ordóñez R, Reiter RJ,
González-Gallego J and Mauriz JL: Melatonin and endoplasmic
reticulum stress: Relation to autophagy and apoptosis. J Pineal
Res. 59:292–307. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang S, Tian W, Duan X, Zhang Q, Cao L,
Liu C, Li G, Wang Z, Zhang J, Li J, et al: Melatonin attenuates
diabetic cardiomyopathy by increasing autophagy of cardiomyocytes
via regulation of VEGF-B/GRP78/PERK signaling pathway. Cardiovasc
Diabetol. 23:192024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang L, Liu K, Liu Z, Tao H, Fu X, Hou J,
Jia G and Hou Y: In pre-clinical study fetal hypoxia caused
autophagy and mitochondrial impairment in ovary granulosa cells
mitigated by melatonin supplement. J Adv Res. 64:15–30. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xu S, Li L, Wu J, An S, Fang H, Han Y,
Huang Q, Chen Z and Zeng Z: Melatonin attenuates sepsis-induced
small-intestine injury by upregulating SIRT3-Mediated
oxidative-stress inhibition, mitochondrial protection, and
autophagy induction. Front Immunol. 12:6256272021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
De Almeida Chuffa LG, Seiva FRF, Silveira
HS, Cesário RC, da Silva Tonon K, Simão VA, Zuccari DAPC and Reiter
RJ: Melatonin regulates endoplasmic reticulum stress in diverse
pathophysiological contexts: A comprehensive mechanistic review. J
Cell Physiol. 239:e313832024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lebeau PF, Wassef H, Byun JH, Platko K,
Ason B, Jackson S, Dobroff J, Shetterly S, Richards WG, Al-Hashimi
AA, et al: The loss-of-function PCSK9Q152H variant increases ER
chaperones GRP78 and GRP94 and protects against liver injury. J
Clin Invest. 131:e1286502021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cubillos-Ruiz JR, Bettigole SE and
Glimcher LH: Tumorigenic and immunosuppressive effects of
endoplasmic reticulum stress in cancer. Cell. 168:692–706. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Vargas JNS, Hamasaki M, Kawabata T, Youle
RJ and Yoshimori T: The mechanisms and roles of selective autophagy
in mammals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 24:167–185. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li M, Hao B, Zhang M, Reiter RJ, Lin S,
Zheng T, Chen X, Ren Y, Yue L, Abay B, et al: Melatonin enhances
radiofrequency-induced NK antitumor immunity, causing cancer
metabolism reprogramming and inhibition of multiple pulmonary tumor
development. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 6:3302021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xing J, Xu H, Liu C, Wei Z, Wang Z, Zhao L
and Ren L: Melatonin ameliorates endoplasmic reticulum stress in
N2a neuroblastoma cell hypoxia-reoxygenation injury by activating
the AMPK-Pak2 pathway. Cell Stress Chaperones. 24:621–633. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cos S, Verduga R, Fernández-Viadero C,
Megías M and Crespo D: Effects of melatonin on the proliferation
and differentiation of human neuroblastoma cells in culture.
Neurosci Lett. 216:113–136. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lee WJ, Chen LC, Lin JH, Cheng TC, Kuo CC,
Wu CH, Chang HW, Tu SH and Ho YS: Melatonin promotes neuroblastoma
cell differentiation by activating hyaluronan synthase 3-induced
mitophagy. Cancer Med. 8:4821–4835. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
García-Santos G, Antolín I, Herrera F,
Martín V, Rodriguez-Blanco J, del Pilar Carrera M and Rodriguez C:
Melatonin induces apoptosis in human neuroblastoma cancer cells. J
Pineal Res. 41:130–135. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Singrang N, Nopparat C, Panmanee J and
Govitrapong P: Melatonin inhibits Hypoxia-induced Alzheimer's
disease pathogenesis by regulating the amyloidogenic pathway in
human neuroblastoma cells. Int J Mol Sci. 25:52252024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen X and Cubillos-Ruiz JR: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress signals in the tumour and its microenvironment.
Nat Rev Cancer. 21:71–88. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Choi SI, Lee E, Akuzum B, Jeong JB, Maeng
YS, Kim TI and Kim EK: Melatonin reduces endoplasmic reticulum
stress and corneal dystrophy-associated TGFBIp through activation
of endoplasmic reticulum-associated protein degradation. J Pineal
Res. 632017.doi: 10.1111/jpi.12426.
|
|
37
|
Qi Q, Feng L, Liu J, Xu D, Wang G and Pan
X: Melatonin alleviates BPA-induced testicular apoptosis and
endoplasmic reticulum stress. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed).
29:952024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang S, Bian W, Zhen J, Zhao L and Chen W:
Melatonin-mediated Pak2 activation reduces cardiomyocyte death
through suppressing hypoxia reoxygenation Injury-induced
endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 74:20–29.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu Z, Wang XY, Wang HW, Liu SL, Zhang C,
Liu F, Guo Y and Gao FH: Autophagic degradation of CDK4 is
responsible for G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in NVP-BEZ235-treated
neuroblastoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 25:23855172024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu Z, Cecarini V, Cuccioloni M, Bonfili
L, Gong C, Angeletti M and Eleuteri AM: Ginsenosides Rg1 and Rg2
activate autophagy and attenuate oxidative stress in neuroblastoma
cells overexpressing Aβ(1–42). Antioxidants (Basel). 13:3102024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Binder P, Binder P, Wang S, Radu M, Zin M,
Collins L, Khan S, Li Y, Sekeres K, Humphreys N, et al: Pak2 as a
novel therapeutic target for cardioprotective endoplasmic reticulum
stress response. Circ Res. 124:696–711. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|