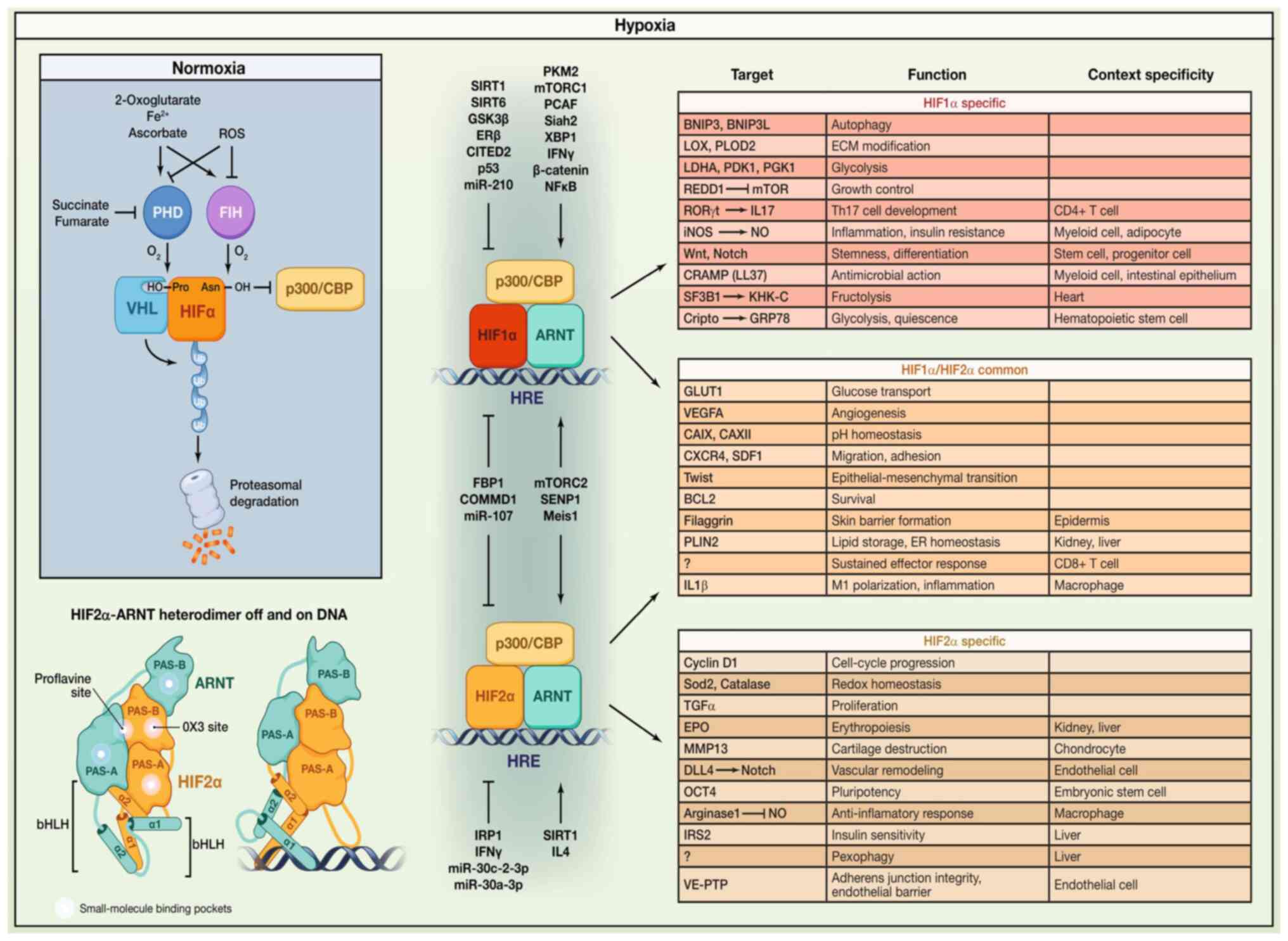
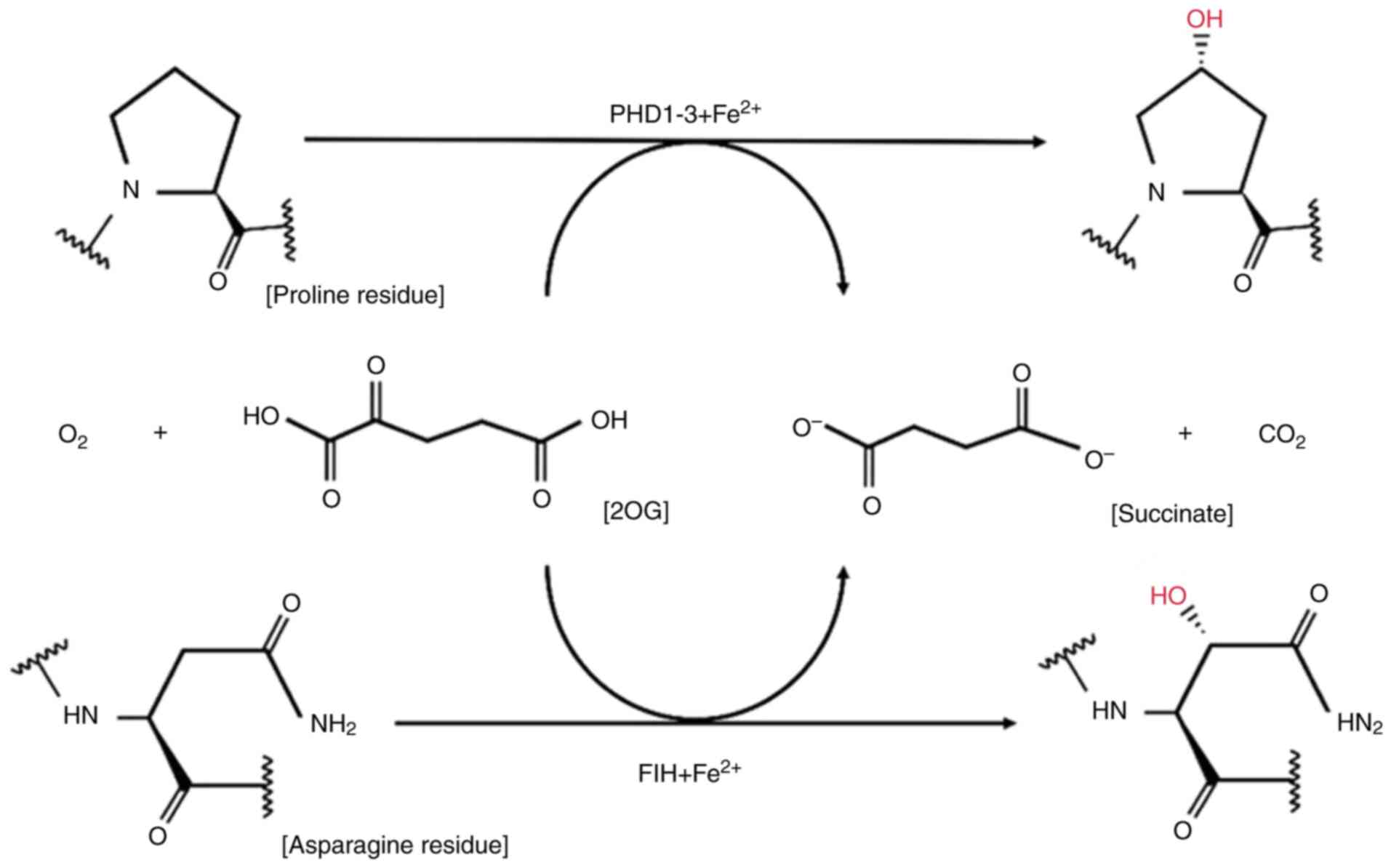
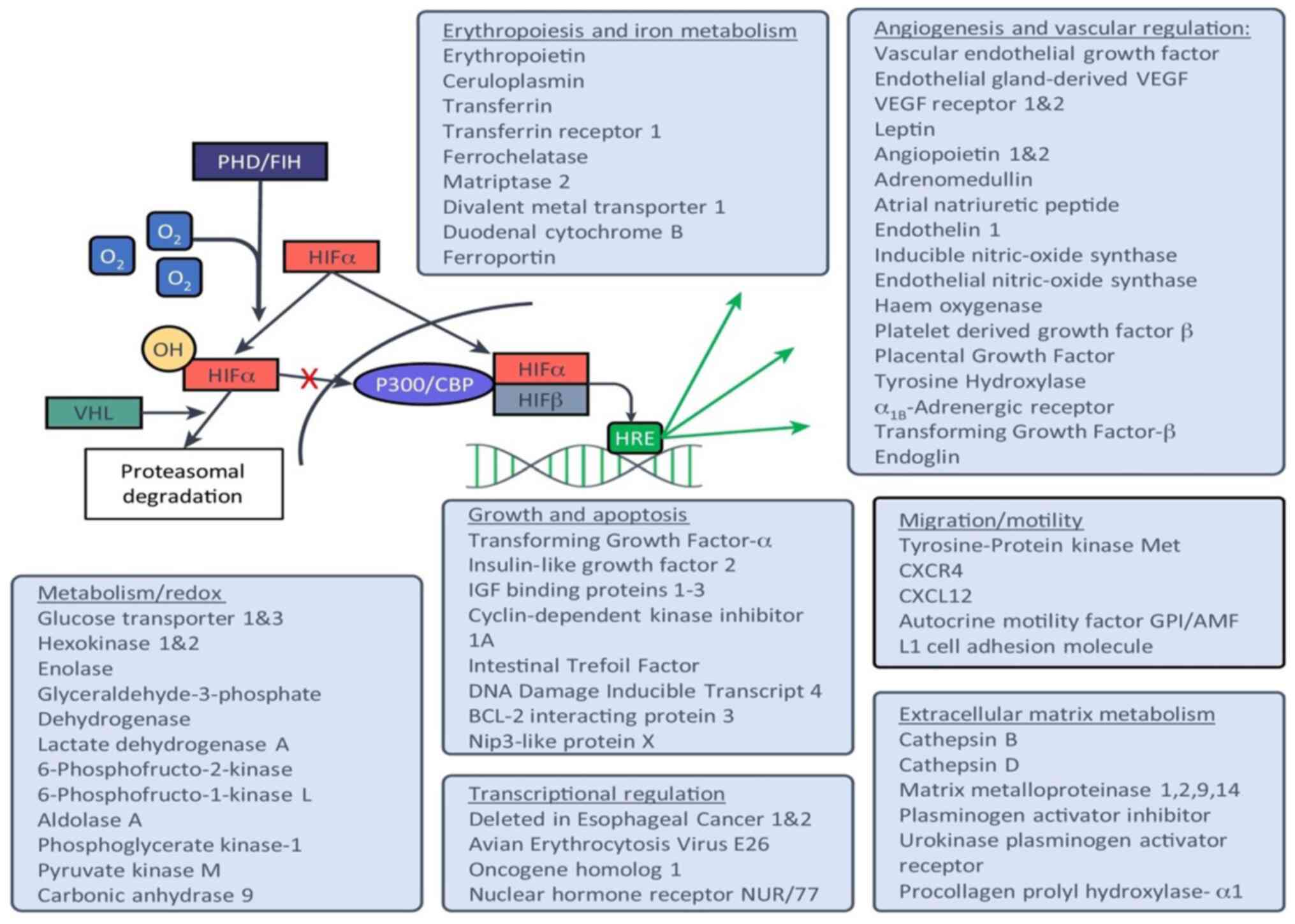
|
1
|
Holmquist-Mengelbier L, Fredlund E,
Lofstedt T, Noguera R, Navarro S, Nilsson H, Pietras A,
Vallon-Christersson J, Borg A, Gradin K, et al: Recruitment of
HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha to common target genes is differentially
regulated in neuroblastoma: HIF-2alpha promotes an aggressive
phenotype. Cancer Cell. 10:413–423. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xie Y, Shi X, Sheng K, Han G, Li W, Zhao
Q, Jiang B, Feng J, Li J and Gu Y: PI3K/Akt signaling transduction
pathway, erythropoiesis and glycolysis in hypoxia (Review). Mol Med
Rep. 19:783–791. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stolze IP, Mole DR and Ratcliffe PJ:
Regulation of HIF: Prolyl hydroxylases. Novartis Found Symp.
272:15–25. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ehdaie B and Theodorescu D: Predicting
tumor outcomes in urothelial bladder carcinoma: Turning pathways
into clinical biomarkers of prognosis. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther.
8:1103–1110. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pugh CW: Modulation of the hypoxic
response. Adv Exp Med Biol. 903:259–271. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hewitson KS, McNeill LA and Schofield CJ:
Modulating the hypoxia-inducible factor signaling pathway:
Applications from cardiovascular disease to cancer. Curr Pharm Des.
10:821–833. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Thompson CB: Into thin air: How we sense
and respond to hypoxia. Cell. 167:9–11. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wong BW, Kuchnio A, Bruning U and
Carmeliet P: Emerging novel functions of the oxygen-sensing prolyl
hydroxylase domain enzymes. Trends Biochem Sci. 38:3–11. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ladroue C, Carcenac R, Leporrier M, Gad S,
Le Hello C, Galateau-Salle F, Feunteun J, Pouysségur J, Richard S
and Gardie B: PHD2 mutation and congenital erythrocytosis with
paraganglioma. N Engl J Med. 359:2685–2692. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Eltzschig HK, Eckle T and Grenz A: PHD2
mutation and congenital erythrocytosis with paraganglioma. N Engl J
Med. 360:1361–1362. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Berra E, Benizri E, Ginouves A, Volmat V,
Roux D and Pouyssegur J: HIF prolyl-hydroxylase 2 is the key oxygen
sensor setting low steady-state levels of HIF-1alpha in normoxia.
EMBO J. 22:4082–4090. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang J, Zhao Q, Mooney SM and Lee FS:
Sequence determinants in hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha for
hydroxylation by the prolyl hydroxylases PHD1, PHD2, and PHD3. J
Biol Chem. 277:39792–39800. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Metzen E, Berchner-Pfannschmidt U, Stengel
P, Marxsen JH, Stolze I, Klinger M, Huang WQ, Wotzlaw C,
Hellwig-Bürgel T, Jelkmann W, et al: Intracellular localisation of
human HIF-1 alpha hydroxylases: Implications for oxygen sensing. J
Cell Sci. 116:1319–1326. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Van Welden S, Laukens D, Ferdinande L, De
Vos M and Hindryckx P: Differential expression of prolyl
hydroxylase 1 in patients with ulcerative colitis versus patients
with Crohn's disease/infectious colitis and healthy controls. J
Inflamm (Lond). 10:362013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Berra E, Ginouves A and Pouyssegur J: The
hypoxia-inducible-factor hydroxylases bring fresh air into hypoxia
signalling. EMBO Rep. 7:41–45. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kaelin WG Jr and Ratcliffe PJ: Oxygen
sensing by metazoans: The central role of the HIF hydroxylase
pathway. Mol Cell. 30:393–402. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lisy K and Peet DJ: Turn me on: Regulating
HIF transcriptional activity. Cell Death Differ. 15:642–649. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Depping R, Jelkmann W and Kosyna FK:
Nuclear-cytoplasmatic shuttling of proteins in control of cellular
oxygen sensing. J Mol Med (Berl). 93:599–608. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Urrutia AA, Guan N, Mesa-Ciller C, Afzal
A, Davidoff O and Haase VH: Inactivation of HIF-prolyl
4-hydroxylases 1, 2 and 3 in NG2-expressing cells induces
HIF2-mediated neurovascular expansion independent of
erythropoietin. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 231:e135472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Souma T, Nezu M, Nakano D, Yamazaki S,
Hirano I, Sekine H, Dan T, Takeda K, Fong GH, Nishiyama A, et al:
Erythropoietin synthesis in renal myofibroblasts is restored by
activation of hypoxia signaling. J Am Soc Nephrol. 27:428–438.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pan Y, Mansfield KD, Bertozzi CC, Rudenko
V, Chan DA, Giaccia AJ and Simon MC: Multiple factors affecting
cellular redox status and energy metabolism modulate
hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase activity in vivo and in
vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 27:912–925. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
van der Wel H, Ercan A and West CM: The
Skp1 prolyl hydroxylase from Dictyostelium is related to the
hypoxia-inducible factor-alpha class of animal prolyl
4-hydroxylases. J Biol Chem. 280:14645–14655. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cummins EP, Berra E, Comerford KM,
Ginouves A, Fitzgerald KT, Seeballuck F, Godson C, Nielsen JE,
Moynagh P, Pouyssegur J and Taylor CT: Prolyl hydroxylase-1
negatively regulates IkappaB kinase-beta, giving insight into
hypoxia-induced NFkappaB activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:18154–18159. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ozer A, Wu LC and Bruick RK: The candidate
tumor suppressor ING4 represses activation of the hypoxia inducible
factor (HIF). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:7481–7486. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Takeda K and Fong GH: Prolyl hydroxylase
domain 2 protein suppresses hypoxia-induced endothelial cell
proliferation. Hypertension. 49:178–184. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Epstein AC, Gleadle JM, McNeill LA,
Hewitson KS, O'Rourke J, Mole DR, Mukherji M, Metzen E, Wilson MI,
Dhanda A, et al: C. elegans EGL-9 and mammalian homologs define a
family of dioxygenases that regulate HIF by prolyl hydroxylation.
Cell. 107:43–54. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fong GH and Takeda K: Role and regulation
of prolyl hydroxylase domain proteins. Cell Death Differ.
15:635–641. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Aprelikova O, Chandramouli GV, Wood M,
Vasselli JR, Riss J, Maranchie JK, Linehan WM and Barrett JC:
Regulation of HIF prolyl hydroxylases by hypoxia-inducible factors.
J Cell Biochem. 92:491–501. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Appelhoff RJ, Tian YM, Raval RR, Turley H,
Harris AL, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ and Gleadle JM: Differential
function of the prolyl hydroxylases PHD1, PHD2, and PHD3 in the
regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor. J Biol Chem.
279:38458–38465. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ivan M, Kondo K, Yang H, Kim W, Valiando
J, Ohh M, Salic A, Asara JM, Lane WS and Kaelin WG Jr: HIFalpha
targeted for VHL-mediated destruction by proline hydroxylation:
Implications for O2 sensing. Science. 292:464–468. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Moffitt PE, Wilson GR and Preston RL:
Comparative response of castrate and intact male rats to
diethylstilbestrol. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 148:650–652. 1975.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bruick RK and McKnight SL: A conserved
family of prolyl-4-hydroxylases that modify HIF. Science.
294:1337–1340. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lee KE and Simon MC: SnapShot:
Hypoxia-inducible factors. Cell. 163:1288. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hirsila M, Koivunen P, Gunzler V,
Kivirikko KI and Myllyharju J: Characterization of the human prolyl
4-hydroxylases that modify the hypoxia-inducible factor. J Biol
Chem. 278:30772–30780. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hagen T, Taylor CT, Lam F and Moncada S:
Redistribution of intracellular oxygen in hypoxia by nitric oxide:
Effect on HIF1alpha. Science. 302:1975–1978. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tarhonskaya H, Chowdhury R, Leung IK, Loik
ND, McCullagh JS, Claridge TD, Schofield CJ and Flashman E:
Investigating the contribution of the active site environment to
the slow reaction of hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase
domain 2 with oxygen. Biochem J. 463:363–372. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Abboud MI, McAllister TE, Leung IKH,
Chowdhury R, Jorgensen C, Domene C, Mecinović J, Lippl K, Hancock
RL, Hopkinson RJ, et al: 2-Oxoglutarate regulates binding of
hydroxylated hypoxia-inducible factor to prolyl hydroxylase domain
2. Chem Commun (Camb). 54:3130–3133. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Osipyants AI, Smirnova NA, Khristichenko
AY, Hushpulian DM, Nikulin SV, Chubar TA, Zakhariants AA, Tishkov
VI, Gazaryan IG and Poloznikov AA: Enzyme-substrate reporters for
evaluation of substrate specificity of HIF prolyl hydroxylase
isoforms. Biochemistry (Mosc). 82:1207–1214. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cockman ME, Lippl K, Tian YM, Pegg HB,
Figg WD Jnr, Abboud MI, Heilig R, Fischer R, Myllyharju J,
Schofield CJ and Ratcliffe PJ: Lack of activity of recombinant HIF
prolyl hydroxylases (PHDs) on reported non-HIF substrates. Elife.
8:e464902019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gollnick SO, Owczarczak B and Maier P:
Photodynamic therapy and anti-tumor immunity. Lasers Surg Med.
38:509–515. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
McDonough MA, Li V, Flashman E, Chowdhury
R, Mohr C, Liénard BM, Zondlo J, Oldham NJ, Clifton IJ, Lewis J, et
al: Cellular oxygen sensing: Crystal structure of hypoxia-inducible
factor prolyl hydroxylase (PHD2). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:9814–9819. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Strowitzki MJ, Cummins EP and Taylor CT:
Protein hydroxylation by hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)
hydroxylases: Unique or ubiquitous? Cells. 8:3842019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Thevenod F, Schreiber T and Lee WK: Renal
hypoxia-HIF-PHD-EPO signaling in transition metal nephrotoxicity:
Friend or foe? Arch Toxicol. 96:1573–1607. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kruempel JCP, Miller HA, Schaller ML,
Fretz A, Howington M, Sarker M, Huang S and Leiser SF: Hypoxic
response regulators RHY-1 and EGL-9/PHD promote longevity through a
VHL-1-independent transcriptional response. Geroscience.
42:1621–1633. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ozurumba E, Mathew O, Ranganna K, Choi M
and Oyekan A: Regulation of hypoxia inducible factor/prolyl
hydroxylase binding domain proteins 1 by PPARalpha and high salt
diet. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 29:165–173. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Souvenir R, Flores JJ, Ostrowski RP,
Manaenko A, Duris K and Tang J: Erythropoietin inhibits HIF-1alpha
expression via upregulation of PHD-2 transcription and translation
in an in vitro model of hypoxia-ischemia. Transl Stroke Res.
5:118–127. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Demandt JAF, van Kuijk K, Theelen TL,
Marsch E, Heffron SP, Fisher EA, Carmeliet P, Biessen EAL and
Sluimer JC: Whole-body prolyl hydroxylase domain (PHD) 3 deficiency
increased plasma lipids and hematocrit without impacting plaque
size in low-density lipoprotein receptor knockout mice. Front Cell
Dev Biol. 9:6642582021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Duan LJ, Takeda K and Fong GH:
Hematological, hepatic, and retinal phenotypes in mice deficient
for prolyl hydroxylase domain proteins in the liver. Am J Pathol.
184:1240–1250. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tojo Y, Sekine H, Hirano I, Pan X, Souma
T, Tsujita T, Kawaguchi S, Takeda N, Takeda K, Fong GH, et al:
Hypoxia signaling cascade for erythropoietin production in
hepatocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 35:2658–2672. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lindholm ME, Fischer H, Poellinger L,
Johnson RS, Gustafsson T, Sundberg CJ and Rundqvist H: Negative
regulation of HIF in skeletal muscle of elite endurance athletes: A
tentative mechanism promoting oxidative metabolism. Am J Physiol
Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 307:R248–R255. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hata M, Yoshitake I, Wakui S, Unosawa S,
Kimura H, Hata H and Shiono M: Long-term patency rate for radial
artery vs. saphenous vein grafts using same-patient materials. Circ
J. 75:1373–1377. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wolf D, Muralidharan A and Mohan S: Role
of prolyl hydroxylase domain proteins in bone metabolism.
Osteoporos Sarcopenia. 8:1–10. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wu C, Rankin EB, Castellini L, Alcudia JF,
LaGory EL, Andersen R, Rhodes SD, Wilson TL, Mohammad KS, Castillo
AB, et al: Oxygen-sensing PHDs regulate bone homeostasis through
the modulation of osteoprotegerin. Genes Dev. 29:817–831. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhang J, Kasim V, Xie YD, Huang C,
Sisjayawan J, Ariyanti AD, Yan XS, Wu XY, Liu CP, Yang L, et al:
Inhibition of PHD3 by salidroside promotes neovascularization
through cell-cell communications mediated by muscle-secreted
angiogenic factors. Sci Rep. 7:439352017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Tian J, Bao X, Yang F, Tang X, Jiang Q, Li
Y, Yao K and Yin Y: Elevation of intracellular alpha-ketoglutarate
levels inhibits osteoclastogenesis by suppressing the NF-kappaB
signaling pathway in a PHD1-dependent manner. Nutrients.
15:7012023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kapitsinou PP, Rajendran G, Astleford L,
Michael M, Schonfeld MP, Fields T, Shay S, French JL, West J and
Haase VH: The endothelial prolyl-4-hydroxylase domain
2/hypoxia-inducible factor 2 axis regulates pulmonary artery
pressure in mice. Mol Cell Biol. 36:1584–1594. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Chu HX and Jones NM: Changes in
hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) and regulatory prolyl
hydroxylase (PHD) enzymes following hypoxic-ischemic injury in the
neonatal rat. Neurochem Res. 41:515–522. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yang M, Su H, Soga T, Kranc KR and Pollard
PJ: Prolyl hydroxylase domain enzymes: Important regulators of
cancer metabolism. Hypoxia (Auckl). 2:127–142. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Miikkulainen P, Hogel H, Seyednasrollah F,
Rantanen K, Elo LL and Jaakkola PM: Hypoxia-inducible factor
(HIF)-prolyl hydroxylase 3 (PHD3) maintains high HIF2A mRNA levels
in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J Biol Chem. 294:3760–3771.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Koren A, Rijavec M, Krumpestar T, Kern I,
Sadikov A, Čufer T and Korošec P: Gene expression levels of the
prolyl hydroxylase domain proteins PHD1 and PHD2 but not PHD3 are
decreased in primary tumours and correlate with poor prognosis of
patients with surgically resected non-small-cell lung cancer.
Cancers (Basel). 13:23092021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Deschoemaeker S, Di Conza G, Lilla S,
Martín-Pérez R, Mennerich D, Boon L, Hendrikx S, Maddocks OD, Marx
C, Radhakrishnan P, et al: PHD1 regulates p53-mediated colorectal
cancer chemoresistance. EMBO Mol Med. 7:1350–1365. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Jokilehto T and Jaakkola PM: The role of
HIF prolyl hydroxylases in tumour growth. J Cell Mol Med.
14:758–770. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Harnoss JM, Gebhardt JM, Radhakrishnan P,
Leowardi C, Burmeister J, Halligan DN, Yuan S, Kennel KB,
Strowitzki MJ, Schaible A, et al: Prolyl hydroxylase inhibition
mitigates pouchitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 26:192–205. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Bakshi HA, Mishra V, Satija S, Mehta M,
Hakkim FL, Kesharwani P, Dua K, Chellappan DK, Charbe NB,
Shrivastava G, et al: Dynamics of prolyl hydroxylases levels during
disease progression in experimental colitis. Inflammation.
42:2032–2036. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Taniguchi CM, Finger EC, Krieg AJ, Wu C,
Diep AN, LaGory EL, Wei K, McGinnis LM, Yuan J, Kuo CJ and Giaccia
AJ: Cross-talk between hypoxia and insulin signaling through Phd3
regulates hepatic glucose and lipid metabolism and ameliorates
diabetes. Nat Med. 19:1325–1330. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Huang M, Paglialunga S, Wong JM, Hoang M,
Pillai R and Joseph JW: Role of prolyl hydroxylase domain proteins
in the regulation of insulin secretion. Physiol Rep. 4:e127222016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Hickey MM, Lam JC, Bezman NA, Rathmell WK
and Simon MC: von Hippel-Lindau mutation in mice recapitulates
Chuvash polycythemia via hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha signaling
and splenic erythropoiesis. J Clin Invest. 117:3879–3889.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Gordeuk VR and Prchal JT: Vascular
complications in Chuvash polycythemia. Semin Thromb Hemost.
32:289–294. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Watts ER and Walmsley SR: Inflammation and
hypoxia: HIF and PHD isoform selectivity. Trends Mol Med. 25:33–46.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Minamishima YA: Hypoxic response as a
therapeutic target of human diseases. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi.
155:40–45. 2020.(In Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Lawson H, Holt-Martyn JP, Dembitz V,
Kabayama Y, Wang LM, Bellani A, Atwal S, Saffoon N, Durko J, van de
Lagemaat LN, et al: The selective prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor IOX5
stabilizes HIF-1alpha and compromises development and progression
of acute myeloid leukemia. Nat Cancer. 5:916–937. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Yu Y, Su Y, Yang S, Liu Y, Lin Z, Das NK,
Wu Q, Zhou J, Sun S, Li X, et al: Activation of Intestinal
HIF2alpha ameliorates iron-refractory anemia. Adv Sci (Weinh).
11:e23070222024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Locatelli F, Del Vecchio L, De Nicola L
and Minutolo R: Are all erythropoiesis-stimulating agents created
equal? Nephrol Dial Transplant. 36:1369–1377. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zhu Y, Wang Y, Jia Y, Xu J and Chai Y:
Roxadustat promotes angiogenesis through HIF-1alpha/VEGF/VEGFR2
signaling and accelerates cutaneous wound healing in diabetic rats.
Wound Repair Regen. 27:324–334. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Cirillo F, Resmini G, Angelino E, Ferrara
M, Tarantino A, Piccoli M, Rota P, Ghiroldi A, Monasky MM, Ciconte
G, et al: HIF-1alpha directly controls WNT7A expression during
myogenesis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 8:5935082020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Li X, Cui XX, Chen YJ, Wu TT, Xu H, Yin H
and Wu YC: Therapeutic potential of a prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor
FG-4592 for Parkinson's diseases in vitro and in vivo: Regulation
of redox biology and mitochondrial function. Front Aging Neurosci.
10:1212018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Singh C, Hoppe G, Tran V, McCollum L,
Bolok Y, Song W, Sharma A, Brunengraber H and Sears JE: Serine and
1-carbon metabolism are required for HIF-mediated protection
against retinopathy of prematurity. JCI Insight. 4:e1293982019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Schley G, Klanke B, Kalucka J, Schatz V,
Daniel C, Mayer M, Goppelt-Struebe M, Herrmann M, Thorsteinsdottir
M, Palsson R, et al: Mononuclear phagocytes orchestrate prolyl
hydroxylase inhibition-mediated renoprotection in chronic
tubulointerstitial nephritis. Kidney Int. 96:378–396. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Han F, Wu G, Han S, Li Z, Jia Y, Bai L, Li
X, Wang K, Yang F, Zhang J, et al: Hypoxia-inducible factor
prolyl-hydroxylase inhibitor roxadustat (FG-4592) alleviates
sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Respir Physiol Neurobiol.
281:1035062020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Chen C, Yan S, Qiu S, Geng Z and Wang Z:
HIF/Ca(2+)/NO/ROS is critical in roxadustat treating bone fracture
by stimulating the proliferation and migration of BMSCs. Life Sci.
264:1186842021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Zhang P, Du J, Zhao H, Cheng Y, Dong S,
Yang Y, Li B, Gao F, Sun X, Cai J and Liu C: Radioprotective
effects of roxadustat (FG-4592) in haematopoietic system. J Cell
Mol Med. 23:349–356. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Chen H, Cheng Q, Wang J, Zhao X and Zhu S:
Long-term efficacy and safety of hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl
hydroxylase inhibitors in anaemia of chronic kidney disease: A
meta-analysis including 13,146 patients. J Clin Pharm Ther.
46:999–1009. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Kansagra KA, Parmar D, Jani RH, Srinivas
NR, Lickliter J, Patel HV, Parikh DP, Heading H, Patel HB, Gupta
RJ, et al: Phase I clinical study of ZYAN1, A novel
prolyl-hydroxylase (PHD) inhibitor to evaluate the safety,
tolerability, and pharmacokinetics following oral administration in
healthy volunteers. Clin Pharmacokinet. 57:87–102. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Singh AK, Carroll K, Perkovic V, Solomon
S, Jha V, Johansen KL, Lopes RD, Macdougall IC, Obrador GT, Waikar
SS, et al: Daprodustat for the treatment of anemia in patients
undergoing dialysis. N Engl J Med. 385:2325–2335. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Singh AK, Carroll K, McMurray JJV, Solomon
S, Jha V, Johansen KL, Lopes RD, Macdougall IC, Obrador GT, Waikar
SS, et al: Daprodustat for the treatment of anemia in patients not
undergoing dialysis. N Engl J Med. 385:2313–2324. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Fishbane S, Pollock CA, El-Shahawy M,
Escudero ET, Rastogi A, Van BP, Frison L, Houser M, Pola M, Little
DJ, et al: Roxadustat versus epoetin alfa for treating anemia in
patients with chronic kidney disease on dialysis: Results from the
randomized phase 3 ROCKIES study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 33:850–866.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Fishbane S, El-Shahawy MA, Pecoits-Filho
R, Escudero ET, Rastogi A, Van BP, Frison L, Houser M, Pola M,
Little DJ, et al: Roxadustat for treating anemia in patients with
CKD not on dialysis: Results from a randomized phase 3 study. J Am
Soc Nephrol. 32:737–755. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Chen N, Hao C, Peng X, Lin H, Yin A, Hao
L, Tao Y, Liang X, Liu Z, Xing C, et al: Roxadustat for anemia in
patients with kidney disease not receiving dialysis. N Engl J Med.
381:1001–1010. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Perkovic V, Blackorby A, Cizman B, Carroll
K, Cobitz AR, Davies R, DiMino TL, Jha V, Johansen KL, Lopes RD, et
al: The ASCEND-ND trial: Study design and participant
characteristics. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 37:2157–2170. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Testi I, Calcagni A, Barton K, Gooch J and
Petrushkin H: Hypotony in uveitis: An overview of medical and
surgical management. Br J Ophthalmol. 107:1765–1770. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Kurata Y, Tanaka T and Nangaku M: An
evaluation of roxadustat for the treatment of anemia associated
with chronic kidney disease. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 23:19–28.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Eckardt KU, Agarwal R, Aswad A, Awad A,
Block GA, Bacci MR, Farag YMK, Fishbane S, Hubert H, Jardine A, et
al: Safety and efficacy of vadadustat for anemia in patients
undergoing dialysis. N Engl J Med. 384:1601–1612. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Provenzano R, Tumlin J, Zabaneh R, Chou J,
Hemmerich S, Neff TB and Yu KP: Oral hypoxia-inducible factor
prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor roxadustat (FG-4592) for treatment of
anemia in chronic kidney disease: A placebo-controlled study of
pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles in hemodialysis
patients. J Clin Pharmacol. 60:1432–1440. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Akizawa T, Tanaka-Amino K, Otsuka T and
Yamaguchi Y: Factors affecting doses of roxadustat versus
darbepoetin alfa for anemia in nondialysis patients. Am J Nephrol.
52:702–713. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Kokado Y, Kawai K, Nanjo T, Kinoshita S
and Kondo K: In vitro and clinical pharmacokinetic studies of the
effects of iron-containing agents on vadadustat, an oral
hypoxia-inducible factor-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor. Clin Ther.
43:1408–1418. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Hansen MB, Kondziella D, Danielsen ER,
Larsen VA, Jansen EC and Hyldegaard O: Cerebral proton magnetic
resonance spectroscopy demonstrates reversibility of
N-acetylaspartate/creatine in gray matter after delayed
encephalopathy due to carbon monoxide intoxication: A case report.
J Med Case Rep. 8:2112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Gossage L, Eisen T and Maher ER: VHL, the
story of a tumour suppressor gene. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:55–64. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Chen N, Hao C, Liu BC, Lin H, Wang C, Xing
C, Liang X, Jiang G, Liu Z, Li X, et al: Roxadustat treatment for
anemia in patients undergoing long-term dialysis. N Engl J Med.
381:1011–1022. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Pfeffer MA, Burdmann EA, Chen CY, Cooper
ME, de Zeeuw D, Eckardt KU, Feyzi JM, Ivanovich P, Kewalramani R,
Levey AS, et al: A trial of darbepoetin alfa in type 2 diabetes and
chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 361:2019–2032. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Cygulska K, Wejner-Mik P, Plewka M, Figiel
L, Chrzanowski L and Kasprzak JD: Roxadustat: Another drug that
causes pulmonary hypertension? Report of first human case. Pol Arch
Intern Med. 129:344–345. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Zhu X, Jiang L, Wei X, Long M and Du Y:
Roxadustat: Not just for anemia. Front Pharmacol. 13:9717952022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Semenza GL: The genomics and genetics of
oxygen homeostasis. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 21:183–204. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Wu TY, Liu FY, Ouzhou L, Cui CY, Qi XB and
Su B: A genetic adaptive pattern-low hemoglobin concentration in
the Himalayan highlanders. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi.
29:481–493. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Arsenault PR, Song D, Chung YJ, Khurana TS
and Lee FS: The zinc finger of prolyl hydroxylase domain protein 2
is essential for efficient hydroxylation of hypoxia-inducible
factor alpha. Mol Cell Biol. 36:2328–2343. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Tashi T, Reading NS, Wuren T, Zhang X,
Moore LG, Hu H, Tang F, Shestakova A, Lorenzo F, Burjanivova T, et
al: Gain-of-function EGLN1 prolyl hydroxylase (PHD2 D4E:C127S) in
combination with EPAS1 (HIF-2alpha) polymorphism lowers hemoglobin
concentration in Tibetan highlanders. J Mol Med (Berl). 95:665–670.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Peng Y, Cui C, He Y, Ouzhuluobu Zhang H,
Yang D, Zhang Q, Bianbazhuoma Yang L, He Y, et al: Down-regulation
of EPAS1 transcription and genetic adaptation of tibetans to
high-altitude hypoxia. Mol Biol Evol. 34:818–830. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Lorenzo FR, Huff C, Myllymaki M, Olenchock
B, Swierczek S, Tashi T, Gordeuk V, Wuren T, Ri-Li G, McClain DA,
et al: A genetic mechanism for Tibetan high-altitude adaptation.
Nat Genet. 46:951–956. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Gesang L, Gusang L, Dawa C, Gesang G and
Li K: Whole-Genome sequencing identifies the egl nine homologue 3
(egln3/phd3) and protein phosphatase 1 regulatory inhibitor subunit
2 (PPP1R2P1) associated with high-altitude polycythemia in Tibetans
at high altitude. Dis Markers. 2019:59464612019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Song D, Peng K, Palmer BE and Lee FS: The
ribosomal chaperone NACA recruits PHD2 to cotranslationally modify
HIF-α. EMBO J. 41:e1120592022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Yuan X, Ruan W, Bobrow B, Carmeliet P and
Eltzschig HK: Targeting hypoxia-inducible factors: Therapeutic
opportunities and challenges. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 23:175–200.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Stockmann C and Fandrey J: Hypoxia-induced
erythropoietin production: A paradigm for oxygen-regulated gene
expression. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 33:968–979. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Simonson TS, McClain DA, Jorde LB and
Prchal JT: Genetic determinants of Tibetan high-altitude
adaptation. Hum Genet. 131:527–533. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Hassin O and Oren M: Drugging p53 in
cancer: One protein, many targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 22:127–144.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Zheng J, Deng Y, Huang B and Chen X:
Efficacy and safety of immune checkpoint inhibitors combined with
chemotherapy as first-line treatment for extensive-stage small cell
lung cancer: a meta-analysis based on mixed-effect models. Front
Med (Lausanne). 10:11989502023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|