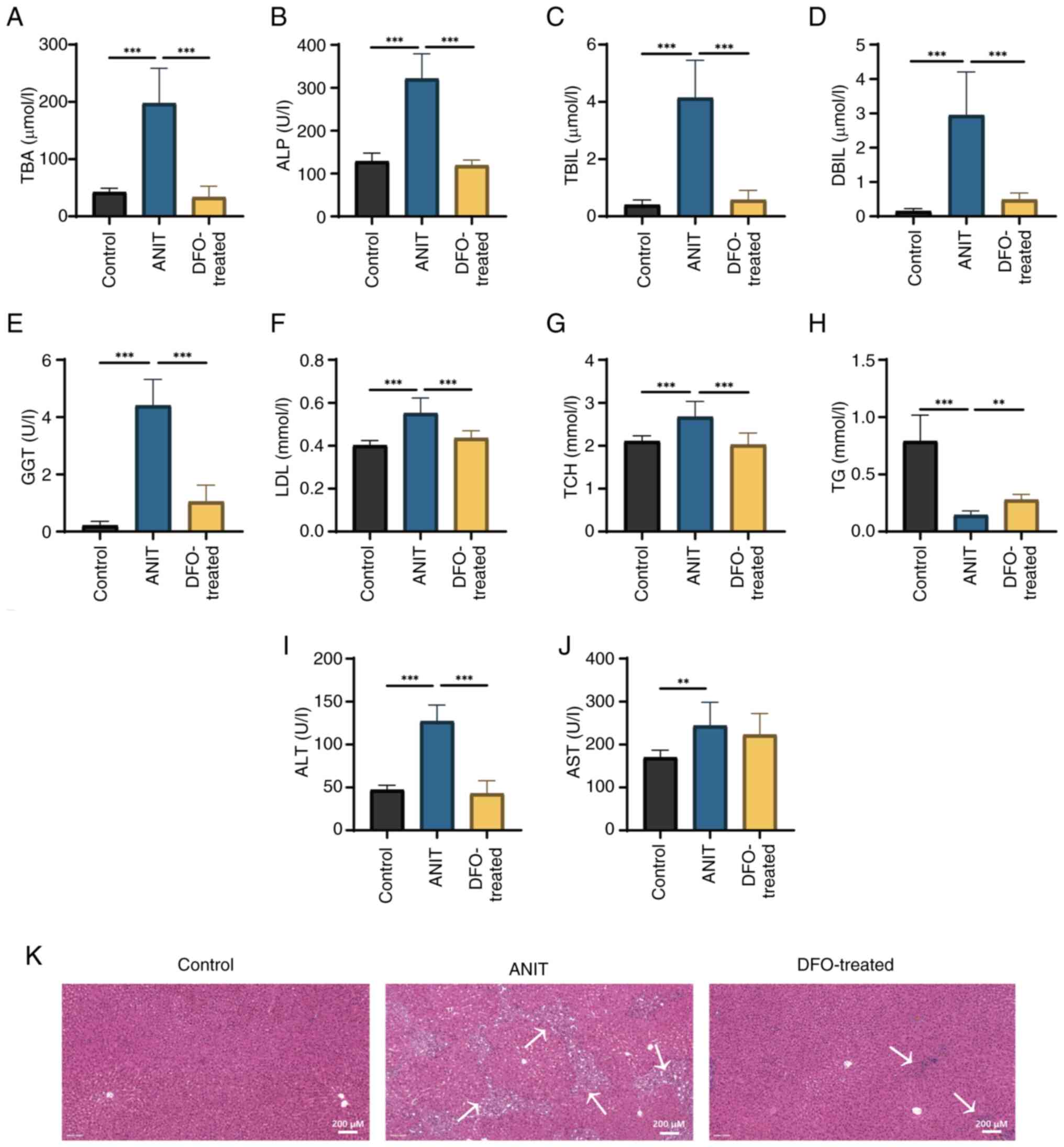
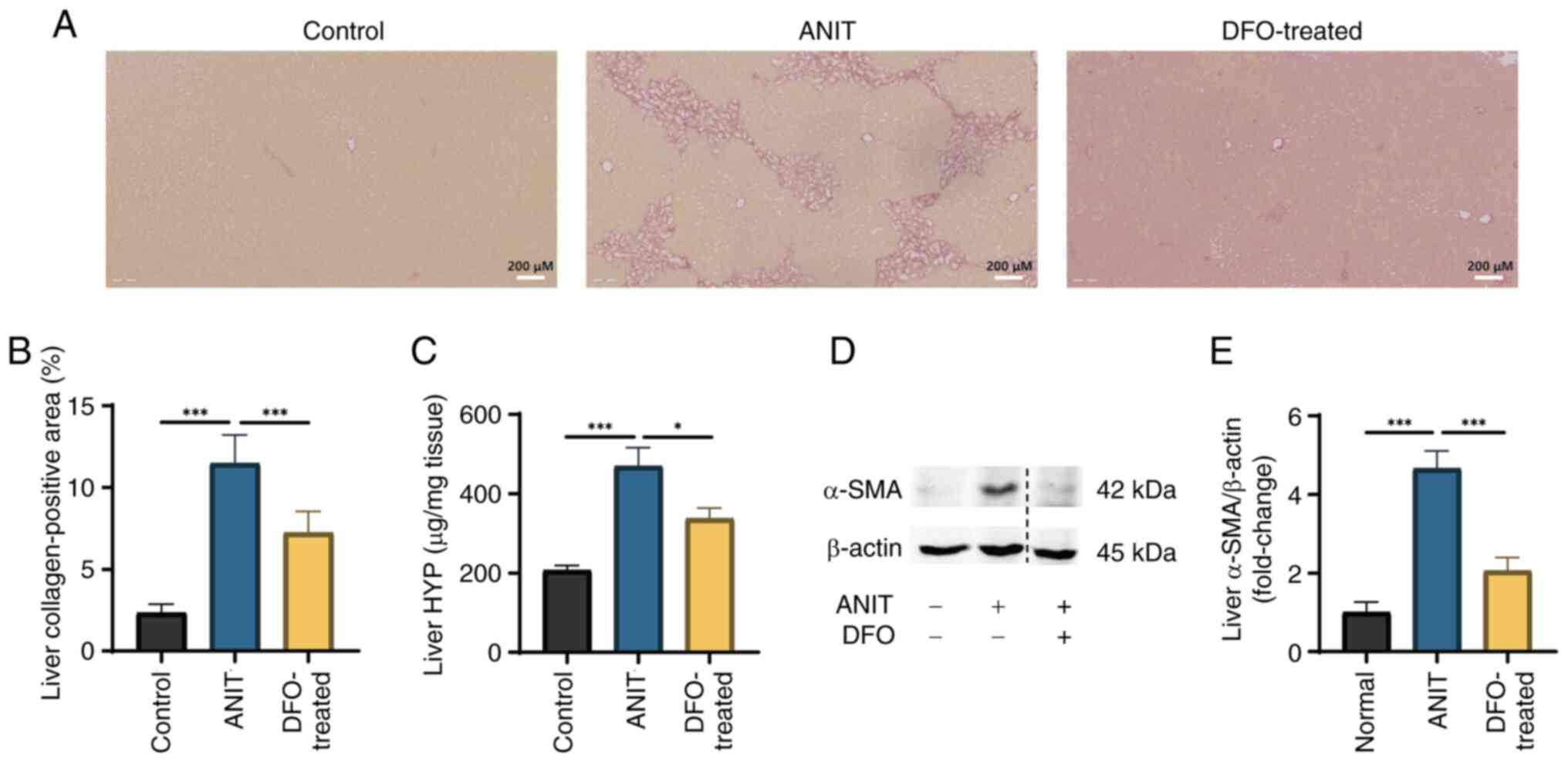
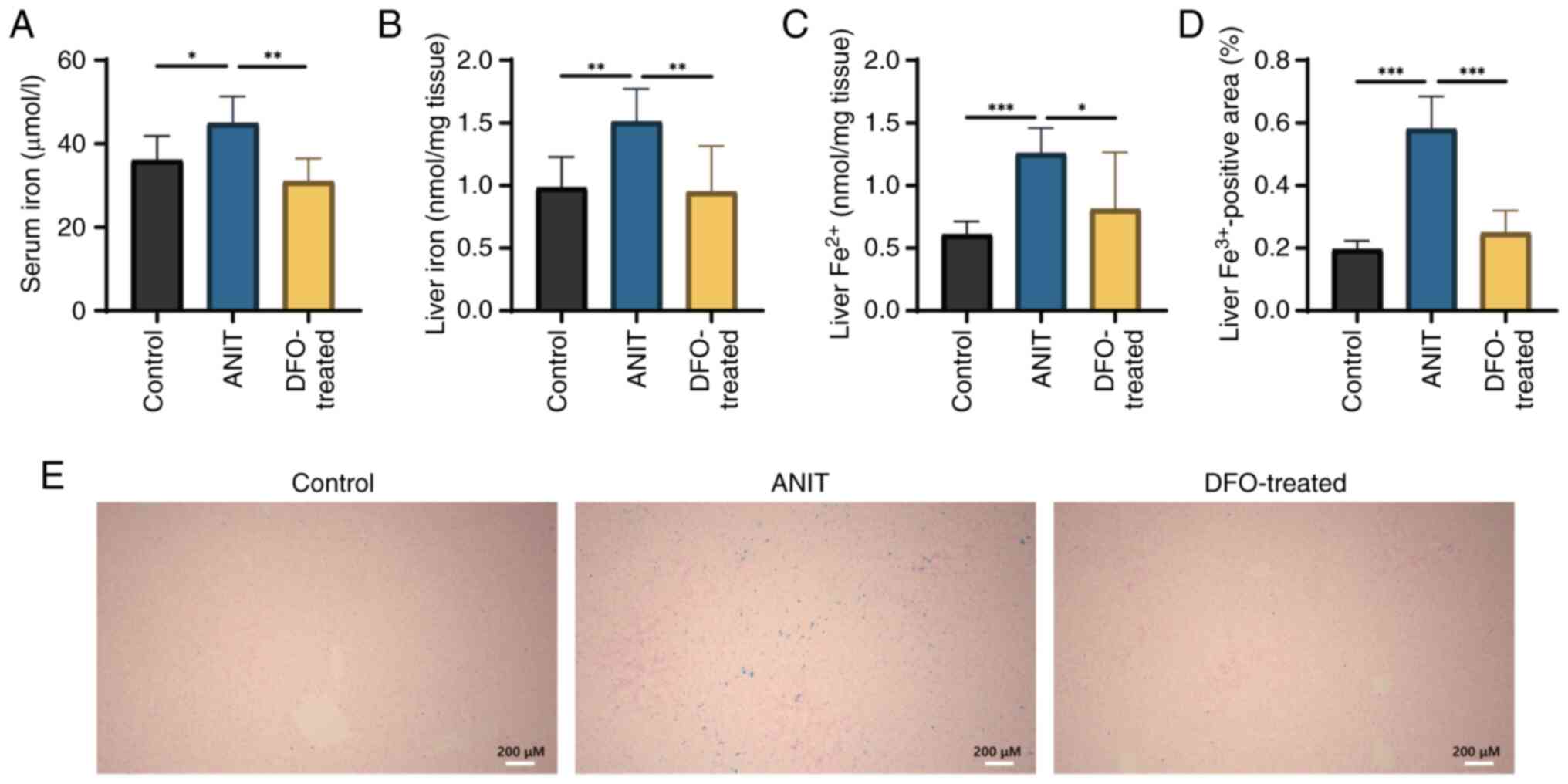
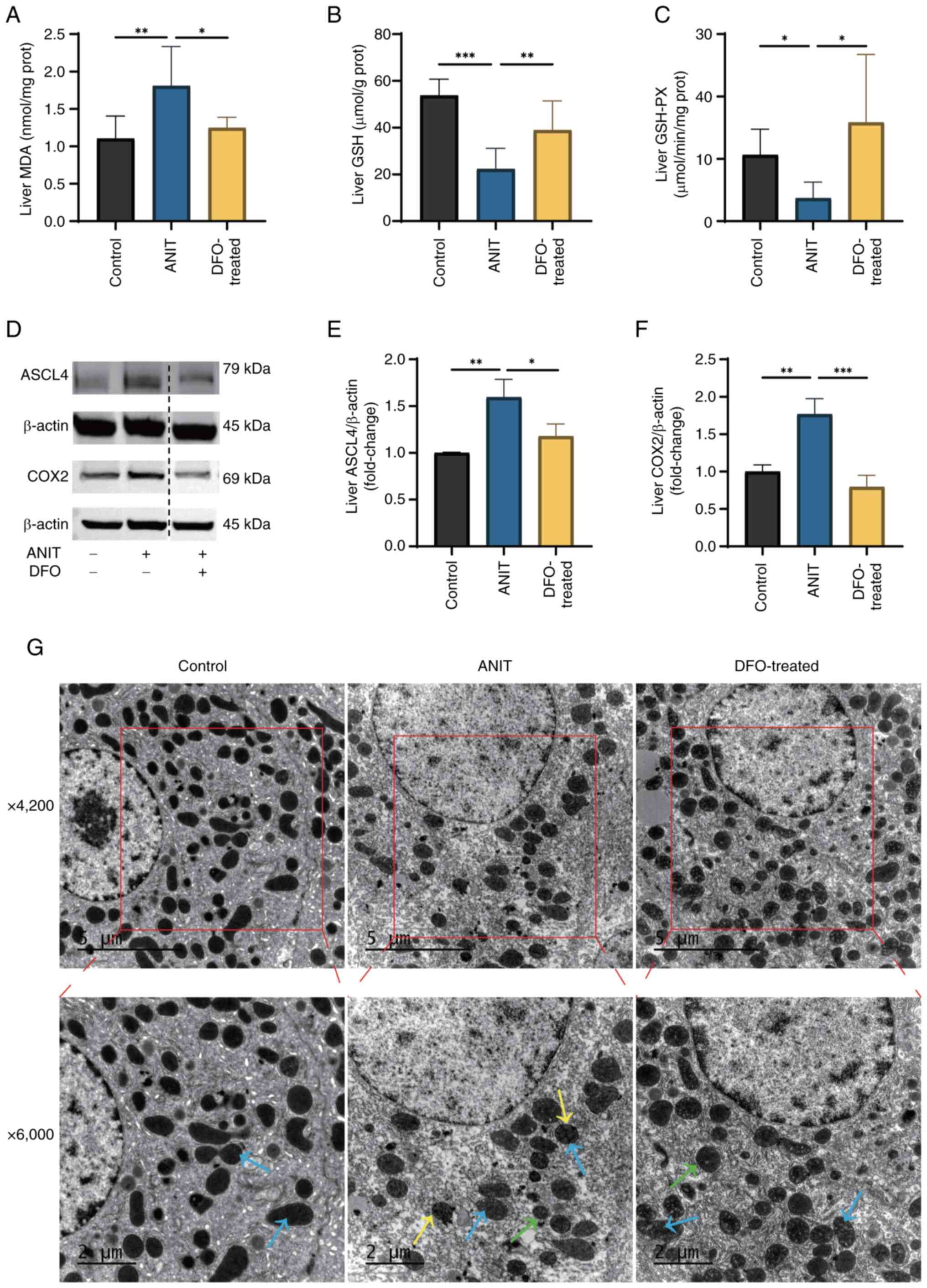
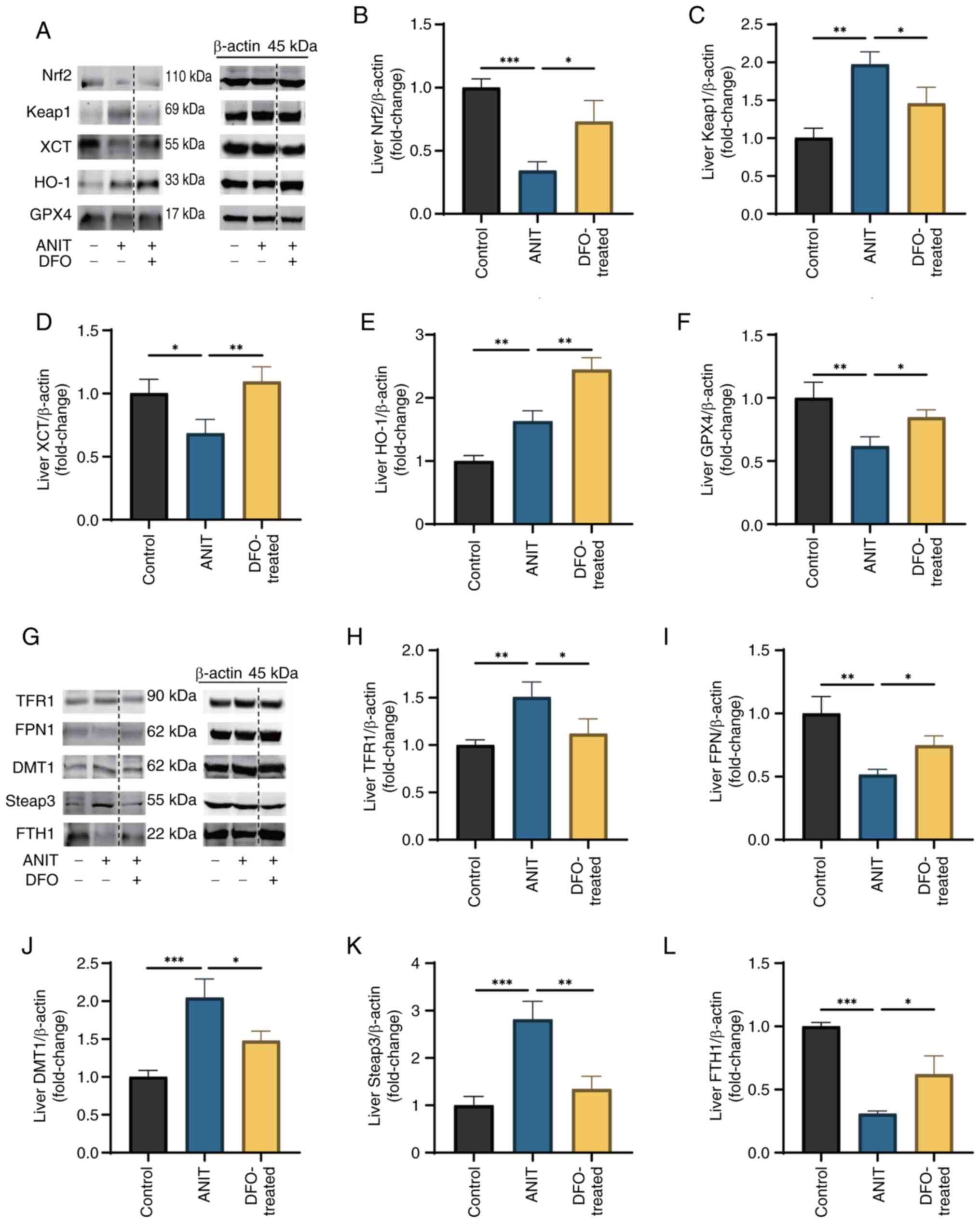
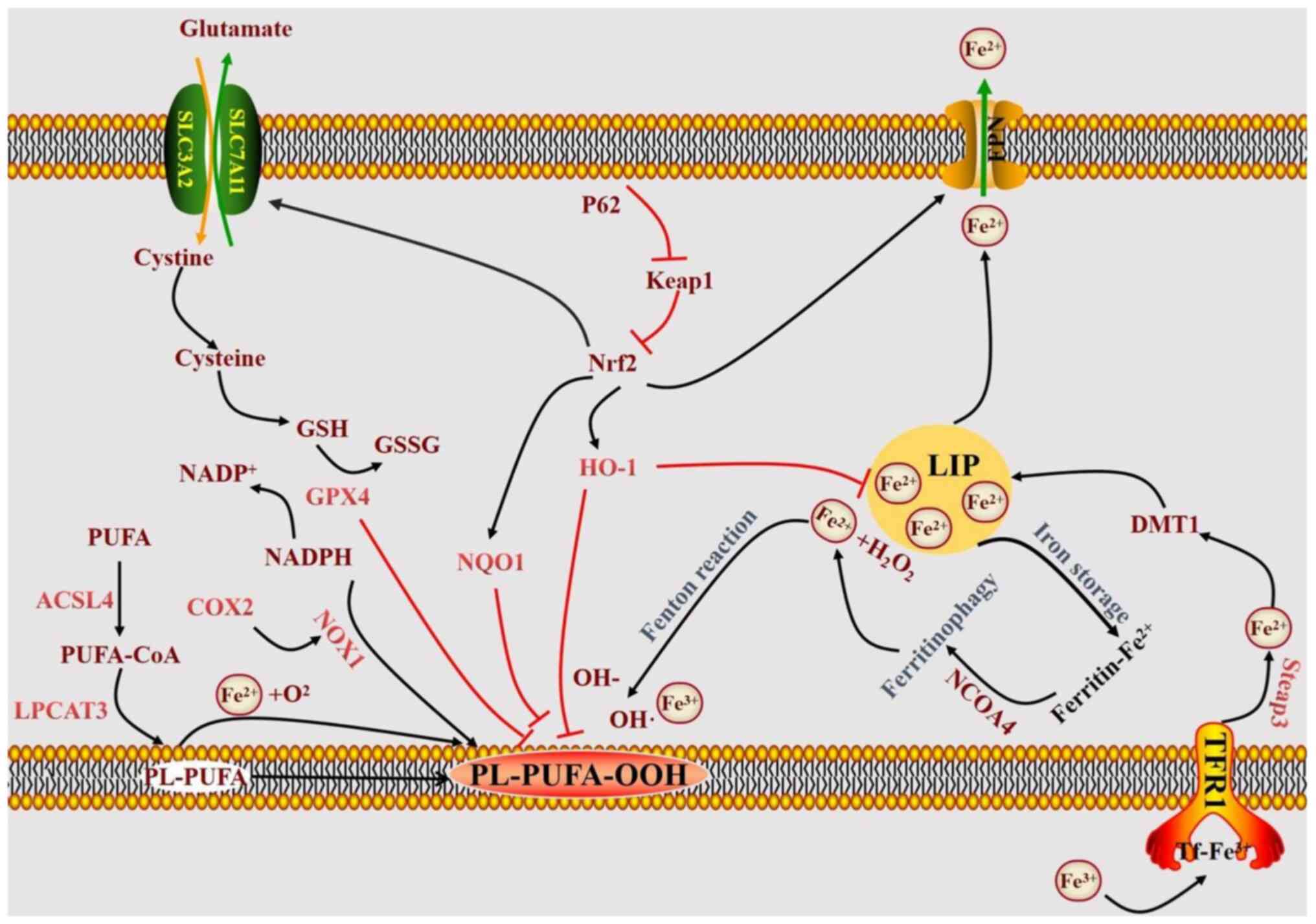
|
1
|
Karpen SJ, Kelly D, Mack C and Stein P:
Ileal bile acid transporter inhibition as an anticholestatic
therapeutic target in biliary atresia and other cholestatic
disorders. Hepatol Int. 14:677–689. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pollock G and Minuk GY: Diagnostic
considerations for cholestatic liver disease. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 32:1303–1309. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bortolini M, Almasio P, Bray G, Budillon
G, Coltorti M, Frezza M, Okolicsanyi L, Salvagnini M and Williams
R: Multicentre survey of the prevalence of intrahepatic cholestasis
in 2520 consecutive patients with newly diagnosed chronic liver
disease. Drug Invest. 4 (Suppl 4):S83–S89. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Xie W, Cao Y, Xu M, Wang J, Zhou C, Yang
X, Geng X, Zhang W, Li N and Cheng J: Prognostic significance of
elevated cholestatic enzymes for fibrosis and hepatocellular
carcinoma in hospital discharged chronic viral hepatitis patients.
Sci Rep. 7:102892017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ibrahim SH, Kamath BM, Loomes KM and
Karpen SJ: Cholestatic liver diseases of genetic etiology: Advances
and controversies. Hepatology. 75:1627–1646. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta
R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS,
et al: Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell
death. Cell. 149:1060–1072. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bayir H, Dixon SJ, Tyurina YY, Kellum JA
and Kagan VE: Ferroptotic mechanisms and therapeutic targeting of
iron metabolism and lipid peroxidation in the kidney. Nat Rev
Nephrol. 19:315–336. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang W: Iron turns to wild when the
transferrin is away. Blood. 136:649–650. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Buckley CD, Barone F, Nayar S, Benezech C
and Caamano J: Stromal cells in chronic inflammation and tertiary
lymphoid organ formation. Annu Rev Immunol. 33:715–745. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Forrester SJ, Kikuchi DS, Hernandes MS, Xu
Q and Griendling KK: Reactive oxygen species in metabolic and
inflammatory signaling. Circ Res. 122:877–902. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang WB, Yang F, Wang Y, Jiao FZ, Zhang
HY, Wang LW and Gong ZJ: Inhibition of HDAC6 attenuates LPS-induced
inflammation in macrophages by regulating oxidative stress and
suppressing the TLR4-MAPK/NF-ĸB pathways. Biomed Pharmacother.
117:1091662019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xie Y, Hou W, Song X, Yu Y, Huang J, Sun
X, Kang R and Tang D: Ferroptosis: Process and function. Cell Death
Differ. 23:369–379. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Han C, Liu Y, Dai R, Ismail N, Su W and Li
B: Ferroptosis and its potential role in human diseases. Front
Pharmacol. 11:2392020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang Y and Tang M: PM2.5 induces
ferroptosis in human endothelial cells through iron overload and
redox imbalance. Environ Pollut. 254:1129372019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jiang X, Stockwell BR and Conrad M:
Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 22:266–282. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lyberopoulou A, Chachami G, Gatselis NK,
Kyratzopoulou E, Saitis A, Gabeta S, Eliades P, Paraskeva E, Zachou
K, Koukoulis GK, et al: Low serum hepcidin in patients with
autoimmune liver diseases. PLoS One. 10:e01354862015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Marques O, Horvat NK, Zechner L, Colucci
S, Sparla R, Zimmermann S, Neufeldt CJ, Altamura S, Qiu R, Mudder
K, et al: Inflammation-driven NF-kappab signaling represses
ferroportin transcription in macrophages via HDAC1 and HDAC3.
Blood. 145:866–880. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xie X, Chang L, Zhu X, Gong F, Che L,
Zhang R, Wang L, Gong C, Fang C, Yao C, et al: Rubiadin mediates
the upregulation of hepatic hepcidin and alleviates iron overload
via BMP6/SMAD1/5/9-signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 26:13852025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Delesderrier E, Monteiro JDC, Freitas S,
Pinheiro IC, Batista MS and Citelli M: Can iron and polyunsaturated
fatty acid supplementation induce ferroptosis? Cell Physiol
Biochem. 57:24–41. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu C, Liu Z, Dong Z, Liu S, Kan H and
Zhang S: Multifaceted interplays between the essential players and
lipid peroxidation in ferroptosis. J Genet Genomics. 52:1071–1081.
2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tsuchida T and Friedman SL: Mechanisms of
hepatic stellate cell activation. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
14:397–411. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yu Y, Jiang L, Wang H, Shen Z, Cheng Q,
Zhang P, Wang J, Wu Q, Fang X, Duan L, et al: Hepatic transferrin
plays a role in systemic iron homeostasis and liver ferroptosis.
Blood. 136:726–739. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Q, Qu Y, Zhang Q, Li F, Li B, Li Z,
Dong Y, Lu L and Cai X: Exosomes derived from hepatitis b
virus-infected hepatocytes promote liver fibrosis via mir-222/TFRC
axis. Cell Biol Toxicol. 39:467–481. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang L, Xie P, Wu J, Yu J, Li X, Ma H, Yu
T, Wang H, Ye J, Wang J and Zheng H: Deferoxamine treatment
combined with sevoflurane postconditioning attenuates myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury by restoring HIF-1/BNIP3-mediated
mitochondrial autophagy in GK rats. Front Pharmacol. 11:62020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Duscher D, Neofytou E, Wong VW, Maan ZN,
Rennert RC, Inayathullah M, Januszyk M, Rodrigues M, Malkovskiy AV,
Whitmore AJ, et al: Transdermal deferoxamine prevents
pressure-induced diabetic ulcers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
112:94–99. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
National RCUC, . Guide for the Care and
Use of Laboratory Animals. National Academies Press; Washington,
DC: 2011
|
|
27
|
Liu X, Wang J, Li M, Qiu J, Li X, Qi L,
Liu J, Liu P, Xie G and Wang X: Farnesoid × receptor is an
important target for the treatment of disorders of bile acid and
fatty acid metabolism in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
combined with cholestasis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 38:1438–1446.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang H, Jiang C, Yang Y, Li J, Wang Y,
Wang C and Gao Y: Resveratrol ameliorates iron overload induced
liver fibrosis in mice by regulating iron homeostasis. PeerJ.
10:e135922022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xiang D, Liu Y, Zu Y, Yang J, He W, Zhang
C and Liu D: Calculus bovis sativus alleviates estrogen
cholestasis-induced gut and liver injury in rats by regulating
inflammation, oxidative stress, apoptosis, and bile acid profiles.
J Ethnopharmacol. 302:1158542023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhuang Y, Ortega-Ribera M, Thevkar Nagesh
P, Joshi R, Huang H, Wang Y, Zivny A, Mehta J, Parikh SM and Szabo
G: Bile acid-induced IRF3 phosphorylation mediates cell death,
inflammatory responses, and fibrosis in cholestasis-induced liver
and kidney injury via regulation of ZBP1. Hepatology. 79:752–767.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang WS and Stockwell BR: Ferroptosis:
Death by lipid peroxidation. Trends Cell Biol. 26:165–176. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Alajbeg IZ, Lapic I, Rogic D, Vuletic L,
Andabak Rogulj A, Illes D, Knezović Zlatarić D, Badel T, Vrbanovic
E and Alajbeg I: Within-subject reliability and between-subject
variability of oxidative stress markers in saliva of healthy
subjects: A longitudinal pilot study. Dis Markers.
2017:26974642017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hakkoymaz H, Nazik S, Seyithanoglu M,
Guler O, Sahin AR, Cengiz E and Yazar FM: The value of
ischemia-modified albumin and oxidative stress markers in the
diagnosis of acute appendicitis in adults. Am J Emerg Med.
37:2097–2101. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tangvarasittichai S: Oxidative stress,
insulin resistance, dyslipidemia and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
World J Diabetes. 6:456–480. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Moore DD, Kato S, Xie W, Mangelsdorf DJ,
Schmidt DR, Xiao R and Kliewer SA: International union of
pharmacology. LXII. The NR1h and NR1i receptors: Constitutive
androstane receptor, pregnene × receptor, farnesoid × receptor
alpha, farnesoid × receptor beta, liver × receptor alpha, liver ×
receptor beta, and vitamin d receptor. Pharmacol Rev. 58:742–759.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kagan VE, Mao G, Qu F, Angeli JP, Doll S,
Croix CS, Dar HH, Liu B, Tyurin VA, Ritov VB, et al: Oxidized
arachidonic and adrenic PEs navigate cells to ferroptosis. Nat Chem
Biol. 13:81–90. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Doll S, Proneth B, Tyurina YY, Panzilius
E, Kobayashi S, Ingold I, Irmler M, Beckers J, Aichler M, Walch A,
et al: ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular
lipid composition. Nat Chem Biol. 13:91–98. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang WS, Kim KJ, Gaschler MM, Patel M,
Shchepinov MS and Stockwell BR: Peroxidation of polyunsaturated
fatty acids by lipoxygenases drives ferroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 113:E4966–E4975. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Daiber A, Di Lisa F, Oelze M,
Kroller-Schon S, Steven S, Schulz E and Munzel T: Crosstalk of
mitochondria with NADPH oxidase via reactive oxygen and nitrogen
species signalling and its role for vascular function. Br J
Pharmacol. 174:1670–1689. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
You Y, Qian Z, Jiang Y, Chen L, Wu D, Liu
L, Zhang F, Ning X, Zhang Y and Xiao J: Insights into the
pathogenesis of gestational and hepatic diseases: The impact of
ferroptosis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 12:14828382024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Teschke R: Treatment of drug-induced liver
injury. Biomedicines. 11:152022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lewerenz J, Hewett SJ, Huang Y, Lambros M,
Gout PW, Kalivas PW, Massie A, Smolders I, Methner A, Pergande M,
et al: The cystine/glutamate antiporter system x(c)(−) in health
and disease: From molecular mechanisms to novel therapeutic
opportunities. Antioxid Redox Signal. 18:522–555. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kan X, Yin Y, Song C, Tan L, Qiu X, Liao
Y, Liu W, Meng S, Sun Y and Ding C: Newcastle-disease-virus-induced
ferroptosis through nutrient deprivation and ferritinophagy in
tumor cells. iScience. 24:1028372021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sun X, Ou Z, Chen R, Niu X, Chen D, Kang R
and Tang D: Activation of the p62-keap1-NRF2 pathway protects
against ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology.
63:173–184. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yoo S, Kim M, Bae JY, Lee SA and Koh G:
Bardoxolone methyl inhibits ferroptosis through the Keap1-Nrf2
pathway in renal tubular epithelial cells. Mol Med Rep. 32:2672025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ichimura Y, Waguri S, Sou YS, Kageyama S,
Hasegawa J, Ishimura R, Saito T, Yang Y, Kouno T, Fukutomi T, et
al: Phosphorylation of p62 activates the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway during
selective autophagy. Mol Cell. 51:618–631. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chen Y, Ma L, Yan Y, Wang X, Cao L, Li Y
and Li M: Ophiopogon japonicus polysaccharide reduces
doxorubicin-induced myocardial ferroptosis injury by activating
Nrf2/GPX4 signaling and alleviating iron accumulation. Mol Med Rep.
31:362025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xiao P, Huang H, Zhao H, Liu R, Sun Z, Liu
Y, Chen N and Zhang Z: Edaravone dexborneol protects against
cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced blood-brain barrier damage by
inhibiting ferroptosis via activation of nrf-2/HO-1/GPX4 signaling.
Free Radic Biol Med. 217:116–125. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hu T, Wei G, Xi M, Yan J, Wu X, Wang Y,
Zhu Y, Wang C and Wen A: Synergistic cardioprotective effects of
danshensu and hydroxysafflor yellow a against myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury are mediated through the Akt/Nrf2/HO-1
pathway. Int J Mol Med. 38:83–94. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lin Q, Li S, Jin H, Cai H, Zhu X, Yang Y,
Wu J, Qi C, Shao X, Li J, et al: Mitophagy alleviates
cisplatin-induced renal tubular epithelial cell ferroptosis through
ROS/HO-1/GPX4 axis. Int J Biol Sci. 19:1192–1210. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Choi AM and Alam J: Heme oxygenase-1:
Function, regulation, and implication of a novel stress-inducible
protein in oxidant-induced lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
15:9–19. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Fisher AL, Wang CY, Xu Y, Joachim K, Xiao
X, Phillips S, Moschetta GA, Alfaro-Magallanes VM and Babitt JL:
Functional role of endothelial transferrin receptor 1 in iron
sensing and homeostasis. Am J Hematol. 97:1548–1559. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Deng P, Li J, Lu Y, Hao R, He M, Li M, Tan
M, Gao P, Wang L, Hong H, et al: Chronic cadmium exposure triggered
ferroptosis by perturbing the STEAP3-mediated glutathione redox
balance linked to altered metabolomic signatures in humans. Sci
Total Environ. 905:1670392023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Gao X, Hu W, Qian D, Bai X, He H, Li L and
Sun S: The mechanisms of ferroptosis under hypoxia. Cell Mol
Neurobiol. 43:3329–3341. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Nairz M, Fritsche G, Brunner P, Talasz H,
Hantke K and Weiss G: Interferon-gamma limits the availability of
iron for intramacrophage salmonella typhimurium. Eur J Immunol.
38:1923–1936. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ge W, Jie J, Yao J, Li W, Cheng Y and Lu
W: Advanced glycation end products promote osteoporosis by inducing
ferroptosis in osteoblasts. Mol Med Rep. 25:1402022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Chen GH, Song CC, Pantopoulos K, Wei XL,
Zheng H and Luo Z: Mitochondrial oxidative stress mediated
Fe-induced ferroptosis via the NRF2-ARE pathway. Free Radic Biol
Med. 180:95–107. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Holden P and Nair LS: Deferoxamine: An
angiogenic and antioxidant molecule for tissue regeneration. Tissue
Eng Part B Rev. 25:461–470. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zeng Z, Huang H, Zhang J, Liu Y, Zhong W,
Chen W, Lu Y, Qiao Y, Zhao H, Meng X, et al: HDM induce airway
epithelial cell ferroptosis and promote inflammation by activating
ferritinophagy in asthma. FASEB J. 36:e223592022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Mohammed A, Abd Al Haleem EN, El-Bakly WM
and El-Demerdash E: Deferoxamine alleviates liver fibrosis induced
by CCl4 in rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 43:760–768. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Liu MX, Gu YY, Nie WY, Zhu XM, Qi MJ, Zhao
RM, Zhu WZ and Zhang XL: Formononetin induces ferroptosis in
activated hepatic stellate cells to attenuate liver fibrosis by
targeting NADPH oxidase 4. Phytother Res. 38:5988–6003. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Xie J, Ye Z, Li L, Xia Y, Yuan R, Ruan Y
and Zhou X: Ferrostatin-1 alleviates oxalate-induced renal tubular
epithelial cell injury, fibrosis and calcium oxalate stone
formation by inhibiting ferroptosis. Mol Med Rep. 26:2562022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|