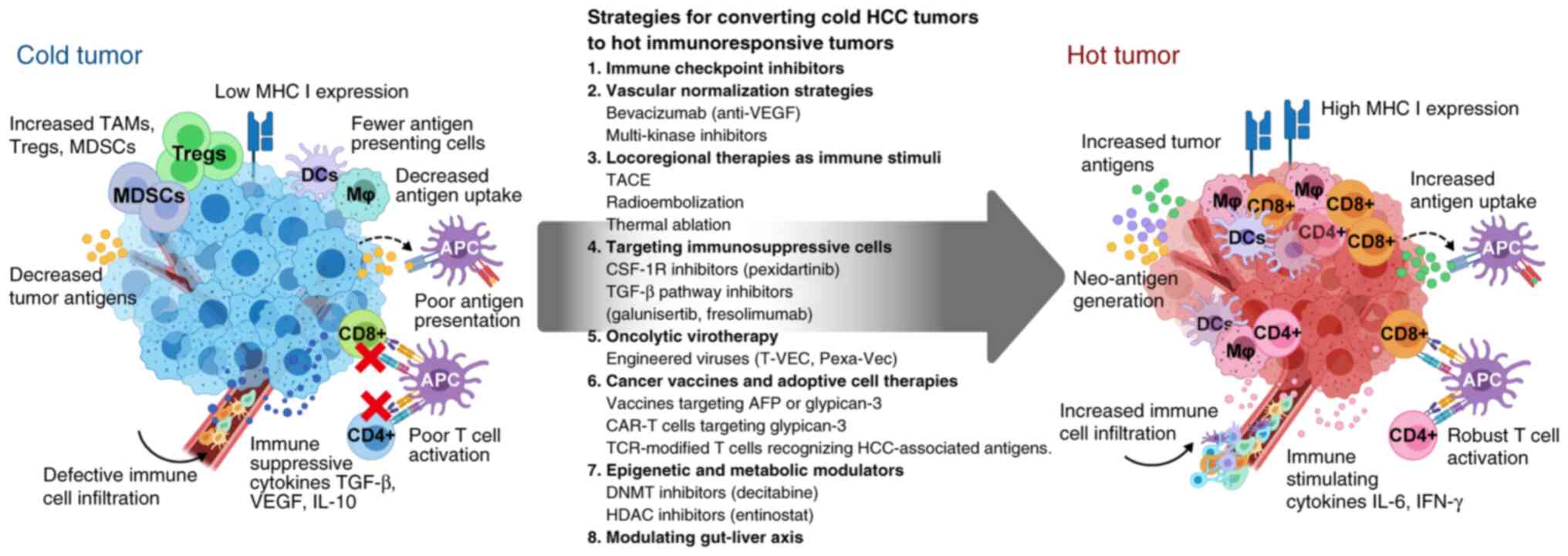
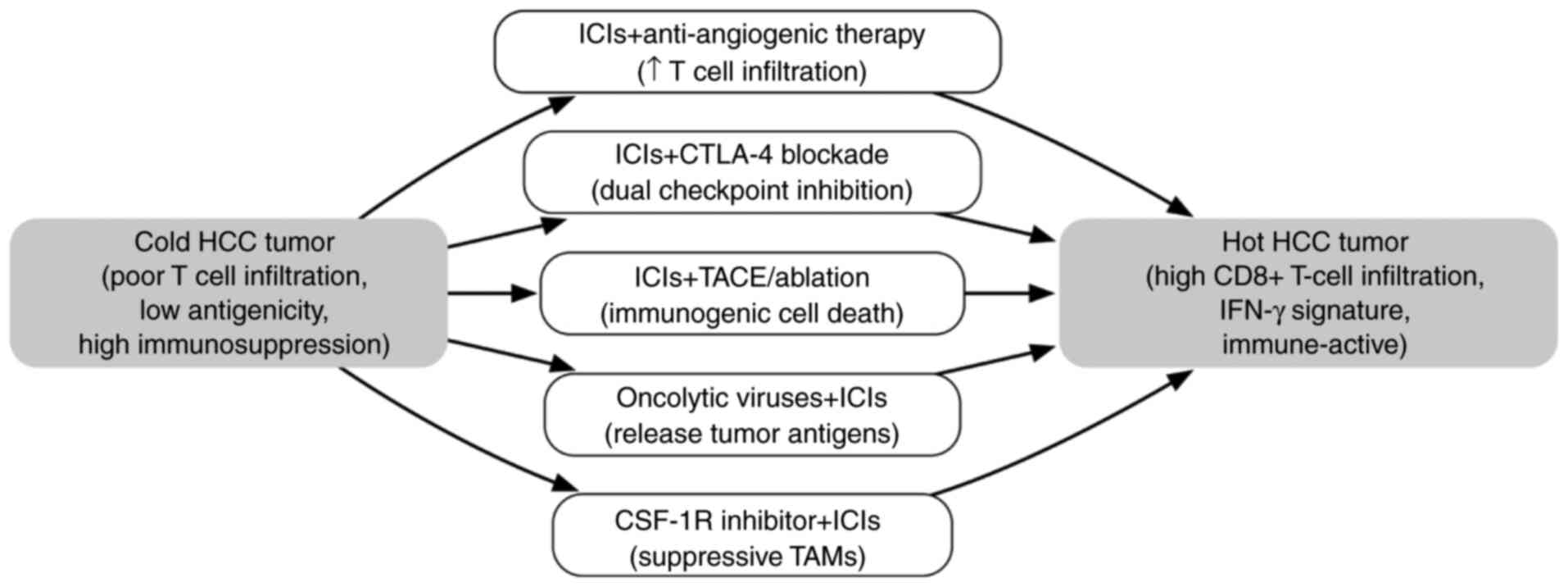
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249.
2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Villanueva A: Hepatocellular carcinoma. N
Engl J Med. 380:1450–1462. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ker CG: Hepatobiliary surgery in Taiwan:
The past, present, and future. Part I; biliary surgery. Formos J
Surg. 57:1–10. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sangro B, Gomez-Martin C, de la Mata M,
Iñarrairaegui M, Garralda E, Barrera P, Riezu-Boj JI, Larrea E,
Alfaro C, Sarobe P, et al: A clinical trial of CTLA-4 blockade with
tremelimumab in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and chronic
hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 59:81–88. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Llovet JM, Castet F, Heikenwalder M, Maini
MK, Mazzaferro V, Pinato DJ, Pikarsky E, Zhu AX and Finn RS:
Immunotherapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol.
19:151–172. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yau T, Kang YK, Kim TY, El-Khoueiry AB,
Santoro A, Sangro B, Melero I, Kudo M, Hou MM, Matilla A, et al:
Efficacy and safety of nivolumab plus ipilimumab in patients with
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma previously treated with
sorafenib: The checkmate 040 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol.
6:e2045642020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Childs A, Aidoo-Micah G, Maini MK and
Meyer T: Immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. JHEP Rep.
6:1011302024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ho DW, Tsui YM, Chan LK, Sze KM, Zhang X,
Cheu JW, Chiu YT, Lee JM, Chan AC, Cheung ET, et al: Single-cell
RNA sequencing shows the immunosuppressive landscape and tumor
heterogeneity of HBV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat
Commun. 12:36842021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Galon J and Bruni D: Approaches to treat
immune hot, altered and cold tumours with combination
immunotherapies. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 18:197–218. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pinyol R, Sia D and Llovet JM: Immune
exclusion-Wnt/CTNNB1 class predicts resistance to immunotherapies
in HCC. Clin Cancer Res. 25:2021–2023. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Giraud J, Chalopin D, Blanc JF and Saleh
M: Hepatocellular carcinoma immune landscape and the potential of
immunotherapies. Front Immunol. 12:6556972021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
De Marchi P, Leal LF, da Silva LS, Cavagna
RO, da Silva FAF, da Silva VD, da Silva EC, Saito AO, de Lima VCC
and Reis RM: Gene expression profiles (GEPs) of immuno-oncologic
pathways as predictors of response to checkpoint inhibitors in
advanced NSCLC. Transl Oncol. 39:1018182024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hernandez S, Lazcano R, Serrano A, Powell
S, Kostousov L, Mehta J, Khan K, Lu W and Solis LM: Challenges and
opportunities for immunoprofiling using a spatial high-plex
technology: The NanoString GeoMx(®) digital spatial
profiler. Front Oncol. 12:8904102022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bruni D, Angell HK and Galon J: The immune
contexture and Immunoscore in cancer prognosis and therapeutic
efficacy. Nat Rev Cancer. 20:662–680. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pfister D, Núñez NG, Pinyol R, Govaere O,
Pinter M, Szydlowska M, Gupta R, Qiu M, Deczkowska A, Weiner A, et
al: NASH limits anti-tumour surveillance in immunotherapy-treated
HCC. Nature. 592:450–456. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang Q, He Y, Luo N, Patel SJ, Han Y, Gao
R, Modak M, Carotta S, Haslinger C, Kind D, et al: Landscape and
dynamics of single immune cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell.
179:829–845.e20. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yi Q, Yang J, Wu Y, Wang Y, Cao Q and Wen
W: Immune microenvironment changes of liver cirrhosis: Emerging
role of mesenchymal stromal cells. Front Immunol. 14:12045242023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Montella L, Sarno F, Ambrosino A, Facchini
S, D'antò M, Laterza M, Fasano M, Quarata E, Ranucci RAN, Altucci
L, et al: The role of immunotherapy in a tolerogenic environment:
Current and future perspectives for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Cells. 10:19092021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shu QH, Ge Y, Hua X, Gao XQ, Pan JJ, Liu
DB, Xu GL, Ma JL and Jia WD: Prognostic value of polarized
macrophages in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after
curative resection. J Cell Mol Med. 20:1024–1035. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xue R, Zhang Q, Cao Q, Kong R, Xiang X,
Liu H, Feng M, Wang F, Cheng J, Li Z, et al: Liver tumour immune
microenvironment subtypes and neutrophil heterogeneity. Nature.
612:141–147. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ghaedi M and Ohashi P: ILC
transdifferentiation: Roles in cancer progression. Cell Res.
30:562–563. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim HD, Song G, Park S, Jung M, Kim MH,
Kang H, Yoo C, Yi K, Kim KH, Eo S, et al: Association between
expression level of PD1 by tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells and
features of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology.
155:1936–1950. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fu J, Xu D, Liu Z, Shi M, Zhao P, Fu B,
Zhang Z, Yang H, Zhang H, Zhou C, et al: Increased regulatory T
cells correlate with CD8 T-cell impairment and poor survival in
hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Gastroenterology. 132:2328–2239.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yan J, Liu XL, Xiao G, Li NL, Deng YN, Han
L, Yin LC, Ling LJ and Liu LX: Prevalence and clinical relevance of
T-Helper cells, Th17 and Th1, in hepatitis B virus-related
hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 9:e960802014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hu C, You W, Kong D, Huang Y, Lu J, Zhao
M, Jin Y, Peng R, Hua D, Kuang DM and Chen Y: tertiary lymphoid
structure-associated B cells enhance CXCL13+CD103+CD8+
tissue-resident memory T-Cell response to programmed cell death
protein 1 blockade in cancer immunotherapy. Gastroenterology.
166:1069–1084. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ford K, Hanley C, Mellone M, Szyndralewiez
C, Heitz F, Wiesel P, Wood O, Machado M, Lopez MA, Ganesan AP, et
al: NOX4 inhibition potentiates immunotherapy by overcoming
cancer-associated fibroblast-mediated CD8 T-cell exclusion from
tumors. Cancer Res. 80:1846–1860. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Deng HJ, Kan A, Lyu N, Mu L, Han Y, Liu L,
Zhang Y, Duan Y, Liao S, Li S, et al: Dual vascular endothelial
growth factor receptor and fibroblast growth factor receptor
inhibition elicits antitumor immunity and enhances programmed cell
death-1 checkpoint blockade in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver
Cancer. 9:338–357. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yin Y, Feng W, Chen J, Chen X, Wang G,
Wang S, Xu X, Nie Y, Fan D, Wu K and Xia L: Immunosuppressive tumor
microenvironment in the progression, metastasis, and therapy of
hepatocellular carcinoma: From bench to bedside. Exp Hematol Oncol.
13:722024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yeung O, Lo C, Ling C, Qi X, Geng W, Li C,
Ng KT, Forbes SJ, Guan XY, Poon RT, et al: Alternatively activated
(M2) macrophages promote tumour growth and invasiveness in
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 62:607–616. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Marchesi F and
Garlanda C: Macrophages as tools and targets in cancer therapy. Nat
Rev Drug Discov. 21:799–820. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhu Y, Tan H, Wang J, Zhuang H, Zhao H and
Lu X: Molecular insight into T cell exhaustion in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Pharmacol Res. 203:1071612024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sia D, Jiao Y, Martinez-Quetglas I, Kuchuk
O, Villacorta-Martin C, de Moura MC, Putra J, Camprecios G,
Bassaganyas L, Akers N, et al: Identification of an immune-specific
class of hepatocellular carcinoma, based on molecular features.
Gastroenterology. 153:812–826. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Guo T and Xu J: Cancer-associated
fibroblasts: A versatile mediator in tumor progression, metastasis,
and targeted therapy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 43:1095–1116. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gao D, Fang L, Liu C, Yang M, Yu X, Wang
L, Zhang W, Sun C and Zhuang J: Microenvironmental regulation in
tumor progression: Interactions between cancer-associated
fibroblasts and immune cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 167:1156222023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu ZL, Zhu LL, Liu JH, Pu ZY, Ruan ZP and
Chen J: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 and its
association with tumor immune regulatory gene expression in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Aging (Albany NY). 12:25172–25188. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Allen E, Jabouille A, Rivera LB,
Lodewijckx I, Missiaen R, Steri V, Feyen K, Tawney J, Hanahan D,
Michael IP and Bergers G: Combined antiangiogenic and anti-PD-L1
therapy stimulates tumor immunity through HEV formation. Sci Transl
Med. 9:eaak96792017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Apte RS, Chen DS and Ferrara N: VEGF in
signaling and disease: Beyond discovery and development. Cell.
176:1248–1264. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Singh K: Spontaneous regression of
hepatocellular carcinoma from autoinfarction and implications on
liver transplantation. ACG Case Rep J. 9:e008252022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Luke JJ, Bao R, Sweis RF, Spranger S and
Gajewski TF: WNT/β-catenin pathway activation correlates with
immune exclusion across human cancers. Clin Cancer Res.
25:3074–3083. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Harding JJ, Nandakumar S, Armenia J,
Khalil DN, Albano M, Ly M, Shia J, Hechtman JF, Kundra R, El Dika
I, et al: Prospective genotyping of hepatocellular carcinoma:
Clinical implications of next-generation sequencing for matching
patients to targeted and immune therapies. Clin Cancer Res.
25:2116–2126. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gao X, Qiao X, Xing X, Huang J, Qian J,
Wang Y, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Li M, Cui J and Yang Y: Matrix
stiffness-upregulated MicroRNA-17-5p attenuates the intervention
effects of metformin on HCC invasion and metastasis by targeting
the PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway. Front Oncol. 10:15632020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li H, Wu K, Tao K, Chen L, Zheng Q, Lu XM,
Liu J, Shi L, Liu C, Wang G and Zou W: Tim-3/galectin-9 signaling
pathway mediates T-cell dysfunction and predicts poor prognosis in
patients with hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 56:1342–1351. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Trehanpati N and Vyas AK: Immune
regulation by T regulatory cells in hepatitis B virus-related
inflammation and cancer. Scand J Immunol. 85:175–181. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hoechst B, Voigtlaender T, Ormandy L,
Gamrekelashvili J, Zhao F, Wedemeyer H, Lehner F, Manns MP, Greten
TF and Korangy F: Myeloid derived suppressor cells inhibit natural
killer cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma via the
NKp30 receptor. Hepatology. 50:799–807. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yeung W, Liu L, Chen Z, Lo C and Man K:
Delta PD-1 expressed M2 macrophages promote liver tumor recurrence
after transplantation. Transplantation. 102 (Suppl 7):S250–S251.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Xie Q, Zhang P, Wang Y, Mei W and Zeng C:
Overcoming resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors in
hepatocellular carcinoma: Challenges and opportunities. Front
Oncol. 12:9587202022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Argentiero A, Delvecchio A, Fasano R,
Andriano A, Caradonna IC, Memeo R and Desantis V: The complexity of
the tumor microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma and emerging
therapeutic developments. J Clin Med. 12:74692023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Vaupel P and Multhoff G: Adenosine can
thwart antitumor immune responses elicited by radiotherapy.
Strahlenther Onkol. 192:279–287. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Karimi M, Geramizadeh B and Malek-Hosseini
S: Tolerance induction in liver. Int J Organ Transplant Med.
6:45–54. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Karrar A, Broomé U, Uzunel M, Qureshi AR
and Sumitran-Holgersson S: Human liver sinusoidal endothelial cells
induce apoptosis in activated T cells: A role in tolerance
induction. Gut. 56:243–252. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Casey L, Hughes K, Saunders M, Miller S,
Pearson R and Shea L: Mechanistic contributions of Kupffer cells
and liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in nanoparticle-induced
antigen-specific immune tolerance. Biomaterials. 283:1214572022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wang Y, Liu TT, Tang W, Deng B, Chen Y,
Zhu JM and Shen X: Hepatocellular carcinoma cells induce regulatory
T cells and lead to poor prognosis via production of transforming
growth factor-β1. Cell Physiol Biochem. 38:306–318. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kakita N, Kanto T, Itose I, Kuroda S,
Inoue M, Matsubara T, Higashitani K, Miyazaki M, Sakakibara M,
Hiramatsu N, et al: Comparative analyses of regulatory T cell
subsets in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A crucial role
of CD25-FOXP3- T cells. Int J Cancer. 131:2573–2783. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Liu Y, Yang H, Li T and Zhang N:
Immunotherapy in liver cancer: Overcoming the tolerogenic liver
microenvironment. Front Immunol. 15:14602822024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Patseas D, El-Masry A, Liu Z, Ramachandran
P and Triantafyllou E: Myeloid cells in chronic liver inflammation.
Cell Mol Immunol. 22:1237–1261. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Chakravarthy A, Pasini E, Zhao X, To J,
Shen SYR, Fischer S, Ghanekar A, Vogel A, Grant RC, Knox J, et al:
Evolutionary dynamics of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma under
divergent immune selection pressures. Front Oncol. 15:15370872025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yang Z, Cheng C, Li Z, Wang H, Zhang M,
Xie E, He X, Liu B, Sun H, Wang J, et al: Advancing liver cancer
treatment with dual-targeting CAR-T therapy. J Nanobiotechnol.
23:4622025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Taylor BC and Balko JM: Mechanisms of
MHC-I downregulation and role in immunotherapy response. Front
Immunol. 13:8448662022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Hazini A, Fisher K and Seymour L:
Deregulation of HLA-I in cancer and its central importance for
immunotherapy. J Immunother Cancer. 9:e0028992021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M, Galle PR, Ducreux
M, Kim TY, Kudo M, Breder V, Merle P, Kaseb AO, et al: Atezolizumab
plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J
Med. 382:1894–1905. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Nishida N and Kudo M: Immune checkpoint
blockade for the treatment of human hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatol Res. 48:622–634. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wei SC, Levine JH, Cogdill AP, Zhao Y,
Anang NAS, Andrews MC, Sharma P, Wang J, Wargo JA, Pe'er D and
Allison JP: Distinct cellular mechanisms underlie Anti-CTLA-4 and
Anti-PD-1 checkpoint blockade. Cell. 170:1120–1133.e17. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Abou-Alfa GK, Lau G, Kudo M, Chan SL,
Kelley RK, Furuse J, Sukeepaisarnjaroen W, Kang YK, Dao TV, De Toni
EN, et al: Plain language summary of the HIMALAYA study:
Tremelimumab and durvalumab for unresectable hepatocellular
carcinoma (liver cancer). Future Oncol. 19:2505–2516. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Taddei TH, Brown DB, Yarchoan M,
Mendiratta-Lala M and Llovet JM: Critical update: AASLD practice
guidance on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 82:272–274. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Brackenier C, Kinget L, Cappuyns S,
Verslype C, Beuselinck B and Dekervel J: Unraveling the synergy
between atezolizumab and bevacizumab for the treatment of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 15:3482023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Hatzidakis A, Müller L, Krokidis M and
Kloeckner R: Local and regional therapies for hepatocellular
carcinoma and future combinations. Cancers (Basel). 14:24692022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Duffy AG, Ulahannan SV, Makorova-Rusher O,
Rahma O, Wedemeyer H, Pratt D, Davis JL, Hughes MS, Heller T,
ElGindi M, et al: Tremelimumab in combination with ablation in
patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol.
66:545–551. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Leuchte K, Staib E, Thelen M, Gödel P,
Lechner A, Zentis P, Garcia-Marquez M, Waldschmidt D, Datta RR,
Wahba R, et al: Microwave ablation enhances tumor-specific immune
response in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 70:893–907. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Zhang Z, Liu X, Chen D and Yu J:
Radiotherapy combined with immunotherapy: The dawn of cancer
treatment. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 7:2582022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Sangro B, Kudo M, Erinjeri JP, Qin S, Ren
Z, Chan SL, Arai Y, Heo J, Mai A, Escobar J, et al: Durvalumab with
or without bevacizumab with transarterial chemoembolisation in
hepatocellular carcinoma (EMERALD-1): A multiregional, randomised,
double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet.
405:216–232. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
AstraZeneca. A phase III, randomized,
double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi center study of durvalumab
monotherapy or in combination with bevacizumab as adjuvant therapy
in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who are at high risk of
recurrence after curative hepatic resection or ablation.
ClinicalTrialsgov Identifier: NCT04276941. Available from:.
https://clinicaltrialsgov/study/NCT038474282019.
|
|
72
|
Sangro B, Galle PR, Kelley RK, Charoentum
C, De Toni EN, Ostapenko Y, Heo J, Cheng AL, Woods AW, Gupta C, et
al: Patient-reported outcomes from the phase III HIMALAYA study of
tremelimumab plus durvalumab in unresectable hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 42:2790–2799. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Llovet JM, Kudo M, Merle P, Meyer T, Qin
S, Ikeda M, Xu R, Edeline J, Ryoo BY, Ren Z, et al: Lenvatinib plus
pembrolizumab versus lenvatinib plus placebo for advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma (LEAP-002): A randomised, double-blind,
phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 24:1399–1410. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Qin S, Chan S, Gu S, Bai Y, Ren Z, Lin X,
Chen Z, Jia W, Jin Y, Guo Y, et al: Camrelizumab plus rivoceranib
versus sorafenib as first-line therapy for unresectable
hepatocellular carcinoma (CARES-310): A randomised, open-label,
international phase 3 study. Lancet. 402:1133–1146. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Kudo M, Finn R, Ikeda M, Sung M, Baron A,
Okusaka T, Kobayashi M, Kumada H, Kaneko S, Pracht M, et al: A
phase 1b study of lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab in patients with
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Extended analysis of study
116. Liver Cancer. 13:451–458. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Jenkins F, Johnson JE, Collichio F and
Ollila D: Talimogene laherparepvec and novel injectable oncolytic
viruses in the management of metastatic melanoma. J Transl Genet
Genom. 5:396–413. 2021.
|
|
77
|
Ridolfi R, Flamini E, Riccobon A, De Paola
F, Maltoni R, Gardini A, Ridolfi L, Medri L, Poletti G and Amadori
D: Adjuvant adoptive immunotherapy with tumour-infiltrating
lymphocytes and modulated doses of interleukin-2 in 22 patients
with melanoma, colorectal and renal cancer, after radical
metastasectomy, and in 12 advanced patients. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 46:185–193. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Fujiwara T, Yakoub MA, Chandler A, Christ
AB, Yang G, Ouerfelli O, Rajasekhar VK, Yoshida A, Kondo H, Hata T,
et al: CSF1/CSF1R signaling inhibitor pexidartinib (PLX3397)
reprograms tumor-associated macrophages and stimulates T-cell
infiltration in the sarcoma microenvironment. Mol Cancer Ther.
20:1388–1399. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Zhu Y, Yang J, Xu D, Gao XM, Zhang Z, Hsu
JL, Li CW, Lim SO, Sheng YY, Zhang Y, et al: Disruption of
tumour-associated macrophage trafficking by the osteopontin-induced
colony-stimulating factor-1 signalling sensitises hepatocellular
carcinoma to anti-PD-L1 blockade. Gut. 68:1653–1666. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Flores-Toro JA, Luo D, Gopinath A,
Sarkisian MR, Campbell JJ, Charo IF, Singh R, Schall TJ, Datta M,
Jain RK, et al: CCR2 inhibition reduces tumor myeloid cells and
unmasks a checkpoint inhibitor effect to slow progression of
resistant murine gliomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 117:1129–1138.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Li X, Yao W, Yuan Y, Chen P, Li B, Li JQ,
Chu R, Song H, Xie D, Jiang X and Wang H: Targeting of
tumour-infiltrating macrophages via CCL2/CCR2 signalling as a
therapeutic strategy against hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut.
66:157–167. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Shan F, Somasundaram A, Bruno TC, Workman
CJ and Vignali DAA: Therapeutic targeting of regulatory T cells in
cancer. Trends Cancer. 8:944–961. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Faivre S, Santoro A, Kelley RK, Gane E,
Costentin CE, Gueorguieva I, Smith C, Cleverly A, Lahn MM, Raymond
E, et al: Novel transforming growth factor beta receptor I kinase
inhibitor galunisertib (LY2157299) in advanced hepatocellular
carcinoma. Liver Int. 39:1468–1477. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Morris JC, Tan AR, Olencki TE, Shapiro GI,
Dezube BJ, Reiss M, Hsu FJ, Berzofsky JA and Lawrence DP: Phase I
study of GC1008 (fresolimumab): A human anti-transforming growth
factor-beta (TGFβ) monoclonal antibody in patients with advanced
malignant melanoma or renal cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 9:e903532014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Gunderson AJ, Yamazaki T, McCarty K, Fox
N, Phillips M, Alice A, Blair T, Whiteford M, O'Brien D, Ahmad R,
et al: TGFβ suppresses CD8+ T cell expression of CXCR3 and tumor
trafficking. Nat Commun. 11:17492020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Abdallah N, Kim S, Ayash L, Klimecki S,
Ventimiglia M, Alavi A, Ratanatharathorn V, Uberti J and Deol A:
Does use of biosimilar G-CSF change plerixafor utilization during
stem cell mobilization for autologous stem cell transplant? Bone
Marrow Transplant. 55:1655–1657. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Hecht JR, Oberoi A, Cabanas EG, Chon HJ,
Digklia A, Rottey S, Jimenez MM, Chaney M, Hippenmeyer J, Lawrence
T, et al: Phase Ib/II trial of talimogene laherparepvec alone and
with pembrolizumab in advanced solid tumors with liver metastases
and hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncologist. 30:oyae2032025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Raman S, Pless M, Cubillo A, Calvo A,
Hecht R, Liu C, Chan E, Chesney J and Prat A: 3:36 PM Abstract No.
375 Early safety from a phase 1, multicenter, open-label clinical
trial of talimogene laherparepvec (T-VEC) injected into liver
tumors. JVIR. 29:S1612018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Heo J, Reid T, Ruo L, Breitbach C, Rose S,
Bloomston M, Cho M, Lim HY, Chung HC, Kim CW, et al: Randomized
dose-finding clinical trial of oncolytic immunotherapeutic vaccinia
JX-594 in liver cancer. Nat Med. 19:329–336. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Abou-Alfa GK, Galle PR, Chao Y, Erinjeri
J, Heo J, Borad MJ, Luca A, Burke J, Pelusio A, Agathon D, et al:
PHOCUS: A phase 3, randomized, open-label study of sequential
treatment with pexa-vec (JX-594) and sorafenib in patients with
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Cancer. 13:248–264. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Butterfield LH, Ribas A, Dissette VB, Lee
Y, Yang JQ, De la Rocha P, Duran SD, Hernandez J, Seja E, Potter
DM, et al: A phase I/II trial testing immunization of
hepatocellular carcinoma patients with dendritic cells pulsed with
four alpha-fetoprotein peptides. Clin Cancer Res. 12:2817–2825.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Sawada Y, Yoshikawa T, Nobuoka D,
Shirakawa H, Kuronuma T, Motomura Y, Mizuno S, Ishii H, Nakachi K,
Konishi M, et al: Phase I trial of a glypican-3-derived peptide
vaccine for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: immunologic evidence
and potential for improving overall survival. Clin Cancer Res.
18:3686–3696. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Ikeda M, Okusaka T, Ohno I, Mitsunaga S,
Kondo S, Ueno H, Morizane C, Gemmoto K, Suna H, Ushida Y and Furuse
J: Phase I studies of peptide vaccine cocktails derived from GPC3,
WDRPUH and NEIL3 for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.
Immunotherapy. 13:371–385. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Kwak J, Nguyen H, Camai A, Huffman G,
Mekvanich S, Kenney N, Zhu X, Randolph TW and Houghton AM: CXCR1/2
antagonism inhibits neutrophil function and not recruitment in
cancer. Oncoimmunology. 13:23846742024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Kim Y, Kim G, Kim S, Cho B, Kim SY, Do EJ,
Bae DJ, Kim S, Kweon MN, Song JS, et al: Fecal microbiota
transplantation combined with anti-PD-1 inhibitor for unresectable
or metastatic solid cancers refractory to anti-PD-1 inhibitor. Cell
Host Microbe. 32:1380–1393.e9. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Song C, Zhang J, Wen R, Li Q, Zhou J, Liu
X, Wu Z, Lv Y and Wu R: Improved anti-hepatocellular carcinoma
effect by enhanced Co-delivery of Tim-3 siRNA and sorafenib via
multiple pH triggered drug-eluting nanoparticles. Mater Today Bio.
16:1003502022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Choukér A, Thiel M, Lukashev D, Ward J,
Kaufmann I, Apasov S, Sitkovsky MV and Ohta A: Critical role of
hypoxia and A2A adenosine receptors in liver tissue-protecting
physiological anti-inflammatory pathway. Mol Med. 14:116–123. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Srivastava A, Moufarrij S, Hadley M,
Chisholm S, Lopez-Acevedo M, Villagra A and Chiappinelli K:
Abstract 1395: HDAC6 and DNMT inhibition affect immunogenicity of
ovarian cancer cells: A rationale for combining epigenetic and
immune therapy in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 78 (Suppl
13):13952018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Chen H, Li Z, Qiu L, Dong X, Chen G, Shi
Y, Cai L, Liu W, Ye H, Zhou Y, et al: Personalized neoantigen
vaccine combined with PD-1 blockade increases CD8+ tissue-resident
memory T-cell infiltration in preclinical hepatocellular carcinoma
models. J Immunother Cancer. 10:e0043892022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Shi D, Shi Y, Kaseb AO, Qi X, Zhang Y, Chi
J, Lu Q, Gao H, Jiang H, Wang H, et al: Chimeric antigen
receptor-glypican-3 T-cell therapy for advanced hepatocellular
carcinoma: Results of phase I trials. Clin Cancer Res.
26:3979–3989. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Chattopadhyay S, Hazra R, Mallick A, Gayen
S and Roy S: A review exploring the fusion of oncolytic viruses and
cancer immunotherapy: An innovative strategy in the realm of cancer
treatment. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1879:1891102024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Teng CF, Wang T, Shih FY, Shyu WC and Jeng
LB: Therapeutic efficacy of dendritic cell vaccine combined with
programmed death 1 inhibitor for hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 36:1988–1996. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Lee EHJ, Murad JP, Christian L, Gibson J,
Yamaguchi Y, Cullen C, Gumber D, Park AK, Young C, Monroy I, et al:
Antigen-dependent IL-12 signaling in CAR T cells promotes regional
to systemic disease targeting. Nat Commun. 14:47372023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Zhu W, Peng Y, Wang L, Hong Y, Jiang X, Li
Q, Liu H, Huang L, Wu J, Celis E, et al: Identification of
α-fetoprotein-specific T-cell receptors for hepatocellular
carcinoma immunotherapy. Hepatology. 68:574–589. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Topper MJ, Vaz M, Marrone KA, Brahmer JR
and Baylin SB: The emerging role of epigenetic therapeutics in
immuno-oncology. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 17:75–90. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Yang W, Feng Y, Zhou J, Cheung O, Cao J,
Wang J, Tang W, Tu Y, Xu L, Wu F, et al: A selective HDAC8
inhibitor potentiates antitumor immunity and efficacy of immune
checkpoint blockade in hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Transl Med.
13:eaaz68042021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Yau T, Park JW, Finn RS, Cheng AL,
Mathurin P, Edeline J, Kudo M, Harding JJ, Merle P, Rosmorduc O, et
al: Nivolumab versus sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
(CheckMate 459): A randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3
trial. Lancet Oncol. 23:77–90. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Finn RS, Ryoo BY, Merle P, Kudo M,
Bouattour M, Lim HY, Breder V, Edeline J, Chao Y, Ogasawara S, et
al: Pembrolizumab as second-line therapy in patients with advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma in KEYNOTE-240: A randomized,
double-blind, phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 38:193–202. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Cheng X, Li J, Feng L, Feng S, Wu X and Li
Y: The role of hypoxia-related genes in TACE-refractory
hepatocellular carcinoma: Exploration of prognosis, immunological
characteristics and drug resistance based on onco-multi-OMICS
approach. Front Pharmacol. 13:10110332022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Trommer M, Yeo SY, Persigehl T, Bunck A,
Grüll H, Schlaak M, Theurich S, von Bergwelt-Baildon M,
Morgenthaler J, Herter JM, et al: Abscopal effects in
radio-immunotherapy-response analysis of metastatic cancer patients
with progressive disease under anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint
inhibition. Front Pharmacol. 10:5112019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Steffin D, Ghatwai N, Montalbano A, Rathi
P, Courtney AN, Arnett AB, Fleurence J, Sweidan R, Wang T, Zhang H,
et al: Interleukin-15-armored GPC3-CAR T cells for patients with
solid cancers. Res Sq. 3:rs.3.rs–4103623. 2024.
|
|
112
|
Luo X, Cui H, Cai L, Zhu W, Yang WC,
Patrick M, Zhu S, Huang J, Yao X, Yao Y, et al: Selection of a
clinical lead TCR targeting alpha-fetoprotein-positive liver cancer
based on a balance of risk and benefit. Front Immunol. 11:6232020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Lee JH, Tak WY, Lee Y, Heo MK, Song JS,
Kim HY, Park SY, Bae SH, Lee JH, Heo J, et al: Adjuvant
immunotherapy with autologous dendritic cells for hepatocellular
carcinoma, randomized phase II study. Oncoimmunology.
6:e13283352017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Adachi Y, Kamiyama H, Ichikawa K, Ozawa Y,
Fukushima S, Satoshi G, Yamaguchi S, Matsuki M, Miyano SW, Yokoi A,
et al: Abstract 6637: Inhibition of FGFR signaling by lenvatinib
activates tumor interferon gamma signaling pathway and potentiates
antitumor activity of anti-PD-1 antibody. Cancer Res. 80:66372020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Leslie J, Mackey JBG, Jamieson T,
Ramon-Gil E, Drake TM, Fercoq F, Clark W, Gilroy K, Hedley A, Nixon
C, et al: CXCR2 inhibition enables NASH-HCC immunotherapy. Gut.
71:2093–2106. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Sun C, Wang B and Hao S: Adenosine-A2A
receptor pathway in cancer immunotherapy. Front Immunol.
13:8372302022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Angell H and Galon J: From the immune
contexture to the immunoscore: The role of prognostic and
predictive immune markers in cancer. Curr Opin Immunol. 25:261–267.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Paik J: Nivolumab plus relatlimab: First
approval. Drugs. 82:925–931. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Finn RS, Ryoo BY, Hsu CH, Li D, Burgoyne
AM, Cotter C, Badhrinarayanan S, Wang Y, Yin A, Edubilli TR, et al:
Tiragolumab in combination with atezolizumab and bevacizumab in
patients with unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic
hepatocellular carcinoma (MORPHEUS-Liver): A randomised,
open-label, phase 1b-2, study. Lancet Oncol. 26:214–226. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Kelley RK, Oliver JW, Hazra S, Benzaghou
F, Yau T, Cheng AL and Rimassa L: Cabozantinib in combination with
atezolizumab versus sorafenib in treatment-naive advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma: COSMIC-312 Phase III study design. Future
Oncol. 16:1525–1536. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Gutteridge TP, Kelly AB and Laurens KR:
Increased likelihood of distressing and functionally impairing
psychotic-like experiences among children with co-occurring
internalising and externalising problems. Schizophr Res.
252:225–230. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Exposito MJ, Akce M, Alvarez J, Assenat E,
Balart L, Baron A, Decaens T, Heurgue-Berlot A, Martin A, Paik S,
et al: Abstract No. 526 CheckMate-9DX: phase 3, randomized,
double-blind study of adjuvant nivolumab vs placebo for patients
with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) at high risk of recurrence
after curative resection or ablation. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 30
(Suppl 1):S227–S228. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Du JS, Hsu SH and Wang SN: The current and
prospective adjuvant therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Cancers (Basel). 16:14222024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Knox J, Cheng A, Cleary S, Galle P, Kokudo
N, Lencioni R and Fan J: A phase 3 study of durvalumab with or
without bevacizumab as adjuvant therapy in patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma at high risk of recurrence after curative
hepatic resection or ablation: EMERALD-2. Ann Oncol. 30:iv59–iv60.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Xia X, Li X, Feng G, Zheng C, Liang H and
Zhou G: Intra-arterial interleukin-12 gene delivery combined with
chemoembolization: Anti-tumor effect in a rabbit hepatocellular
carcinoma (HCC) model. Acta Radiol. 54:684–689. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Karapetyan L, Luke JJ and Davar D:
Toll-Like receptor 9 agonists in cancer. Onco Targets Ther.
13:10039–10060. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Katz SC, Burga RA, McCormack E, Wang LJ,
Mooring W, Point GR, Khare PD, Thorn M, Ma Q, Stainken BF, et al:
Phase I hepatic immunotherapy for metastases study of
intra-arterial chimeric antigen receptor-modified T-cell therapy
for CEA+ liver metastases. Clin Cancer Res. 21:3149–3159. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Reynolds K, Thomas M and Dougan M:
Diagnosis and management of hepatitis in patients on checkpoint
blockade. Oncologist. 23:991–997. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
De Martin E, Fulgenzi CAM, Celsa C,
Laurent-Bellue A, Torkpour A, Lombardi P, D'Alessio A and Pinato
DJ: Immune checkpoint inhibitors and the liver: balancing
therapeutic benefit and adverse events. Gut. 74:1165–1177. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Andrews MC, Duong CPM, Gopalakrishnan V,
Iebba V, Chen WS, Derosa L, Khan MAW, Cogdill AP, White MG, Wong
MC, et al: Gut microbiota signatures are associated with toxicity
to combined CTLA-4 and PD-1 blockade. Nat Med. 27:1432–1441. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Zhou G, Zhang N, Meng K and Pan F:
Interaction between gut microbiota and immune checkpoint
inhibitor-related colitis. Front Immunol. 13:10016232022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Strouse J, Chan KK, Baccile R, He G,
Louden DKN, Giurcanu M, Singh A, Rieth J, Abdel-Wahab N, Katsumoto
TR, et al: Impact of steroid-sparing immunosuppressive agents on
tumor outcome in the context of cancer immunotherapy with highlight
on melanoma: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis.
Front Immunol. 15:14994782024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Syed S, Hines J, Baccile R, Rouhani S and
Reid P: Studying outcomes after steroid-sparing immunosuppressive
agent vs. steroid-only treatment for immune-related adverse events
in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and melanoma: A retrospective
case-control study. Cancers (Basel). 16:18922024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|