Introduction
High-mobility group (HMG) nucleosomal-binding domain
2 (HMGN2) is an abundant conserved protein that acts as a
non-histone nuclear DNA-binding protein. Studies have suggested
that HMGN2 interacts with transcription factors and chromatin,
leading to the modulation of gene transcription (1–4). A
previous study revealed that the HMGN2 protein is secreted by
activated peripheral blood mononuclear cells, CD8+ T
cells and γδ T cells, where it induces tumour cell apoptosis
(5,6). However, the precise mechanism of
action of HMGN2 remains to be elucidated. Cytolytic T lymphocytes
(CTLs) are key antitumour immune cells that are rich in cytoplasmic
granules. Upon degranulation, CTLs secrete cytotoxic molecules,
such as TNF-α, IFN-γ and IL-2, against target cells (7). Cytoplasmic granules in CTLs contain
perforin, granzymes, granulysin and other effector molecules
involved in the antitumour response (8,9).
A study by Li et al (10) reported that the N-terminal
structure of HMGN2 can recognize and adhere to tumour cells. In
addition, Fan et al (11)
revealed that HMGN2 can modulate DNA transcription and translation,
thus inducing tumour cell apoptosis. Despite these findings, the
detailed mechanism by which HMGN2 affects tumour cells remains to
be elucidated.
The oligosaccharyltransferase (OST) subunit STT3
(STT3) protein is an important enzyme of the OST complex, which
consists of two isoforms in mammalian cells: STT3A and STT3B. As
the catalytic subunits of the OST complex, STT3 isoforms can
initiate N-glycosylation by catalysing the transfer of a 14-sugar
core glycan from dolichol to the asparagine residues of substrates
(12). Evidence indicates that the
expression of STT3 isoforms, including STT3A and STT3B, which are
upregulated during epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), is
important for the glycosylation and stabilization of programmed
cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD-L1), thus facilitating immune evasion in
tumour cells (13).
The present study aimed to identify the receptors of
HMGN2 on tumour cell membranes and to investigate the underlying
mechanisms of HMGN2 in human tongue squamous carcinoma CAL-27
cells.
Materials and methods
Cell culture
The human tongue squamous cell carcinoma cell line
CAL-27 was obtained from the Biobank of West China Hospital of
Stomatology Sichuan University (Chengdu, China). The cells were
cultured in DMEM (cat. no. 10-013-CVRC; Corning, Inc.) supplemented
with 10% foetal bovine serum (cat. no. A5256701; Gibco; Thermo
Fisher Scientific, Inc.) in a cell culture dish at 37°C in a
humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2.
Effect of HMGN2 on CAL-27 cells
Recombinant HMGN2 with an N-terminal His-tag
expressed in Escherichia coli and purified to >90% purity
(cat. no. RPB057Hu01) was purchased from CLOUD-CLONE CORP., and
diluted with PBS.
A total of ~1×105 CAL-27 cells were
seeded and cultured in 12-well plates until sub-confluent, after
which His-tagged HMGN2 (0, 5, 10 and 20 µg/ml) was added and the
cells were incubated at 37°C for 24 h. The control group was
treated with PBS. After the cells were washed with 1X PBS, a
FLUOVIEW FV3000 bright-field microscope (Olympus Corporation) was
used to observe the cellular state and images were captured.
A total of 20 µg/ml fluorescein isothiocyanate
(FITC)-labelled HMGN2 was added for incubation with CAL-27 cells at
37°C for 10 min, 1 and 2 h, as described in a previous study
(5). Nuclear staining of CAL-27
cells was performed using Hoechst 33258 (cat. no. A3466; APExBIO
Technology LLC) at room temperature for 10 min. After the cells
were washed with 1X PBS, a FLUOVIEW FV3000 confocal laser scanning
microscope (Olympus Corporation) was used to observe the cellular
state and images were captured.
Apoptosis analysis
An Annexin V-FITC apoptosis detection kit (cat. no.
K2003; APExBIO Technology LLC) was used to detect apoptosis
according to the manufacturer's instructions. A total of
~1×105 CAL-27 cells were seeded and cultured in 12-well
plates until sub-confluent, after which His-tagged HMGN2 (20 µg/ml)
was added for incubation at 37°C for 12 or 24 h. The cells were
then washed with 1X PBS and resuspended in 500 µl 1X binding buffer
(cat. no. K2003; APExBIO Technology LLC). Subsequently, 5 µl
Annexin V-FITC and 5 µl PI were added, and the samples were
incubated in the dark at room temperature for 20 min. A CytoFLEX
flow cytometer (Beckman Coulter, Inc.) was used for apoptosis
analysis. The flow cytometry data were analyzed using Kaluza
Analysis software (version 2.4.0; Beckman Coulter, Inc.).
Immunoprecipitation and mass
spectrometry (IP/MS)
After washing with 1X PBS, ~1×107 CAL-27
cells cultured in 100-mm culture dishes were incubated with 20
µg/ml His-tagged HMGN2 at 37°C for 60 min. Cells were harvested by
scraping in 1X PBS, and membrane proteins were isolated using a
commercial membrane protein extraction kit (cat. no. EX1110;
Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd.) with the
following steps: The cells were centrifuged at 500 × g for 5 min at
4°C, washed twice with 1X PBS, and resuspended in chilled Membrane
Protein Extraction Buffer A. The suspension was shaken at 4°C for
30 min, followed by centrifugation at 12,000 × g for 5 min at 4°C.
The supernatant was collected, incubated in a 37°C water bath for
10 min, and then centrifuged at 1,000 × g for 5 min at 37°C. The
lower phase was retained, mixed with chilled Membrane Protein
Extraction Buffer B, incubated on ice for 2 min and then at 37°C
for 5 min, and centrifuged again at 1,000 × g for 5 min at 37°C.
After removing the upper liquid, the pelleted membrane proteins
were dissolved in chilled Membrane Protein Solubilization Buffer C.
Protease Inhibitor D was added to all extraction and solubilization
buffers prior to use. Total protein was extracted from cells lysed
in RIPA buffer (cat. no. HY-K1001; MedChemExpress) supplemented
with a protease inhibitor cocktail (cat. no. K1019; APExBIO
Technology LLC). The protein extracts (500 µl) were then incubated
with rabbit anti-HMGN2 antibody (dilution, 1:250; cat. no.
10953-1-AP; Proteintech Group, Inc.) or control IgG (dilution,
1:250; cat. no. B30011; Abmart Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd.)
at room temperature for 2 h, after which 20 µl protein A/G beads
(cat. no. K1305; APExBIO Technology LLC) were added and incubated
at room temperature for 1 h. After elution with IP eluent (cat. no.
T10007; Abmart Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd.), the
antibody-protein complex was resolved via SDS-PAGE and Coomassie
blue staining was performed at room temperature for 2 h. The
SDS-PAGE gel and beads binding the antibody-protein complex of the
membrane protein were processed for protein identification by PTM
BIO LLC using in-gel tryptic digestion and liquid
chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analysis.
For in-gel tryptic digestion, gel slices were
destained, reduced with dithiothreitol, alkylated with
iodoacetamide, and digested overnight with trypsin (37°C). Peptides
were extracted and dried under a stream of nitrogen gas at 320°C,
and subsequently analyzed by LC-MS/MS. Peptides were separated on a
home-made reversed-phase analytical column (15 cm × 75 µm) using an
EASY-nLC 1000 UPLC system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). The
mobile phase consisted of solvent A (0.1% formic acid and 2%
acetonitrile in water) and solvent B (0.1% formic acid and 98%
acetonitrile in water). The following gradient was applied at a
flow rate of 400 nl/min with the column temperature set to 60°C:
0–16 min, 6–23% B; 16–24 min, 23–35% B; 24–27 min, 35–80% B; 27–30
min, 80% B. The injection volume was 3 µl, corresponding to 1.5 µg
of peptides, and no internal standards were employed. MS was
performed on a Q Exactive Plus (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.)
with a nanospray ionization source in positive ion mode (2.0 kV).
Full MS scans (350–1,800 m/z) were acquired at a resolution of
70,000, followed by data-dependent MS/MS scans (NCE 28; resolution,
17,500) of the top 20 ions with dynamic exclusion of 15.0 sec.
Automatic gain control was set to 5×104. MS/MS data were
searched using the MaxQuant search engine (version 1.6.15.0;
http://www.maxquant.org/maxquant/)
with trypsin/P as enzyme (≤2 missed cleavages). The precursor
tolerance was 10 ppm and the fragment tolerance was 0.02 Da.
Carbamidomethylation of cysteine was set as a fixed modification,
and methionine oxidation was included as a variable modification.
Peptide confidence was set to high with an ion score >20.
Immunofluorescence
A total of ~1×105 CAL-27 cells were
seeded on microscope coverslips in 12-well plates and cultured at
37°C. The cells were then washed with 1X PBS, fixed with 4%
paraformaldehyde at room temperature for 20 min, permeabilized with
0.01% Triton X-100 and blocked with 5% BSA (cat. no. AWB-6015;
Abmart Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd.) at room temperature for
1 h, before they were incubated with primary antibodies against
STT3B (dilution, 1:100; cat. no. 15323-1-AP; Proteintech Group,
Inc.) or PD-L1 (dilution, 1:100; cat. no. A27937; ABclonal Biotech
Co., Ltd.) at 4°C overnight. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (cat.
no. C3362; APExBIO Technology LLC). After being washed three times
with 1X PBS, the cells were incubated with an FITC-conjugated
secondary antibody (dilution, 1:100; cat. no. AS011; ABclonal
Biotech Co., Ltd.) at room temperature for 2 h. The cells were
subsequently visualized using a FLUOVIEW FV3000 confocal laser
scanning microscope (Olympus Corporation) and images were
captured.
Western blot analysis
The downstream validation of the IP/MS results was
conducted by western blotting, as outlined subsequently. After
incubation with 20 µg/ml His-tagged HMGN2 at 37°C for 10 and 60
min, proteins were extracted from CAL-27 cells using RIPA buffer
(cat. no. HY-K1001; MedChemExpress), which primarily consists of 50
mM Tris (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl, 1% Triton X-100, 1% sodium
deoxycholate and 0.1% SDS, as well as sodium orthovanadate and
EDTA. Protein quantification was performed using the Enhanced BCA
Protein Assay Kit (cat. no. P0010S; Beyotime Biotechnology)
according to the manufacturer's instructions. The protein extracts
were subsequently separated by 10% SDS-PAGE (10 µg per lane),
before being transferred to PVDF membranes. The membranes were
blocked with 5% fat-free milk at room temperature for 1 h and were
subsequently incubated with primary antibodies against HMGN2
(dilution, 1:1,000; cat. no. 10953-1-AP; Proteintech Group, Inc.),
STT3B (dilution, 1:1,000; cat. no. 15323-1-AP; Proteintech Group,
Inc.), PD-L1 (dilution, 1:1,000; cat. no. A27937; ABclonal Biotech
Co., Ltd.), gasdermin D (GSDMD; dilution, 1:1,000; cat. no.
ab210070; Abcam), caspase-1 (dilution, 1:1,000; cat. no. 2225; Cell
Signaling Technology, Inc.) and GAPDH (dilution, 1:5,000; cat. no.
AC002; ABclonal Biotech Co., Ltd.) at 4°C overnight. The antibodies
against caspase-1 and GSDMD were also used to detect their
respective cleaved forms (cleaved caspase-1 and GSDMD-N). After
being washed, the membranes were incubated at room temperature for
2 h with a horseradish peroxidase-labelled secondary antibody
(dilution, 1:5,000; cat. nos. AS014 and AS003; ABclonal Biotech
Co., Ltd.). Protein bands were subsequently visualized using an
enhanced chemiluminescence reagent (cat. no. WBULS0500;
MilliporeSigma; Merck KGaA) and imaged with a ChemiDoc MP Imaging
system (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.). Protein expression levels were
semi-quantified using ImageJ software (version 1.8.0; National
Institutes of Health).
Depletion of STT3B
Antibody-mediated depletion is an established method
for selectively eliminating cell populations expressing target
proteins, as documented in previous literature (14). Antibody-dependent cell-mediated
cytotoxicity is a recognized consideration, with certain
therapeutic antibodies, such as PD-L1 inhibitors, demonstrating
potent efficacy in cancer treatment through their depletion
mechanisms (15). In 2014, our
laboratory demonstrated that ~50% of HMGN2 was depleted from the
supernatant of FITC-labelled activated CD8+ T cells
using an anti-human HMGN2 antibody (5). In addition, the tumour-killing
capacity of γδ T cells can be functionally blocked by anti-human
HMGN2 antibodies (6). Building
upon this methodology, CAL-27 cells incubated with 10 µg/ml
anti-STT3B antibody (cat. no. 15323-1-AP; Proteintech Group, Inc.)
at 37°C for 2 h in the present study were designated the
‘STT3B-depleted’ group.
Fluorescence-labelled HMGN2
transmembrane transport assay with anti-STT3B antibodies
A total of ~1×105 CAL-27 cells were
seeded in 35-mm glass bottom dishes with 10-mm microwells. After
being washed with PBS, the cells were divided into three groups:
The control, HMGN2 and STT3B-depleted groups. Cells in the depleted
group were treated with 10 µg/ml anti-STT3B antibody (cat. no.
15323-1-AP; Proteintech Group, Inc.) at 37°C for 2 h. Subsequently,
20 µg/ml FITC-labelled HMGN2 was added and the cells were incubated
at 37°C for 10 min. Nuclear staining of CAL-27 cells was performed
using Hoechst 33258 (cat. no. A3466; APExBIO Technology LLC) at
room temperature for 10 min. Cells not treated with anti-STT3B
antibody were used as a positive control (HMGN2 group). The control
group was treated with PBS. Imaging was performed using a FLUOVIEW
FV3000 confocal laser scanning microscope (Olympus
Corporation).
Protein-protein docking between STT3B
and HMGN2
The Protein Data Bank (PDB) format and FASTA
sequences of the STT3B protein structural domain were downloaded
from the PDB database (https://www.rcsb.org/structure/6S7T). The protein
structure of HMGN2 was predicted using Swiss-Model (https://swissmodel.expasy.org/) according to the
FASTA sequence obtained from the National Center for Biotechnology
Information database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/3151).
The rigid protein-protein docking module ZDOCK
(version 3.0.2; http://zdock.umassmed.edu/) was used to identify the
docking sites between STT3B and HMGN2, and ZDOCK scores were
calculated. Using AlphaFold3 (16)
(https://www.alphafoldserver.com), the 3D
structure of STT3B was simulated with HMGN2. The predictive
structures were visualized using Discovery Studio 2019 Client
(BIOVIA; Dassault Systèmes S.E.).
Statistical analysis
GraphPad Prism software (version 8.0.1; Dotmatics)
was used for all statistical analyses. Experiments were performed
in three independent biological replicates. The quantitative data
are shown as the mean ± SEM. Comparisons between two groups were
performed using unpaired Student's two-tailed t-tests, whereas
statistical comparisons among more than two groups were performed
by one-way analysis of variance followed by a Bonferroni post hoc
correction. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically
significant difference.
Results
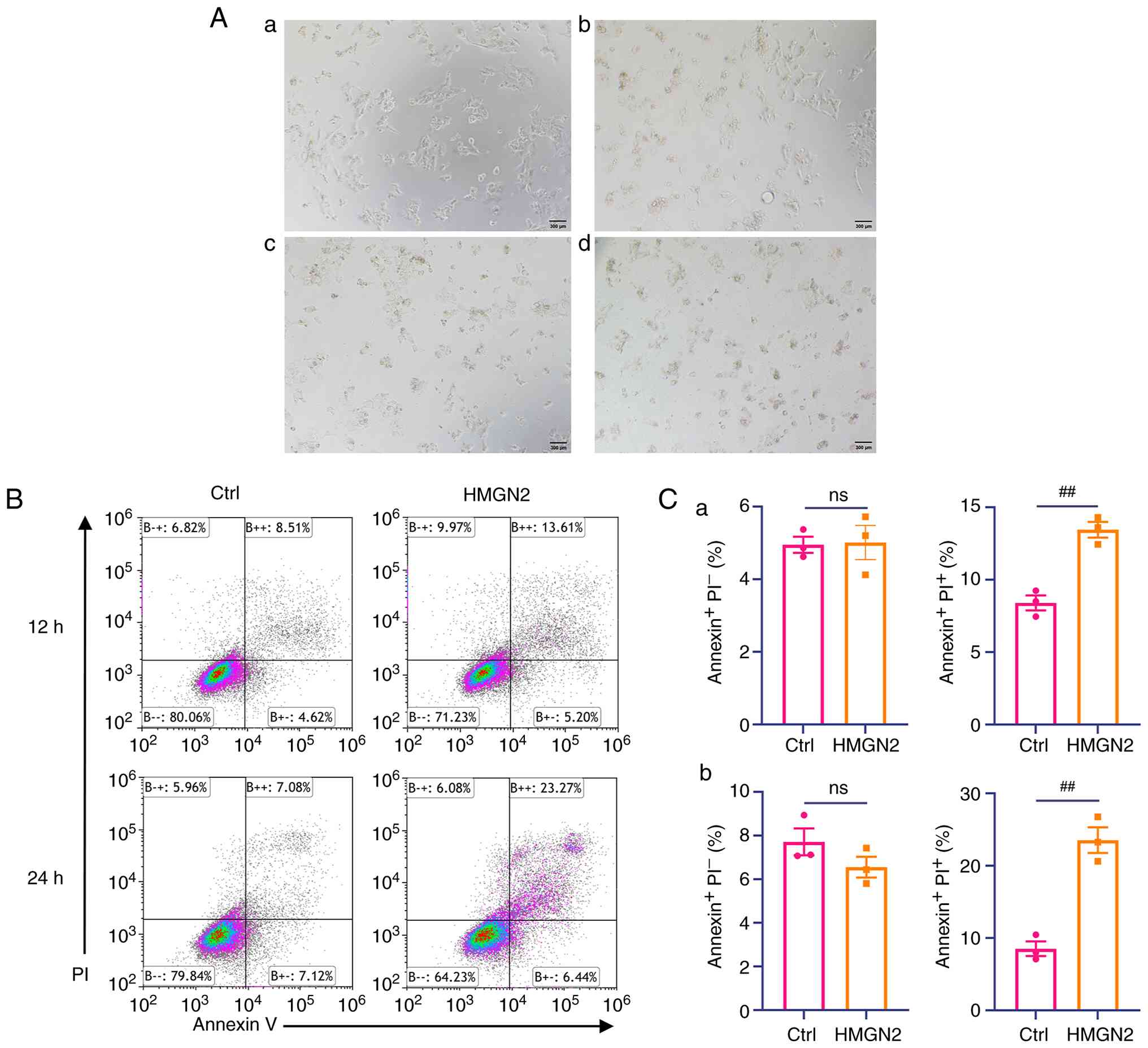
Functional identification of the
antitumour activity of the HMGN2 protein in CAL-27 cells
After the cells were incubated with various
concentrations of HMGN2 for 24 h, the apoptotic response of CAL-27
cells was assessed by bright-field microscopy (Fig. 1A). In addition, the HMGN2 protein
was incubated with CAL-27 cells at 37°C for 12 and 24 h, and the
cells were subject to flow cytometry. Analysis of flow cytometry
results revealed that compared with that in the control group, the
relative percentage of CAL-27 cells undergoing late apoptosis was
significantly greater following HMGN2 incubation. A total of ~14
and 23% of the CAL-27 cells treated with HMGN2 for 12 and 24 h,
respectively, were Annexin V+ and propidium
iodide+ (Fig. 1B and
C). This was significantly higher than the values observed in
the control group. The present results suggested that HMGN2 induced
the apoptosis of CAL-27 cells.
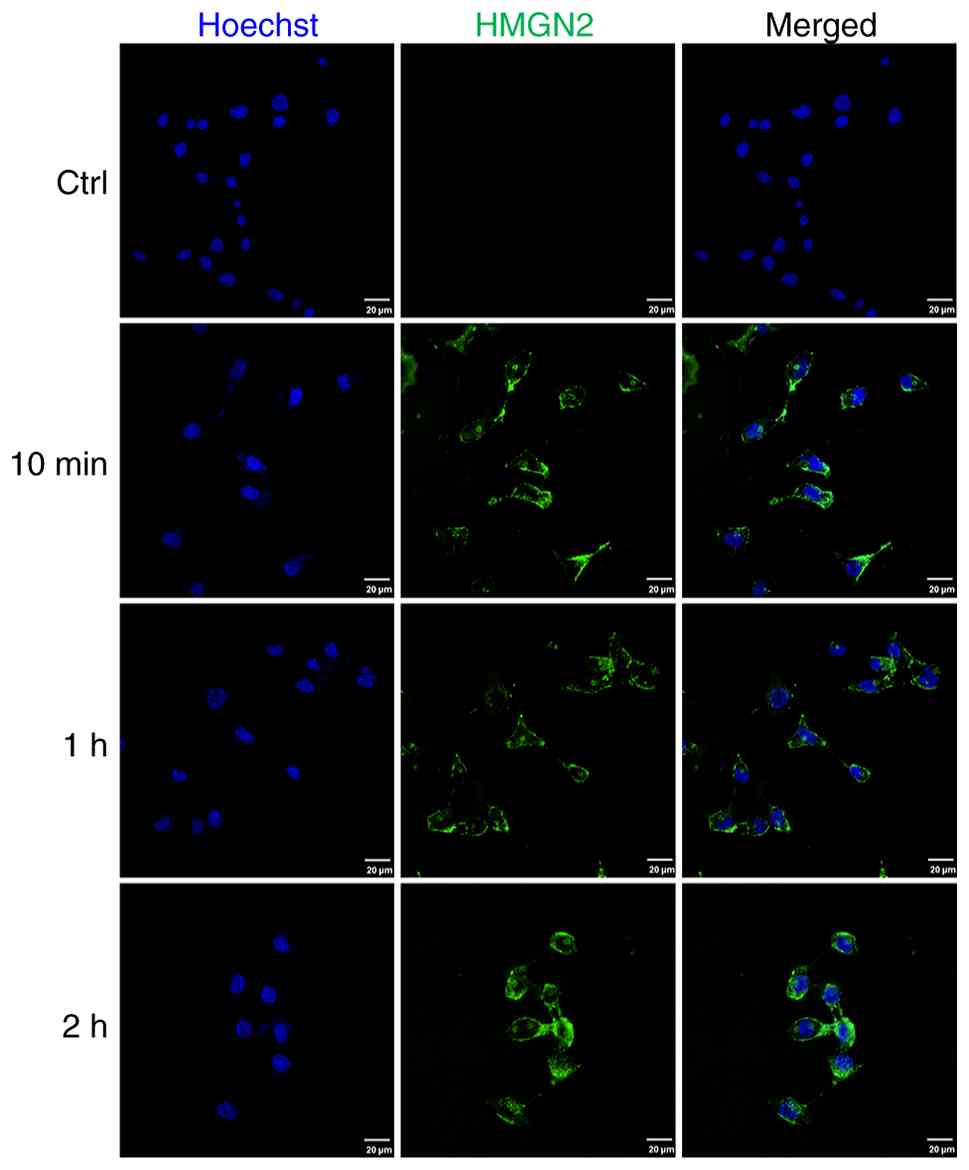
HMGN2 binds to the membrane and is
transported into tumour cells
CAL-27 cells were incubated with FITC-labelled HMGN2
for 10 min, 1 and 2 h, and were subsequently detected by confocal
laser scanning microscopy. The results revealed that FITC-labelled
HMGN2 was localised to the membranes of CAL-27 cells and could be
transported into the cells (Fig.
2).
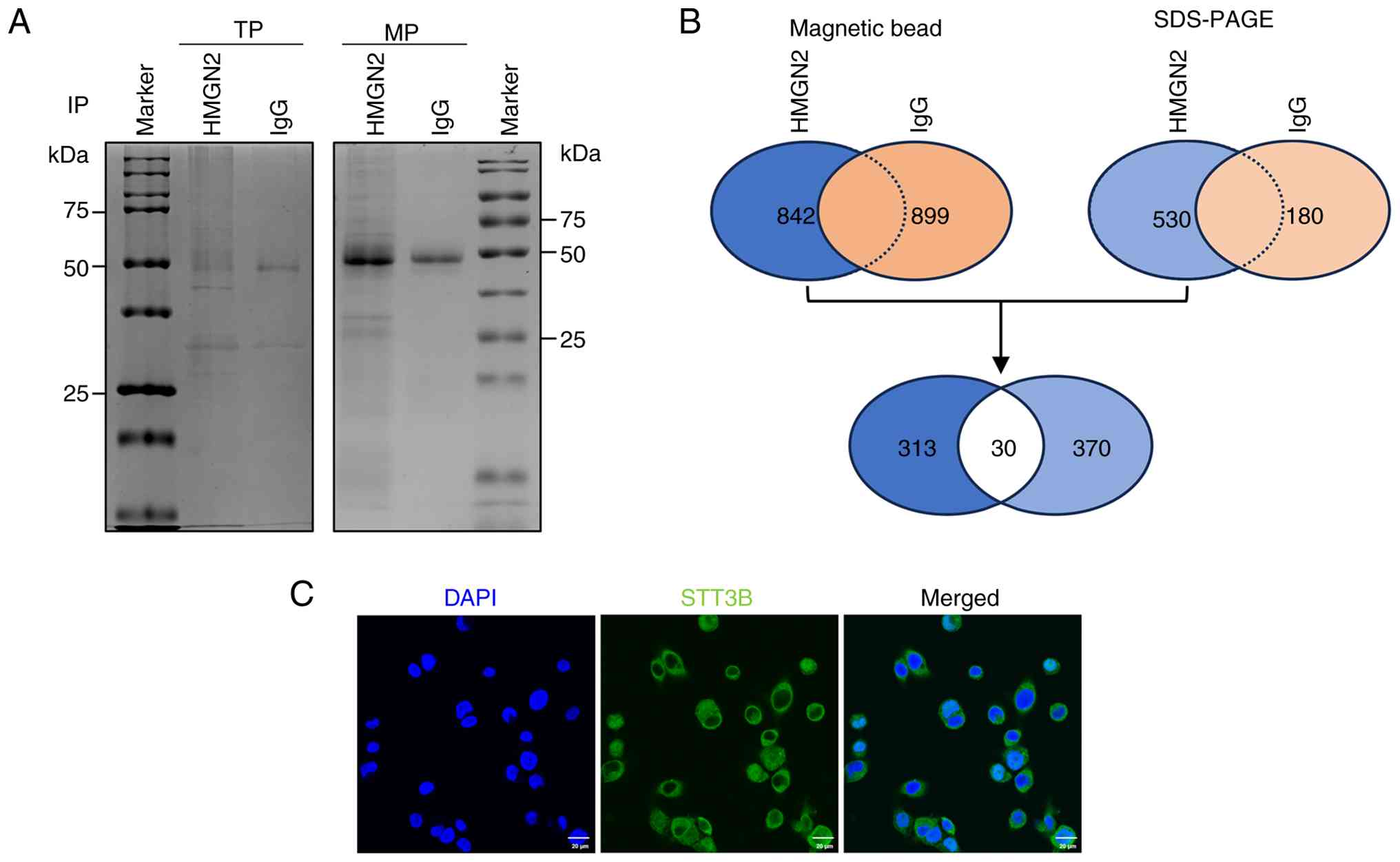
IP/MS indicates that STT3B is a
receptor of HMGN2 on CAL-27 cell membranes
The present study performed IP/MS to identify the
notable receptors associated with HMGN2. After incubation with
HMGN2, the total proteins and membrane proteins of CAL-27 cells
were extracted and immunoprecipitated using magnetic beads so that
the interacting proteins could be visualized by Coomassie blue
staining after SDS-PAGE (Fig. 3A).
Membrane proteins were subsequently identified via mass
spectrometry.
The results of magnetic bead analysis revealed 842
proteins that were immunoprecipitated by the anti-HMGN2 antibody
and 530 proteins identified via SDS-PAGE. The results of magnetic
bead analysis revealed 899 proteins that were immunoprecipitated by
the anti-IgG antibody and 180 proteins identified via SDS-PAGE.
However, only 313 proteins were detected after immunoprecipitation
with the anti-HMGN2 antibody and not with anti-IgG according to the
results of magnetic bead analysis. Similarly, only 370 proteins
exclusive to the anti-HMGN2 antibody were detected via SDS-PAGE.
The results from magnetic bead and gel analyses were subsequently
combined to obtain the 30 top proteins that interact with HMGN2
(Fig. 3B). Only 6 of the 30
proteins screened were located on the membranes of cells, among
which STT3B had the highest protein score and propensity score
matching (PSM) value (Table I).
Immunofluorescence staining supported the subcellular localization
of STT3B on cell membranes (Fig.
3C).
 | Table I.Screened proteins identified by mass
spectrometry. |
Table I.
Screened proteins identified by mass
spectrometry.
| Gene name | Molecular weight,
kDa | Protein score | Unique
peptides | Propensity score
matching | Subcellular
localization |
|---|
| STT3B | 93.6 | 94 | 3 | 3 | Plasma
membrane |
| SSR3 | 21.1 | 66 | 3 | 1 | Plasma
membrane |
| ERMP1 | 100.2 | 41 | 2 | 2 | Plasma
membrane |
| TMEM41B | 32.5 | 39 | 1 | 1 | Plasma
membrane |
| MMP14 | 65.9 | 33 | 1 | 1 | Plasma
membrane |
| STX5 | 39.6 | 25 | 1 | 1 | Plasma
membrane |
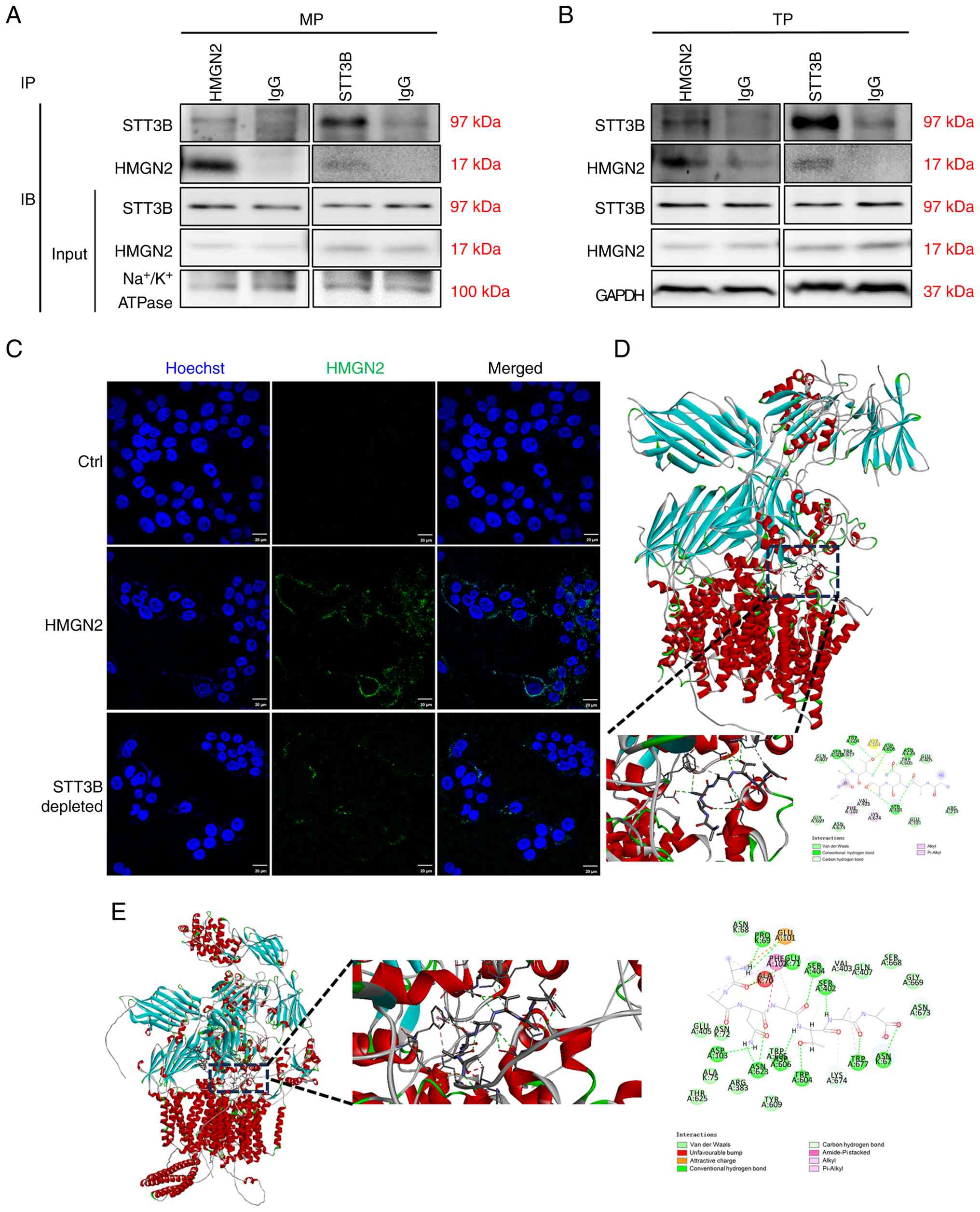
STT3B is an important receptor of
HMGN2 on CAL-27 cell membranes
Given that CAL-27 cells respond to HMGN2, the
present study examined the interaction effects of HMGN2 and STT3B
on total protein and membrane proteins in CAL-27 cells.
Immunoprecipitation results indicated that STT3B physically
interacted with HMGN2 (Fig. 4A and
B). To determine whether STT3B was important for HMGN2
translocation into CAL-27 cells, STT3B was blocked on the membrane
using an anti-STT3B antibody, and the results revealed that
compared with that of the positive control, which was incubated
with the FITC-labelled HMGN2 protein, the level of FITC-labelled
HMGN2 protein on the membranes of CAL-27 cells visibly decreased in
the presence of the anti-STT3B antibody (Fig. 4C).
The present study also predicted the best position
for the interaction between HMGN2 and STT3B using rigid
protein-protein docking (Fig. 4D and
E). The highest ZDOCK score for an interaction was 1,846.143.
Furthermore, simulated HMGN2 formed hydrogen bonds at amino acid
sites such as Asn3-Asp103, Asn3-Asn623 and Ala4-Ser404 (Table II). AlphaFold3 simulated the
interaction structure of STT3B and HMGN2 in which hydrogen bonds
were shown to have formed, including at sites such as Ala7-Asn67,
Ala7-Trp677 and Ala6-Ser402. The interface predicted template
modeling score and predicted template modeling score were 0.78 and
0.80, respectively (Table III),
indicating a good predictive power regarding the aforementioned
binding structure. Comprehensive analysis revealed that the
proteins HMGN2 and STT3B formed a stable protein docking model.
 | Table II.Analysis of ZDOCK results. |
Table II.
Analysis of ZDOCK results.
| Receptor | Ligand | ZDOCK score | Hydrogen bond
interaction | Hydrophobic
interaction |
|---|
| STT3B | HMGN2 | 1,846.143 | Asn3-Asp103;
Asn3-Asn623; Ala2-Ser404; Ala4-Ser404; Thr5-Trp604;
Thr5-Asp606 | Ala4-Phe102;
Ala7-Lys674 |
 | Table III.Analysis of AlphaFold3 results. |
Table III.
Analysis of AlphaFold3 results.
| Receptor | Ligand | ipTM score | pTM score | Hydrogen bond
interaction | Hydrophobic
interaction |
|---|
| STT3B | HMGN2 | 0.78 | 0.80 | Ala7-Asn67;
Ala7-Trp677; Ala6-Ser402; Thr5-Trp604; Thr5-Asp606; Ala4-Ser404;
Asn3-Asn623; Asn3-Asp103; Asn3-Asn623; Ala1-Pro69; Ala1-Glu71 | Ala6-Trp677;
Ala4-Phe102; Asn3-Phe102; Ala2-Phe102 |
HMGN2 promotes the nuclear
translocation of membrane PD-L1, activating the
PD-L1/caspase-1/GSDMD axis
After incubation with HMGN2, the expression of STT3B
was upregulated, which further supported the association between
STT3B and HMGN2 (Fig. 5A and B).
Few studies have examined the function of STT3B in cancer cell
death, but STT3B has been shown to mediate the glycosylation of
PD-L1, which induces immune evasion (13). PD-L1, an immune checkpoint
regulator, shields cancer cells from host immune responses
(17). However, PD-L1 can also
trigger pyroptosis in cancer cells, indicating that PD-L1 is a
signalling mediator that affects tumour outcomes (18). In addition to apoptosis,
ferroptosis and necrosis, pyroptosis serves an important role in
tumour cell death and is characterized as a GSDM-mediated mode of
programmed cell death. In terms of the molecular mechanism of
pyroptosis, caspase-1, −4, −5, −11 and −3 have been shown to cleave
GSDMD or GSDME to induce pyroptosis (19). The results of the present study
revealed that the expression of PD-L1/caspase-1/GSDMD axis
components was significantly upregulated in response to HMGN2
stimulation (Fig. 5A and B), while
the cleavage ratios of both caspase-1 and GSDMD showed no
statistically significant alterations. In addition, treatment with
HMGN2 was shown to induce the nuclear translocation of PD-L1 from
the membranes of cancer cells (Fig.
5C).
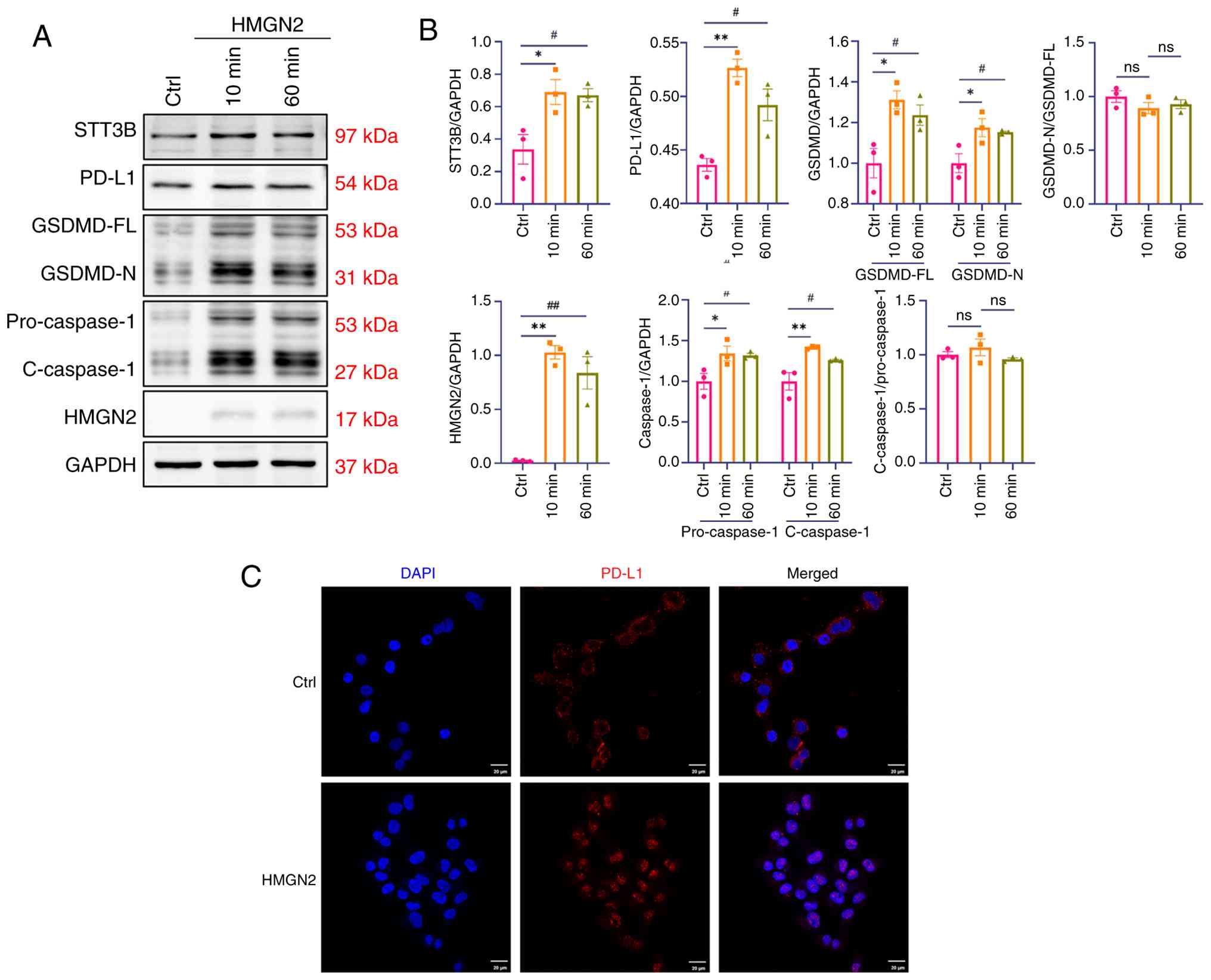 | Figure 5.HMGN2 induces pyroptosis in CAL-27
cells through the PD-L1/caspase-1/GSDMD axis. (A) Representative
western blot analysis of the PD-L1/caspase-1/GSDMD axis, and the
HMGN2 and STT3B proteins in CAL-27 cells after incubation with 20
µg/ml HMGN2 for 10 or 60 min. The Ctrl group was treated with PBS.
(B) Semi-quantitative analyses of the PD-L1/caspase-1/GSDMD axis,
and the HMGN2 and STT3B proteins in CAL-27 cells (n=3). (C)
Representative images showing PD-L1 translocation in CAL-27 cells
treated with HMGN2. The Ctrl group was treated with PBS. Scale bar,
20 µm. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. *P<0.05 and
**P<0.01; #P<0.05 and ##P<0.01.
Ctrl, control; ns, not significant; HMGN2, high-mobility group
nucleosomal-binding domain 2; PD-L1, programmed cell death 1 ligand
1; GSDMD-N, N-terminal domain of gasdermin D; GSDMD-FL, full-length
gasdermin D; STT3B, oligosaccharyltransferase subunit STT3B;
C-caspase-1, cleaved caspase-1. |
Discussion
HMG proteins constitute an abundant family of
non-histone proteins localised in the cell nuclei of vertebrates
and invertebrates (5). The HMG
protein family comprises three subfamilies: HMGB, HMGA and HMGN,
which each perform a distinct nuclear function (11). However, other peptides in the HMG
protein family also have important roles. For example, as an
abundant, highly conserved cellular protein, HMGB1 is considered a
nuclear DNA-binding protein (20).
A decade-long search revealed HMGB1 as a late toxic cytokine of
endotoxaemia (21–23). Upon release by macrophages in
response to endotoxins, HMGB1 triggers the activation of various
proinflammatory mediators, which can be fatal to healthy animals
(24). Additionally, HMGB1-3
operate as universal sentinel proteins for nucleic acid-mediated
innate immune responses (25).
HMGA proteins modulate the transcription of a number
of genes through interactions with transcription factors and
altering the structure of chromatin. HMGA proteins have been shown
to be involved in both benign and malignant neoplasia via numerous
pathways. A number of benign human mesenchymal tumours show HMGA
gene rearrangements. Conversely, malignant tumours exhibit
wild-type HMGA protein upregulation, which is frequently a cause of
neoplastic cell transformation (26,27).
The HMGN family comprises five chromatin
architectural proteins present in higher vertebrates (28). HMGN5, located on human chromosome
Xq13.3, is a prominent member of the HMGN family, and exhibits a
functional nucleotide-binding domain and a negatively charged
C-terminus (28). The HMGN5
protein can rapidly translocate into the nucleus and interact with
nucleosomes, thereby affecting transcription (29). Previous studies have indicated that
the expression of the HMGN5 gene is upregulated in numerous human
tumours and that HMGN5 is activated in tumour models (30,31).
HMGN2 is one of the most abundant non-histone
nuclear proteins in both vertebrates and invertebrates, which
participates in chromatin remodelling and transcriptional
activation (1–4). Additionally, HMGN2 is associated with
the recognition of various types of tumour cells (32–34),
antineoplastic activity (5,35,36)
and the prediction of various tumours (37–40).
Previous studies have demonstrated that HMGN2 expressed by
CD8+ T cells has strong antitumour effects through rapid
recognition and transport into tumour cells (5,41).
For example, a study performed by Li et al (42) demonstrated that T cells engineered
to express HMGN2, designated ‘HMGN2-T cells’, effectively kill
cancer cells and enhance the secretion of IL-2 and TNF-α.
Similarly, Su et al (5)
showed that HMGN2 released by CD8+ T cells can enter
tumour cells and induce cell death. However, the specific mechanism
by which HMGN2 affects tumour cells remains to be fully elucidated,
raising the important question of how HMGN2 identifies and
interacts with tumour cells. The present study aimed to detect
receptors of HMGN2 on tumour cell membranes and to elucidate the
mechanism through which HMGN2 molecule induces tumour cell
apoptosis.
To provide evidence of the antitumour effect of
HMGN2, the present study first incubated CAL-27 cells with HMGN2
and assessed their degree of apoptosis via flow cytometry. Given
the precise location of FITC-labelled HMGN2 on the membranes of
CAL-27 cells, the present study hypothesized that the presence of a
specific receptor on the cell membrane was responsible for
mediating signal communication between HMGN2 and CAL-27 cells,
leading to tumour cell death. In the present study, six proteins
were identified to be localized to the cytoplasmic membrane through
qualitative screening via IP/MS, in which STT3B emerged as the
preferred protein, exhibiting the highest protein score, unique
peptide count and PSM value.
The immunoprecipitation results verified the
interaction between HMGN2 and STT3B; however, the evidence was not
significant enough to establish the notable role of STT3B in the
communication between HMGN2 and CAL-27 cells. To further validate
the importance of STT3B, the present study blocked the STT3B
protein on the membranes of CAL-27 cells with an anti-STT3B
antibody. The resulting findings underscored the importance of
STT3B in the interaction between HMGN2 and CAL-27 cells.
Additionally, the present study predicted binding conformations and
binding sites of HMGN2 to STT3B using ZDOCK and AlphaFold3. Both
models revealed numerous hydrogen bond interactions, including
Thr5-Trp604, Thr5-Asp606, Ala4-Ser404, Asn3-Asn623 and Asn3-Asp103,
indicating that HMGN2 interacted with CAL-27 cells by binding to
the membrane protein STT3B. However, the predicted binding residues
for the HMGN2-STT3B interaction, as generated by ZDOCK and
AlphaFold3, require further validation through site-directed
mutagenesis studies.
Research has shown that upregulation of the STT3
isoforms STT3A and STT3B during EMT acts as a key mediator of
tumour immune evasion by promoting PD-L1 glycosylation and
stabilization (13). In the
present study, the expression levels of STT3B and PD-L1 were found
to be upregulated following incubation with HMGN2, which was
consistent with the findings of the previous study; these results
suggested that the upregulation of STT3B expression stimulated by
HMGN2 resulted in the glycosylation and stabilization of PD-L1,
thus leading to tumour cell death. This observation conflicted with
the notion that stabilization of PD-L1 by STT3B promotes immune
evasion (43,44). However, this discrepancy can be
addressed by considering STT3B/PD-L1 as a dual-function signalling
mediator that may simultaneously trigger pyroptosis while also
facilitating immune evasion (17,45).
Notably, the precise mechanism governing this dual STT3B/PD-L1
functionality remains to be elucidated, thereby constraining a more
comprehensive understanding of the multifaceted roles of PD-L1 in
tumour biology.
Pyroptosis is defined as a GSDM-mediated form of
programmed necrosis (46,47). Numerous studies have established
that caspase-1-mediated pyroptosis serves as an important innate
immune defence mechanism (46–49).
Notably, GSDMD has been identified as a key substrate of both
inflammatory caspases, such as caspase-1, and non-canonical
caspases, such as caspase-4, −5 and −11, and is considered the
primary executor of pyroptotic cell death (49–51).
A previous in vitro study revealed that GSDMD cleavage is
increased in CTLs and contributes to the antitumour function of
CD8+ T cells, indicating that GSDMD is important for the
ability of CTLs to kill tumour cells (52). Therefore, the present study
hypothesized that GSDMD may have been involved in HMGN2-induced
tumour cell death. The findings of the present study revealed that
HMGN2 upregulated the expression of caspase-1/GSDMD pathway
components, revealing an underlying signalling pathway through
which HMGN2 may have induced tumour cell death via activation of
the canonical pyroptosis pathway. HMGN2 upregulated caspase-1 and
GSDMD protein levels but did not significantly alter their cleavage
ratios. This ‘priming’ phenotype is not uncommonly observed in
immune-related cell death pathways, suggesting a priming mechanism
in which protein accumulation precedes proteolytic activation
(53,54). Additionally, PD-L1 was translocated
from the plasma membrane to the nucleus; this translocation has
been previously reported to mediate GSDMC expression and caspase-8
activation, leading to pyroptosis of tumour cells (18). However, the regulatory effect of
PD-L1 on the GSDM family remains to be fully elucidated. Further
questions arise regarding how HMGN2 activated STT3B expression and
whether HMGN2 influenced the gene expression of the GSDM family.
Given that HMGN2 has been confirmed to regulate the activity of
transcriptional regulatory factors (1,4) and
chromatin (2,3), additional studies are required to
elucidate its precise role in these processes.
There are several limitations of the present study
that merit consideration. Primarily, while the observed
upregulation of GSDMD, a key mediator of pyroptosis, resulted in
the conclusion that observed cell death was consistent with
pyroptotic processes, direct visualization of characteristic
morphological features through live-cell imaging, such as membrane
pore formation, cell swelling or large bubble formation, is
required to provide additional evidence of this.
Additionally, although the present investigation
built upon existing literature and focused primarily on the role of
HMGN2 in promoting pyroptosis, the mechanistic basis by which PD-L1
may have concurrently mediated pyroptosis and immune escape has not
been fully explored. To improve understanding of this dual
functionality, future studies involving STT3B and PD-L1 knockdown
or neutralization, combined with detailed analysis of downstream
signalling events, would be highly informative.
Furthermore, while the findings of the present study
demonstrated coordinated protein-level changes along the
STT3B/PD-L1/caspase-1/GSDMD axis, the precise sequence of events
and causal relationships within this signalling cascade remain to
be fully established. Further studies employing specific inhibitors
or systematic loss-of-function approaches may help to clarify the
regulatory hierarchy of this pathway and establish mechanistic
causality.
From a methodological standpoint, the antibody-based
STT3B depletion approach employed in the present study was based on
established protocols and the present specific experimental
context. Nevertheless, the use of genetic perturbation methods,
such as CRISPR/Cas9 or stable RNA interference, in future work
could offer more definitive mechanistic insights.
Finally, all experimental findings in the present
study are based on the CAL-27 tongue squamous cell carcinoma model.
Further validation across a broader range of cancer models,
including additional squamous cell carcinoma subtypes and
non-squamous malignancies, would help to assess the
generalizability of the proposed mechanism. In addition, in
vivo studies using immunocompetent mouse models would be
valuable to validate the physiological relevance of this pathway
and to more comprehensively evaluate the therapeutic potential of
HMGN2 within an intact tumour microenvironment.
In conclusion, extracellular HMGN2 may induce
pyroptosis in tumour cells through the STT3B/PD-L1/caspase-1/GSDMD
axis, indicating the capacity of HMGN2 in antitumour immunotherapy,
as well as a new mechanism through which CTLs induce antitumour
effects.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The present work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation
of Sichuan Province (grant no. 2022YFS0118) and the
Interdisciplinary Research Project of the State Key Laboratory of
Oral Diseases (grant no. 2022KXK0402).
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be
requested from the corresponding author.
Authors' contributions
WH was responsible for the conceptualization and
methodology of the present study, as well as contributing to the
investigation, formal analysis and composition of the original
draft. HC, BC and JC contributed towards the formal analysis of the
present study. PZ contributed towards the conceptualization,
funding acquisition, and reviewing and editing the manuscript. YF
was responsible for conceptualization of the study, as well as
reviewing and editing the manuscript. WH and YF confirm the
authenticity of all the raw data. All authors read and approved the
final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Craig JM, Turner TH, Harrell JC and
Clevenger CV: Prolactin drives a dynamic STAT5A/HDAC6/HMGN2
Cis-regulatory landscape exploitable in ER+ breast cancer.
Endocrinology. 162:bqab0362021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
He B, Zhu I, Postnikov Y, Furusawa T,
Jenkins L, Nanduri R, Bustin M and Landsman D: Multiple epigenetic
factors co-localize with HMGN proteins in A-compartment chromatin.
Epigenetics Chromatin. 15:232022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang S, Postnikov Y, Lobanov A, Furusawa
T, Deng T and Bustin M: H3K27ac nucleosomes facilitate HMGN
localization at regulatory sites to modulate chromatin binding of
transcription factors. Commun Biol. 5:1592022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Eliason S, Su D, Pinho F, Sun Z, Zhang Z,
Li X, Sweat M, Venugopalan SR, He B, Bustin M and Amendt BA: HMGN2
represses gene transcription via interaction with transcription
factors Lef-1 and Pitx2 during amelogenesis. J Biol Chem.
298:1022952022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Su L, Hu A, Luo Y, Zhou W, Zhang P and
Feng Y: HMGN2, a new anti-tumor effector molecule of
CD8+ T cells. Mol Cancer. 13:1782014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen J, Fan Y, Cui B, Li X, Yu Y, Du Y,
Chen Q, Feng Y and Zhang P: HMGN2: An antitumor effector molecule
of γδT cells. J Immunother. 41:118–124. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xia A, Zhang Y, Xu J, Yin T and Lu XJ: T
cell dysfunction in cancer immunity and immunotherapy. Front
Immunol. 10:17192019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mahaki H, Ravari H, Kazemzadeh G, Lotfian
E, Daddost RA, Avan A, Manoochehri H, Sheykhhasan M, Mahmoudian RA
and Tanzadehpanah H: Pro-inflammatory responses after peptide-based
cancer immunotherapy. Heliyon. 10:e322492024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Najafi M, Farhood B and Mortezaee K:
Contribution of regulatory T cells to cancer: A review. J Cell
Physiol. 234:7983–7993. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li Q, Chen J, Li X, Cui B, Fan Y, Geng N,
Chen Q, Zhang P and Feng Y: Increased expression of high-mobility
group nucleosomal-binding domain 2 protein in various tumor cell
lines. Oncol Lett. 15:4517–4522. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fan B, Shi S, Shen X, Yang X, Liu N, Wu G,
Guo X and Huang N: Effect of HMGN2 on proliferation and apoptosis
of MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 17:1160–1166.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Breitling J and Aebi M: N-linked protein
glycosylation in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 5:a0133592013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hsu JM, Xia W, Hsu YH, Chan LC, Yu WH, Cha
JH, Chen CT, Liao HW, Kuo CW, Khoo KH, et al: STT3-dependent PD-L1
accumulation on cancer stem cells promotes immune evasion. Nat
Commun. 9:19082018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sutton MS, Bucsan AN, Lehman CC, Kamath M,
Pokkali S, Magnani DM, Seder R, Darrah PA and Roederer M:
Antibody-mediated depletion of select leukocyte subsets in blood
and tissue of nonhuman primates. Front Immunol. 15:13596792024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen Z, Kankala RK, Yang Z, Li W, Xie S,
Li H, Chen AZ and Zou L: Antibody-based drug delivery systems for
cancer therapy: Mechanisms, challenges, and prospects.
Theranostics. 12:3719–3746. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Abramson J, Adler J, Dunger J, Evans R,
Green T, Pritzel A, Ronneberger O, Willmore L, Ballard AJ, Bambrick
J, et al: Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular
interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature. 630:493–500. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xiong W, Gao Y, Wei W and Zhang J:
Extracellular and nuclear PD-L1 in modulating cancer immunotherapy.
Trends Cancer. 7:837–846. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hou J, Zhao R, Xia W, Chang CW, You Y, Hsu
JM, Nie L, Chen Y, Wang YC, Liu C, et al: PD-L1-mediated gasdermin
C expression switches apoptosis to pyroptosis in cancer cells and
facilitates tumour necrosis. Nat Cell Biol. 22:1264–1275. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu W, Peng J, Xiao M, Cai Y, Peng B,
Zhang W, Li J, Kang F, Hong Q, Liang Q, et al: The implication of
pyroptosis in cancer immunology: Current advances and prospects.
Genes Dis. 10:2339–2350. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang Z, Simovic MO, Edsall PR, Liu B,
Cancio TS, Batchinsky AI, Cancio LC and Li Y: HMGB1 inhibition to
ameliorate organ failure and increase survival in trauma.
Biomolecules. 12:1012022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tang D, Kang R, Xiao W, Zhang H, Lotze MT,
Wang H and Xiao X: Quercetin prevents LPS-induced high-mobility
group box 1 release and proinflammatory function. Am J Respir Cell
Mol Biol. 41:651–660. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tang Y, Lv B, Wang H, Xiao X and Zuo X:
PACAP inhibit the release and cytokine activity of HMGB1 and
improve the survival during lethal endotoxemia. Int
Immunopharmacol. 8:1646–1651. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Czura CJ, Wang H and Tracey KJ: Dual roles
for HMGB1: DNA binding and cytokine. J Endotoxin Res. 7:315–321.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang S and Zhang Y: HMGB1 in inflammation
and cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 13:1162020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yanai H, Ban T, Wang Z, Choi MK, Kawamura
T, Negishi H, Nakasato M, Lu Y, Hangai S, Koshiba R, et al: HMGB
proteins function as universal sentinels for nucleic-acid-mediated
innate immune responses. Nature. 462:99–103. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
De Martino M, Fusco A and Esposito F: HMGA
and cancer: A review on patent literatures. Recent Pat Anticancer
Drug Discov. 14:258–267. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Meireles Da Costa N, Ribeiro Pinto LF,
Nasciutti LE and Palumbo A Jr: The prominent role of HMGA proteins
in the early management of gastrointestinal cancers. Biomed Res
Int. 2019:20595162019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nanduri R, Furusawa T and Bustin M:
Biological functions of HMGN chromosomal proteins. Int J Mol Sci.
21:4492020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rochman M, Postnikov Y, Correll S, Malicet
C, Wincovitch S, Karpova TS, McNally JG, Wu X, Bubunenko NA,
Grigoryev S and Bustin M: The interaction of NSBP1/HMGN5 with
nucleosomes in euchromatin counteracts linker histone-mediated
chromatin compaction and modulates transcription. Mol Cell.
35:642–656. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mou J, Huang M, Wang F, Xu X, Xie H, Lu H,
Li M, Li Y, Kong W and Chen J: HMGN5 escorts oncogenic STAT3
signaling by regulating the chromatin landscape in breast cancer
tumorigenesis. Mol Cancer Res. 20:1724–1738. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yao K, He L, Gan Y, Liu J, Tang J, Long Z
and Tan J: HMGN5 promotes IL-6-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition of bladder cancer by interacting with Hsp27. Aging
(Albany NY). 12:7282–7298. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
He B, Deng T, Zhu I, Furusawa T, Zhang S,
Tang W, Postnikov Y, Ambs S, Li CC, Livak F, et al: Binding of HMGN
proteins to cell specific enhancers stabilizes cell identity. Nat
Commun. 9:52402018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nanduri R, Furusawa T, Lobanov A, He B,
Xie C, Dadkhah K, Kelly MC, Gavrilova O, Gonzalez FJ and Bustin M:
Epigenetic regulation of white adipose tissue plasticity and energy
metabolism by nucleosome binding HMGN proteins. Nat Commun.
13:73032022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Morande PE, Borge M, Abreu C, Galletti J,
Zanetti SR, Nannini P, Bezares RF, Pantano S, Dighiero G, Oppezzo
P, et al: Surface localization of high-mobility group
nucleosome-binding protein 2 on leukemic B cells from patients with
chronic lymphocytic leukemia is related to secondary autoimmune
hemolytic anemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 56:1115–1122. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wu Z, Huang Y, Yuan W, Wu X, Shi H, Lu M
and Xu A: Expression, tumor immune infiltration, and prognostic
impact of HMGs in gastric cancer. Front Oncol. 12:10569172022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liang G, Xu E, Yang C, Zhang C, Sheng X
and Zhou X: Nucleosome-binding protein HMGN2 exhibits antitumor
activity in human SaO2 and U2-OS osteosarcoma cell lines. Oncol
Rep. 33:1300–1306. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lin J, Cai Y, Wang Z, Ma Y, Pan J, Liu Y
and Zhao Z: Novel biomarkers predict prognosis and drug-induced
neuroendocrine differentiation in patients with prostate cancer.
Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 13:10059162023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bin-Alee F, Arayataweegool A,
Buranapraditkun S, Mahattanasakul P, Tangjaturonrasme N, Hirankarn
N, Mutirangura A and Kitkumthorn N: Transcriptomic analysis of
peripheral blood mononuclear cells in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma patients. Oral Diseases. 27:1394–1402. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yu B, Geng C, Wu Z, Zhang Z, Zhang A, Yang
Z, Huang J, Xiong Y, Yang H and Chen Z: A CIC-related-epigenetic
factors-based model associated with prediction, the tumor
microenvironment and drug sensitivity in osteosarcoma. Sci Rep.
14:13082024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Antony F, Deantonio C, Cotella D, Soluri
MF, Tarasiuk O, Raspagliesi F, Adorni F, Piazza S, Ciani Y, Santoro
C, et al: High-throughput assessment of the antibody profile in
ovarian cancer ascitic fluids. Oncoimmunology. 8:e16148562019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hu A, Dong X, Liu X, Zhang P, Zhang Y, Su
N, Chen Q and Feng Y: Nucleosome-binding protein HMGN2 exhibits
antitumor activity in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett.
7:115–120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li H, Wu X, Bu D, Wang L, Xu X, Wang Y,
Liu Y and Zhu P: Recombinant jurkat cells (HMGN2-T cells) secrete
cytokines and inhibit the growth of tumor cells. J Mol Histol.
53:741–751. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sun Z, Ma X, Zhao C, Fan L, Yin S and Hu
H: Delta-tocotrienol disrupts PD-L1 glycosylation and reverses
PD-L1-mediated immune suppression. Biomed Pharmacother.
170:1160782024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Xu S, Wang H, Zhu Y, Han Y, Liu L, Zhang
X, Hu J, Zhang W, Duan S, Deng J, et al: Stabilization of EREG via
STT3B-mediated N-glycosylation is critical for PDL1 upregulation
and immune evasion in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J
Oral Sci. 16:472024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Blasco MT and Gomis RR: PD-L1 controls
cancer pyroptosis. Nat Cell Biol. 22:1157–1159. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Anderson MJ, den Hartigh AB and Fink SL:
Molecular mechanisms of pyroptosis. Methods Mol Biol. 2641:1–16.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shi J, Gao W and Shao F: Pyroptosis:
Gasdermin-mediated programmed necrotic cell death. Trends Biochem
Sci. 42:245–254. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li Y and Jiang Q: Uncoupled pyroptosis and
IL-1β secretion downstream of inflammasome signaling. Front
Immunol. 14:11283582023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zuo Y, Chen L, Gu H, He X, Ye Z, Wang Z,
Shao Q and Xue C: GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis: A critical mechanism
of diabetic nephropathy. Expert Rev Mol Med. 23:e232021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Huang Y, Wang S, Huang F, Zhang Q, Qin B,
Liao L, Wang M, Wan H, Yan W, Chen D, et al: c-FLIP regulates
pyroptosis in retinal neurons following oxygen-glucose
deprivation/recovery via a GSDMD-mediated pathway. Ann Anat.
235:1516722021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chen Y, Long T, Chen J, Wei H, Meng J,
Kang M, Wang J, Zhang X, Xu Q, Zhang C and Xiong K: WTAP
participates in neuronal damage by protein translation of NLRP3 in
an m6A-YTHDF1-dependent manner after traumatic brain injury. Int J
Surg. 110:5396–5408. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Xi G, Gao J, Wan B, Zhan P, Xu W, Lv T and
Song Y: GSDMD is required for effector CD8+ T cell responses to
lung cancer cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 74:1057132019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yan H, Luo B, Wu X, Guan F, Yu X, Zhao L,
Ke X, Wu J and Yuan J: Cisplatin induces pyroptosis via activation
of MEG3/NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD pathway in Triple-negative breast
cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 17:2606–2621. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Liu Y, Fang Y, Chen X, Wang Z, Liang X,
Zhang T, Liu M, Zhou N, Lv J, Tang K, et al: Gasdermin E-mediated
target cell pyroptosis by CAR T cells triggers cytokine release
syndrome. Sci Immunol. 5:eaax79692020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|