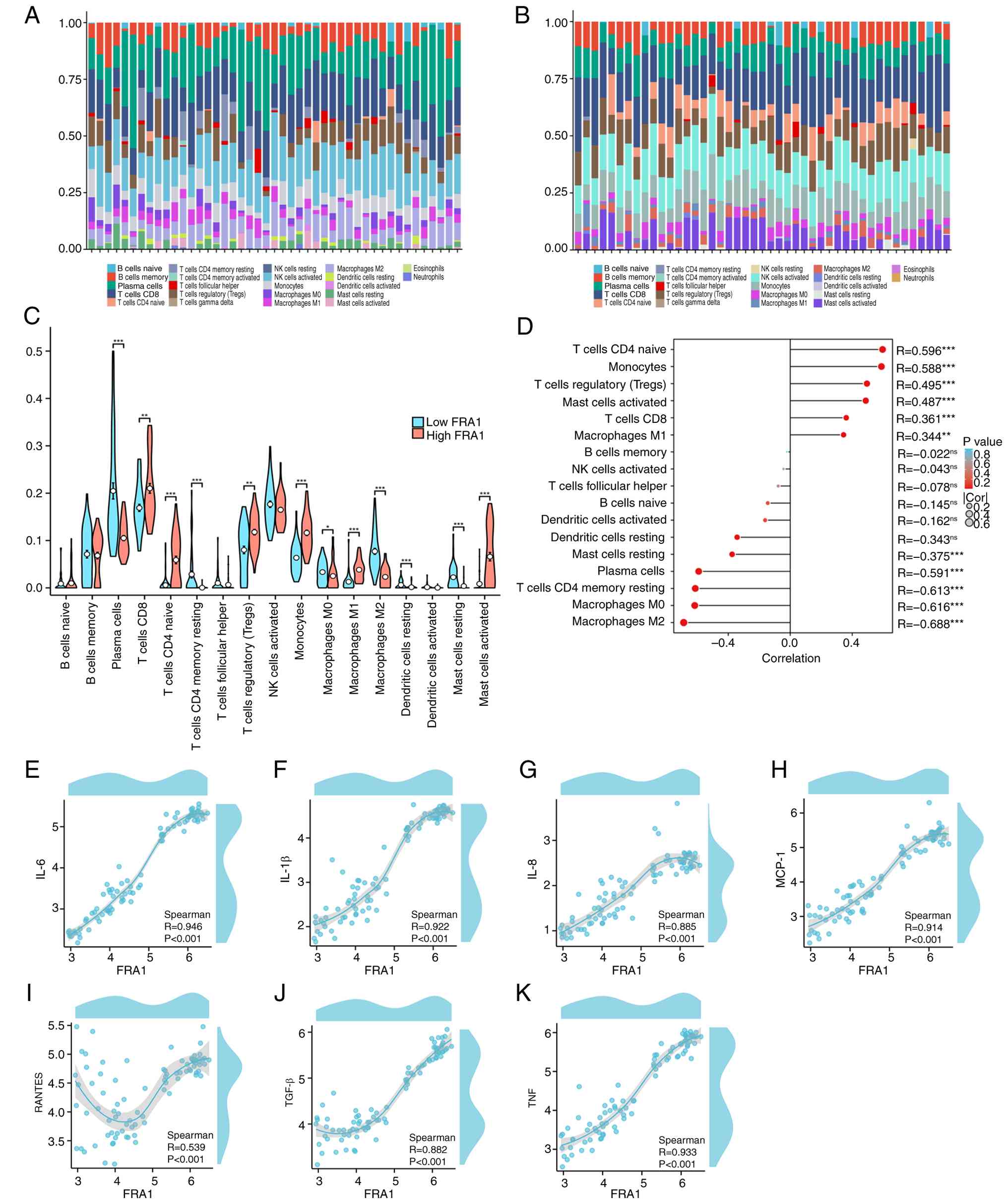
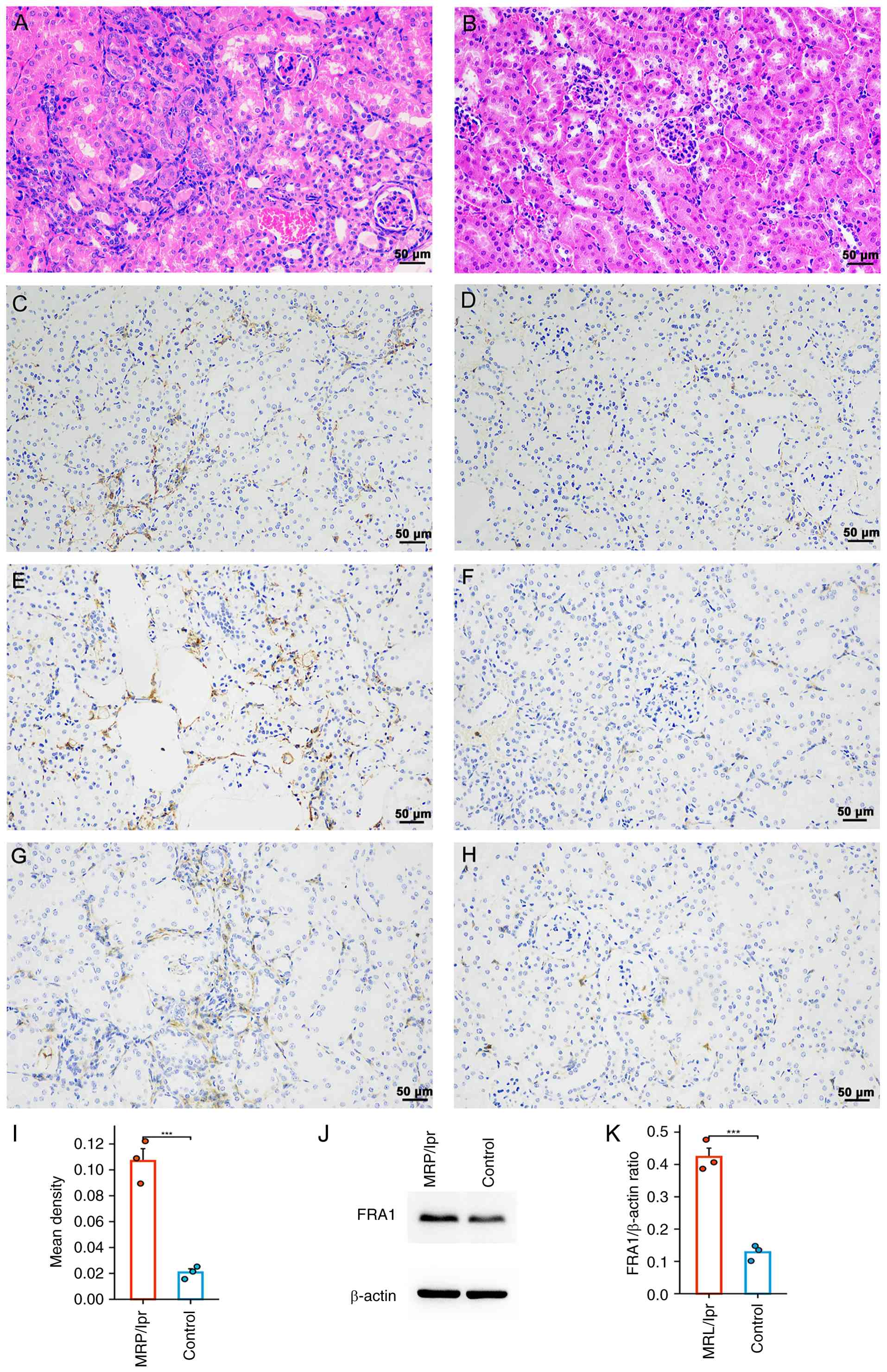
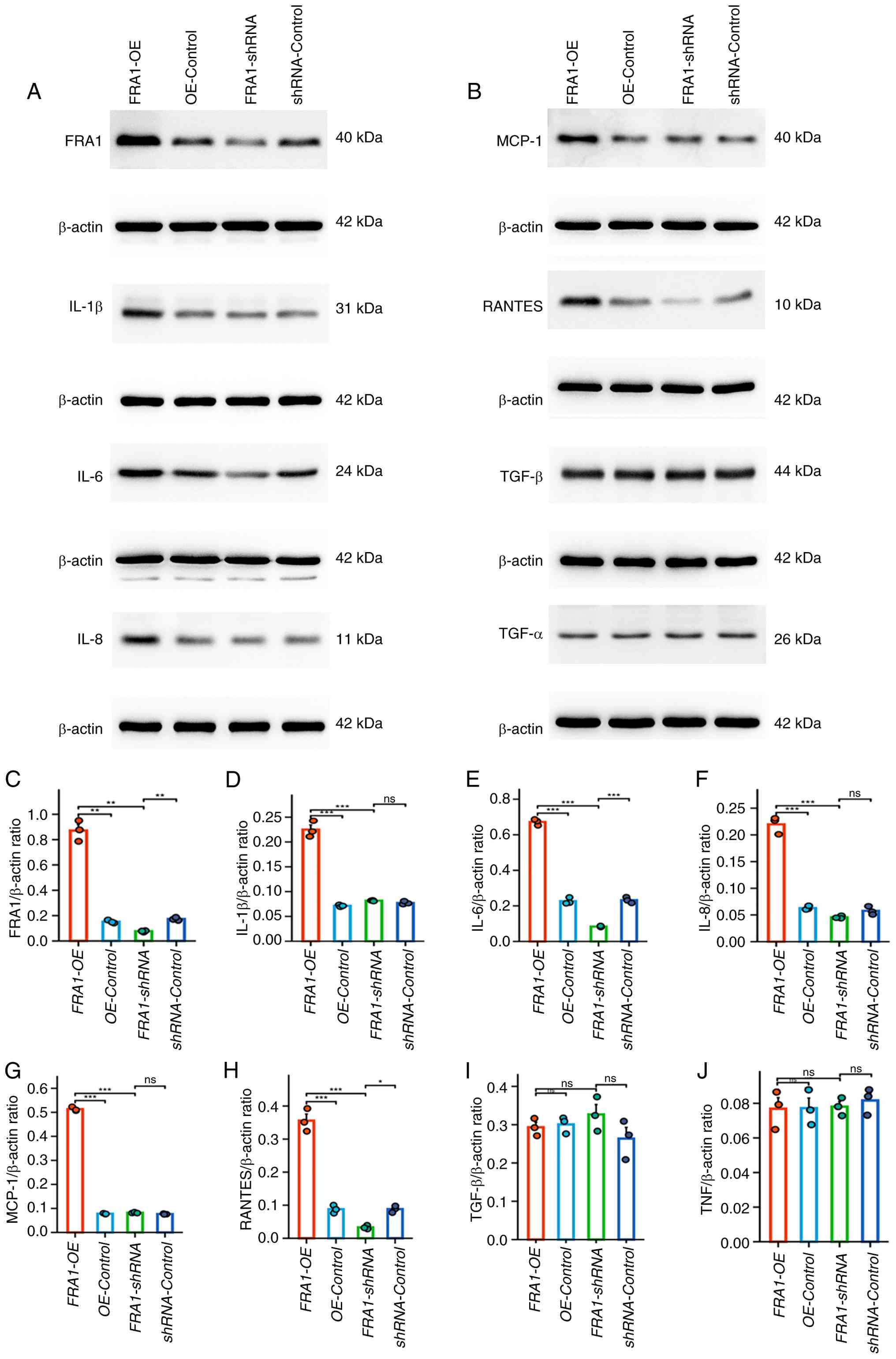
|
1
|
Singh S, Saxena R and Palmer BF: Lupus
nephritis. Am J Med Sci. 337:451–460. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pons-Estel GJ, Serrano R, Plasín MA,
Espinosa G and Cervera R: Epidemiology and management of refractory
lupus nephritis. Autoimmun Rev. 10:655–663. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Guimarães JAR, Furtado SDC, Lucas ACDS,
Mori B and Barcellos JFM: Diagnostic test accuracy of novel
biomarkers for lupus nephritis-An overview of systematic reviews.
PLoS One. 17:e02750162022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Qi J, Wu T, Wang J, Zhang J, Chen L, Jiang
Z, Li Y, Jiang H, Sun Q, Gu Q and Ying Z: Research trends and
frontiers in lupus nephritis: A bibliometric analysis from 2012 to
2022. Int Urol Nephrol. 56:781–794. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kostopoulou M, Pitsigavdaki S and Bertsias
G: Lupus nephritis: Improving treatment options. Drugs. 82:735–748.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Parodis I, Rovin BH, Tektonidou MG, Anders
HJ, Malvar A, Mok CC and Mohan C: Lupus nephritis. Nat Rev Dis
Primers. 11:692025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cen B, Liao W, Wang Z, Gao L, Wei Y, Huang
W, He S, Wang W, Liu X, Pan X and Ji A: Gelofusine attenuates
tubulointerstitial injury induced by cRGD-conjugated siRNA by
regulating the TLR3 signaling pathway. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids.
11:300–311. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Parikh SV, Madhavan S, Shapiro J, Knight
R, Rosenberg AZ, Parikh CR, Rovin B and Menez S; Kidney Precision
Medicine Project, : Characterization of glomerular and
tubulointerstitial proteomes in a case of nonsteroidal
anti-inflammatory drug-attributed acute kidney injury: A clinical
pathologic molecular correlation. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol.
18:402–410. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hong S, Healy H and Kassianos AJ: The
emerging role of renal tubular epithelial cells in the
immunological pathophysiology of lupus nephritis. Front Immunol.
11:5789522020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gomes MF, Mardones C, Xipell M, Blasco M,
Solé M, Espinosa G, García-Herrera A, Cervera R and Quintana LF:
The extent of tubulointerstitial inflammation is an independent
predictor of renal survival in lupus nephritis. J Nephrol.
34:1897–1905. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rijnink EC, Teng YKO, Wilhelmus S,
Almekinders M, Wolterbeek R, Cransberg K, Bruijn JA and Bajema IM:
Clinical and histopathologic characteristics associated with renal
outcomes in lupus nephritis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 12:734–743.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tesch GH: Review: Serum and urine
biomarkers of kidney disease: A pathophysiological perspective.
Nephrology (Carlton). 15:609–616. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hill GS, Delahousse M, Nochy D, Mandet C
and Bariéty J: Proteinuria and tubulointerstitial lesions in lupus
nephritis. Kidney Int. 60:1893–1903. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pamfil C, Makowska Z, De Groof A, Tilman
G, Babaei S, Galant C, Montigny P, Demoulin N, Jadoul M, Aydin S,
et al: Intrarenal activation of adaptive immune effectors is
associated with tubular damage and impaired renal function in lupus
nephritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 77:1782–1789. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Wang S and Lan HY:
Macrophages promote renal fibrosis through direct and indirect
mechanisms. Kidney Int Suppl (2011). 4:34–38. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen H, Liu N and Zhuang S: Macrophages in
renal injury, repair, fibrosis following acute kidney injury and
targeted therapy. Front Immunol. 13:9342992022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang XD, Huang XF, Yan QR and Bao CD:
Aberrant activation of the WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway in lupus
nephritis. PLoS One. 9:e848522014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gröne EF, Federico G, Nelson PJ, Arnold B
and Gröne HJ: The hormetic functions of Wnt pathways in tubular
injury. Pflugers Arch. 469:899–906. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shaulian E and Karin M: AP-1 as a
regulator of cell life and death. Nat Cell Biol. 4:E131–E136. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Madrigal P and Alasoo K: AP-1 takes centre
stage in enhancer chromatin dynamics. Trends Cell Biol. 28:509–511.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gozdecka M and Breitwieser W: The roles of
ATF2 (activating transcription factor 2) in tumorigenesis. Biochem
Soc Trans. 40:230–234. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
He YY, Zhou HF, Chen L, Wang YT, Xie WL,
Xu ZZ, Xiong Y, Feng YQ, Liu GY, Li X, et al: The Fra-1: Novel role
in regulating extensive immune cell states and affecting
inflammatory diseases. Front Immunol. 13:9547442022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Grötsch B, Brachs S, Lang C, Luther J,
Derer A, Schlötzer-Schrehardt U, Bozec A, Fillatreau S, Berberich
I, Hobeika E, et al: The AP-1 transcription factor Fra1 inhibits
follicular B cell differentiation into plasma cells. J Exp Med.
211:2199–2212. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li QR, Ni WP, Lei NJ, Yang JY, Xuan XY,
Liu PP, Gong GM, Yan F, Feng YS, Zhao R and Du Y: The
overexpression of Fra1 disorders the inflammatory cytokine
secretion by mTEC of myasthenia gravis thymus. Scand J Immunol.
88:e126762018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cuarental L, Ribagorda M, Ceballos MI,
Pintor-Chocano A, Carriazo SM, Dopazo A, Vazquez E, Suarez-Alvarez
B, Cannata-Ortiz P, Sanz AB, et al: The transcription factor Fosl1
preserves Klotho expression and protects from acute kidney injury.
Kidney Int. 103:686–701. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Qian W, Wang X and Zi Y: Screening and
bioinformatics analysis of IgA nephropathy gene based on GEO
databases. Biomed Res Int. 2019:87940132019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu T, Zhuang XX, Li Zhu X, Wu X, Juan Qin
X, Bing Wei L, Chen Gao Y and Rong Gao J: Inhibition of METTL3
promotes mesangial cell mitophagy and attenuates glomerular damage
by alleviating FOSL1 m6A modifications via IGF2BP2-dependent
mechanisms. Biochem Pharmacol. 236:1168672025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Parikh SV, Malvar A, Song H, Shapiro J,
Mejia-Vilet JM, Ayoub I, Almaani S, Madhavan S, Alberton V, Besso
C, et al: Molecular profiling of kidney compartments from serial
biopsies differentiate treatment responders from non-responders in
lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 102:845–865. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mejia-Vilet JM, Parikh SV, Song H, Fadda
P, Shapiro JP, Ayoub I, Yu L, Zhang J, Uribe-Uribe N and Rovin BH:
Immune gene expression in kidney biopsies of lupus nephritis
patients at diagnosis and at renal flare. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
34:1197–1206. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Almaani S, Prokopec SD, Zhang J, Yu L,
Avila-Casado C, Wither J, Scholey JW, Alberton V, Malvar A, Parikh
SV, et al: Rethinking lupus nephritis classification on a molecular
level. J Clin Med. 8:15242019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
World Medical Association, . World medical
association declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical
research involving human subjects. JAMA. 310:2191–2194. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Newman AM, Liu CL, Green MR, Gentles AJ,
Feng W, Xu Y, Hoang CD, Diehn M and Alizadeh AA: Robust enumeration
of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat Methods.
12:453–457. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li Y, Ding T, Chen J, Ji J, Wang W, Ding
B, Ge W, Fan Y and Xu L: The protective capability of Hedyotis
diffusa Willd on lupus nephritis by attenuating the IL-17
expression in MRL/lpr mice. Front Immunol. 13:9438272022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Festing MFW and Altman DG: Guidelines for
the design and statistical analysis of experiments using laboratory
animals. ILAR J. 43:244–258. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang RN, Wen Q, He WT, Yang JH, Zhou CY,
Xiong WJ and Ma L: Optimized protocols for γδ T cell expansion and
lentiviral transduction. Mol Med Rep. 19:1471–1480. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Uchida N, Green R, Ballantine J, Skala LP,
Hsieh MM and Tisdale JF: Kinetics of lentiviral vector transduction
in human CD34(+) cells. Exp Hematol. 44:106–115. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sanber KS, Knight SB, Stephen SL, Bailey
R, Escors D, Minshull J, Santilli G, Thrasher AJ, Collins MK and
Takeuchi Y: Construction of stable packaging cell lines for
clinical lentiviral vector production. Sci Rep. 5:90212015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Malhotra D: Targeting epitope-specific T
cells and modelling protein hypercitrullination in rheumatoid
arthritis. [Master's thesis]. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University;
2024, Available from:. https://macsphere.mcmaster.ca/bitstream/11375/30359/2/Malhotra_Devon_2024August_MedicalSciences.pdf
|
|
41
|
Jian J, Liu Y, Zheng Q, Wang J, Jiang Z,
Liu X, Chen Z, Wan S, Liu H and Wang L: The E3 ubiquitin ligase
TRIM39 modulates renal fibrosis induced by unilateral ureteral
obstruction through regulating proteasomal degradation of PRDX3.
Cell Death Discov. 10:172024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chernova I: Lupus nephritis: Immune cells
and the kidney microenvironment. Kidney360. 5:1394–1401. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cheng Y, Liu L, Ye Y, He Y, Hu W, Ke H,
Guo ZY and Shao G: Roles of macrophages in lupus nephritis. Front
Pharmacol. 15:14777082024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sun L, Rautela J, Delconte RB,
Souza-Fonseca-Guimaraes F, Carrington EM, Schenk RL, Herold MJ,
Huntington ND, Lew AM, Xu Y and Zhan Y: GM-CSF quantity has a
selective effect on granulocytic vs. monocytic myeloid development
and function. Front Immunol. 9:19222018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Shakweer MM, Behairy M, Elhefnawy NG and
Elsaid TW: Value of Foxp3 expressing T-regulatory cells in renal
tissue in lupus nephritis; an immunohistochemical study. J
Nephropathol. 5:105–110. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kalim H, Pratama MZ, Nugraha AS,
Prihartini M, Chandra A, Sholihah AI, Qonita F and Handono K:
Regulatory T cells compensation failure cause the dysregulation of
immune response in pristane induced lupus mice model. Malays J Med
Sci. 25:17–26. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wu Y, Zhang W, Liao Y, Sun T and Liu Y and
Liu Y: Immune cell aberrations in systemic lupus erythematosus:
Navigating the targeted therapies toward precision management. Cell
Mol Biol Lett. 30:732025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jiang C, Wang H, Xue M, Lin L, Wang J, Cai
G and Shen Q: Reprograming of peripheral Foxp3+
regulatory T cell towards Th17-like cell in patients with active
systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol. 209:1082672019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Espeli M, Bökers S, Giannico G, Dickinson
HA, Bardsley V, Fogo AB and Smith KG: Local renal autoantibody
production in lupus nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 22:296–305. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Cao S, Schnelzer A, Hannemann N, Schett G,
Soulat D and Bozec A: The transcription factor FRA-1/AP-1 controls
lipocalin-2 expression and inflammation in sepsis model. Front
Immunol. 12:7016752021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hannemann N, Cao S, Eriksson D, Schnelzer
A, Jordan J, Eberhardt M, Schleicher U, Rech J, Ramming A, Uebe S,
et al: Transcription factor Fra-1 targets arginase-1 to enhance
macrophage-mediated inflammation in arthritis. J Clin Invest.
129:2669–2684. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Mittelstadt ML and Patel RC: AP-1 mediated
transcriptional repression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 by
recruitment of histone deacetylase 1 in response to interferon β.
PLoS One. 7:e421522012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cash H, Relle M, Menke J, Brochhausen C,
Jones SA, Topley N, Galle PR and Schwarting A: Interleukin 6 (IL-6)
deficiency delays lupus nephritis in MRL-Faslpr mice: the IL-6
pathway as a new therapeutic target in treatment of autoimmune
kidney disease in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol.
37:60–70. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Alharazy S, Kong NC, Mohd M, Shah SA,
Ba'in A and Abdul Gafor AH: Urine monocyte chemoattractant
protein-1 and lupus nephritis disease activity: Preliminary report
of a prospective longitudinal study. Autoimmune Dis.
2015:9620462015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Chan RWY, Lai FMM, Li EKM, Tam LS, Chow
KM, Li PKT and Szeto CC: Messenger RNA expression of RANTES in the
urinary sediment of patients with lupus nephritis. Nephrology
(Carlton). 11:219–225. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Roh YS, Park S, Lim CW and Kim B:
Depletion of Foxp3+ Regulatory T cells promotes profibrogenic
milieu of cholestasis-induced liver injury. Dig Dis Sci.
60:2009–2018. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ahnstedt H, Roy-O'Reilly M, Spychala MS,
Mobley AS, Bravo-Alegria J, Chauhan A, Aronowski J, Marrelli SP and
McCullough LD: Sex differences in adipose tissue CD8+ T
cells and regulatory T cells in middle-aged mice. Front Immunol.
9:6592018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Rovin BH, Lu L and Zhang X: A novel
interleukin-8 polymorphism is associated with severe systemic lupus
erythematosus nephritis. Kidney Int. 62:261–265. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Scheller J, Chalaris A, Schmidt-Arras D
and Rose-John S: the pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of the
cytokine interleukin-6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:878–888. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Mishra RK, Potteti HR, Tamatam CR,
Elangovan I and Reddy SP: c-Jun is required for nuclear
factor-κB-dependent, LPS-stimulated fos-related antigen-1
transcription in alveolar macrophages. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
55:667–674. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wang Q, Ni H, Lan L, Wei X, Xiang R and
Wang Y: Fra-1 protooncogene regulates IL-6 expression in
macrophages and promotes the generation of M2d macrophages. Cell
Res. 20:701–712. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Reck M, Baird DP, Veizades S, Sutherland
C, Bell RMB, Hur H, Cairns C, Janas PP, Campbell R, Nam A, et al:
Multiomic analysis of human kidney disease identifies a tractable
inflammatory and pro-fibrotic tubular cell phenotype. Nat Commun.
16:47452025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Song D, Lian Y and Zhang L: The potential
of activator protein 1 (AP-1) in cancer targeted therapy. Front
Immunol. 14:12248922023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|