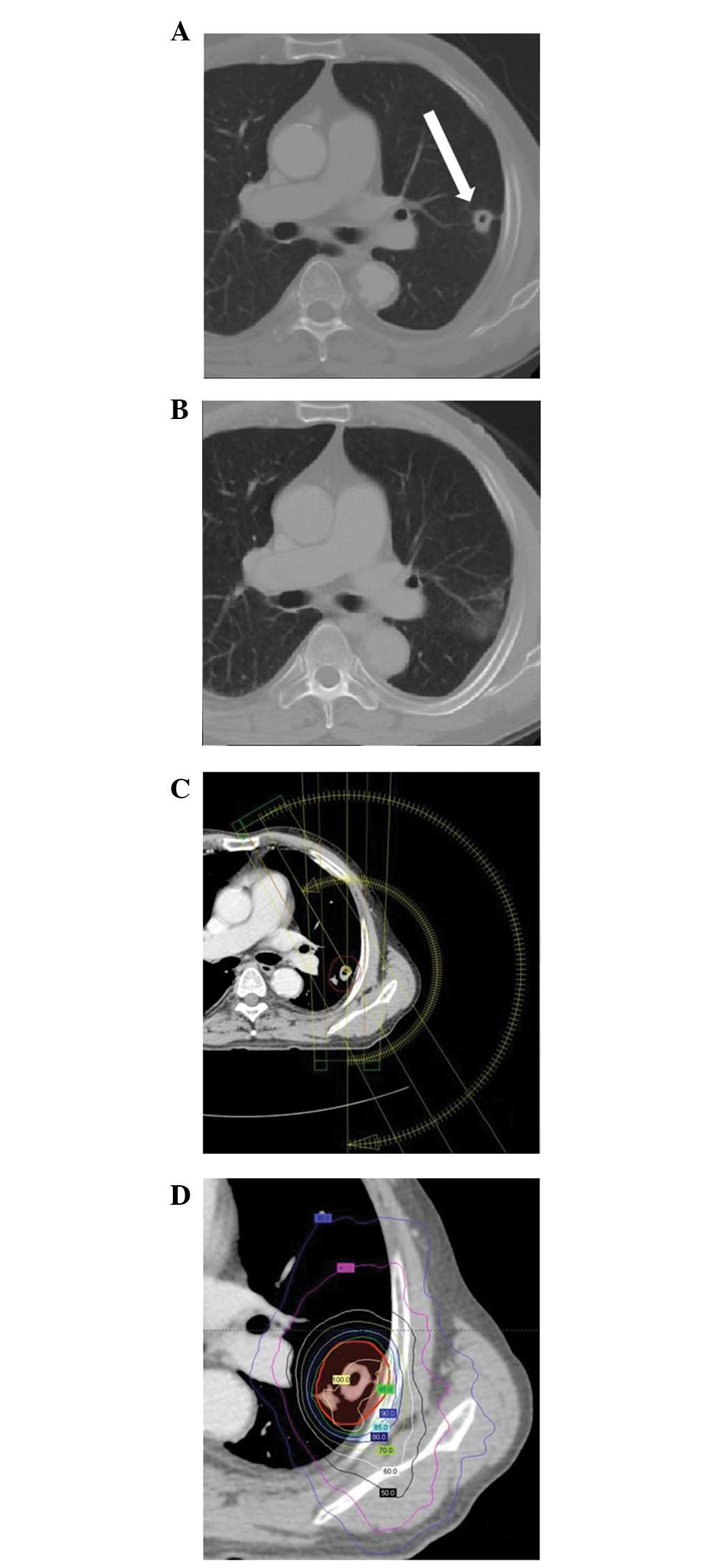
|
1
|
Chang MY and Sugarbaker DJ: Surgery for
early stage non-small cell lung cancer. Semin Surg Oncol. 21:74–84.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Baumann P, Nyman J, Hoyer M, et al:
Outcome in a prospective phase II trial of medically inoperable
stage I non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with
stereotactic body radiotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 27:3290–3296. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Rowell NP and Williams CJ: Radical
radiotherapy for stage I/II non-small cell lung cancer in patients
not sufficiently fit for or declining surgery (medically
inoperable): a systematic review. Thorax. 56:628–638. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Qiao X, Tullgren O, Lax I, Sirzen F and
Lewensohn R: The role of radiotherapy in treatment of stage I
non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 41:1–11. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Buyyounouski MK, Balter P, Lewis B, et al:
Stereotactic body radiotherapy for early-stage non-small-cell lung
cancer: report of the ASTRO Emerging Technology Committee. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 78:3–10. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nagata Y, Takayama K, Matsuo Y, et al:
Clinical outcomes of a phase I/II study of 48 Gy of stereotactic
body radiotherapy in 4 fractions for primary lung cancer using a
stereotactic body frame. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
63:1427–1431. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Timmerman R, Paulus R, Galvin J, et al:
Stereotactic body radiation therapy for inoperable early stage lung
cancer. JAMA. 303:1070–1076. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bral S, Gevaert T, Linthout N, et al:
Prospective, risk-adapted strategy of stereotactic body
radiotherapy for early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer: results of
a Phase II trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 80:1343–1349. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Taremi M, Hope A, Dahele M, et al:
Stereotactic body radiotherapy for medically inoperable lung
cancer: prospective, single-center study of 108 consecutive
patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 82:967–973. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Onishi H, Shirato H, Nagata Y, et al:
Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (HypoFXSRT) for stage I
non-small cell lung cancer: updated results of 257 patients in a
Japanese multi-institutional study. J Thorac Oncol. 2(7 Suppl 3):
S94–S100. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Benedict SH, Cardinale RM, Wu Q, Zwicker
RD, Broaddus WC and Mohan R: Intensity-modulated stereotactic
radiosurgery using dynamic micro-multileaf collimation. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 50:751–758. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Videtic GM, Stephans K, Reddy C, et al:
Intensity-modulated radiotherapy-based stereotactic body
radiotherapy for medically inoperable early-stage lung cancer:
excellent local control. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 77:344–349.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
McGrath SD, Matuszak MM, Yan D, Kestin LL,
Martinez AA and Grills IS: Volumetric modulated arc therapy for
delivery of hypofractionated stereotactic lung radiotherapy: A
dosimetric and treatment efficiency analysis. Radiother Oncol.
95:153–157. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Keall P: 4-dimensional computed tomography
imaging and treatment planning. Semin Radiat Oncol. 14:81–90. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Grills IS, Hugo G, Kestin LL, et al:
Image-guided radiotherapy via daily online cone-beam CT
substantially reduces margin requirements for stereotactic lung
radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 70:1045–1056. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG,
Greene FL and Trotti A: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th edition.
Springer; New York: 2010
|
|
17
|
No authors listed. World Medical
Association Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical
research involving human subjects. JAMA. 284:3043–3045. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
The Radiation Therapy Oncology Group
Clinical Trials (Available from: http://www.rtog.org/ClinicalTrials/ProtocolTable.aspx).
|
|
19
|
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, et
al: New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised
RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 45:228–247. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Mohammed N, Grills IS, Wong CY, et al:
Radiographic and metabolic response rates following image-guided
stereotactic radiotherapy for lung tumors. Radiother Oncol.
99:18–22. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hof H, Rhein B, Haering P, Kopp-Schneider
A, Debus J and Herfarth K: 4D-CT-based target volume definition in
stereotactic radiotherapy of lung tumours: comparison with a
conventional technique using individual margins. Radiother Oncol.
93:419–423. 2009.
|
|
22
|
Balter JM, Ten Haken RK, Lawrence TS, Lam
KL and Robertson JM: Uncertainties in CT-based radiation therapy
treatment planning associated with patient breathing. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 36:167–174. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Underberg RW, Lagerwaard FJ, Cuijpers JP,
Slotman BJ, van Sörnsen de Koste JR and Senan S: Four-dimensional
CT scans for treatment planning in stereotactic radiotherapy for
stage I lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 60:1283–1290.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cardinale RM, Benedict SH, Wu Q, Zwicker
RD, Gaballa HE and Mohan R: A comparison of three stereotactic
radiotherapy techniques; ARCS vs. noncoplanar fixed fields vs
intensity modulation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 42:431–436.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Holt A, van Vliet-Vroegindeweij C, Mans A,
Belderbos JS and Damen EM: Volumetric-modulated arc therapy for
stereotactic body radiotherapy of lung tumors: a comparison with
intensity-modulated radiotherapy techniques. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 81:1560–1567. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yaes RJ, Patel P and Maruyama Y: On using
the linear-quadratic model in daily clinical practice. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 20:1353–1362. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Palma D and Senan S: Stereotactic
radiation therapy: changing treatment paradigms for stage I
nonsmall cell lung cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 23:133–139. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Stephans KL, Djemil T, Reddy CA, et al: A
comparison of two stereotactic body radiation fractionation
schedules for medically inoperable stage I non-small cell lung
cancer: the Cleveland Clinic experience. J Thorac Oncol. 4:976–982.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|